Vascular Anatomy: Lymphatics Overview
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key terms and concepts related to the lymphatic system, its functions, structures, and components.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Lymphatic System
A network that includes lymph vessels, lymph fluid, specialized immune cells, and lymphatic organs, serving circulatory and immune functions.
Afferent Vessels - bring lymph fluid to lymph node
Efferent Vessels - take lymph fluid away from lymph node
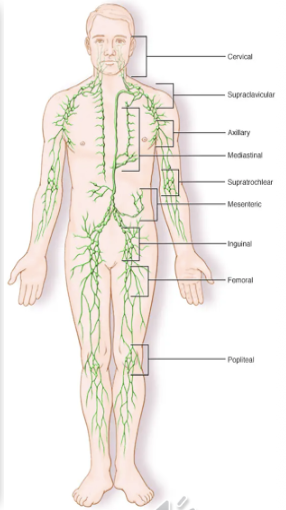
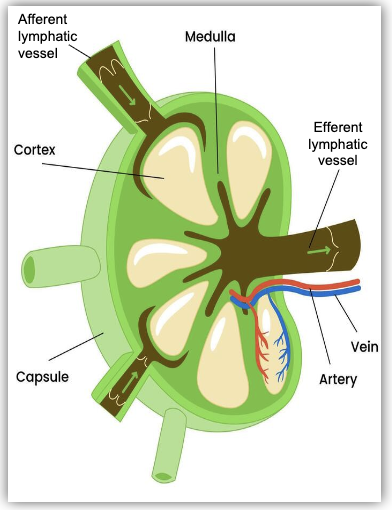
Lymph Nodes
Small, bean-shaped structures distributed throughout the body that filter lymph fluid and house lymphocytes.
Protective fibrous outer capsule
Cortex - B-Lymphocytes
Medulla - lymphocytes, macrophages
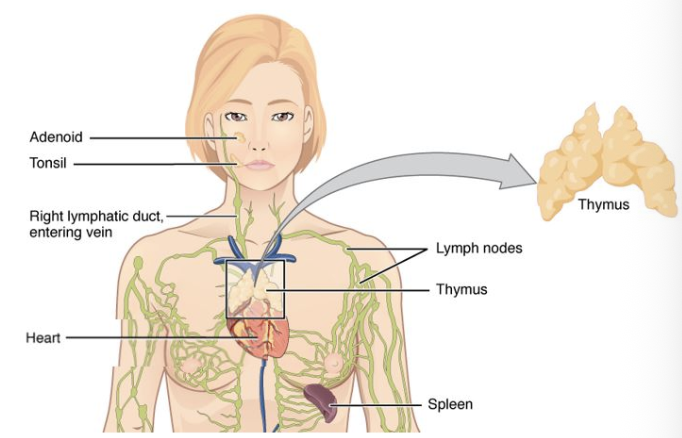
Thymus
An organ divided into lobes located in the mediastinal cavity where T-cells mature.
Supplied by internal thoracic arteries
B-Cells
A type of lymphocyte that produces antibodies and matures in the bone marrow before entering circulation.
Macrophages
Immune cells that ingest and digest pathogens and cellular debris.
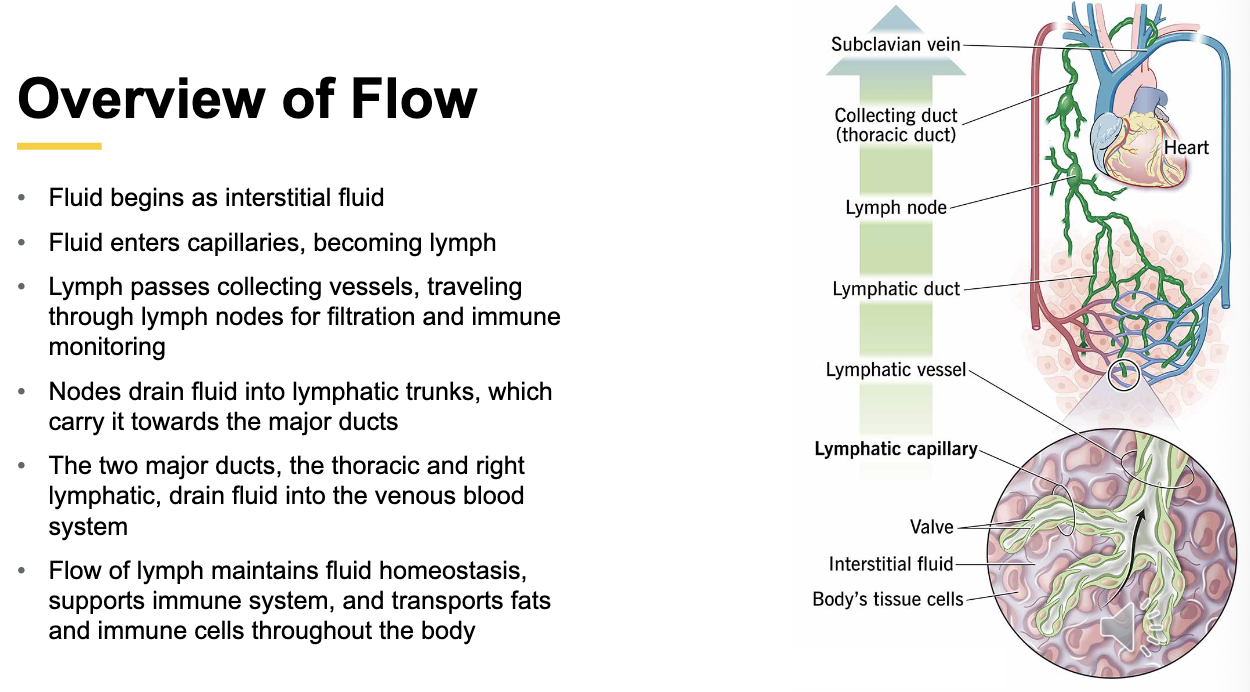
Lymph Fluid
Clear/yellow fluid that circulates through the lymphatic system, composed mainly of water, dissolved proteins, electrolytes, cellular waste, and white blood cells. Transports fats/fat-soluble vitamins from gut.
Originates from interstitial fluid that surrounds body tissues from plasma leaking from capillaries that is collected into lymphatic capillaries
Dumps into venous blood prior to entering heart
lymph nodes cleanse the fluid
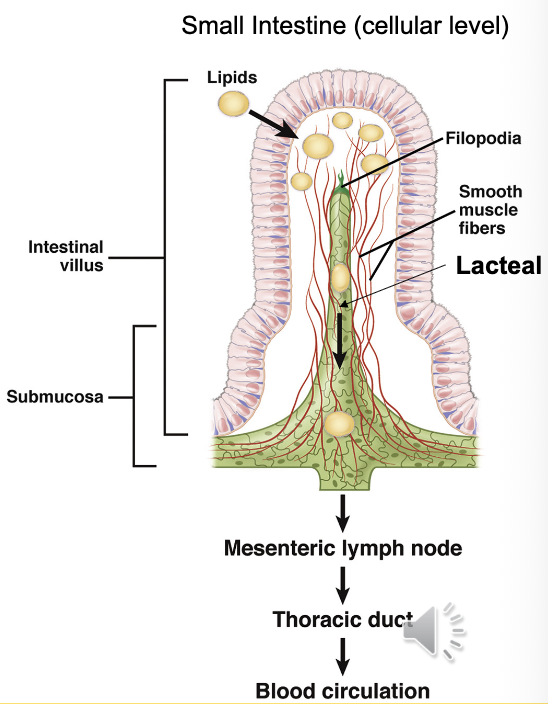
Chylomicrons
Particles formed from dietary fats and fat-soluble nutrients that enter lymphatic capillaries in the small intestine via entry points called lacteals.
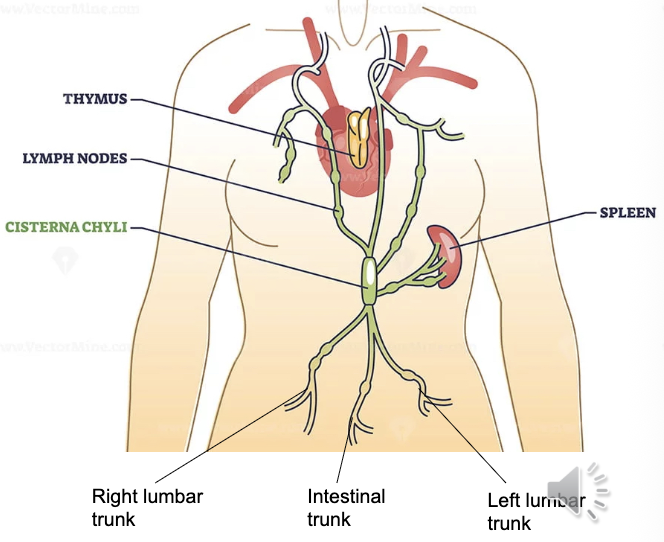
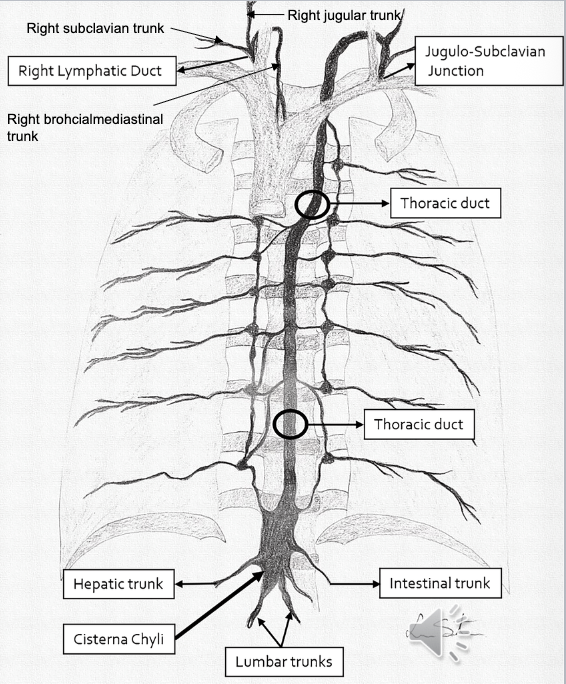
Cisterna Chyli
A sac-like reservoir in the lymphatic system that collects lymph fluid from the lower half of the body. Located in posterior abdominal cavity around L1-2 (post. to aorta)
Origin of Thoracic Duct
Fluid here often cloudy/milky from high fat concentrations via Intestinal Trunk
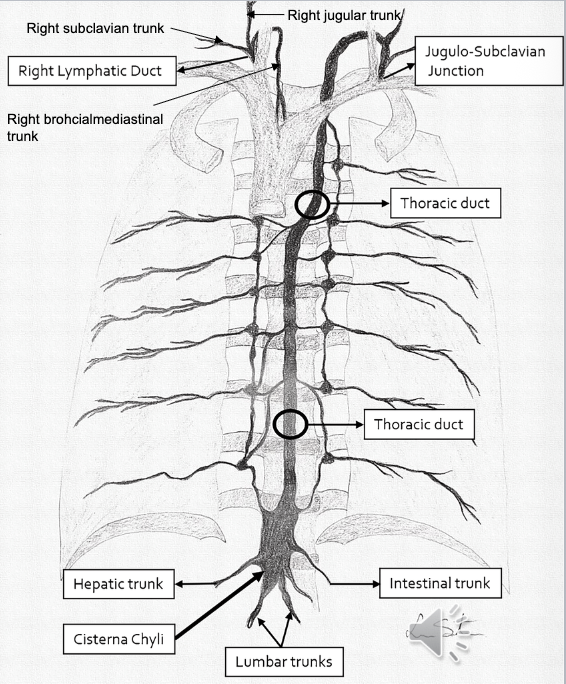
Thoracic Duct
The largest lymphatic vessel (15-18”) that collects lymph from the lower body and left side, delivering it to the venous circulation.
Begins at Cisterna Chyli, ascends thru diaphragm, into posterior mediastinum, to left of midline towards neck, behind left carotid. Dumps into left subclavian and left jugular veins.
Receives lymph from:
Left Jugular Trunk
Left Subclavian Trunk
Left Bronchomediastinal Trunk
Intestinal Trunk
Lumbar Trunk
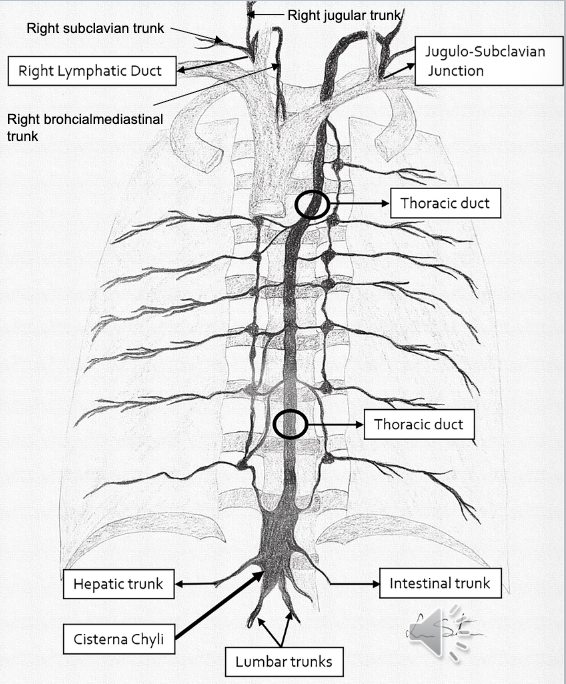
Lymphatic Trunks
Large lymphatic vessels that transport lymph from collecting vessels to ducts that dump into blood stream.
5 main Trunks (4 paired, 1 unpaired):
Jugular: drain head/neck
Subclavian: drain upper limbs, thoracic wall including breast
Bronchialmedistinal: drains thoracic cavity (heart/lungs/trachea/mediastinum)
Lumbar: drains lower limbs, pelvis, kidneys, abd wall; converge into Cisterna Chyli
Intestinal (unpaired): drains stomach/intestines/pancreas/spleen/liver; joins into Cisterna Chyli
Bone Marrow
Primary site of lymphocyte production and maturation.
Reservoir for mature immune cells (memory B cells)
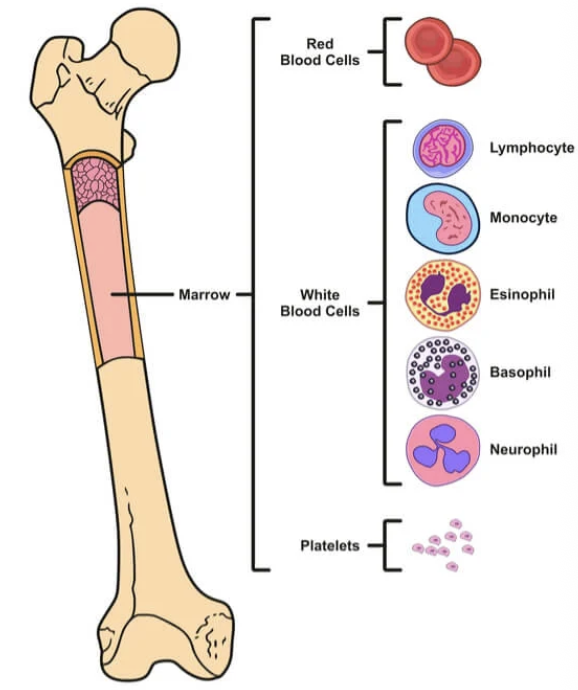
Memory B-Cells
Produce antibodies during immune response
T-Cells
Type of white blood cell that distinguish between foreign invaders and the body's own cells.
Key types include helper T-cells, cytotoxic (killer) T-cells, and regulatory T-cells, which have distinct functions in fighting infection, cancer, and controlling inflammation.
Lacteals
Lymphatic entry point for lipids within the small intestine
*Dietary fats and fat-soluble nutrients enter lymphatic system from GI tract, bypassing liver to enter blood stream directly
Spleen
Largest lymphatic system organ located in LUQ that filters blood, supports immune system, and manages body’s blood cell supply
Consists of fibrous outer layer (capsule) with trabeculae inner extensions dividing organ into compartments
White Pulp: tissues rich in lymphocytes B & T-cells) surrounded by arteries
Red Pulp: majority of spleen tissue, removes old/damaged/misshapen RBCs

Mucosa Lymphoid Tissues
Network of diffuse, unencapsulated lymphoid tissues located on mucous membranes throughout the body; Digestive, Respiratory, and Urinary Tract. Contain a mix of B & T-cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells.
Ex: Peyer’s patches, tonsils/adenoids, bronchial and nasal lymph tissues
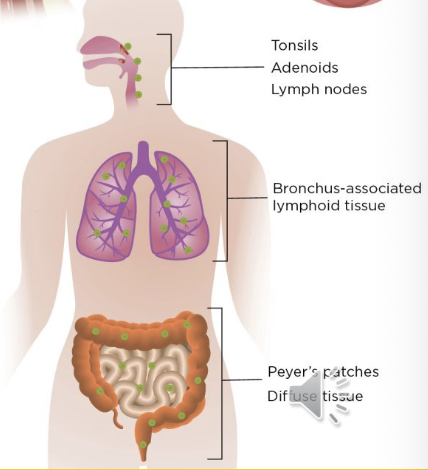
Peyer’s Patches
Clusters of lymphoid tissue in the small intestine's lining. Act as immune sensors that monitor the gut's contents and are central to initiating immune responses to pathogens while also promoting tolerance to food antigens. Specialized cells in the patches capture antigens, triggering an immune response involving B and T lymphocytes, which can lead to the production of protective antibodies and alert other immune cells. Most numerous in distal ileum.

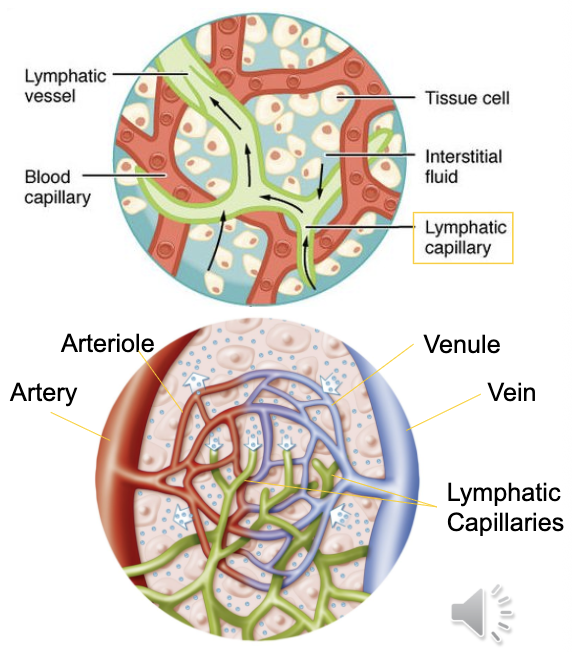
Lymphatic Capillaries
Entry point of lymphatic system located throughout almost all body tissues.
are larger in diameter with thinner walls than blood capillaries
Composed of single layer of epithelial cells with flap-like openings acting as mini valves allow fluids/proteins/waste/pathogens/immune cells to enter
Right Lymphatic Duct
1 of 2 of the largest ducts of the lymphatic system located in right upper thoracic cavity (rt venous angle). Drains right upper quadrant of body.
Convergence of 3 trunks:
Right Jugular Trunk: drains rt side of head/neck
Right Subclavian Trunk: drains right upper extremity
Right Bronchomediastinal Trunk: drains right thoracic cavity/lung/heart
Overview of Flow