SkM - DNA Viruses - complete
1/248
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
249 Terms
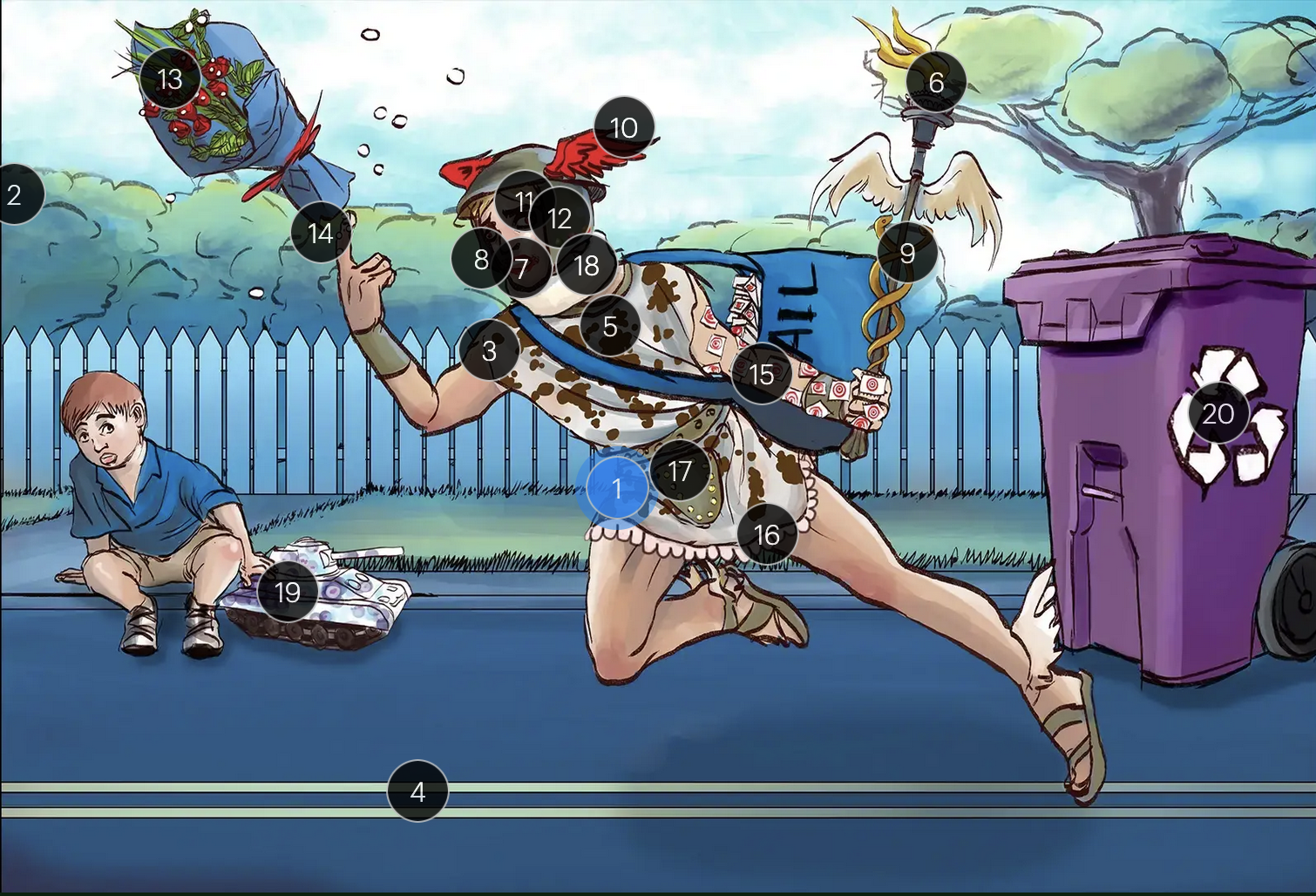
Herpes Simplex Virus Types 1 & 2 (Herpesviridae)
#1 Hermes sprinting
HSV types 1 & 2 (DNA viruses in the Herpesviridae family)
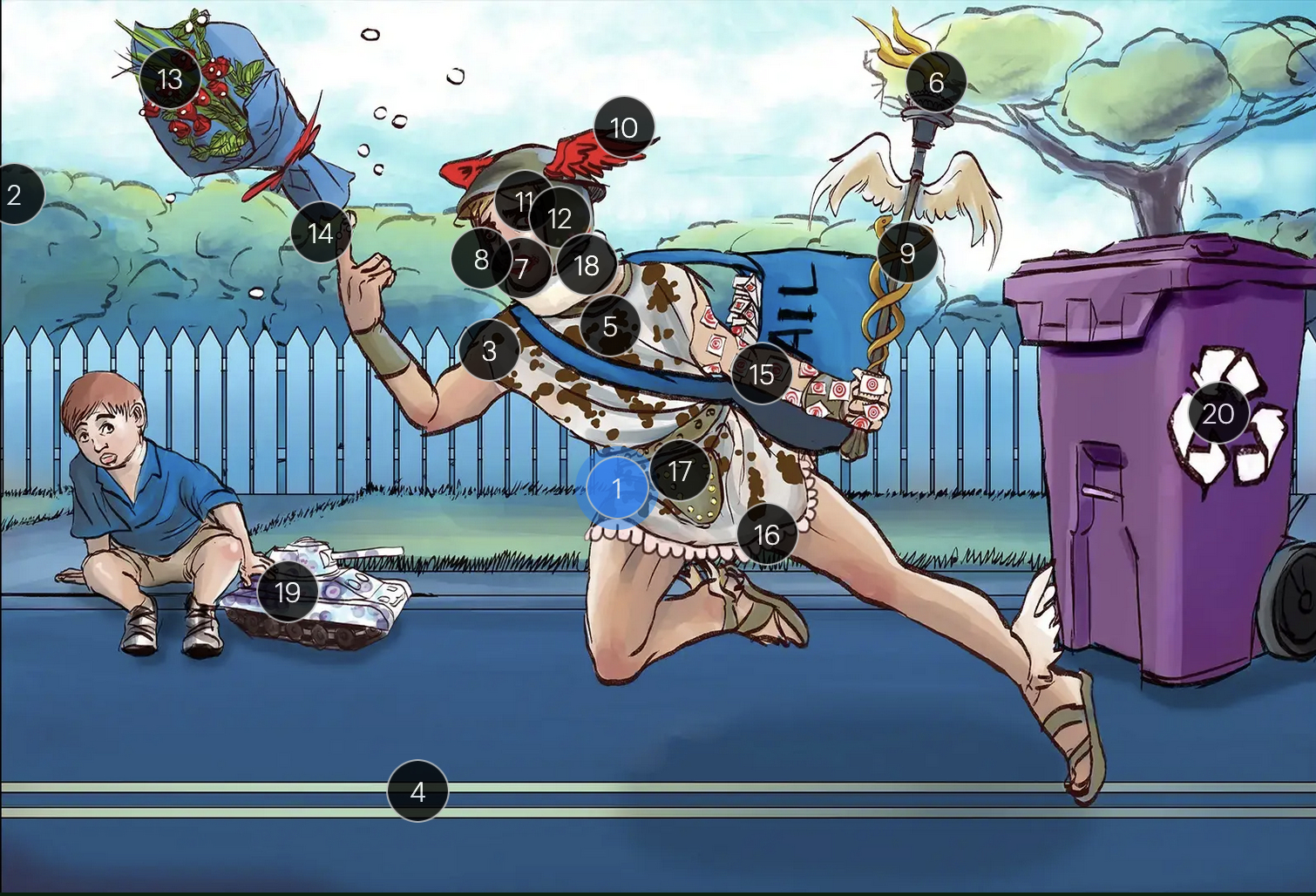
Herpes Simplex Virus Types 1 & 2 (Herpesviridae)
#2 cool colors
HSV 1 & 2 are DNA viruses
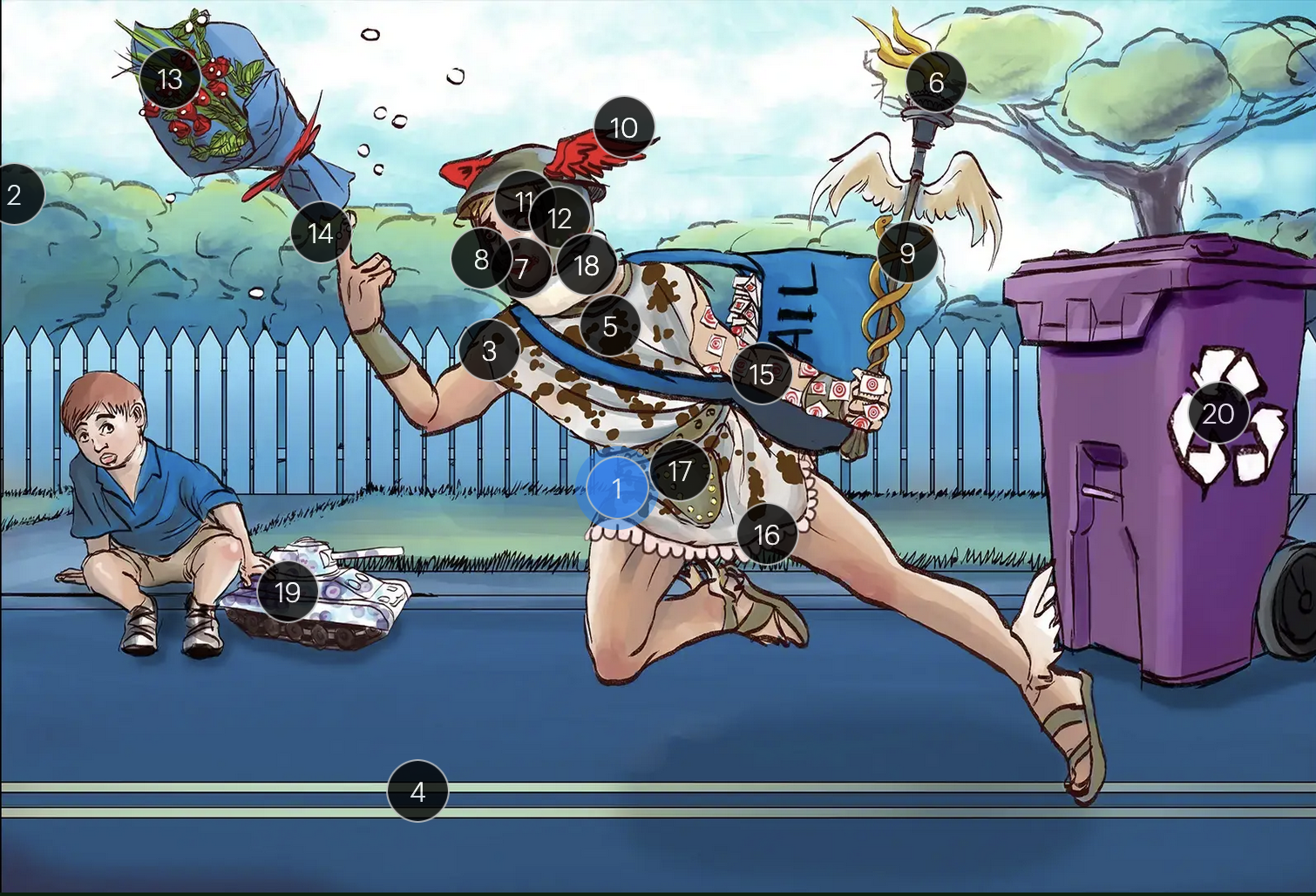
Herpes Simplex Virus Types 1 & 2 (Herpesviridae)
#3 enveloping toga
HSV 1 & 2 are enveloped viruses
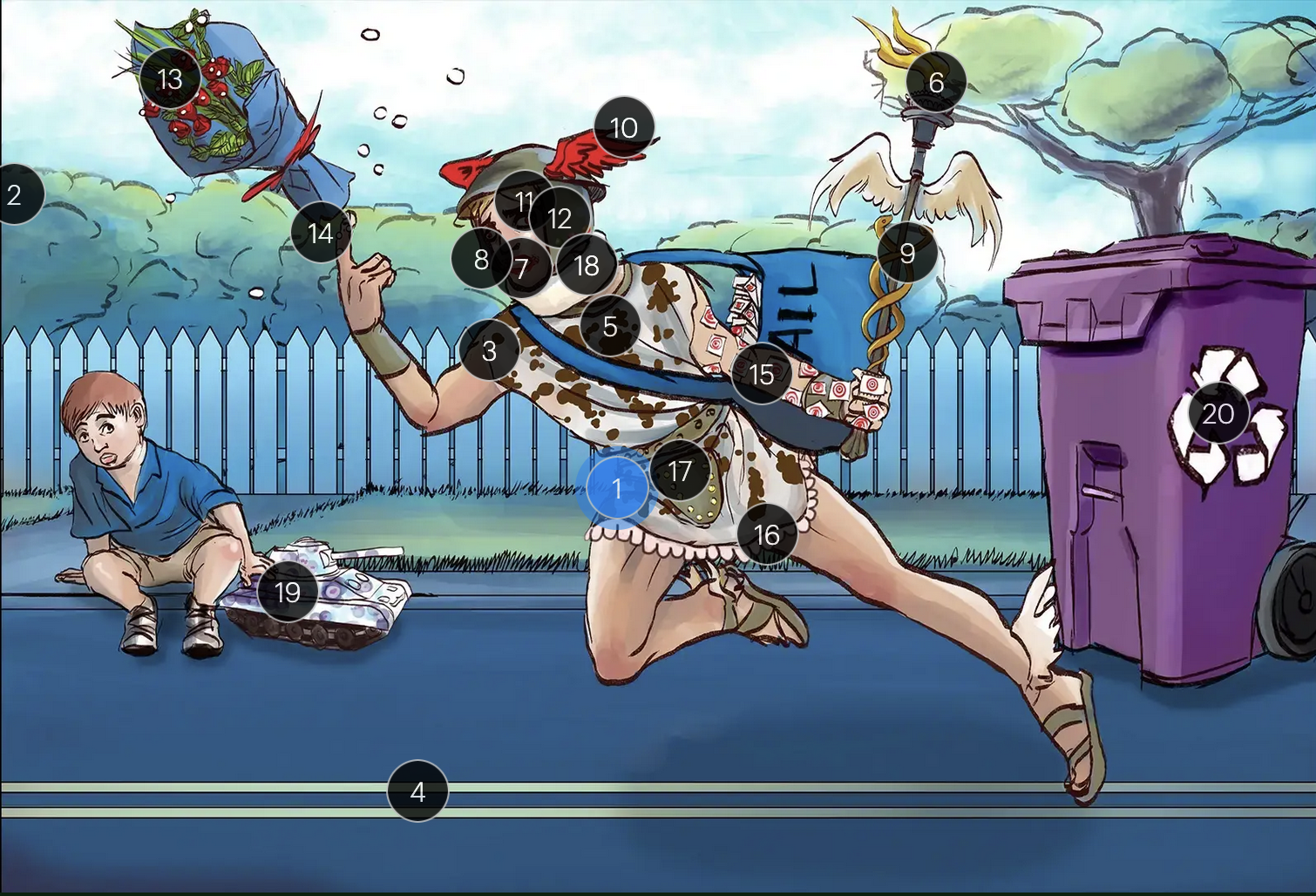
Herpes Simplex Virus Types 1 & 2 (Herpesviridae)
#4 double road lines
HSV 1 & 2 are double stranded, linear DNA viruses
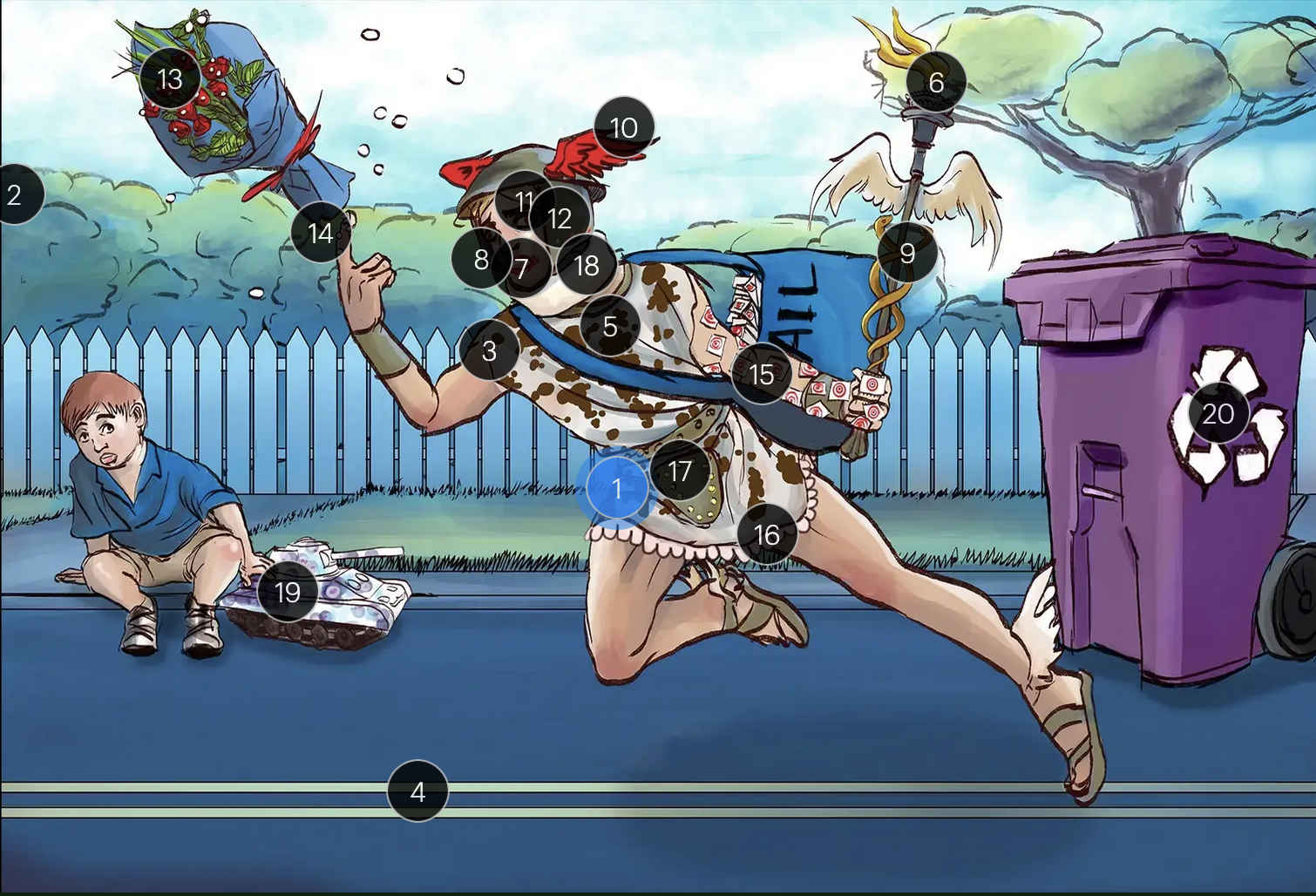
Herpes Simplex Virus Types 1 & 2 (Herpesviridae)
#5 cow spots
intranuclear eosinophilic inclusions, known as Cowdry type A bodies, are characteristic histopath findings in cells infected with HSV (as well as CMV & VZV)
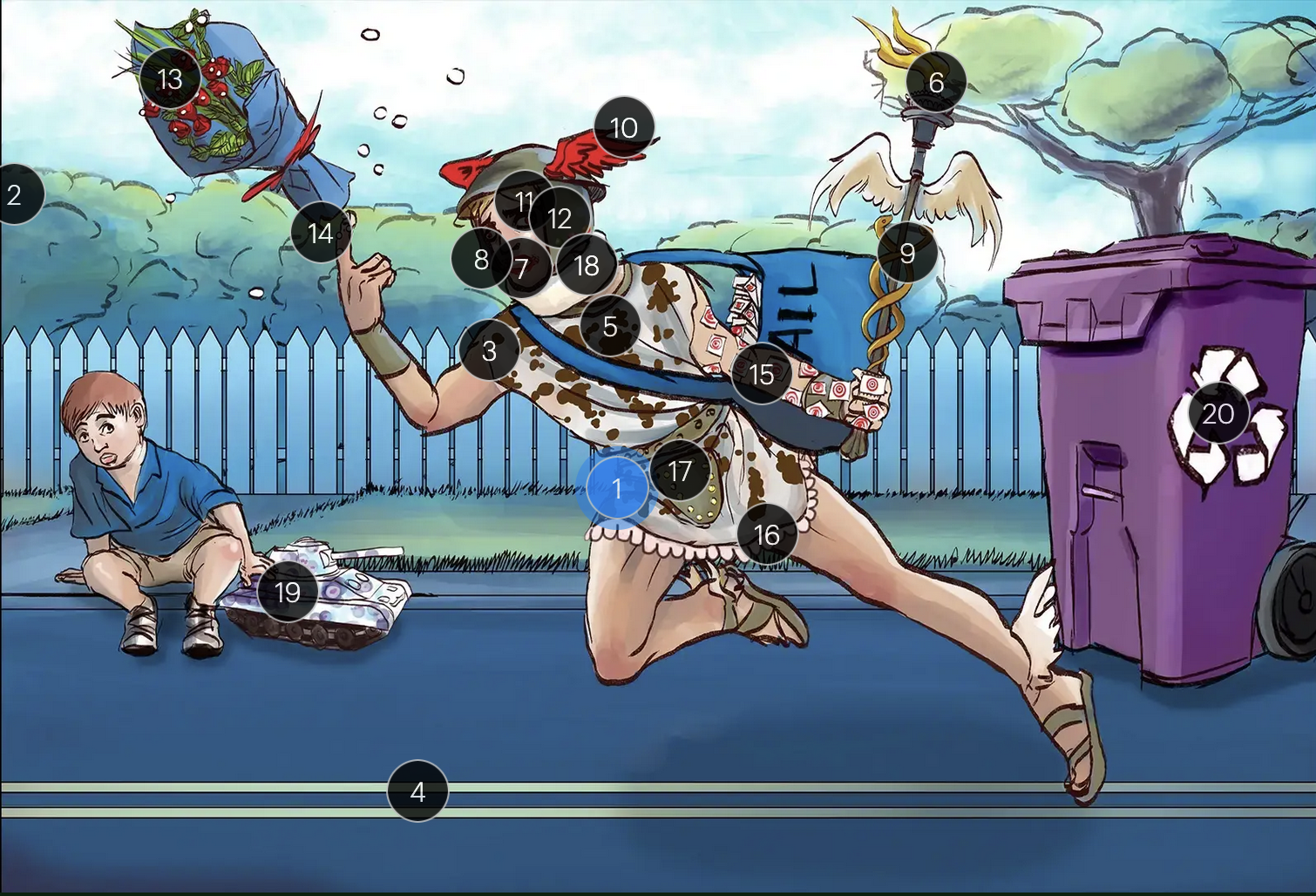
Herpes Simplex Virus Types 1 & 2 (Herpesviridae)
#6 torch
HSV 1 & 2 are considered TORCHeS infections (He) as they can be transmitted vertically
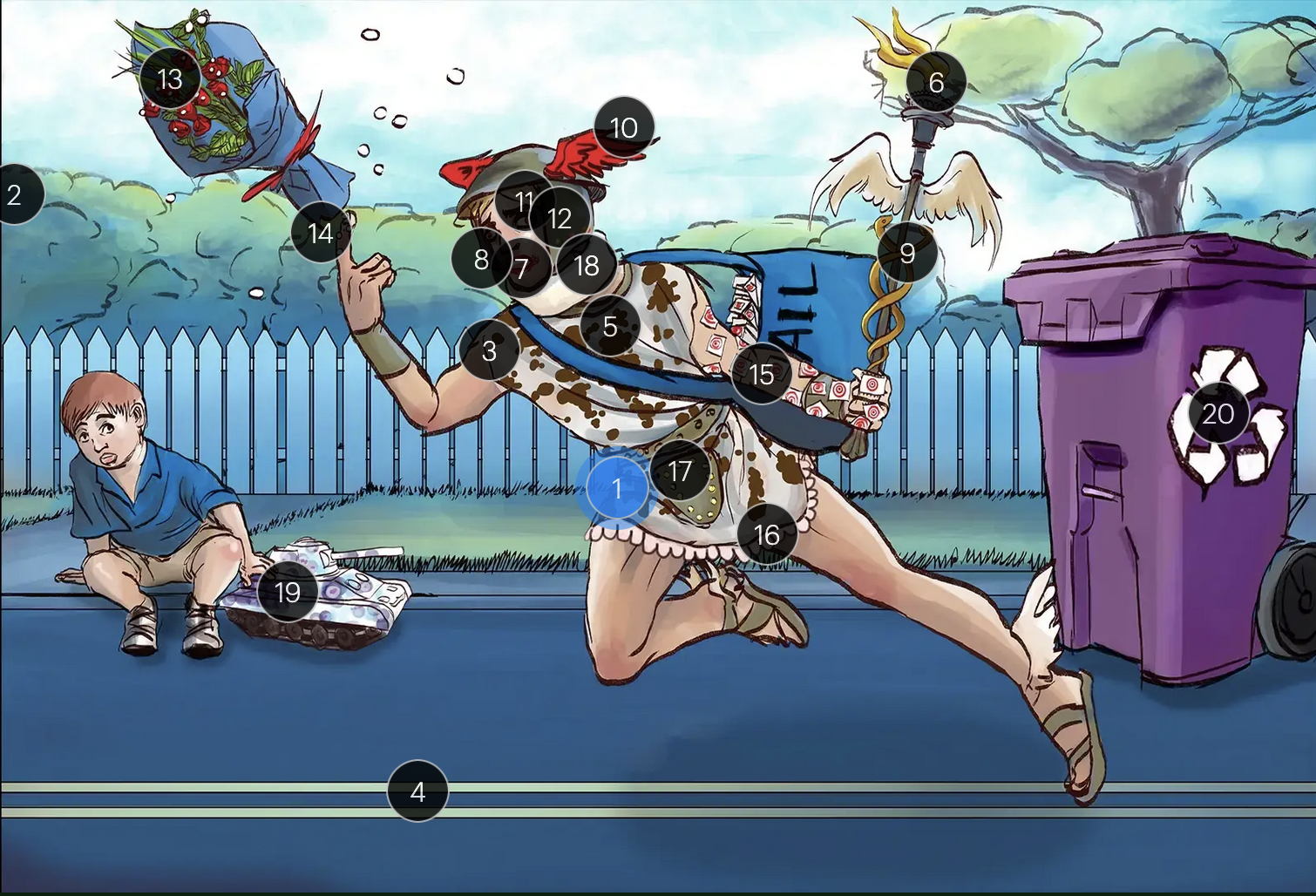
Herpes Simplex Virus Types 1 & 2 (Herpesviridae)
#7 red lips
the primary infection of HSV-1 often manifests as gingivostomatitis, characterized by vesicular lesions and ulcerations within the oral cavity and surrounding perioral region
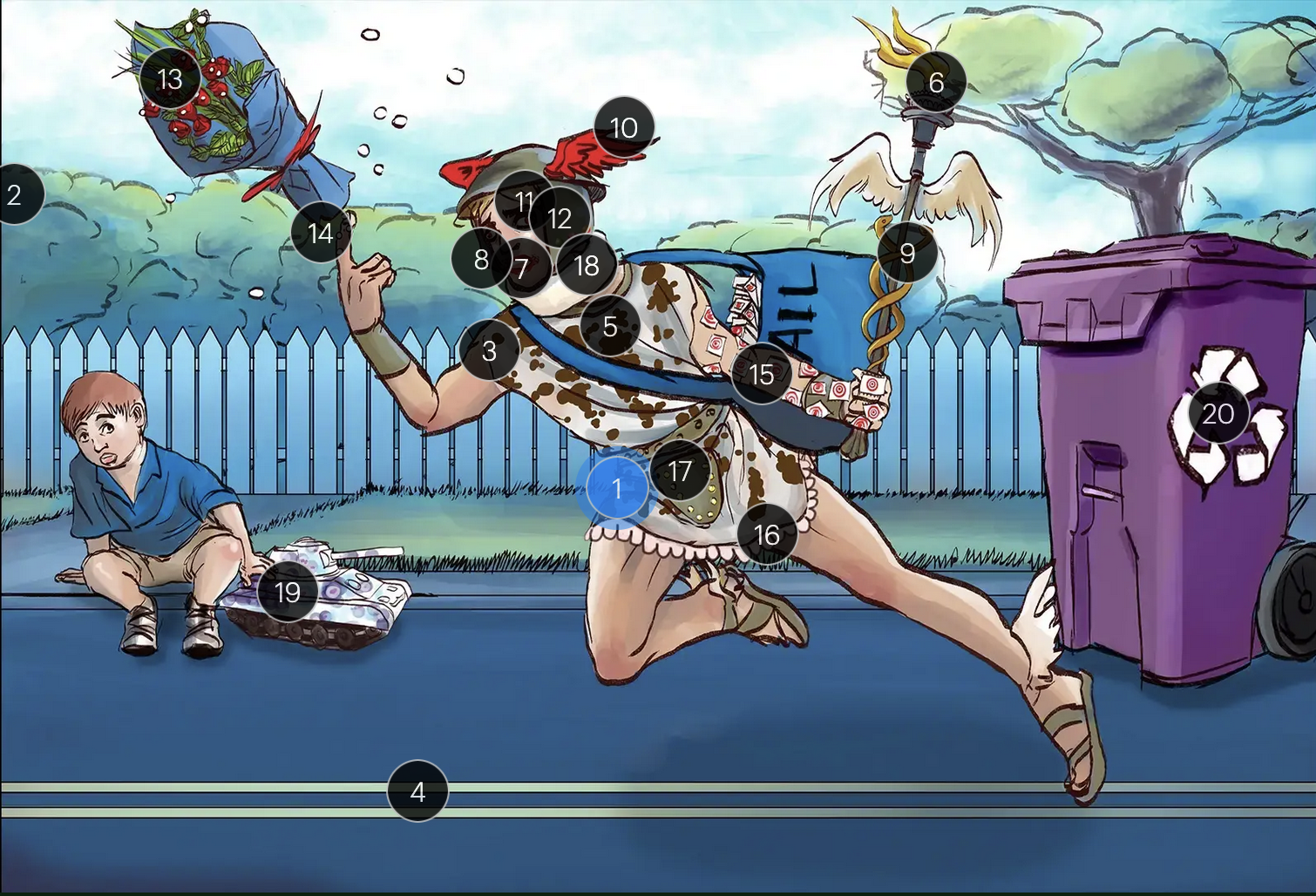
Herpes Simplex Virus Types 1 & 2 (Herpesviridae)
#8 lip ulcers
herpes labialis, colloquially known as cold sores, primarily manifests on the lips and is predominantly caused by HSV-1
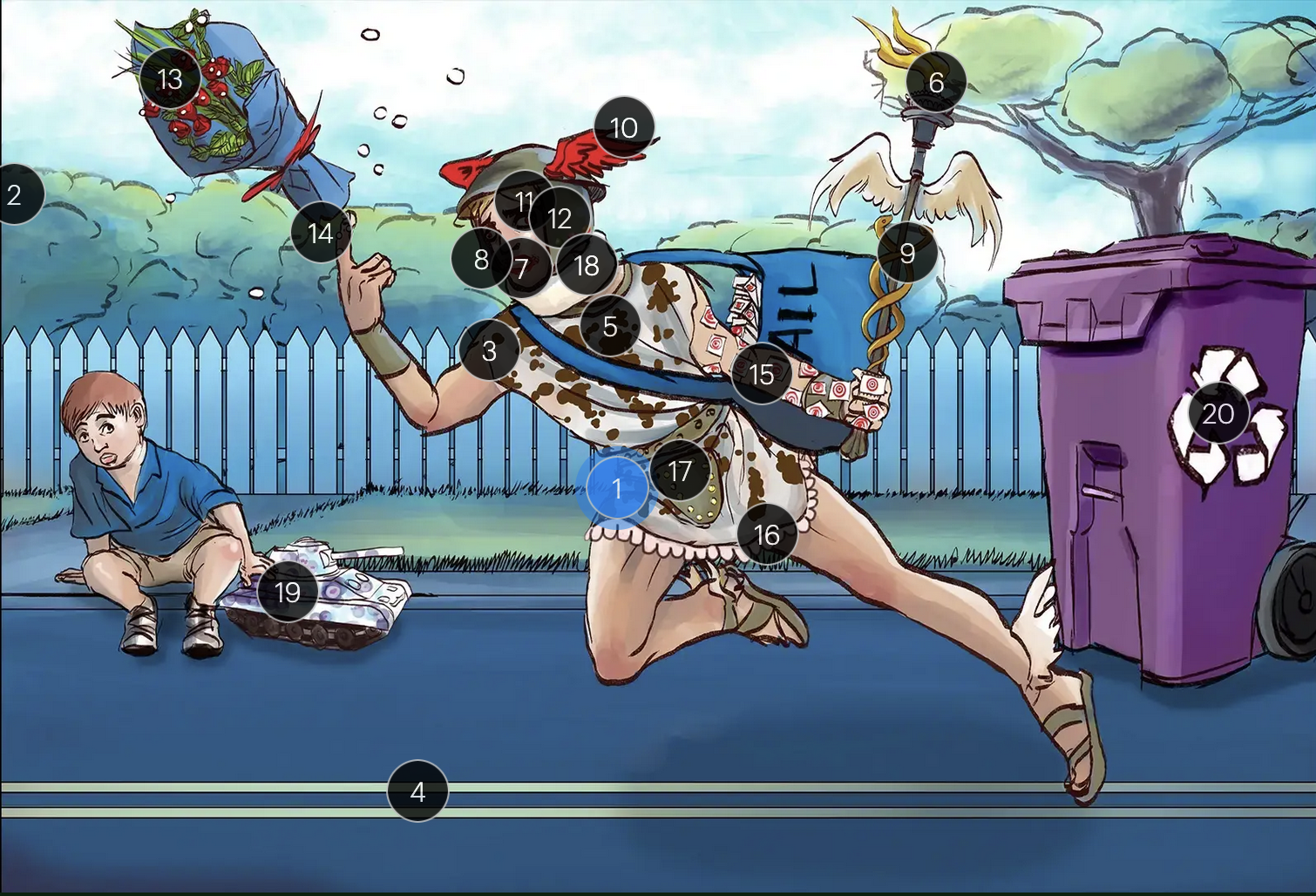
Herpes Simplex Virus Types 1 & 2 (Herpesviridae)
#9 serpent caduceus
keratoconjunctivitis, primarily attributable to HSV-1, is identifiable by serpiginous corneal ulcers on a fluorescein slit lamp examination
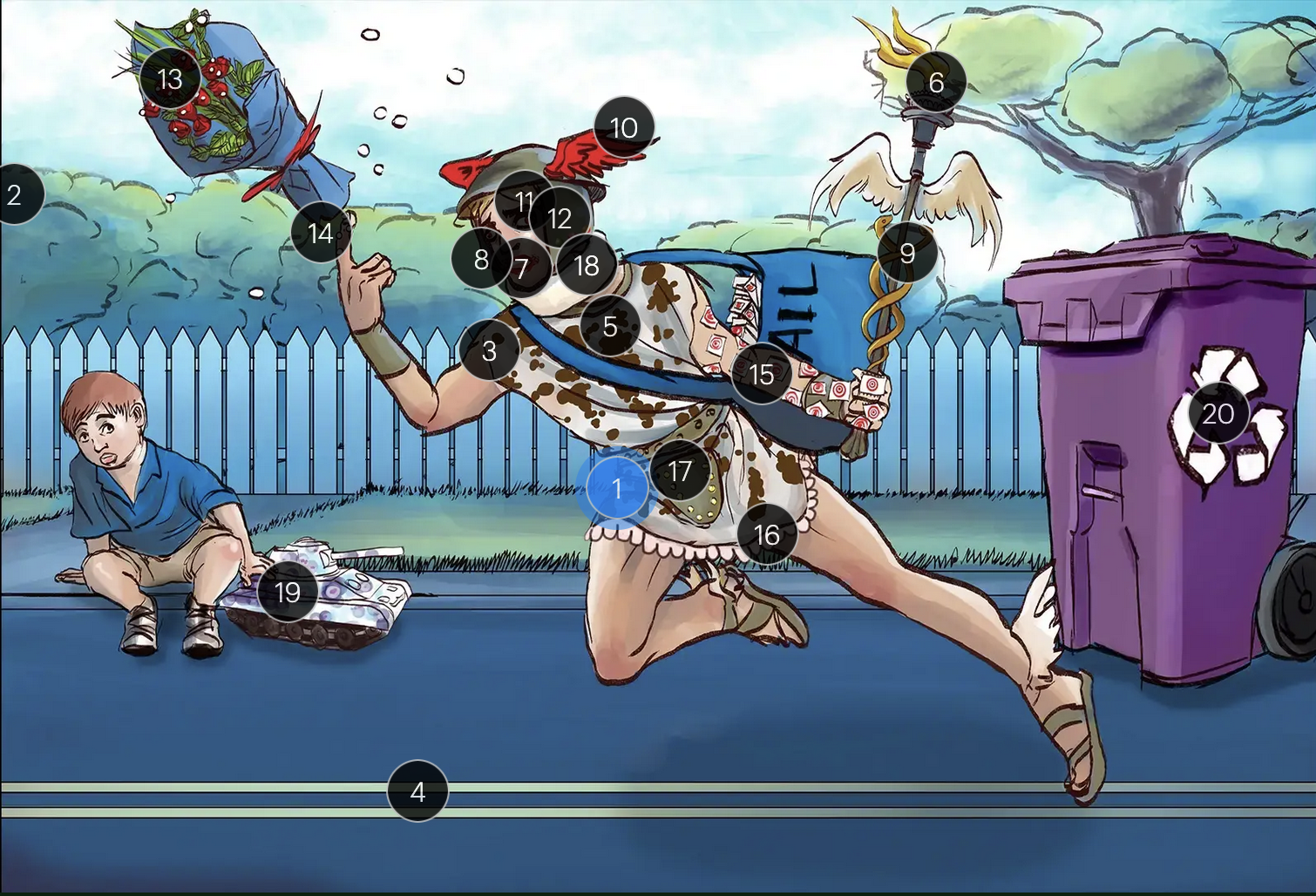
Herpes Simplex Virus Types 1 & 2 (Herpesviridae)
#10 wings on helmet
herpes encephalitis is the most common form of acute encephalitis, almost always caused by latent HSV1
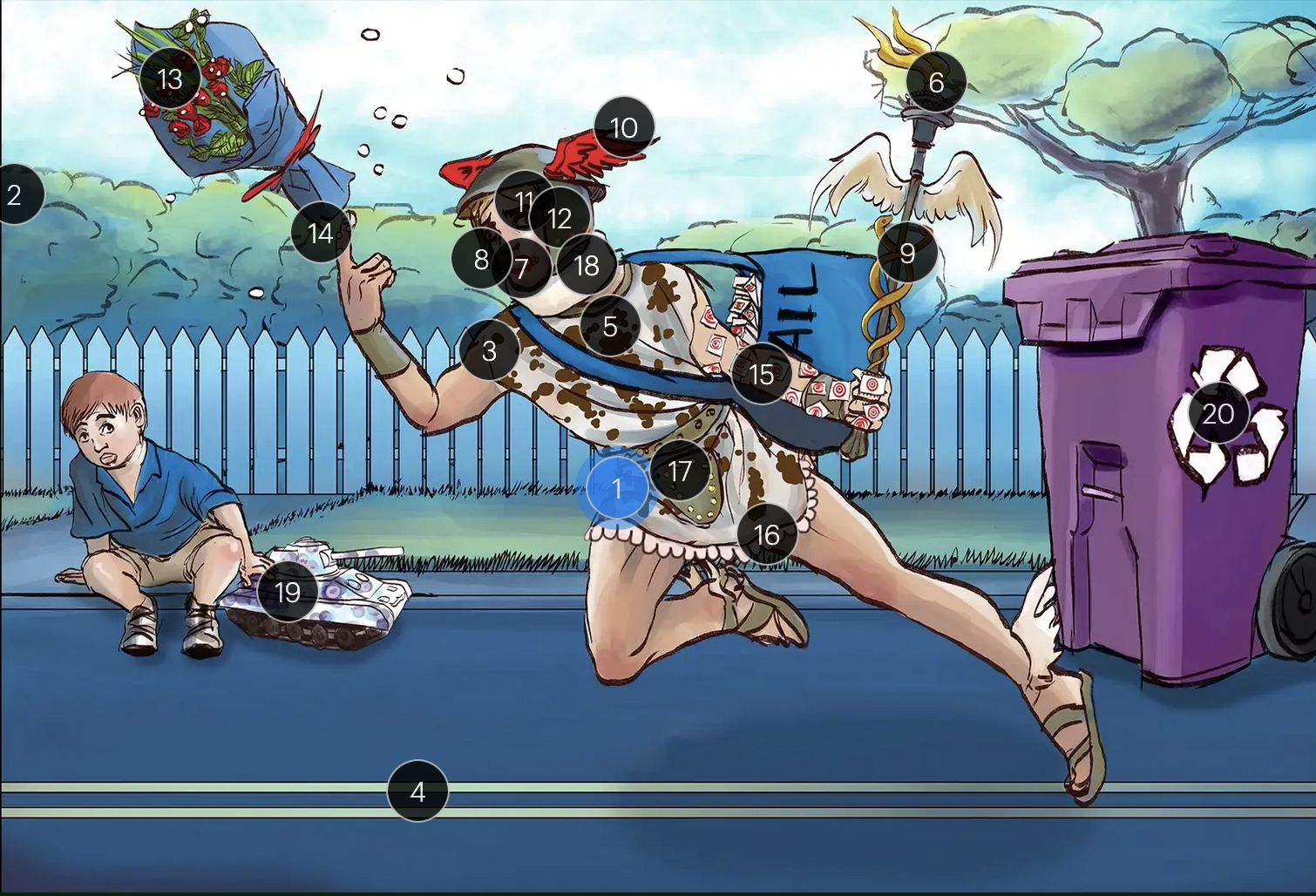
Herpes Simplex Virus Types 1 & 2 (Herpesviridae)
#11 crazy eyes
HSV1 is the most common cause of life-threatening sporadic encephalitis
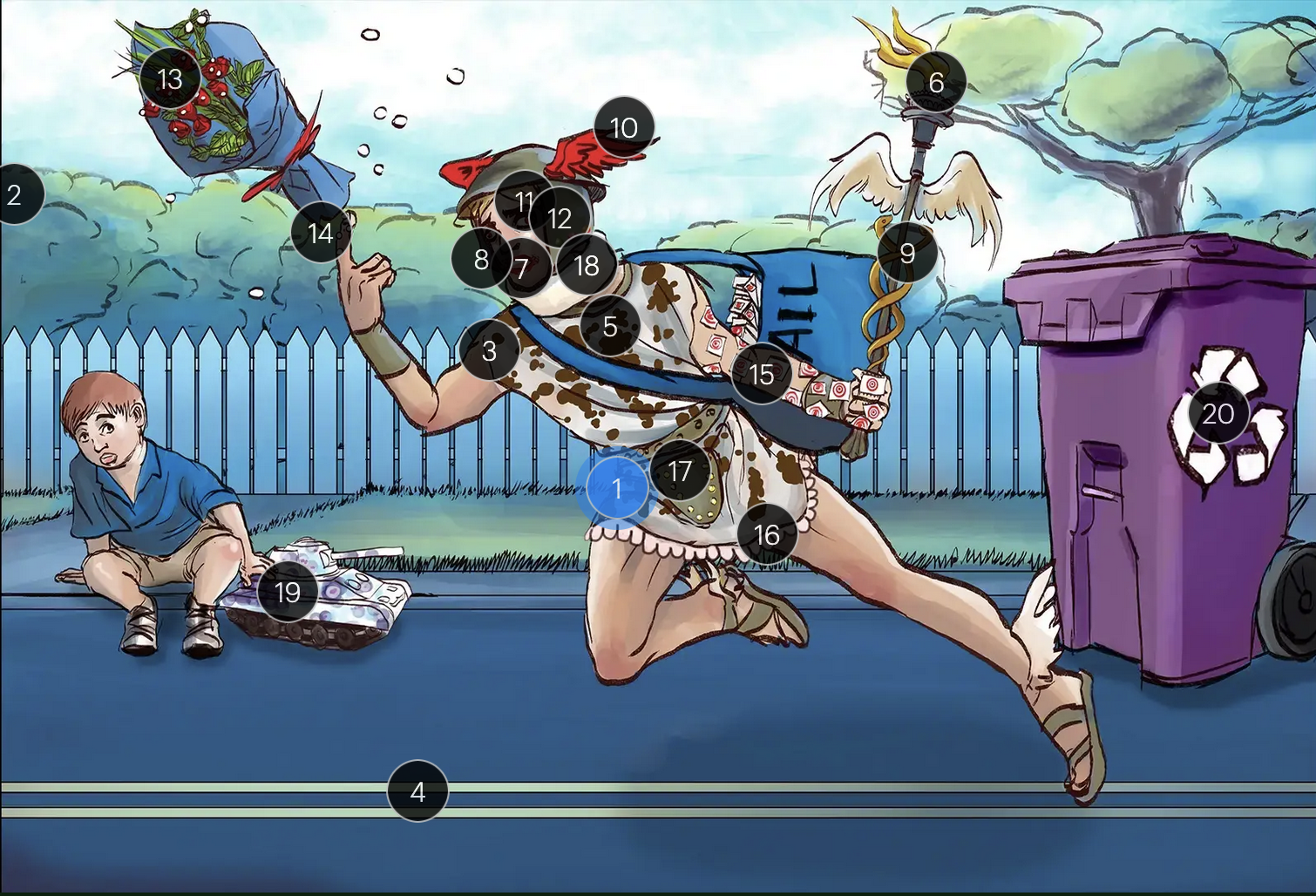
Herpes Simplex Virus Types 1 & 2 (Herpesviridae)
#12 three helmet gems
latent HSV1 typically resides in the trigeminal ganglia, posing a risk for reactivation
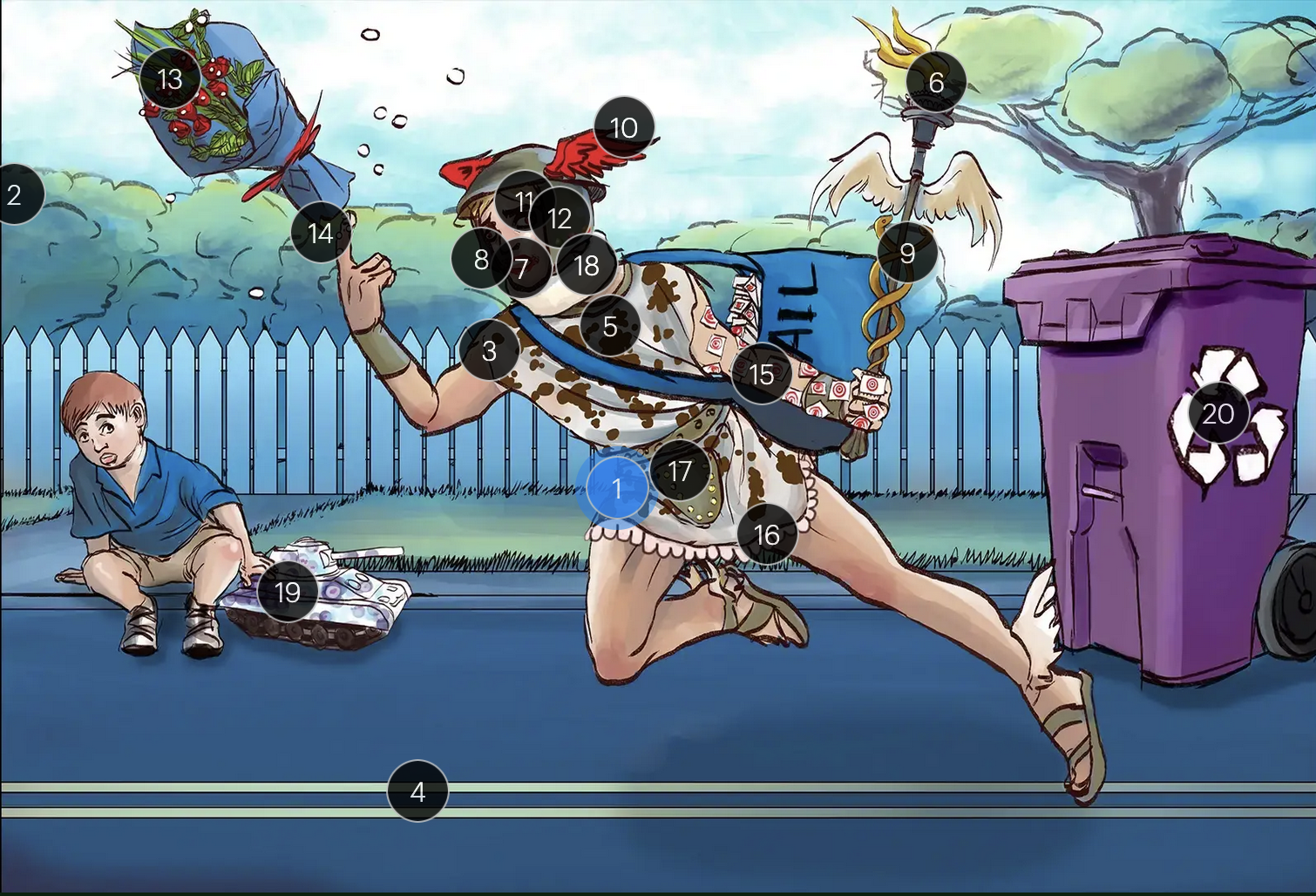
Herpes Simplex Virus Types 1 & 2 (Herpesviridae)
#13 dew drops on roses
HSV lesions appear as grouped vesicles or pustules on an eythematous base and are likened to “dew drops on a rose petal”
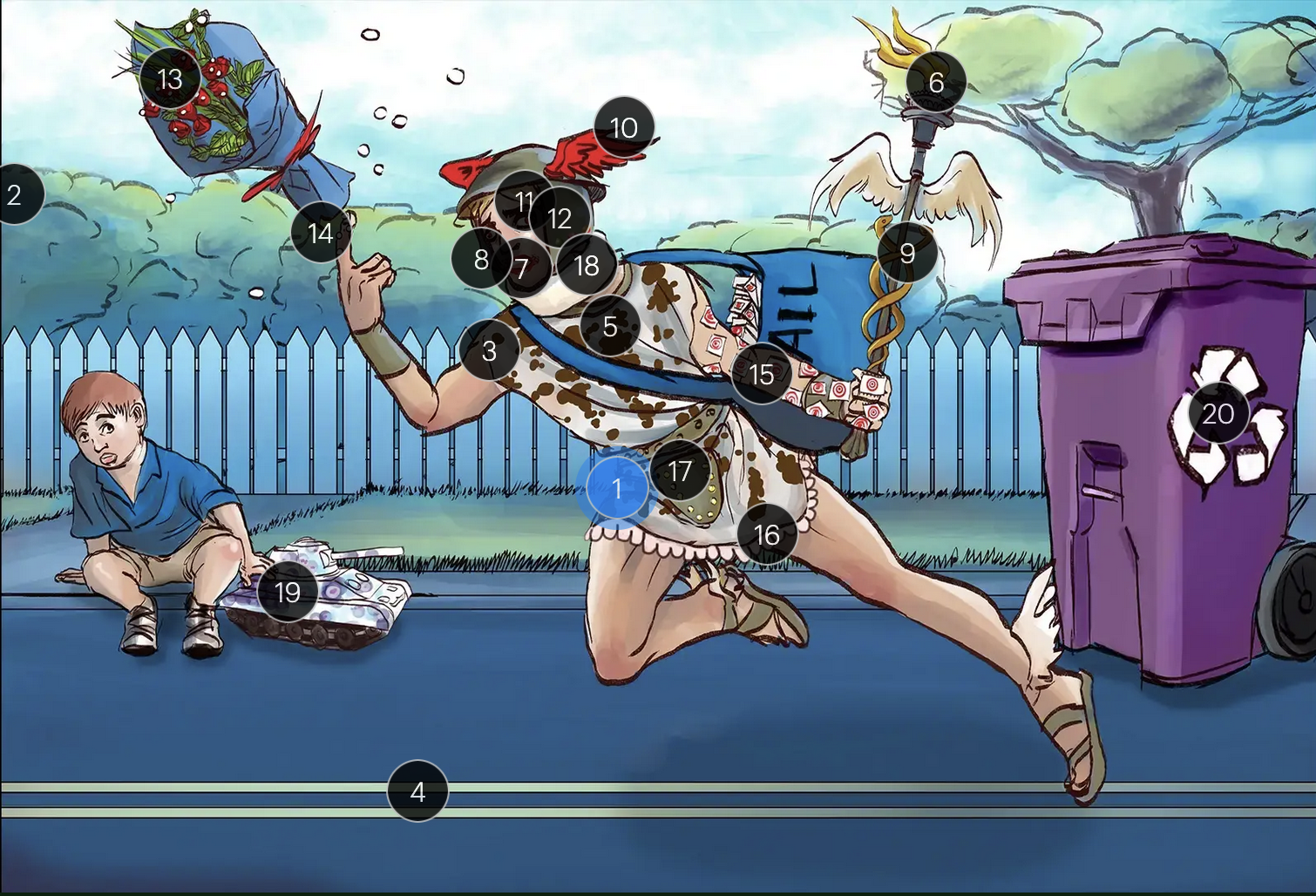
Herpes Simplex Virus Types 1 & 2 (Herpesviridae)
#14 dew drops on finger
herpetic whitlow is an HSV-induced condition characterized by painful lesions on one or more fingers
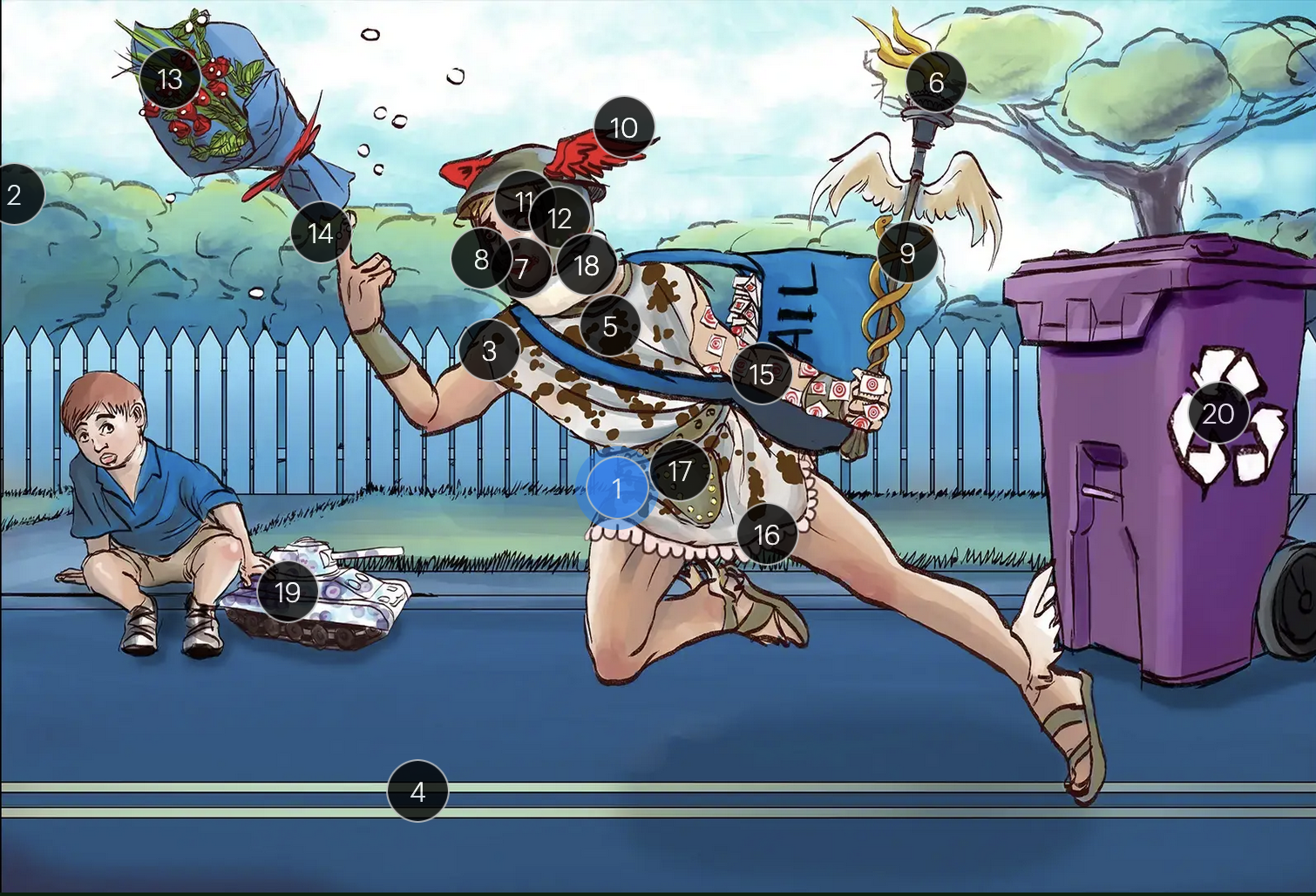
Herpes Simplex Virus Types 1 & 2 (Herpesviridae)
#15 target stamps on hand and arm
erythema multiforme is a hypersensitivity reaction associated with certain medications and infections (such as HSV) that presents with distinct target lesions on the back of the hands and feet and move centrally
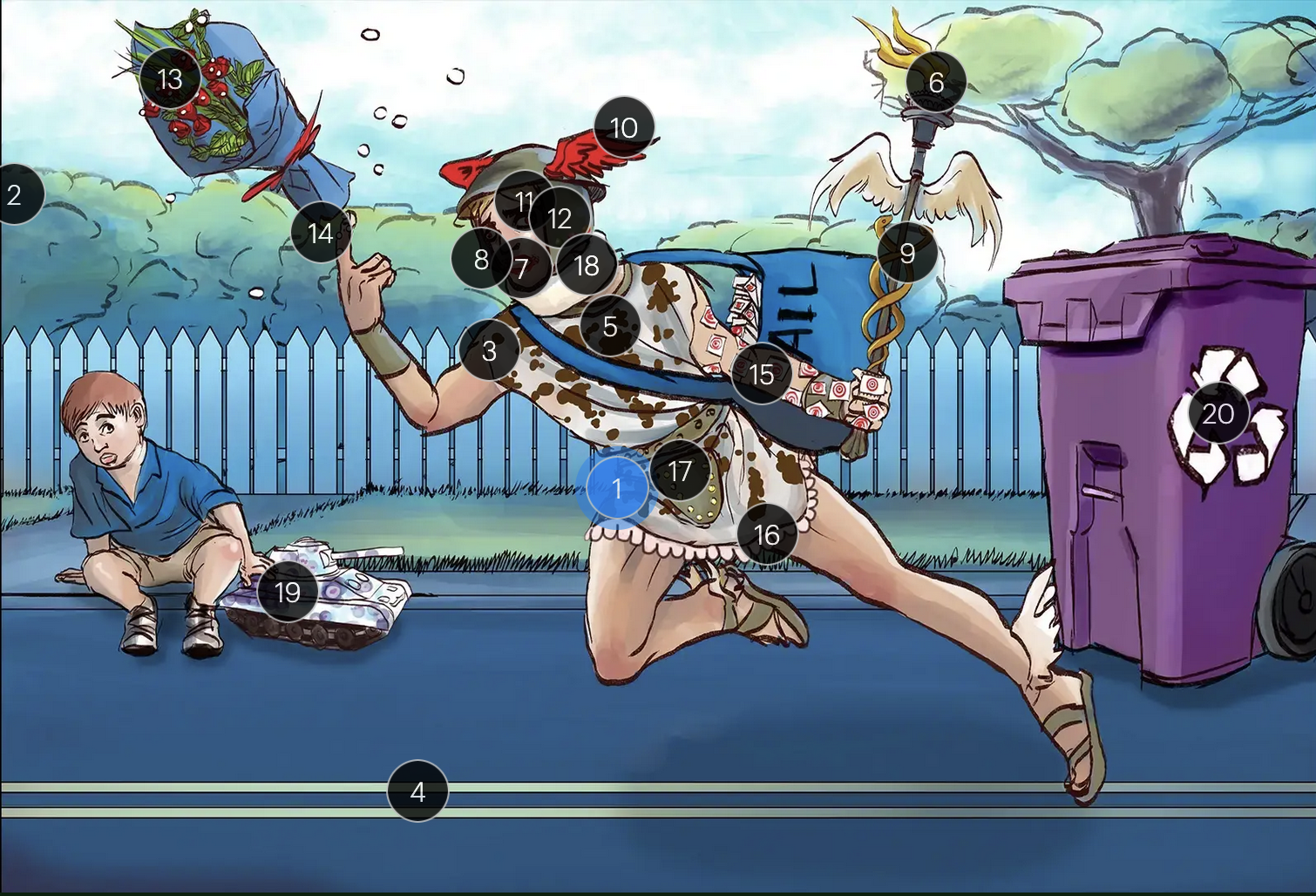
Herpes Simplex Virus Types 1 & 2 (Herpesviridae)
#16 ruffles by groin
during an initial genital herpes outbreak, often caused by HSV2, patients may present with tender lymphadenopathy in the inguinal region
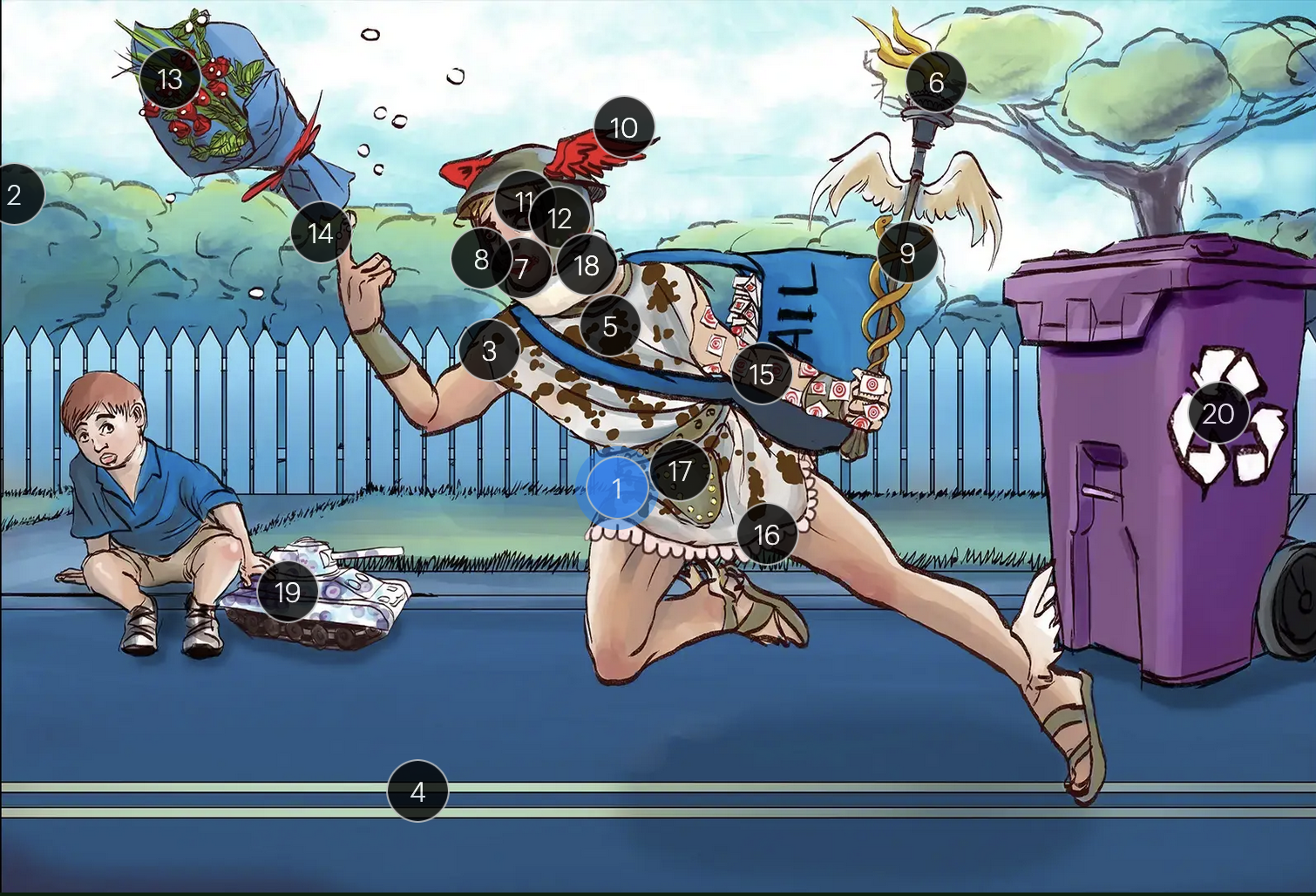
Herpes Simplex Virus Types 1 & 2 (Herpesviridae)
#17 codpiece
HSV2 primarily establishes latency in the sacral ganglia, posing a risk for reactivation
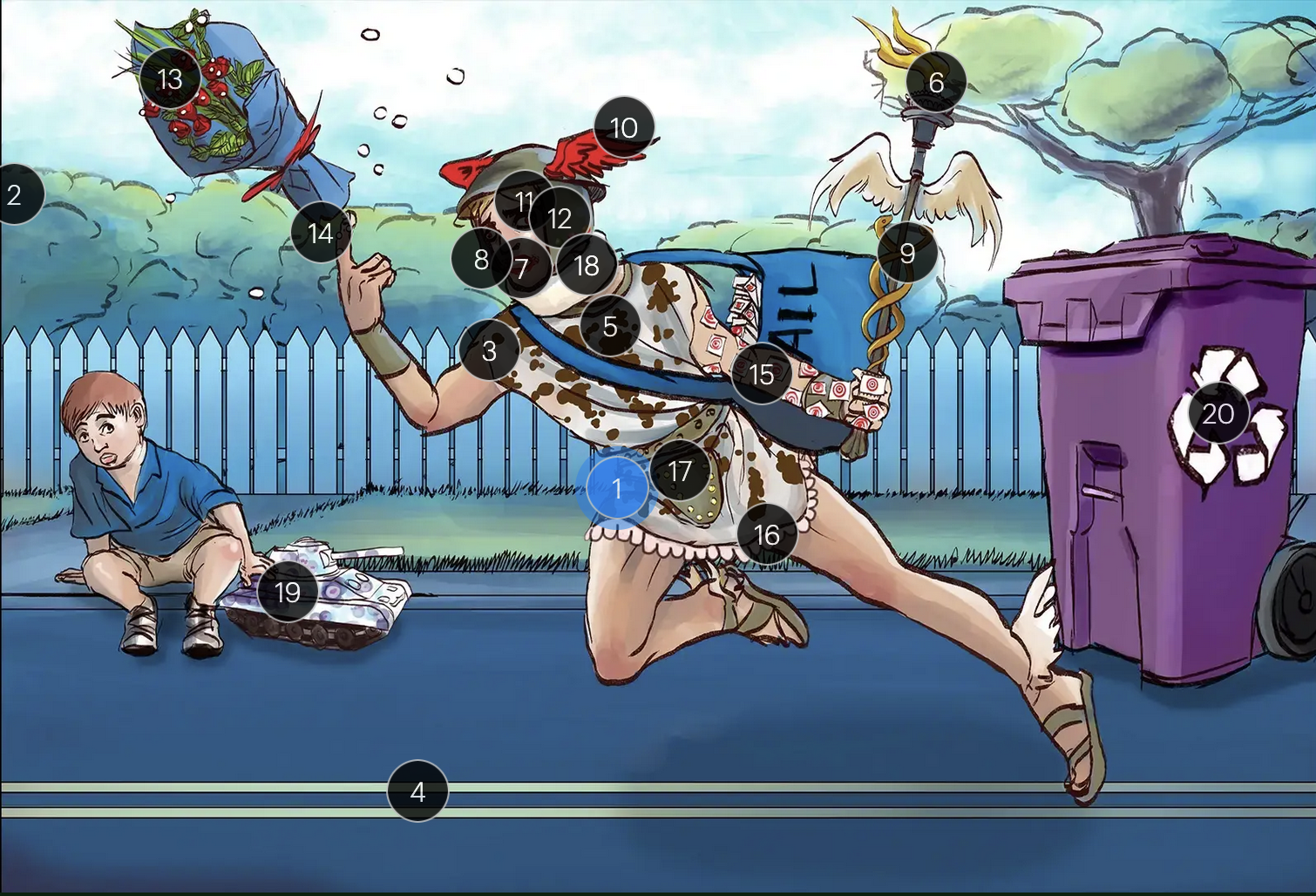
Herpes Simplex Virus Types 1 & 2 (Herpesviridae)
#18 neck brace
HSV2 infections have been linked to cases of aseptic meningitis in both adolescent and adult populations
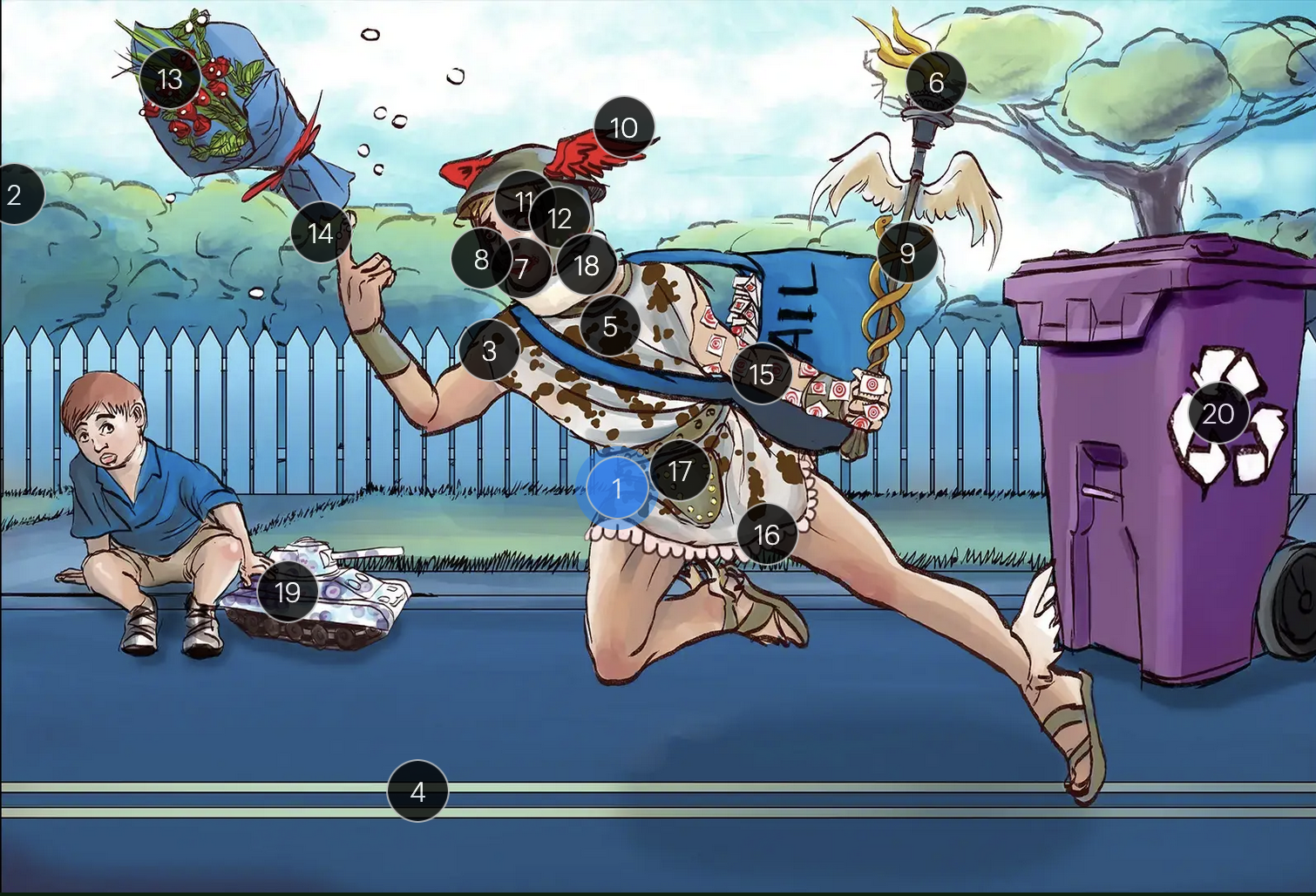
Herpes Simplex Virus Types 1 & 2 (Herpesviridae)
#19 tank + giant spots
the Tzank smear was used historically to visualize multinucleated giant cells infected with HSV; however, multinucleated giant cells can also be seen in other conditions like VZV infections & specific identification requires other tests, such as PCR or viral culture
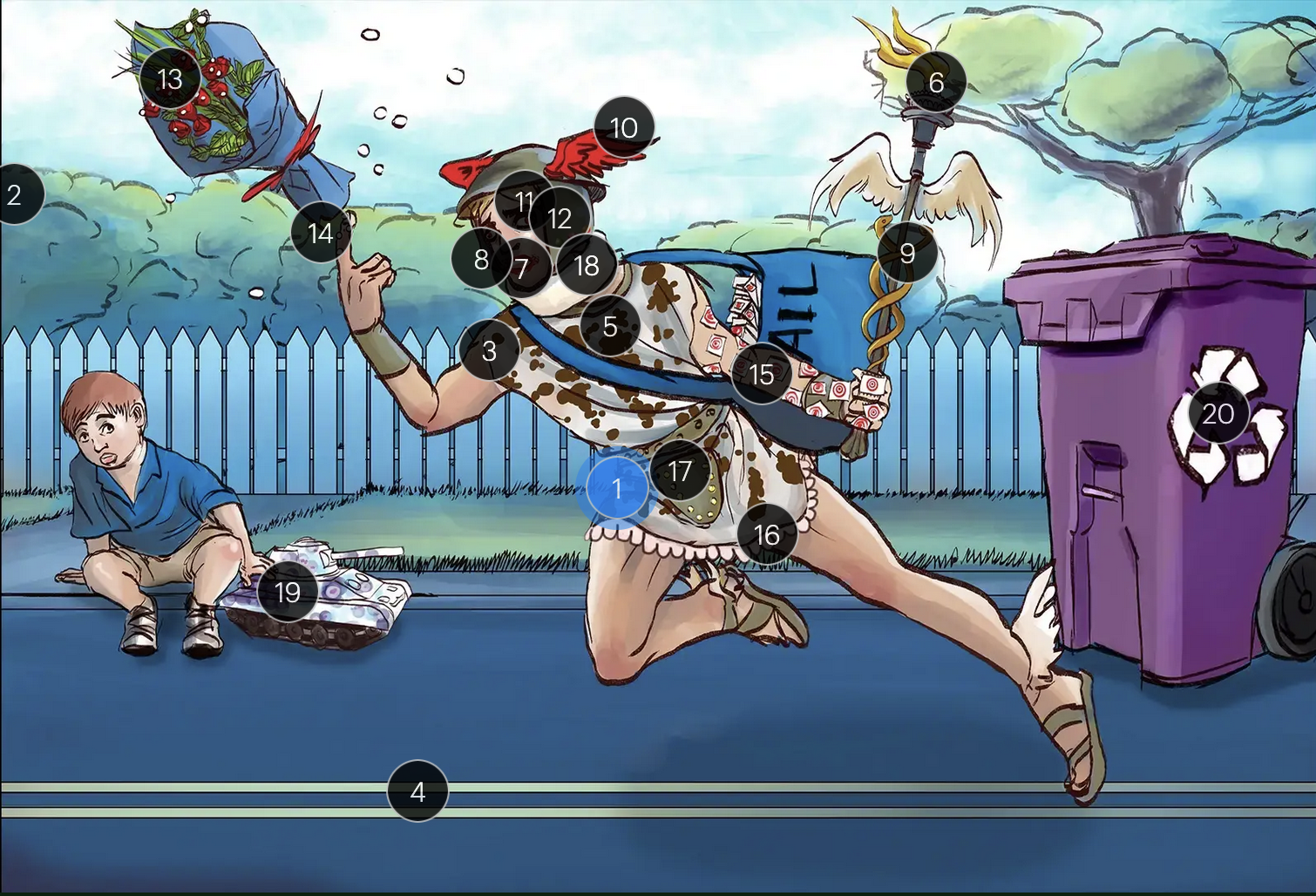
Herpes Simplex Virus Types 1 & 2 (Herpesviridae)
#20 violet recycling bin
prophylactic measures against HSV outbreaks include the use of valacyclovir & acyclovir
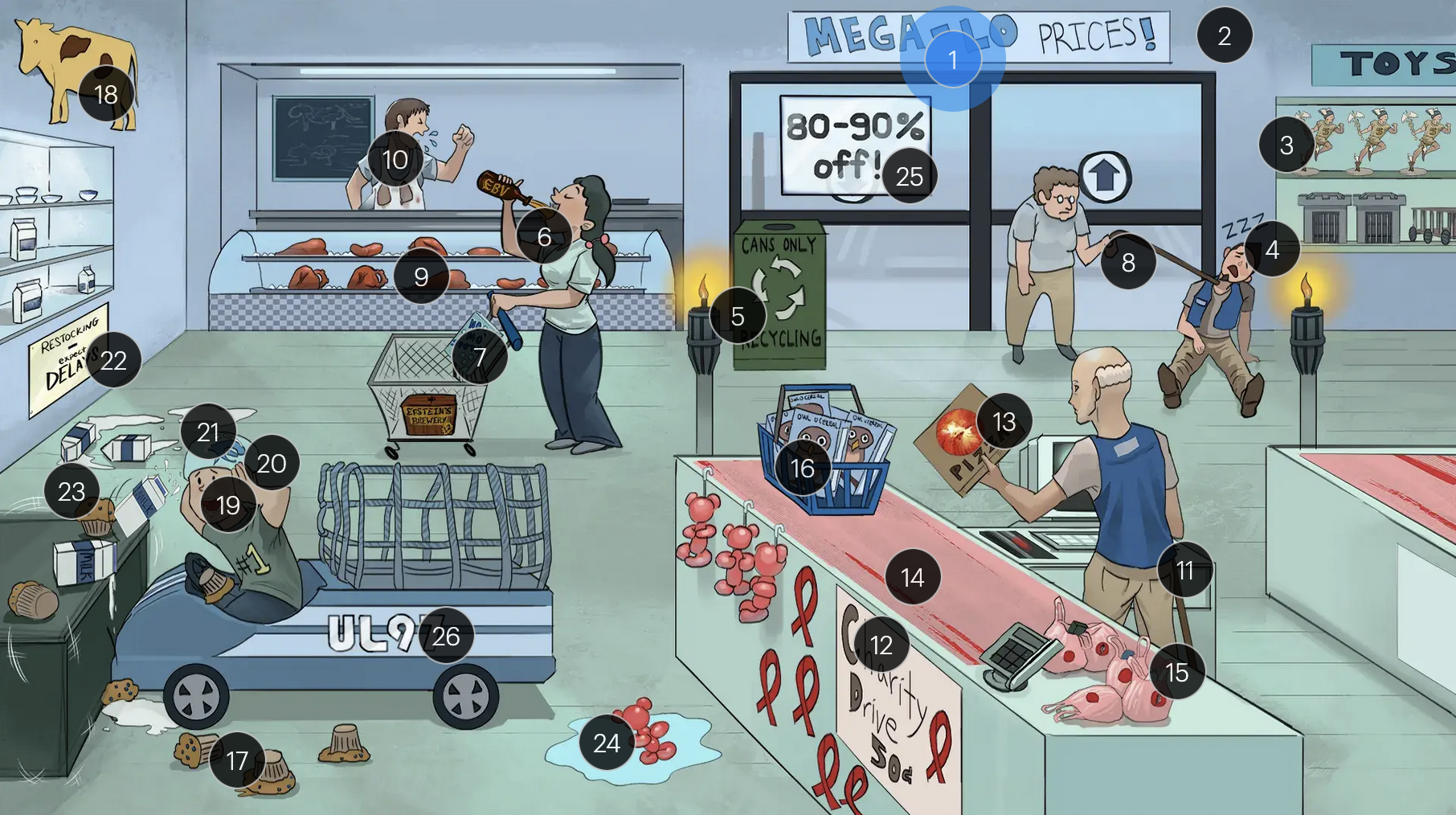

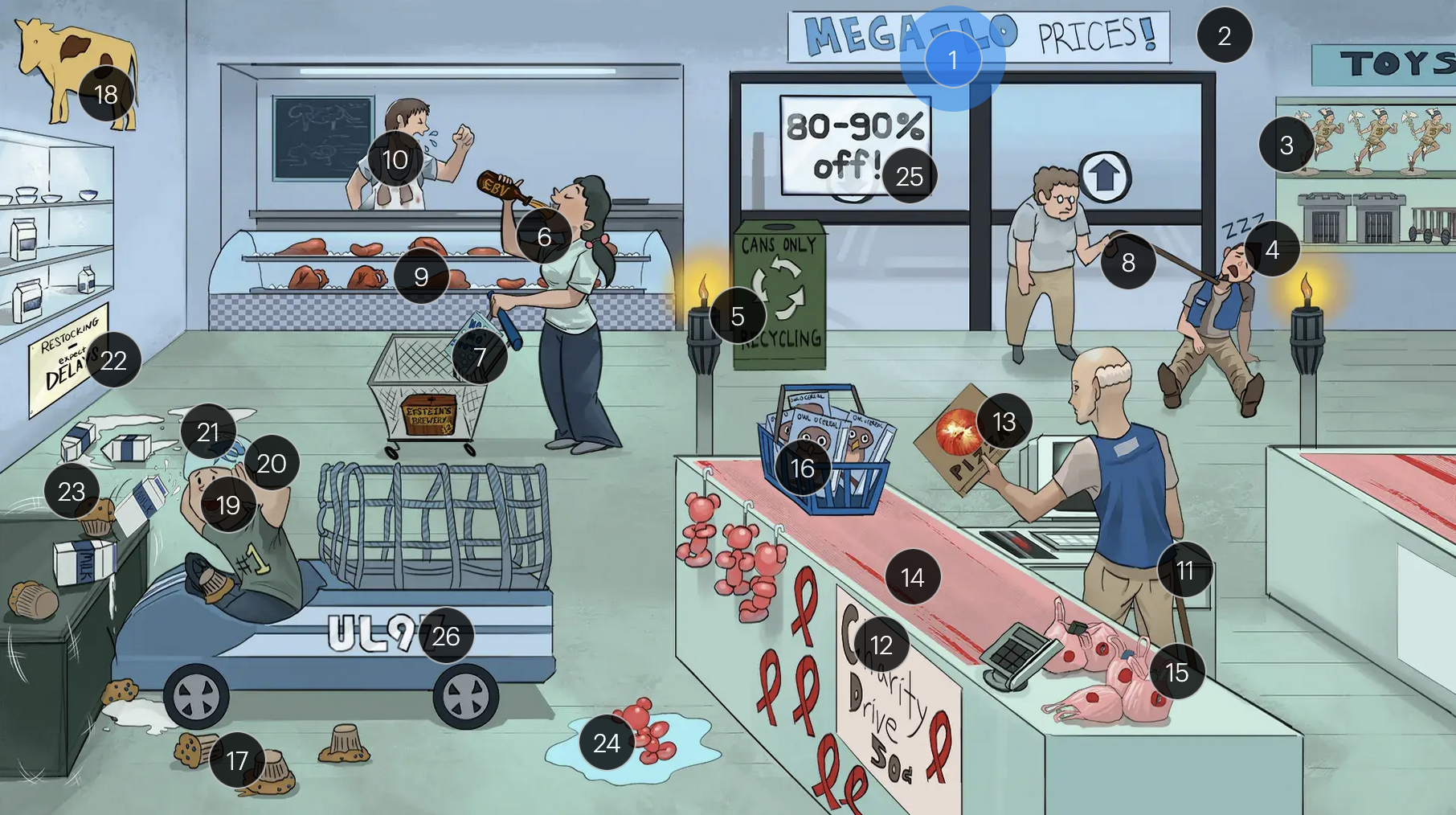
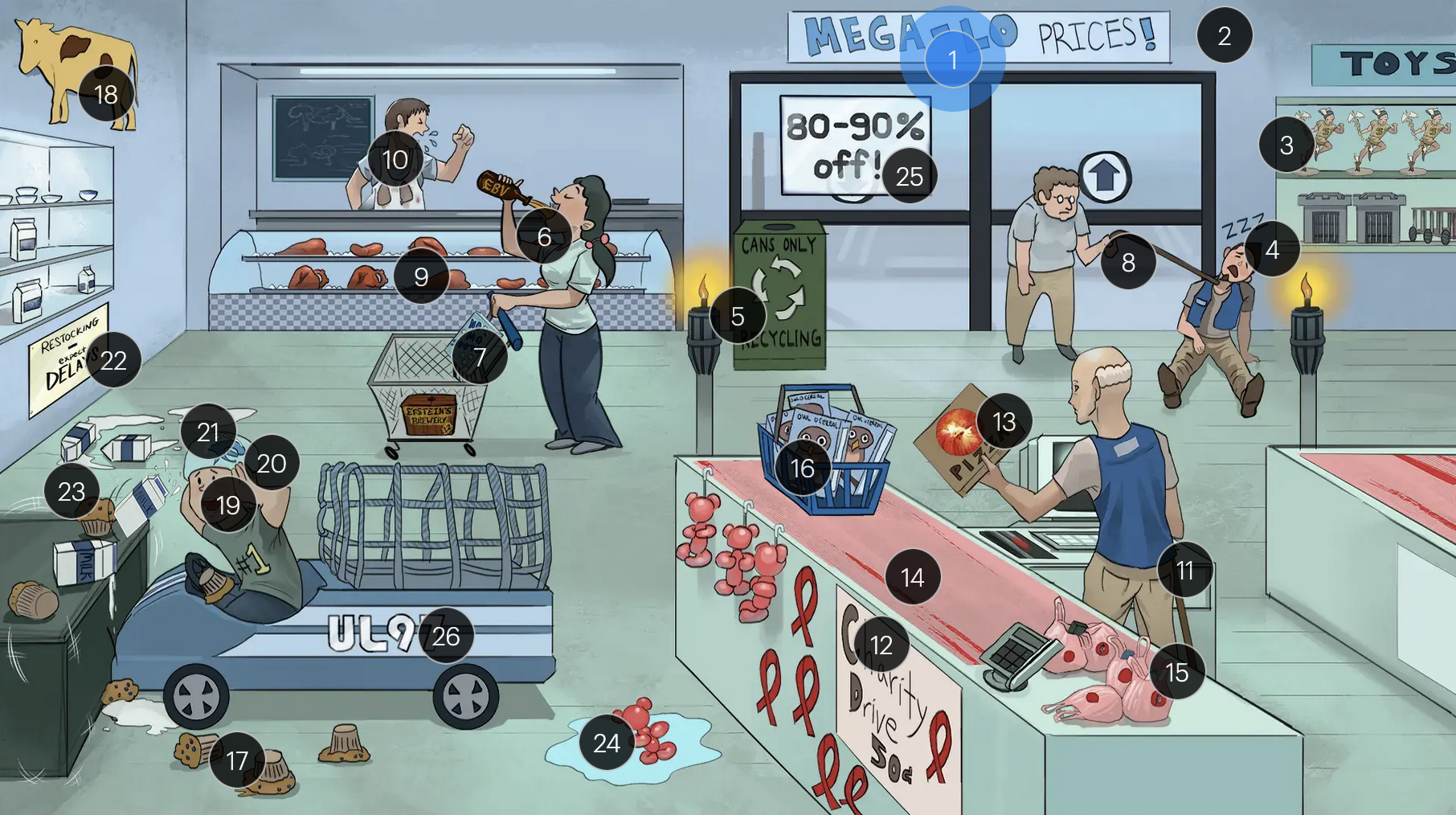
Cytomegalovirus (Herpesviridae)
#1 “Mega-Lo prices!”
Cytomegalovirus (CMV; a DNA virus in the Herpesviridae family)

Cytomegalovirus (Herpesviridae)
#2 cool colors
CMV is a DNA virus

Cytomegalovirus (Herpesviridae)
#3 Hermes toys
CMV is part of the Herpesviridae family

Cytomegalovirus (Herpesviridae)
#4 sleeping + macro-cages
CMV establishes latency in mononuclear myeloid cells (monocytes, MACROPHAGES, dendritic cells)

Cytomegalovirus (Herpesviridae)
#5 torches
CMV is a TORCHeS infection (C) as it can be transmitted vertically, resulting in congenital CMV

Cytomegalovirus (Herpesviridae)
#6 Epstein’s Beer + back of throat
clinical manifestations of CMV infection can resemble those of EBV, presenting with symptoms like fever, sore throat, lymphadenopathy (commonly involving the lymph nodes of the head and neck), and fatigue

Cytomegalovirus (Herpesviridae)
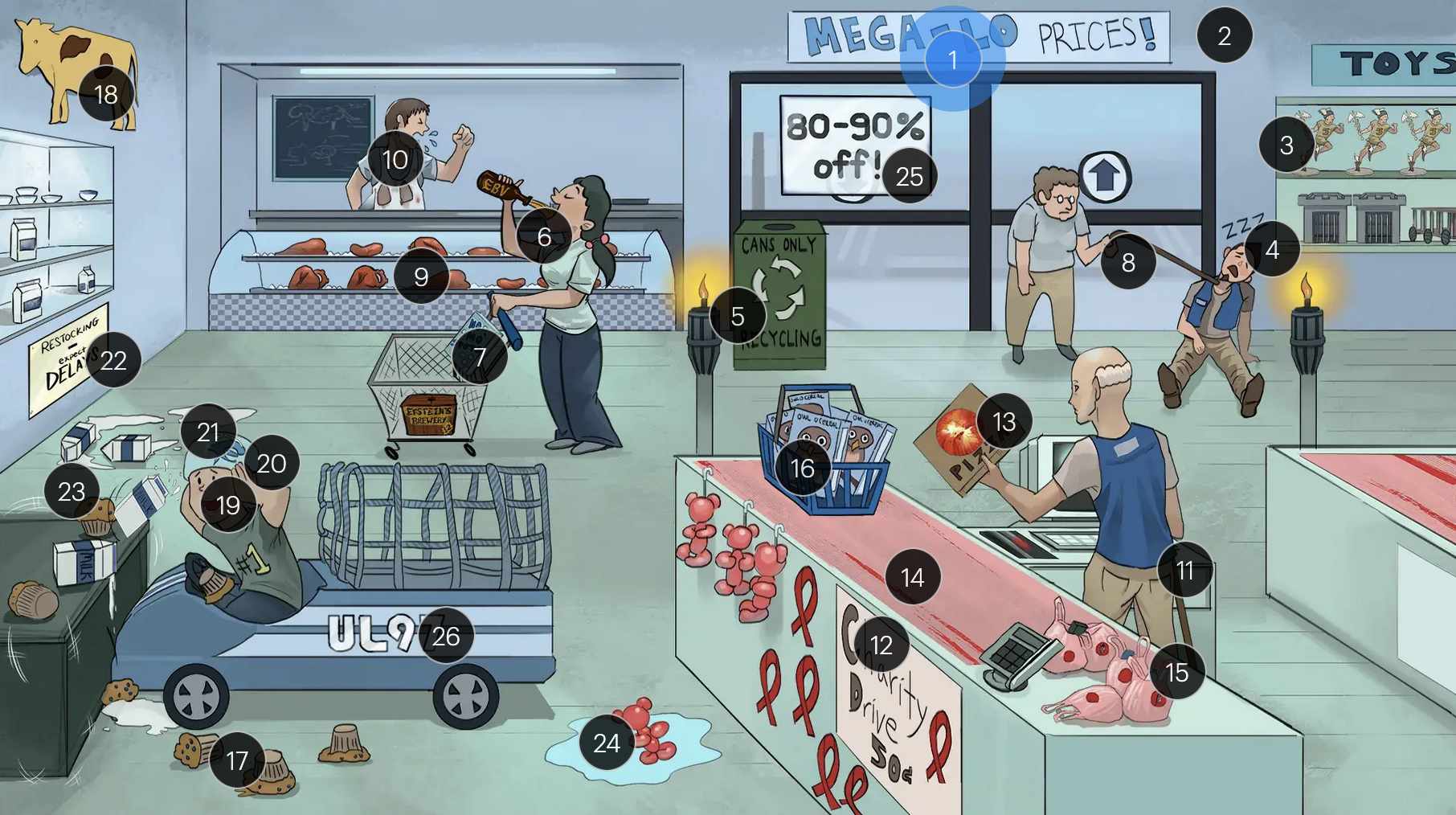
#7 “No Mo’ Spot” detergent
the MonoSpot test can help distinguish between CMV and EBV infections as it is generally positive in EBV infections and negative in CMV infections; however, the monospot test has limitations, and standard laboratory tests for diagnosing both CMV & EBV infection include PCR and serology

Cytomegalovirus (Herpesviridae)
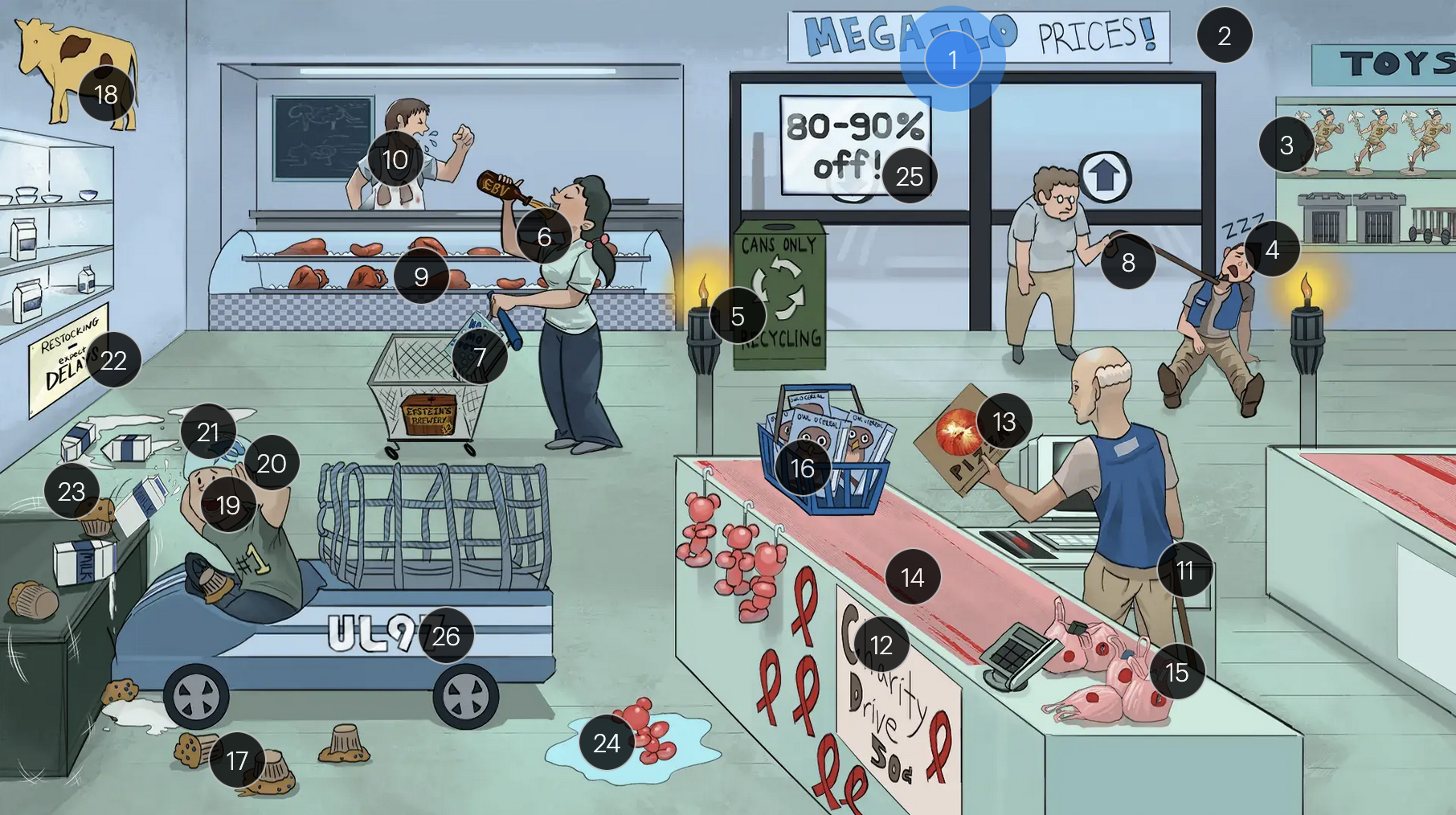
#8 walking man with immunocompromised cane
in immunocompromised individuals, there is an increased risk of CMV reactivation

Cytomegalovirus (Herpesviridae)
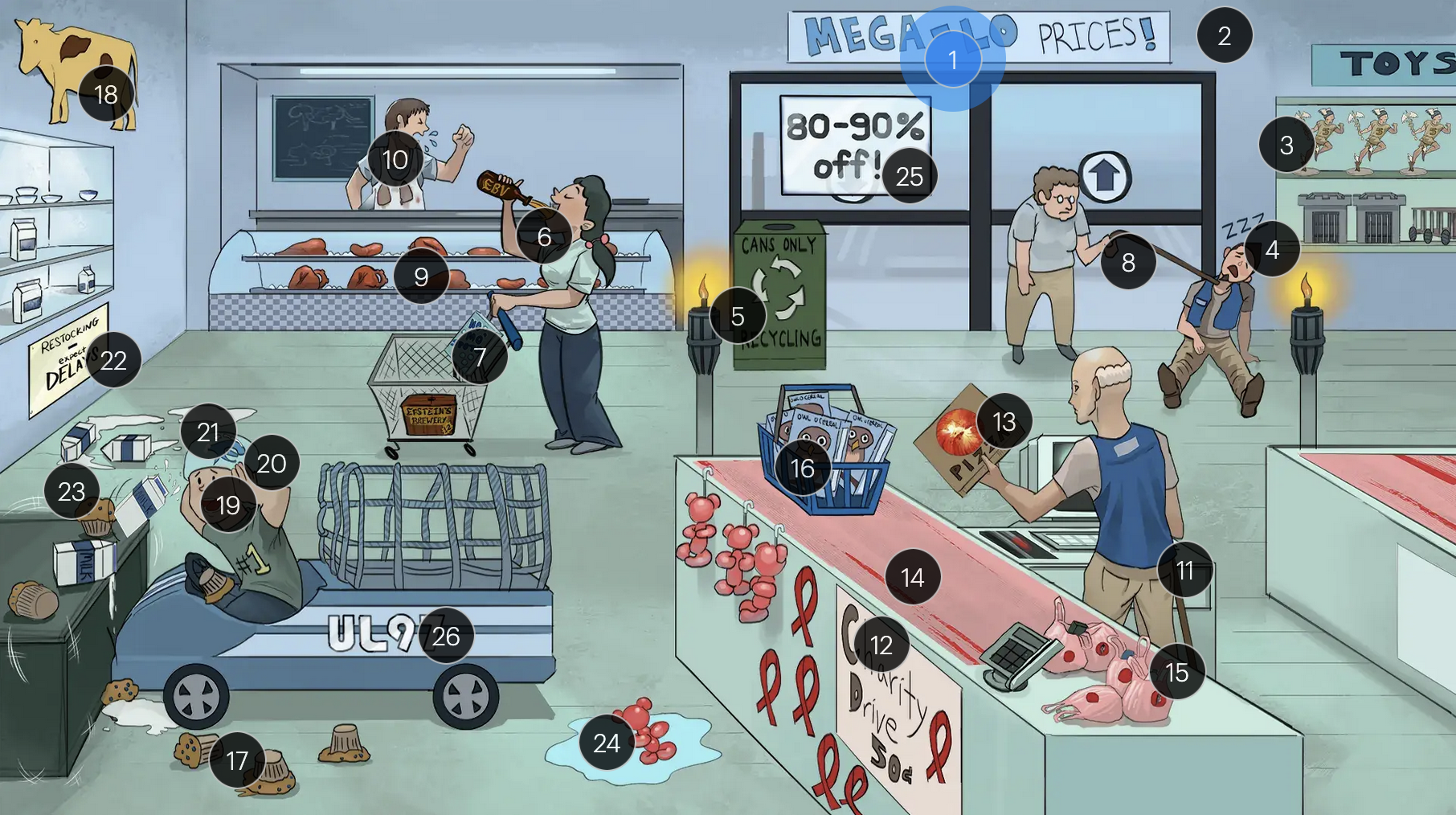
#9 solid organs
patients who receive transplants (especially solid organ, bone marrow, and stem cells) are more likely to get an active CMV infection

Cytomegalovirus (Herpesviridae)
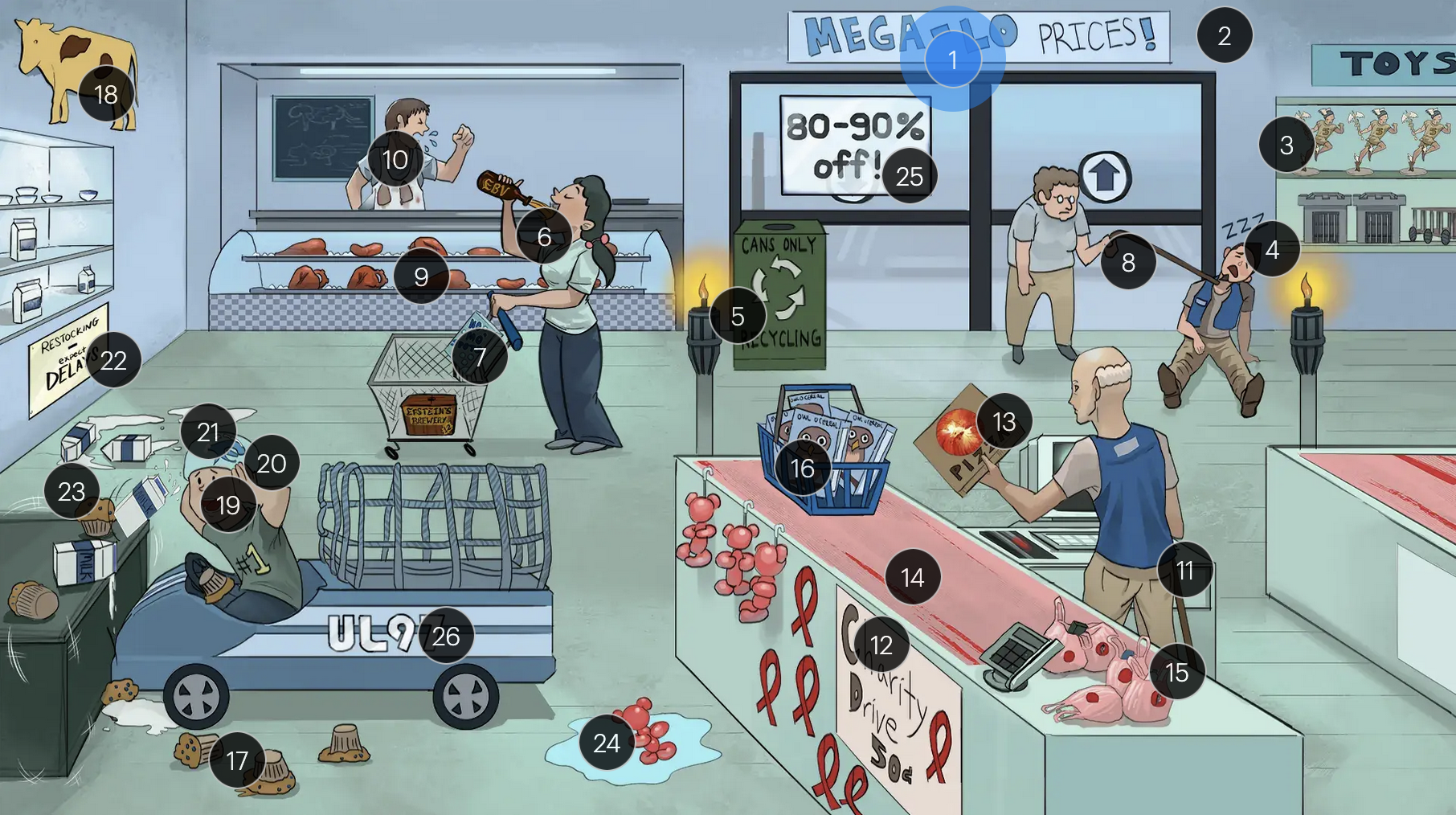
#10 coughing + lung stains
transplant patients are at higher risk for developing CMV pneumonia and pneumonitis (as well as other CMV infections, including hepatitis, gastritis, colitis, and encephalitis)

Cytomegalovirus (Herpesviridae)
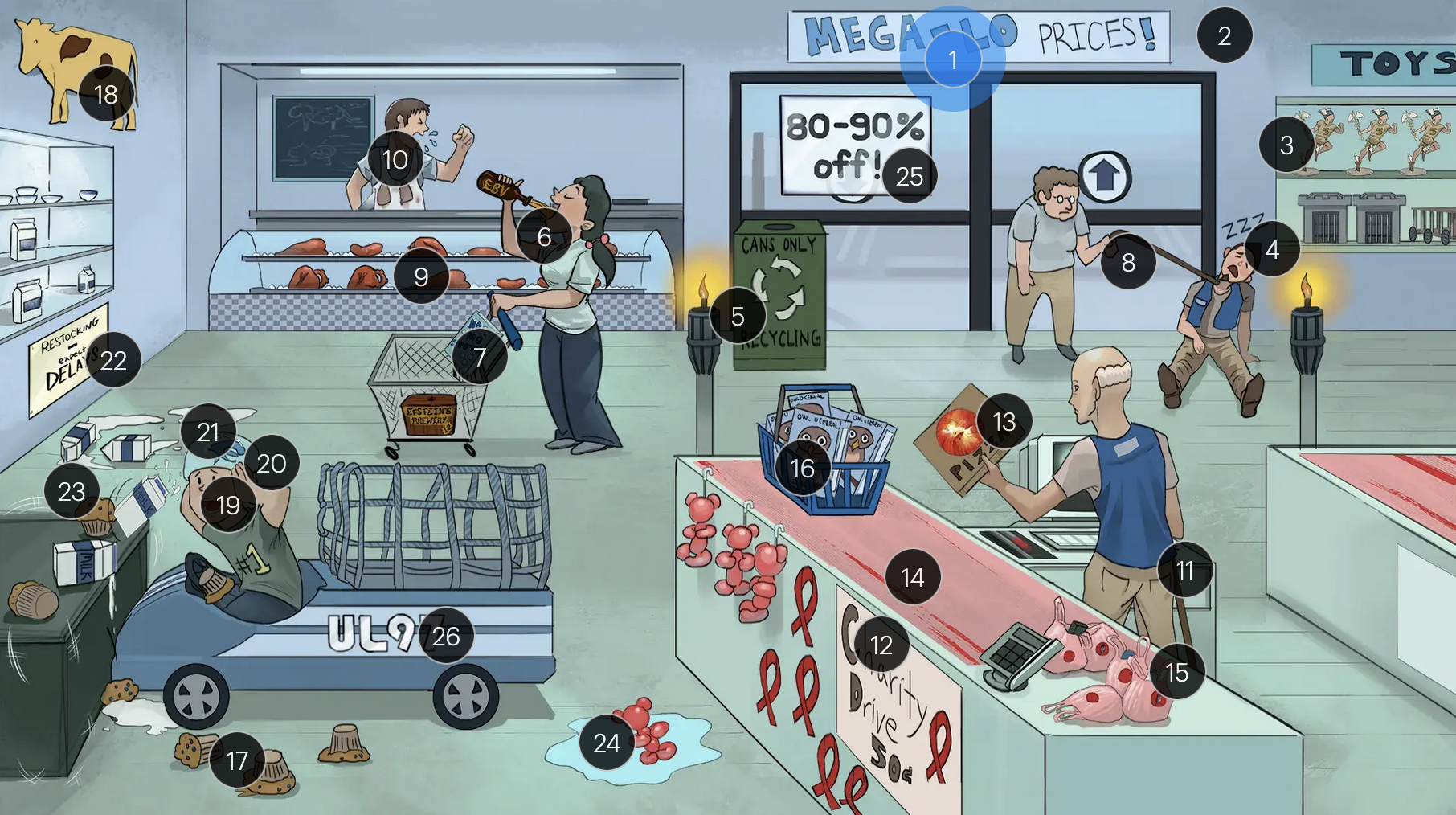
#11 immunocompromised can + AIDS ribbons
immunocompromised individuals, especially those with CD4+ counts below 50 (AIDS patients) are more vulnerable to CMV infections

Cytomegalovirus (Herpesviridae)
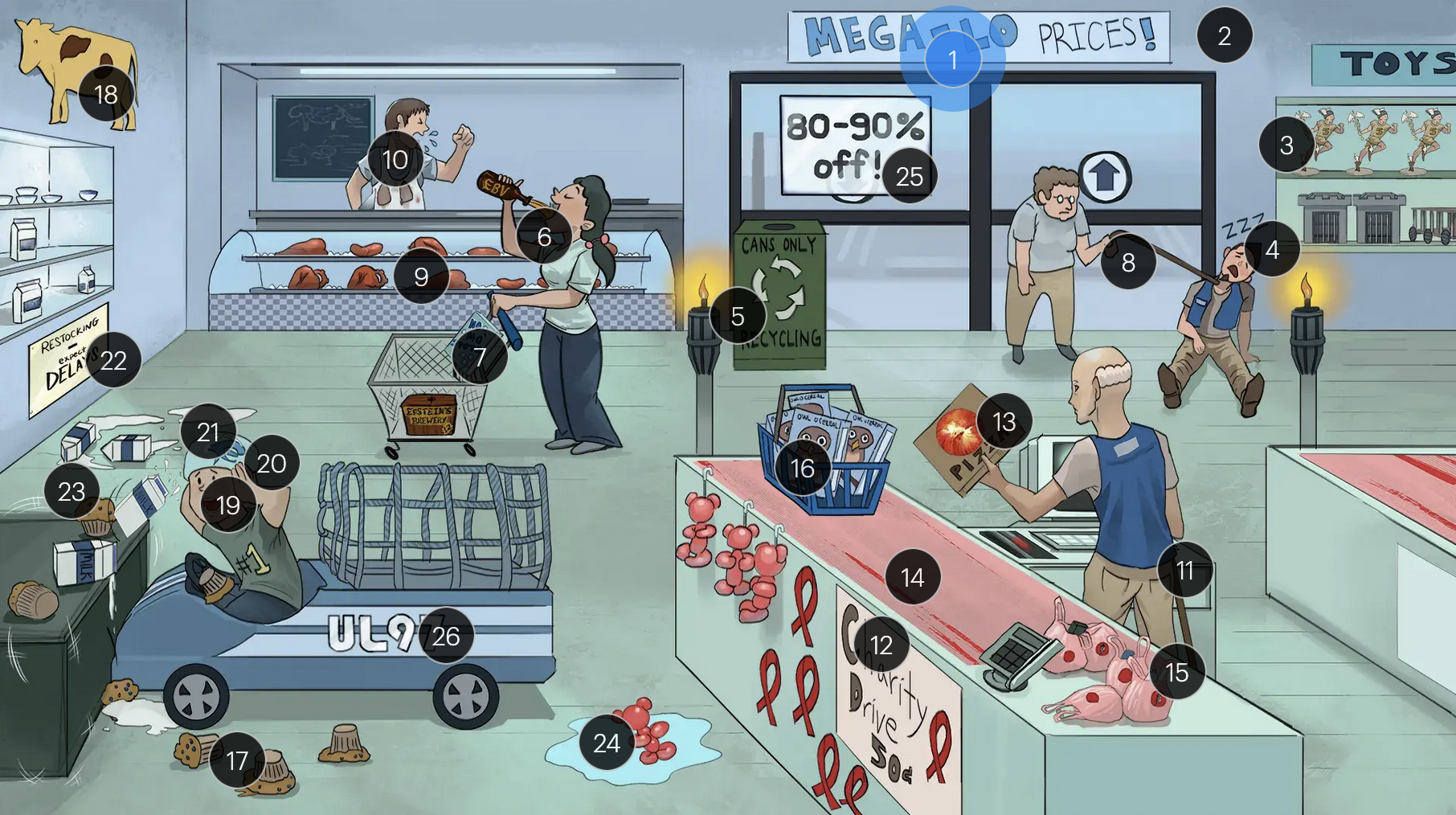
#12 “Charity drive 50Ac”
immunocompromised individuals, especially those with CD4+ counts below 50 (AIDS patients) are more vulnerable to CMV infections

Cytomegalovirus (Herpesviridae)
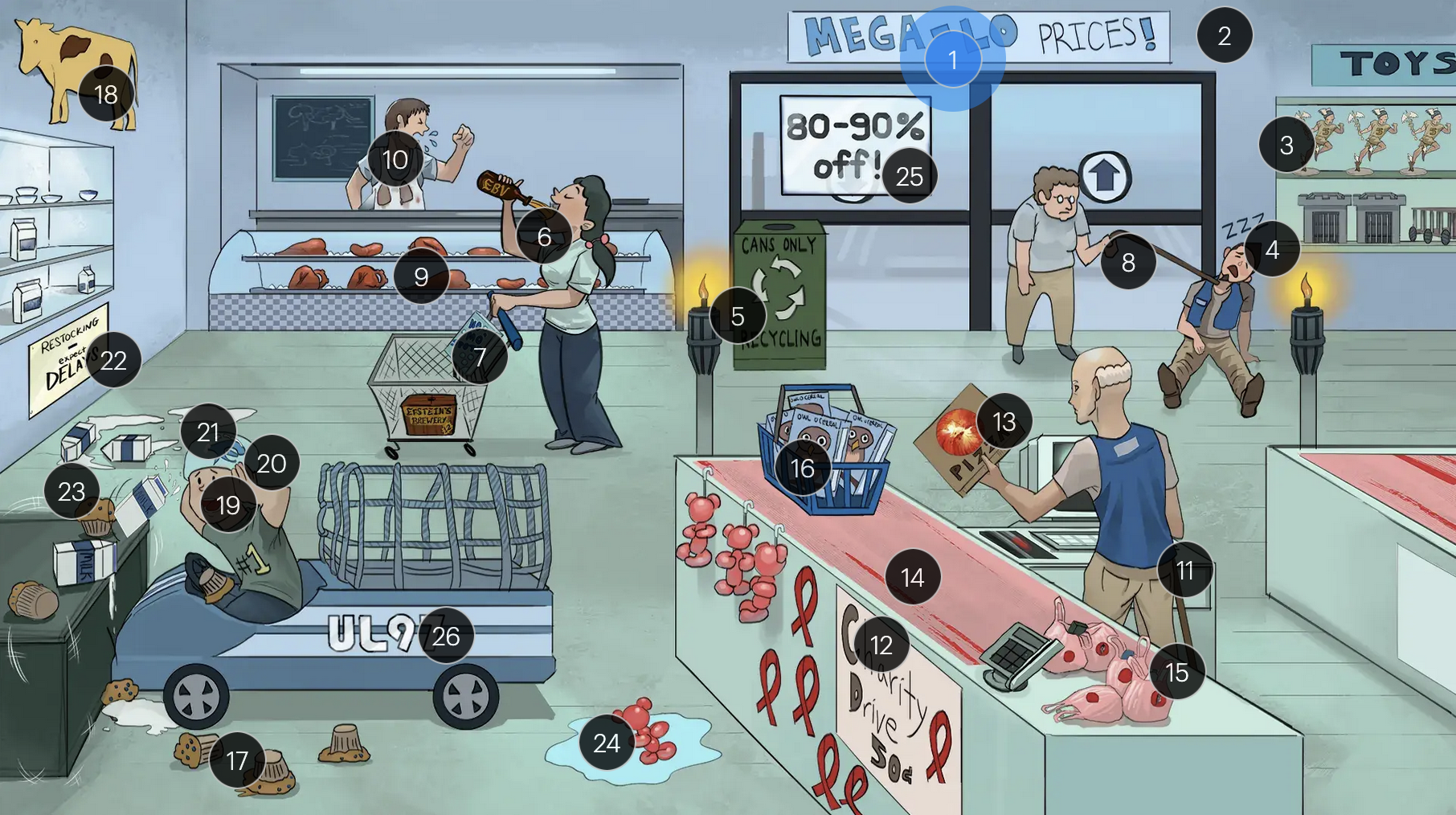
#13 retina pizza
CMV retinitis can manifest in patients with AIDS and is often characterized as “pizza pie” retinopathy due to its distinctive appearance resembling scattered cheese and tomato on a pizza

Cytomegalovirus (Herpesviridae)
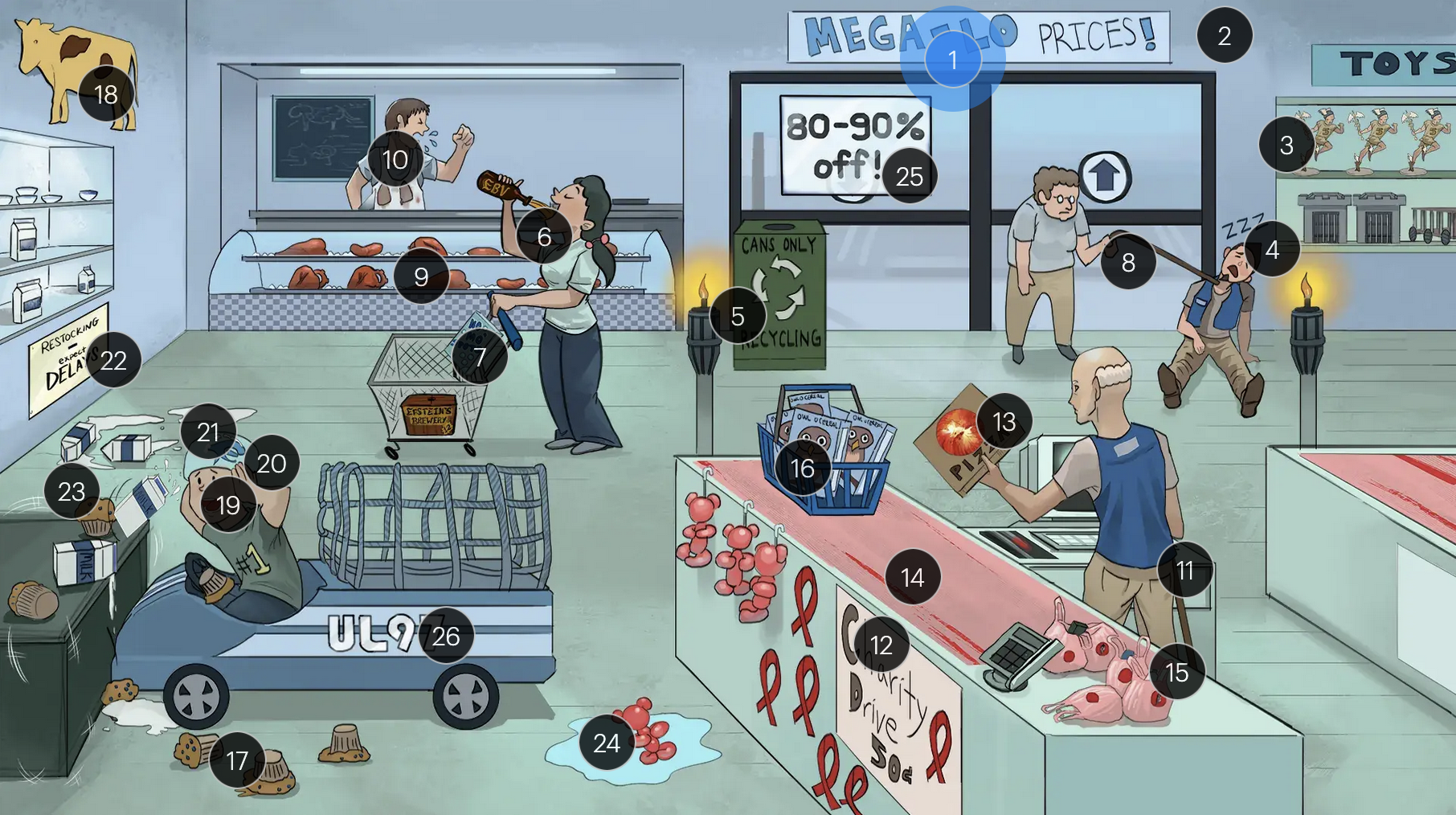
#14 linear tears in conveyor belt
CMV-associated esophagitis in HIV patients typically presents with singular, deep, and linear esophageal ulcers

Cytomegalovirus (Herpesviridae)
#15 torn mucosal bags
CMV colitis can manifest with distinct ulcerative lesions in the colon, leading to symptoms like abdominal pain, hematochezia, and diarrhea

Cytomegalovirus (Herpesviridae)
#16 Owl-O Cereal
on microscopy, CMV infected cells may show characteristic “owl’s eyes” inclusions, cells with large ovoid nuclei containing intranuclear basophilic inclusions

Cytomegalovirus (Herpesviridae)
#17 blueberry muffins
congenital CMV muffins can manifest with a “blueberry muffin” rash, jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly, sensorineural hearing loss, intellectual disabilites/developmental delays, and distinct brain abnormalities like microcephaly, ventriculomegaly, and periventricular calcifications

Cytomegalovirus (Herpesviridae)
#18 yellow cow + spleen and liver spots
congenital CMV muffins can manifest with a “blueberry muffin” rash, jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly, sensorineural hearing loss, intellectual disabilites/developmental delays, and distinct brain abnormalities like microcephaly, ventriculomegaly, and periventricular calcifications

Cytomegalovirus (Herpesviridae)
#19 covering ears
congenital CMV muffins can manifest with a “blueberry muffin” rash, jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly, sensorineural hearing loss, intellectual disabilites/developmental delays, and distinct brain abnormalities like microcephaly, ventriculomegaly, and periventricular calcifications
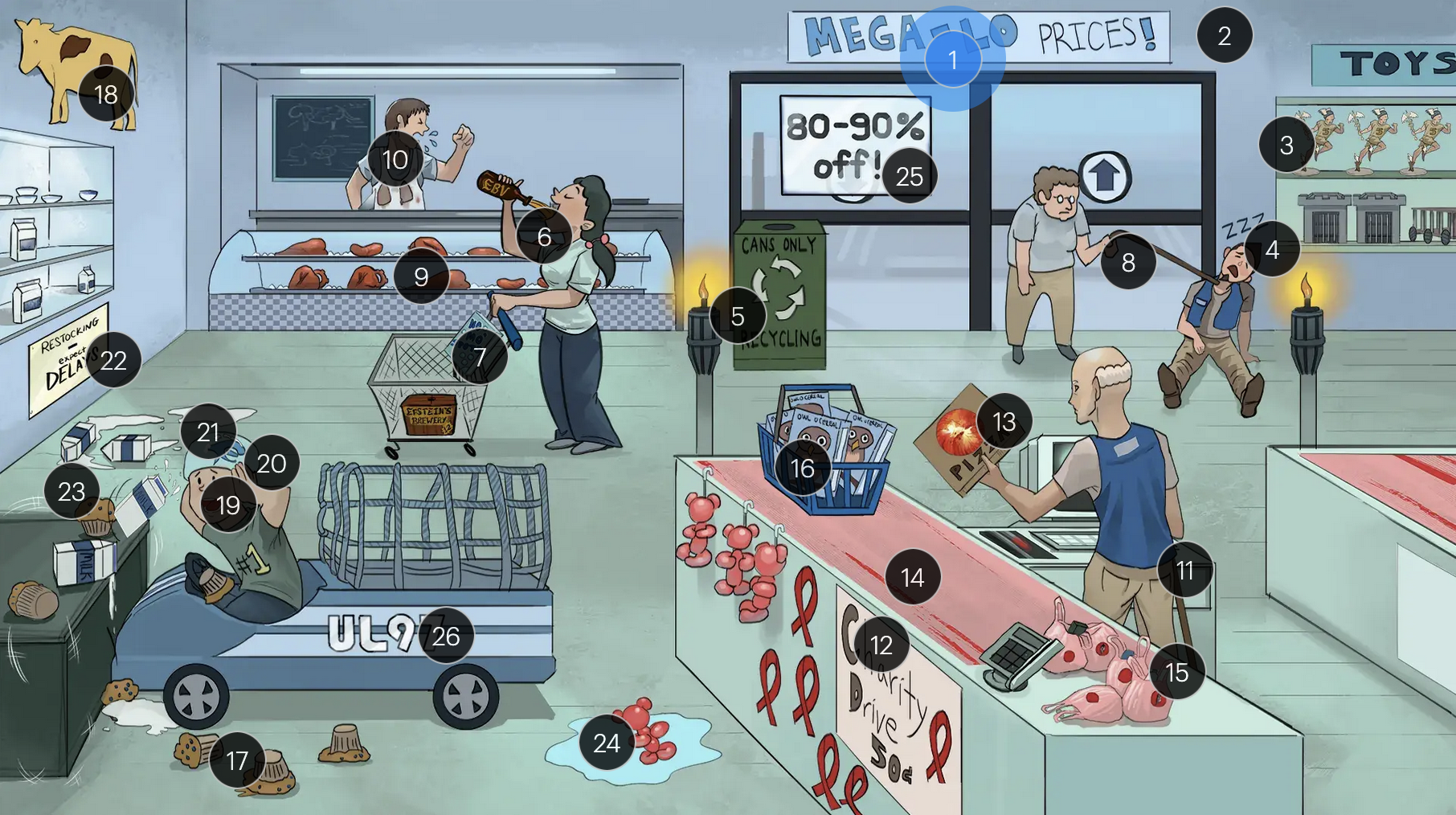

Cytomegalovirus (Herpesviridae)
#20 large helmet vents
congenital CMV muffins can manifest with a “blueberry muffin” rash, jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly, sensorineural hearing loss, intellectual disabilites/developmental delays, and distinct brain abnormalities like microcephaly, ventriculomegaly, and periventricular calcifications
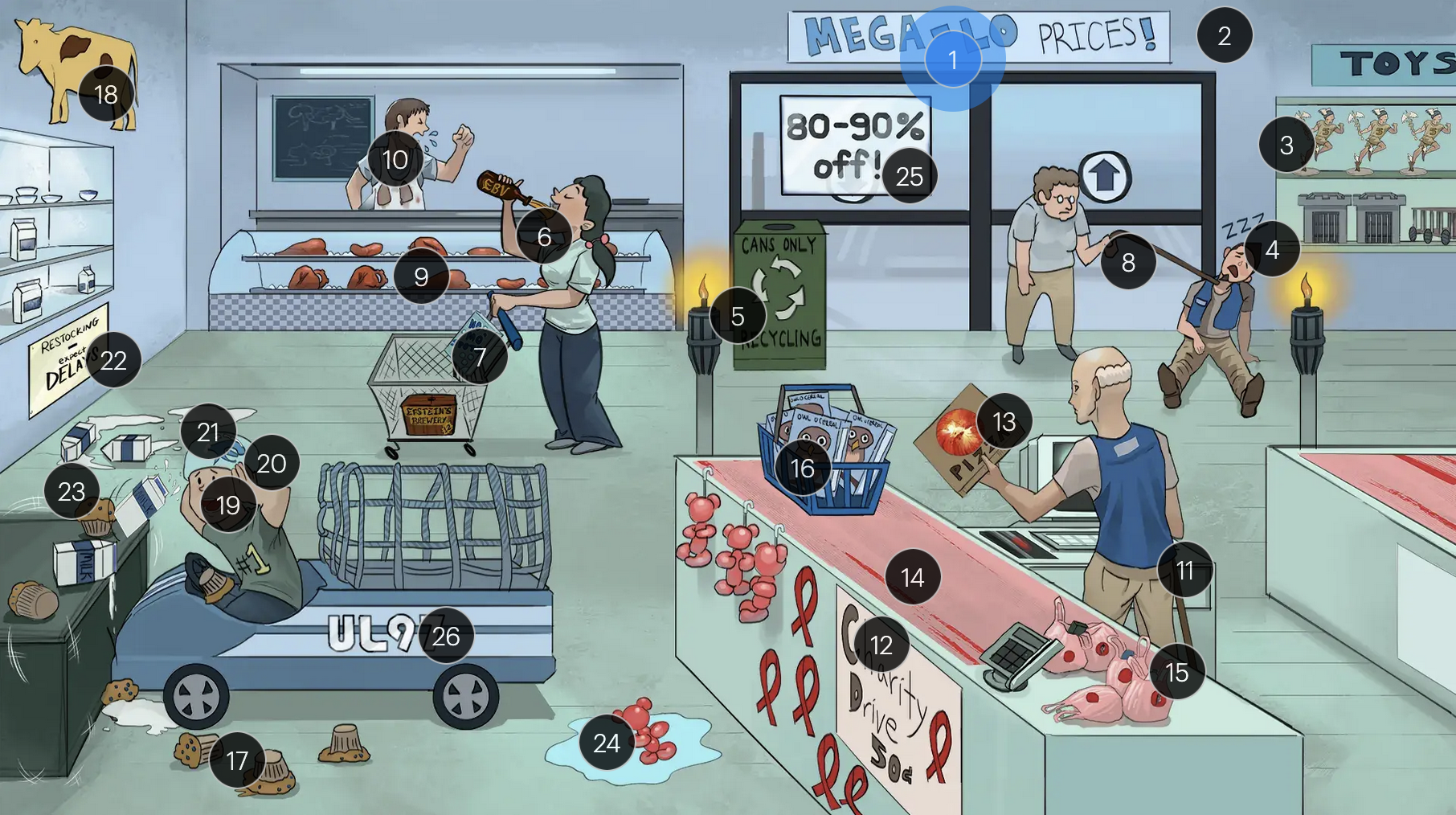

Cytomegalovirus (Herpesviridae)
#21 milk on head
congenital CMV muffins can manifest with a “blueberry muffin” rash, jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly, sensorineural hearing loss, intellectual disabilites/developmental delays, and distinct brain abnormalities like microcephaly, ventriculomegaly, and periventricular/intracranial calcifications
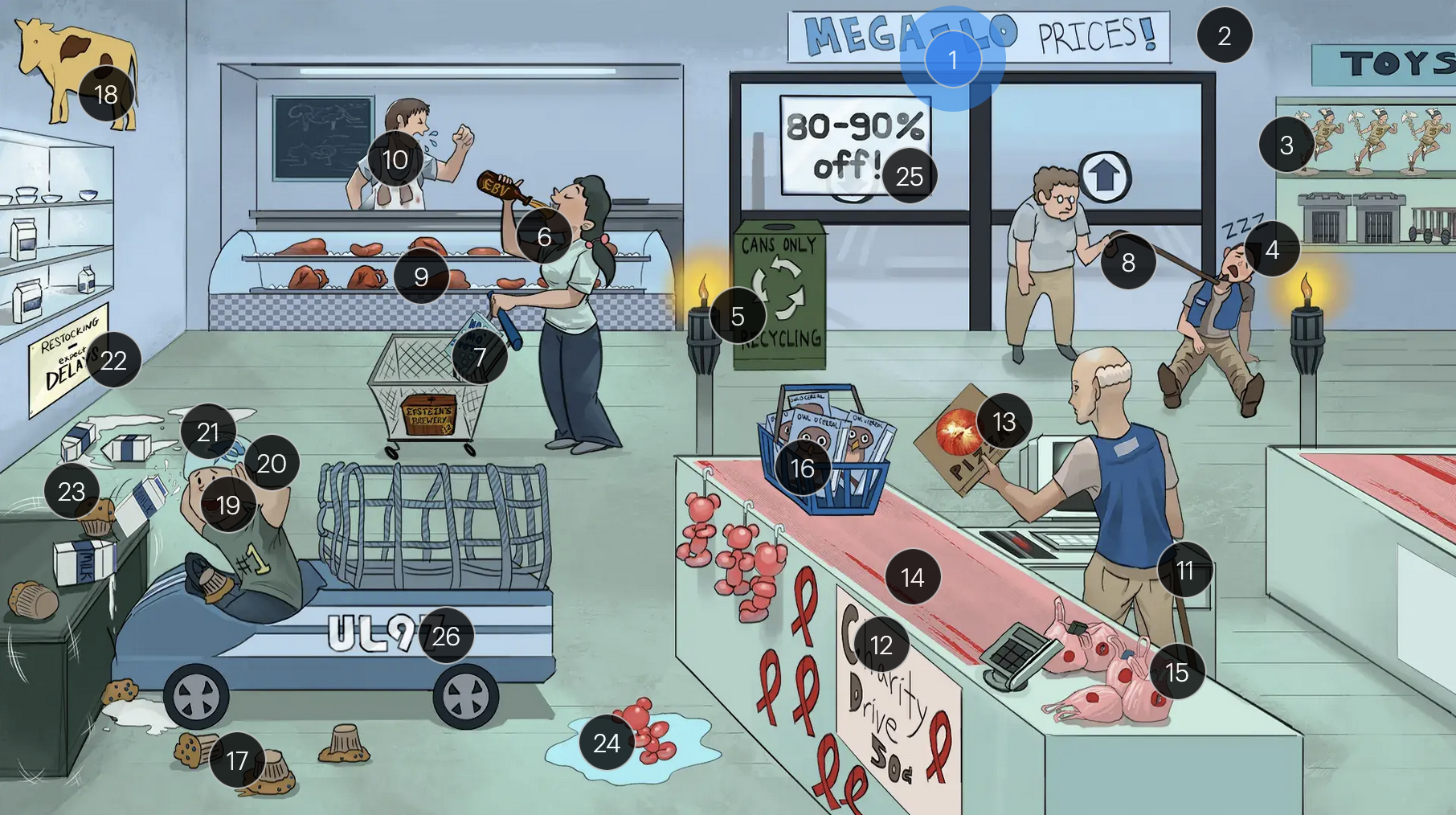

Cytomegalovirus (Herpesviridae)
#22 “Expect DELAYS”
congenital CMV muffins can manifest with a “blueberry muffin” rash, jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly, sensorineural hearing loss, intellectual disabilites/developmental delays, and distinct brain abnormalities like microcephaly, ventriculomegaly, and periventricular calcifications
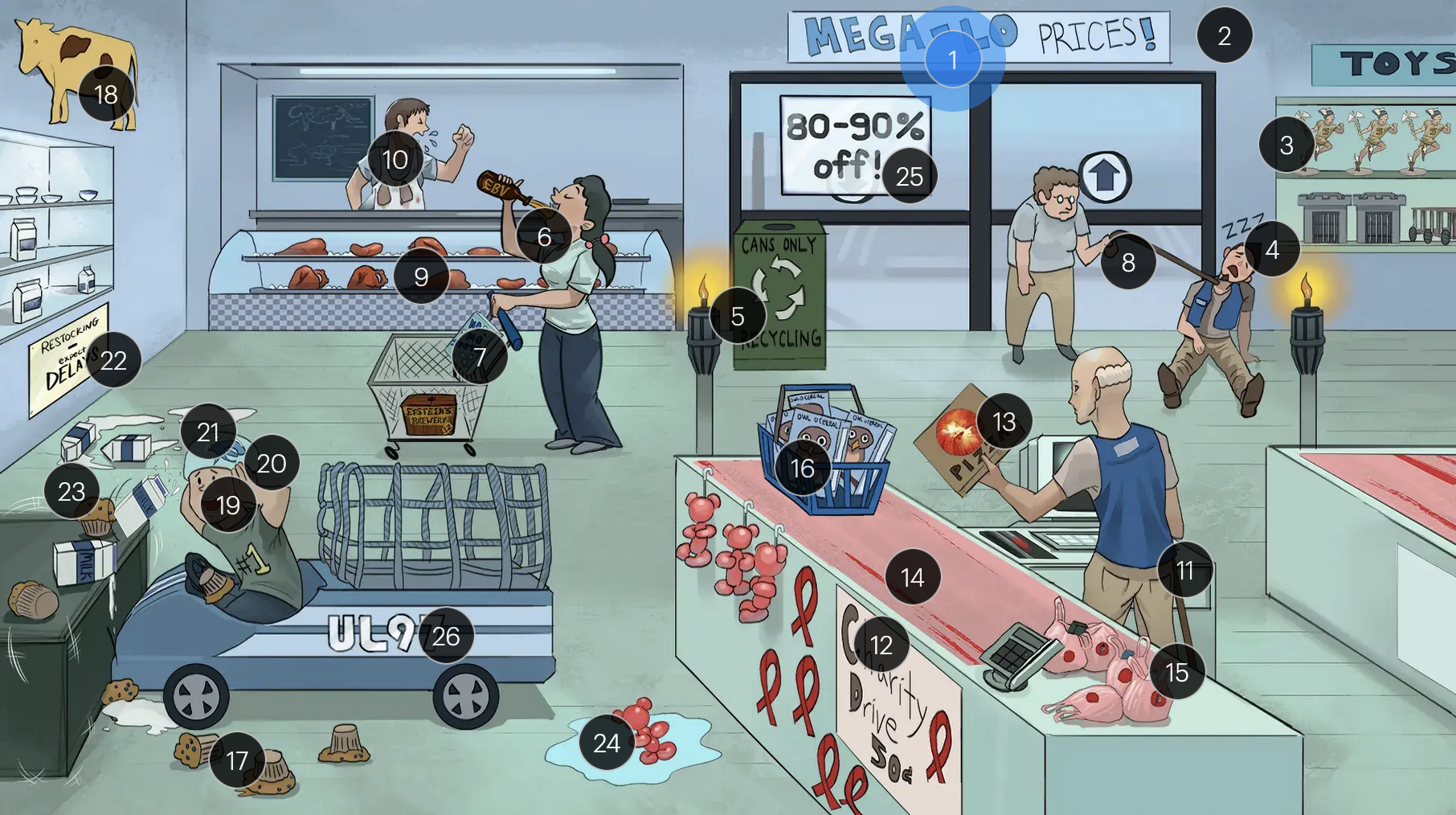

Cytomegalovirus (Herpesviridae)
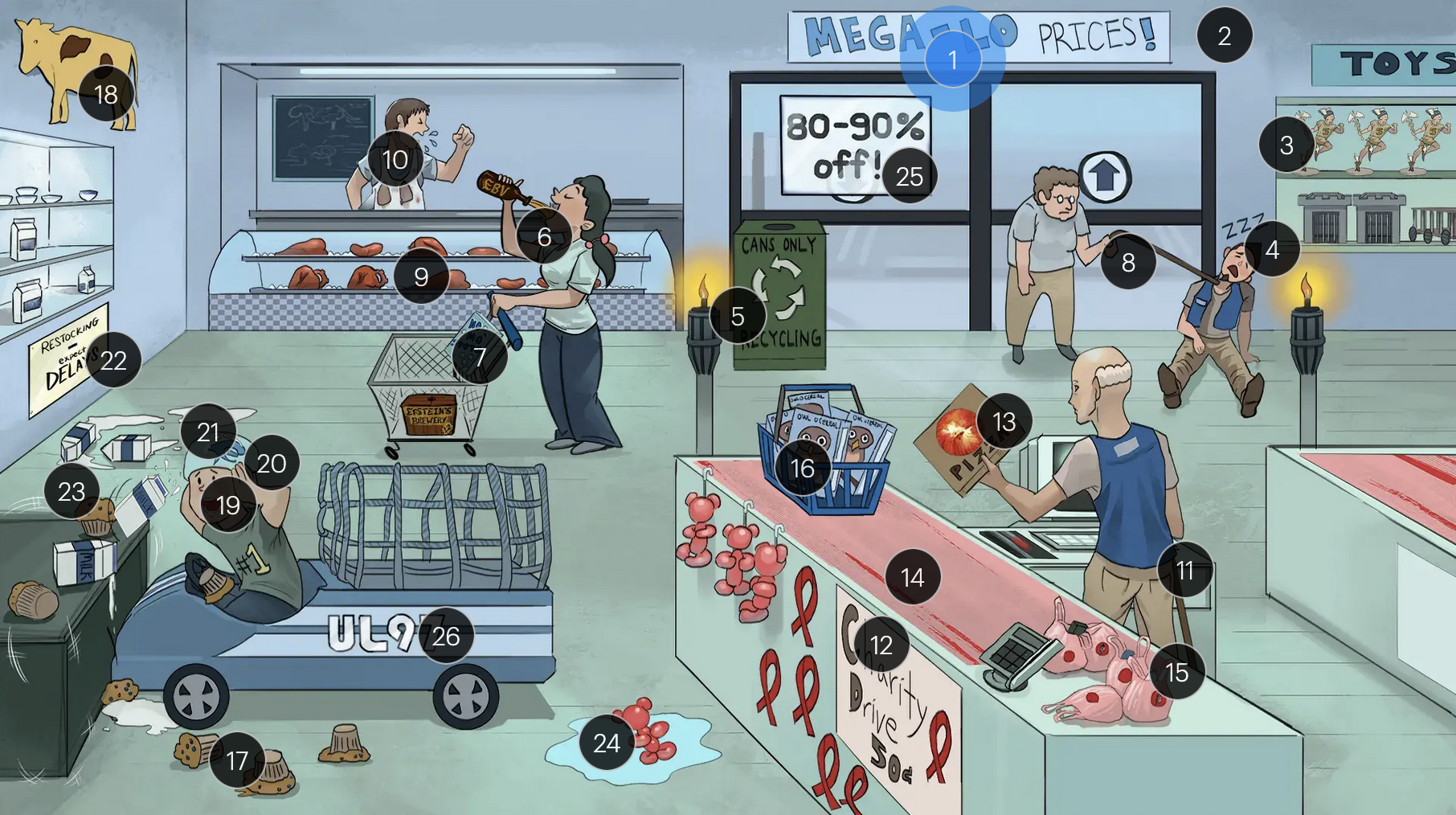
#23 shake lines
congenital CMV muffins can manifest with a “blueberry muffin” rash, jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly, sensorineural hearing loss, intellectual disabilites/developmental delays, and distinct brain abnormalities like microcephaly, ventriculomegaly, and periventricular calcifications, which can lead to seizures

Cytomegalovirus (Herpesviridae)
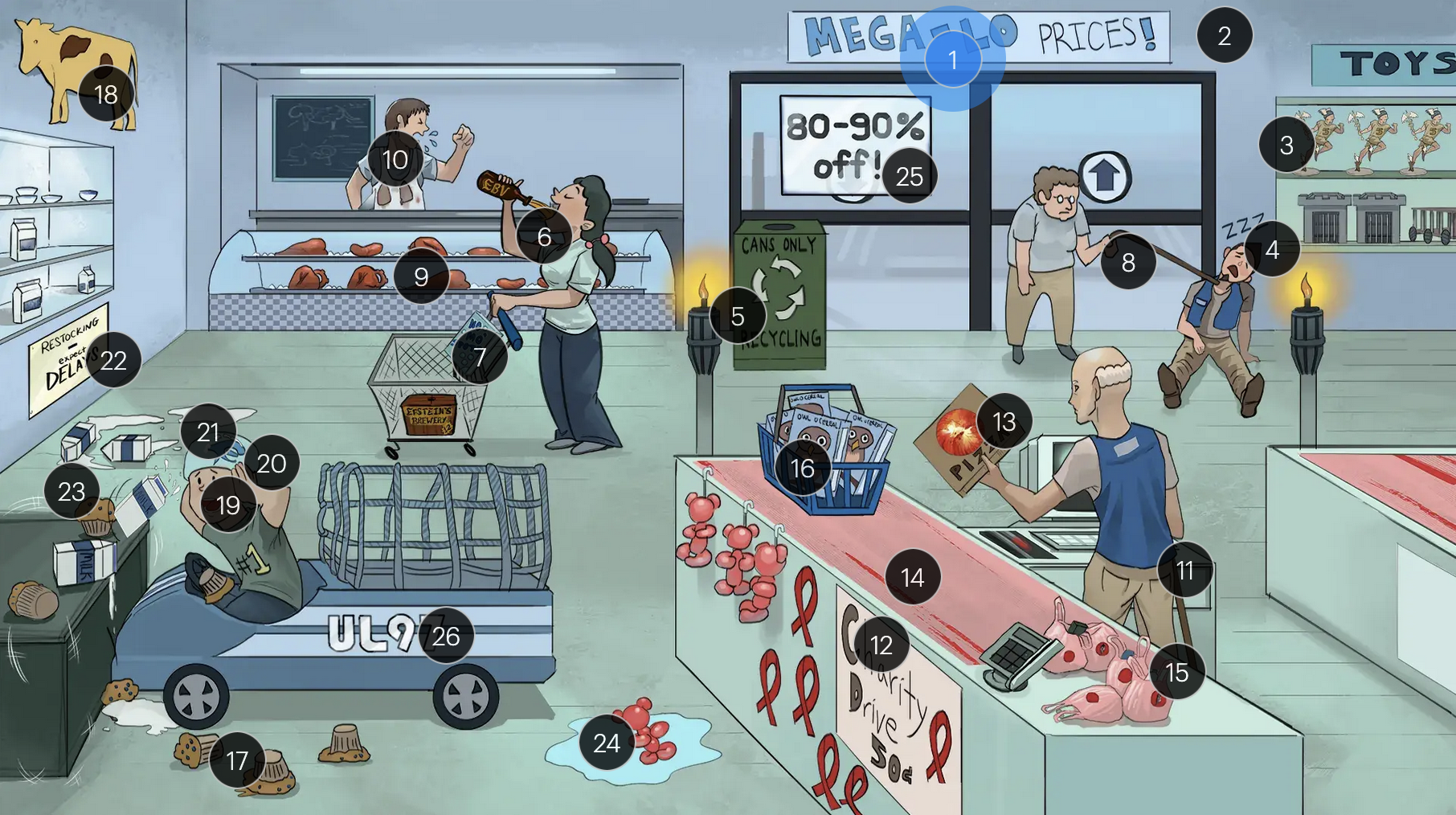
#24 ballon bear in water
congenital CMV infection can result in hydrops fetalis, a condition in which abnormal amounts of fluid build up in two or more fetal compartments

Cytomegalovirus (Herpesviridae)
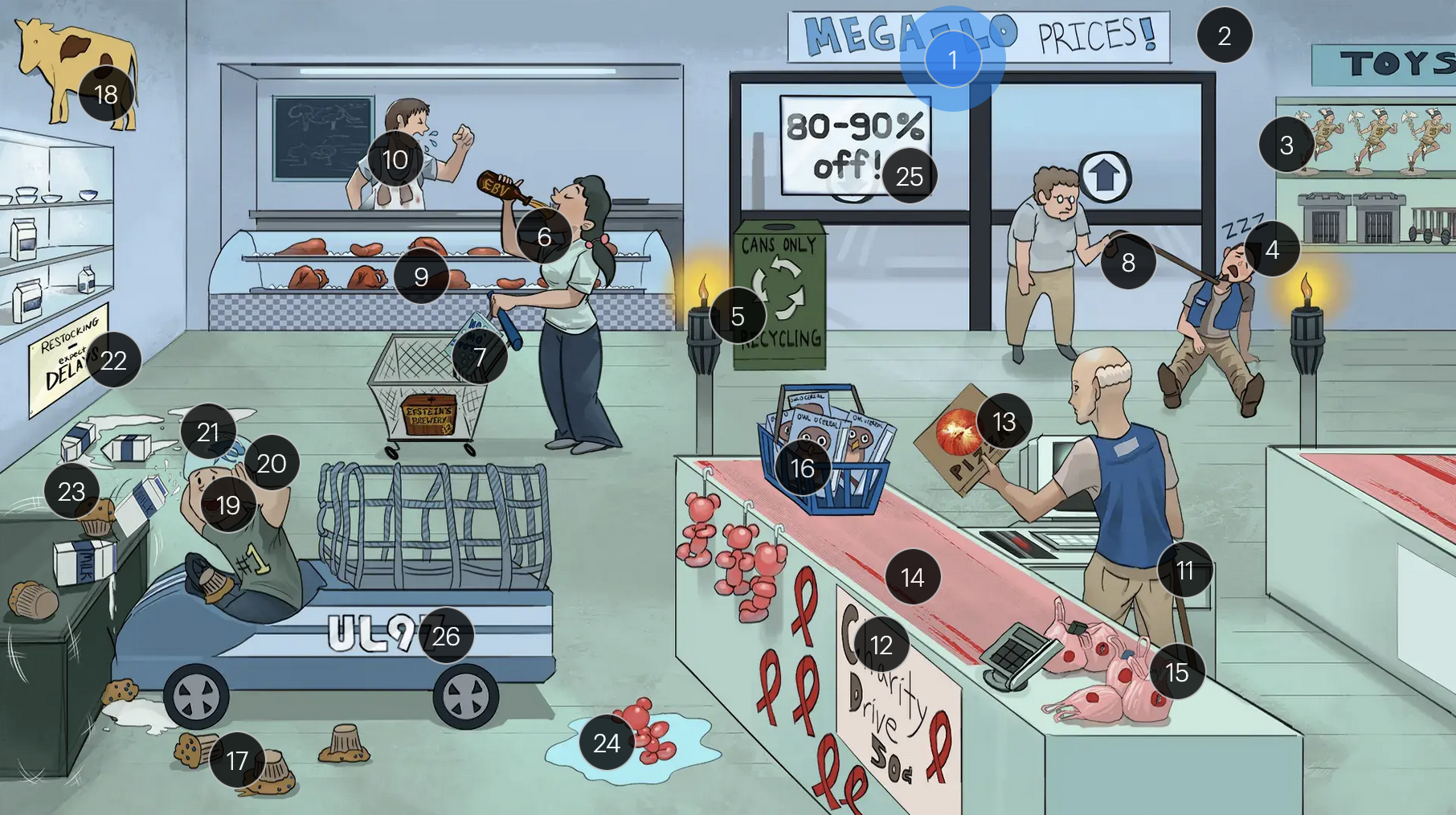
#25 “80-90% off!”
The majority (80-90%) of newborns with congenital CMV infection are asymptomatic

Cytomegalovirus (Herpesviridae)
#26 “UL97” sticker + fast car net
strains of CMV with the UL97 gene mutation demonstrate resistance to ganciclovir, and often require foscarnet for effective management

Epstein-Barr Virus (Herpesviridae)
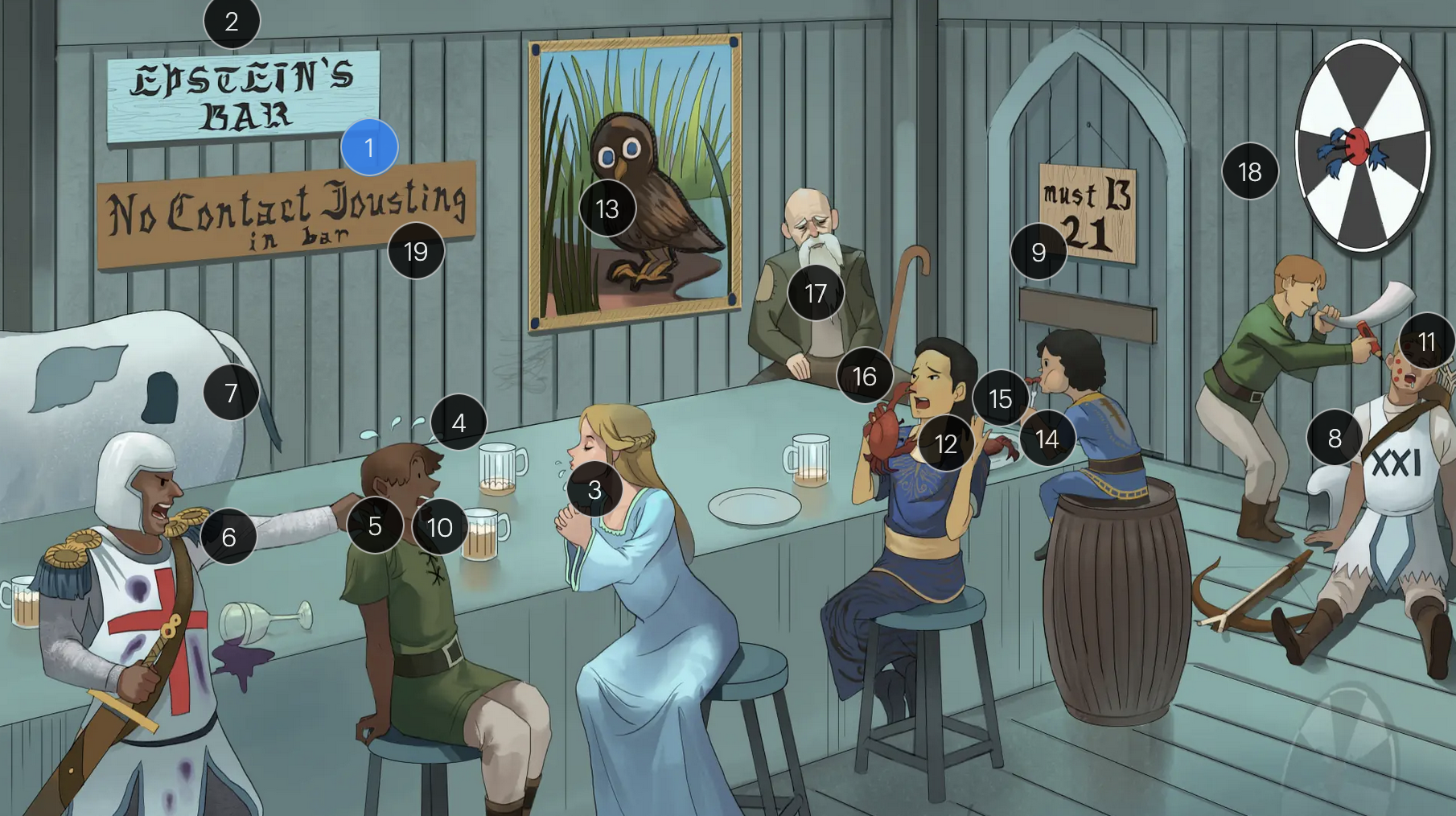
#1 Epstein’s Bar
Epstein-Bar virus (EBV; a FNA virus in the Herpesviridae family)
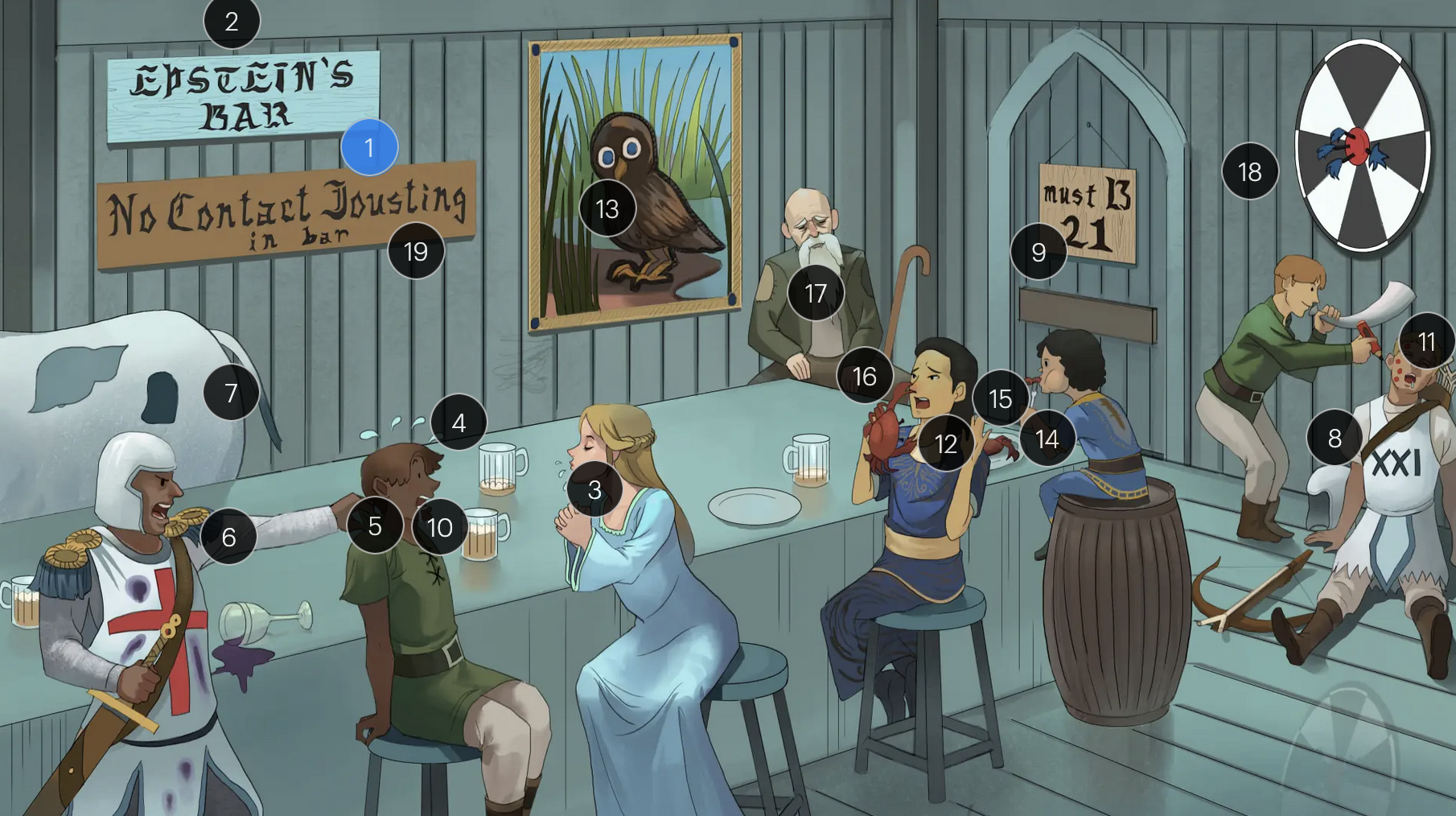

Epstein-Barr Virus (Herpesviridae)
#2 cool colors
EBV is a DNA virus
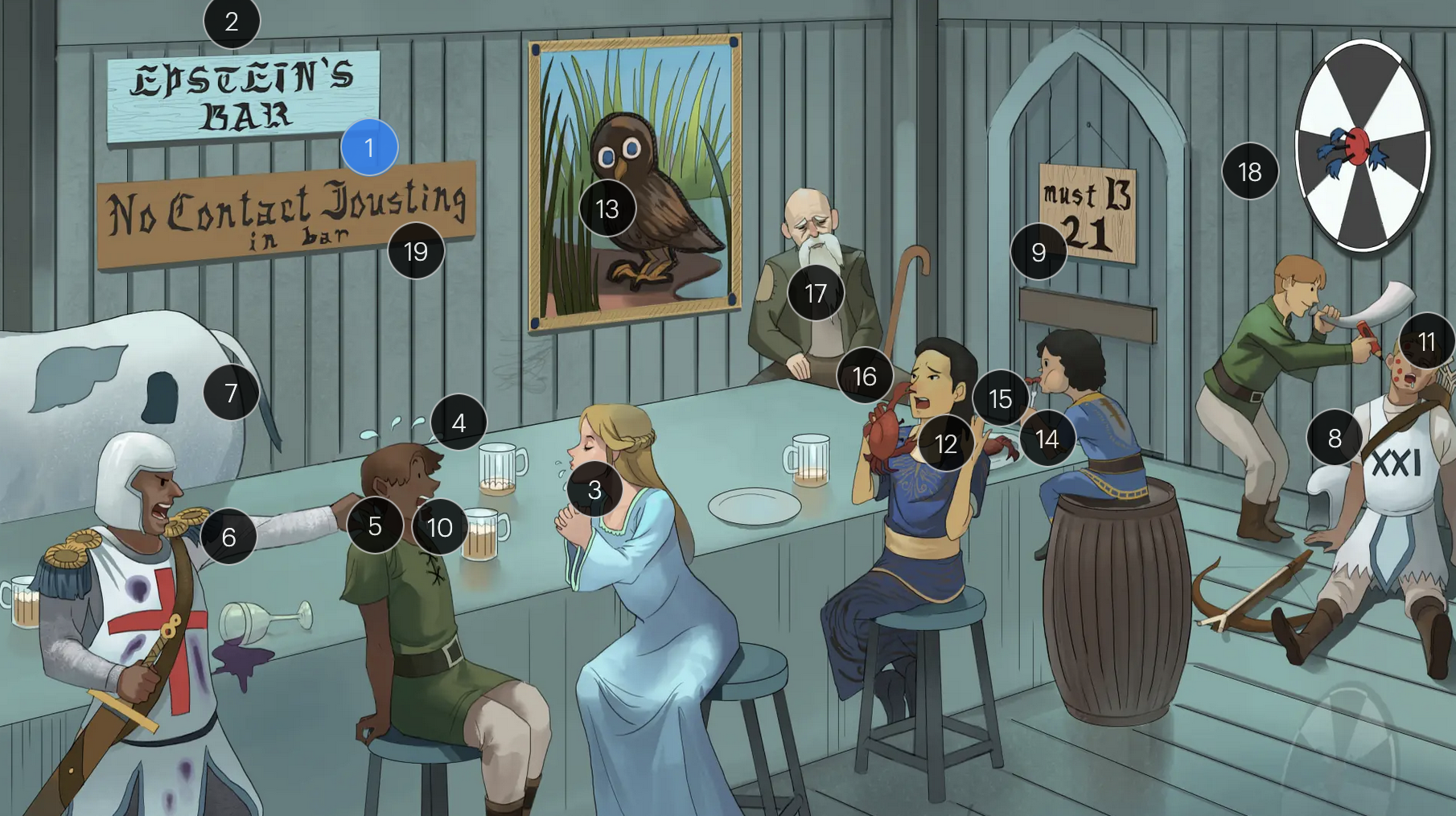

Epstein-Barr Virus (Herpesviridae)
#3 saliva drips
EBV is primarily transmitted via saliva, making close personal contact a common route of spread, especially among young adults and college students
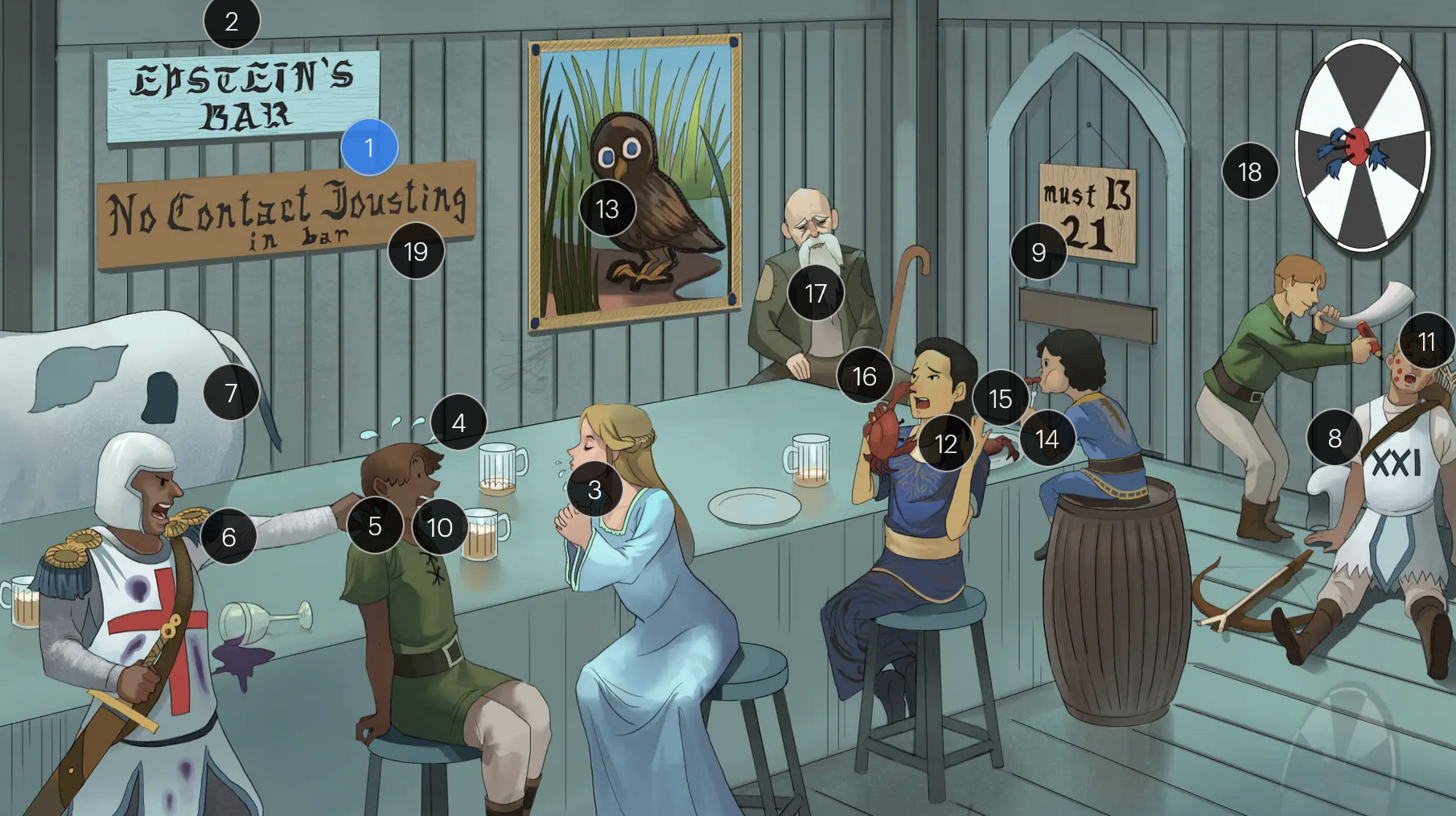

Epstein-Barr Virus (Herpesviridae)
#4 sweat drops
a hallmark of EBV-induced infectious mononucleosis is the presentation of fever, in combination with lymphadenopathy and pharyngitis, forms the classic triad of symptoms frequently observed in affected individuals
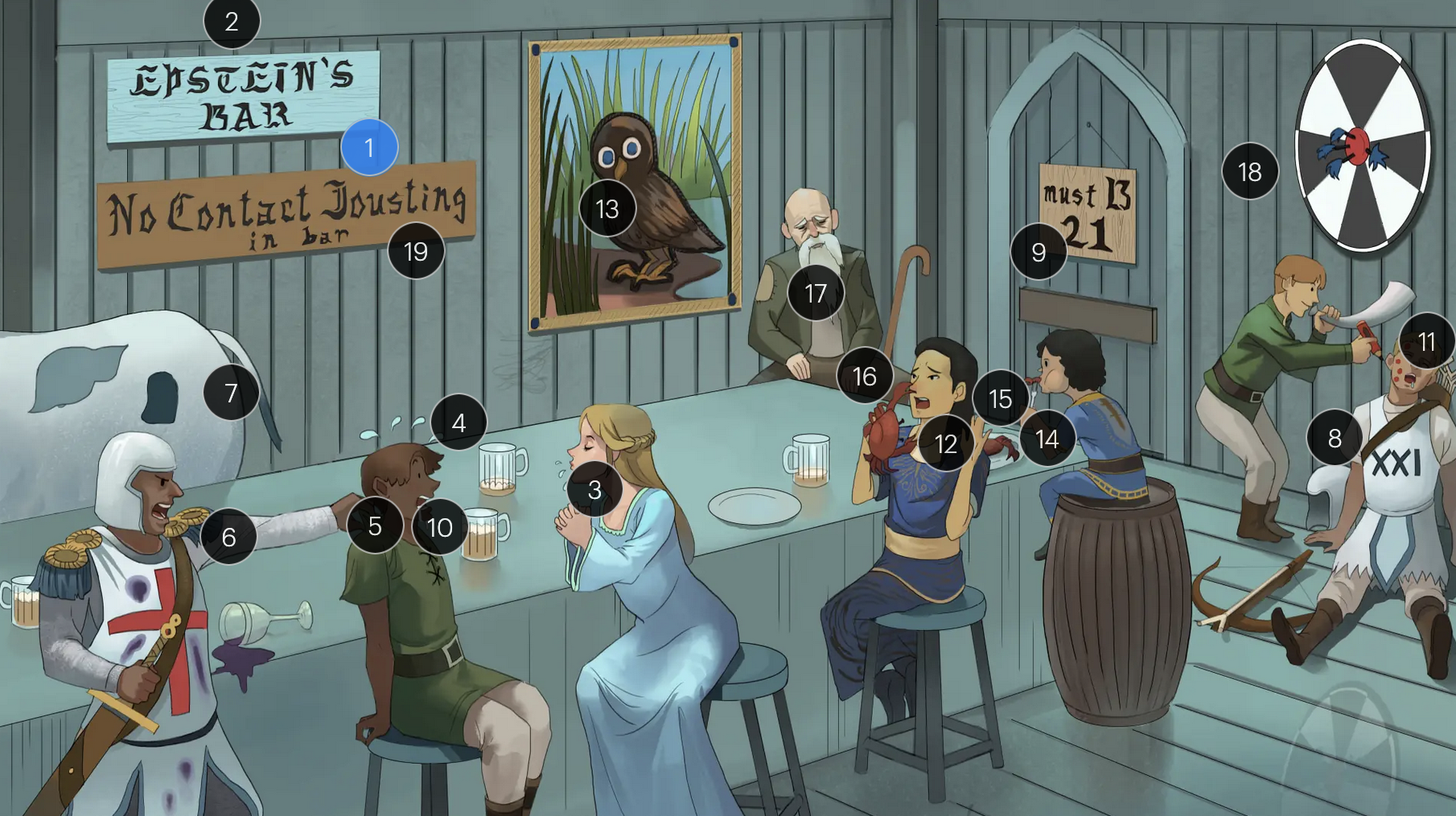

Epstein-Barr Virus (Herpesviridae)
#5 grabbing back of shirt
patients with EBV-induced mononucleosis frequently manifest tender lymphadenopathy, particularly in the posterior cervical region
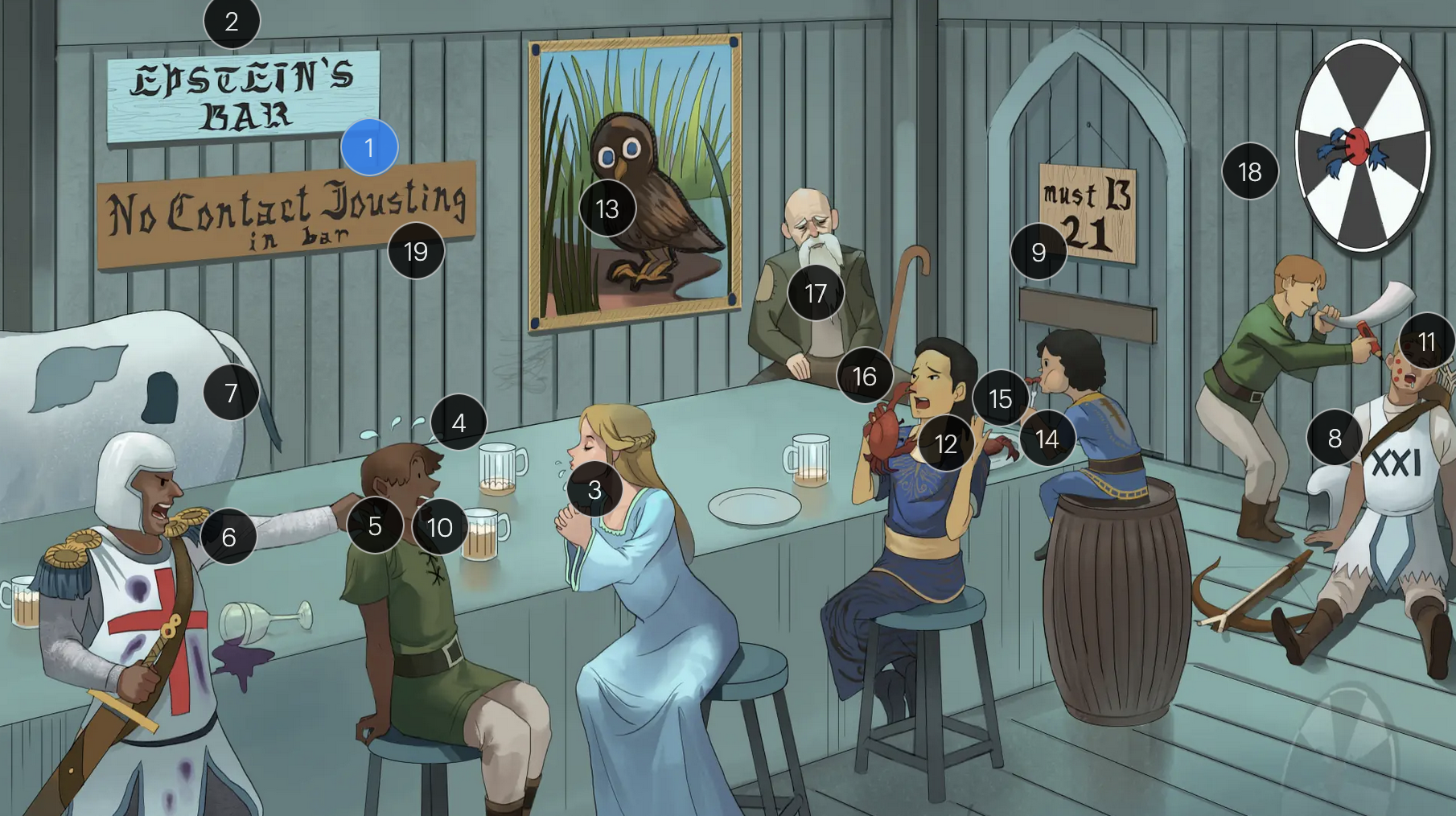

Epstein-Barr Virus (Herpesviridae)
#6 reactive “8” T-knight + atypical stains
EBV infection causes peripheral lymphocutosis and the presence of atypical lymphocytes (also known as Downey cells), abnormally large, reactive CD8+ T-cells with strongly basophilic cytoplasm that respond to EBV-infected B-cells; these atypical lymphocytes can be seen on peripheral blood smear
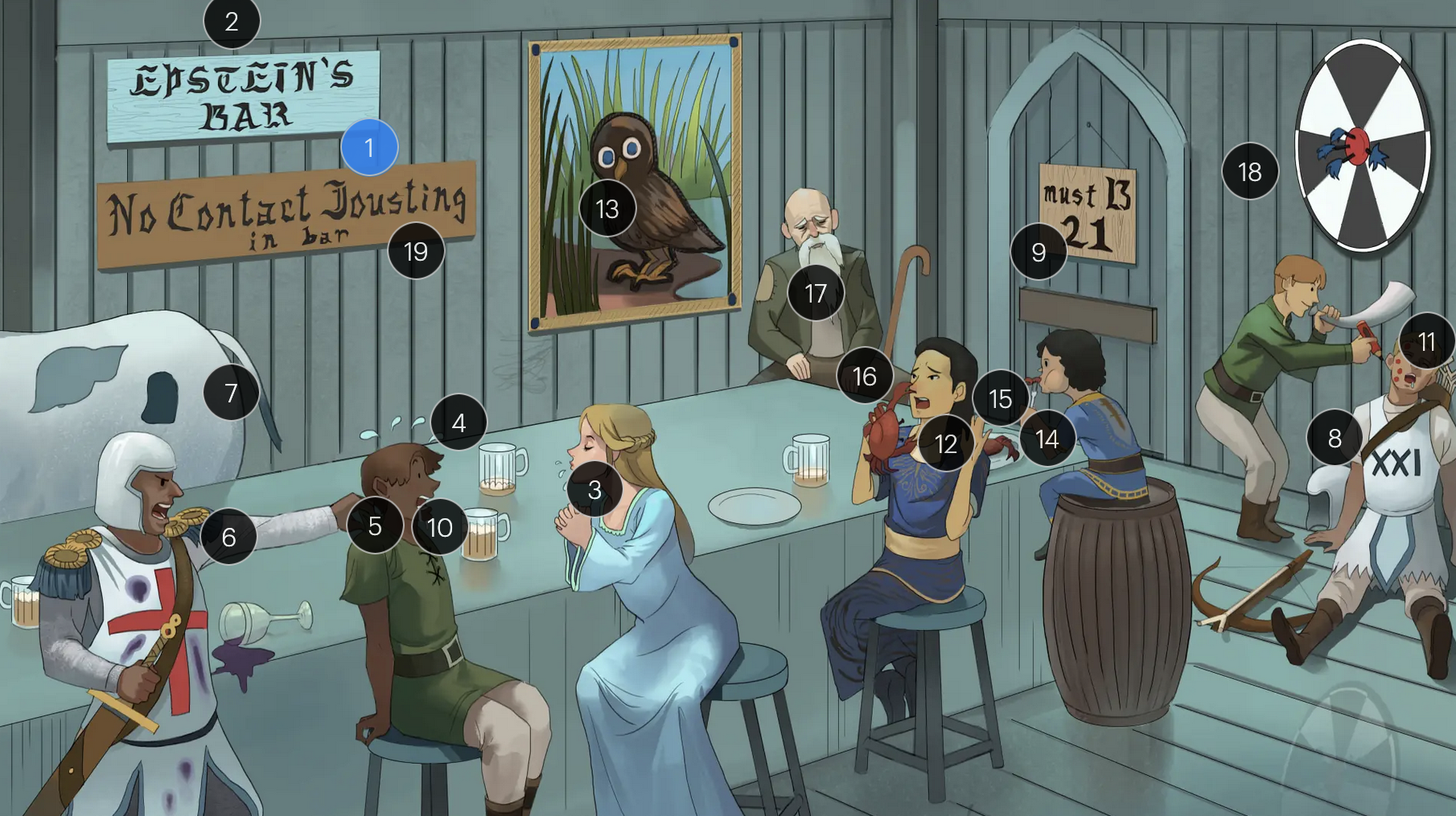

Epstein-Barr Virus (Herpesviridae)
#7 enlarged spleen spot
EBV infection typically leads to a proliferation of mononuclear cells that accumulate within the lymphoid tissue, including the spleem which may result in splenomegaly
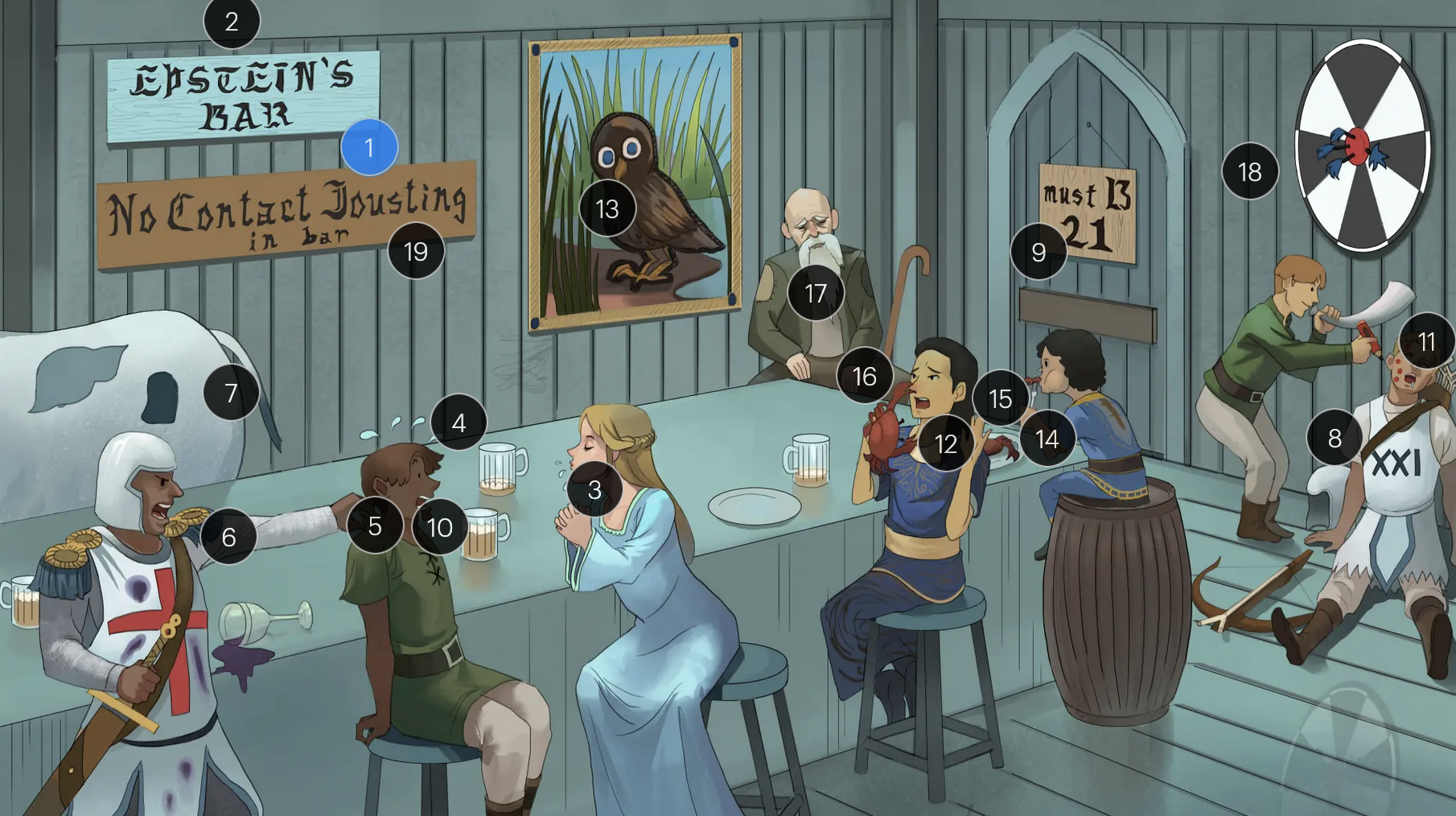

Epstein-Barr Virus (Herpesviridae)
#8 sleeping B-cell archer
EBV maintains latency within B-cells, persisting indefinitely within the host, potentially leading to reactivated EBV under certain conditions or when exposed to certain triggers
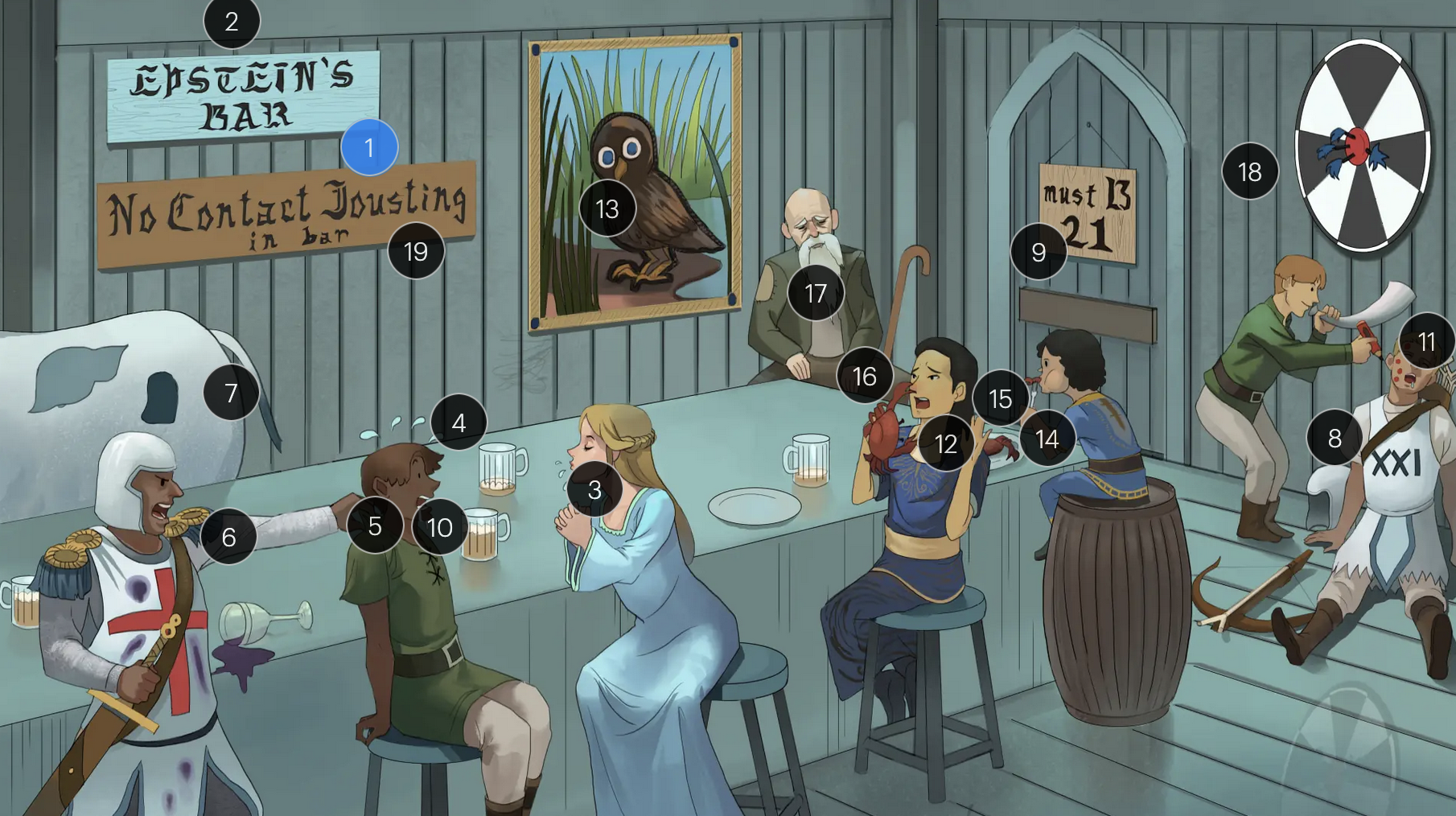

Epstein-Barr Virus (Herpesviridae)
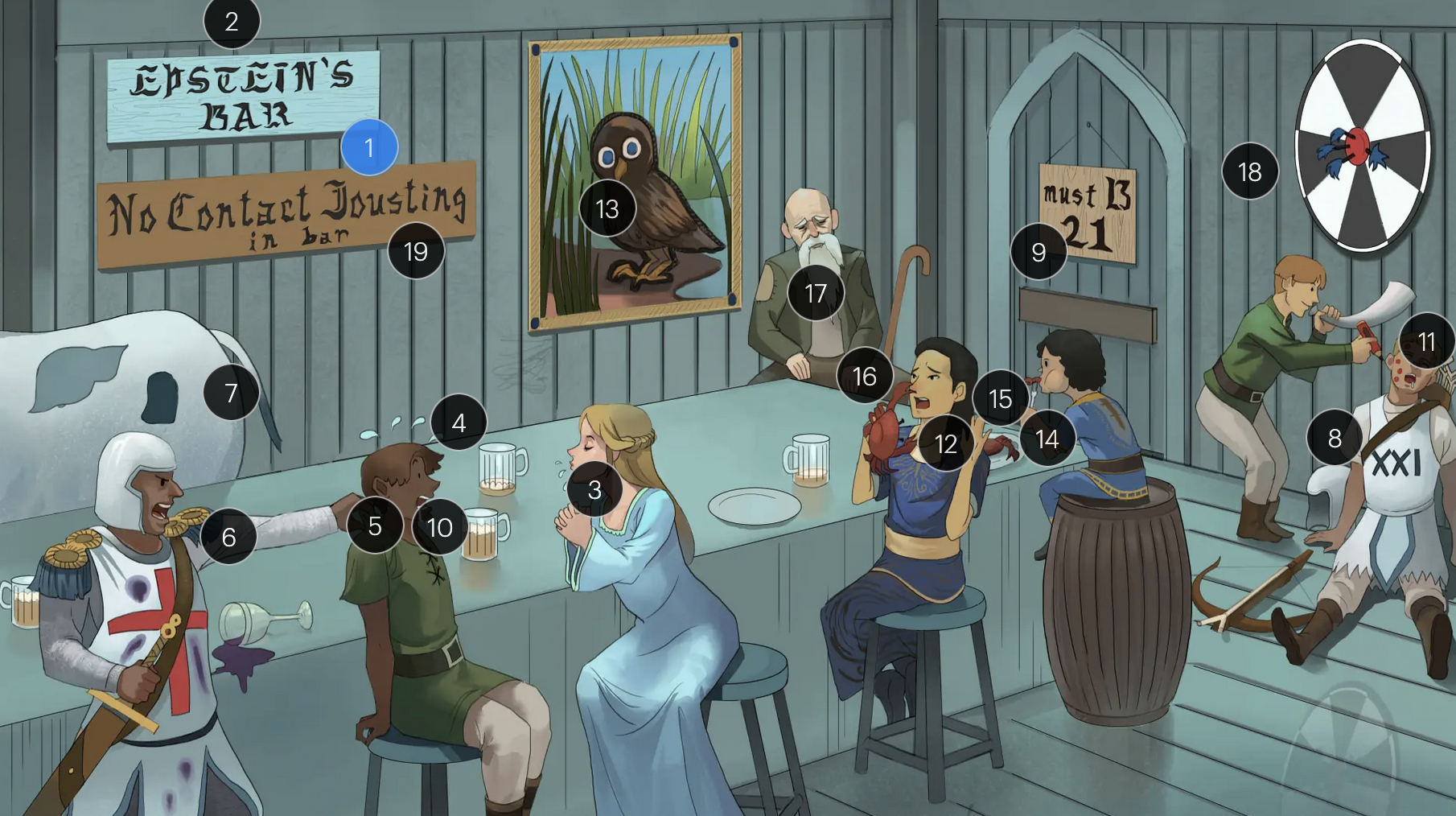
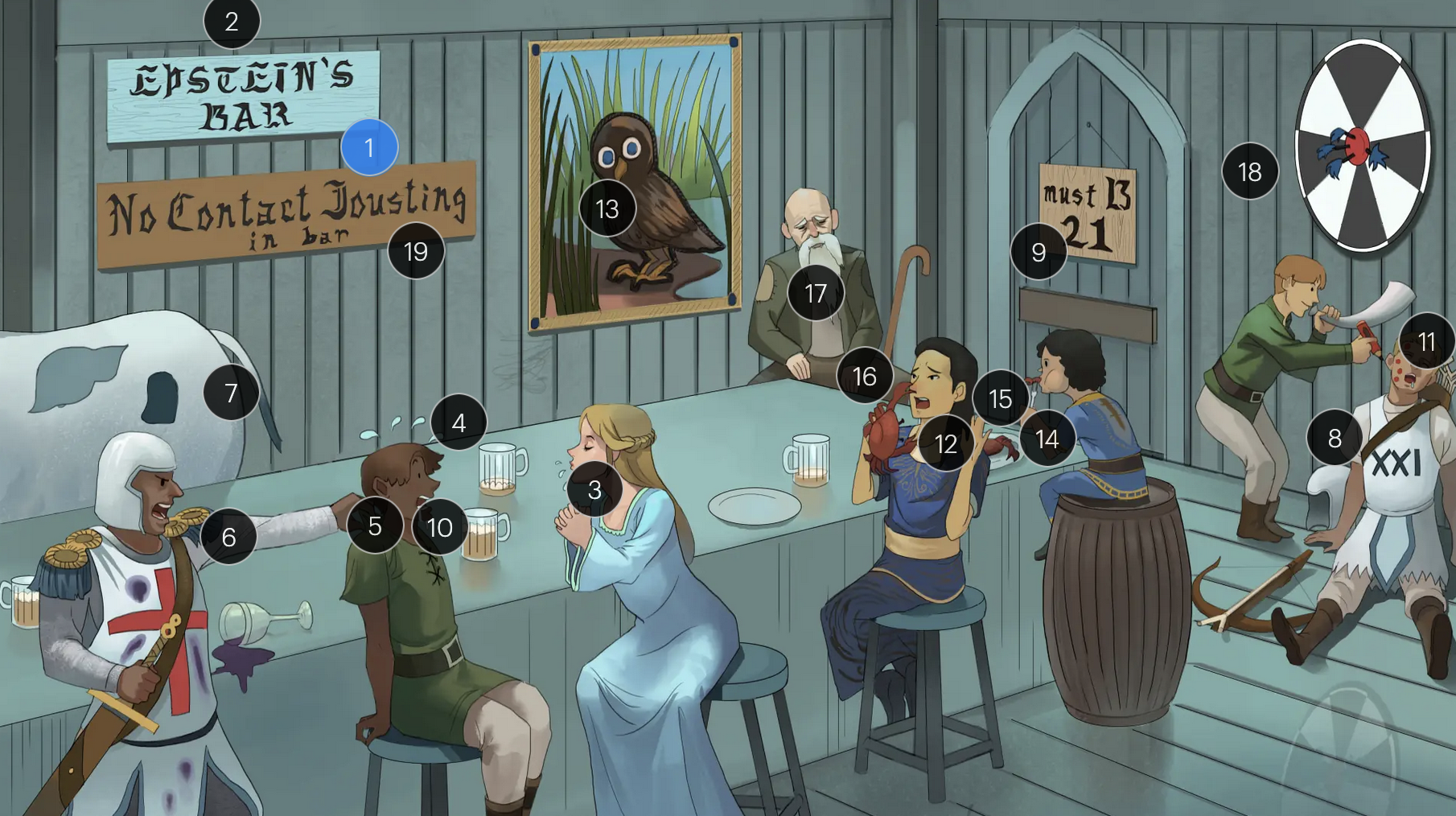
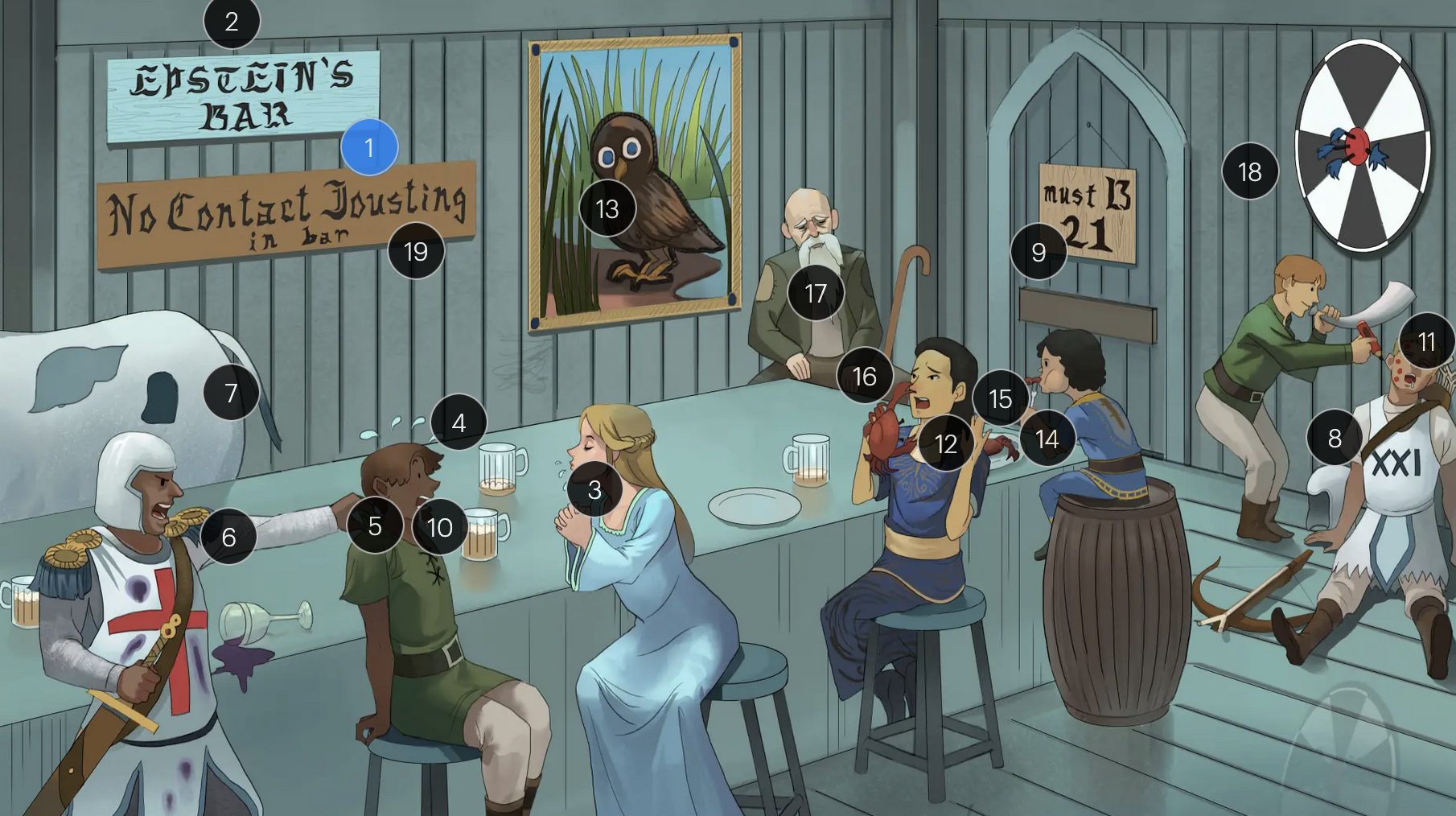
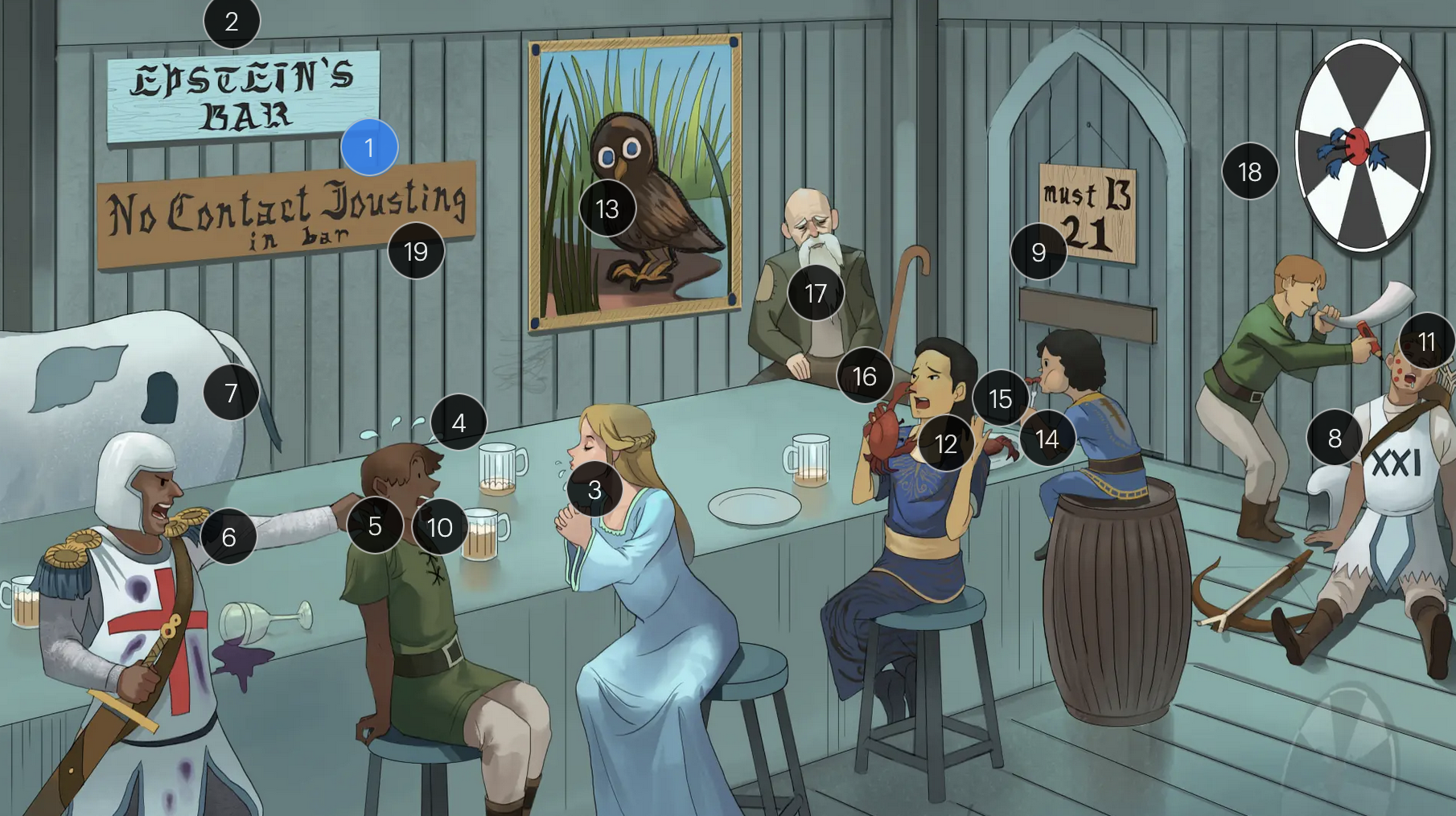
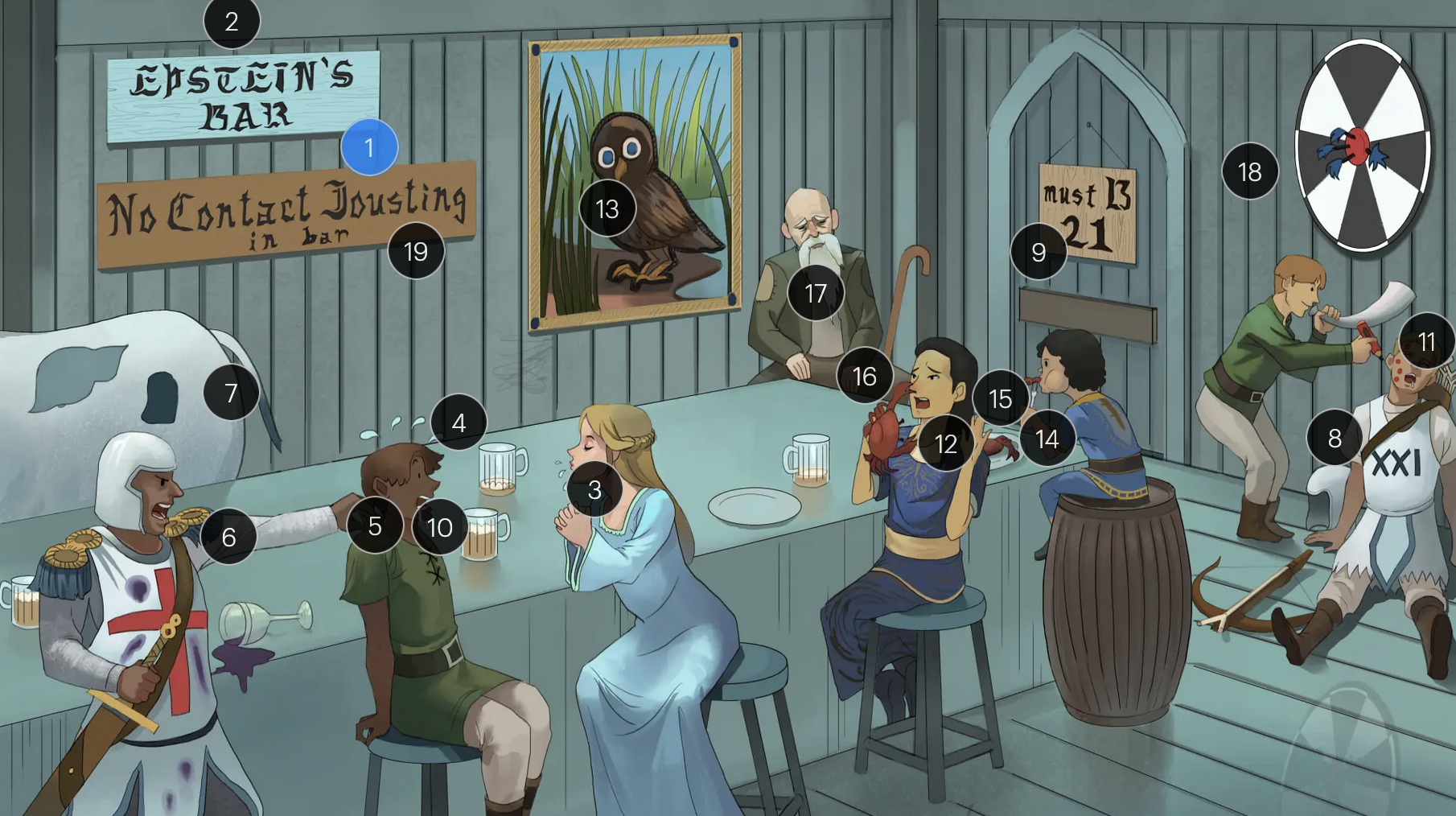
#9 entrance + “must B 21”
to enter host cells, the EBV viral envelope protein gp350 binds to CD21 on the surface of B-cells

Epstein-Barr Virus (Herpesviridae)
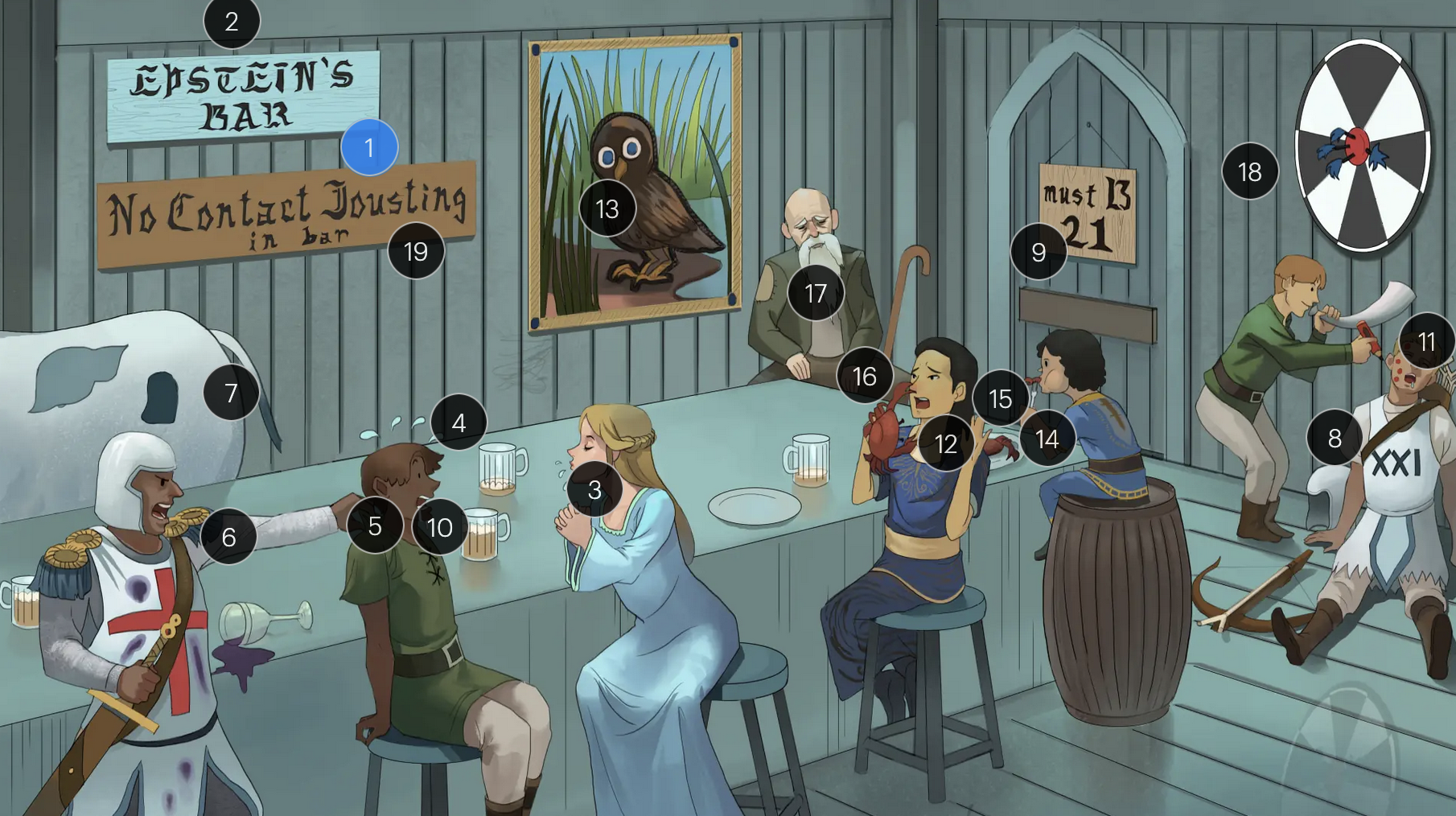
#10 white drool
a common clinical feature of EBV-induced mononucleosis is pharyngitis accompanied by tonsillar exudate

Epstein-Barr Virus (Herpesviridae)
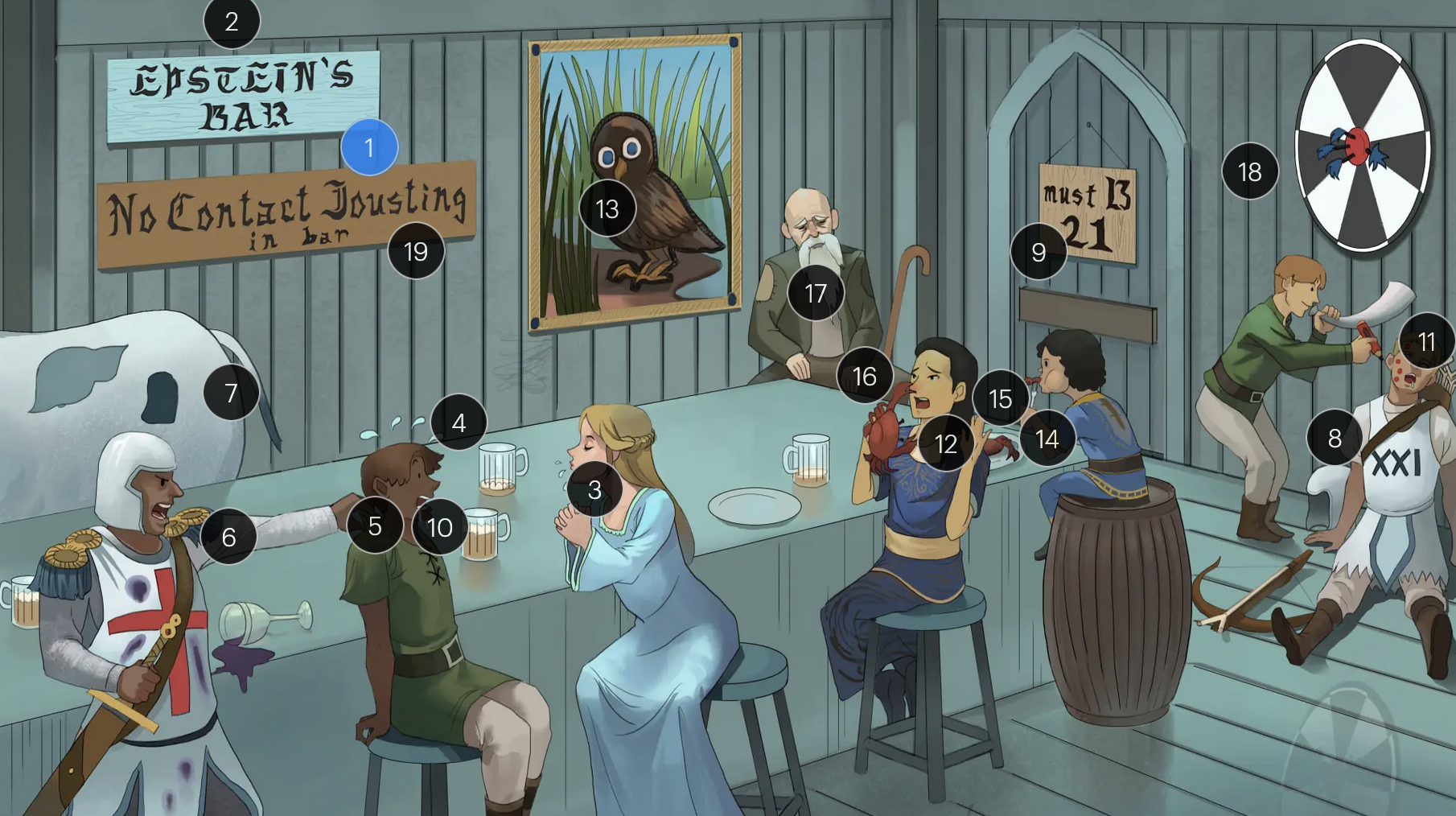
#11 red pencil spots
when patients with an active EBV infection are inadvertently administered penicillin due to suspicion of a bacterial infection, they may develop a characteristic maculopapular rash

Epstein-Barr Virus (Herpesviridae)
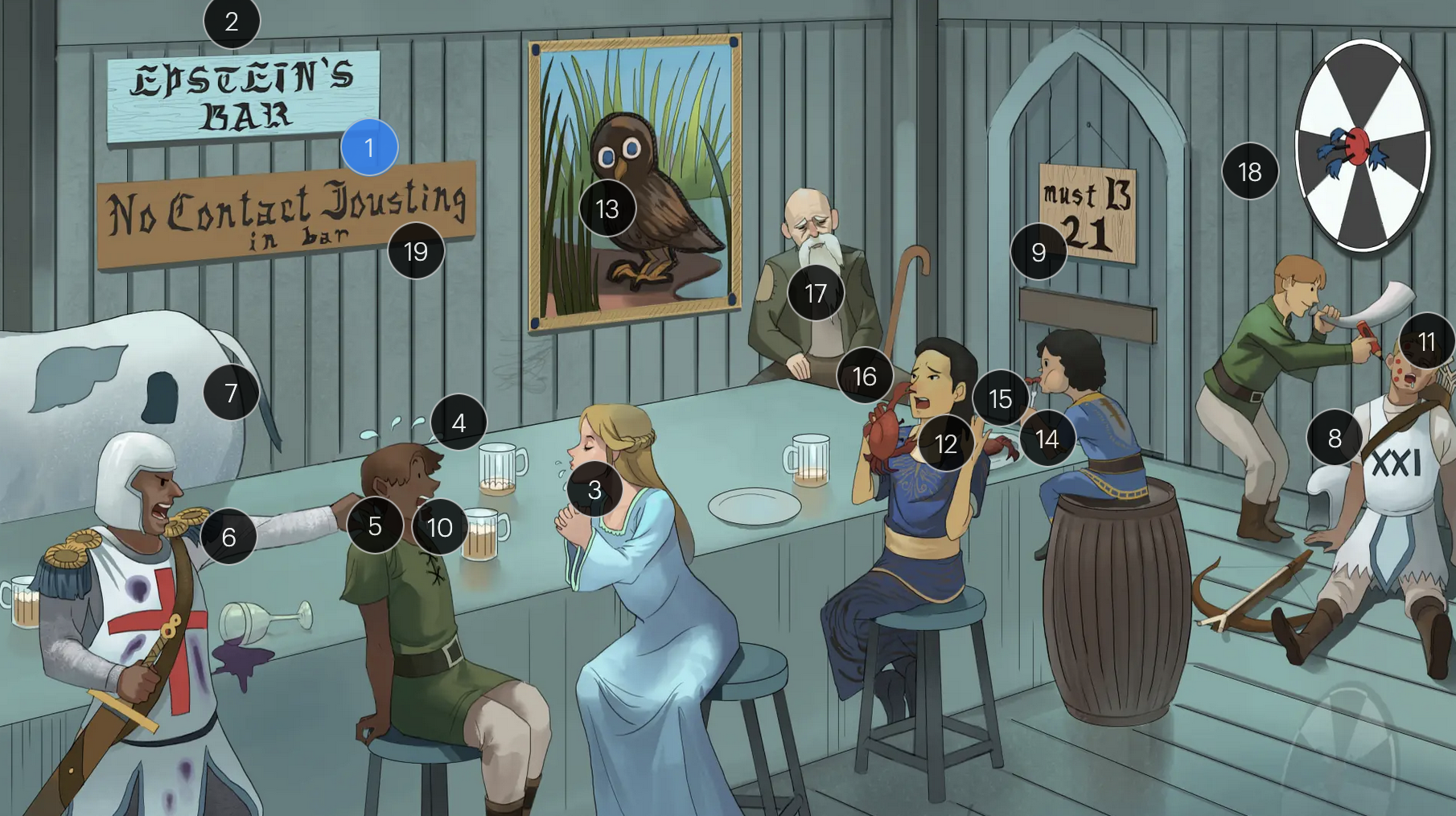
#12 crab meals
EBV infection is associated with a higher risk for development of some cancers, including Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (particularly Burkitt lymphoma)

Epstein-Barr Virus (Herpesviridae)
#13 stern owl’s eyes
Hodgkin lymphoma, which is strongly associated with EBV infection, is characterized by Reed-Sternberg cells, large, abnormal B-cells with a distinctive bilobed nucleus resembling “owl eyes”

Epstein-Barr Virus (Herpesviridae)
#14 bar kid
EBV is associated with a higher risk for development of Burkitt lymphoma, a rare but highly aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma

Epstein-Barr Virus (Herpesviridae)
#15 jaw lump
Endemic Burkitt lymphoma, a specific subtype that occurs predominantly in children in certain regions of equitoral Africa, often presents as a swelling or lesion in the jaw

Epstein-Barr Virus (Herpesviridae)
#16 crab pinching nose
nasopharyngeal carcinoma, a malignancy with a tendency to metastasize, has a strong association with EBV

Epstein-Barr Virus (Herpesviridae)
#17 bearded man + immunocompromised cane
oral hairy leukoplakia, which presents with benign white lesions primarily found on the tongue, is triggered by EBV in individuals with HIV or AIDS
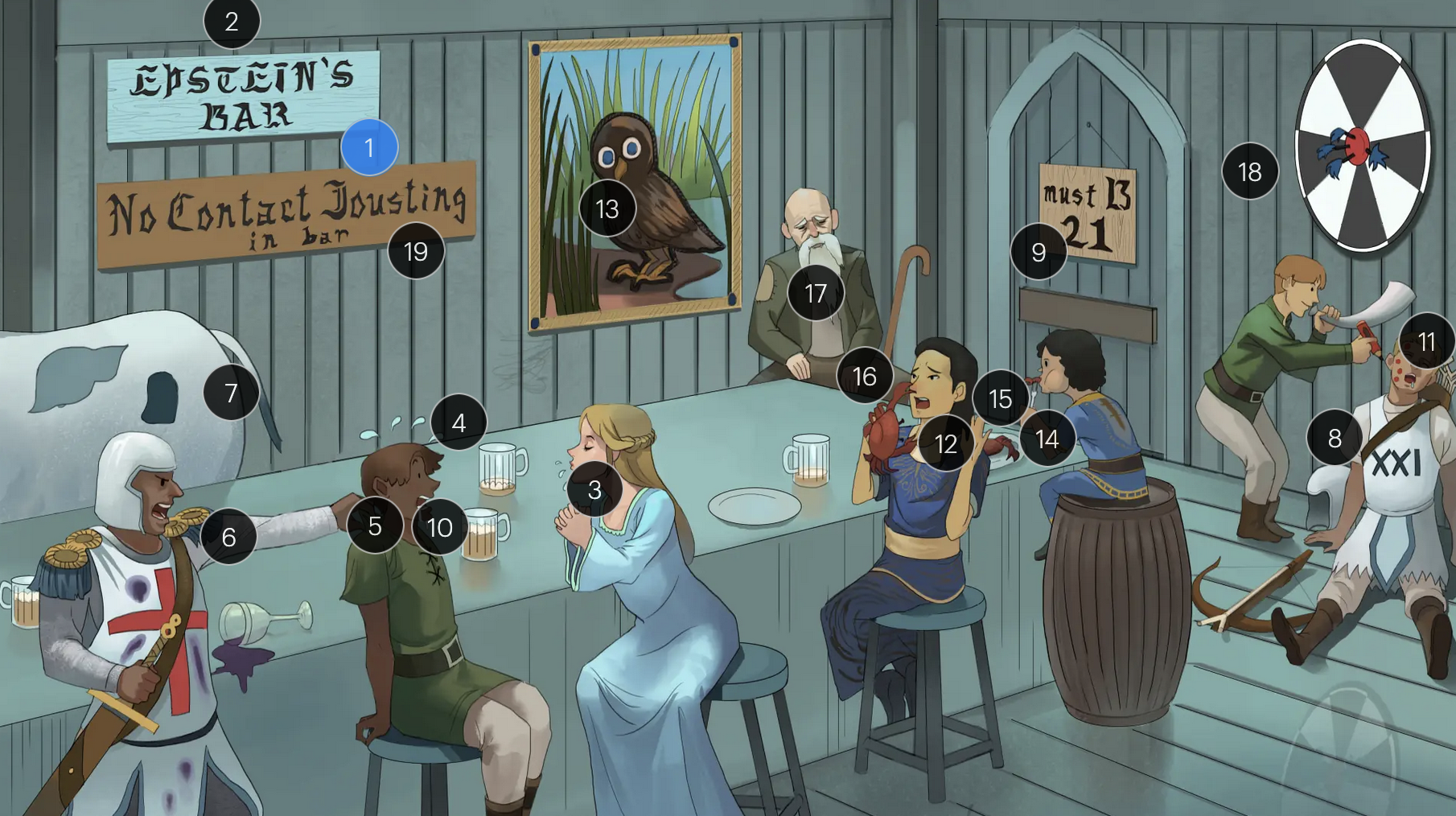

Epstein-Barr Virus (Herpesviridae)
#18 bullseye soit + star darts
the monospot test can be used to provide a quick diagnosis for acute EBV infection by detecting heterophile IgM antibodies, which induce agglutination
the CDC no longer recommends the Monospot test due to low sensitivity and specificity (currently, gold standard = EBV-specific antibodies)
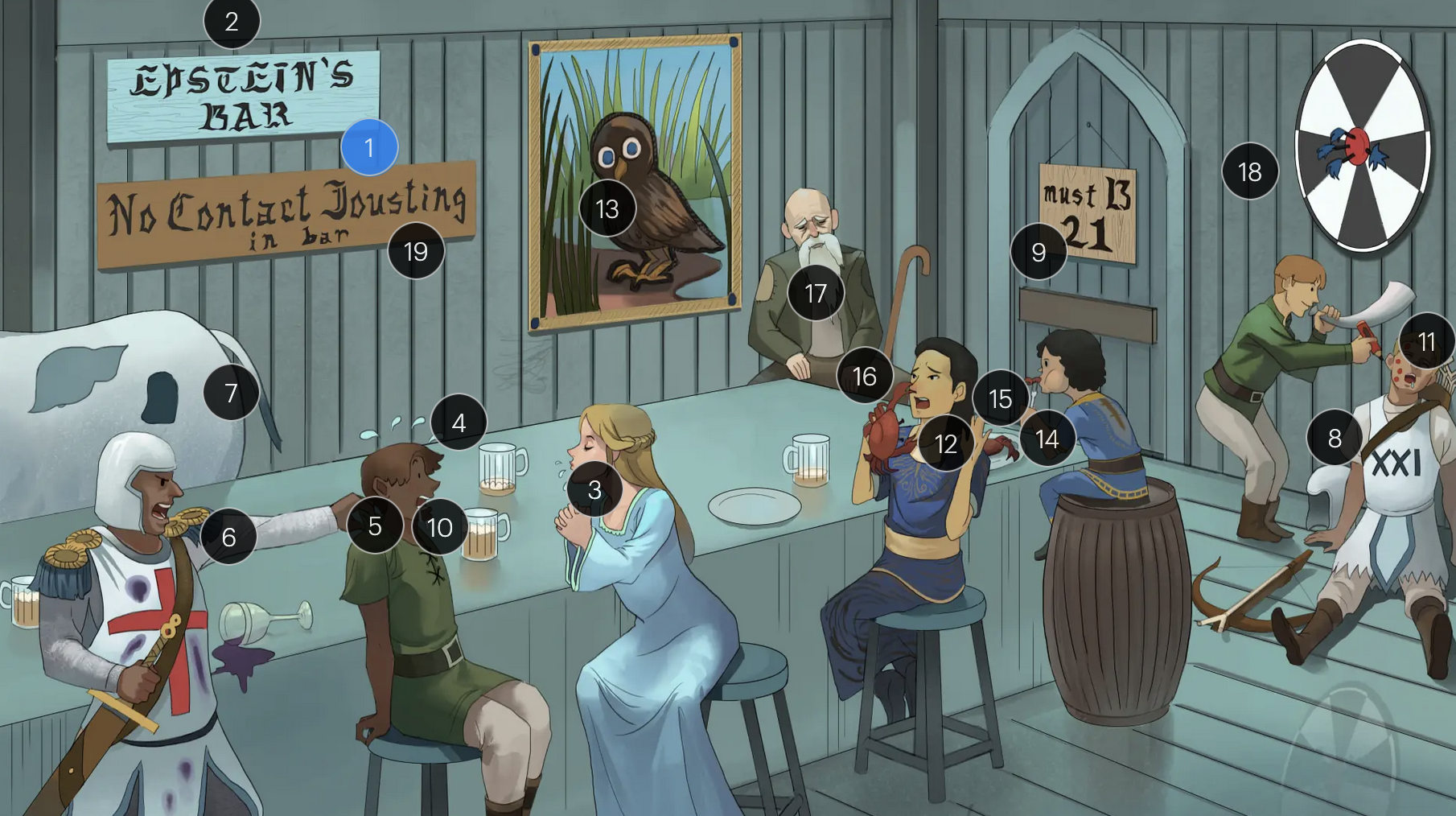

Epstein-Barr Virus (Herpesviridae)
#19 “No contact jousting”
patients with infectious mononucleosis are advised to avoid contact sports for several weeks or until a physician clears them due to the elevated risk of SPLENIC RUPTURE
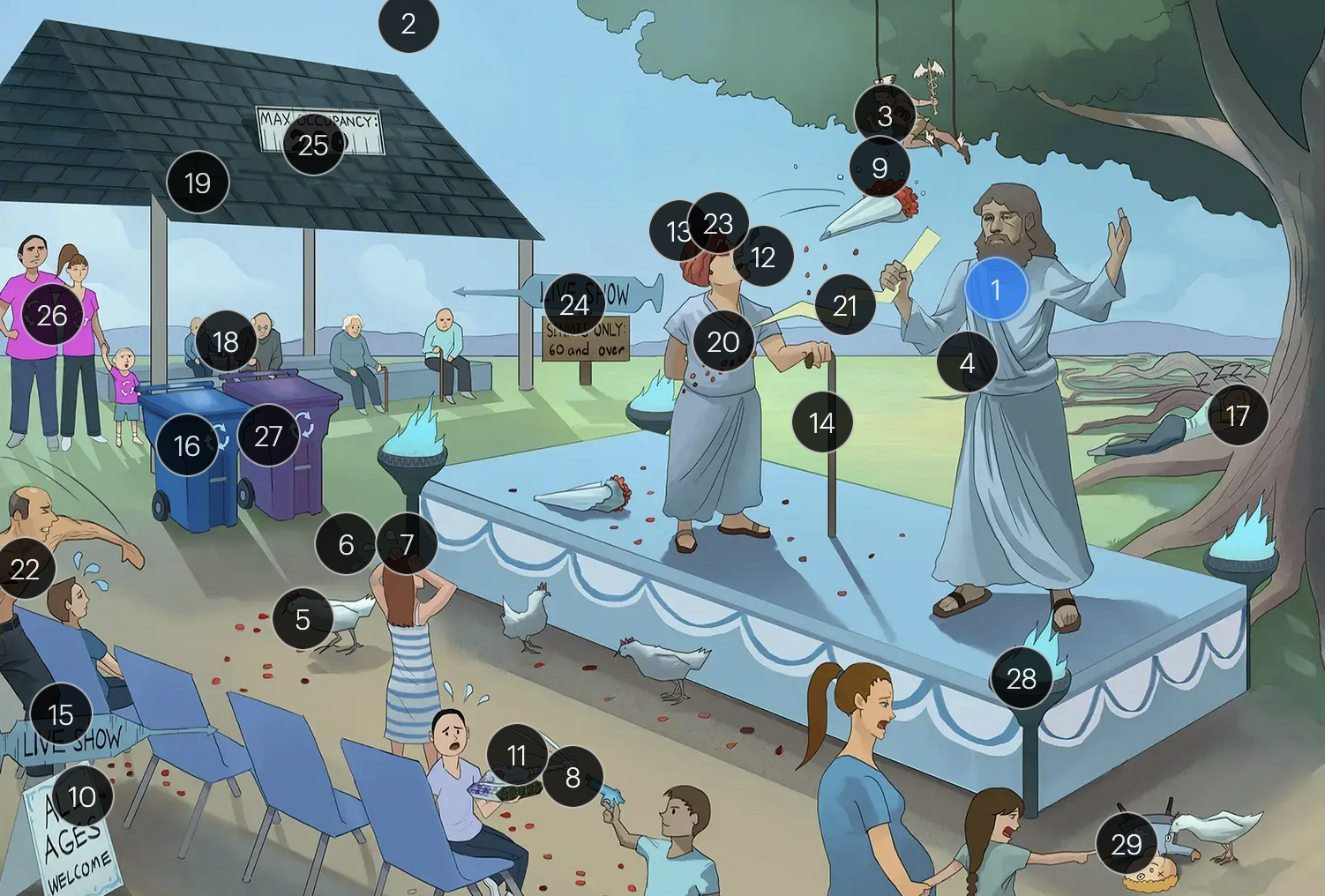
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
#1 Zeus
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV; a DNA virus in the Herpesviridae family)
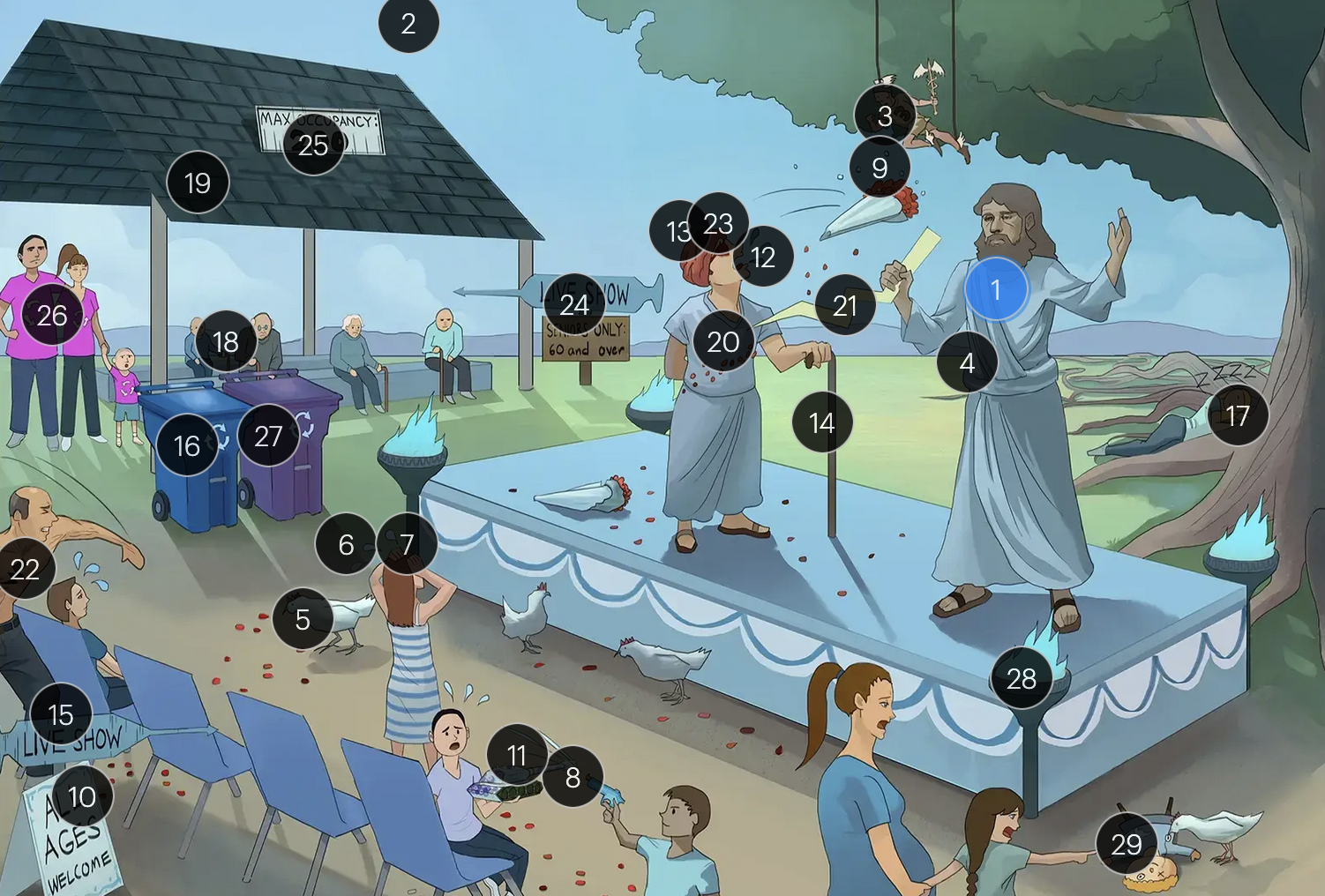
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
#2 cool colors
VZV is a DNA virus
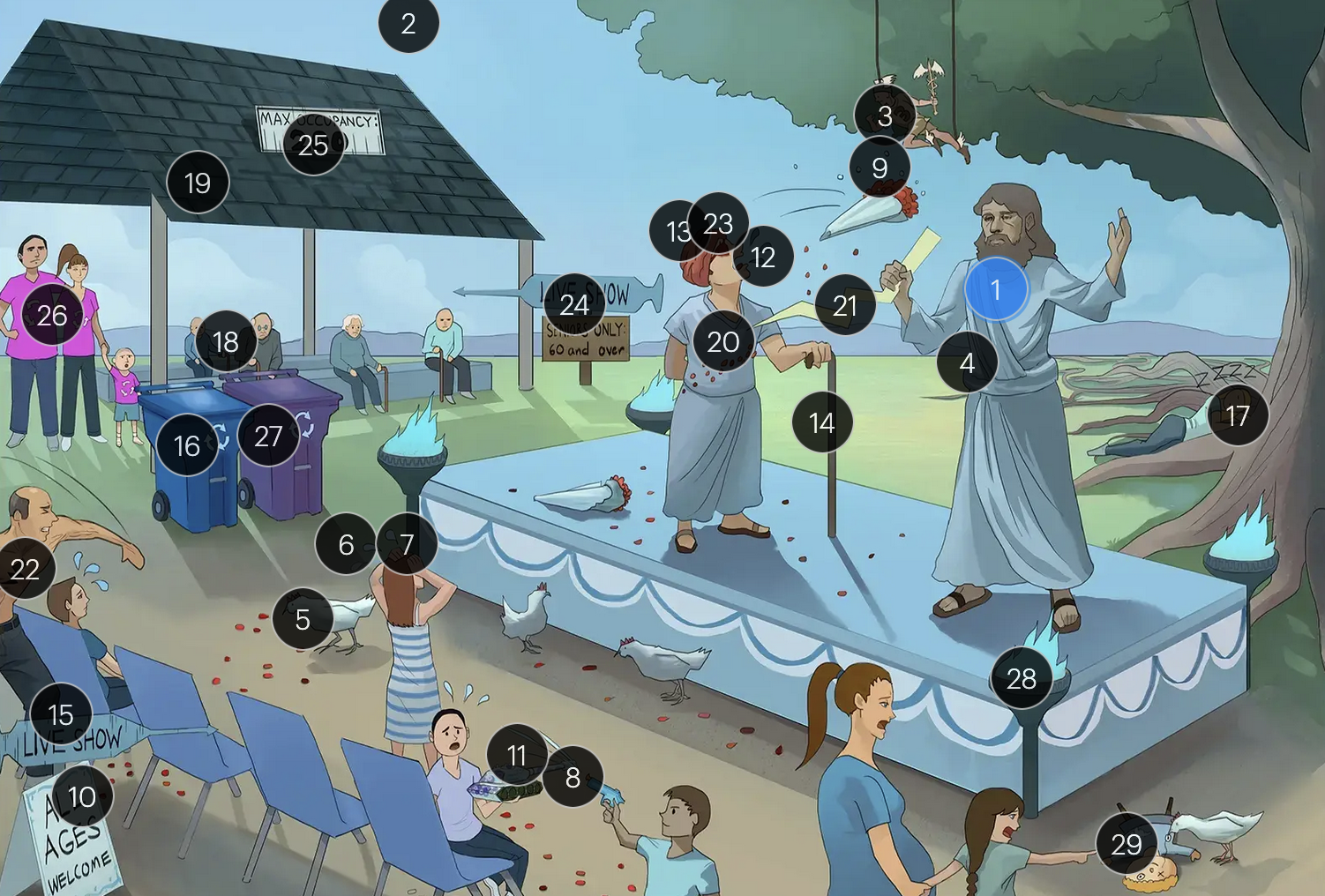
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
#3 Hermes
VZV is in the Herpesviridae family
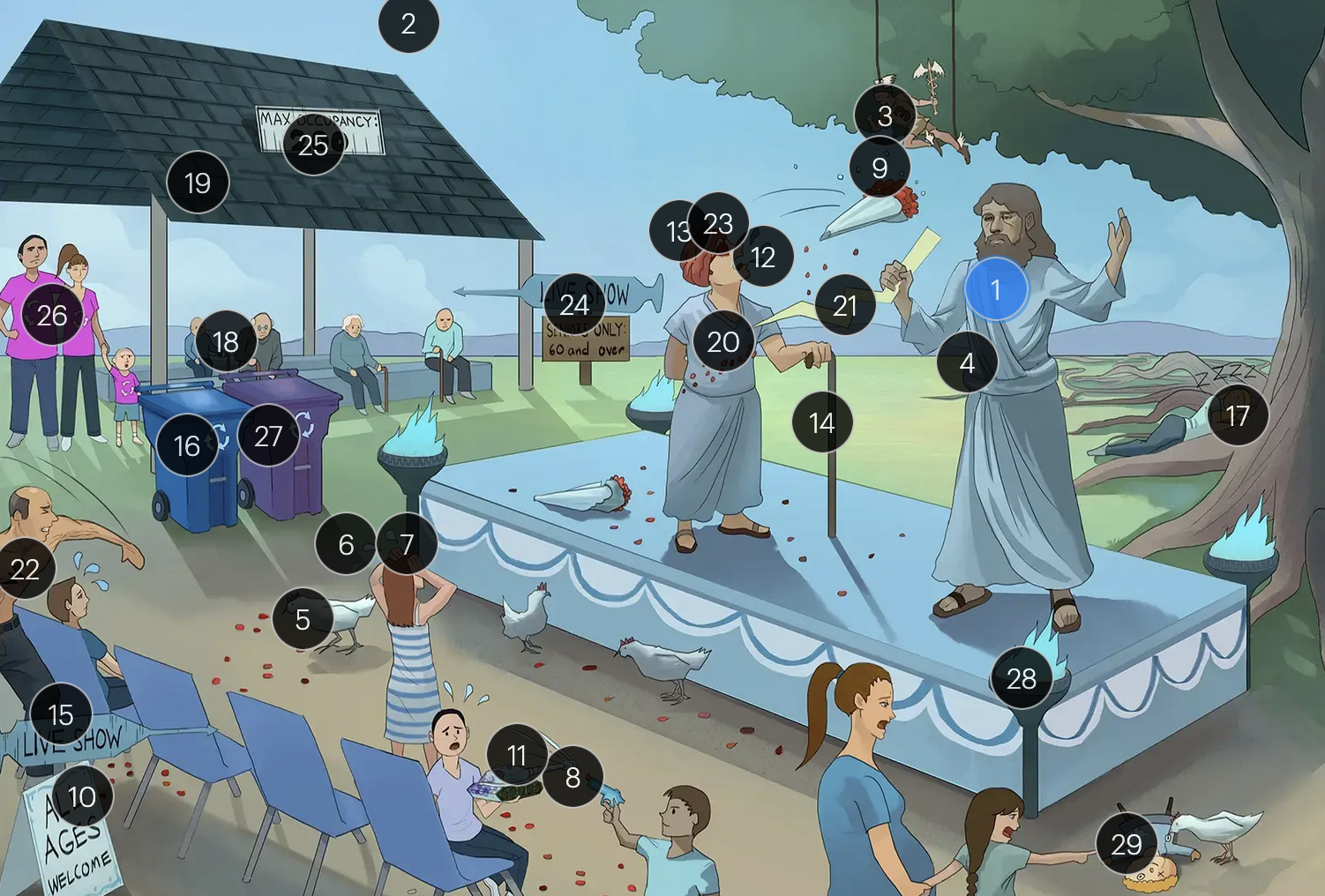
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
#4 wrapped in toga
VZV is an enveloped virus
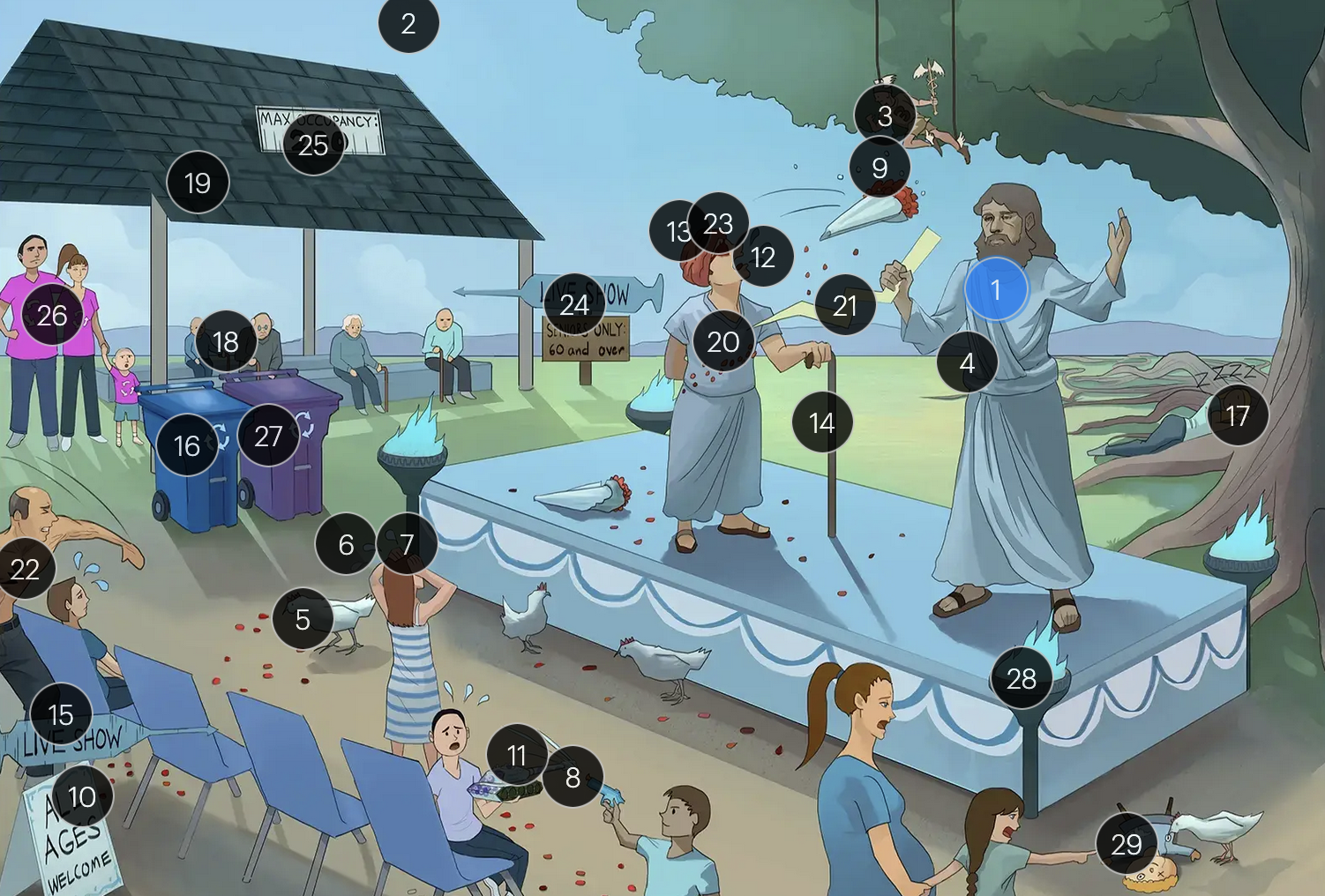
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
#5 chickens
VZV causes chickenpox, which manifests as a pruritic rash characterized by small, fluid-filled blisters
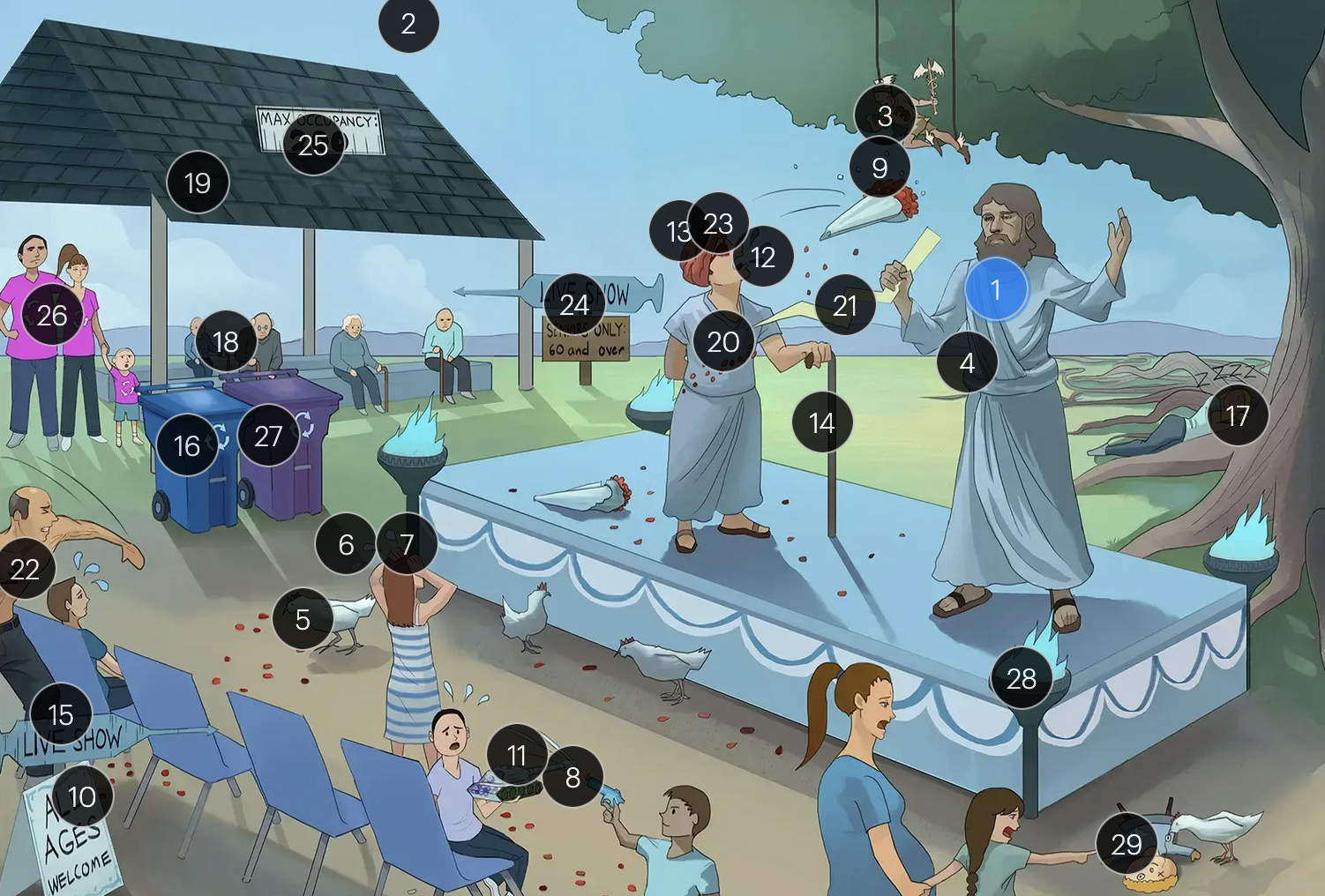
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
#6 sweat
fever, headache, fatigue, and loss of apetite often appear one to two days before development of chickenpox lesions
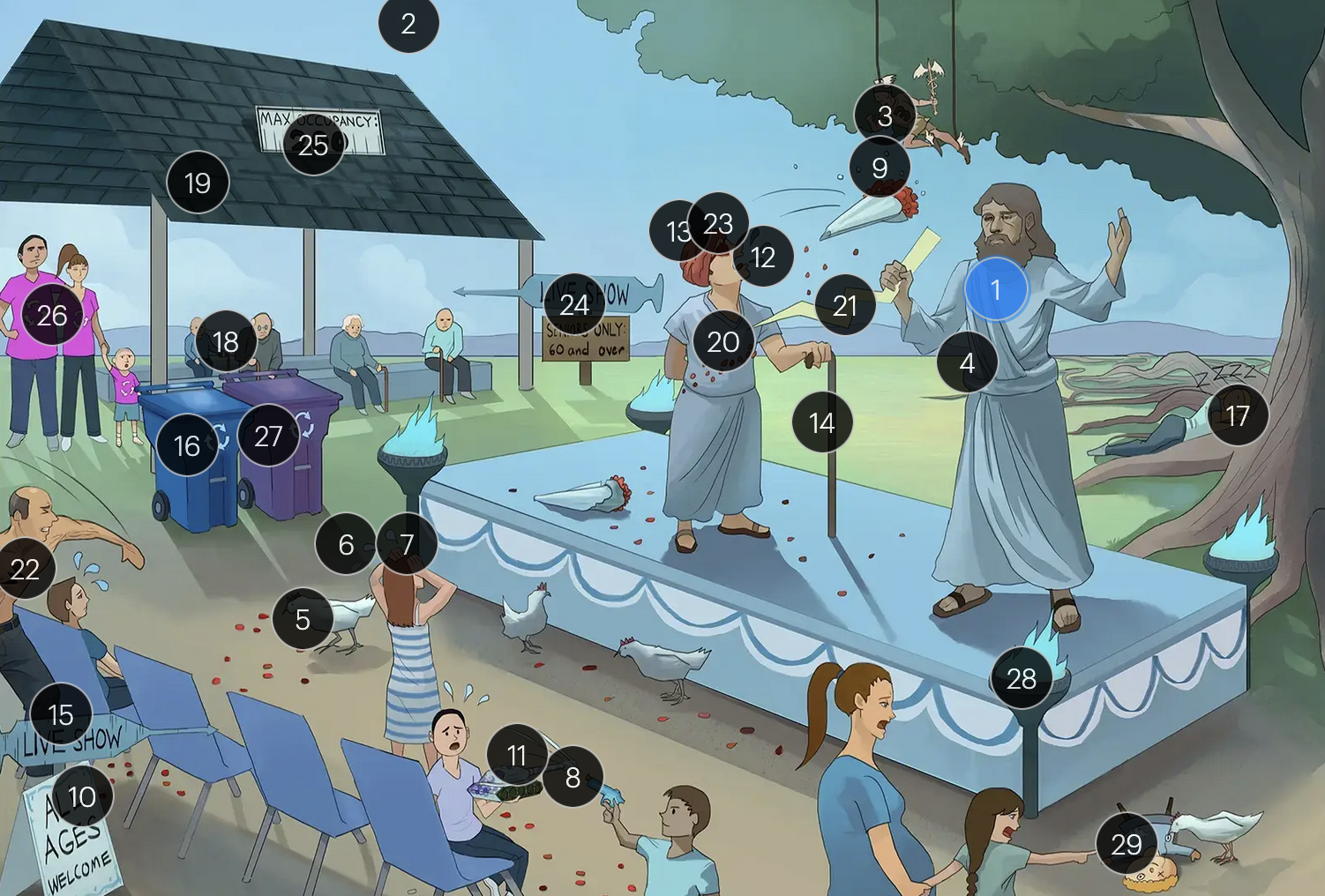
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
#7 holding head
fever, headache, fatigue, and loss of apetite often appear one to two days before development of chickenpox lesions
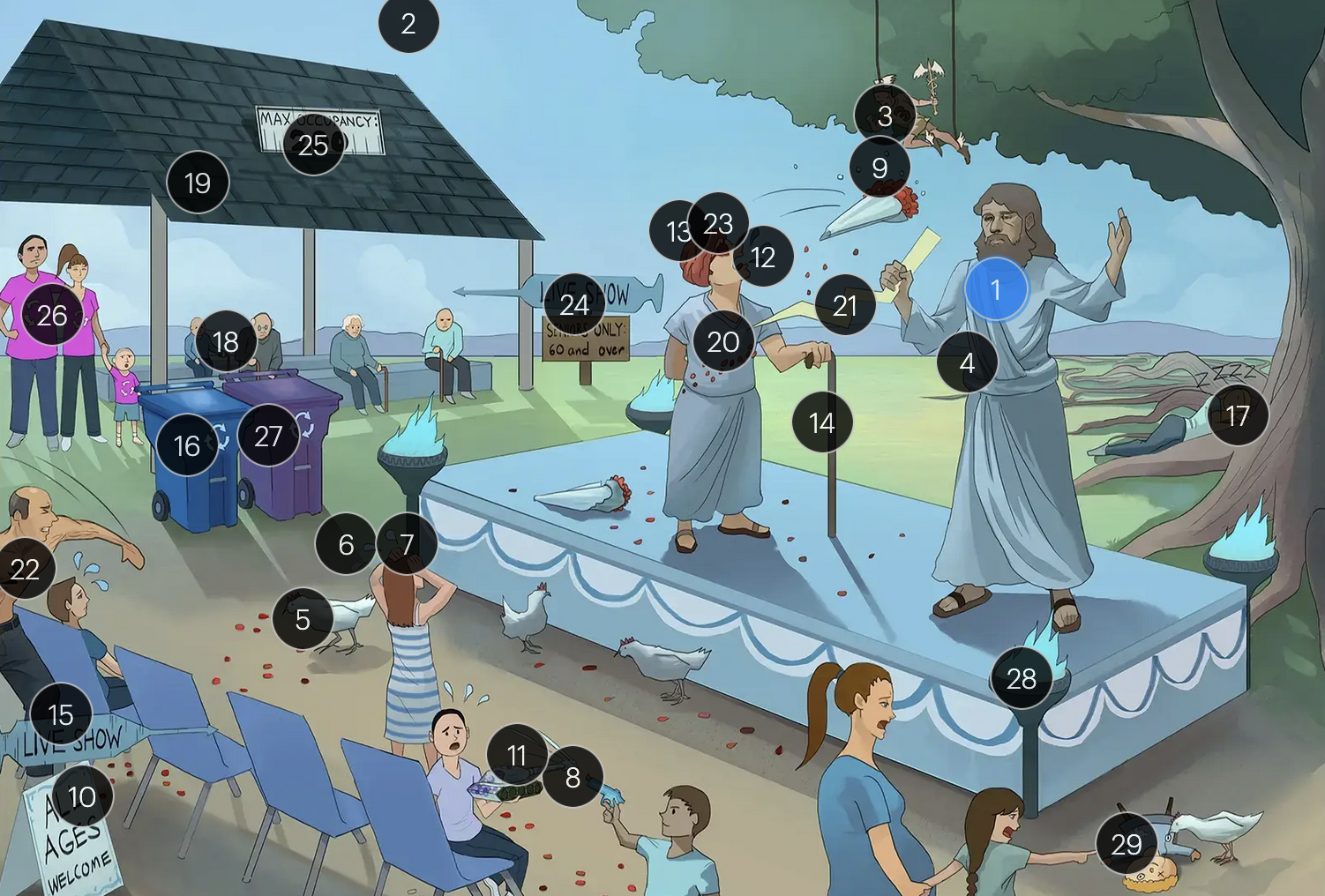
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
#8 water gun spray
VZV is primarily transmitted via respiratory droplets
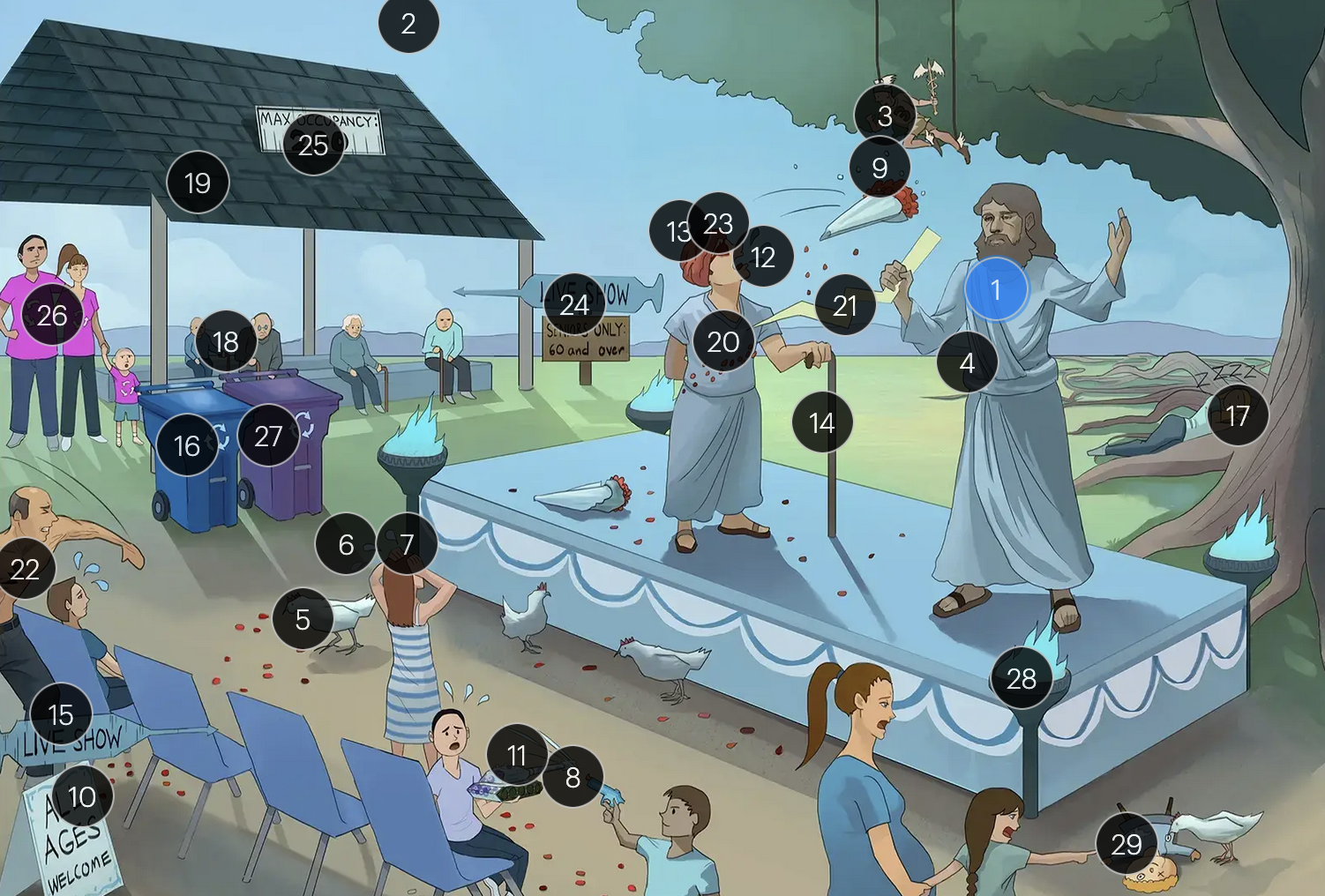
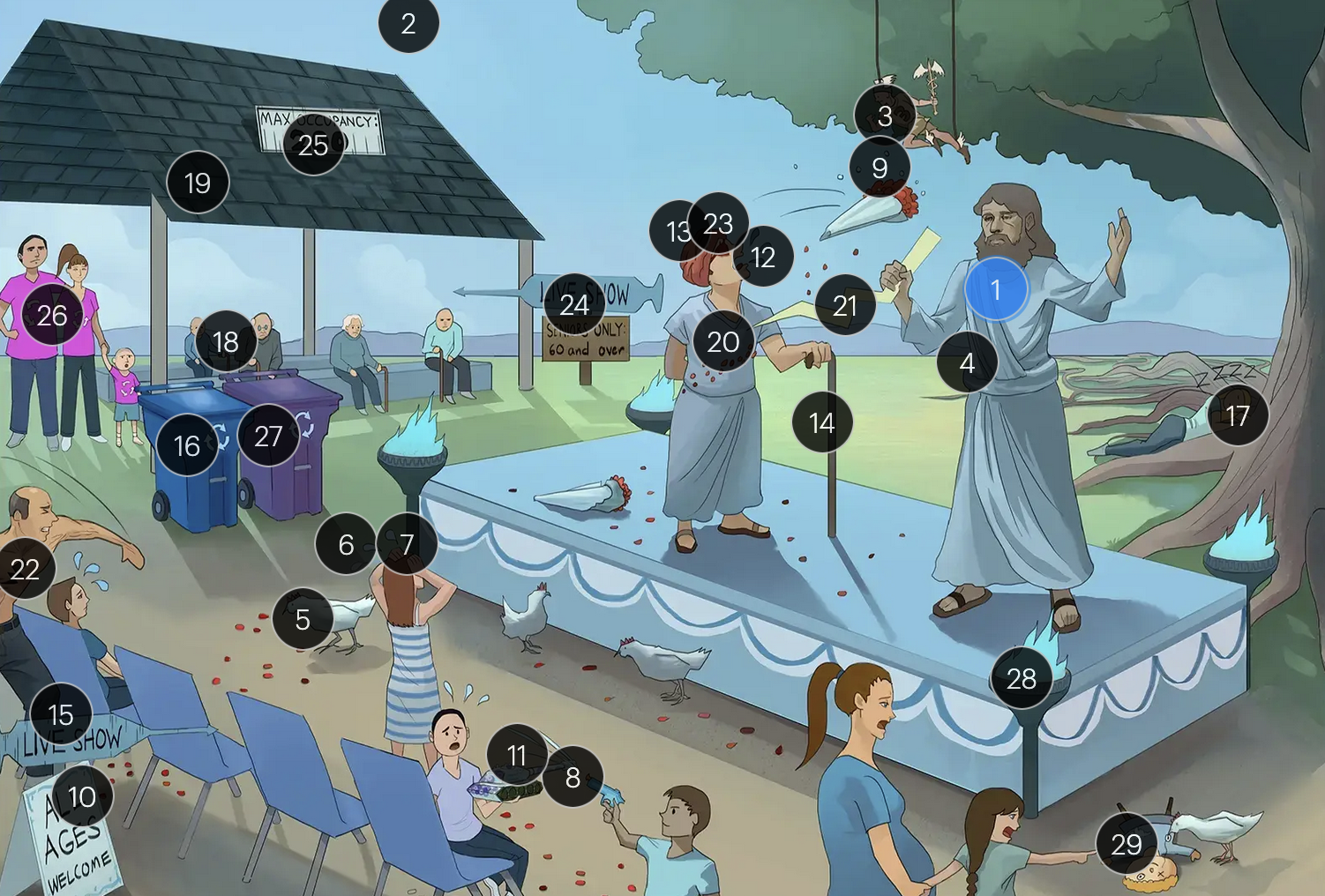
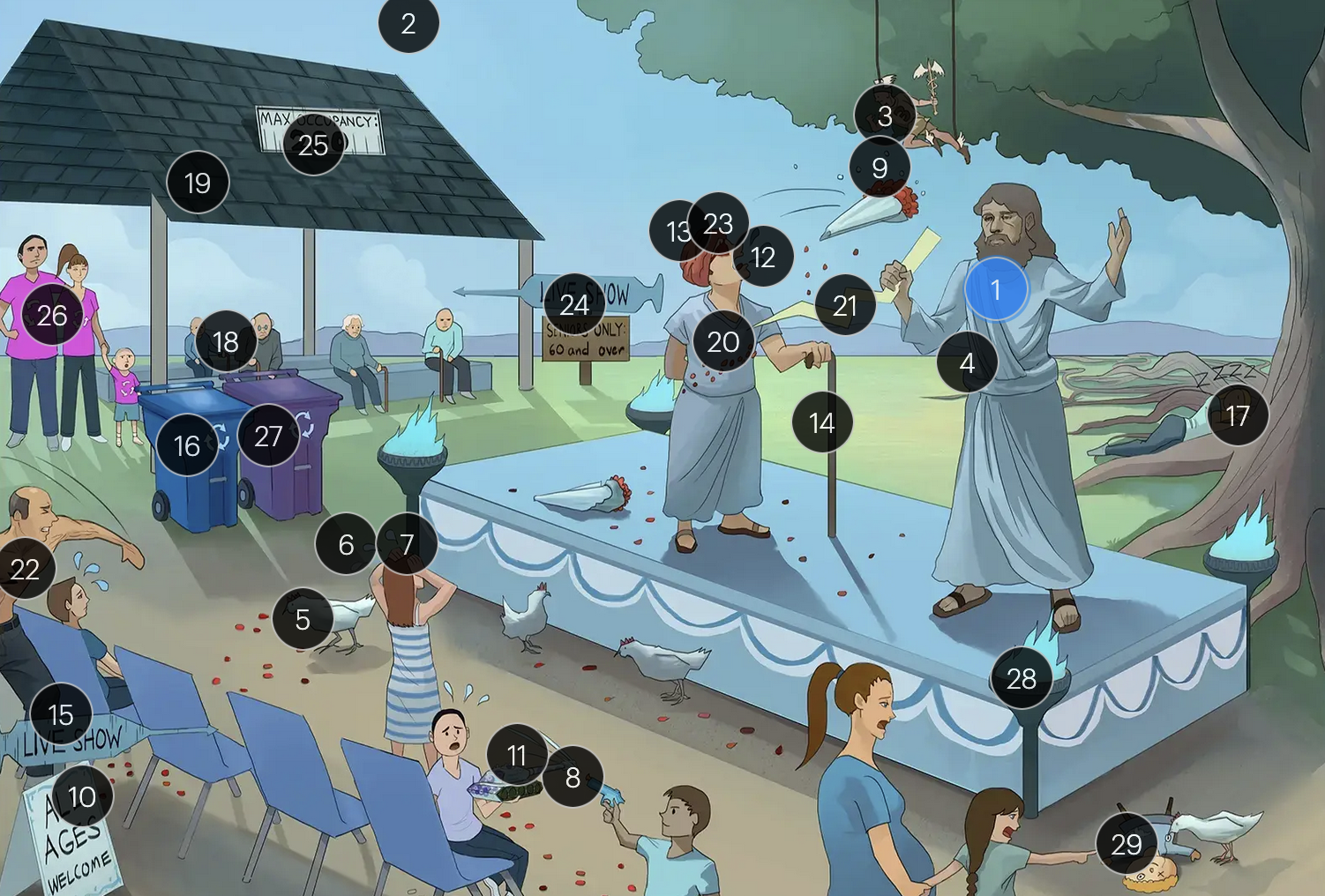
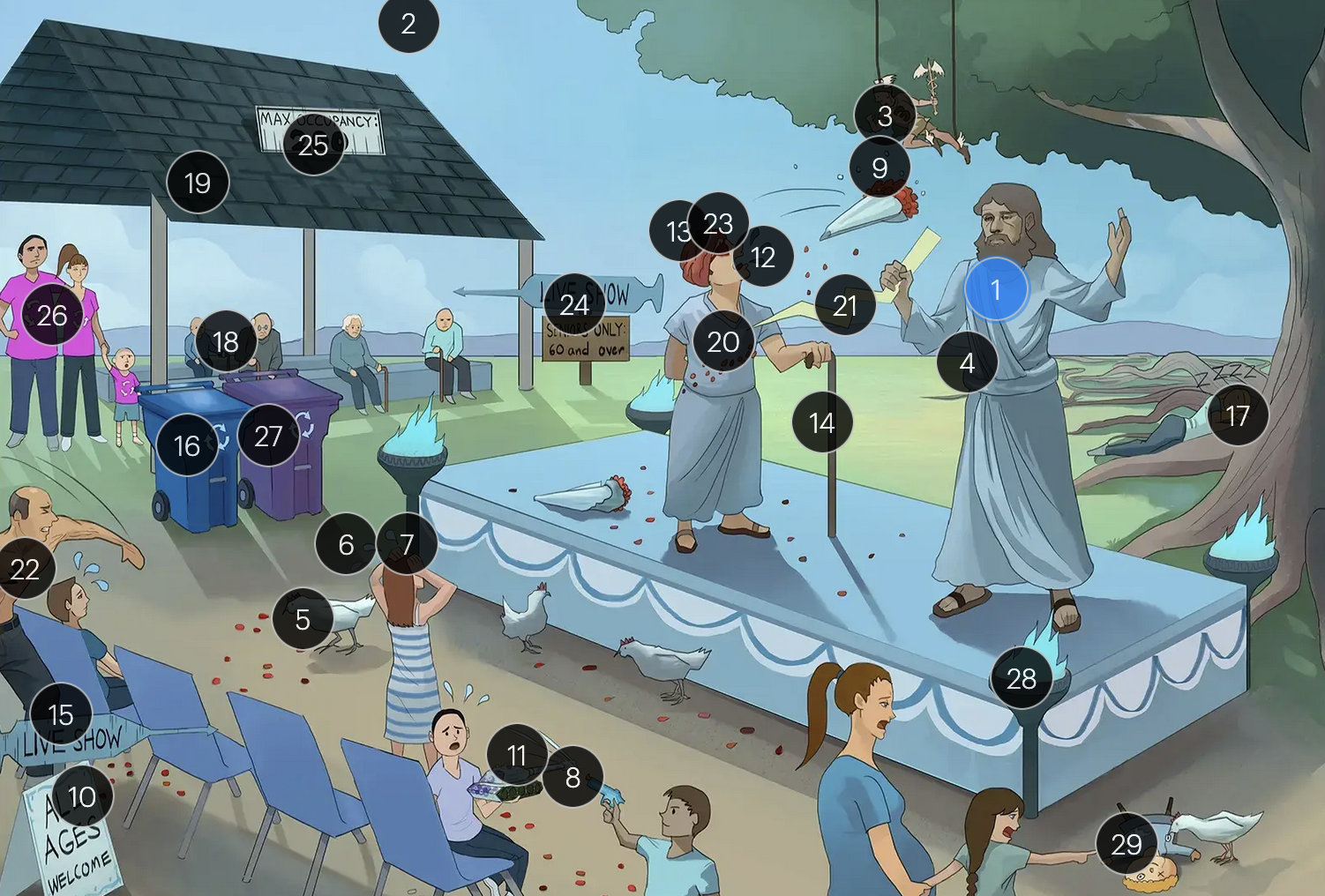
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
#9 dew on rose petals
the vesicular lesions caused by VZV are often likened to “dew drops on a rose petal”
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
#10 “all ages welcome”
chickenpox vesicles typically appear in varying stages of development and healing; this contrasts with many other viral rashes where the entire rash uniformly moves through stages together
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
#11 tank + giant spots
historically, a Tzanck smear to visualize multinucleated giant cells infected with VZV; however, multinucleated giant cells can be seen in other infections like HSV, so more specific identification via other test like PCR is required
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
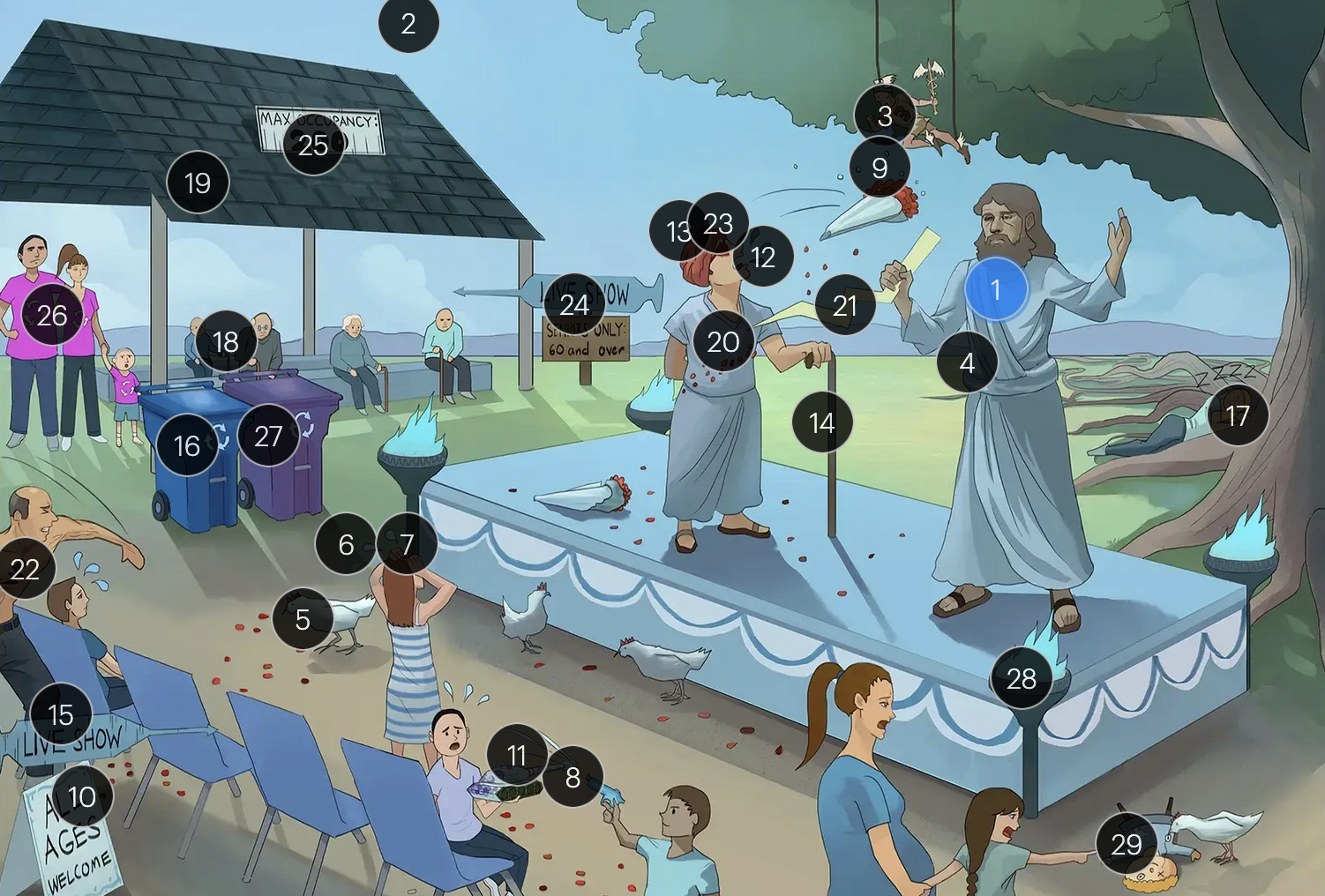
#12 adult coughing
adults are more likely to develop complications from chickenpox (caused by VZV) than children; one of the more serious complications is varicella pneumonia
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
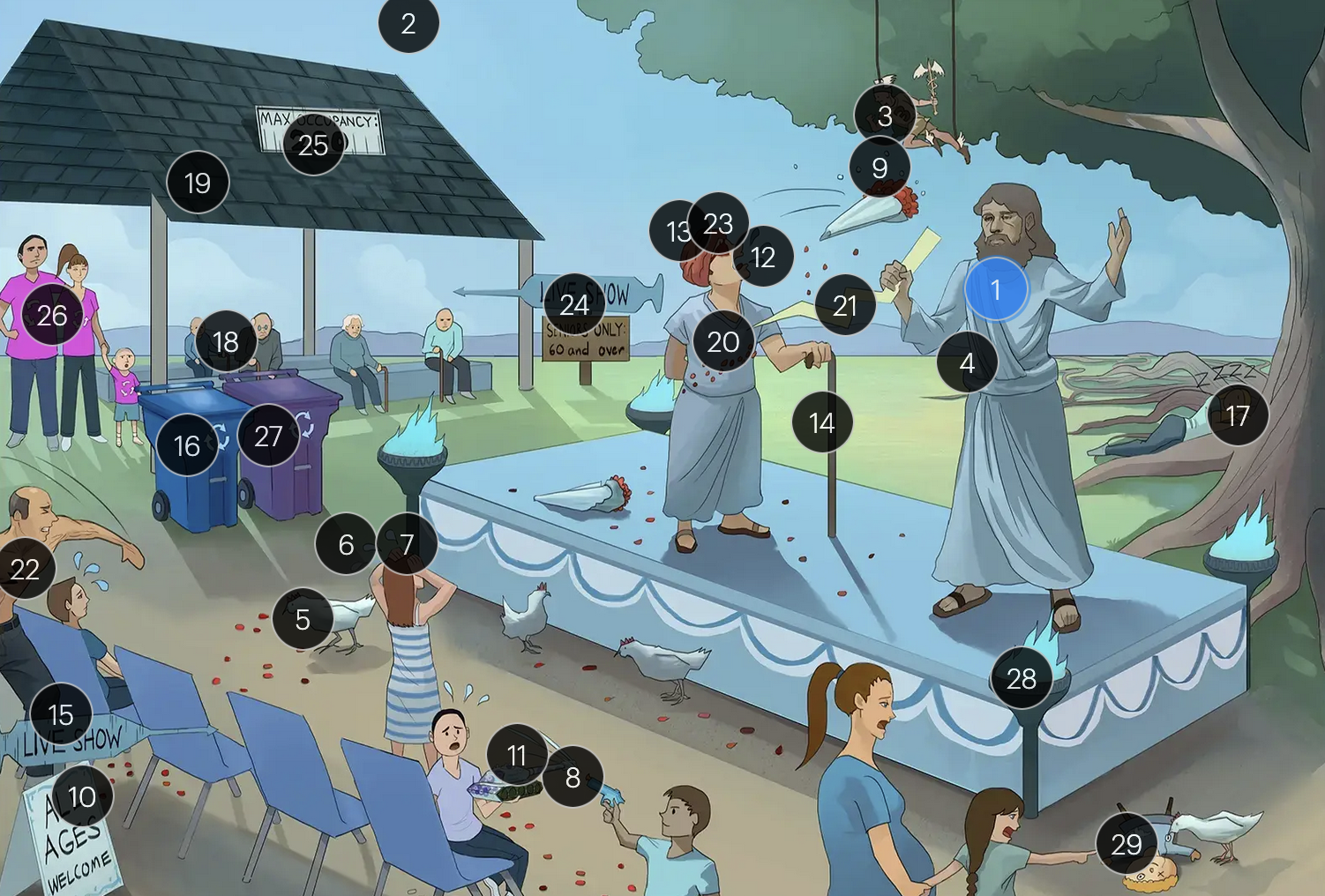
#13 red turban
encephalitis is a rare but serious complication that can arise from VZV
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
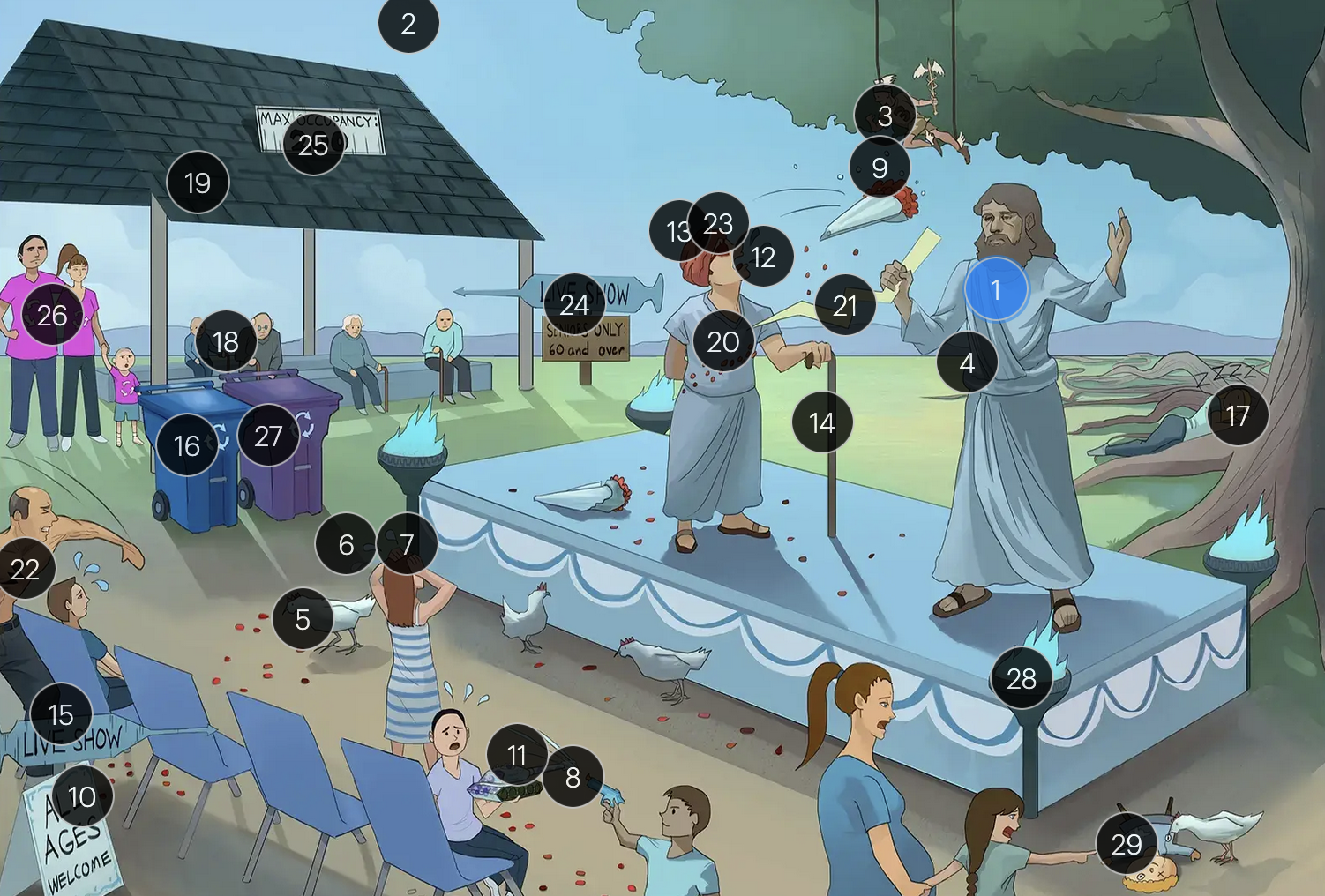
#14 immunocompromised cane
immunocompromised patients have an elevated risk for severe VZV complications, including varicella pneumonia and encephalitis
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
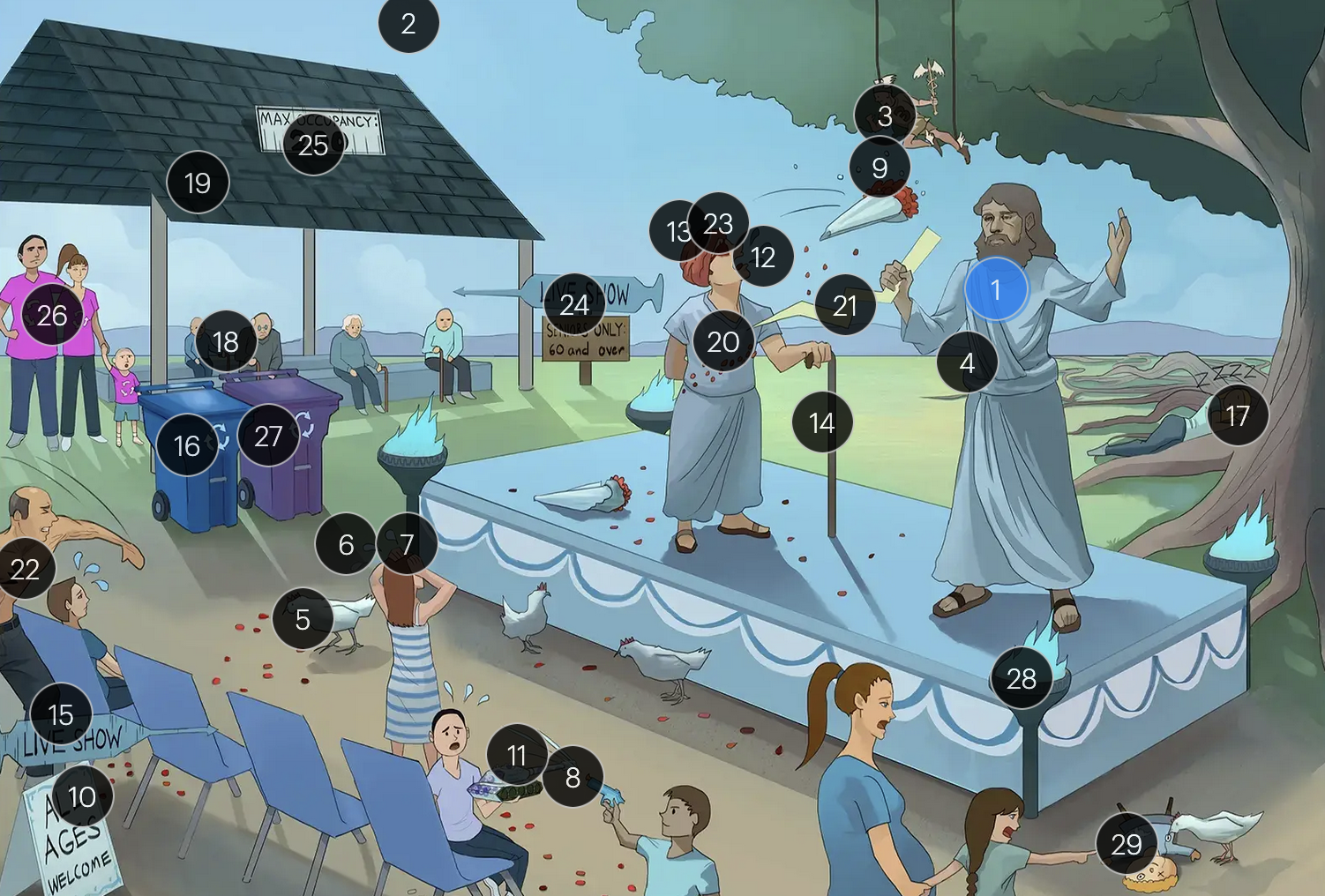
#15 “Live Show” syringe sign
the vaccine for VZV is a live attenuated formulation typically administered in childhood
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
#16 recycling bin
acyclovir reduces the number of lesions and duration of illness if started within 24 hours of rash appearance
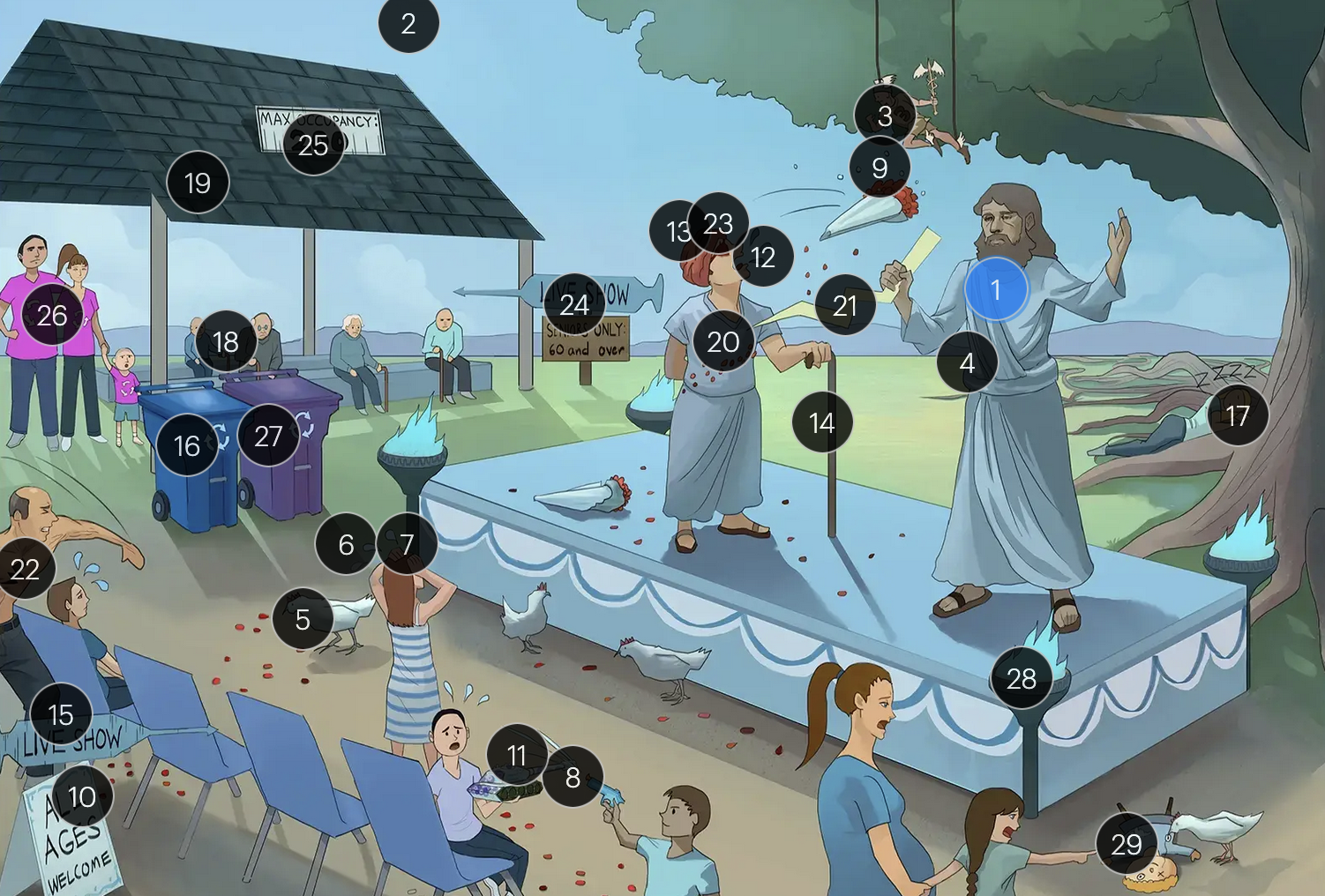
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
#17 sleeping on dorsal tree roots
after an initial chickenpox infection, VZV becomes dormant in the dorsal root ganglia and can reactivate later, causing shingles
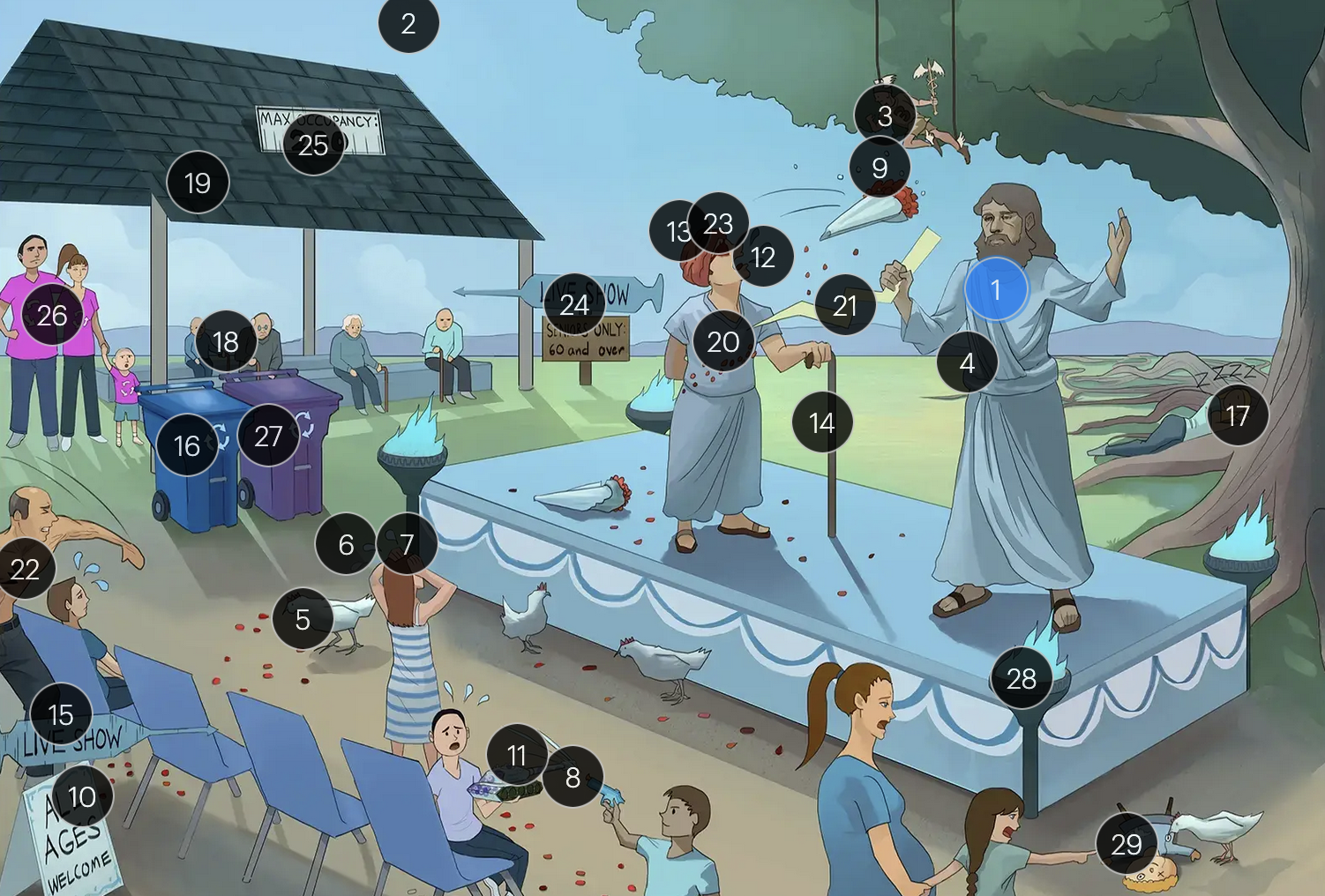
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
#18 elderly people + immunocompromised cane
factors such as stress, aging, decreased immunity, or underlying diseases can trigger the reactivation of V>V, leading to shingles (herpes zoster)
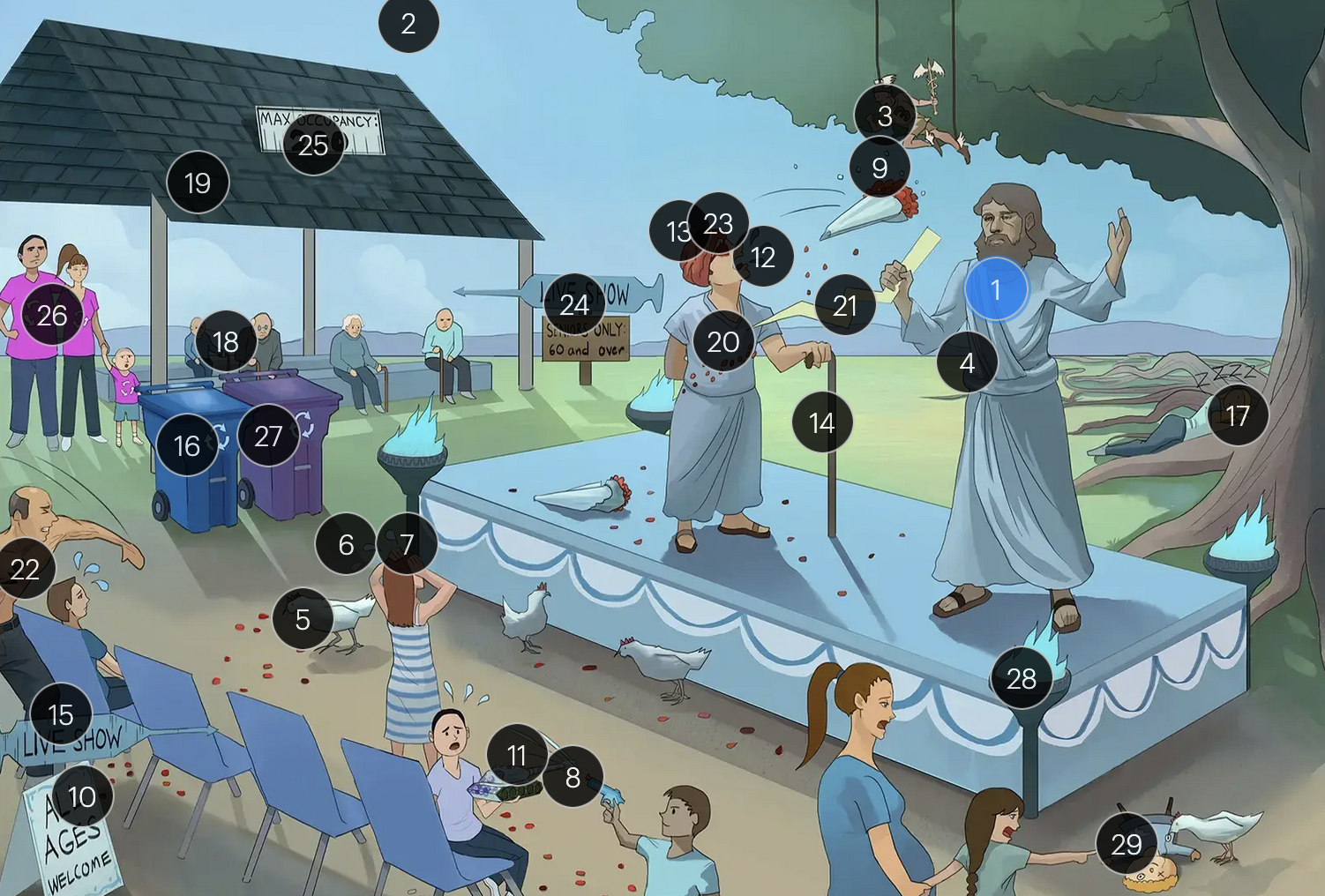
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
#19 shingles
when VZV reactivates, it causes shingles (herpes zoster), which predominantly affects adults over 50 and immunocompromised individuals
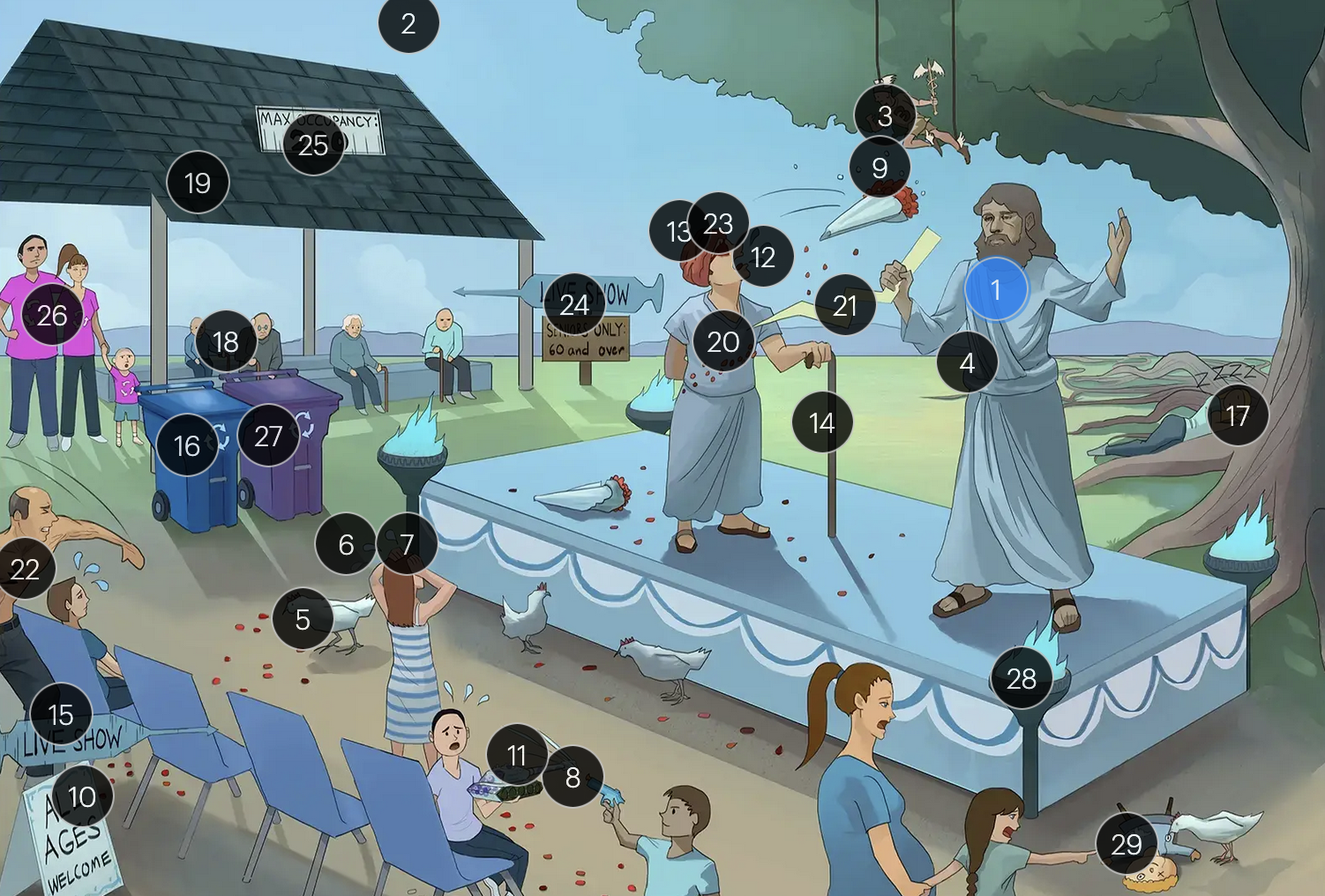
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
#20 rose petals falling across abdomen
shingles presents with a painful rash resembling “dew drops on a rose petal” and typically follows a dermatomal distribution, meaning it appears in the specific area of skin served by one spinal nerve root
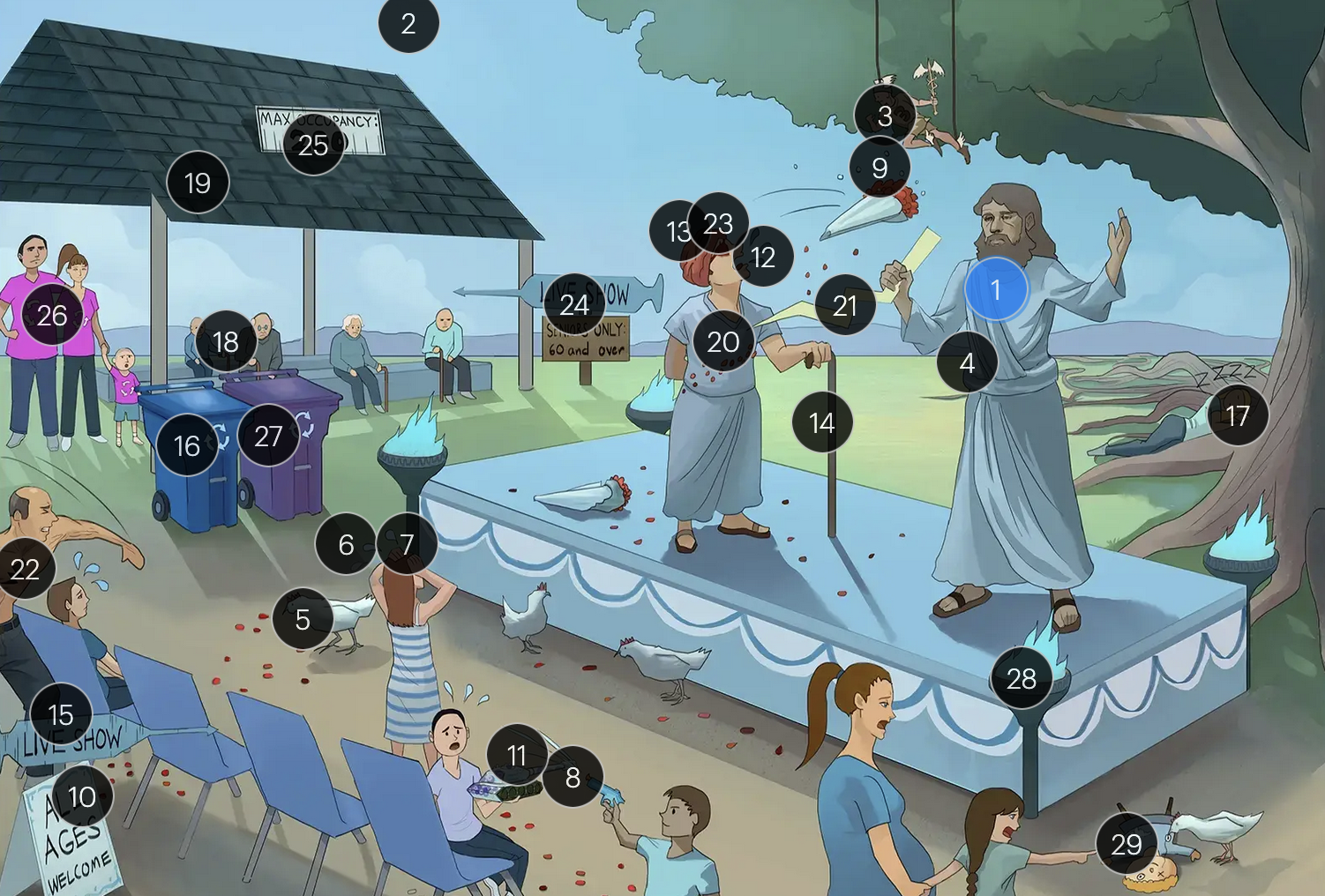
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
#21 pain bolt
shingles is typically characterized by an intensely painful, blistering rash that follows the path of a single spinal nerve root, often exacerbated by even a gentle touch or breeze
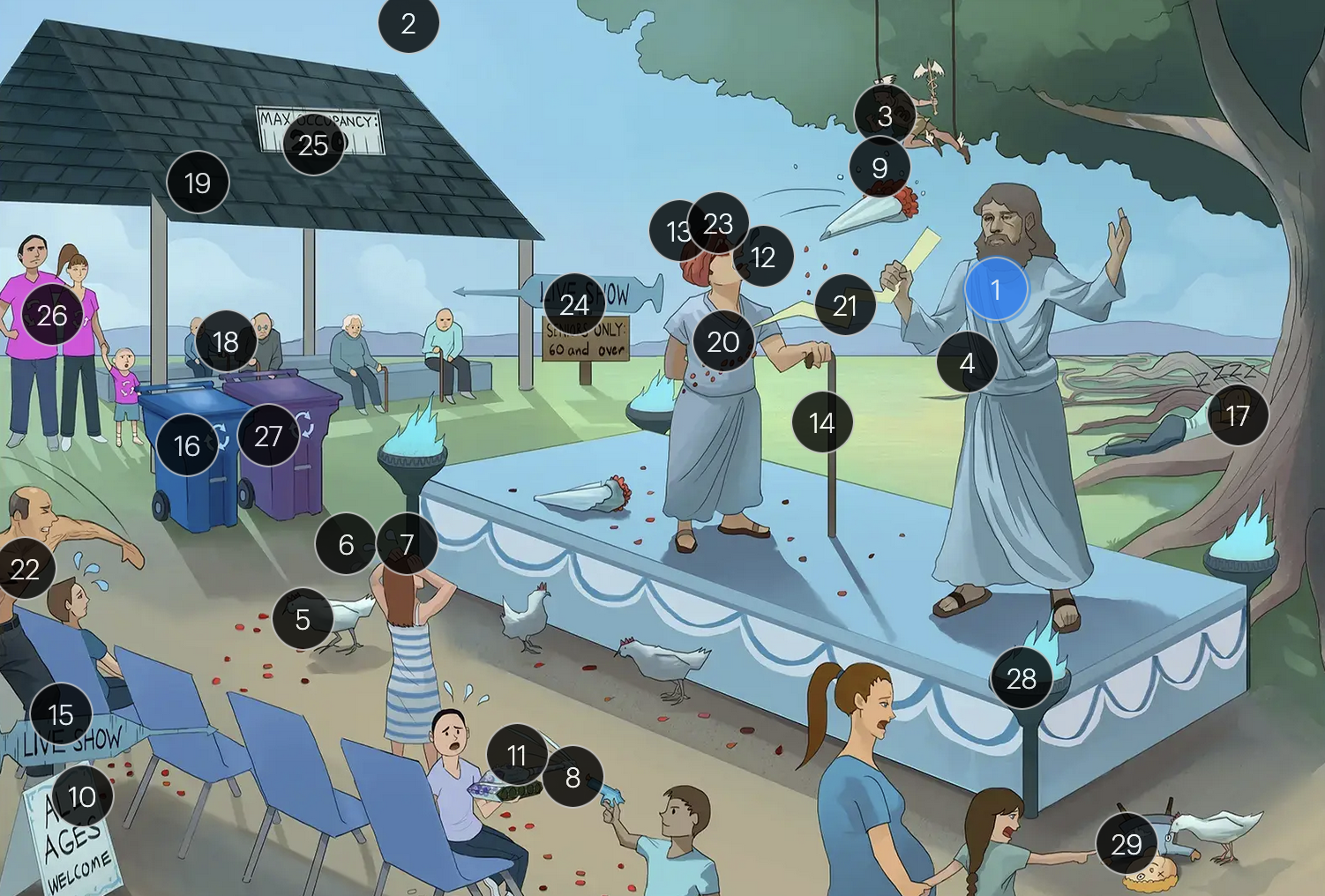
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
#22 chest bolt
postherpetic neuralgia, a potential complication of shingles, results in persistent, burning pain in the affected area, long after the shingles rash has resolved
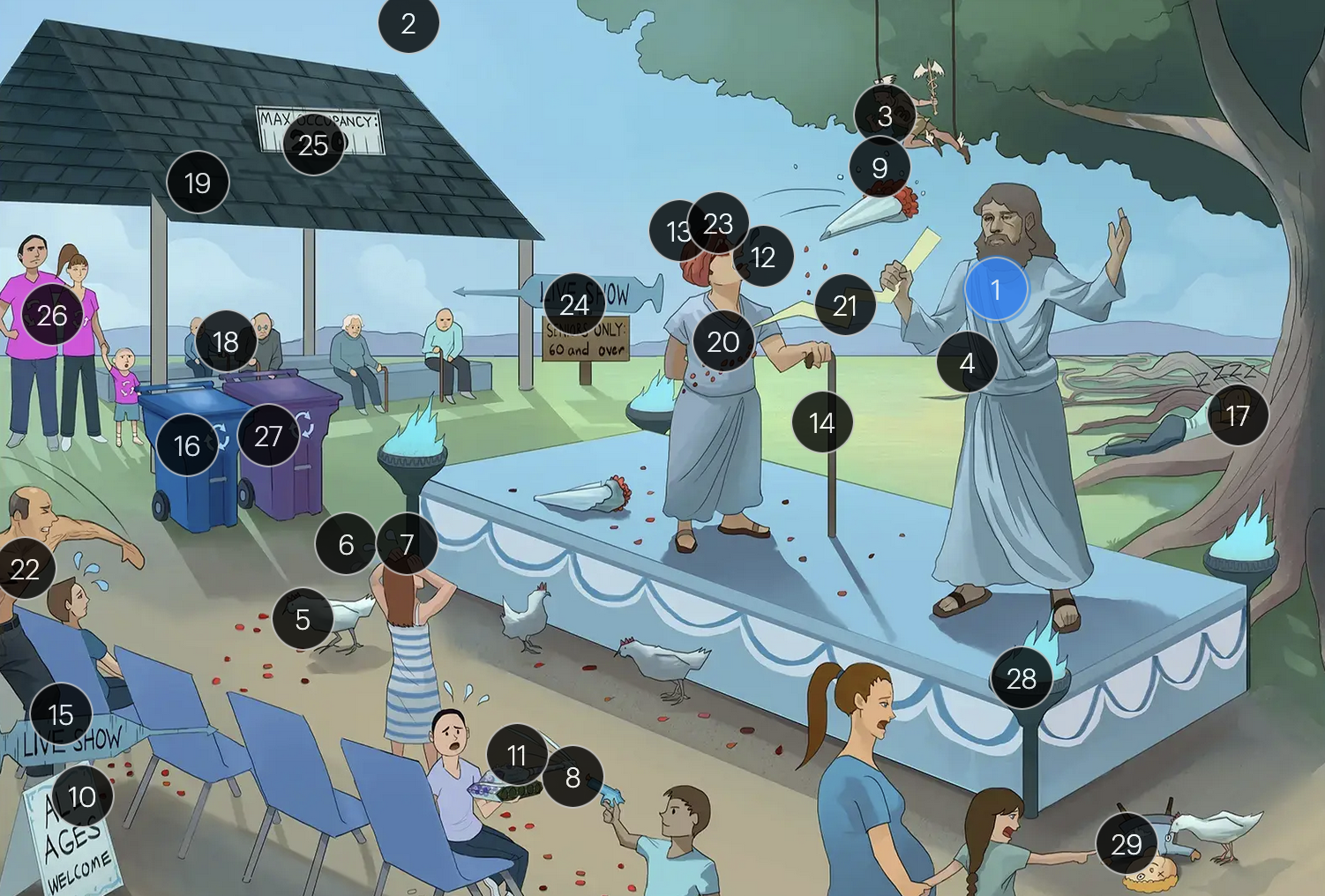
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
#23 red eye patch
herpes zoster opthalmicus results when VZV reactivates in the opthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve (V1), potentially causing vision loss
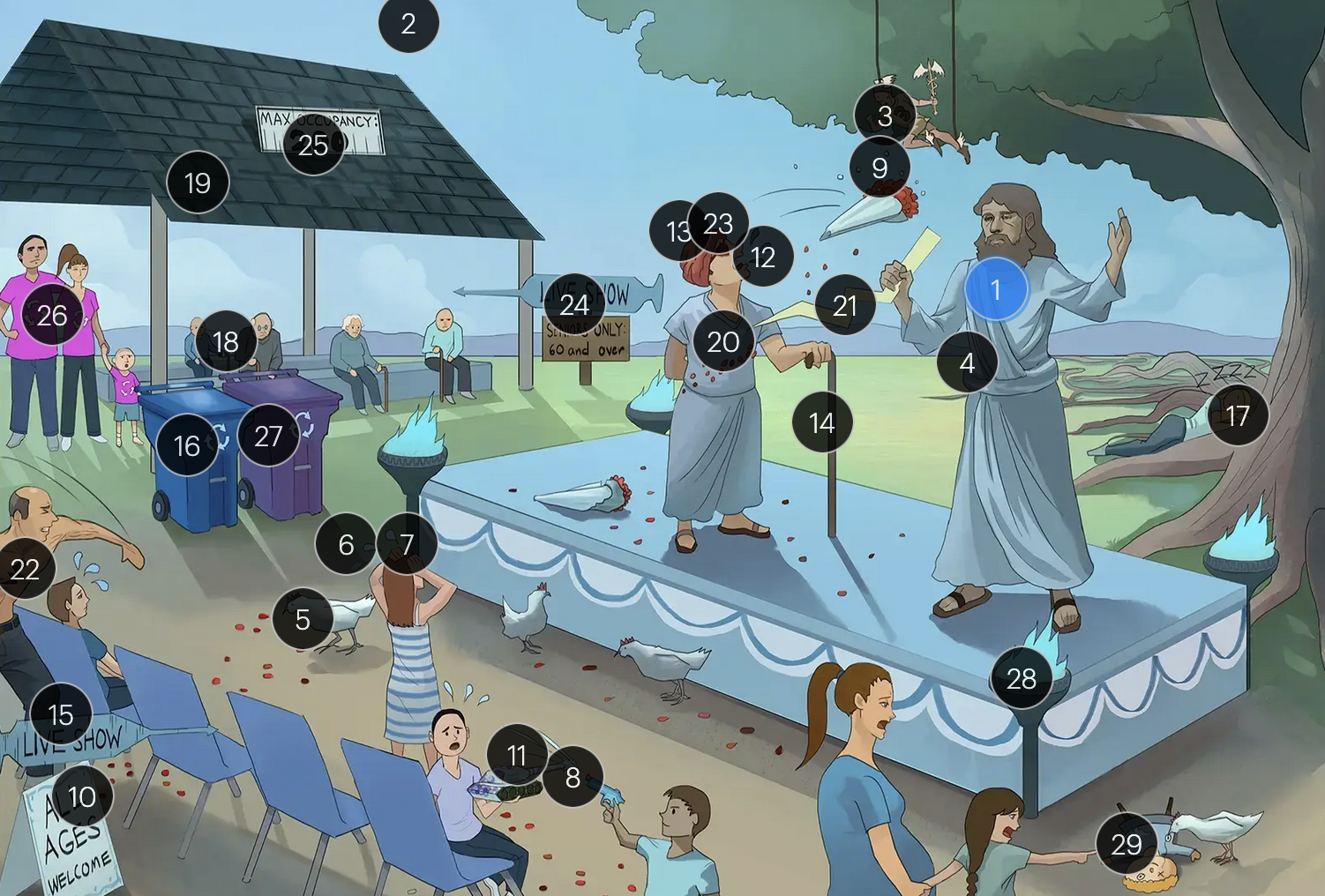
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
#24 “live show - seniors only 60 & over”
historically, the CDC recommended that people 60+ receive Zostavax (live attenuated vaccine), to prevent shingles and post-herpetic neuralgia;
however, SHINGRIX (recombinant subunit vaccine) is now used for shingles prevention
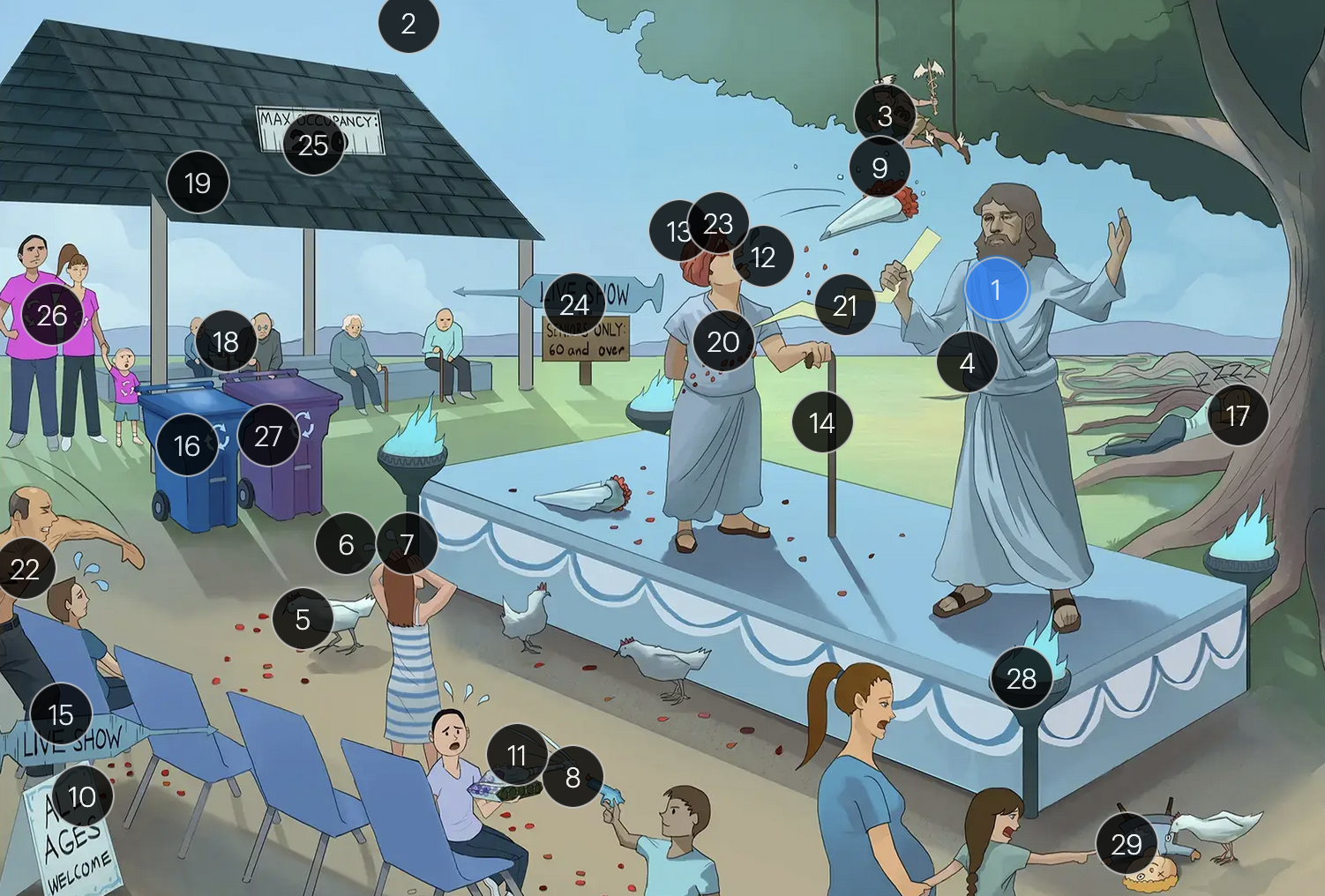
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
#25 “Max occupancy 200”
HIV patients with a CD4+ count exceeding 200 are eligible for the varicella-zoster vaccine
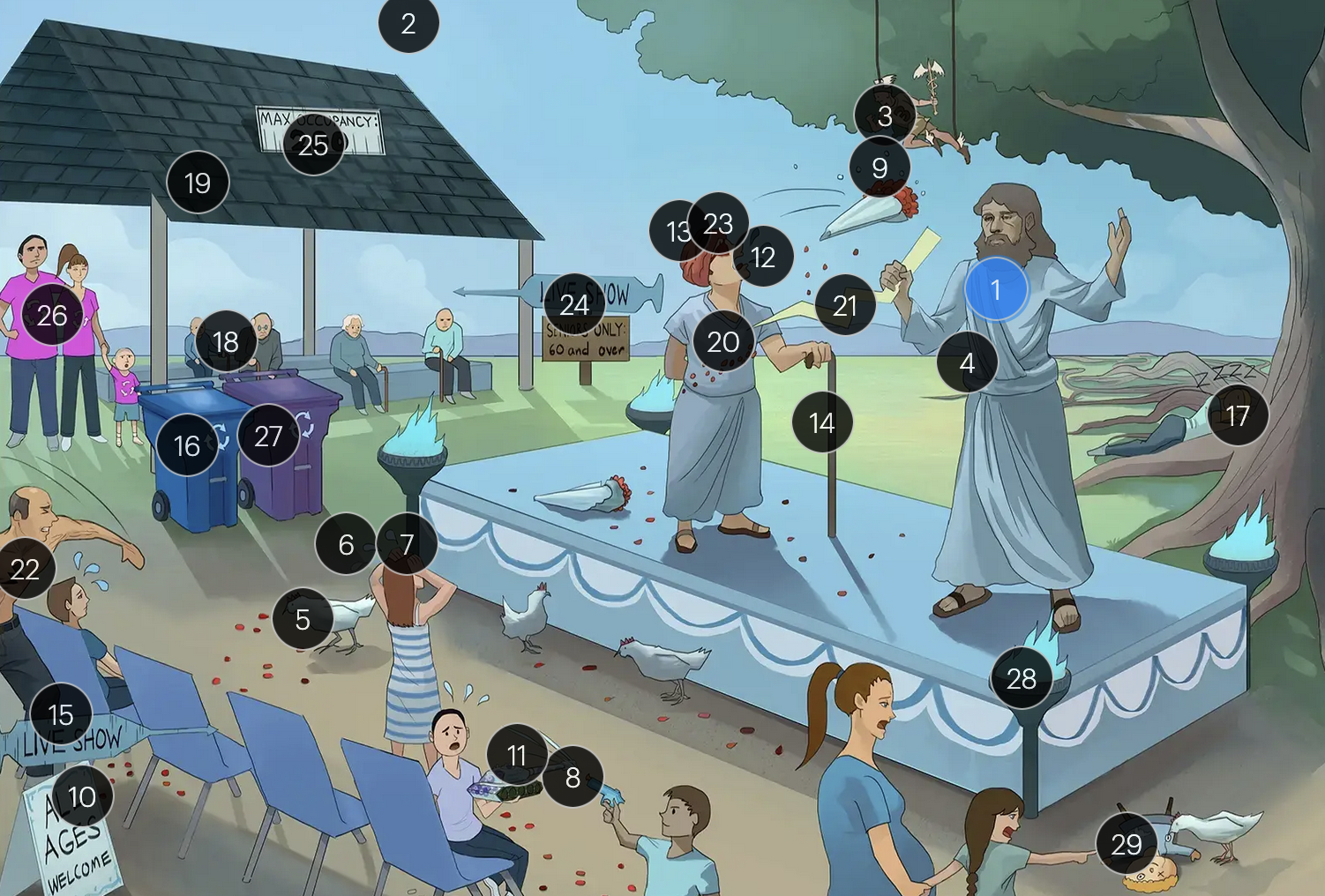
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
#26 Family’s recycling shirts
for VZV-induced shingles, both famciclovir and valacyclovir serve as effective therapeutic options
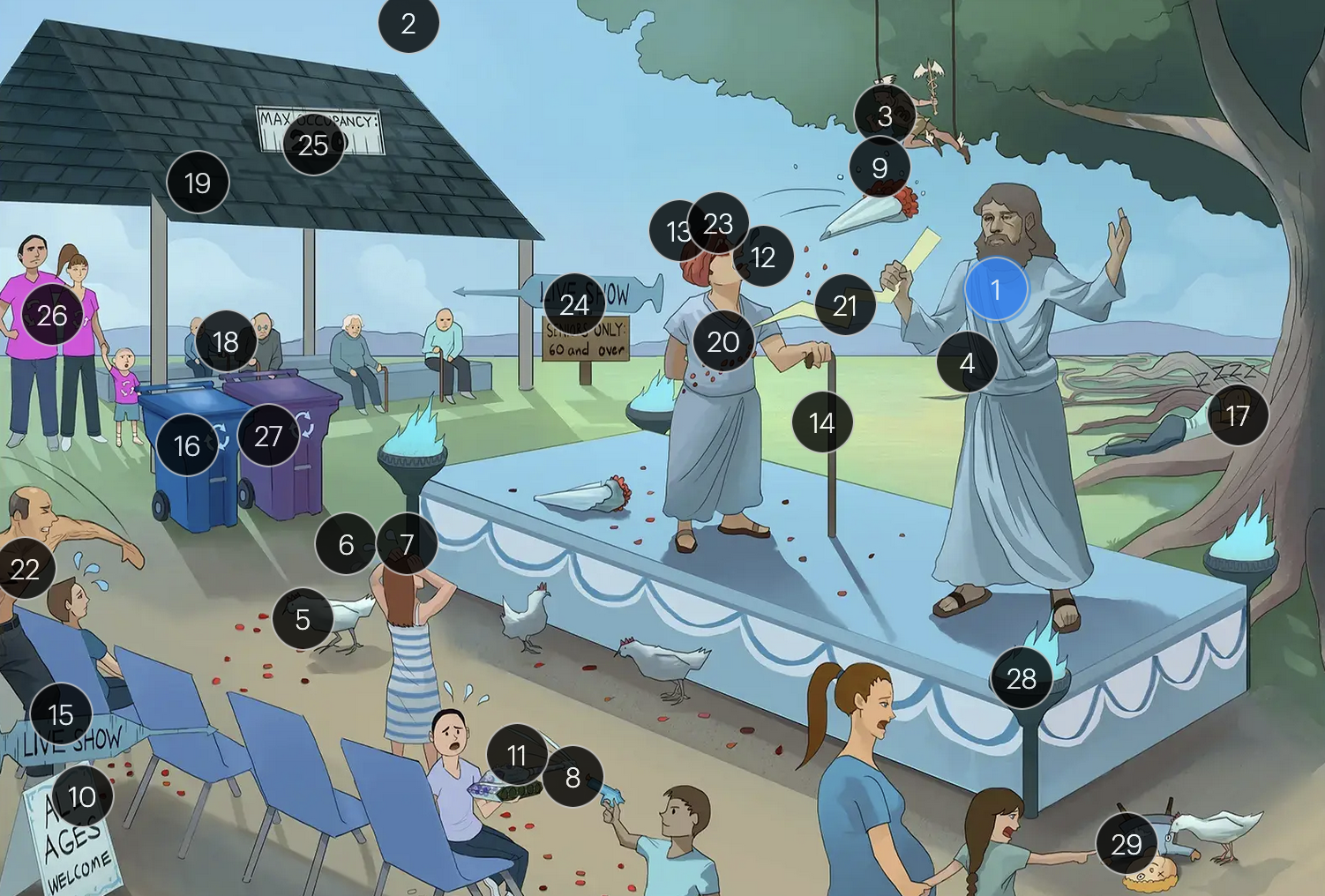
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
#27 violet recycling bin
for VZV-induced shingles, both famciclovir and valacyclovir serve as effective therapeutic options
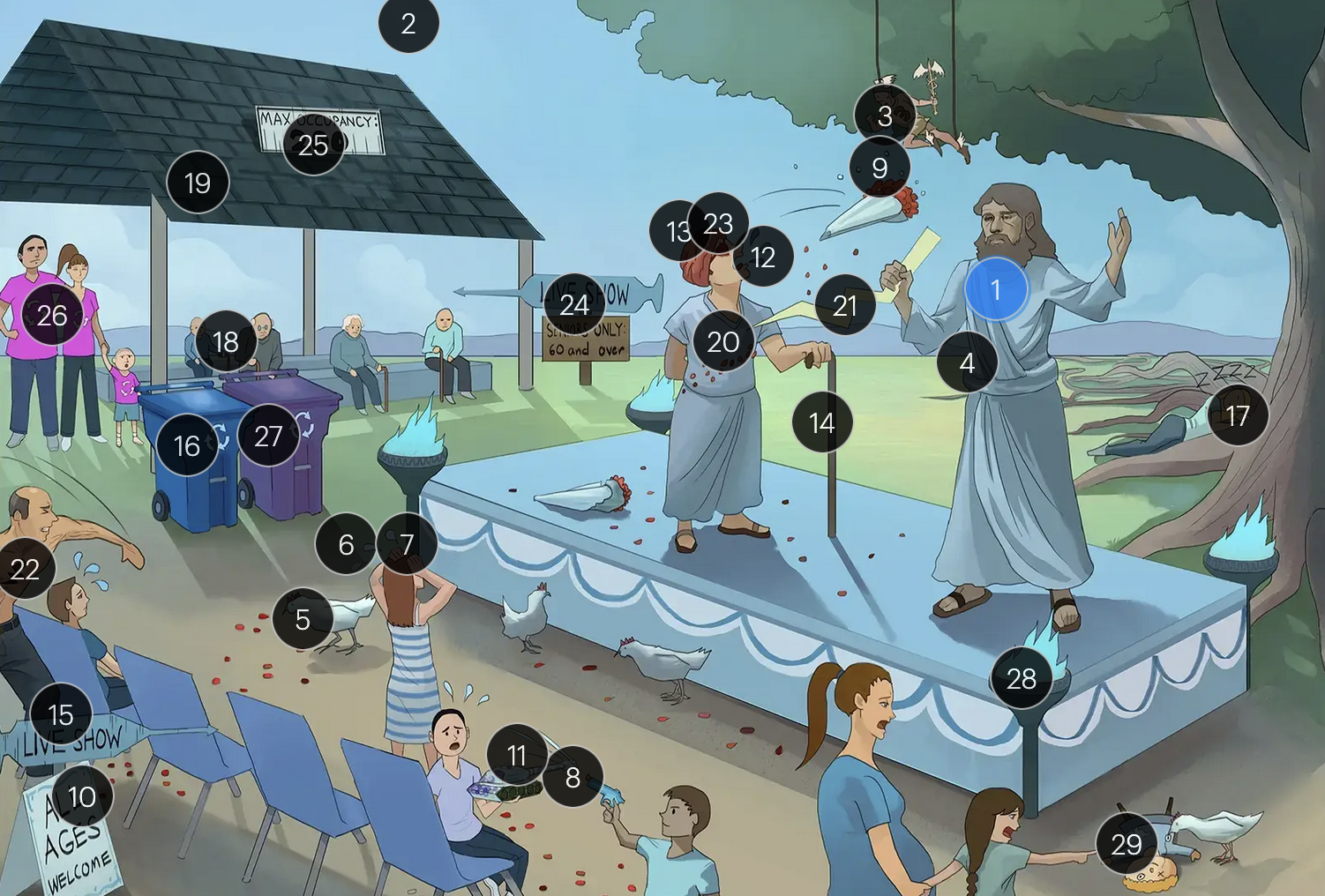
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
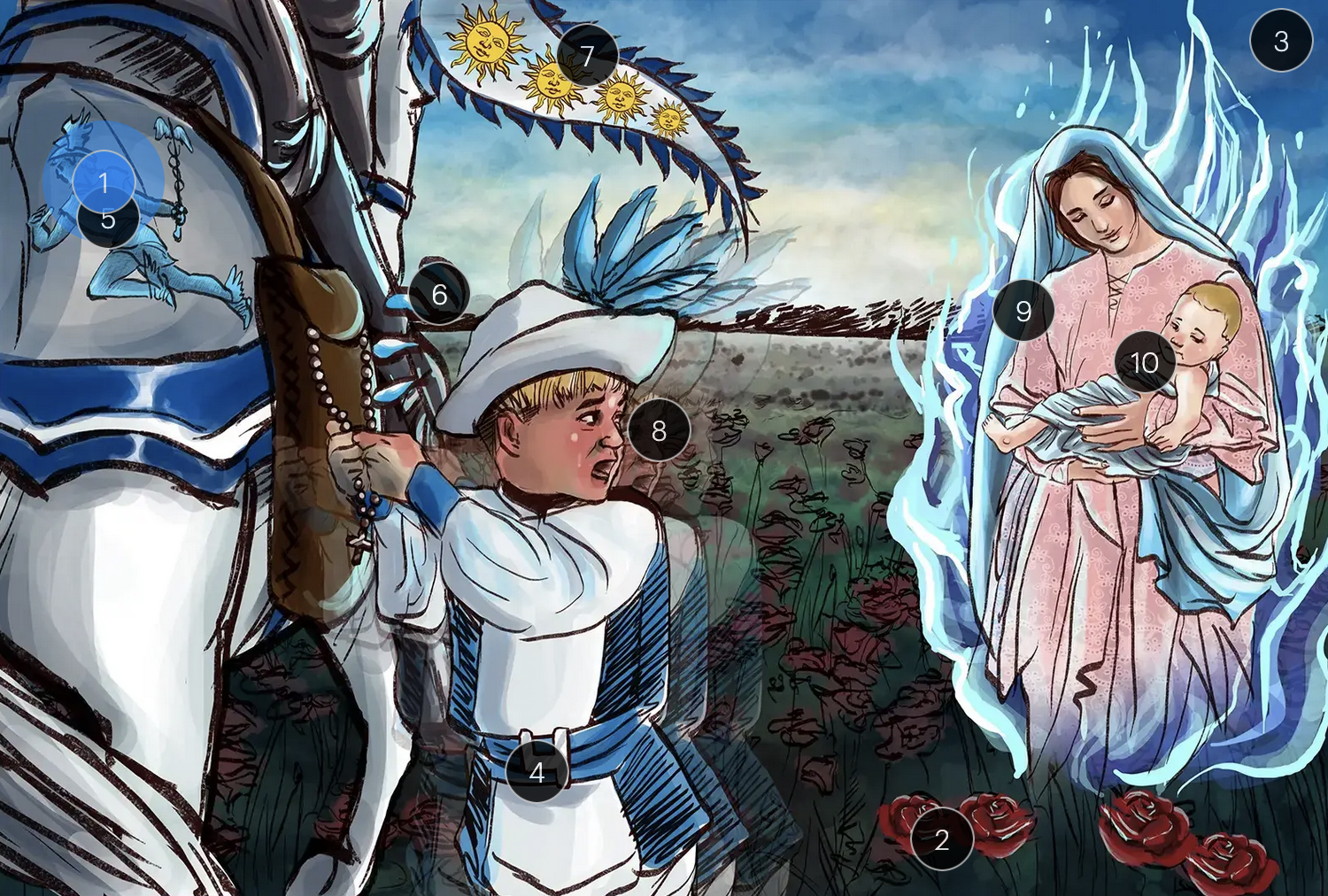
#28 torches
VZV can transmit from mother to fetus and is categorized under the “other” (O) segment of the TORCHeS infections
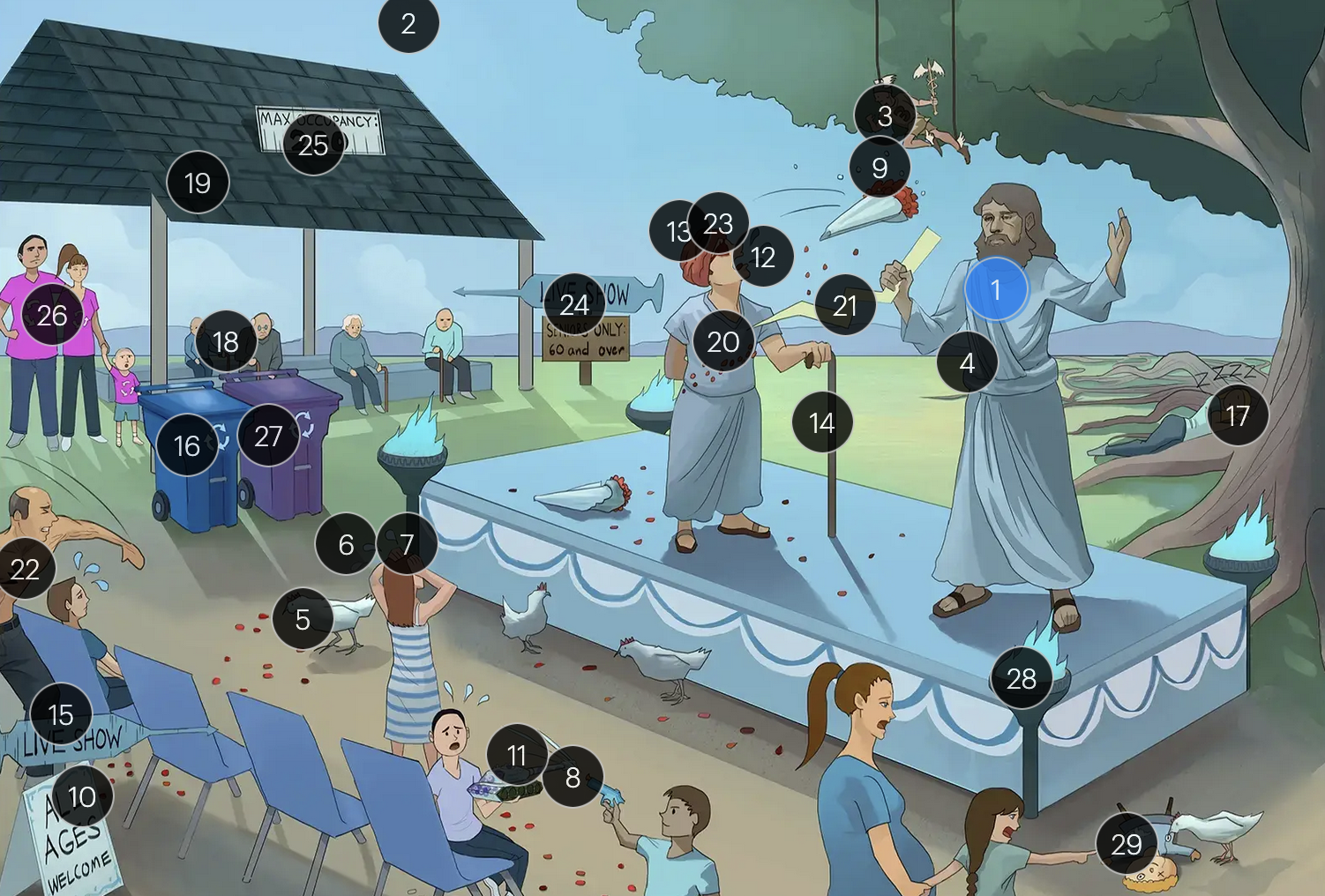
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Herpesviridae)
#29 torn seams + plucked eye + stubby limbs
exposure to VZV during early pregnancy can precipitate congenital varicella syndrome, marked by skin scarring in dermatomal patterns, visual impairment, and underdeveloped limbs
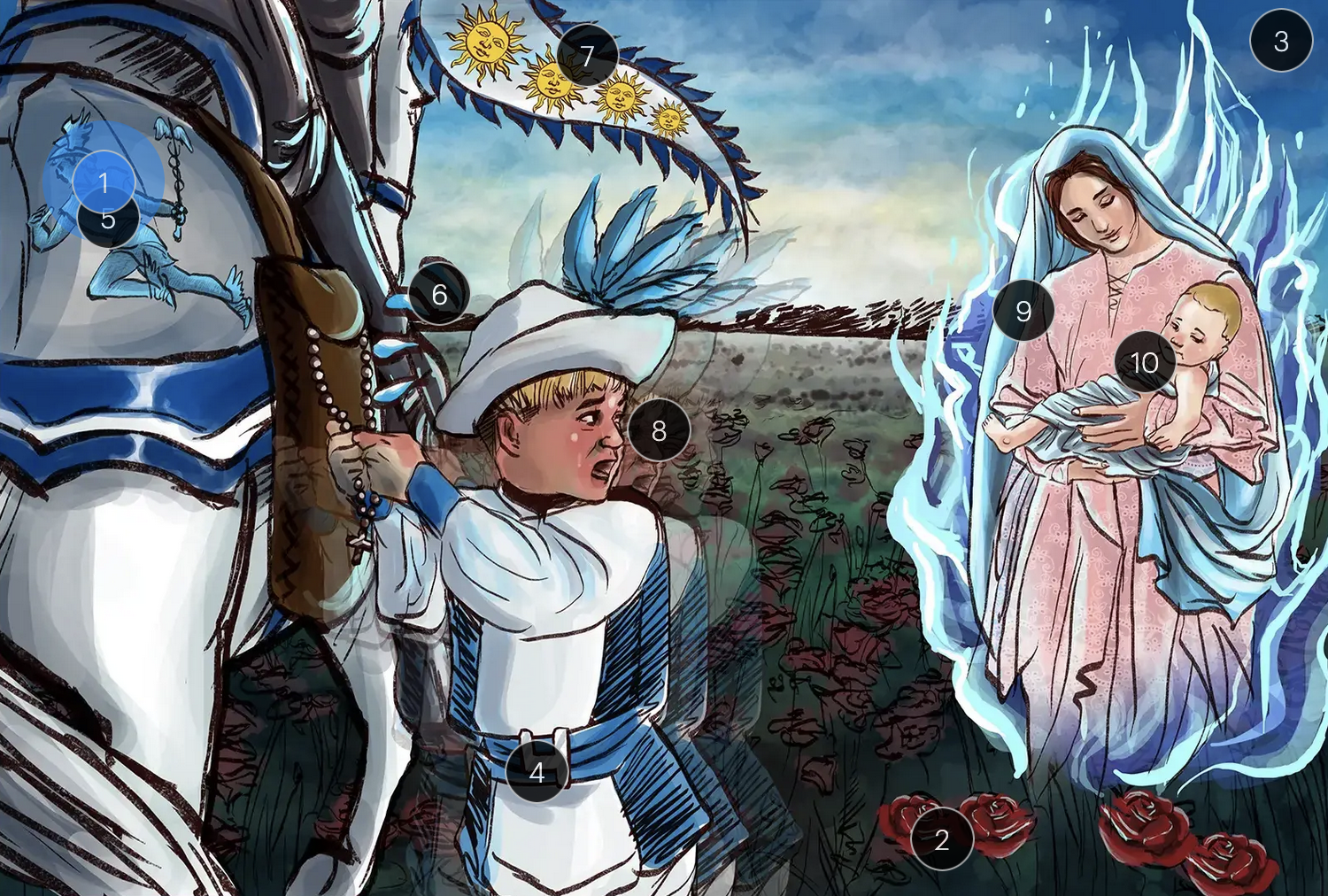

HHV-6 & Roaseola (Herpesviridae)
#1 “6” on Hermes
Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6; a DNA virus in the Herpesviridae family)

HHV-6 & Roaseola (Herpesviridae)
#2 roses
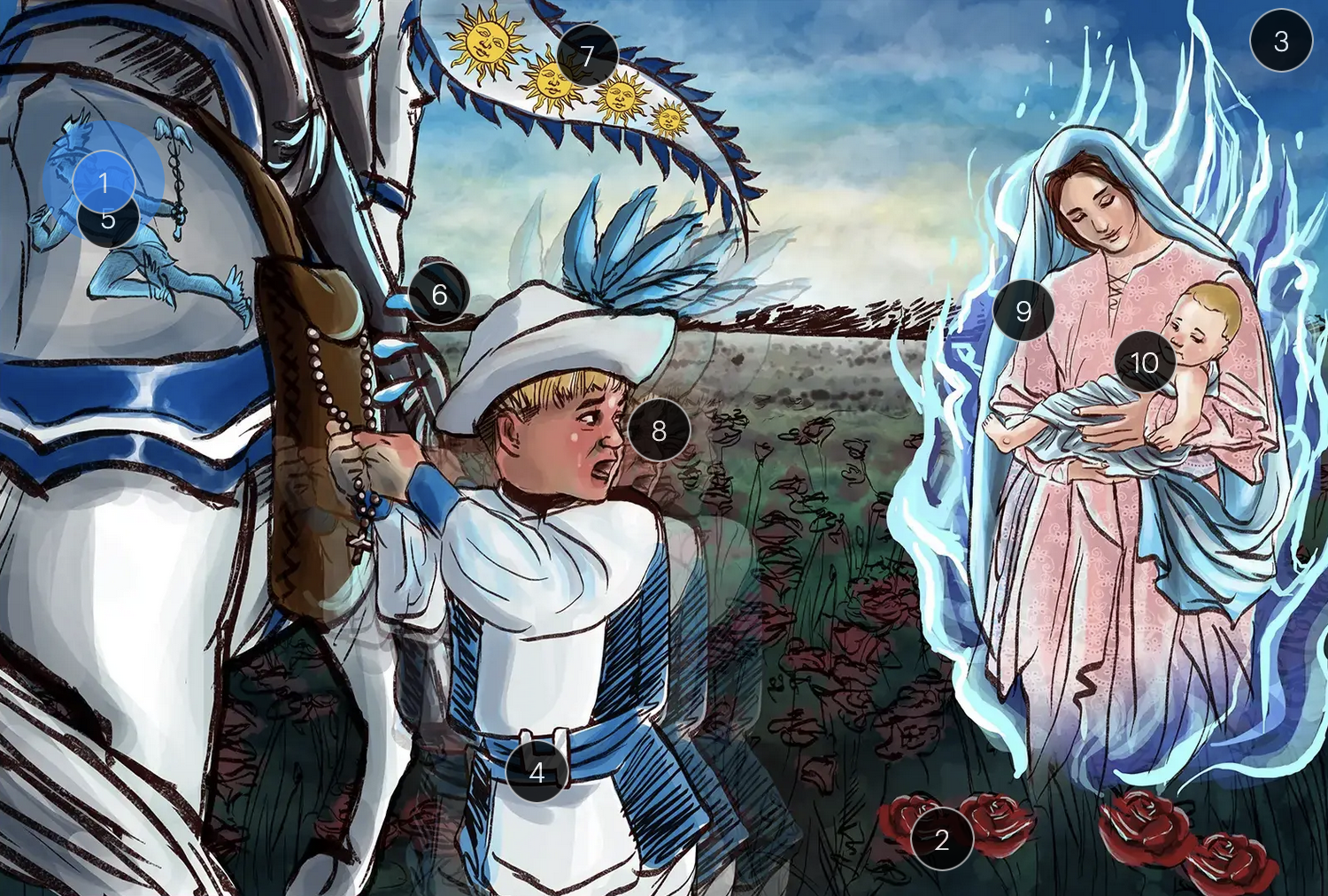
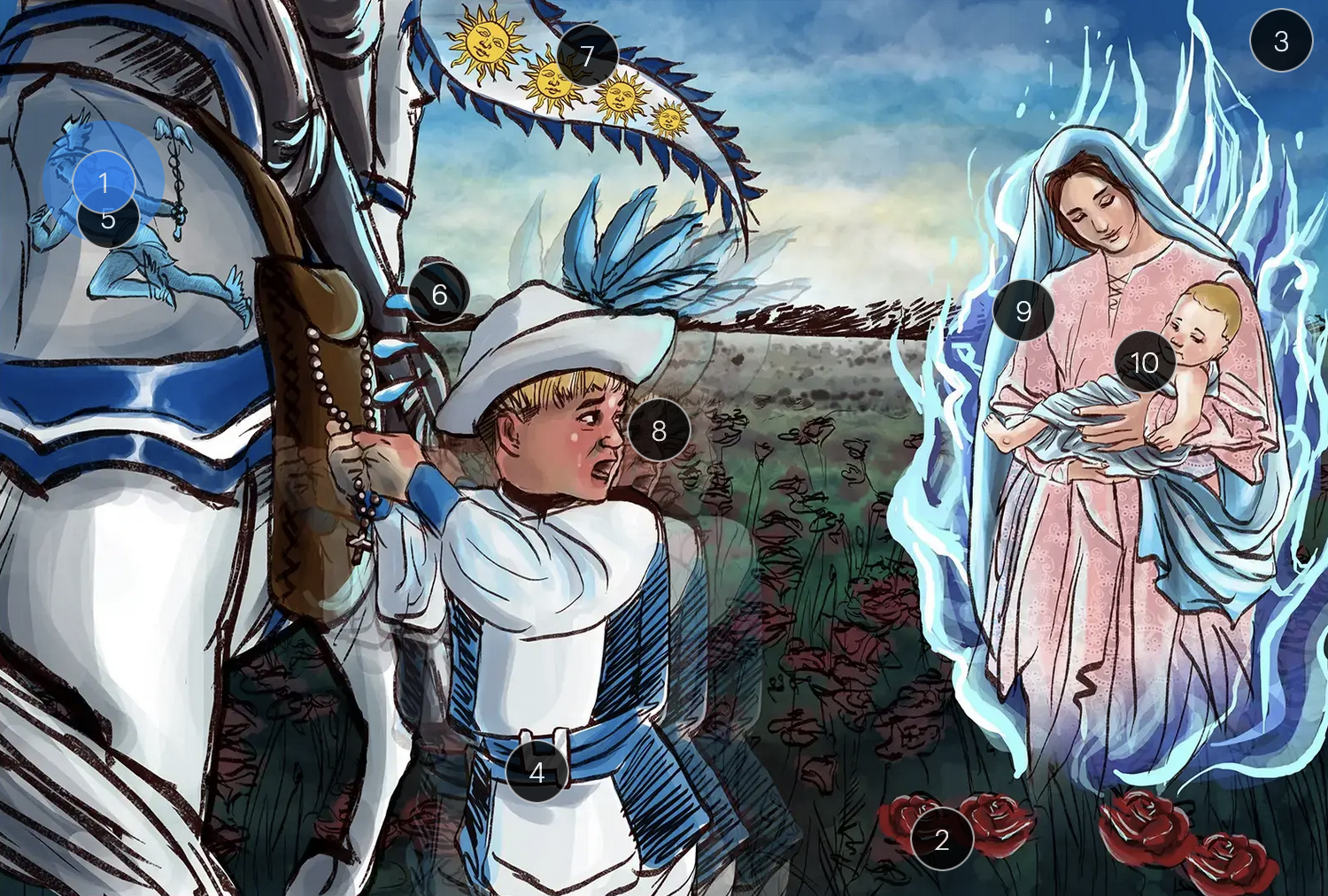
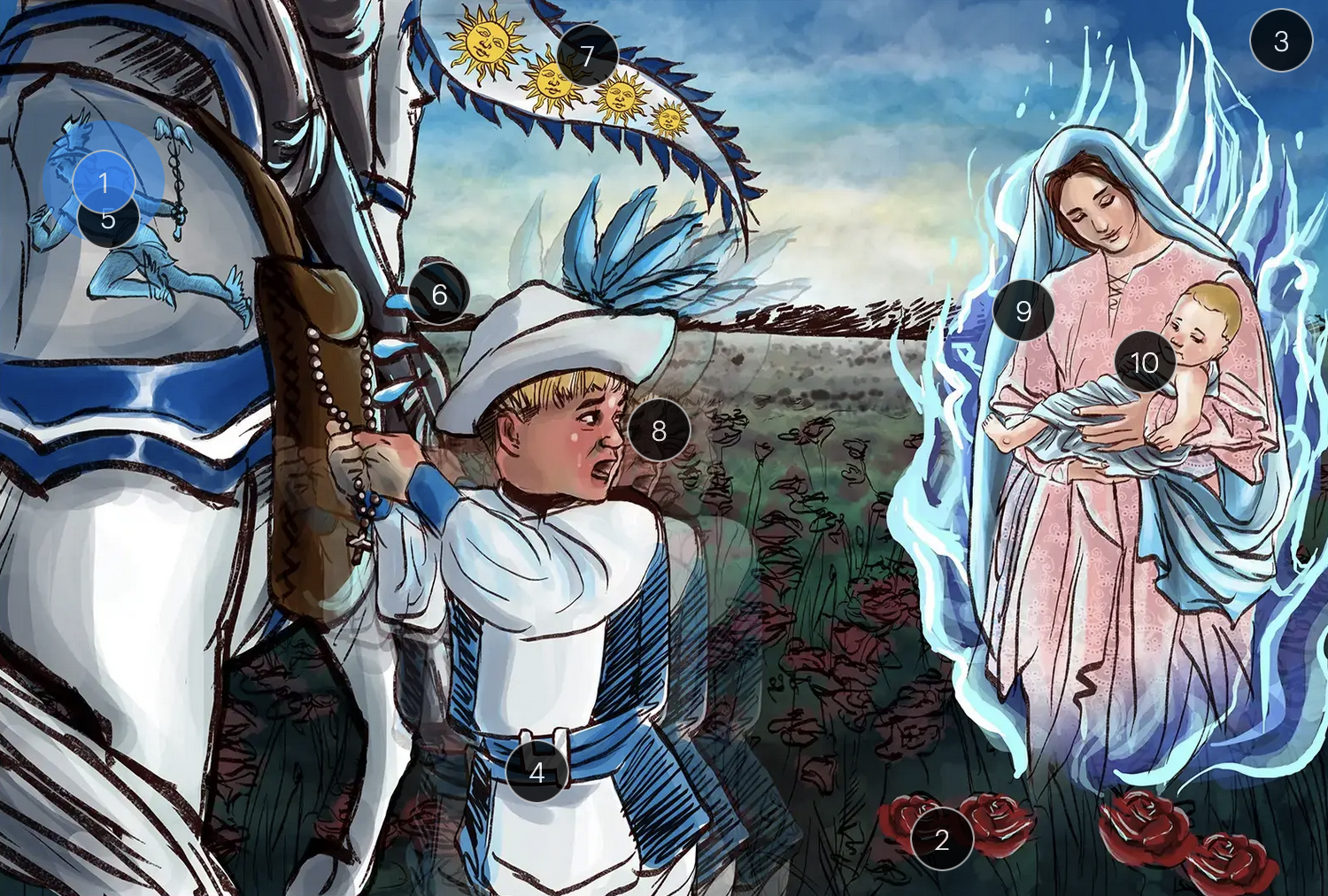
roseola, also known as the sixth disease or exanthem subitum, is primarily caused by HHV6
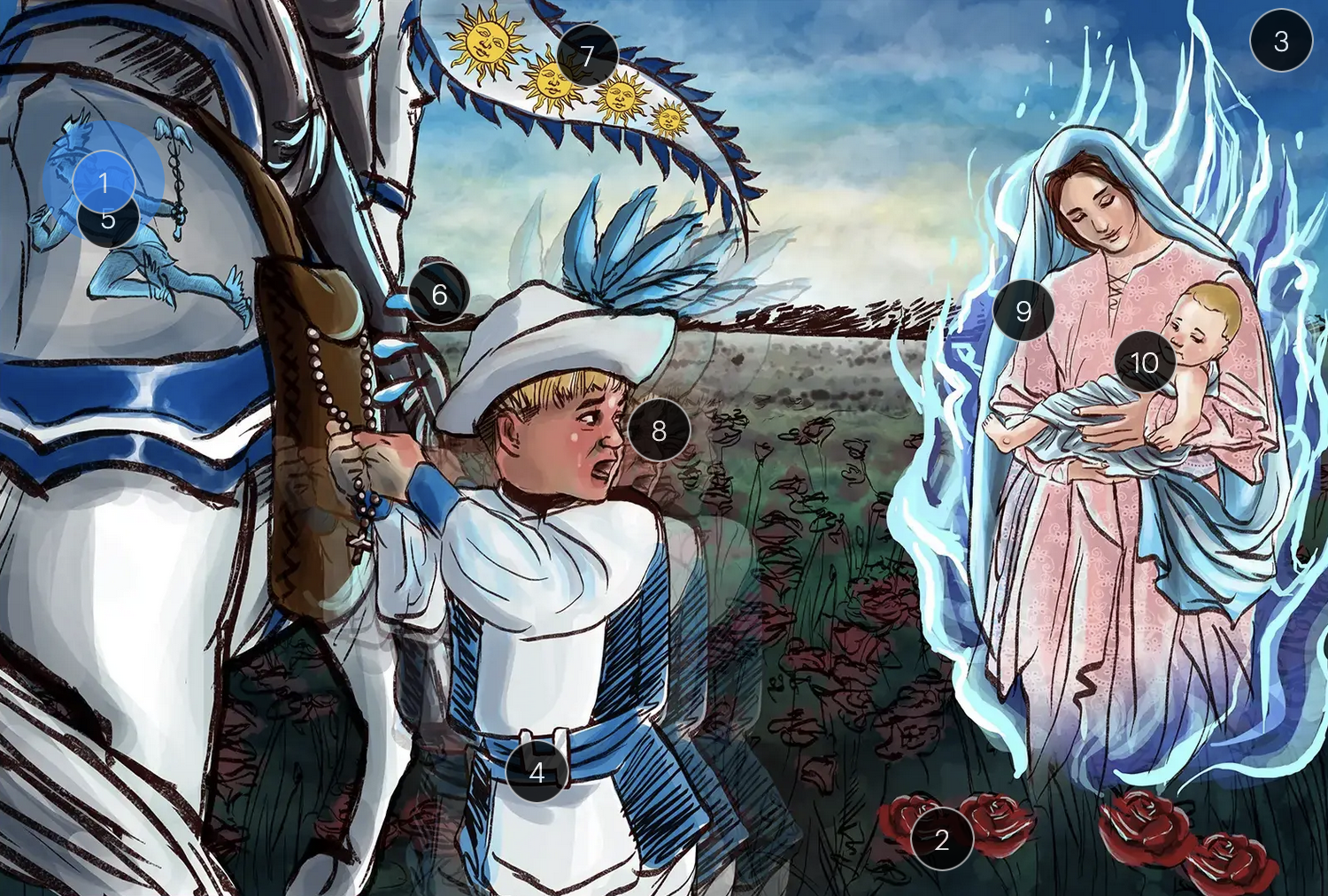

HHV-6 & Roaseola (Herpesviridae)
#3 cool colors
HHV-6 is a DNA virus

HHV-6 & Roaseola (Herpesviridae)
#4 helper squire
HHV6 primarily targets CD4+ helper T-cells, which may result in immunosuppresion

HHV-6 & Roaseola (Herpesviridae)
#5 hermes
HHV6 is part of the Herpesviridae family

HHV-6 & Roaseola (Herpesviridae)
#6 sweat
the fever associated with roseola typically lasts around 4 days (but can vary in duration)