Disordered Brain Exam 2 - CS Anatomy
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is the Corticostriatal Circuit important for?
Motivation - need, want, like
Action - how to achieve goals
Learning - predicts/works
What is liking defined as?
The actual pleasure component of a reward
What is wanting defined as?
Motivation for reward
What is learning defined as?
Associations, representations, and predictions about future rewards depending on past experiences
What is the hub of the Corticostriatal Circuit? What is it metaphorically?
Ventral Striatum, a gate that can open and close for reward
What is associated with the extended amygdala and is an output road from the Ventral Striatum? What is it associated with?
Ventral pallidum, important for pleasure feeling
Describe the primary pathway starting from the VS:
VS —> Ventral Pallidum —> Thalamus —> PFC —> Motivated behavior
Describe the secondary pathway starting from the VS:
VS —> Dorsal Striatum/Pallidum —> Thalamus —> Motor cortices —> movement
What are the inputs to the VS? What do each input give to the VS?
PFC gives goal-directed planning
BLC of amygdala gives sensory cues
Hippocampal formation gives contextual memory
Where is the striatum located on brain? What are the structures that are part of Dorsal Striatum? Ventral Striatum?
Middle, looks like ring thingie, that loops inward to a oval.
Dorsal = Caudate and Putamen, caudate being more upward and medial, putamen being more downward and lateral.
Ventral = Nucleus Accumbens
What is the caudate related to? What is the putamen related to?
Caudate —> dlPFC (executive loop)
Putamen —> Motor cortices (motor)
What is the executive loop? Structures/function?
Caudate —> dlPFC via thalamus and ventral pallidum. Function is for goal planning, goal maintenance, adapting to get reward.
What is the motor loop? Structures/function?
Putamen —> Motor cortex. Function is for the action-related steps and planning actions (actions physically wise, so more specific than executive loop)
What is the motivational loop? Structures/function?
NAcc —> vmPFC and OFC. OFC is related to subjective evaluation of events. Function is desire (motivation to pursue reward)
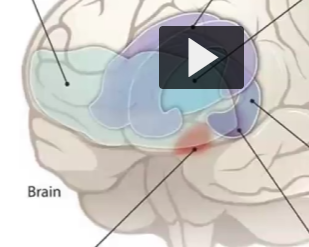
Label the structures in the image
Frontal/light green area = PFC
Purple (above the striatum) = Cingulate gyrus
Blue = Thalamus
Red = NAcc
Two to the right of red in order: Amygdala, then HPC
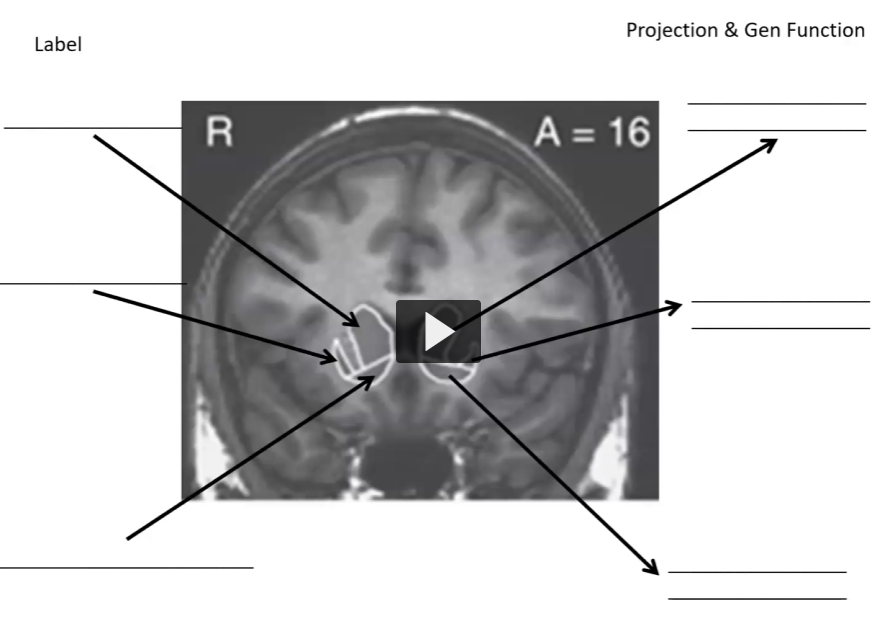
Label
Do on iPad
What is the role of the thalamus in the CS circuit?
Serves as hub for relay of info between PFC and striatum, and is a sensory relay that connects brain regions to info from outside world (via amygdala)
Explain the differences between ventral and dorsal pallidum? What do they project to and from, how?
Ventral pallidum: From VS to PFC, conveys motivation. ALSO excites opioid secretion for liking/pleasure
Dorsal pallidum: From DS to Motor cortices, motivating action
All of these is through thalamic nuclei
Where is amygdala located? Role in CS circuit?
Right in front of the lowest point of the Striatum. Role is that the BLC connects to VS by introducing multimodal sensory info, allowing for learning cues in environment to predict satisfaction
Explain how optogenetics showed BLC to VS relation?
Use EYFP and ChR2… when you inhibit the BLC to VS neurons by using halo rhodopsin, there is no conditioning and sugar intake goes down (no learning occurs!)
Where is the HPC located? Role in CS circuit?
Right behind amygdala. Important for contextualization, of learning context for which specific action satisfies specific motivation.
How does sensory info get to VS? How does context go to VS? How does PFC regulation go to VS?
Sensory = BLC of amygdala
Context = HPC
PFC regulation = Thalamus and ventral pallidum
Where is the hypothalamus located? Role?
Right below the thalamus, it secretes hormones to regulate food and sex
What parts of the PFC are important for CS circuit?
vmPFC and OFC, which is p hard to differentiate. ACC and dlPFC too.
What does the mPFC do?
Integrates bottom-up and top-down processing
What does vmPFC do for you?
Translates projections into subjective evaluations of pleasure, and allows you to be aware of hungry/wants, stomach growling, contextual info, and projects to the dlPFC
What does dlPFC do for you?
Form complex plans for satisfaction and communicates this info to the VS via the vmPFC, putting plans into action by utilizing motor pathway (VS to DS to motor)
What does the dorsal ACC do?
Monitors conflict between expectations and actual outcomes, correcting actions to achieve desired effects and monitors effectiveness of our actions
What is dopamine metaphorically?
The key to the gate that is the VS.
What can override the VS gate?
Threat! (amygdala, CL circuit)
Where is midbrain? What does it do?
Midbrain is like middle of brain kind of like brainstemmy ish. It consists of VTA and substantia nigra, containing many dopamine neurons.
VTA role? Substantia Nigra role?
VTA: neurons that synthesize dopamine and release it to the VS and PFC
Substantia nigra: Dopaminergic neurons that project to the DS and DP to release dopamine and regulate motor output!
What does dopamine do? How does its release occur in response to prediction and reward occurance?
Strengthens pairings, and results in learning. Its about response to cue vs. reward.
At first, dopamine is released when you get the reward. Over time/learning, when you predict it, the dopamine is released earlier (during the prediction part). If no reward, there is a dopamine dip.
Generally, goal directed movement is ______________ by contextual info and emotional significance of stimuli. AKA the gate is _______________. Dopamine ___________________.
limited, gate is closed. But with dopamine, gate opens and leads to behaviors for achieving goals!
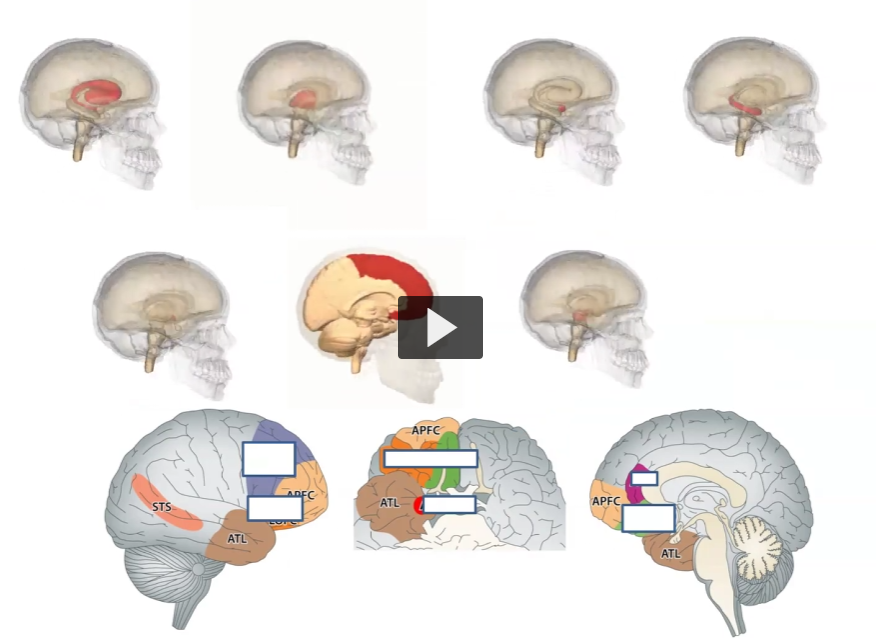
Label the stuff here!
Striatum
Thalamus
Amygdala
Hippocampus
Hypothalamus
PFC
Midbrain
dlPFC on top, OFC on bottom
OFC on top, Amygdala on bottom
ACC on top, OFC on bottom
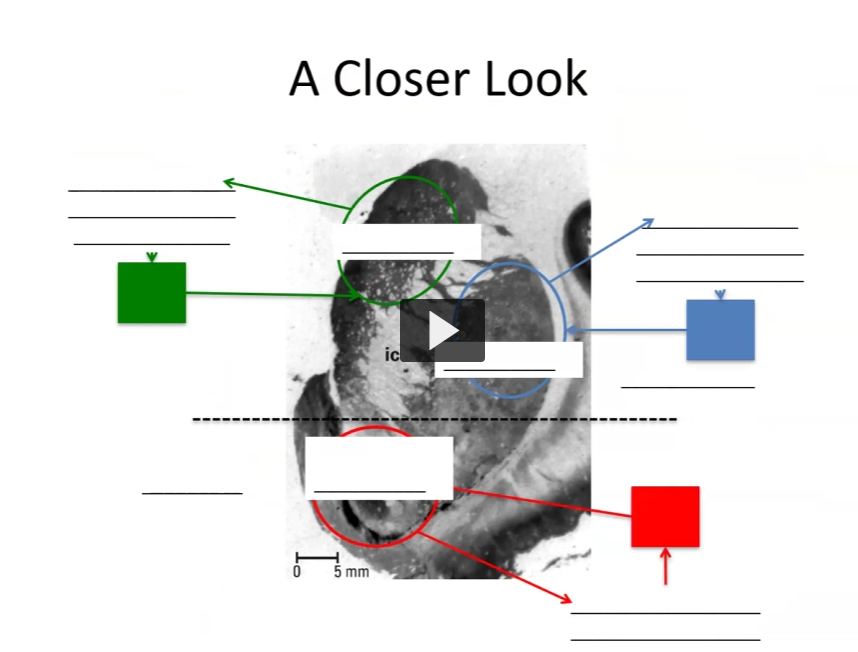
Label + explain.
What is our gate, keymaster, gatemaster?
gate = VS
keymaster = dopamine
gatemaster = amygdala