RX 422: Complex Injectable Formulations
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
What are the "golden rules" for administration of a drug by parenteral route?
1. Drugs MUST be soluble in a compatible vehicle for IV administration (exception nanoparticles/liposomes).
2. Insoluble drugs can be administered by IM, SC or implants in soft tissues only.
3. IV oil administration is ONLY possible with EMULSION systems - W/O or O/W?
Parental Dosage Forms
- Traditional (monophasic)
--- Aqueous Solution
- Modified (multiphasic)
--- Insoluble drugs
----- Inclusion complex
----- oil solution
----- suspension
----- emulsion
--- Controlled/sustained release
----- oil solution
----- suspension
----- microparticles
----- implants
--- targeted delivery
----- liposomes
----- nanoparticles
----- micelles
----- dendrimers
Traditional (monophasic) Parenteral Dosage Forms
Aqueous Solution
Modified (multiphasic) Parenteral Dosage Forms
- Insoluble drugs
--- Inclusion complex
--- oil solution
--- suspension
--- emulsion
- Controlled/sustained release
--- oil solution
--- suspension
--- microparticles
--- implants
- targeted delivery
--- liposomes
--- nanoparticles
--- micelles
--- dendrimers
Insoluble drugs Parenteral Dosage Forms
- Inclusion complex
- oil solution
- suspension
- emulsion
Controlled/sustained release Parenteral Dosage Forms
- oil solution
- suspension
- microparticles
- implants
targeted delivery Parenteral Dosage Forms
- liposomes
- nanoparticles
- micelles
- dendrimers
"Modified injectables" vs "modified release injectables": Modified injectables
- Administration of insoluble drugs in the form of an emulsion
- modified
- Drug targeting (active or passive)
- modified
- Intracellular drug delivery
- modified
- Influenza vaccine
- alum ppt. killed vaccine
- modified
"Modified injectables" vs "modified release injectables": Modified release injectables
- Local therapeutic effect with high local drug concentration without corresponding systemic exposure (e.g., carmustine implants in brain cancer)
- modified release
- Reduce dosing frequency for chronic administration of drugs that have short elimination half-life (e.g., hormone preparations in oil, given as IM or SC "depots")
- modified release
Why long-acting (modified release) injectables, LAIs? Clinical advantages
- Longer duration of action by sustained release of the drug
- Lower plasma levels with less toxic and less systemic exposure, leading to a reduction of side effects
- Reduced injection frequency More cost-effective due to lower dosing levels and drug usage
- Improved patient compliance because of a more convenient user experience
- Enhanced therapeutic efficacy Life cycle management
Why long-acting (modified release) injectables, LAIs? Non-clinical advantages
- Improved stability by encapsulating the compound in a polymer matrix, thus protecting it from environmental influences. Easier storage and transport
- A sustained-release formulation can be a solution for insoluble compounds.
- Opportunity to develop formulations for insoluble compounds
Disadvantages of long acting (modified release) injectables
- It is difficult to reverse the pharmacological effects of a parenteral product.
- It is necessary to study long-term toxicity of residual drug and excipient.
- Any premature release of the drug could be fatal (dose dump).
Prolonged release injectable, IM Volume
2 - 5 ml
Prolonged release injectable, SC Volume
1 - 2 ml
Prolonged release injectable, IM Irritancy
Large vol of mild irritant product should be administered in large skeletal muscle, deltoid, triceps, gluteus maximus etc.
Prolonged release injectable, SC Irritancy
Preferably non-irritant products
Prolonged release injectable, IM Safety
- MUST avoid any vein or artery
- needs trained personnel.
Prolonged release injectable, SC Safety
Less chance of any vein or artery punctures.
Immunological effects of injectable drug delivery
- Practically all molecules or materials, including those made by our own body (i.e., self-antigens), are antigenic (i.e., capable of reacting with components of the immune system)
- Although the immunogenicity of soluble self-proteins is low or absent, practically all recombinant human proteins are immunogenic in patients.
- Conjugation of haptens (i.e., small molecules that can function as B cell epitopes if bound to a carrier) to proteins can render them immunogenic, no matter whether the hapten is an endogenous compound.
- A significant increase in IgG1 levels following subcutaneous administration in mice of foreign proteins or protein-hapten conjugates encapsulated in PLGA particles was observed in comparison with the levels after administration of the free compounds.
Pharmacokinetics for a drug administered as an extended release intramuscular or subcutaneous system (image)
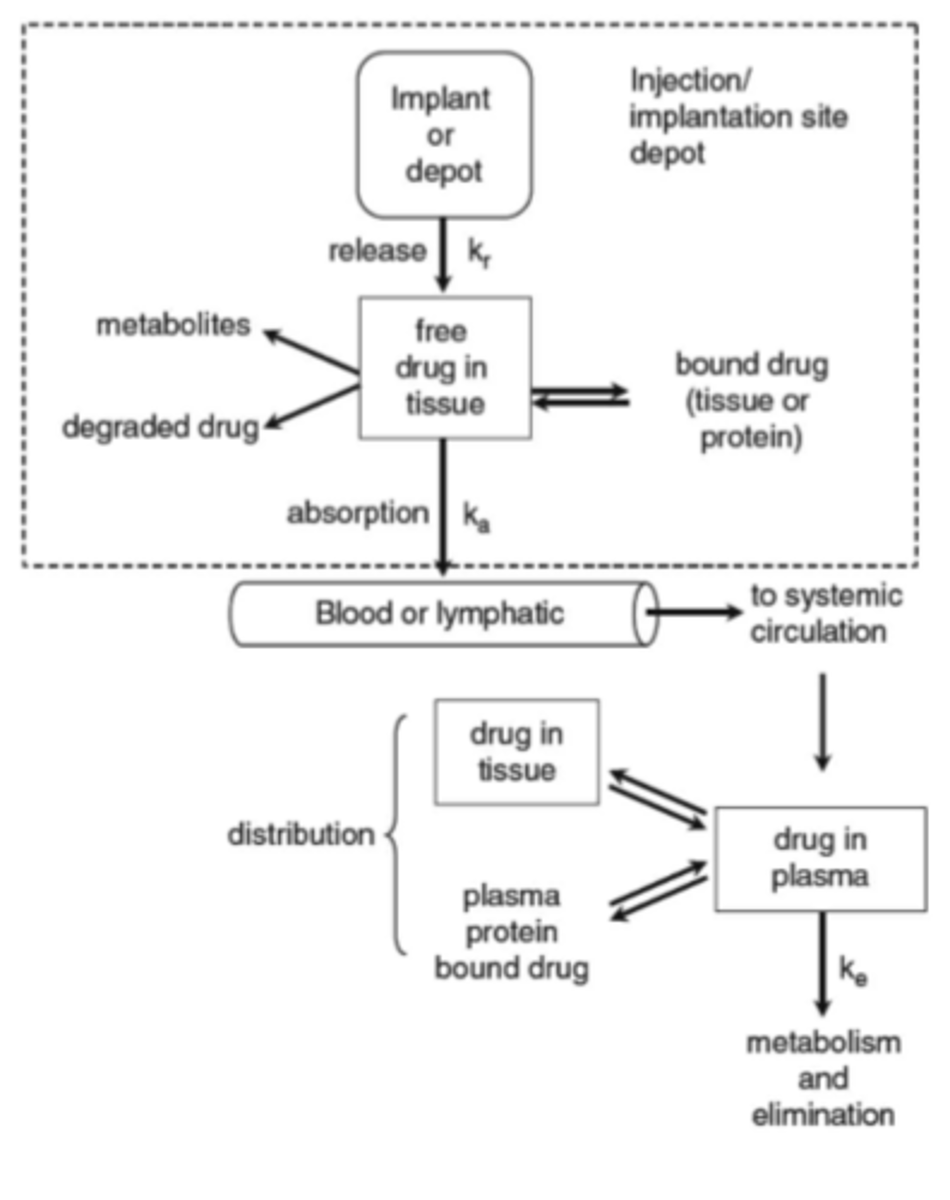
Diseases that could benefit from prolonged release injections or implants
- Diabetes
- Prostate cancer
- Contraception
- Osteoporosis
- Arthritis
Formulations containing cyclodextrins
- Dextrins are a group of low-molecular weight carbohydrates produced by the hydrolysis of starch or glycogen.
- They are mixtures of D-glucose units linked by alpha (1,4) glycoside bonds.
- Cyclical dextrins are called cyclodextrin.
- Due to the nature of orientation of the dextrins, the cyclic oligosaccharide forms a hydrophilic outer surface and a lipophilic central cavity.
- Lipophilic molecules can be incorporated in cyclodextrin molecules as 1:1 inclusion complex.
- The complex releases the drug on dilution and follows a very rapid equilibrium.
- Due to the presence of a number of hydrogen donors and acceptors, they themselves do not permeate through the lipophilic membranes but successfully deliver the drug across the membrane.
- Both the sulfobutyl ether derivative (SBE-ß-CD) and hydroxy propyl derivative (HP-ß-CD) are FDA approved for parenteral products.
- The safety profile of SBE-ß-CD is the best, followed by HP-ß-CD.
Cyclodextrin (image)
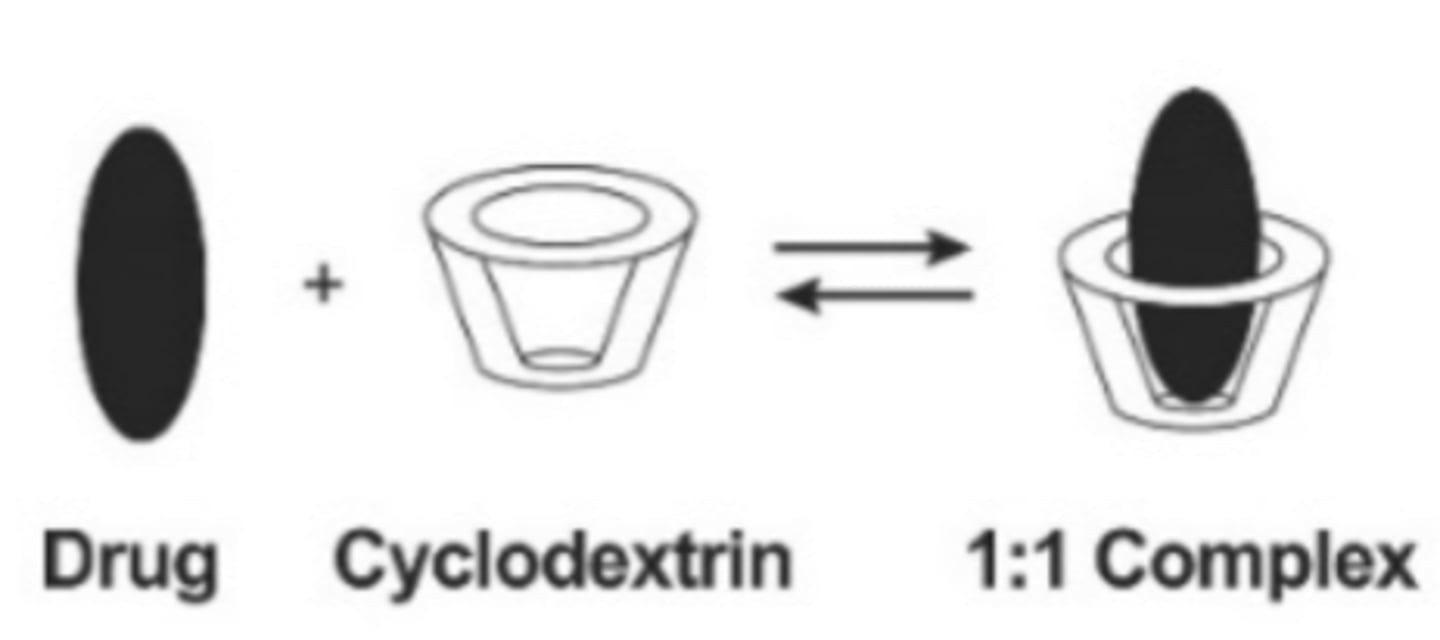
Advantages of cyclodextrin formulations
- Enhancement of solubility
- Enhancement of bioavailability
- Improvement of stability
- Reduction of tissue irritation
- Prevention of physical or chemical incompatibility with other drugs/excipients
- Odor and taste masking
FDA approved cyclodextrin conjugated parenteral
- Voriconazole (Vfend, antifungal), IV, uses SBE7-β-CD
- Ziprazidone (Geodon, antipsychotic), IM, uses SBE7- β -CD
- Aripiprazole (Abilify, antipsychotic), IM, uses SBE7- β -CD
- Telavancin (Vibativ, infection of skin), IV, uses HP5- β -CD
Oily vehicles: Vegetable oils
- Vegetable oils are used as vehicles for most of the modified or modified release parenteral products.
- Synthetic fatty acid esters such as isopropyl myristate and ethyl oleate constitute alternative vehicles.
- Vegetable oils contain various triglycerides in different proportions; castor oil, in particular, deviates from the other oils by the high content of a fatty acid (ricinoleic acid) with a hydroxy group.
- The fatty acid composition of vegetable oils influence vehicle density and viscosity. In general, vegetable oils exhibit an acceptable chemical stability.
- Certain drugs for long-acting formulations are synthesized by esterification of the parent drug to a long-chain fatty acid.
- Based on its extremely low water solubility, a fatty acid ester of a drug dissolves slowly at the injection site after IM injection and is hydrolyzed to the parent drug.
- Once the ester is hydrolyzed intramuscularly, the parent drug becomes available in the systemic circulation.
- Triglycerides containing unsaturated fatty acids might be susceptible to autoxidation, a degradation pathway catalyzed by heat and light.
Oily vehicles: Soybean oil
- Soybean oil is seldom used in parenteral modified release products as it contains phytoestrogens.
- Drug absorption rate depends on the oil/water partition coefficient of the drug.
Oil based injection products could be what?
suspensions (hydrophilic drug) or solution (hydrophobic drug) and provide therapeutic action from one week to about a month.
Commonly used oils in IM products
- Castor oil with benzyl benzoate
- Sesame oil with chlorbutanol
- Sesame oil with benzyl alcohol
- Sesame oil with propyl parahydroxy benzoate
- Cottonseed oil with benzyl benzoate and benzyl alcohol
- Medium-chain triglycerides (several proprietary products)
Aveed notes
a long-acting depot formulation of testosterone undecanoate in castor oil and benzyl benzoate. It offers a novel dosing schedule, with a single 3-mL (750 mg) intramuscular injection given once at initiation of therapy, at 4 weeks, and then every 10 weeks thereafter.
Aqueous suspensions: For hydrophobic drugs
An aqueous suspension of a drug is a saturated solution with suspended solid particulates of the drug; this provides immediate as well as prolonged release of the drug.
Aqueous suspensions: For hydrophilic drugs
The half-life for hydrophilic drugs can be extended by forming a long-chain fatty acid ester. Due to their extremely low water solubility, this fatty acid ester of a drug dissolves slowly at the injection site following IM injection.
example of prodrug formulation
Invega Sustenna; Paliperidone palmitate is the prodrug of paliperidone palmitoyl ester. This formulation is indicated as an injection once every 28 days following an initial titration period.
CABENUVA Example
(cabotegravir extended-release injectable suspension; rilpivirine extended release injectable suspension), co-packaged for intramuscular use. Initial U.S. Approval: 2021
Formulation parameters for optimal therapeutic benefit of aqueous suspensions
- Particle size/surface area of the active ingredient
- Crystal habit of the active ingredient
- pH of the formulation
- Flocculated or deflocculated
- Sedimentation rate of particles
- Zeta potential
Injectable emulsions
- Intravenous fat emulsion (IVFE) is an important source of calories and essential fatty acids for patients receiving parenteral nutrition (PN).
- The first product available in the United States was released in 1961 and was made from safflower oil.
- It consisted of 77% omega-6 fatty acids but lacked alpha linolenic acid, which is an essential fatty acid.
- So, it provided some, but not all, of the essential fatty acids needed for patient's dependent on parenteral nutrition to prevent fatty acid deficiency.
- Since that time, additional products derived from soybean oil have come on the market.
- They include IVFE Intralipid (Baxter; Deerfield, IL), IVFE Liposyn III (Hospira; Lake Forest, IL), and IVFE Nutrilipid (B. Braun; Bethlehem, PA), which are currently available in the United States.
- The soybean oil in these products provides a mixture of omega-6, omega-3, and omega-9 fatty acids.
- About 50% of the emulsion is made up of omega-6 fatty acids, as well as 25% omega-3 and 25% omega-9 fatty acids.
- In addition, Propofol (Diprivan, Astra) and Clevidipine (Cleviprex, The Med Co.) are IV emulsions that are marketed in the US.
Microparticles
- For polymeric particles, the drug is entrapped within the polymer matrix, usually a biodegradable polymeric matrix.
- Since the late 1980's, there have been a number of modified release microparticle delivery systems introduced in the US market.
- Most of the microparticles are based on polylactide (PLA) or polylactide-co-glycolide (PLGA) matrices that modulate the availability of the drug.
The degradation products of PLGA are what?
lactic and glycolic acids, which either are excreted by the kidney or enter the Krebs cycle and are eliminated as carbon dioxide and water.
Drug release could be altered significantly by altering what?
molecular weight and appropriate conjugation, e.g., PLGA-glucose. Microparticulate systems (size range of 10 to 125 uM) are administered by IM route.
Lactides are more ___ (crystalline) while glycolides are more ___.
Hydrophobic; hydrophilic
Degradation profile can be tailored using what?
different molar ratios of lactide and glycolide.
The possible mechanisms of drug release from microsphere are as follows:
- initial release from the surface
- release through the pores
- diffusion through the intact polymer barrier
- diffusion through a water-swollen barrier
- polymer erosion, and bulk degradation
Nanoparticles
- Theoretically, less than 1uM but most nanoparticle formulation are in the range of 100
- 300 nm in diameter.
- Nanoparticles for IV administration are not designed to achieve significant prolonged release of the drug; rather the focus is on reducing drug toxicity, or drug targeting.
ABRAXANE and Nanoparticles
- First marketed IV nanoparticles of paclitaxel conjugated with human albumin (260 mg/m2 administered intravenously over 30 minutes every 3 weeks for breast cancer).
- ABRAXANE for Injectable Suspension (paclitaxel protein-bound particles for injectable suspension) is an albumin-bound form of paclitaxel with a mean particle size of approximately 130 nanometers.
- Paclitaxel exists in the particles in a non-crystalline, amorphous state.
- ABRAXANE is supplied as a white to yellow, sterile, lyophilized powder for reconstitution with 20 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP prior to intravenous infusion.
- Each single-use vial contains 100 mg of paclitaxel and approximately 900 mg of human albumin.
- The use of an in-line filter is not recommended.
- Abraxane contains human serum albumin-paclitaxel nanoparticles of approximately 130 nm in size, where the paclitaxel is present in a non-crystalline, amorphous state.
- Upon intravenous administration, the nanoparticles dissociate rapidly into soluble, albumin bound paclitaxel complexes of approximately 10 nm in size.
- Albumin is known to mediate endothelial caveolar transcytosis of plasma constituents, and in vitro studies demonstrated that the presence of albumin in Abraxane enhances transport of paclitaxel across endothelial cells.
- It is hypothesized that this enhanced trans-endothelial caveolar transport is mediated by the gp-60 albumin receptor, and that there is enhanced accumulation of paclitaxel in the area of tumor due to the albumin-binding protein Secreted Protein Acidic Rich in Cysteine (SPARC)
Abraxane Comparison With Taxol
- Albumin facilitates the administration of water-insoluble compounds
- better dissolution of paclitaxel.
- PK is practically same except for the elimination
- Does not contain CremophorEL (polyoxylated castor oil, solubilizing agent) that causes elevated level of toxicity
- Enables administration of 50% more paclitaxel with least side effects
- Paclitaxel-Cremophor administration is slow while Abraxane can be given over 30 minutes using standard IV line
- Eliminates the need for Cremophor EL known to cause plasticizer leaching from IV bags/tubing
Implants
Nonbiodegradable and biodegradable tissue implants have a long history. Minor surgical procedure is required to insert an implantable system SQ for systemic therapeutic effect or to place the drug delivery system into specific body site for local action.
Buprenorphine (Probuphine) Polymer
Non-biodegradable rod (ethyl vinyl acetate) Each 2.5‐mm × 26‐mm ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) implant contains 80 mg buprenorphine hydrochloride (equivalent to 74.2 mg buprenorphine).
Buprenorphine (Probuphine) Route
Subdermal
Histrelin (Vantas, GnRH analog) Polymer
Non-biodegradable hydrogel (2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate, 2-hydroxypropyl methacrylate, trimethylolpropane trimethacrylate, benzoin methyl ether)
Histrelin (Vantas, GnRH analog) Route
SQ implant
Etonogestrel (Implanon) Polymer
Non-biodegradable rod (ethyl vinyl acetate)
Etonogestrel (Implanon) Route
Subdermal implant
Carmustine (Gliadel) Polymer
Biodegradable polyanhydride wafer
Carmustine (Gliadel) Route
Intracranial implant
Gancyclovir (Vitrasert) Notes
Vitrasert implant is fixed at the pars plana and projects into the vitreous cavity; it releases the drug for 5 to 8 months and must be replaced.
Gancyclovir (Vitrasert) Polymer
Non-biodegradable insert (ethyl vinyl acetate)
Gancyclovir (Vitrasert) Route
Posterior segment of the eye
Fluocinolone acetonide (Retisert) Notes
it releases the drug for 30 months
Fluocinolone acetonide (Retisert) Polymer
A simple tablet encased in a silicone elastomer cup
Fluocinolone acetonide (Retisert) Route
Posterior segment of the eye
Contraceptive implants: Mirena/Liletta (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system)
hormone-releasing system placed in the uterus to prevent pregnancy for up to 5 years, after which a fresh unit is placed for continued contraception.
Contraceptive implants: ParaGard T 380A Intrauterine Copper Contraceptive (ParaGard)
- a Tshaped IUD
- The contraceptive effectiveness of ParaGard is enhanced by copper continuously released into the uterine cavity.
- Possible mechanism(s) by which copper enhances contraceptive efficacy include interference with sperm transport or fertilization, and prevention of implantation. ParaGard® is indicated for intrauterine contraception for up to 10 years.
- However, it is advisable to replace with a new one in every 5 years.
Contraceptive implants: NuvaRing
- flexible plastic (ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer) ring contains estrogen and progestin which work together to prevent ovaries from producing mature eggs.
- Over the course of three weeks, NuvaRing releases a continuous low dose of estrogen and progestin.
- Over a thousand NuvaRing related lawsuits have been filed against Merck.
Contraceptive implants: Annovera
- a reusable donut-shaped (ring), non-biodegradable, flexible vaginal system that is placed in the vagina for three weeks followed by one week out of the vagina, at which time women may experience a period (a withdrawal bleed).
- This schedule is repeated every four weeks for one year (thirteen 28-day menstrual cycles).
- It delivers segesterone & ethinyl estradiol in a steady rate.
- Selection of right IUD mainly depends on 1) length of pregnancy coverage, and 2) desired amount of hormone to be delivered.
In situ forming implants: Thermally induced gelling systems
- undergo sol-to-gel transition when the temperature changes.
- Thermosensitive polymers are especially attractive as they do not require organic solvents, co-polymerization agents or externally applied triggers for their gelation at physiological conditions.
- Despite this, temperature induced phase transitions are controlled by the temperature dependence of certain molecular interactions, such as hydrogen bonds or hydrophobic effects.
- These polymers are characterized by a lower critical gelation temperature (LCGT) and an upper critical gelation temperature (UCGT).
- LCGT and UCGT are functions of the hydrophilic-hydrophobic balance on the polymer backbone as well as the free energy of mixing.
- As the environmental temperature approaches LCGT, polymer-water interactions become unfavorable compared with water-water and polymer-polymer interactions. Therefore, these polymers show reduced viscosity below the LCGT, above which it increases sharply.
- At UCGT, the polymer chains achieve a high kinetic energy and become increasingly randomized, resulting in rupture of the gel structure and a decrease in viscosity. Therefore, polymer systems with a LCGT between room and physiological temperature are excellent candidates for injectable implant systems
In situ forming implants: In situ phase separation systems
- form gel phase as the compatible organic solvent is removed from the site.
- Examples include Atridox® which is used for the periodontal delivery of doxycycline, Eligard®, a subcutaneous depot of leuprolide for the treatment of prostate cancer and Sublocade, a buprenorphine extended-release SC injection.
- Sublocade (buprenorphine extended-release injection, also known as RBP-60001) is a drug device combination product with 18% (weight/weight) buprenorphine base in the ATRIGEL Delivery System is in a prefilled syringe.
- Upon SC injection, Sublocade forms a semi-solid depot, due to phase separation and precipitation of the polymer that releases buprenorphine via diffusion as the ATRIGEL polymer biodegrades.
In situ forming implants (image)
Sterilization Factors to consider: Microorganism contamination - Methods for sterilization
- Dry heat
- Autoclaving (moist heat)
- Formaldehyde
- Ethylene oxide
- Gas plasma
- Filtration
- Irradiation
--- Gamma ray
--- Electron beam
Sterilization Factors to consider: Microorganism contamination - Alteration of physicochemical properties
- Stability of matrix
- Drug release properties
- Toxicity
Sterilization Factors to consider: Endotoxin contamination
- No efficient technique established
- keep production process contamination free
What are the therapeutic benefits of a parenteral CRDDS?
Name a novel parenteral formulation which is not intended to deliver in a controlled release fashion.
Discuss soluble and insoluble drugs and the parenteral route that can be used to administer them.
How are drugs delivered from cyclodextrin complexes?
What is the difference in drug release mechanism from oily vehicles and aqueous suspensions?
What is the basic difference between nanoparticles and microparticles and which routes of administration can be used for them?
Why is PLGA widely used as the drug delivery matrix for parenteral microparticles?
What is the major application of implants?
Discuss the principles of in situ gelling implants.
Which type of emulsion will deliver a water insoluble drug across the blood brain barrier when given via IV?
You cannot give any W/O emulsion or any oil solution by the IV route, and NO suspensions - ONLY O/W type emulsions. An insoluble drug can be solubilized in the inner oil phase and can be administered as O/W emulsion.
How does cyclodextrin enhance permeation of an insoluble drug when given via the IV route?
Hydrophobic drugs solubilized using cyclodextrins can be administered by IV route. Cyclodextrin is just a carrier, it does not permeate. It carries the insoluble drug and delivers it to the membrane for permeation. There are two rate-limiting steps:
1) dissociation of the drug from cyclodextrin and
2) diffusion of the drug through the membrane involved in the process. However, the dissociation rate constant becomes the rate limiting step in most of the cases. Also, it is true that beta-cyclodextrins derivatives are normally used for solubilization of drugs.
We understand that neither emulsions nor nanoparticles are used for prolonged delivery of IV drugs. However, since nanoparticles are a matrix type dosage form with a drug embedded in them, wouldn't it prolong the release of the drug in blood?
Although the main aim of nanoparticulate drug delivery is not prolonged release but rather tissue targeting, it starts releasing the drug as soon as it is administered by the IV route and continues releasing until the polymer matrix is dissolved. However, by the time all the payload of the drug is released, the nanoparticles reach the target area or are engulfed by the macrophages and removed from the body. Therefore, the potential for prolonged IV drug delivery with nanoparticles is limited.