Chemistry - Chapter 1: Atomic Structure, Periodic Table, Electronic Structure
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
atom
smallest unit of an element, neutral (unless otherwise stated)
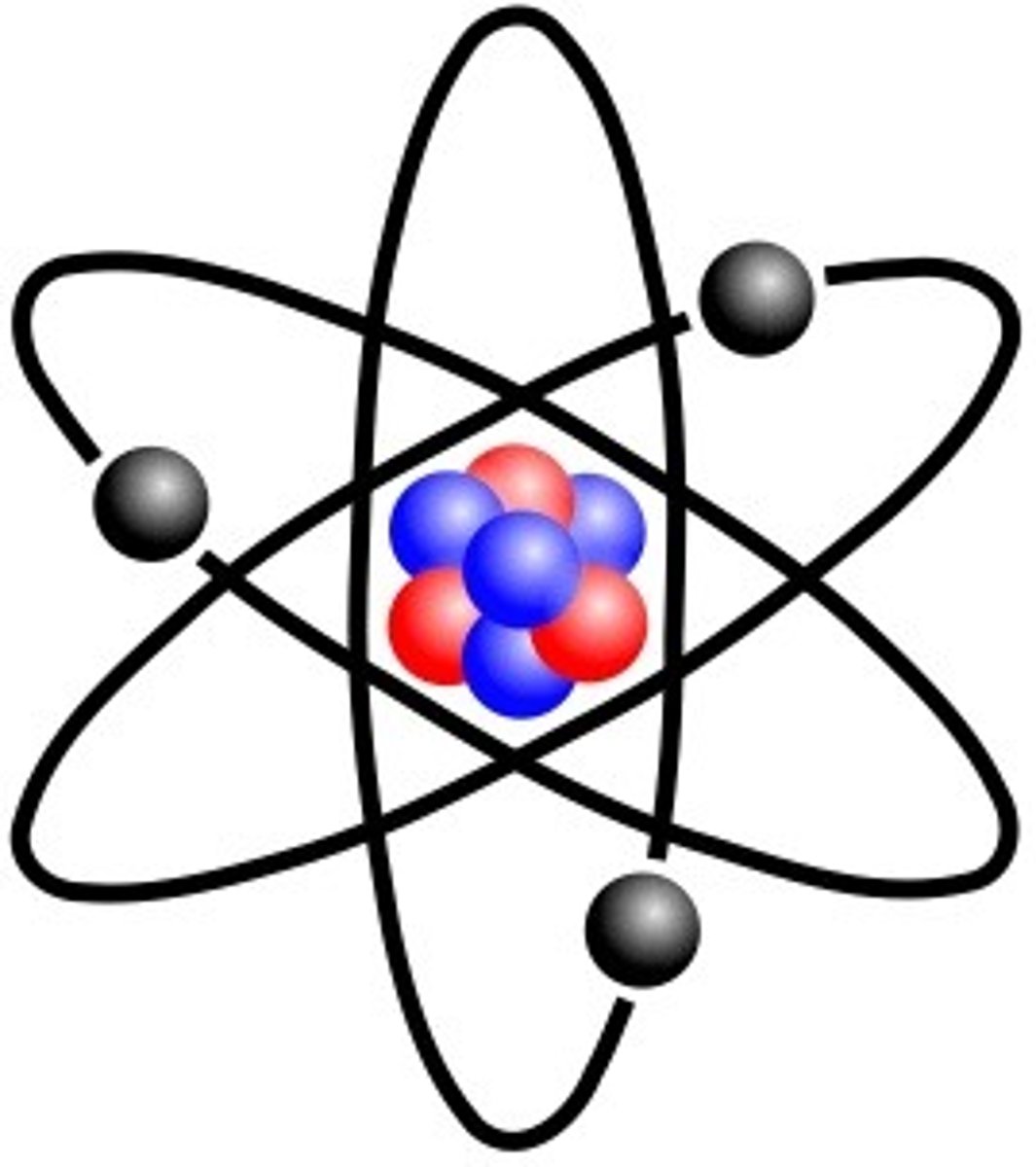
Atoms are made of...
protons, electrons, neutrons
Elements have
unique combinations of protons and electrons in atoms
protons (+1)
positive charge
electrons (-1)
negative charge, smallest particle
number of electrons =
number of protons
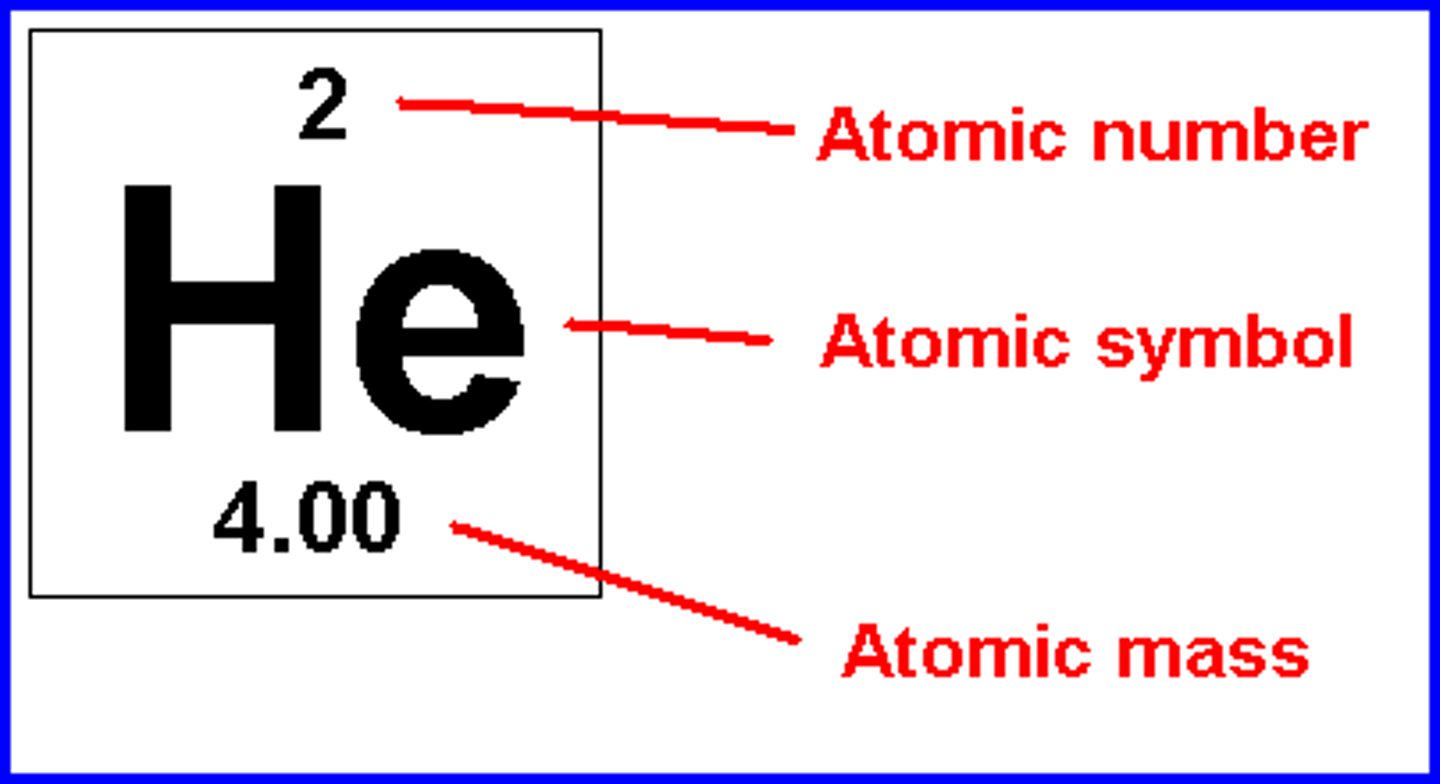
periodic table
describes atoms of every known element
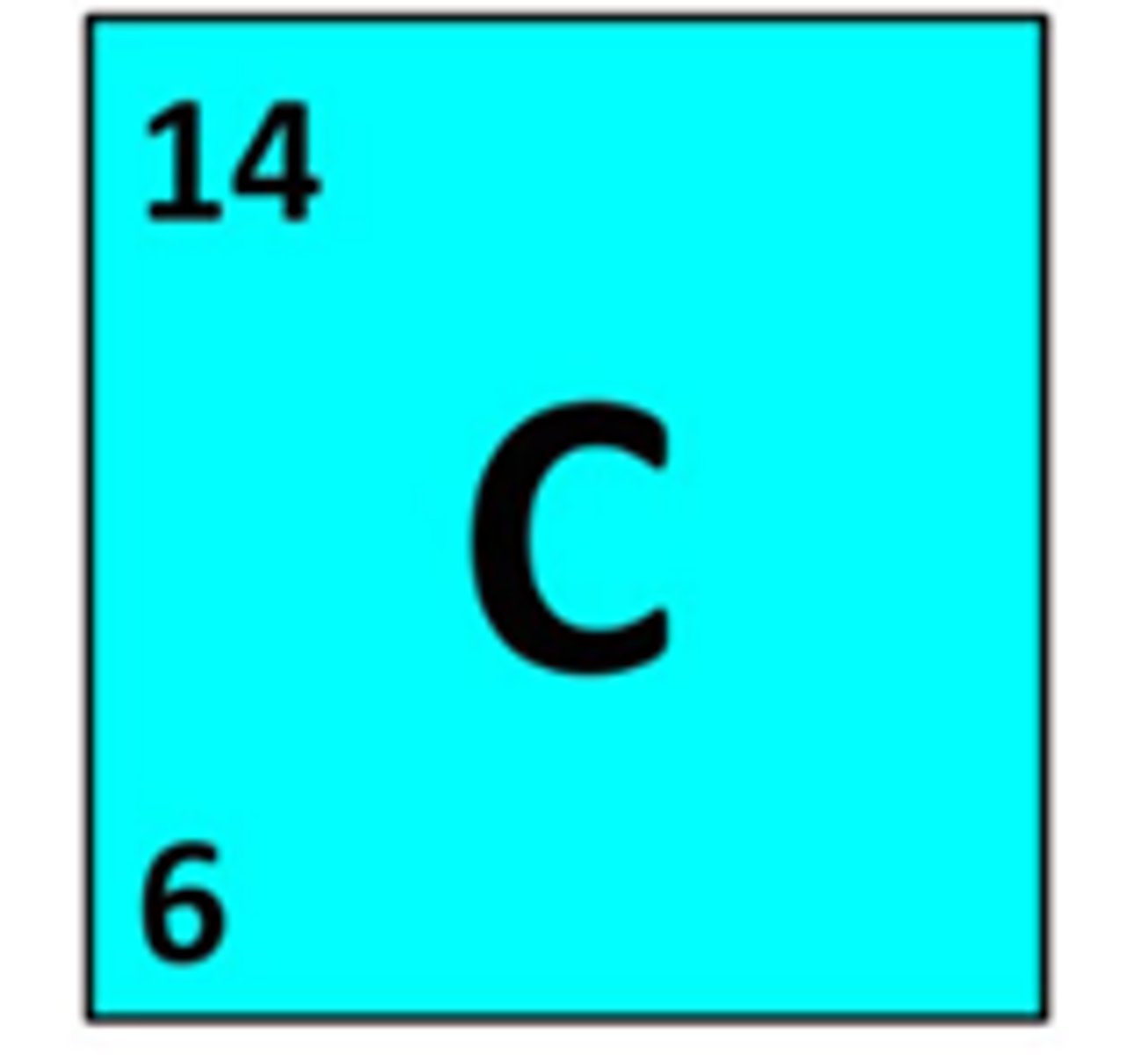
atomic number
number of protons, number above elements

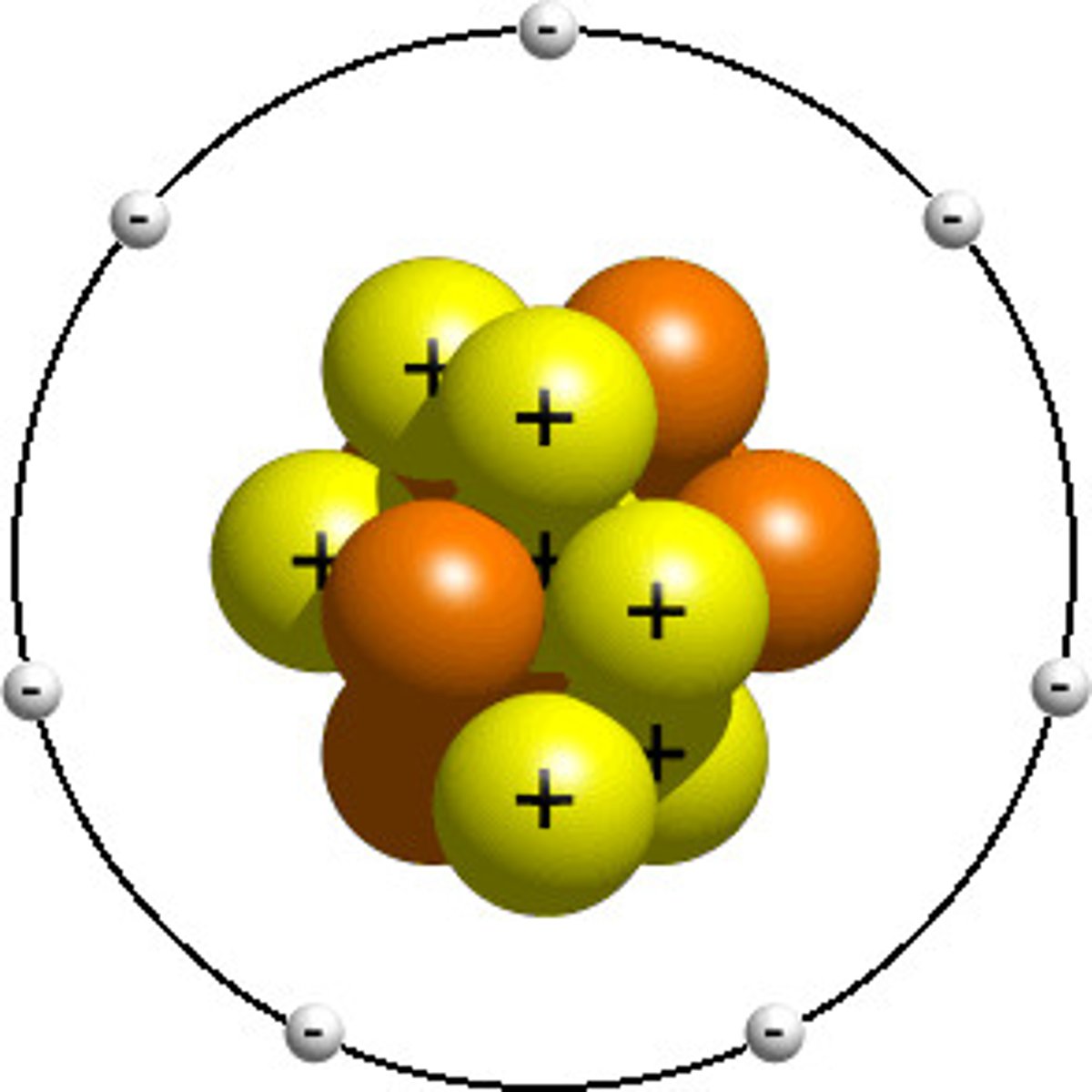
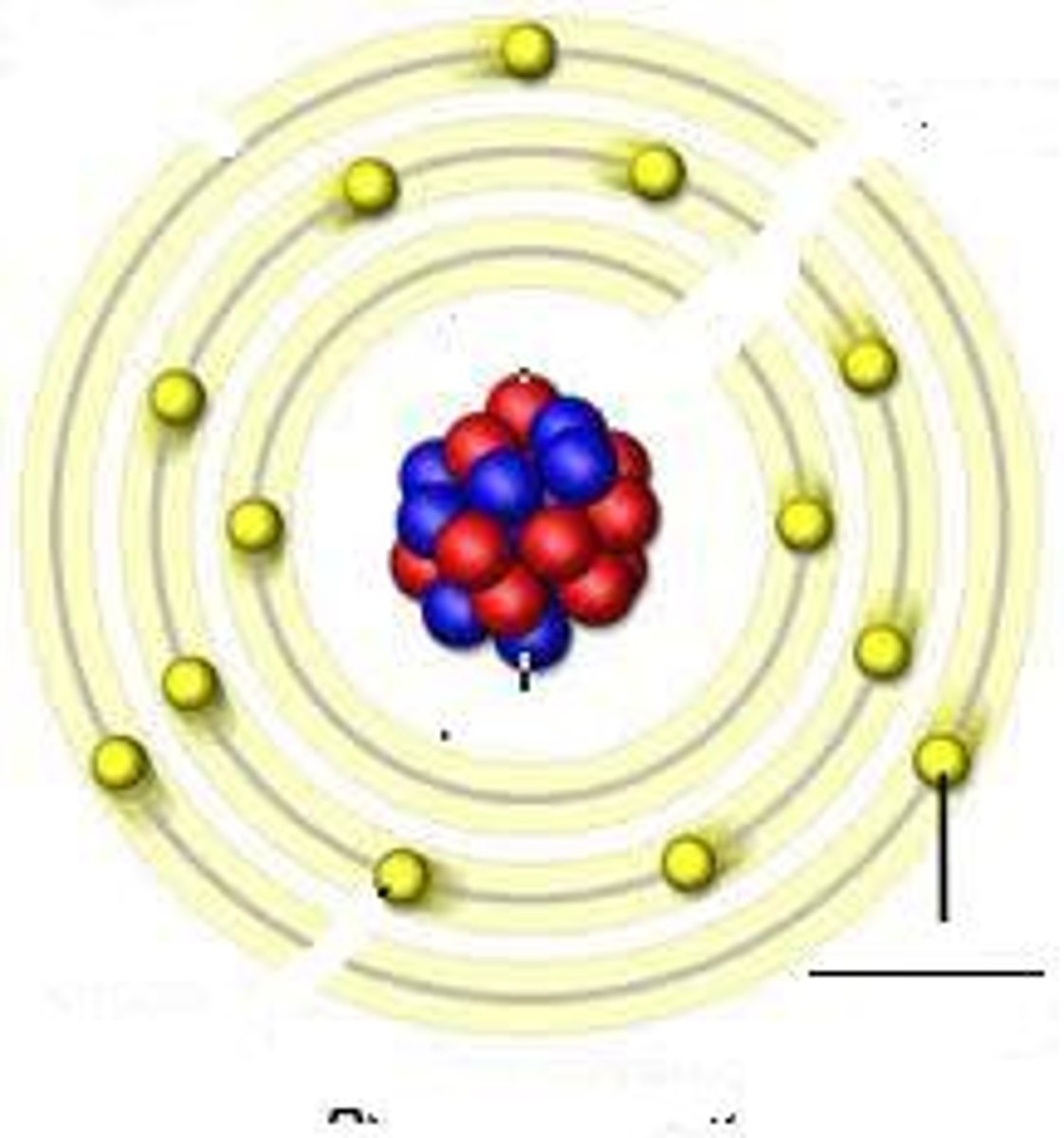
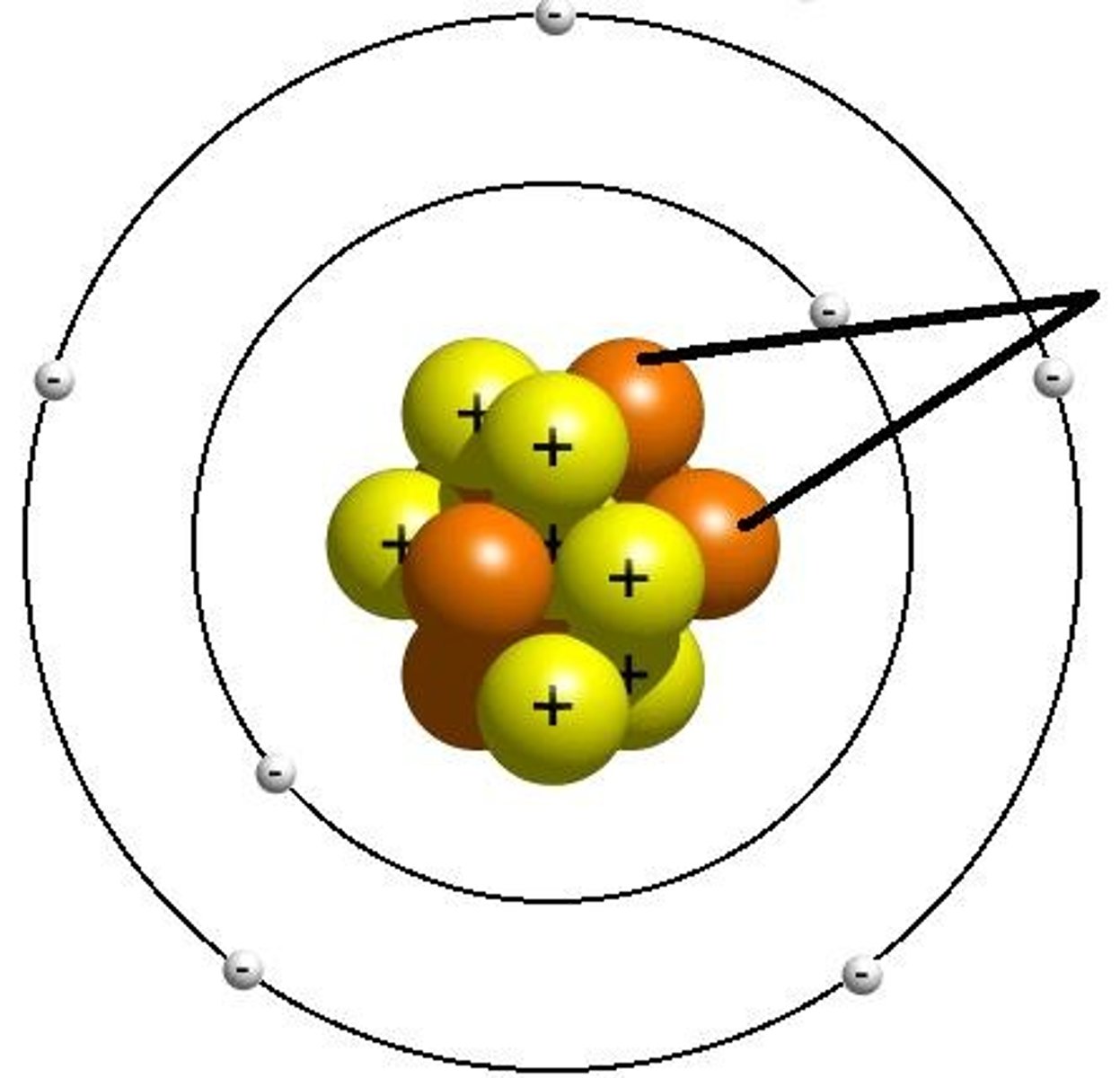
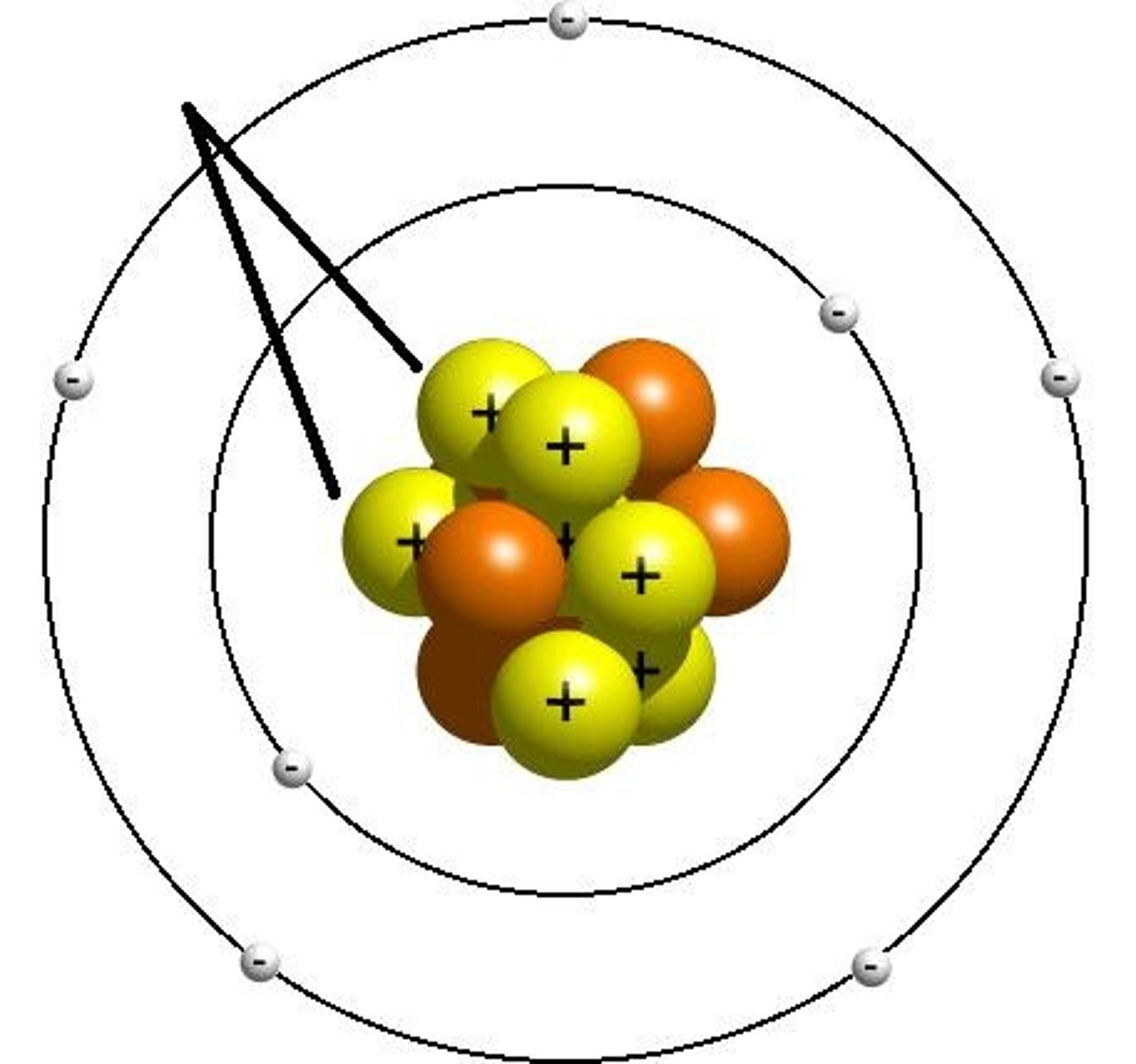
Bohr Atomic Model
shows atom with nucleus at the center and electrons revolving around it
Atomic particle sizes (smallest to largest)
electrons, protons, neutrons
1836 electrons =
1 proton
All elements (except Hydrogen)
have neutrons in the nucleus
neutron (0)
neutral particle, heaviest particle
Every element in the periodic table is
neutral
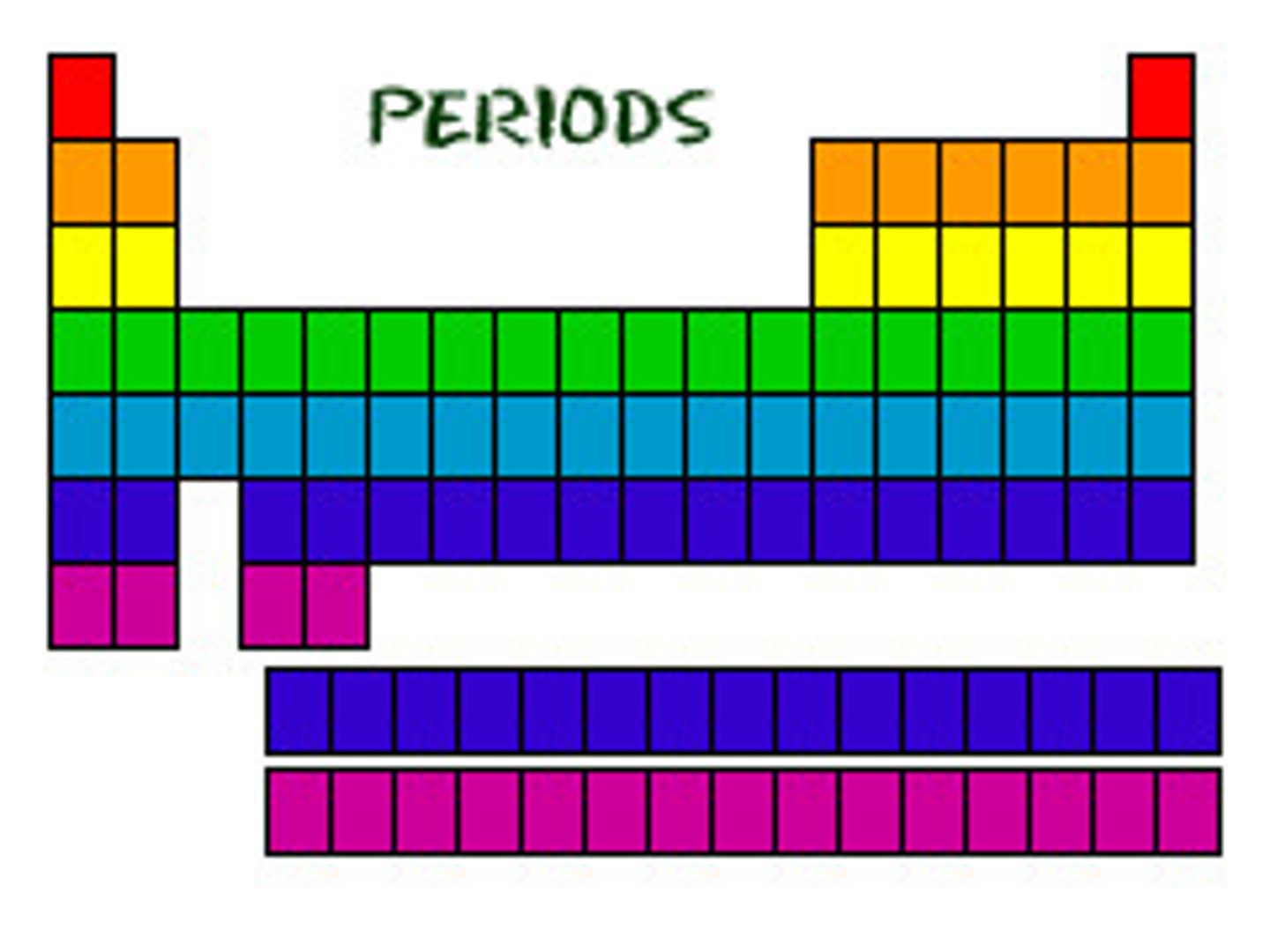
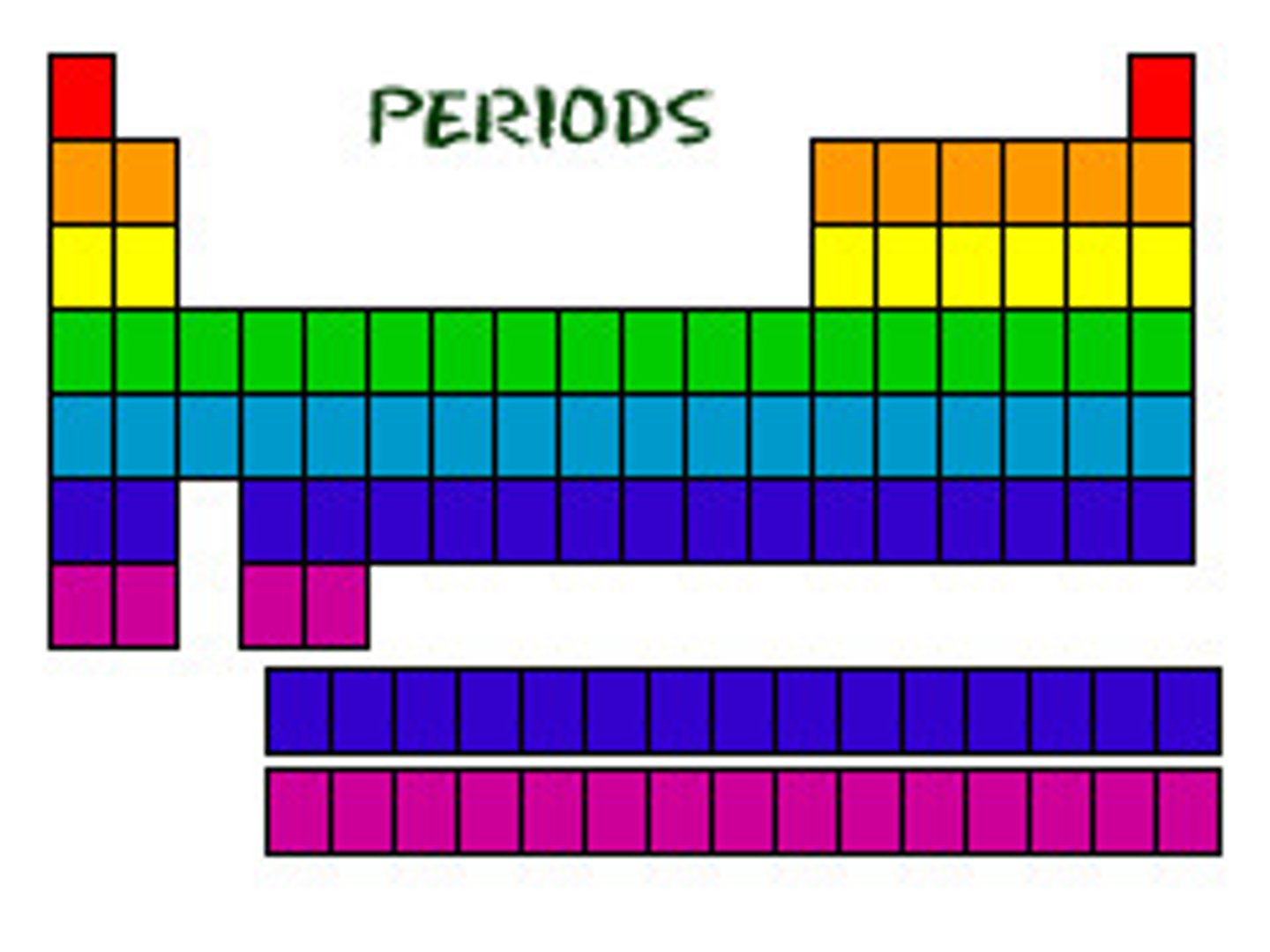
periods
rows on the periodic table
groups/families
columns on the periodic table
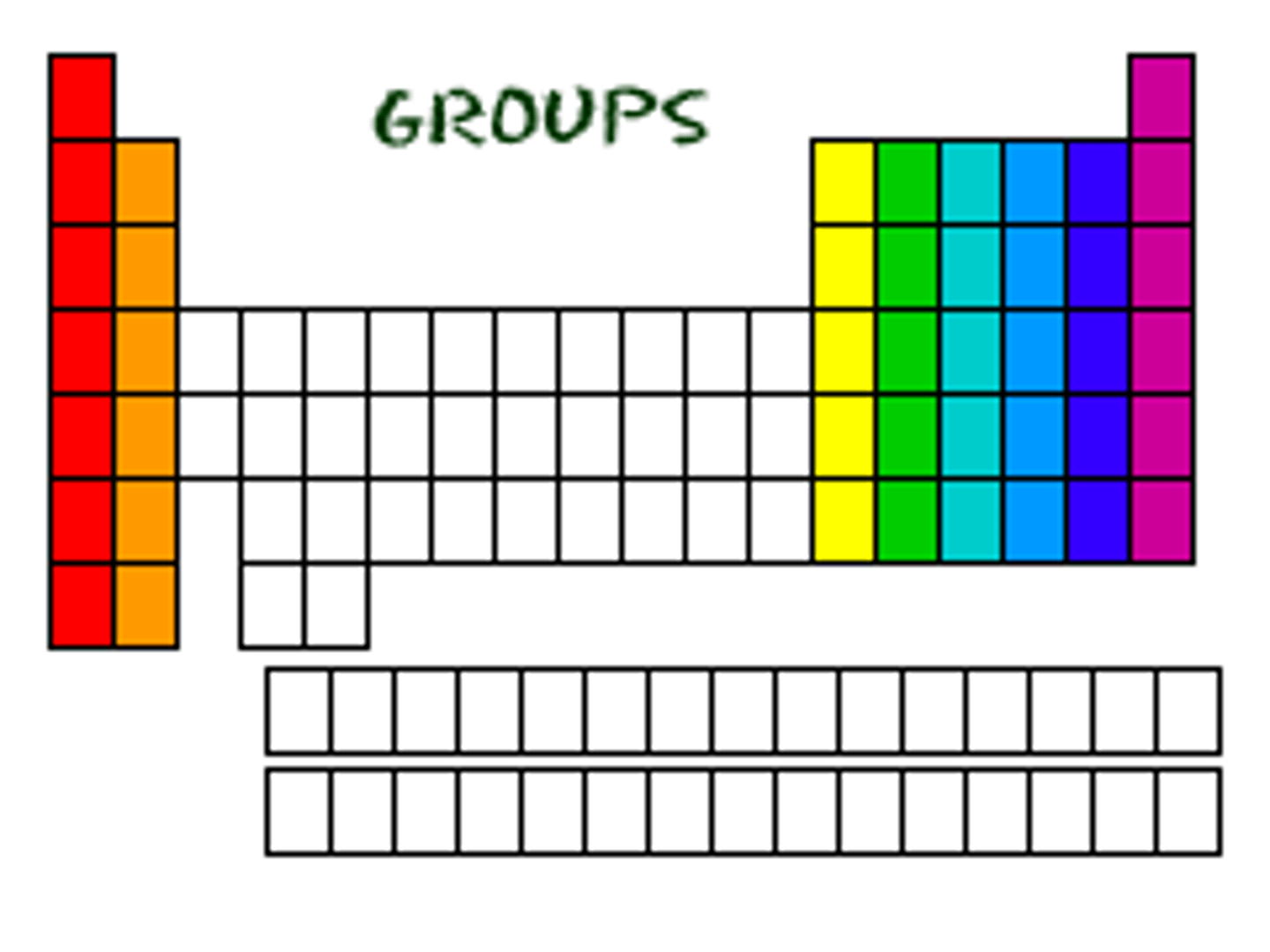
Elements in the same groups/families...
have similar properties
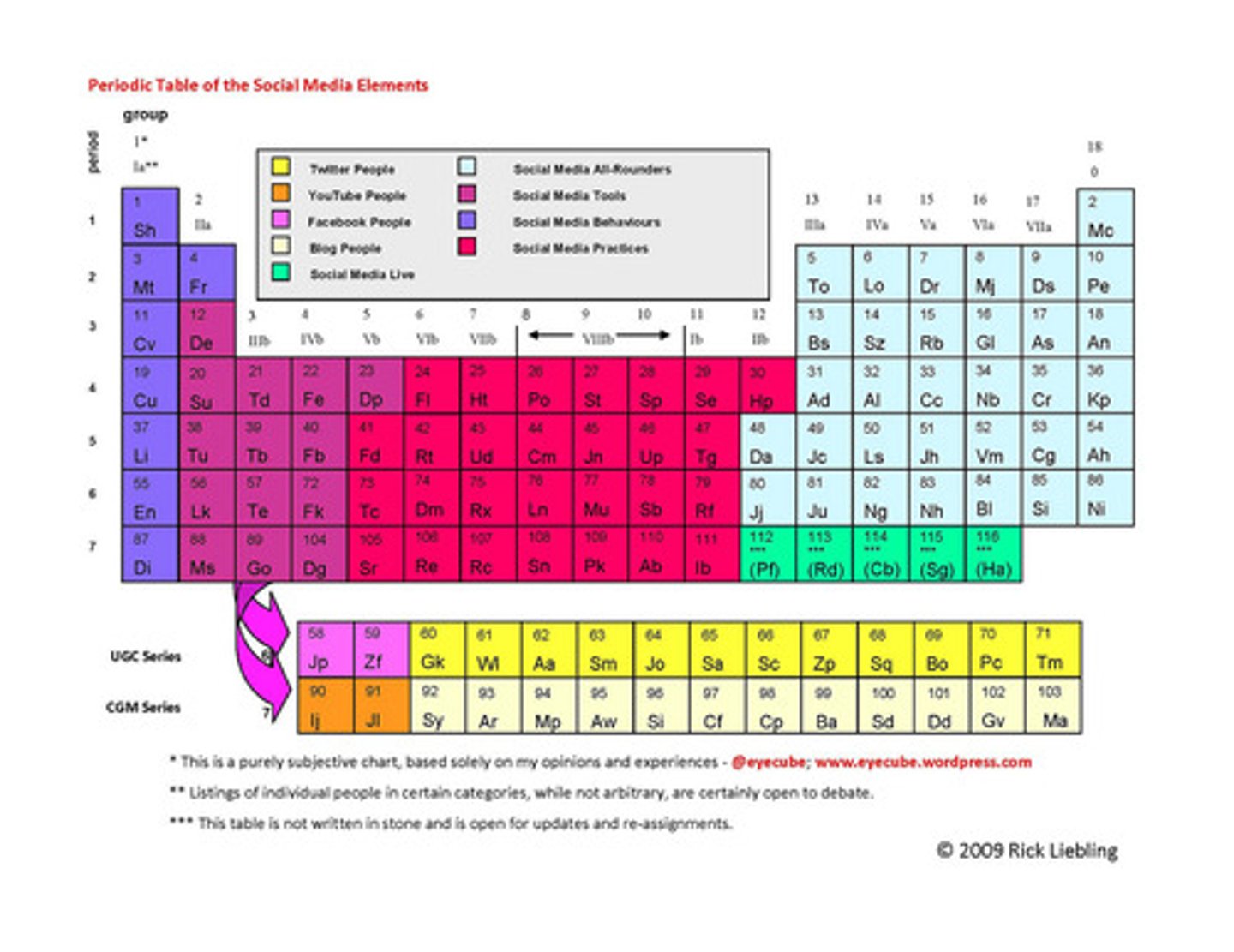
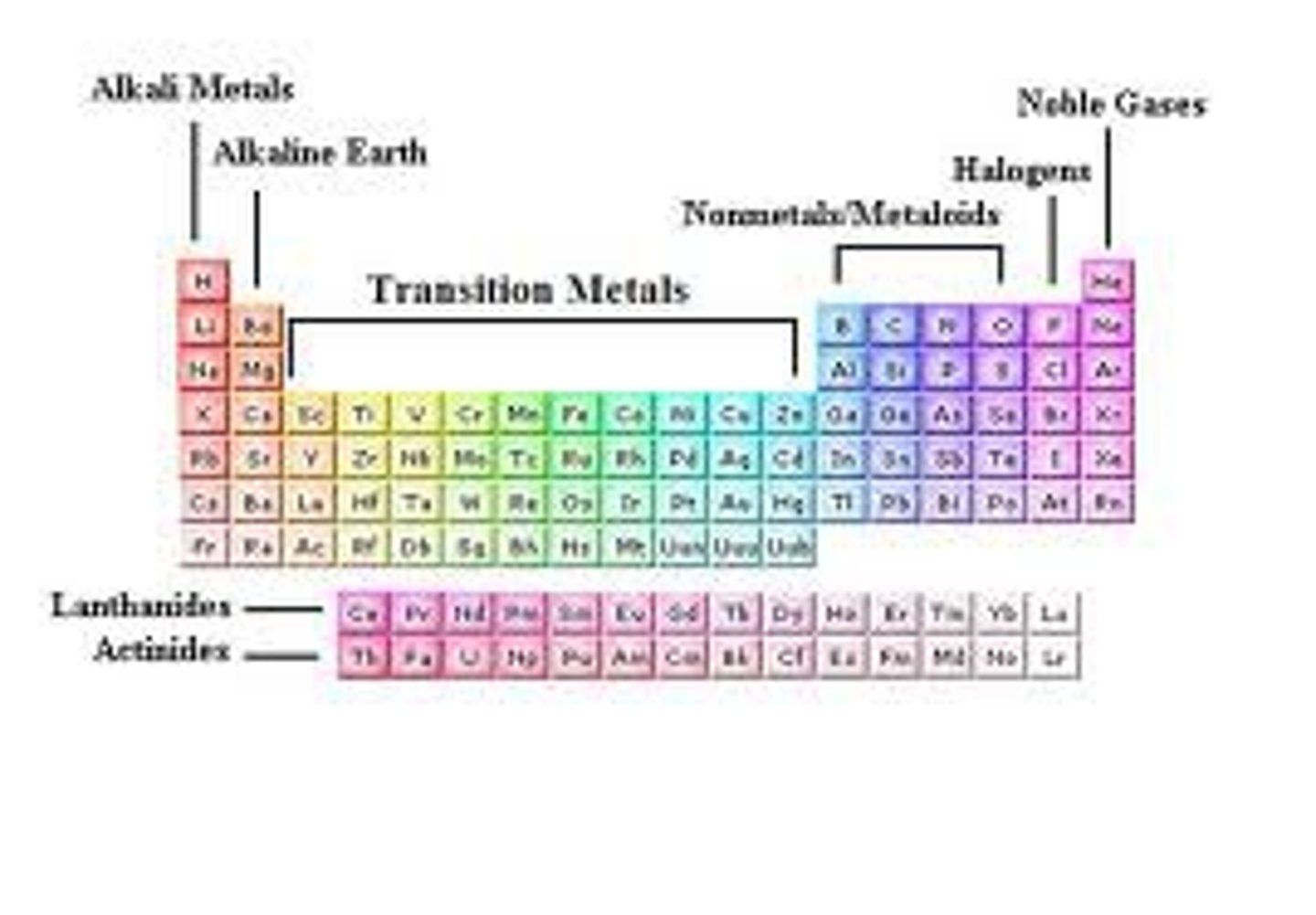
alkali metal (Group IA)
reacts strongly with water to create strong alkaline solutions (Hydrogen not included)
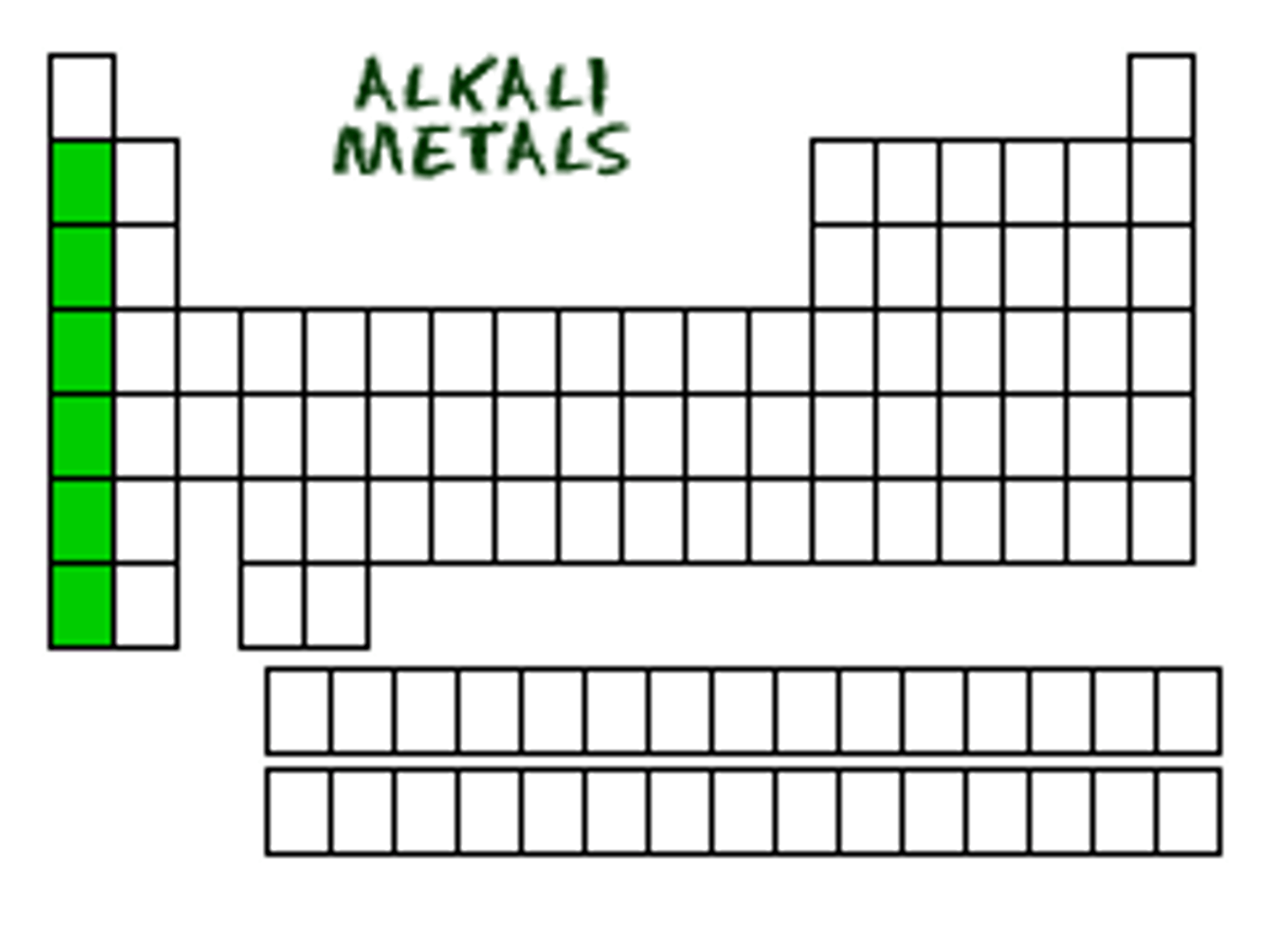
alkaline earth metals (Group IIA)
oxides (chemical compounds of metals and oxygen) that form alkaline solutions in water
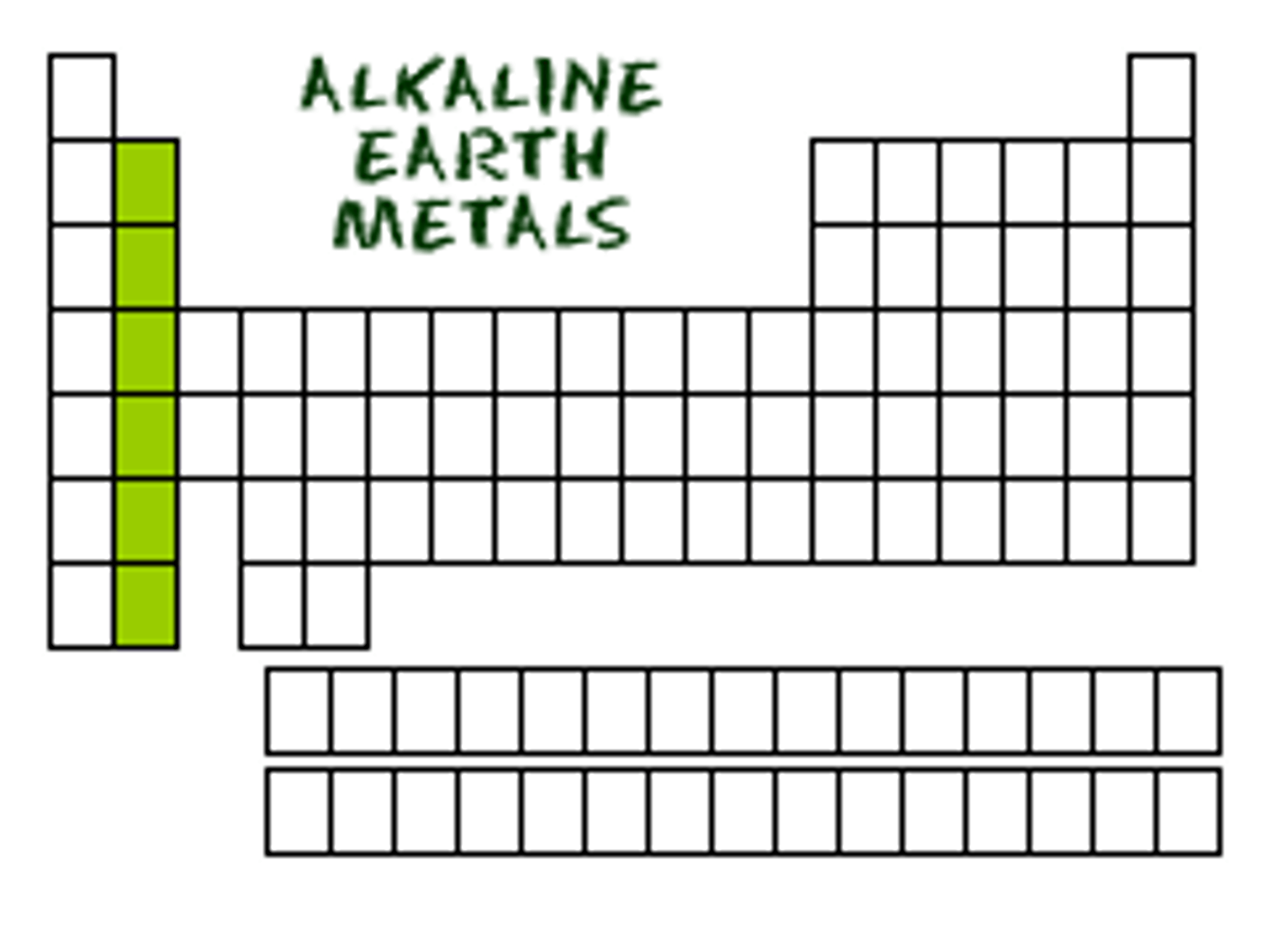
Difference between alkali metals and alkaline earth metals
alkali metals react directly with water, alkaline earth metals' oxides react with water
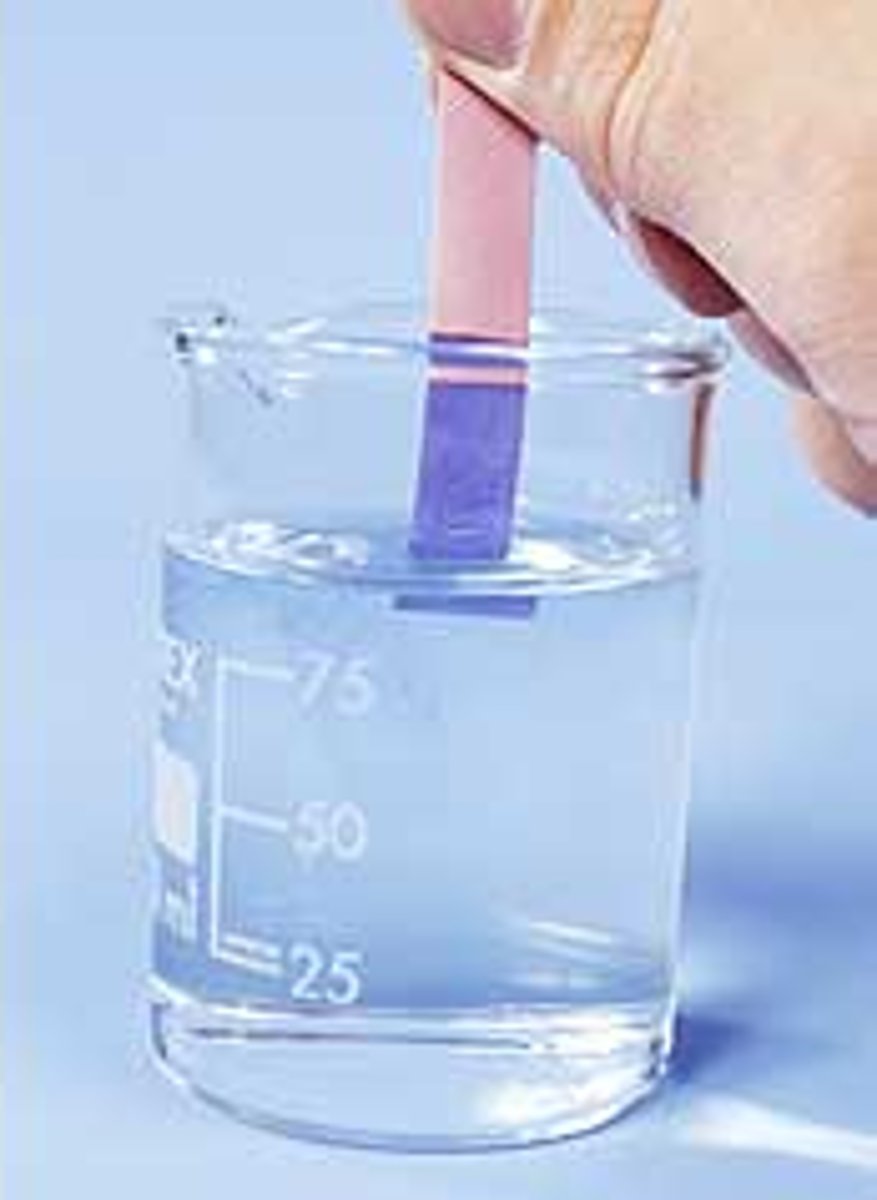

halogens (Group VIIA)
creates salts when combined with metals
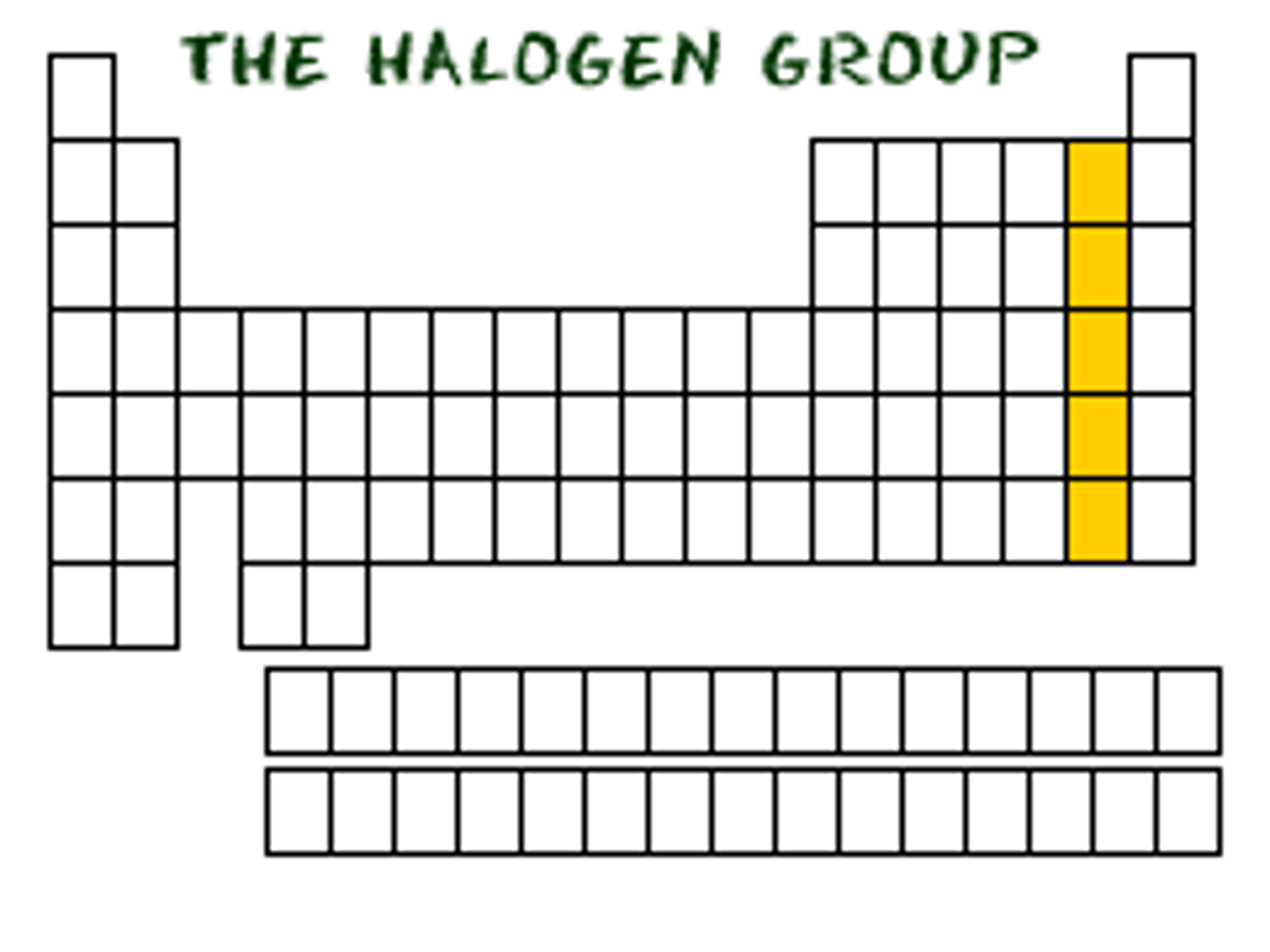
noble gases (Group VIIIA)
nonreactive (stable), gaseous at room temperature
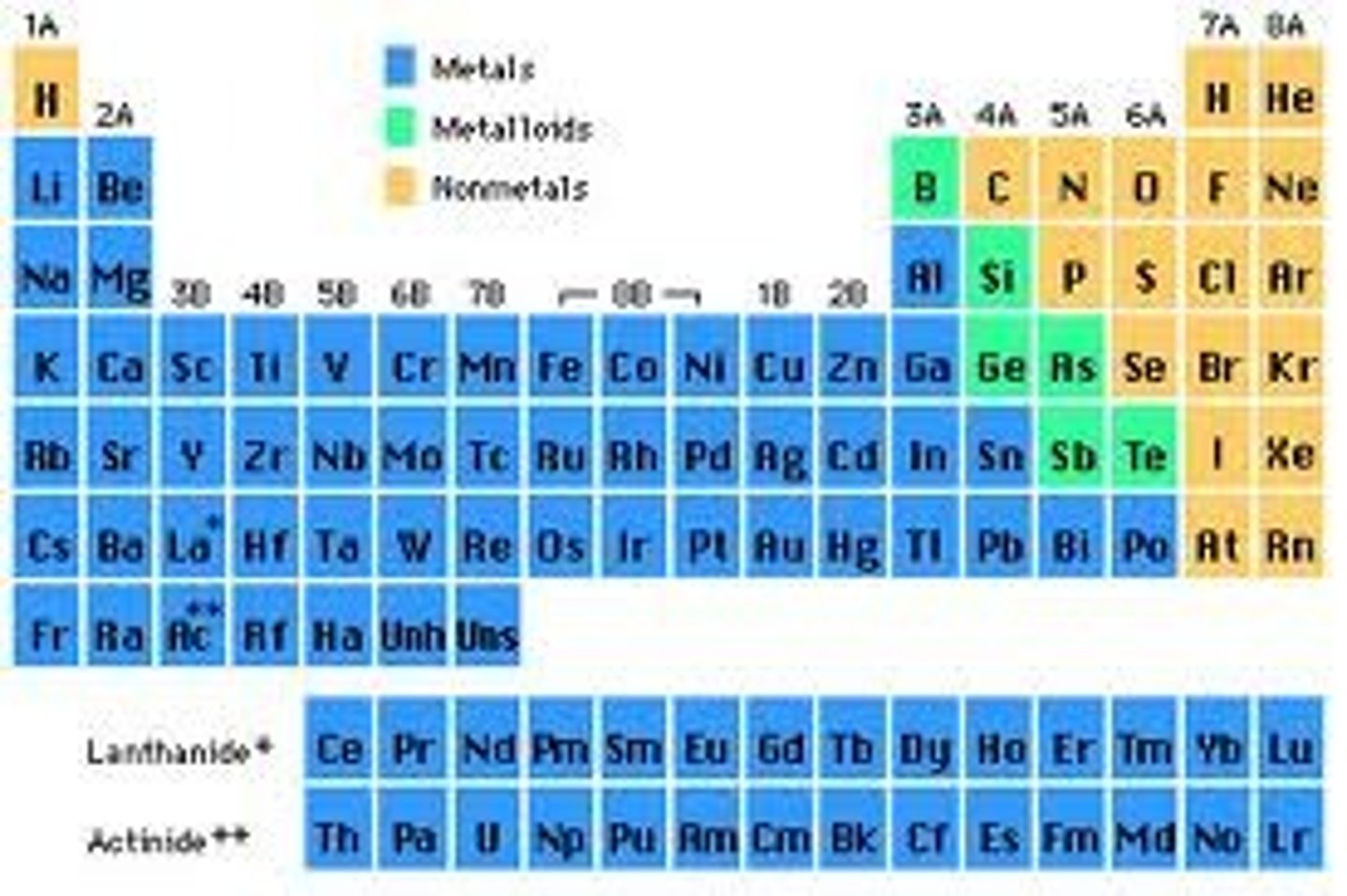
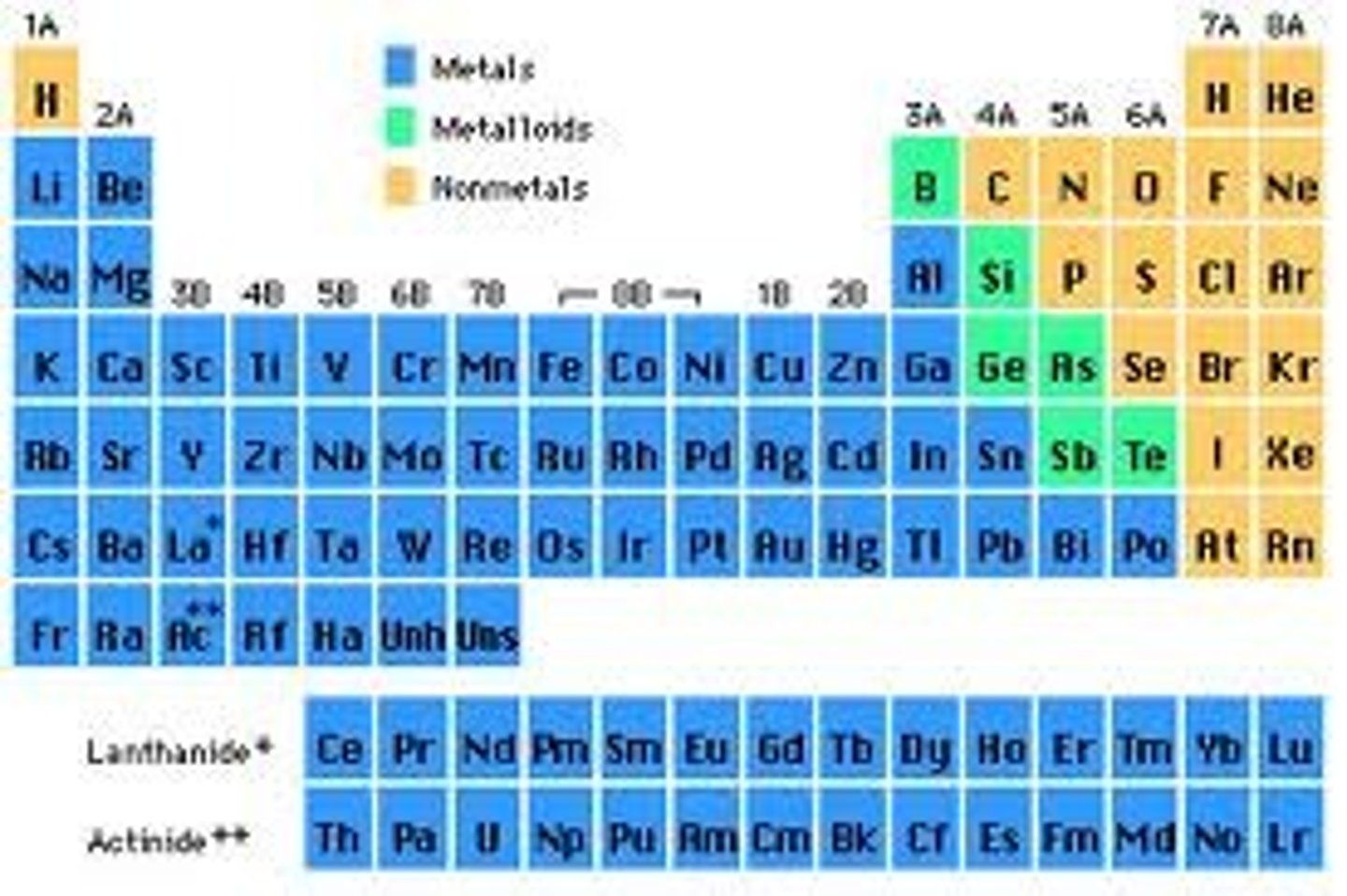
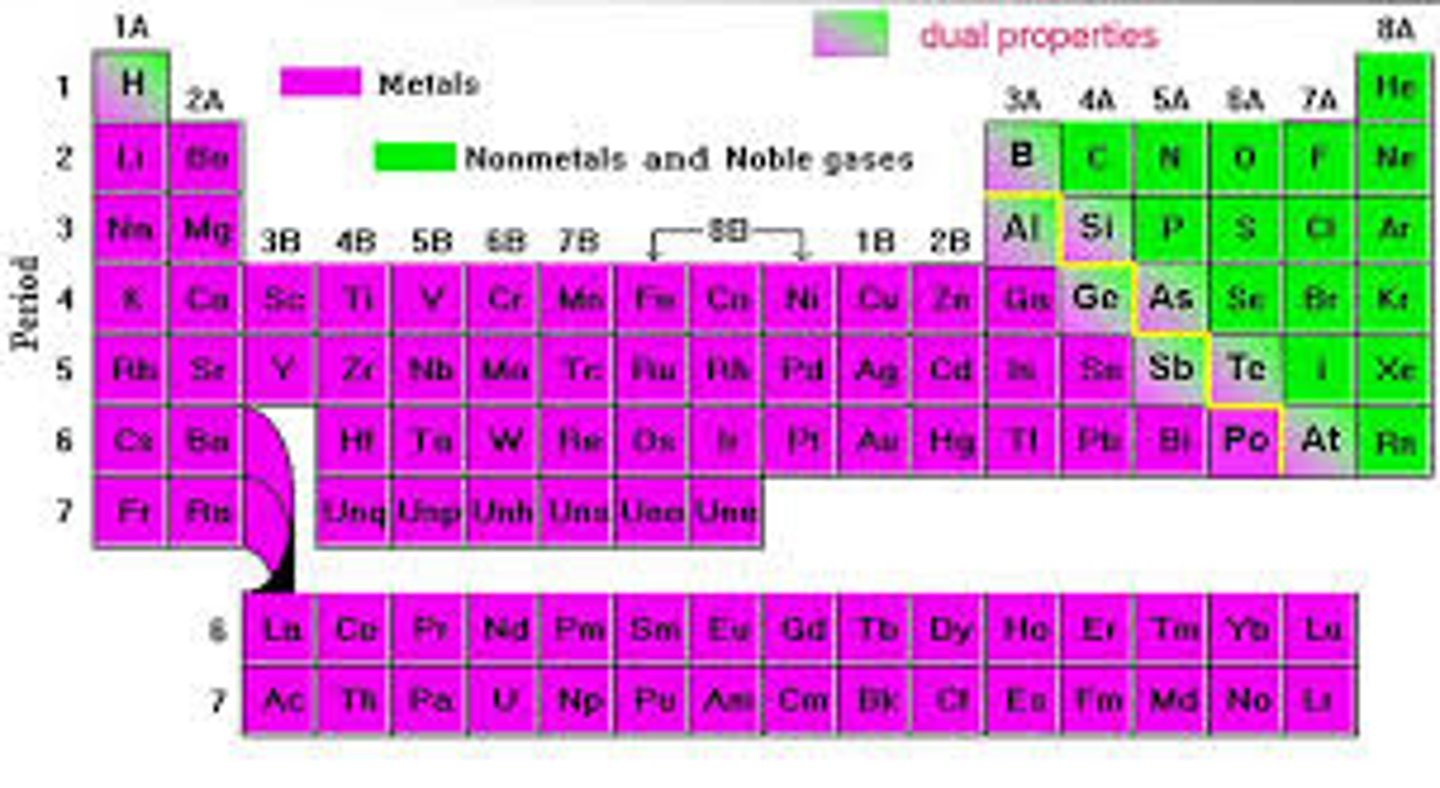
The periodic table is divided into
three classes of elements: metals, nonmetals, metalloids
Elements left of steep-like line on periodic table are...
metals (minus Hydrogen)
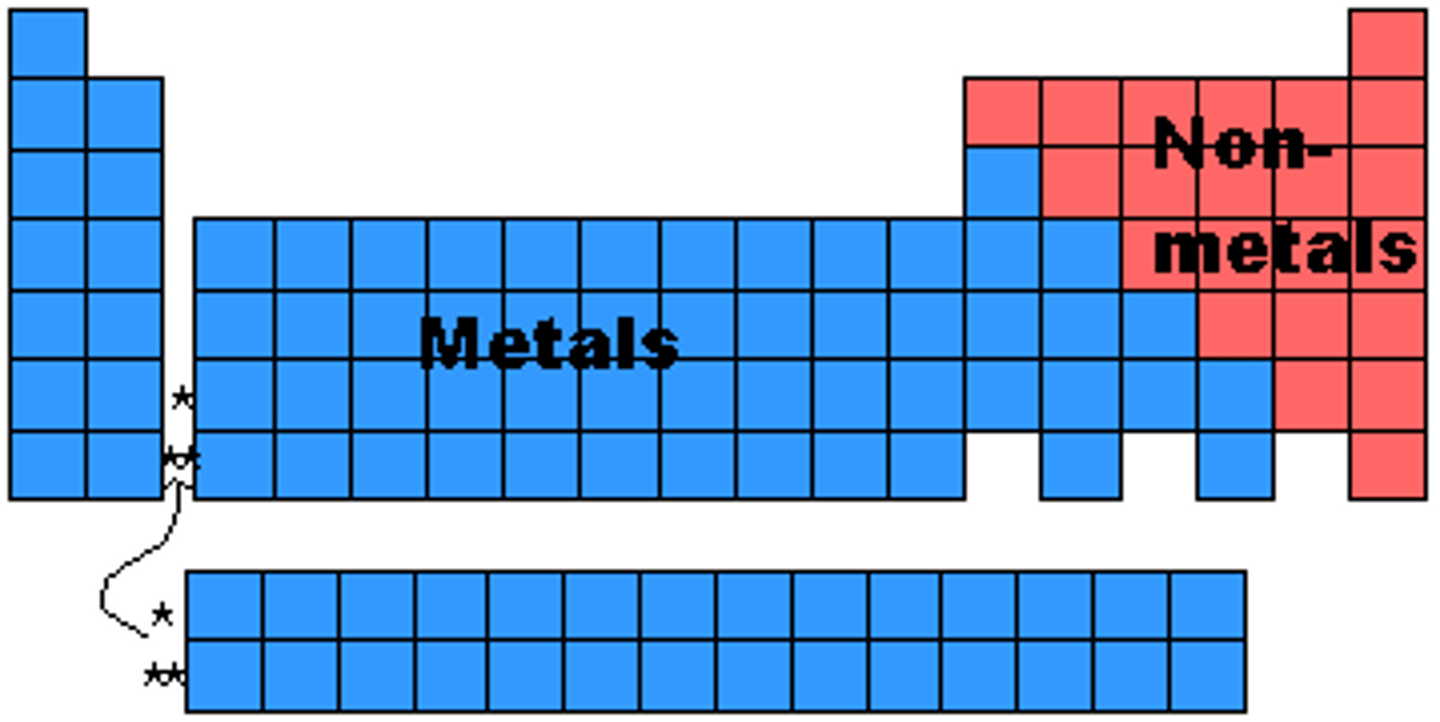
Properties of metals
malleable (can be beaten into fine sheets), ductile (can be drawn into wires), good conductors of heat and electricity, lustrous/shiny and solid at room temperature (except Mercury: liquid at room temp)
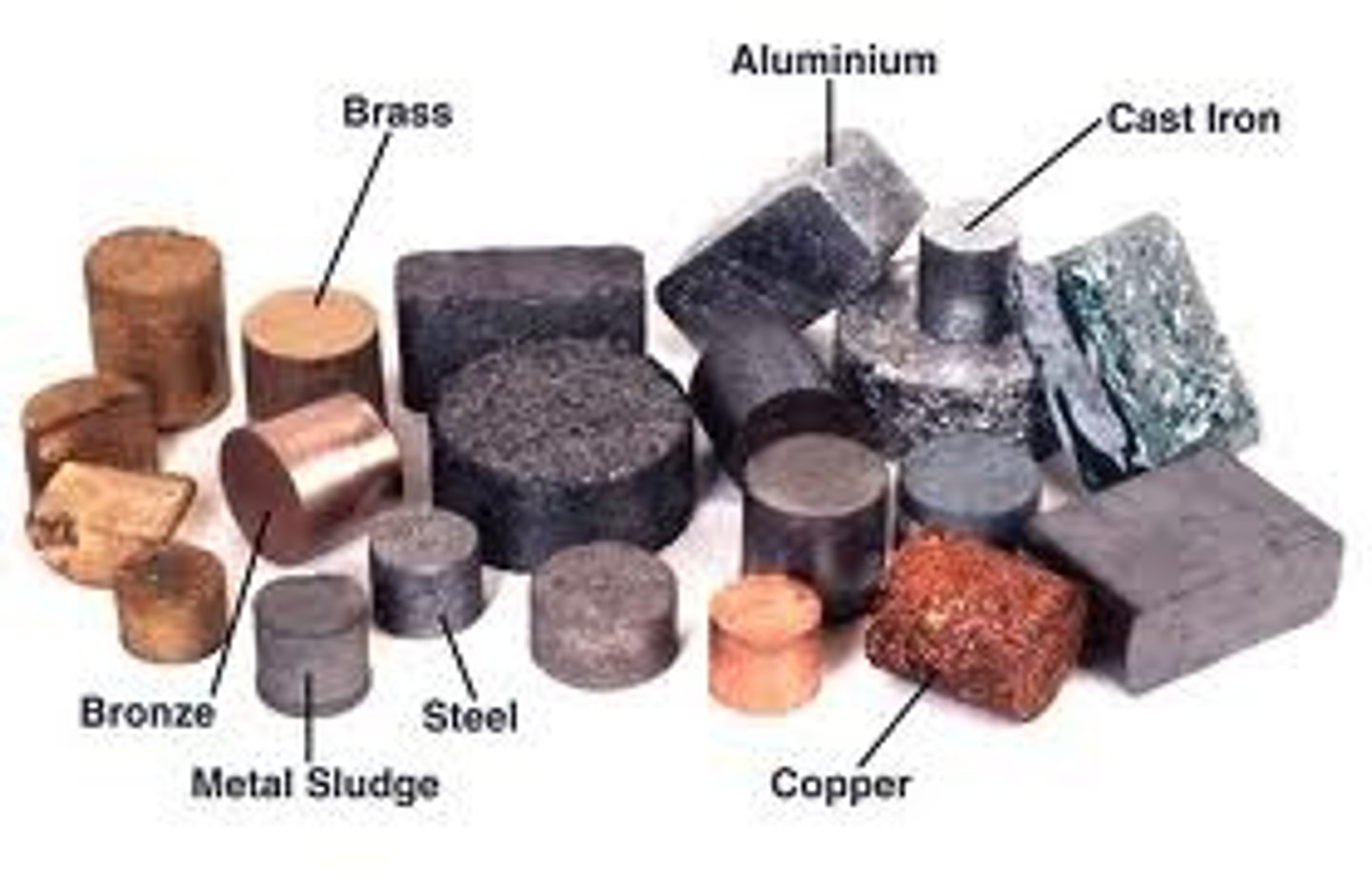

Elements right of steep-like line on periodic table are...
nonmetals
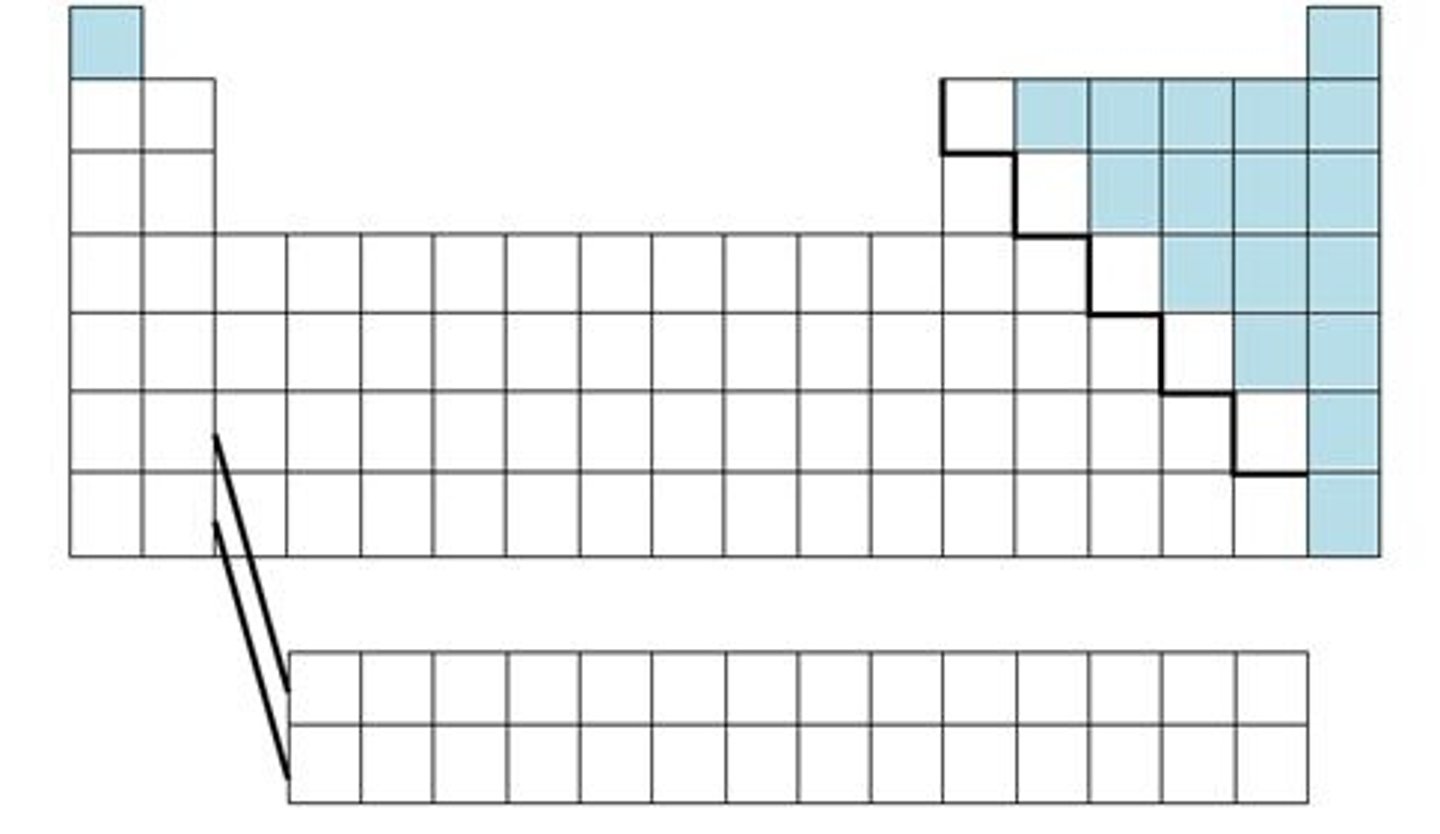
Properties of nonmetals
brittle, poor conductors of heat and electricity, (most are) gases at room temperature

Elements bordering steep-like line on periodic table are...
metalloids
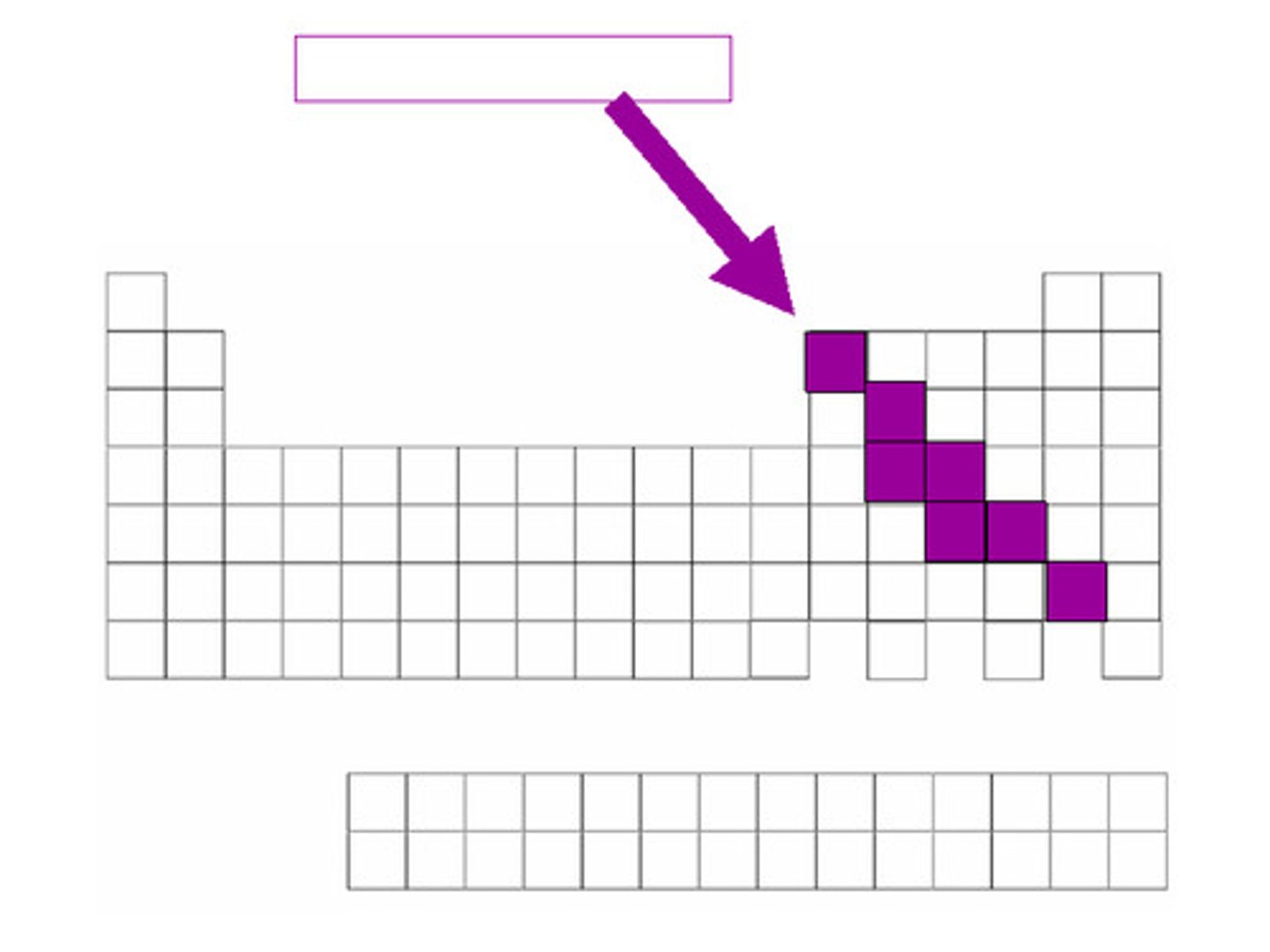
Metalloids
has properties of both metals and nonmetals
How is the atomic number written?
subscript number before symbol
What consists of 99.9% of an atom's mass?
nucleus (protons and neutrons)
mass
amount of matter, determines weight
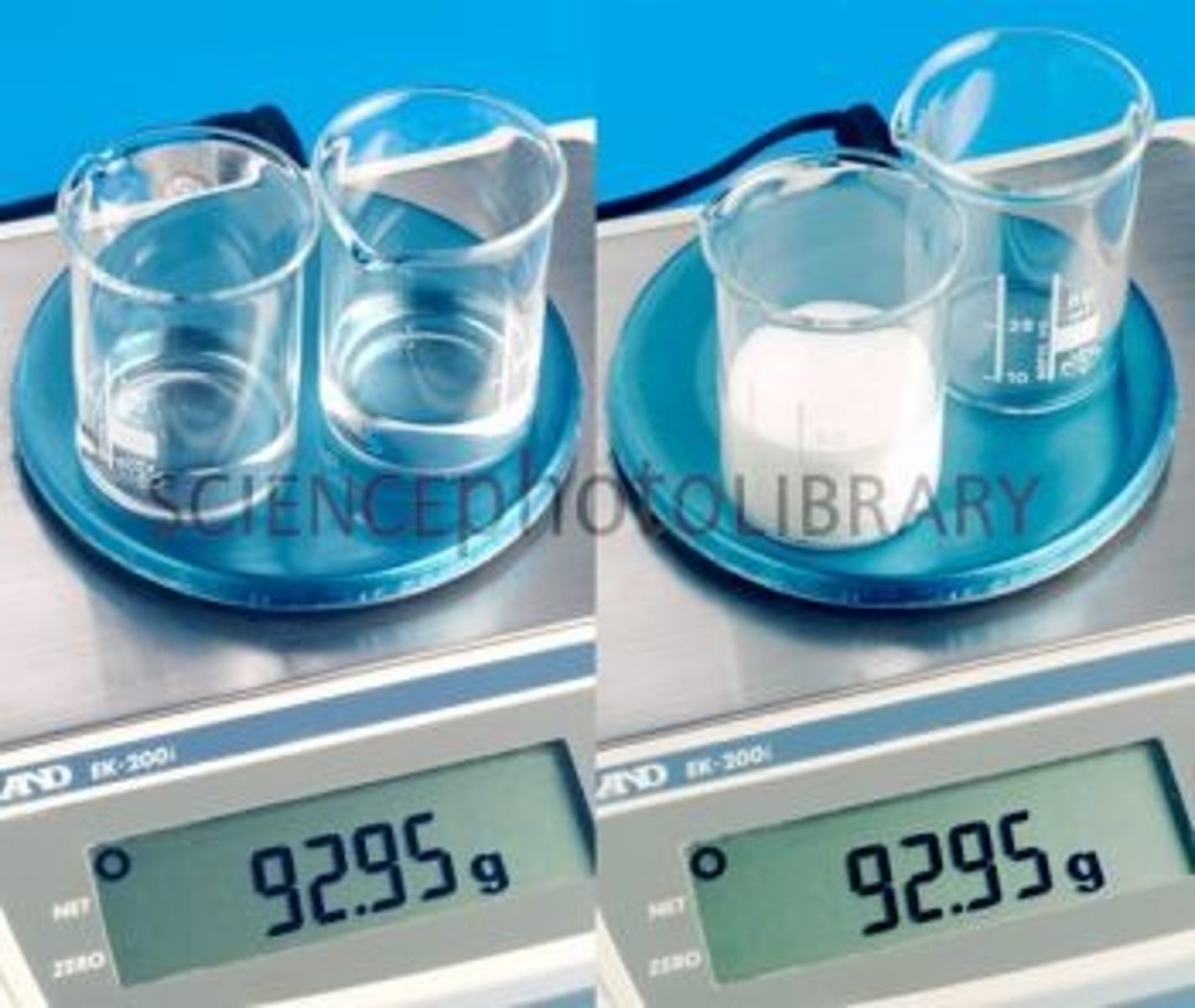

weight
effect of gravity on mass
mass number
mass of protons and neutrons (nucleus), rounded to nearest tenth

How is the mass number written?
superscript number before symbol
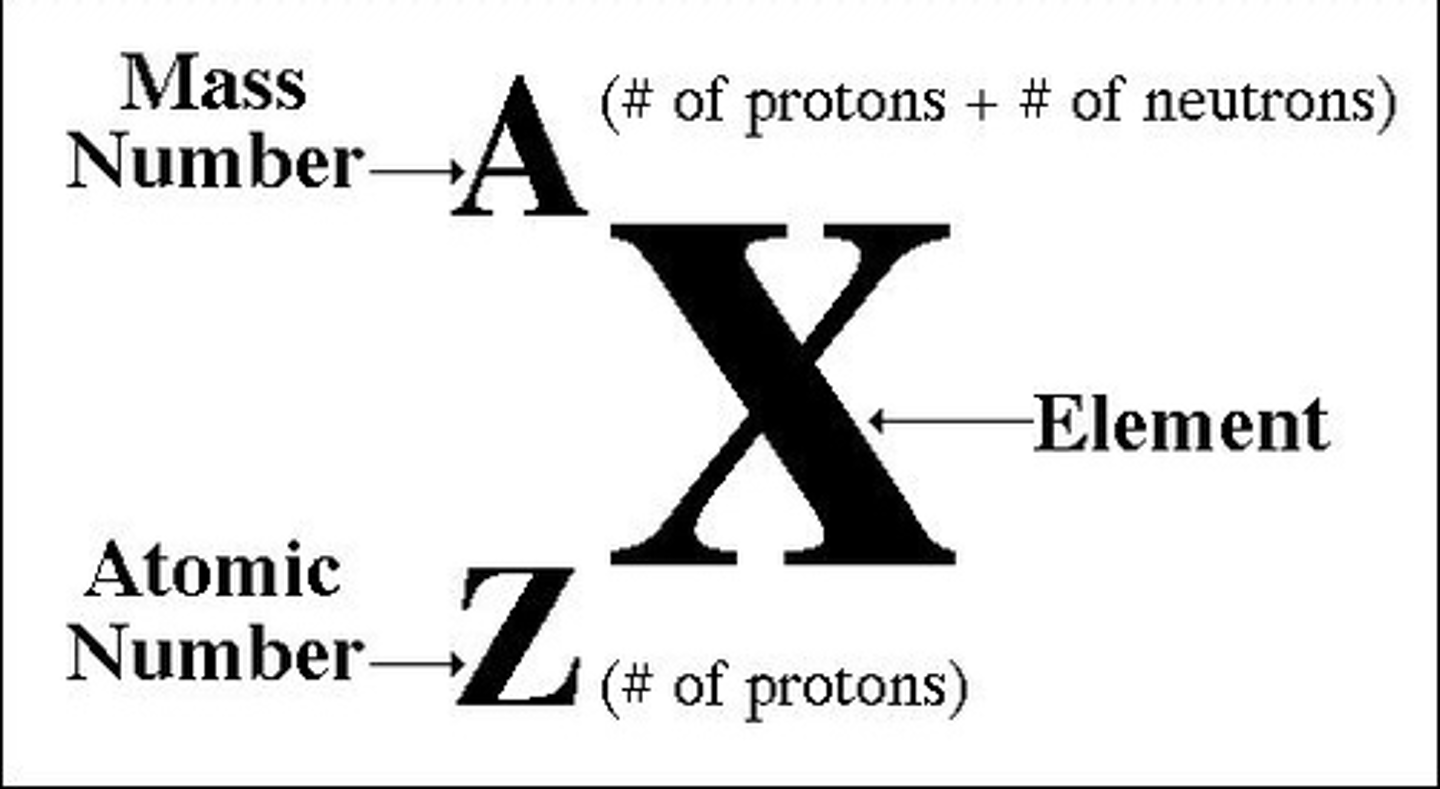
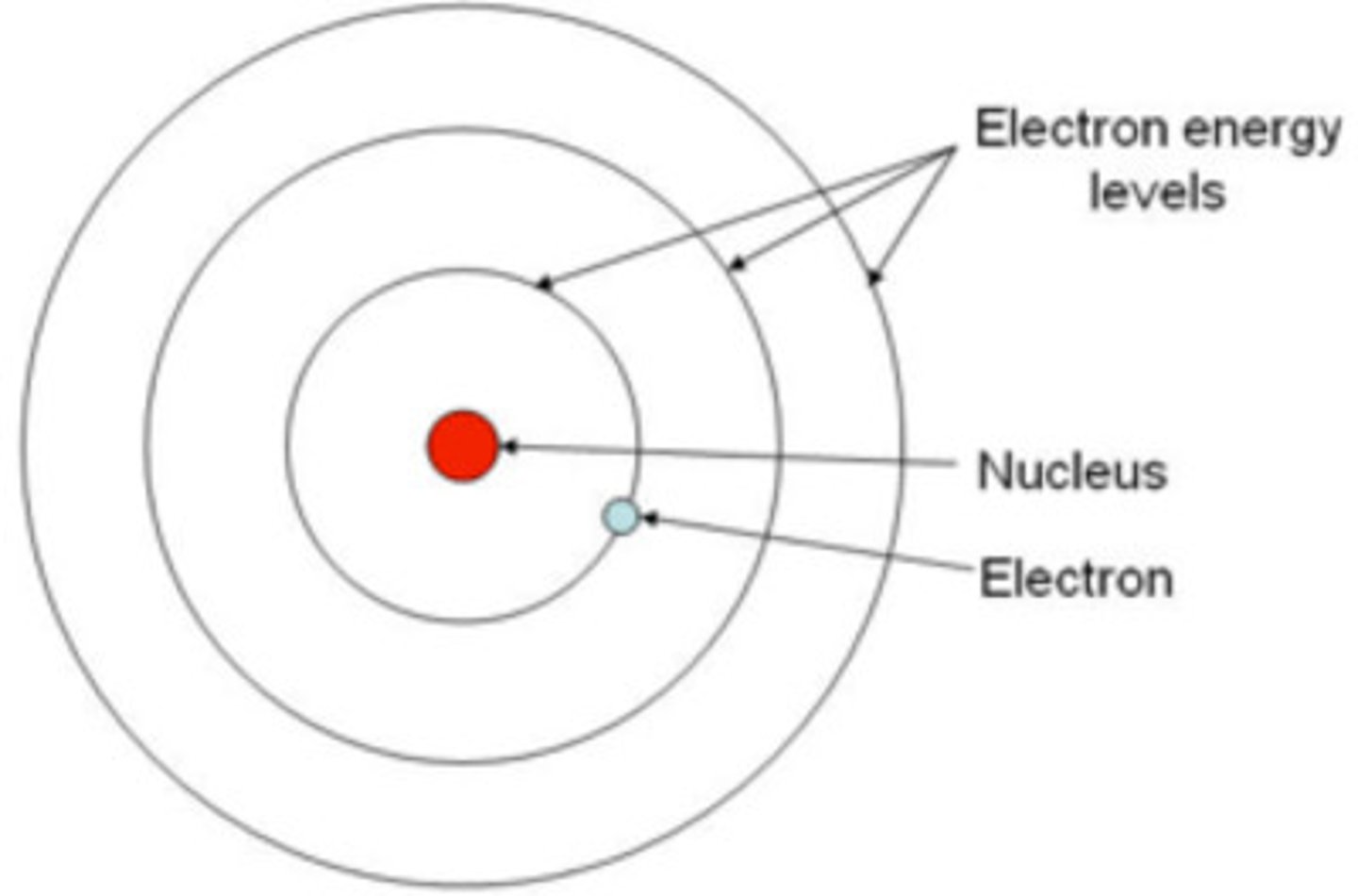
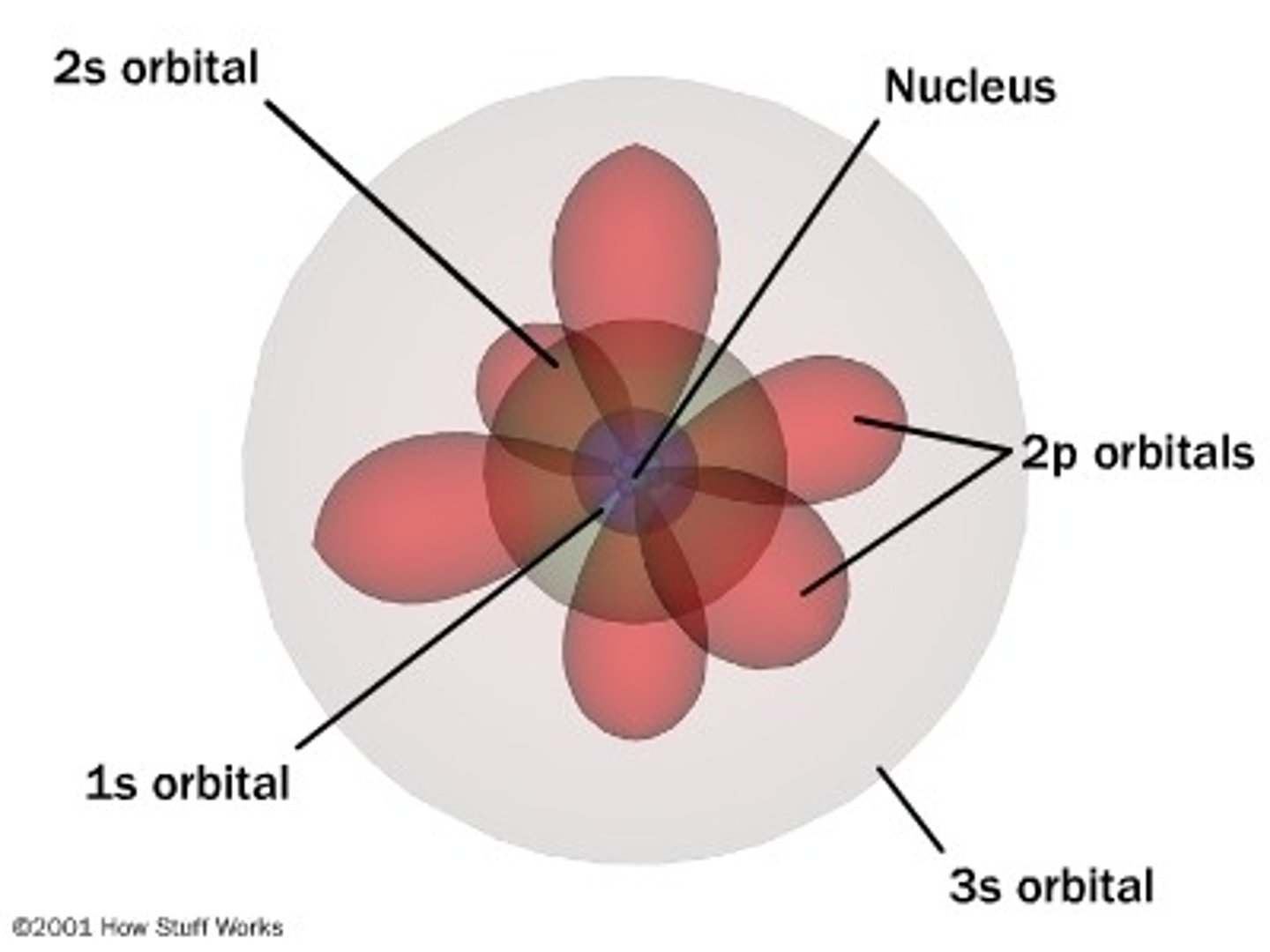
Quantum Atomic Model
3D visualization of electron behavior
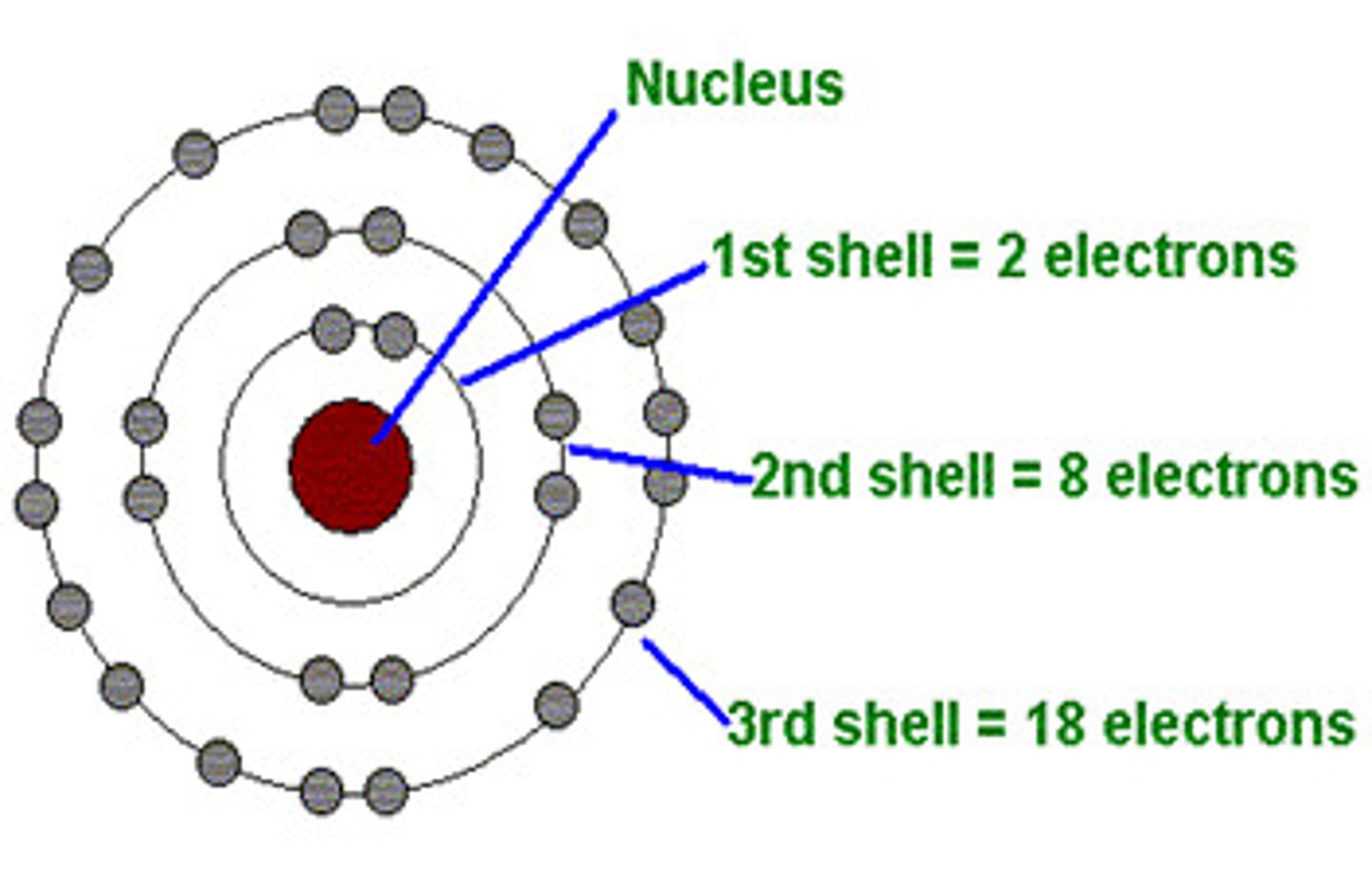
How many shells can electrons occupy?
up to 7 shells
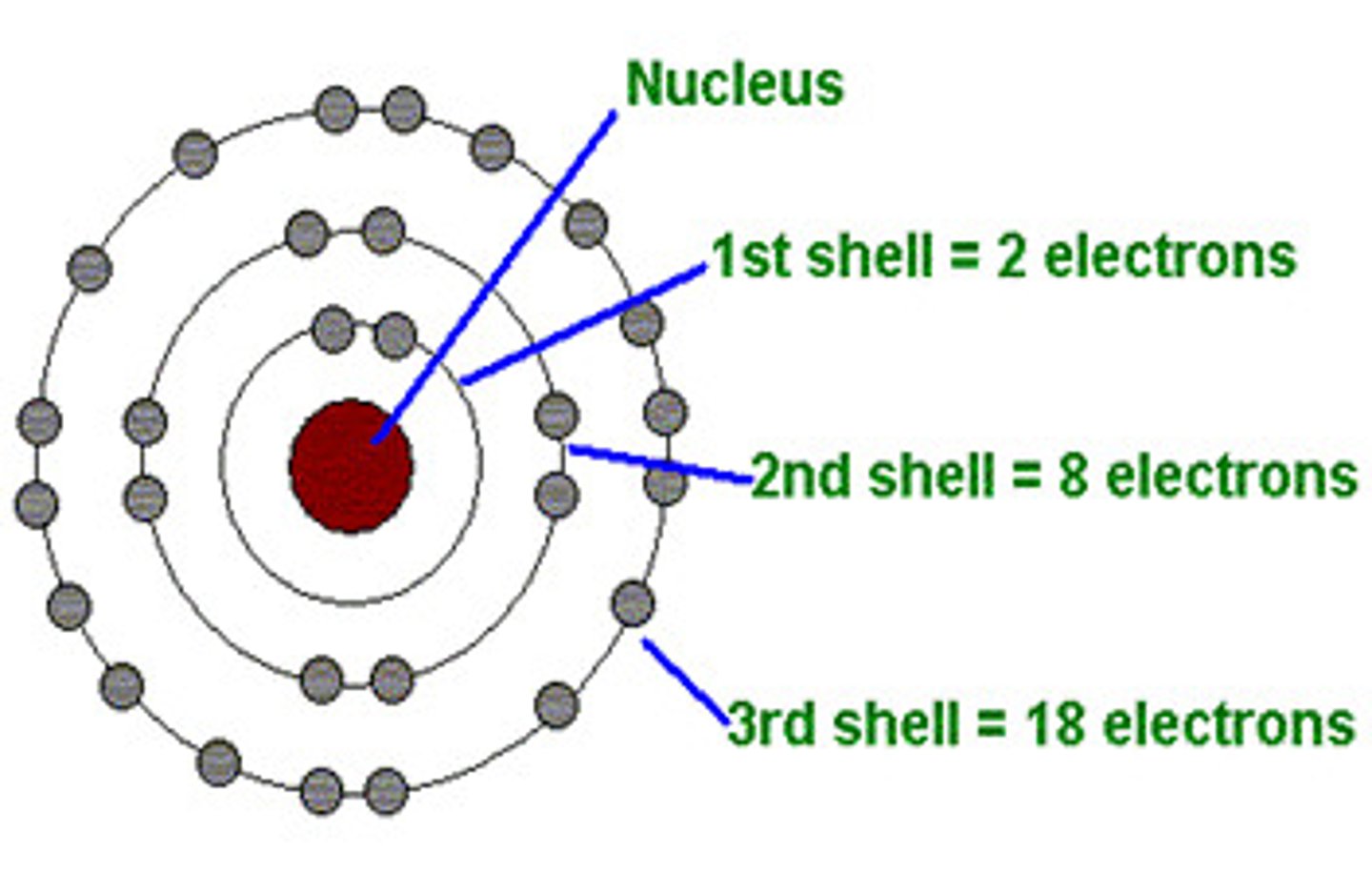
Shells have...
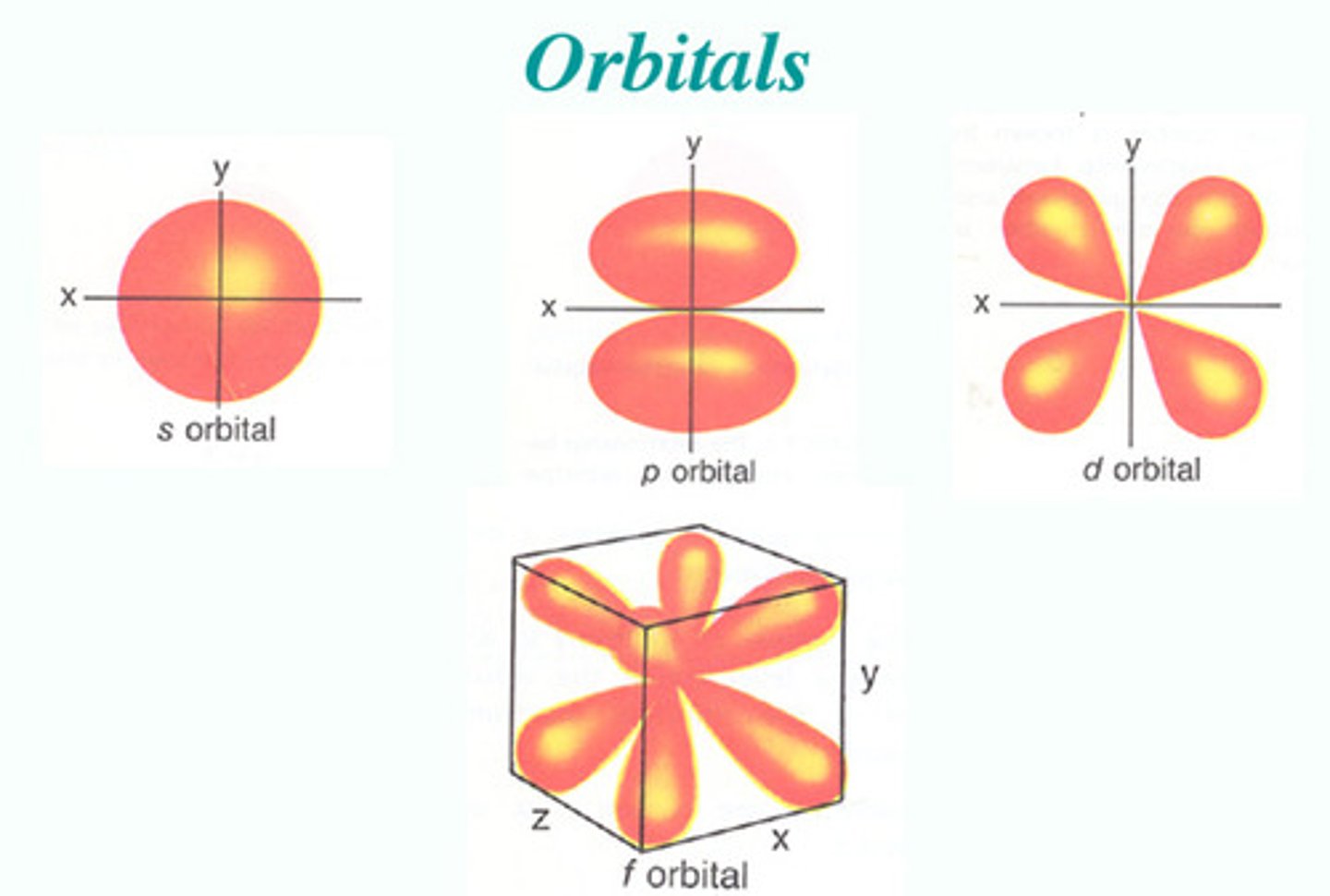
subshells (s, p, d, f)
Subshells have...
orbitals
Which shells do electrons prefer to occupy first?
lower shells, smaller subshells (sometimes occupy smaller subshells on higher shells first)
How many electrons can each subshell's orbitals hold?
only two (two electrons/oribtal)
s subshell
1 orbital (2 electrons)
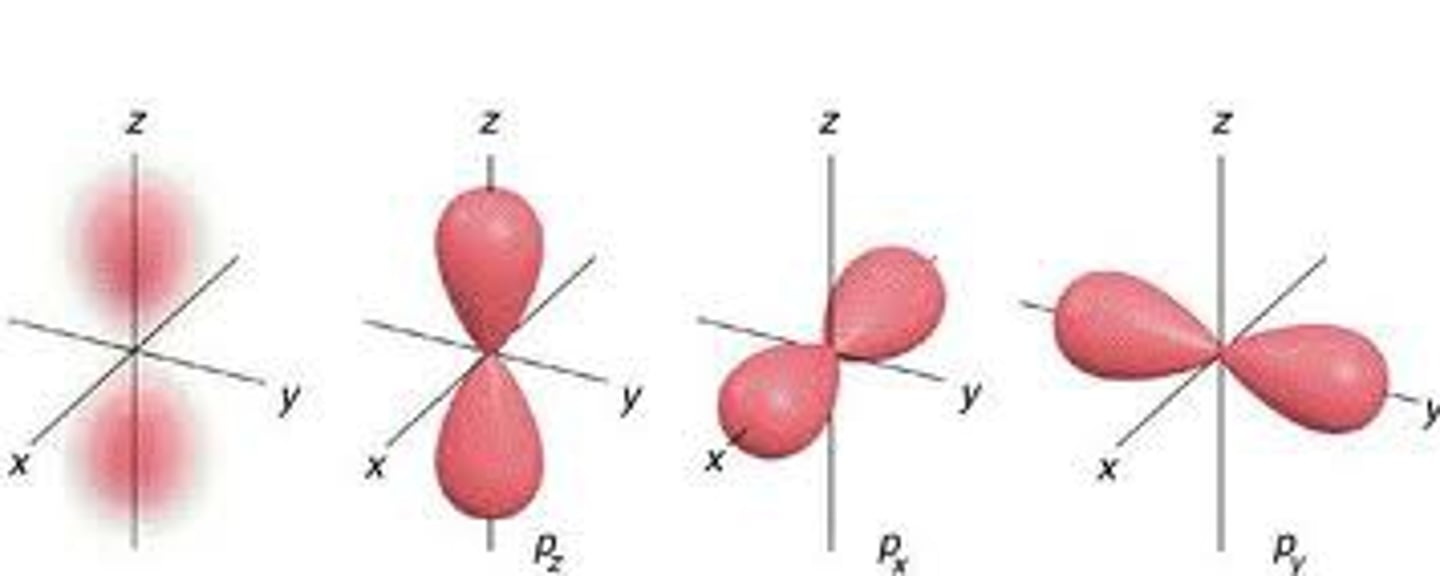
p subshell
3 orbitals (6 electrons)
d subshell
5 orbitals (10 electrons)
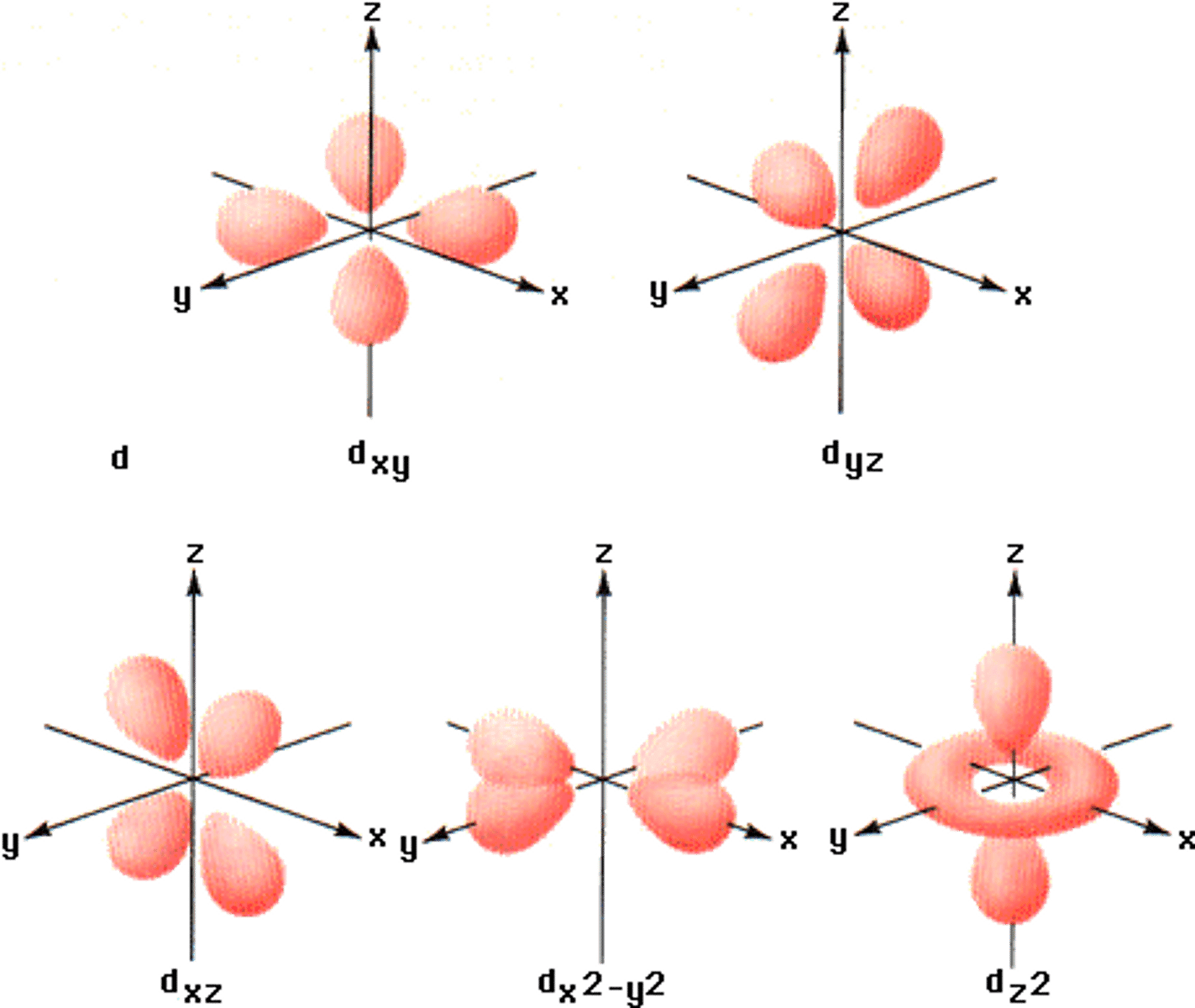
f subshell
7 orbitals (14 electrons)
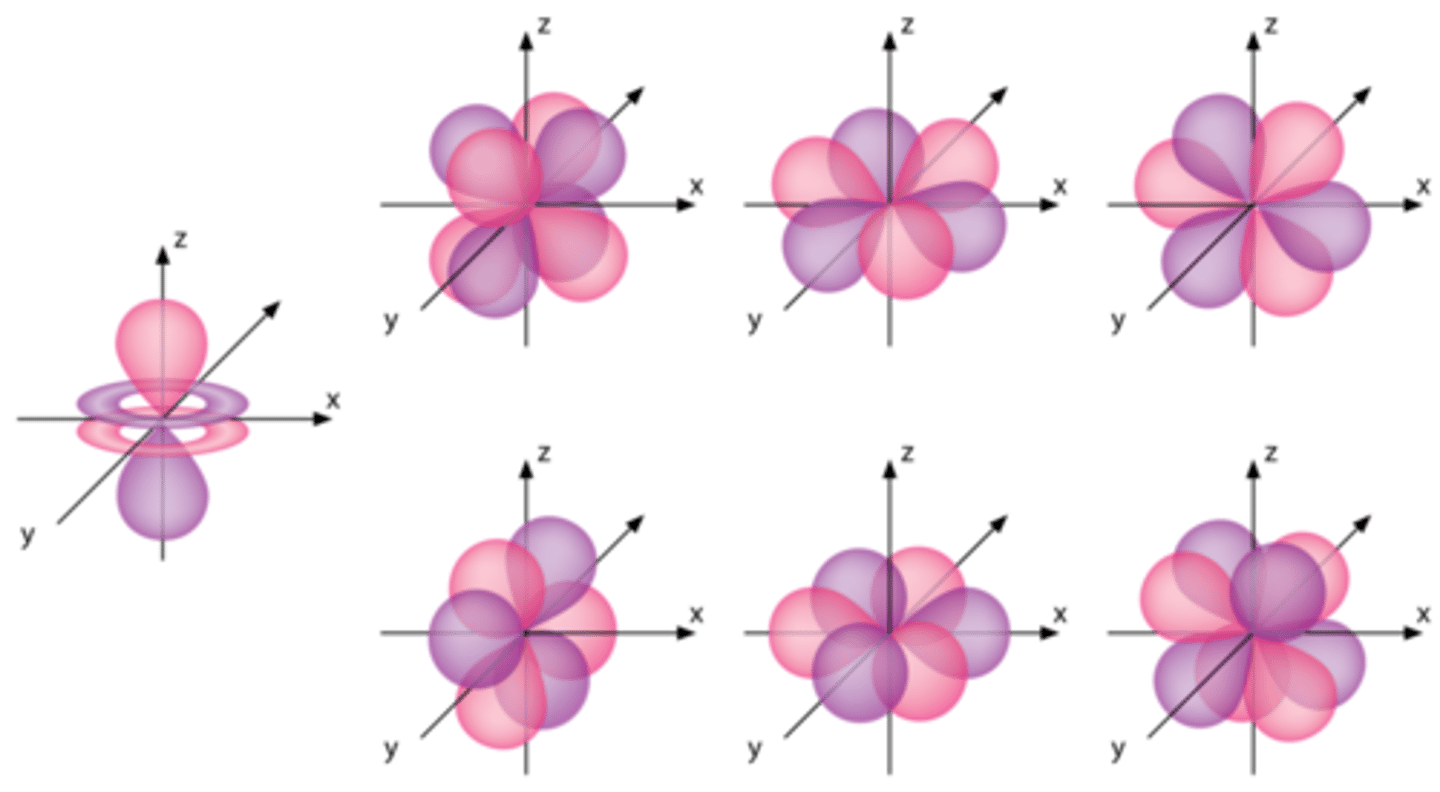
Shell 1
1s
Shell 2
2s, 2p
Shell 3
3s, 3p, 3d
Shells 4-7
s, p, d, f
Electron filling order
1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6d, 7p
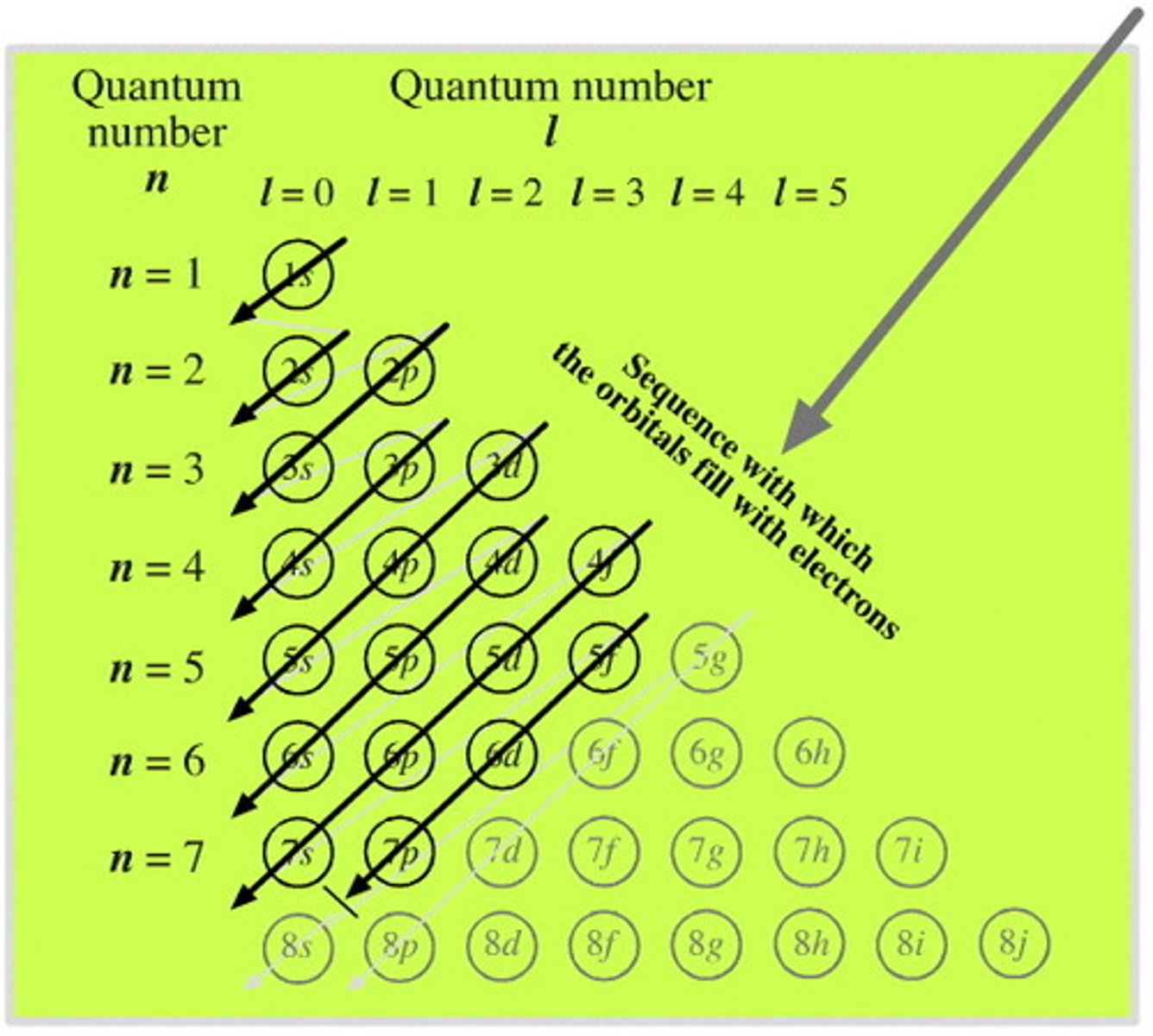
Electron filling order pattern (made by me, skip if you want, starts at 3p)
p, S (higher s), d (lower d/same as p)
Electron filling order pattern (made by me, skip if you want, starts after 5p)
p, S (higher s), f (starts with 4f), d (lower d/same as p)
Electron energy increases as...
subshells are filled
Electron Configuration
superscript numbers are written after orbitals, represents number of electrons in each orbital
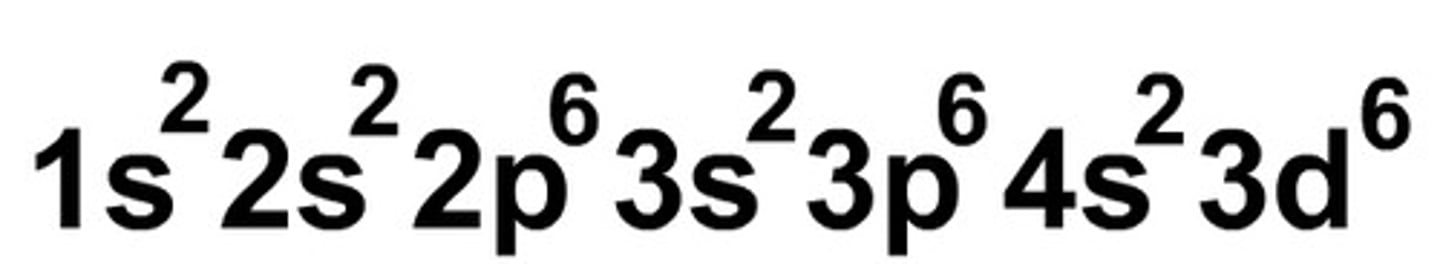
What does the sum of the exponents in the Electron Configuration represent?
number of electrons, used to identify elements (e.g, 1s², 2s², 2p5 = 9 electrons)
Electron Configuration Diagram
uses boxes (orbitals) and arrows (electrons) to represent electrons filling orbitals
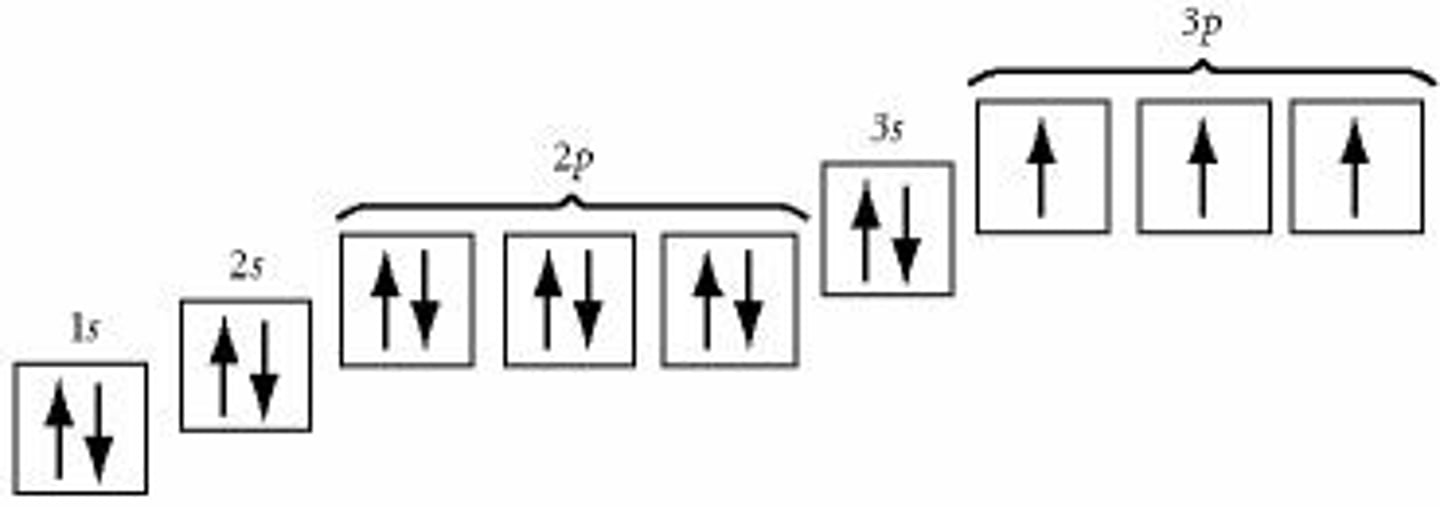
Principle of Maximum Multiplicity
electrons occupy orbitals in the same subshell before pairing with other electrons
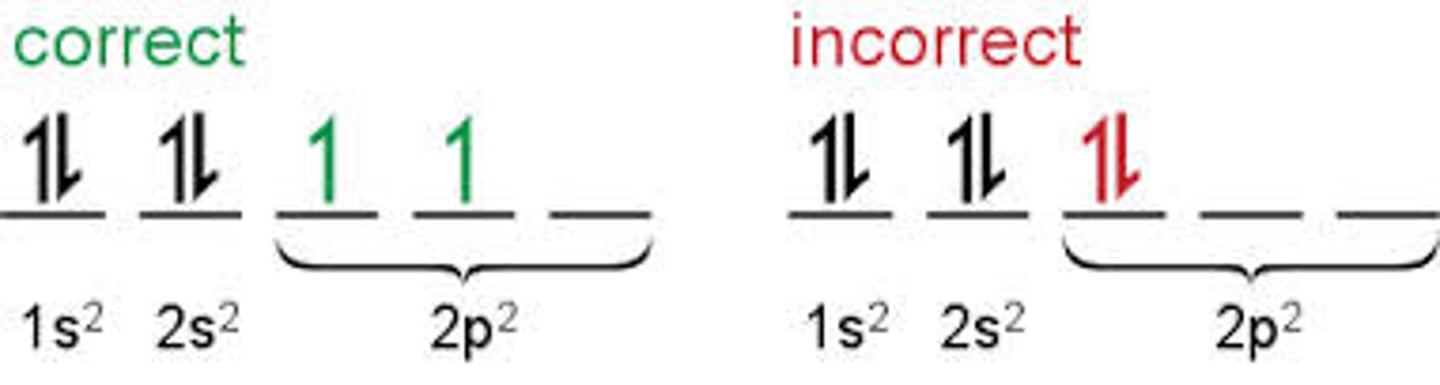
Why do elements have similar properties?
similar electron configurations, similar subshells with similar number of electrons in outermost shell (subshell filled last)
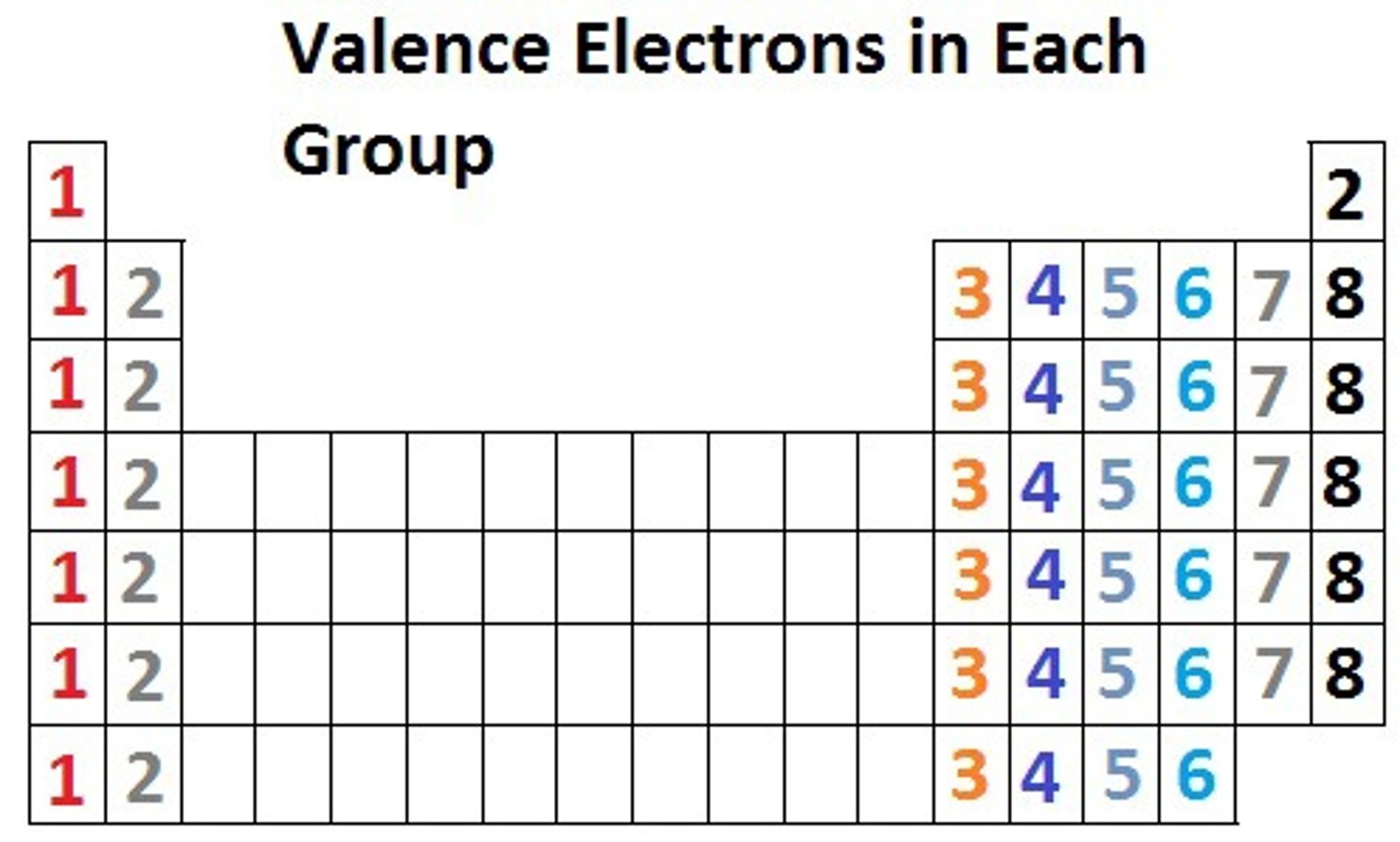
Outermost shell shared by alkali metals
s^1
Outermost shell shared by alkaline earth metals
s²
Outermost shell shared by halogens
p^5
Outermost shell shared by noble gases
p^6