Unit 4: Systems of Particles and Linear Momentum
4.0(2)Studied by 91 people
0%Unit 4: Systems of Particles and Linear Momentum Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/7
Last updated 5:28 AM on 4/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
1
New cards
center of mass
The point in an object where all the mass is concentrated and the object can be balanced. It is also the point where an external force can be applied to cause translational motion without causing any rotational motion.
2
New cards
Center of Gravity
The point where the entire weight of an object can be considered to be concentrated
3
New cards
Center of Mass
The point where the mass of an object is concentrated, taking into account the distribution of its mass. It is the balance point where an object can be supported without any rotation.
4
New cards
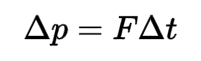
Impulse
A force that causes a change in an object's motion. It is equal to the change in momentum of the object over time.
5
New cards
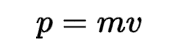
Momentum
The product of an object's mass and velocity. It describes the amount of motion an object has and is conserved in a closed system unless acted upon by an external force.
6
New cards
Linear momentum
The product of an object's mass and velocity, which determines the amount of motion it possesses in a straight line.
7
New cards
Conservation of Linear Momentum
The principle that states that the total momentum of an isolated system remains constant unless acted upon by an external force.
8
New cards
Collisions
It occurs when two or more objects come into contact with each other, resulting in a change in motion or deformation of the objects involved. It can be elastic or inelastic, and can be analyzed using the principles of conservation of momentum and energy.