NPB101: Homeostasis Lectures 2-3
1/55
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Levels of Organization (8; smallest to biggest in a body)
Atom
Molecule
Organelle
Cell
tissue
Organ
System
Organism
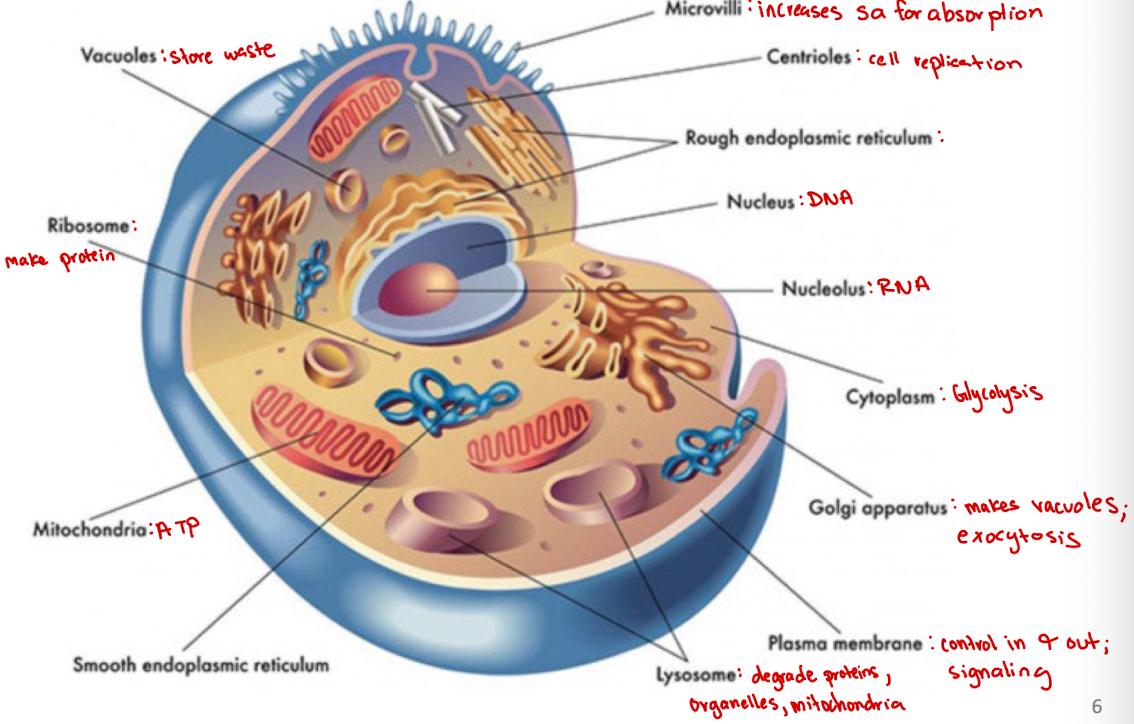
Microvilli
Increases surface area for absorption
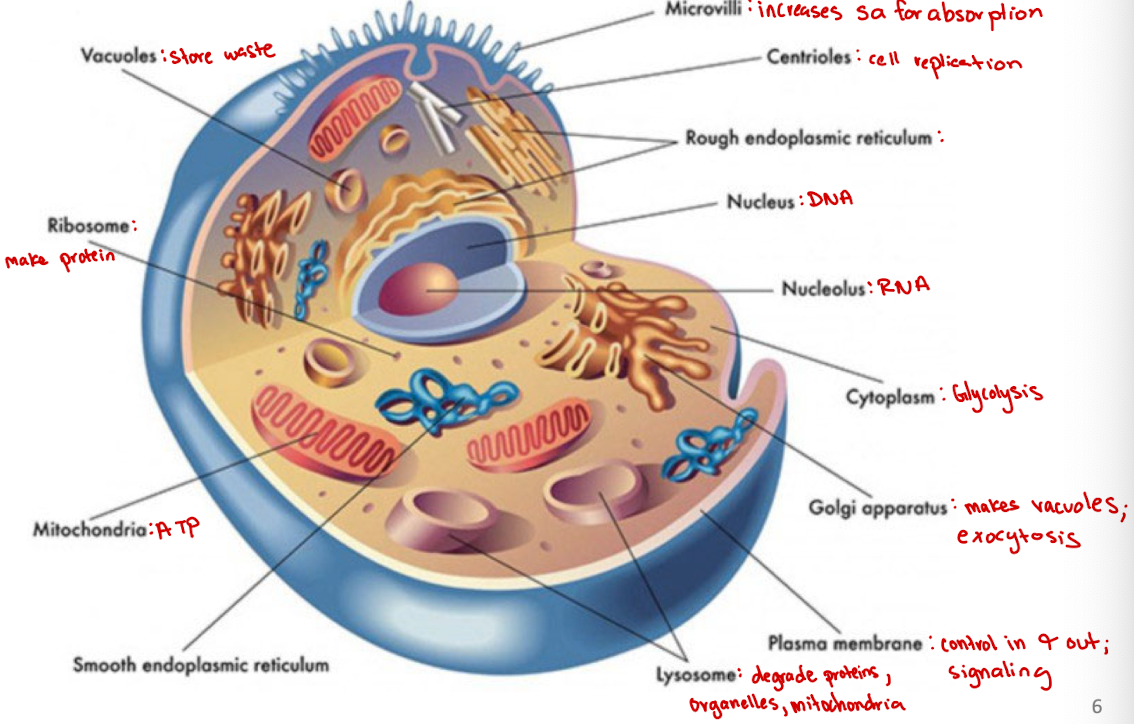
Centrioles
Cell organelle that aids in cell division/replication in animal cells only
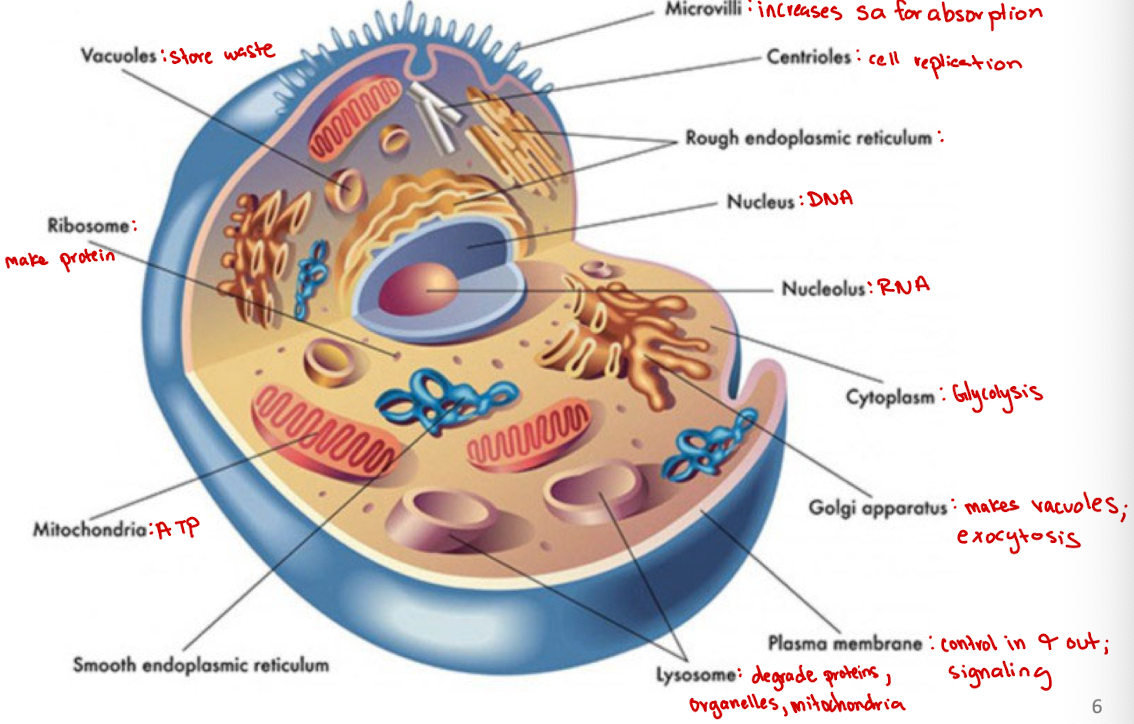
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
modification and packaging of newly synthesized proteins
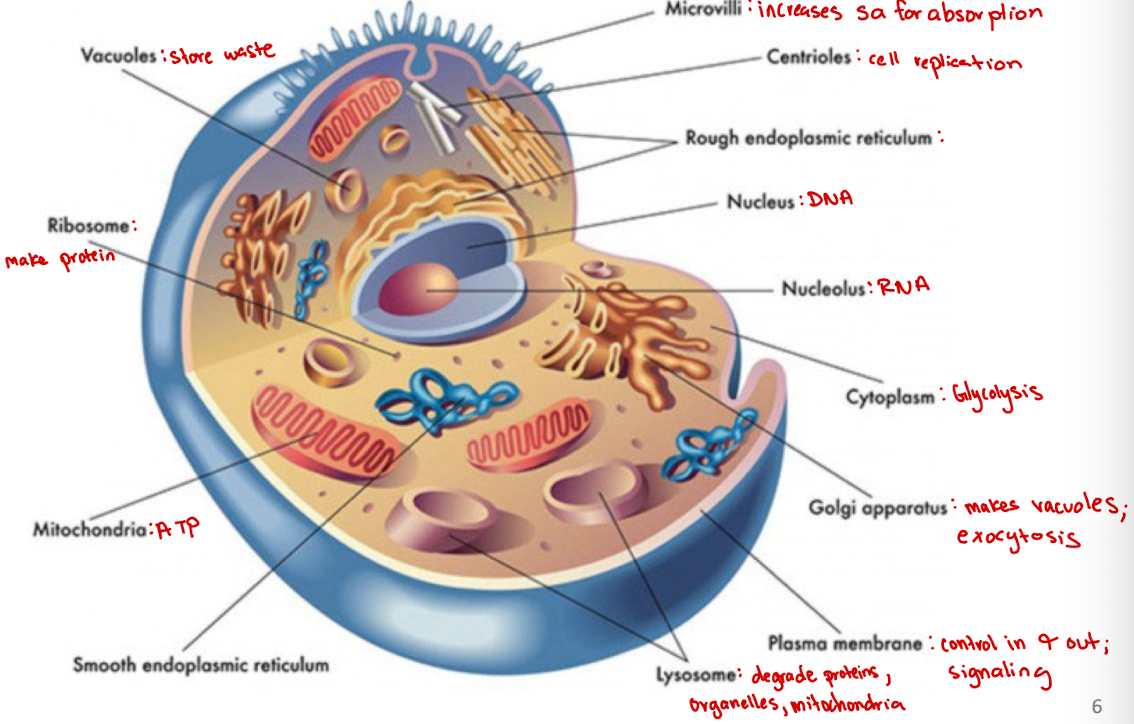
Smooth ER function
synthesis of lipids
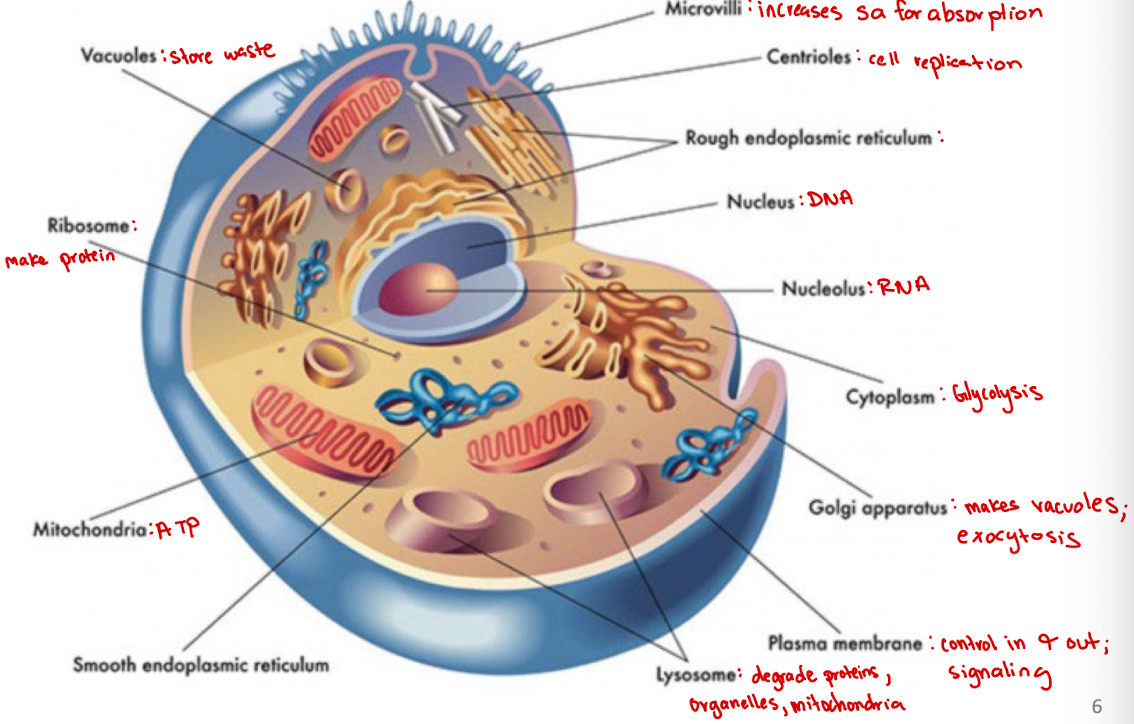
Golgi apparatus
System of membranes that modifies and packages proteins for export by the cell
Adds carbohydrate units needed for signaling
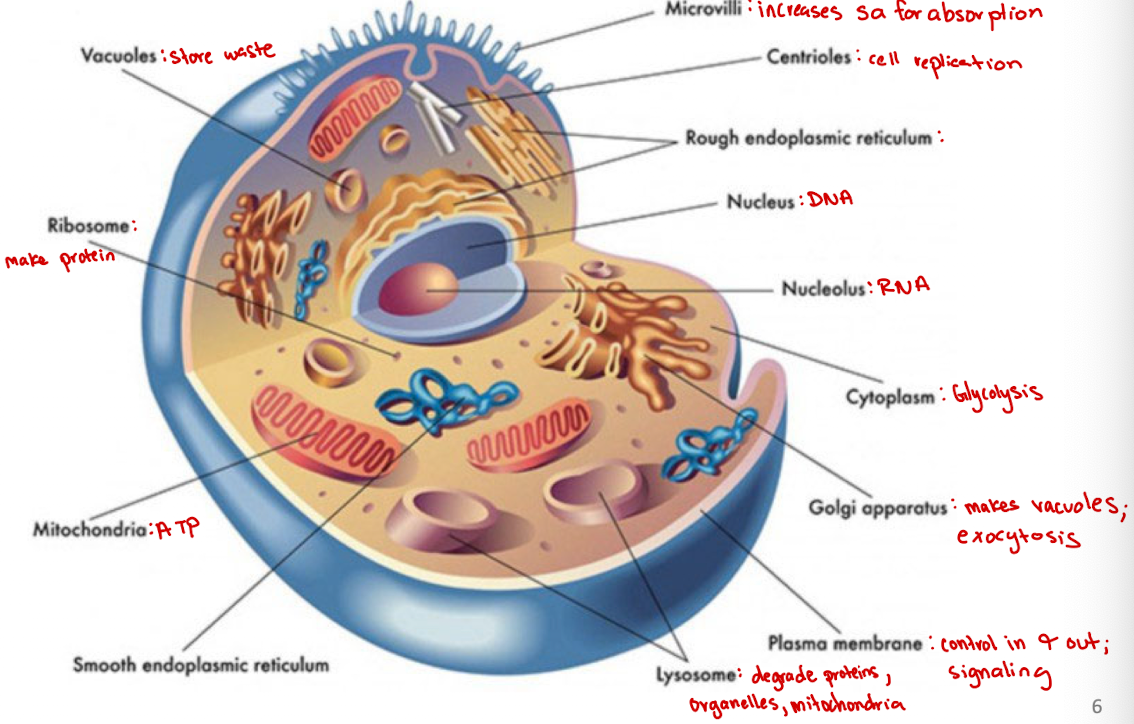
Ribosomes
site of protein synthesis
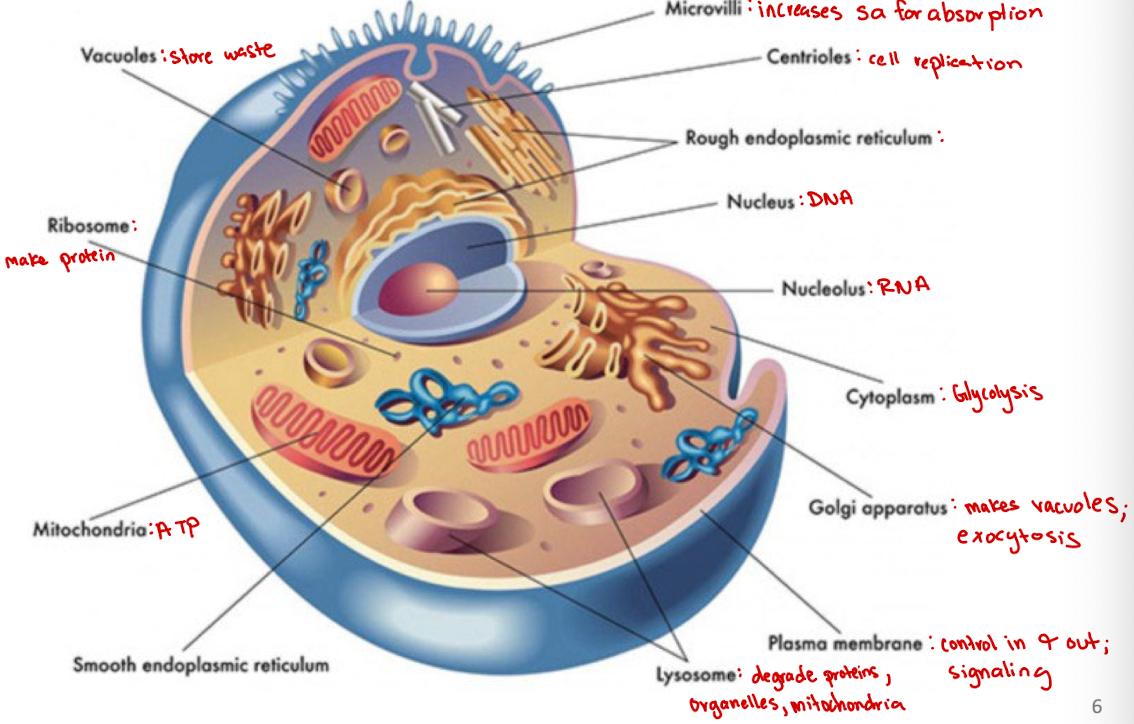
Vacuoles
Store nutrients and water on which a cell can rely for its survival.
Store the waste from the cell and prevents the cell from contamination
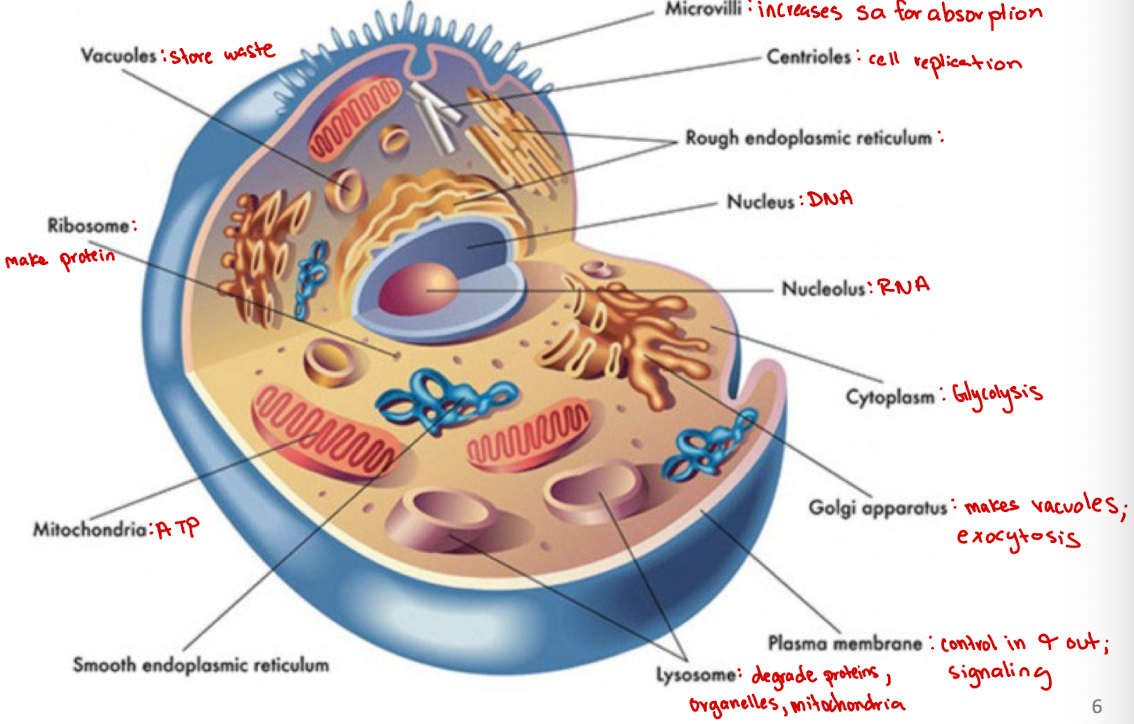
Nucleus
DNA
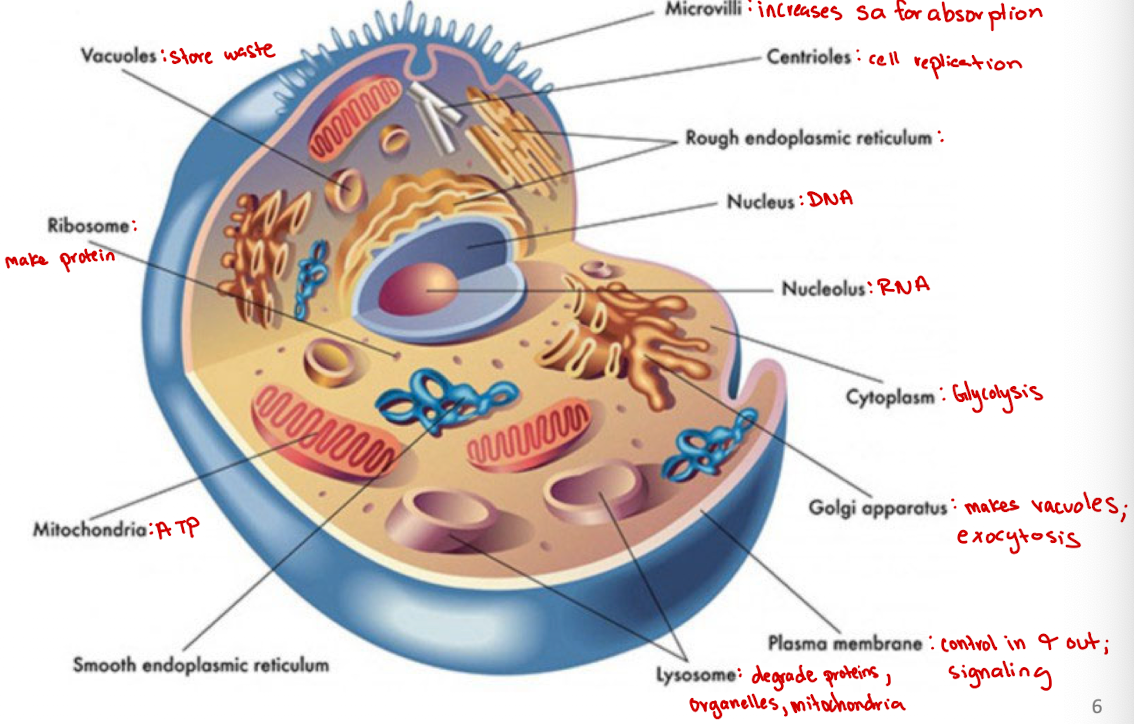
Nucleolus
RNA
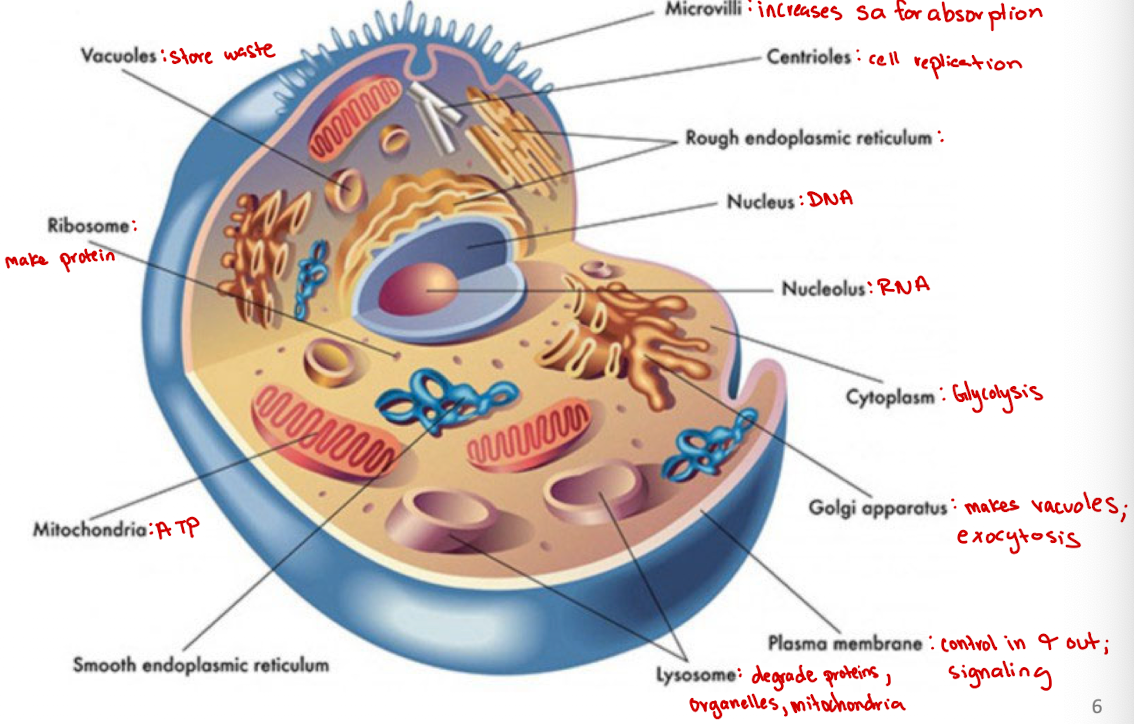
Plasma membrane
selectively permeable barrier that separates the cell’s interior from the external environment, regulating the passage of molecules and maintaining cell integrity
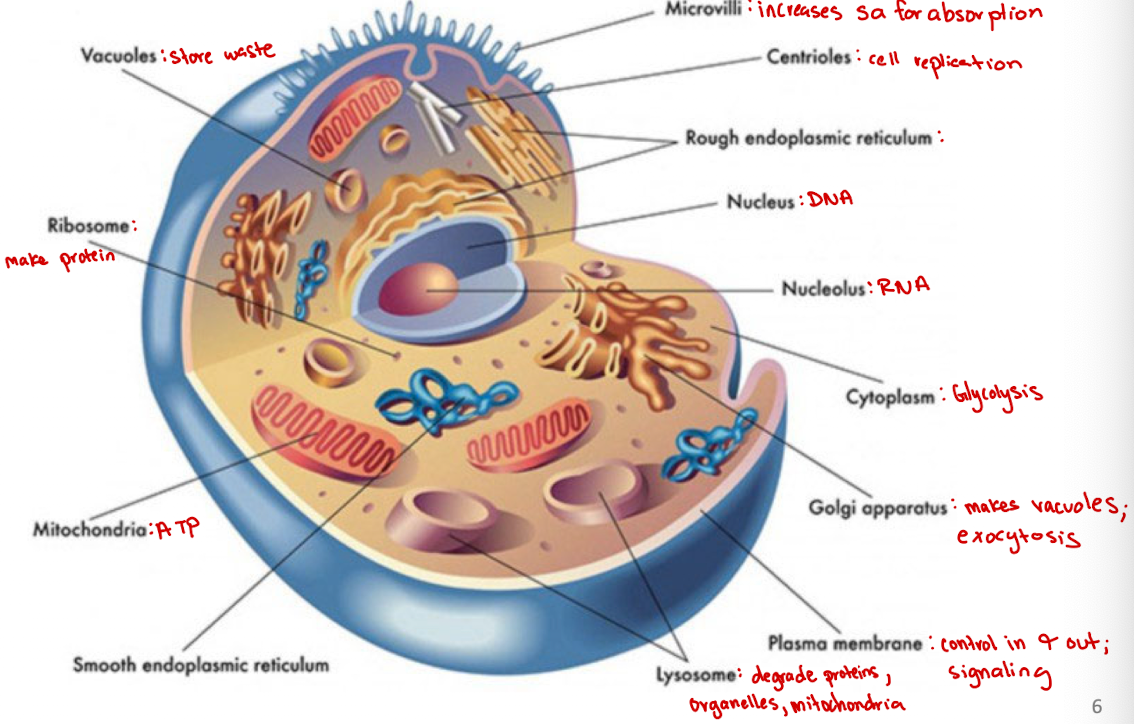
Lysosome
degrade proteins, organelles, mitochondria
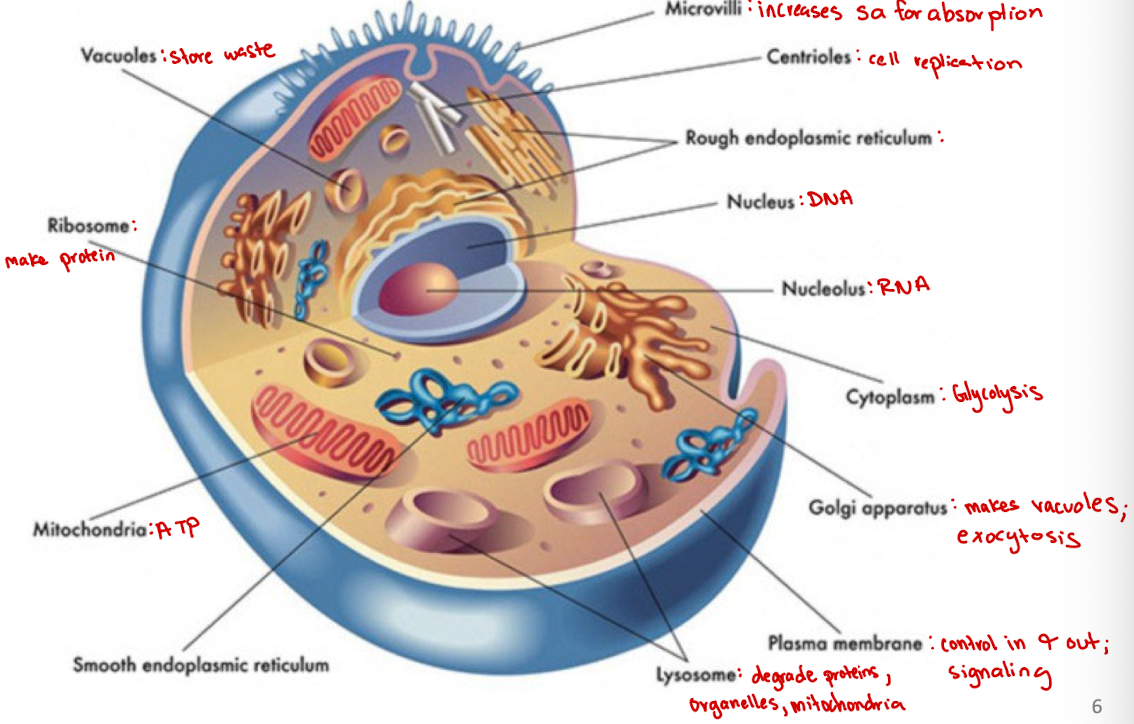
Cytoplasm
jelly-like substance within a cell that contains organelles, enzymes, and various molecules, and is involved in cellular processes (ex. glycolysis)
Four Primary Types of Tissues
Muscle (contraction)
Nervous (signals)
Epithelial (exchange)
Connective (structural support)
Muscle (contraction)
skeletal
cardiac
smooth
Nervous (signals)
central
peripheral
Epithelial (exchange)
Tissue that covers outside of the body and lines organs and cavities
epithelial sheets (form boundaries)
glands (secretion)
Connective (structural support)
Body tissue that provides support for the body and connects all of its parts
tendons
bones
blood
List the body systems (11)
circulatory system
digestive system
respiratory system
urinary system
skeletal system
immune system
muscular system
integumentary system
nervous system
endocrine system
reproductive system
Circulatory system examples
Circulates blood around the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to organs and cells, carrying waste products away
heart, blood vessels, blood
Digestive system
Mechanical and chemical processes that provide nutrients via the mouth, esophagus, stomach and intestines. Eliminates waste from the body
mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, related organs
respiratory system
lungs and major airways
Urinary system
kidneys and associated structures
skeletal system
bones and joints
immune system
WBCs and lymphoid organs
muscular system
skeletal muscles
integumentary system
skin and related structures
nervous system
brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sense organs
endocrine system
all hormone- secreting glands
reproductive system
male and female gonads and related organs
Homeostasis
the maintenance of a dynamic steady state in the internal, environment (Independent of our minds)
Homeostasis Examples
concentration of nutrients
partial pressure of O2 and CO2
Concentration of metabolic waste products
blood pH
Blood osmolarity
concentration of Na+, K+ and other electrolytes
blood volume and pressure
body temperature
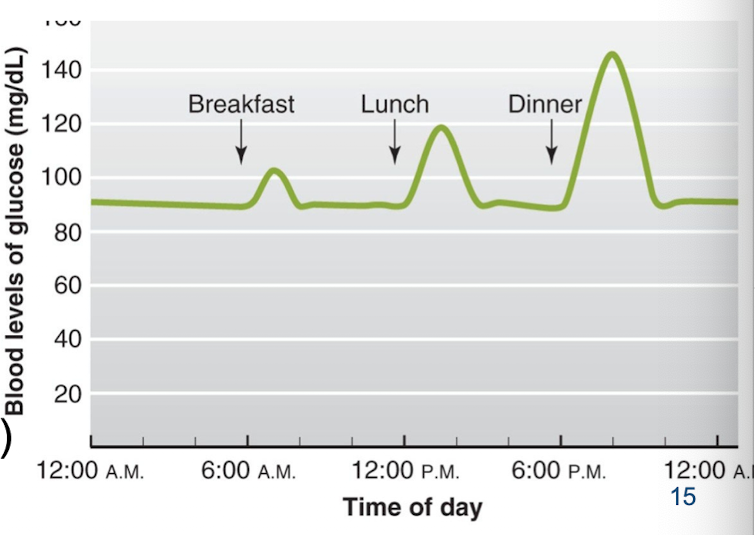
Dynamic constancy and example
Homeostasis refers to the dynamic mechanisms that detect and respond to deviations in physiological variables from their “set point” (set range) values by initiating effector responses that restore the variables to the optimal physiological range.
Example: Deviations in glucose concentration in blood (vary short term, fairly constant in the long term).
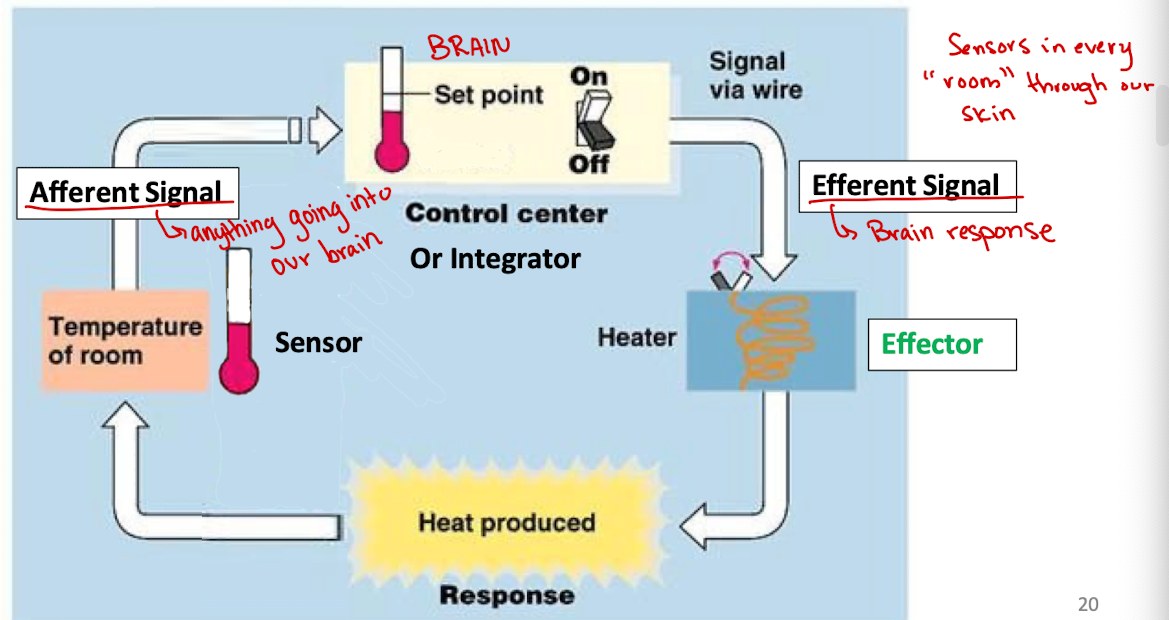
Homeostatic Control System
interconnected network of body components that work together to maintain a given factor relatively constant (never truly constant)
How would the control system maintain homeostasis?
Sensor detected deviation from Set Point
Control Center
Response involving Effectors
Sensor detected deviation from Set Point (Control System)
detect deviations from normal (alpha and beta cells)
Control Center (Control System)
Integrate this information with other information (ex. pancreas)
Response involving Effectors (Control System)
Make adjustments to restore the factor to normal (insulin and glucagon)
Negative feedback
A primary mechanism of homeostasis, whereby a change in a physiological variable that is being monitored triggers a response that counteracts the initial fluctuation.
What do the intrinsic and extrinsic systems generally operate on?
Negative feedback
Afferent Signal
Sends the information from the sensor to the control center/integrator (sometimes it is not needed if the sensor and control center are the same cell)
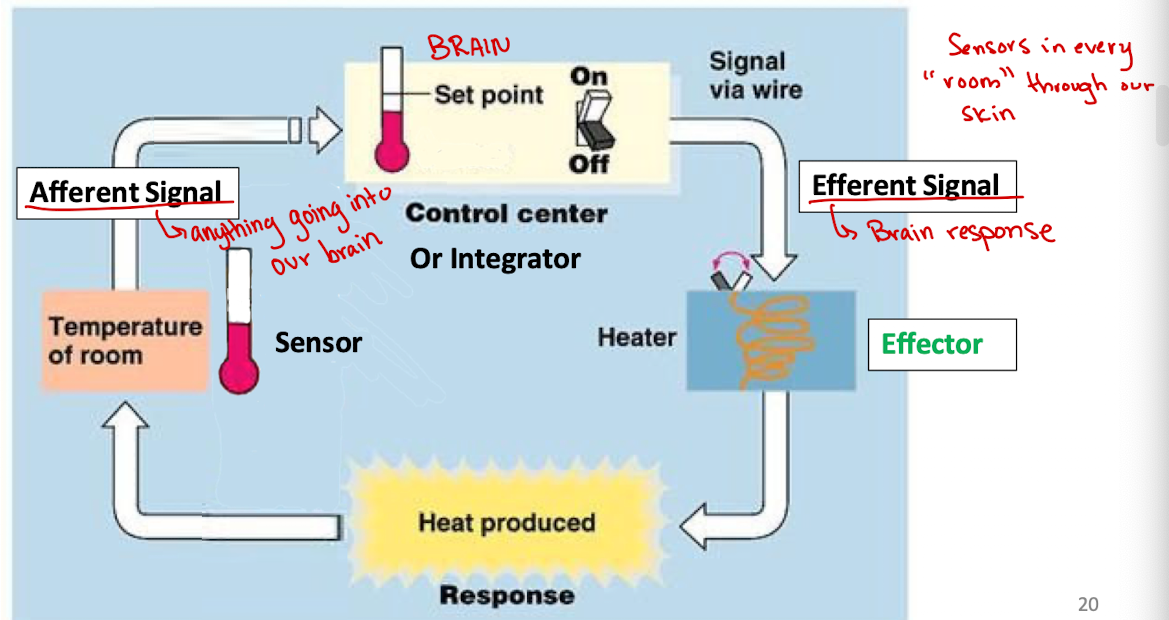
Efferent Signal
Used to send information from the control center to the effectors (cells/organs) that need to perform an action to help restore homeostasis
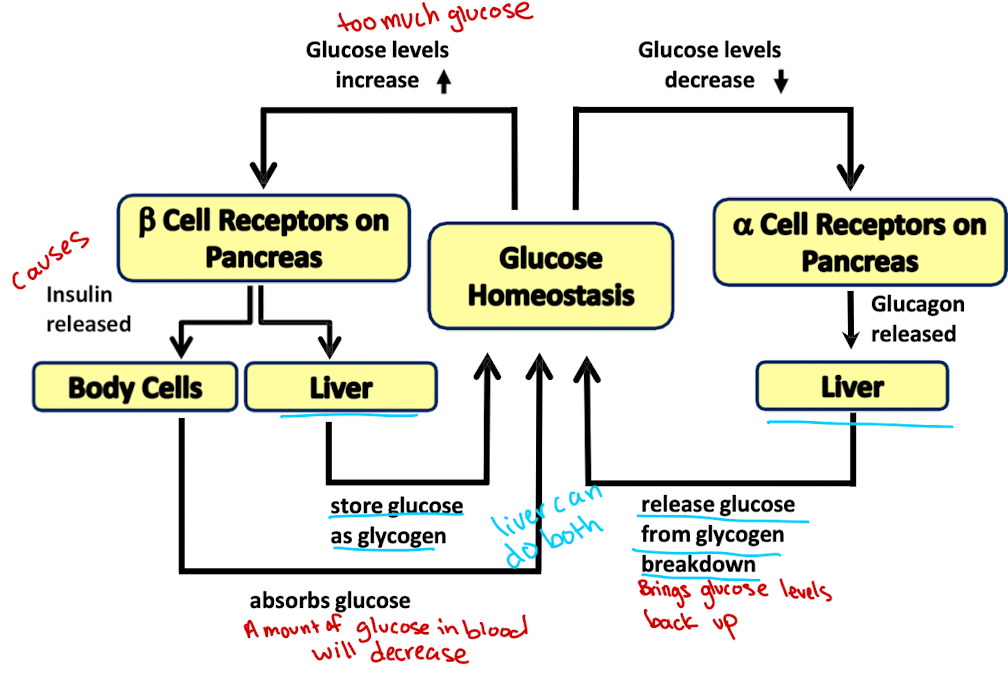
When glucose concentration is high…?
Beta cells of the pancreas release insulin to lower glucose levels
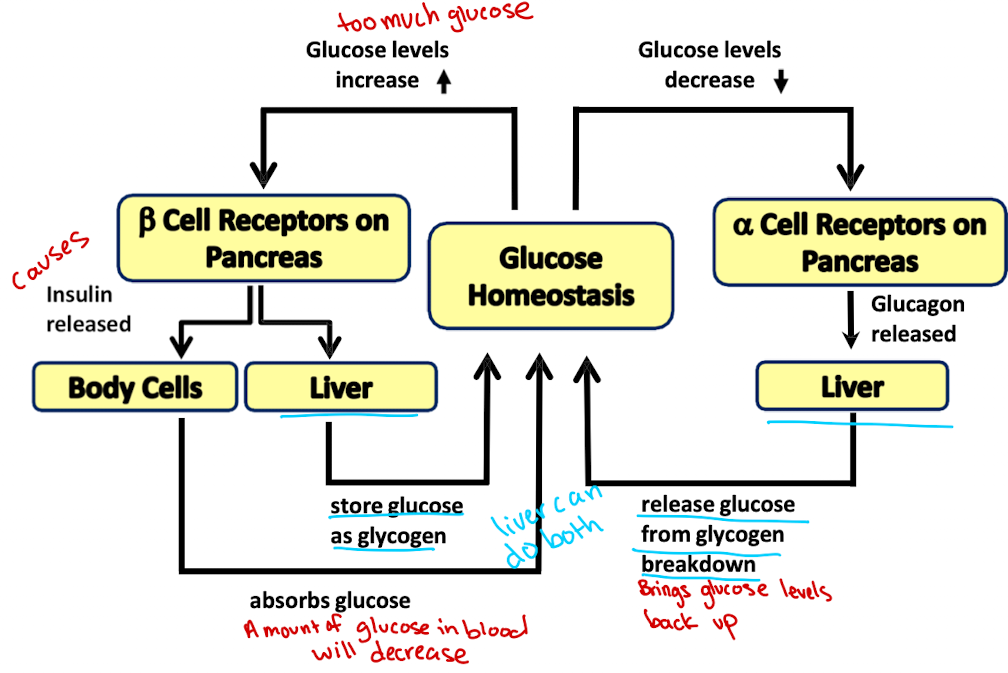
When glucose concentration is low …?
Alpha cells of the pancreas release glucagon to increase glucose levels
Intrinsic (local) control systems
“built in” to an organ or tissue
e.g., increased CO2 production by exercising skeletal muscle leads to relaxation of smooth muscle and dilation of blood vessels, increased blood flow brings more O2
Extrinsic control systems
contained outside of an organ system, permitting coordinated regulation of several organs
e.g., low blood pressure is detected by the nervous system, which causes an increase in heart rate and constriction of blood vessels
e.g., high blood glucose is detected by the endocrine system which exerts hormonal control [insulin]
Pathophysiology
abnormal functioning of the body associated with disease (Disruption in Homeostasis)
What happens when homeostatic disruption becomes very severe?
Death
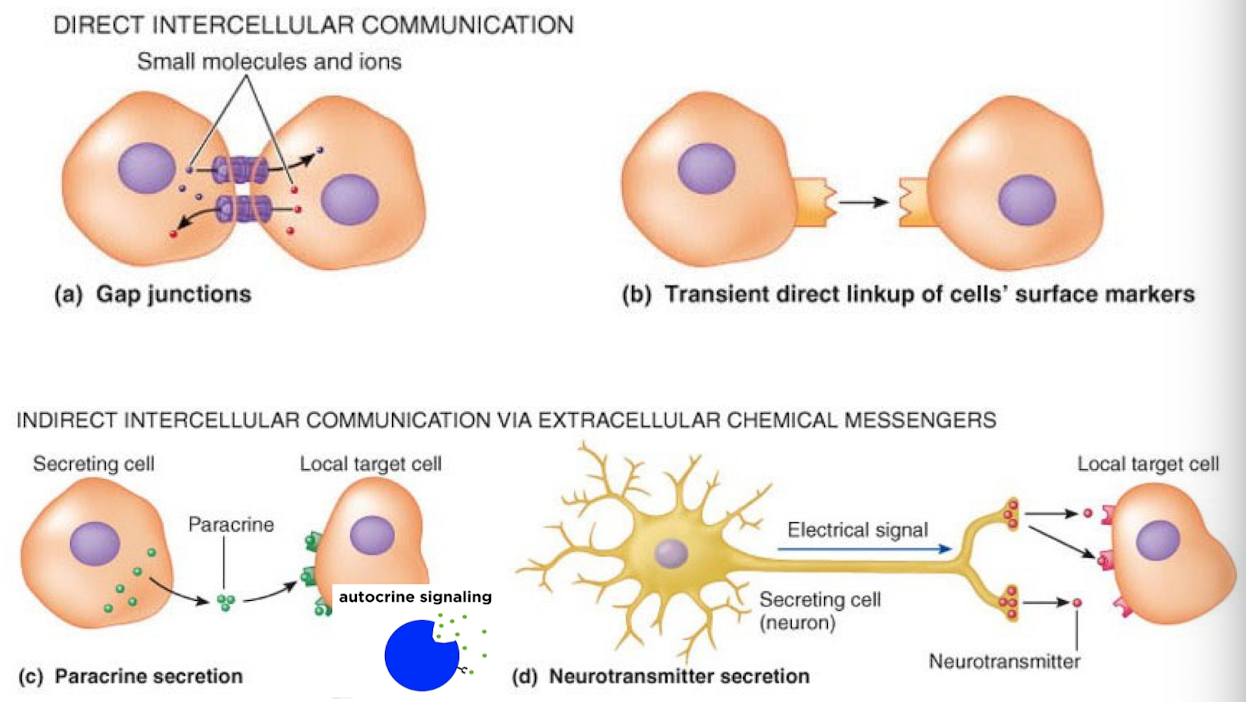
How do cells of the body talk to each other to maintain homeostasis? (3 main, 2 subs each)
Direct Intercellular Communication
Gap Junctions
Transient direct linkup of cells surface markers
Indirect Intercellular Communication via Extracellular Chemical Messengers
Paracrine secretion
Neurotransmitter secretion
Endocrine Signaling
Hormones
Neurohormones
Hormone
extracellular signaling molecule that is released into the blood and acts at its receptors in distal tissues to elicit a physicological response
Nervous system vs Endocrine System
Nervous System
“wired” system
short distance (diffuses across synaptic cleft)
dependent on close anatomic relationship btwn neurons and target cells
fast and brief
Endocrine System
“wireless” system
long distance (carried by blood)
dependent on specificity of target cell binding and responsiveness to particular hormone
slow and long
Does positive feedback contribute to homeostasis?
no
Positive feedback
Amplifies the initial change, moves the system away from the set point, important in processes such as childbirth
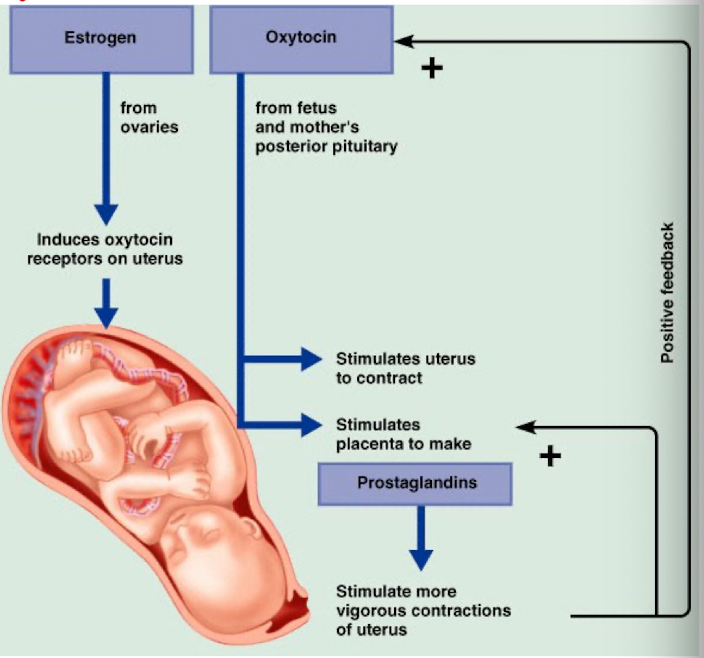
Feedforward mechanisms
operate without detectors and activate homeostatic mechanisms and anticipate when a change is likely to occur
Can be done in response to an anticipated once in a lifetime event
Can be done through body rhythms
Alterations in Homeostasis where set points can change
In sickness
As we age
Throughout the day
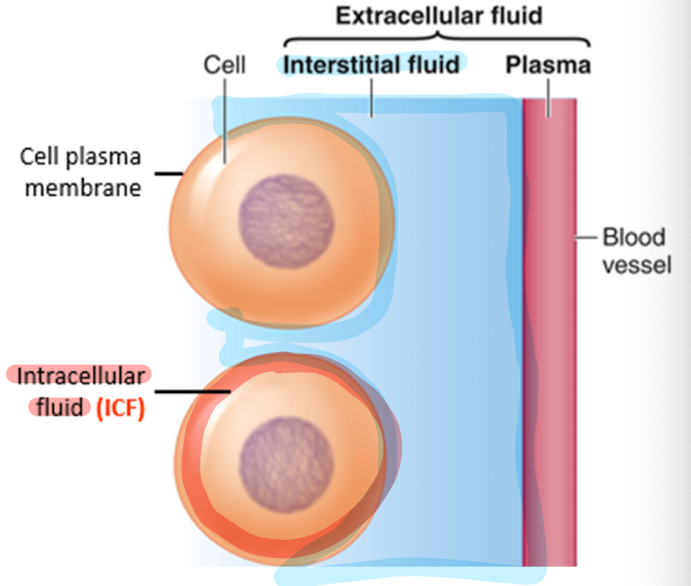
What 3 fluids are exchanged in homeostasis?
Cells exchange materials from the intracellular fluid, with the interstitial fluid (extracellular space) and blood (specifically plasma)