Chemistry Midterm
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/384
Last updated 8:09 PM on 1/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
385 Terms
1
New cards
scientific notation
used when writing very large or very small numbers, expresses a number as a product of a number between 1 and 10 and the appropriate power of 10
2
New cards
english system, metric system, international (SI) system
three unit systems
3
New cards
kilogram (kg)
SI unit for mass
4
New cards
meter (m)
SI unit for length
5
New cards
second (s)
SI unit for time
6
New cards
kelvin (K)
SI unit for temperature
7
New cards
liter (L)
SI unit for volume
8
New cards
accuracy
how close your average answer is to the correct answer
9
New cards
precision
the ability to reproduce results in the lab
10
New cards
not accurate, precise
this picture is showing
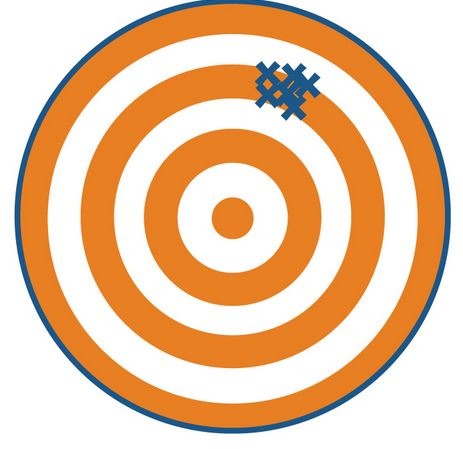

11
New cards
not accurate, not precise
this picture is showing
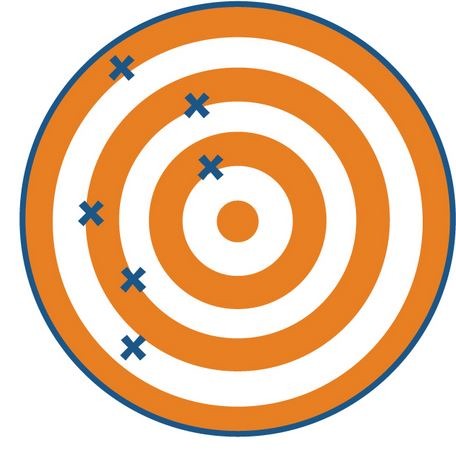
12
New cards
accurate, not precise
this picture is showing
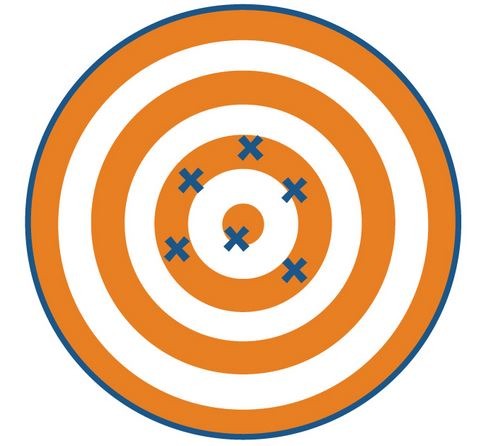

13
New cards
accurate, precise
this picture is showing
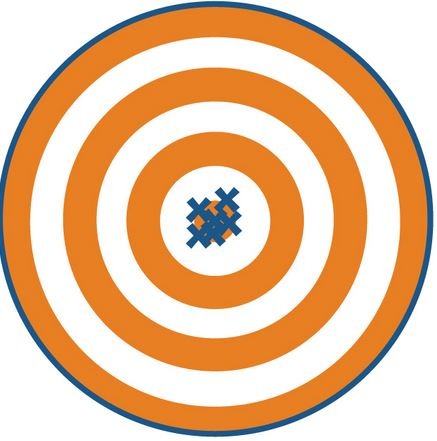

14
New cards
(| accepted - experimental |) / accepted
formula for finding % error
15
New cards
5
less than \___% error is accurate
16
New cards
measurement
always has some degree of uncertainty, should include all certain numbers plus one estimated number
17
New cards
significant figures
all of the numbers recorded in a measurement
18
New cards
certain, estimated
significant figures include all of the \___ numbers and one \___ number
19
New cards
significant
all numbers that are not zeros are \___
20
New cards
significant
all sandwiched zeros are \___
21
New cards
significant
all ending zeros following a decimal are \___
22
New cards
not significant
all leading zeros are \___
23
New cards
left, right, zeros, non-zero
To find the number of significant figures if a decimal is present in a number, you read from \___ to \___, skip any \___, and count from the first \___ number to the end
24
New cards
right, left, zeros, non-zero
To find the number of significant figures if a decimal is absent, you read from \___ to \___, skip any \___, and count from the first \___ number to the end
25
New cards
3
10.0 has \___ sig fig(s)
26
New cards
1
0.0004 has \___ sig fig(s)
27
New cards
1
100 has \___ sig fig(s)
28
New cards
4
101900 has \___ sig fig(s)
29
New cards
infinite
12 eggs has \___ sig fig(s)
30
New cards
least
In multiplication and division, the answer should have the same number of sig figs as the number in the problem with the \___ number of sig figs
31
New cards
greatest smallest, smallest
In addition and subtraction, the answer should be rounded to the same last numerical place as the number in the problem with the \___ \___ numerical place (usually with the \___ number of decimals)
32
New cards
100, defined value, infinite
In the formula for percent error, the \___ that is multiplied is not accounted for when trying to find sig figs because it is a \___ \___ and has an \___ number of sig figs
33
New cards
10^3
the prefix kilo is \___ times the base
34
New cards
kilo
the prefix \___ is 10^3 times the base
35
New cards
10^6
the prefix mega is \___ times the base
36
New cards
mega
the prefix \___ is 10^6 times the base
37
New cards
10^-1
the prefix deci is \___ times the base
38
New cards
deci
the prefix \___ is 10^-1 times the base
39
New cards
10^-2
the prefix centi is \___ times the base
40
New cards
centi
the prefix \___ is 10^-2 times the base
41
New cards
10^-3
the prefix milli is \___ times the base
42
New cards
milli
the prefix \___ is 10^-3 times the base
43
New cards
10^-6
the prefix macro is \___ times the base
44
New cards
macro
the prefix \___ is 10^-6 times the base
45
New cards
10^-9
the prefix nano is \___ times the base
46
New cards
nano
the prefix \___ is 10^-9 times the base
47
New cards
mL
1 cm^3 \= 1 \___
48
New cards
cm^3
1 mL \= 1 \___
49
New cards
L
1 dm^3 \= 1 \___
50
New cards
dm^3
1 L \= 1 \___
51
New cards
defined values, infinite
equivalency statements are \___ \___ and therefore have an \___ number of sig figs
52
New cards
factor label method
a method of using ratios to covert from one unit to another
53
New cards
numerator, denominator
you can change the power of any conversion factor as long as you do it to both the \___ and \___
54
New cards
density
a numerical value that represents the ratio of mass to volume for a given substance
55
New cards
M/V
D\=\___
56
New cards
DV
M\=\___
57
New cards
M/D
V\=\___
58
New cards
water displacement method
to calculate volume of irregularly shaped objects, the \___ is used
59
New cards
mass
In a density graph, the Y axis \= \___
60
New cards
volume
In a density graph, the X axis \= \___
61
New cards
density
In a density graph, the slope \= \___
62
New cards
0
In a density graph, the Y intercept \= \___
63
New cards
rise/run \= mass/volume \= density
equation to find density
64
New cards
mass, volume
In molecular drawings for density, the size or number of particles represents \___ while the size of the container represents \___
65
New cards
physical properties and changes
the matter does not make new or break old chemical bonds
66
New cards
chemical properties and changes
the matter does make new or break old chemical bonds
67
New cards
physical change
ripping is an example of a \___
68
New cards
physical change
bending is an example of a \___
69
New cards
physical changes
phase changes are examples of \___
70
New cards
physical change
dissolving is an example of a \___
71
New cards
chemical change
color change is an example of a \___
72
New cards
chemical change
precipitate formation is an example of a \___
73
New cards
chemical change
gas release (bubbling or fizzing) is an example of a \___
74
New cards
chemical change
heat release or absorption is an example of a \___
75
New cards
chemical change
a lack of a reaction indicates a \___
76
New cards
intrinsic property
a property that is independent of how much of the material is present
77
New cards
extrinsic property
a property that is dependent on the amount of material present
78
New cards
intrinsic properties
density and color are examples of \___
79
New cards
extrinsic properties
mass and volume are examples of \___
80
New cards
solid
the state of matter that is rigid, a fixed shape and volume, have little atomic motion, and are high in density
81
New cards
solid
this picture is showing a \___
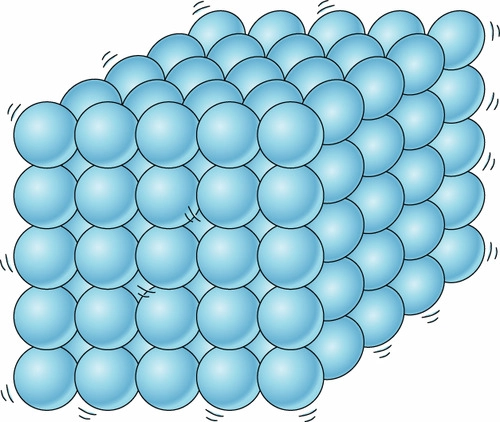
82
New cards
liquid
the state of matter that is fluid, has a definite volume but takes that shape of its container, has some atomic motion, and has medium density
83
New cards
liquid
this picture is showing a \___
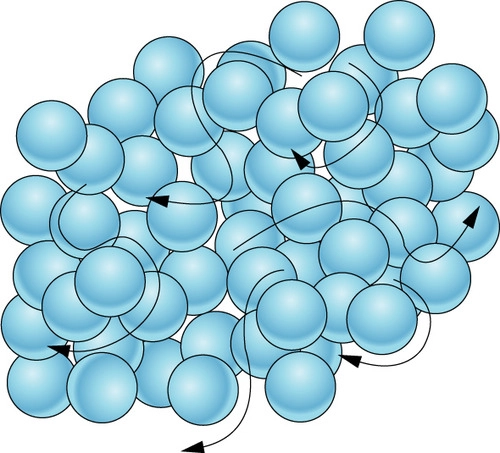
84
New cards
gas
the state of matter that has very unique properties, is compressible, has low density, expands, has no definite shape and volume, and has high atomic motion
85
New cards
gas
this picture is showing a \___
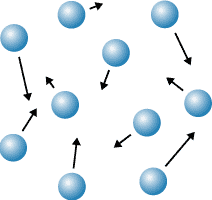
86
New cards
heating/cooling, pressure change
two ways to change the state of matter
87
New cards
physical
changing the state of matter is a \___ change
88
New cards
matter
anything that has mass and takes up space
89
New cards
pure substances, mixtures
two types of matter
90
New cards
physically, chemically
mixtures are \___ combined, not \___ combines
91
New cards
pure substance
a substance that is made up of one kind of matter
92
New cards
uniform, constant
pure substance are \___ and have \___ properties
93
New cards
elements and compounds
two types of pure substances
94
New cards
element
the simplest form of matter that is made of atoms or molecules, can not be broken down, and is identified by number of protons
95
New cards
compound
a chemical combination of two or more different elements that is made of molecules or formula units (ionic compounds), can only be separated with chemical processes, have unique properties when compared to the elements that make up them, and have defined ratios of atoms
96
New cards
mixture
any sample of matter that is made up of at least two different substances, the parts are not chemically combined, and can be separated with physical processes
97
New cards
homogeneous, heterogeneous
two main types of mixtures
98
New cards
heterogeneous mixture
a mixture that does not look uniform throughout
99
New cards
suspension, colloid
two types of heterogeneous mixtures
100
New cards
suspension
a heterogeneous mixture that has two distinct layers