STEPS IN AMALGAM MANIPULATION, CONDENSATION, & CARVING
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
1. Achieve workable mass within min. time
2. Remove oxides from powder particle surface
3. Pulverized pellet particles that can easily attached to mercury
4. Reduce particle size to increase surface area of alloy particles
5. Dissolve part of particles in mercury
Objectives of Trituration Process TRITURATION
homogenous mass
reflective surface
flattens slightly
table top
topic: TRITURATION
A properly triturated amalgam is a _ with slightly_. It _ if dropped on a _.
Achieve workable mass
TOPIC: Objectives of Trituration Process TRITURATION
_within min. time
Dissolve part of particles
TOPIC: Objectives of Trituration Process TRITURATION
_ in mercury
Reduce particle size
alloy particles
TOPIC: Objectives of Trituration Process TRITURATION
_ to increase surface area of_
Pulverized pellet particles
mercury
TOPIC: Objectives of Trituration Process TRITURATION
_ that can easily attached to _
oxideS
powder particle
TOPIC: Objectives of Trituration Process TRITURATION
RemovE_s from_ surface
A properly triturated amalgam is a homogenous mass with slightly reflective surface. It flattens slightly if dropped on a table top.
tRITURATION?
Continuation of trituration, this step is used to improve the homogenous consistency of the mass and assure consistent mix. (2 5 secs).
2. MULLING
improve
homogenous consistency,
mass
consistent mix
TOPIC:
continuation of trituration, this step is used to i_ the _of the_ and assure consistent mix. (2 5 secs).
Operator should have a mental image of preparation before condensing amalgam to aid in locating cavosurface margins during carving procedure.
MATRICING (for Class II cavities)
mental image, preparation, condensing amalgam
Topic: 3. MATRICING (for Class II cavities)
Operator should have a _ of_ before _to aid in locating cavosurface margins during carving procedure.
locating cavosurface margins
Carving procedure
Topic: 3. MATRICING (for Class II cavities)
Operator should have a mental image of preparation before condensing amalgam to aid in _ during _
Squeezes unreacted mercury out of the increments building up the restoration. (3 mins)
Amalgam should be inserted incrementally and condensed with overlapping strokes.
Tooth preparation should be _ to ensure _that is NOT _
4. CONDENSATION
unreacted mercury, increments, restoration
incrementally, condensedoverlapping strokes
Topic: Condensation
Squeezes _out of the _ building up the _. (3 mins)
Amalgam should be inserted_and_ with _.
overpacked
well-condensed marginal amalgam
mercury rich.
Topic: Condensation
Tooth preparation should be _ to ensure _that is NOT _
light stroke,amalgam surface , occlusal, conspicuous portions
burnishing, large burnisher, condensation
Topic: BURNISHING OR SURFACING
After condensation the next procedure is burnishing using a_ proceeding from the _to the tooth surface on the _ AND OTHER_ OF the restorations.
Precarve_ with _ is a form of _
After condensation the next procedure is burnishing using a light stroke proceeding from the amalgam surface to the tooth surface on the occlusal and other conspicuous portions of the restorations.
Precarve burnishing with large burnisher is a form of condensation
BURNISHING OR SURFACING
1.1. Reduce the size and no. of voids on critical & marginal areas of the amalgam
1.2. Bring excess mercury to be discarded during carving
1.3. Adapt amalgam to cavosurface margin
1.4. Conditions the surface before carving.
4 OBJECTIVES OF BURNISHING
voids, critical & marginal areas
discarded during carving
cavosurface margin
Conditions the surface
4 OBJECTIVES OF BURNISHING
1.1. Reduce the size and no. of _on _ of the amalgam
1.2. Bring excess mercury to be _
1.3. Adapt amalgam to _
1.4. _ before carving.
Anatomical sculpturing of amalgam material
Carver should rest partially on external tooth surface adjacent to margins to prevent overcarving.
Deep occlusal grooves invite chipping of amalgam at margins
Thin portions of amalgam left on external surfaces soon break away, giving the appearance that amalgam has grown out of preparation.
CARVING
Anatomical sculpturing
rest partially, external tooth surface,overcarving
occlusal grooves, chipping, margins
break away, appearance , grown out of preparation
_ of amalgam material
Carver should_ on _ adjacent to margins to prevent _.
Deep_ invite _ of amalgam at _
Thin portions of amalgam left on external surfaces soon _, giving the _that amalgam has_.
1.1. Produce restorations w/ no overhangs
1.2. Produce restorations w/ proper physiological contour
1.3. Produce restorations w/ functional non interfering occlusal anatomy
1.4. Produce restorations w/ adequate compatible marginal ridge
1.5. Produce restorations w/ minimal flash.
1.6. Produce restorations w/ proper size, location, extent & inter relationship of contact area.
1.7. Produce restorations w/o interfering w/ periodontium
1.8. Produce restorations w/ physiological compatible embrasure.
8 OBJECTIVES OF CARVING
“Noodles, Pancakes, Fries – Arvee Makes Perfect Instant Plates!”
flash beyond margins
Irregular
larger
preparation outline
Topic: Carving
Undercarved amalgam with _. Note that restoration outline is _ and _ than _
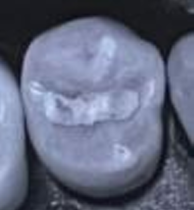
Correctly carved amalgam restoration
Topic: Carving
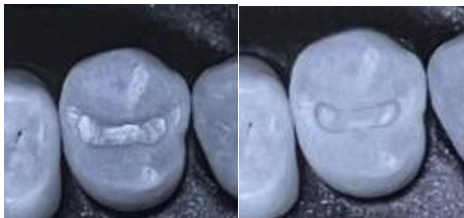
Heavy occlusal contacts
Articulating paper
dark areas
shiny centers
Topic: Carving
_ on new amalgam should be avoided. _ will mark heavy contacts as _ with _.
Heavy occlusal contacts on new amalgam should be avoided. Articulating paper will mark heavy contacts as dark areas with shiny centers.
Topic: Carving
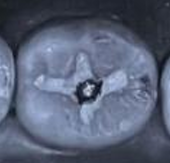
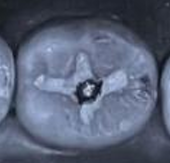
carved out of occlusion
light occlusal contact
contact
indicated by faint markings
Topic: Carving
Amalgam should not be_. Rather, it should have _ or _ as_.
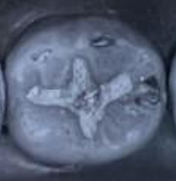
Amalgam should not be carved out of occlusion. Rather, it should have light occlusal contact or contacts as indicated by faint markings.
Topic: Carving
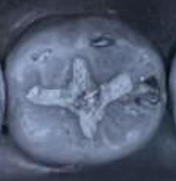
Amalgam flash that was left after carving is removed
Major overhangs are removed
Remove superficial scratches and irregularities.
POLISHING
o Stones or finishing burs, finishing disks
o Pumice, dentifrice, tin oxide
o Rubbercup
When necessary, use fine-grit alumina or carborundum stone to develop continuity of surface from tooth to restoration.
7. FINISHING AND POLISHING
flash, after carving, removed
Major overhangs
superficial scratches , irregularities
Topic: 7. FINISHING AND POLISHING
Amalgam _ that was left_ is _
_ are removed
Remove _and_.
o Stones or finishing burs, finishing disks
o Pumice, dentifrice, tin oxide
o Rubbercup
fine-grit alumina, carborundum stone
continuity of surface
restoration.
7. FINISHING AND POLISHING
POLISHING
When necessary, use _ or _ to develop _ from tooth to _
Use round finishing bur
topic: FINISHING AND POLISHING
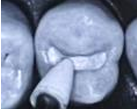
The stone’s or bur’s long axis is held at right angle to the margin
topic: FINISHING AND POLISHING
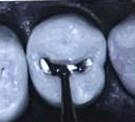
the stone’s or bur’s long axis is held at right angle to the margin
topic: FINISHING AND POLISHING
Initiate polishing with coarse, rubber abrasive point at low speed
topic: FINISHING AND POLISHING
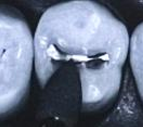
Point should produce smooth, satiny appearance.
topic: FINISHING AND POLISHING
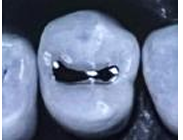
Obtain high polish with medium-grit and fine-girt abrasive
topic: FINISHING AND POLISHING
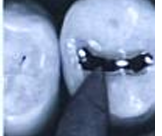
Polished restoration
topic: FINISHING AND POLISHING
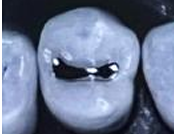
Use round finishing bur
The stone’s or bur’s long axis is held at right angle to the margin
Initiate polishing with coarse, rubber abrasive point at low speed
Point should produce smooth, satiny appearance.
Obtain high polish with medium-grit and fine-girt abrasive
Polished restoration
UITPOP