3. mandibular anesthesia part 1
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
largest branch of trigeminal nerve
V3
Exit via Foramen Ovale and enter the Infratemporal Fossa
Large sensory root
Skin on lower 3rd of the face, lower lip
Skin of temporal region
Mandibular dentition and gingiva
Anterior 2/3rd of the tongue (general sensation)
Small motor root: Muscles of mastication
Also carries nerves fibers from other nuclei:
Autonomic fibers for salivary glands (CN VII)
Special sensory taste fibers (CN VII)
V3
V3 exits (BLANK 1) and enter (BLANK 2)
blank1: foramen ovale blank 2: infratemporal fossa
V3 sensory to
Skin on lower 3rd of the face, lower lip
Skin of temporal region
Mandibular dentition and gingiva
Anterior 2/3rd of the tongue (general sensation)
V3 motor for
MOM
what two nerve fibers are carried via V3?
VII: chorda tympani taste an 2/3rd tongue + autonomic submand and sublingual glands via lingual sensation ant 2/3rd tongue
(and lesser petrosal postganglionic of CN IX via auriculotemporal parotid gland)
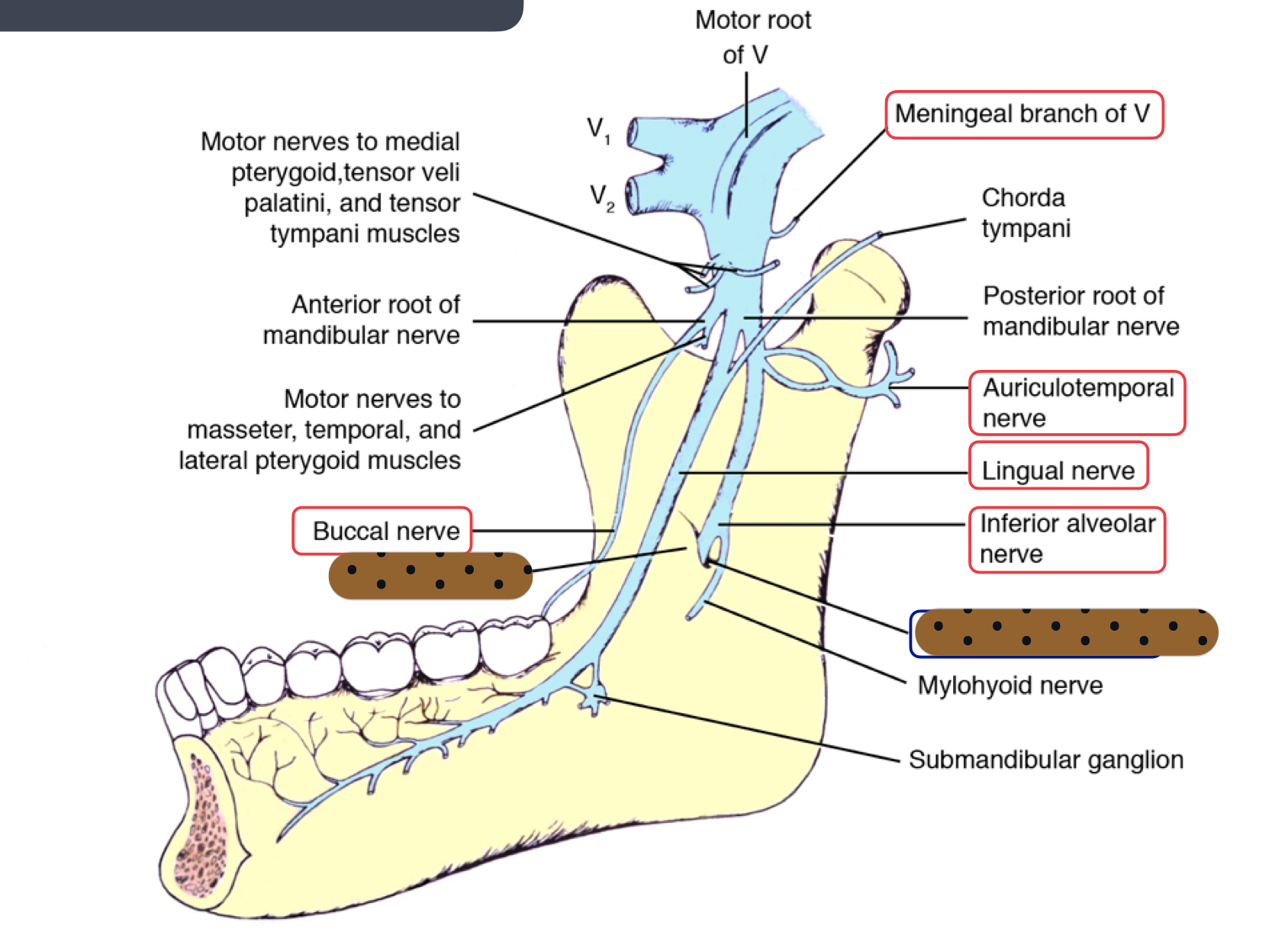
describe motor and sensory anterior division of V3
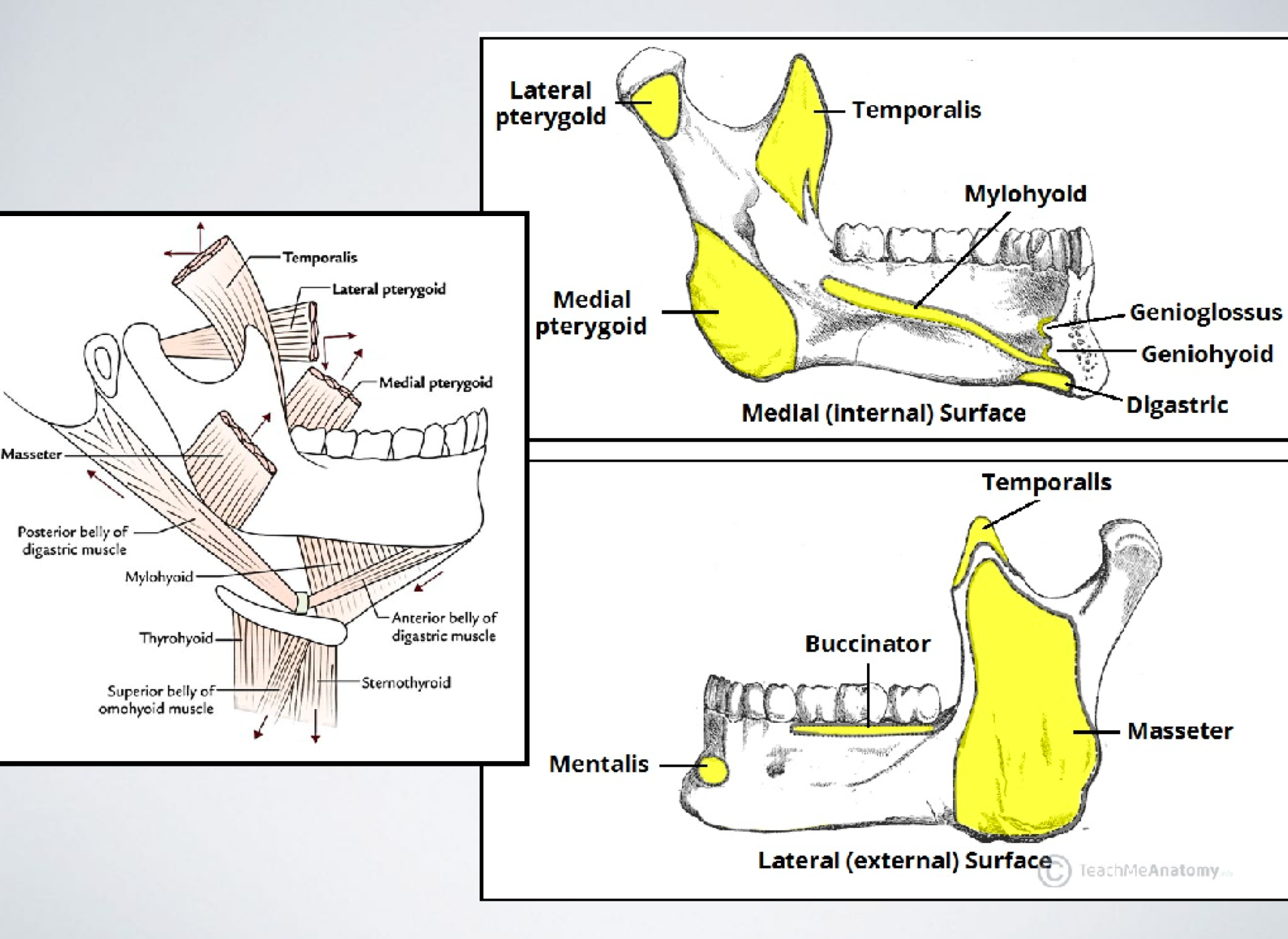
motor MOM: masseter, deep temporal, medial pterygoid, lateral pterygoid + sensory: long buccal
describe motor and sensory posterior division of V3
motor: mylohyoid sensory: auriculotemporal, lingual, IAN (mental and incisive), mylohyoid
which nerve is both motor and sensory and what division of V3?
mylohyoid posterior
which nerve innervates cheek, buccal mucosa, and gingiva of posterior mandible?
(long) buccal n
which nerve continues to floor of the mouth?
lingual
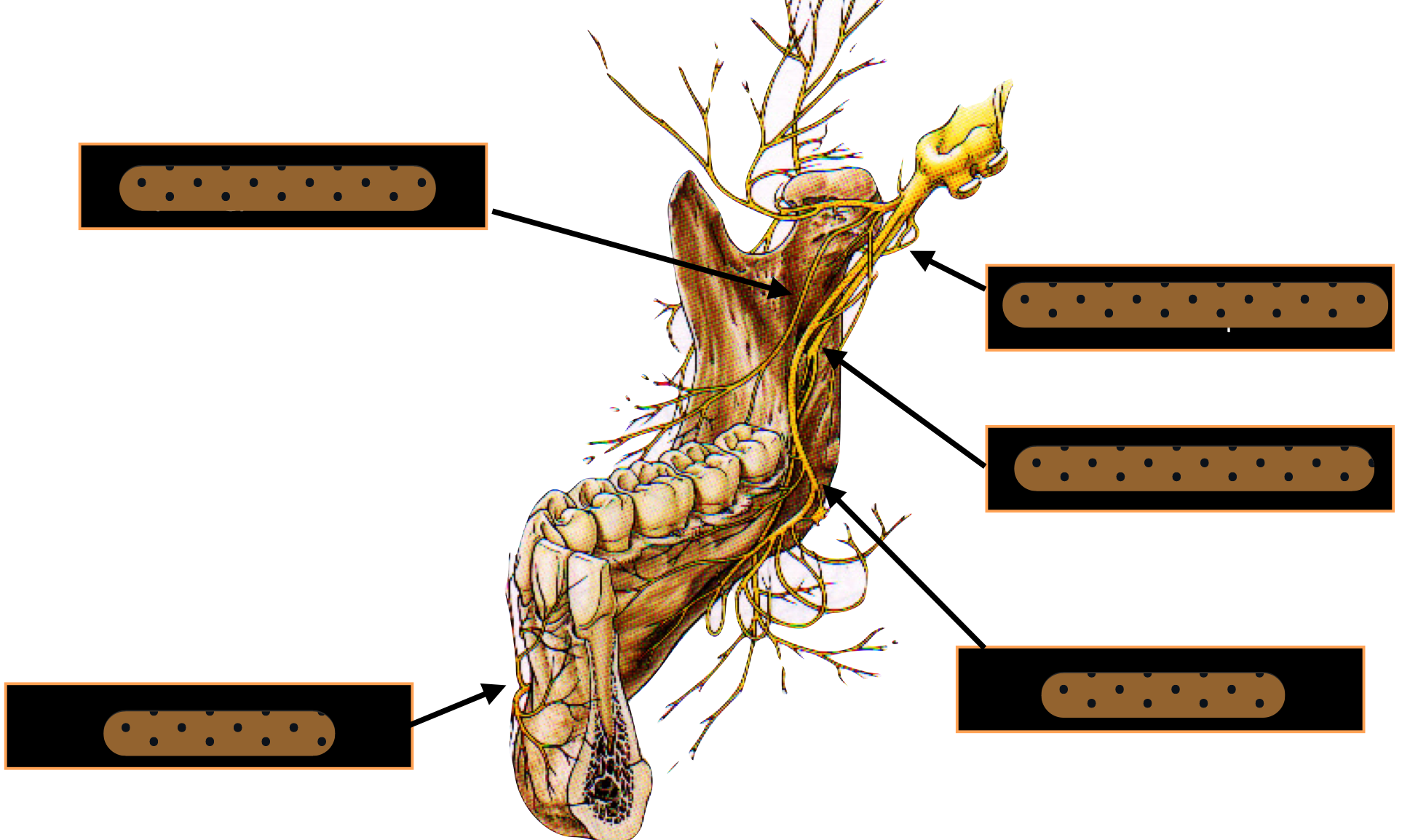
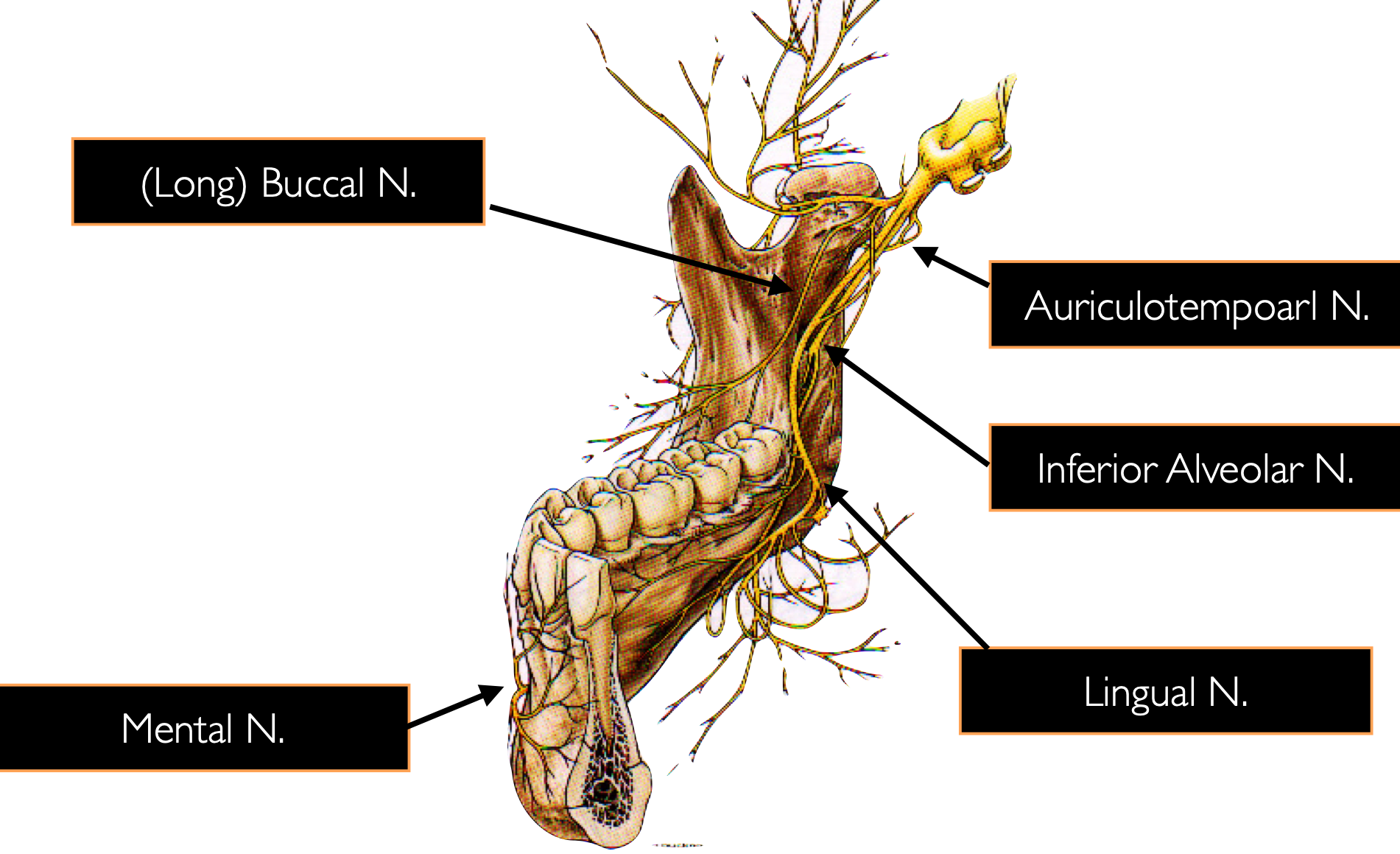
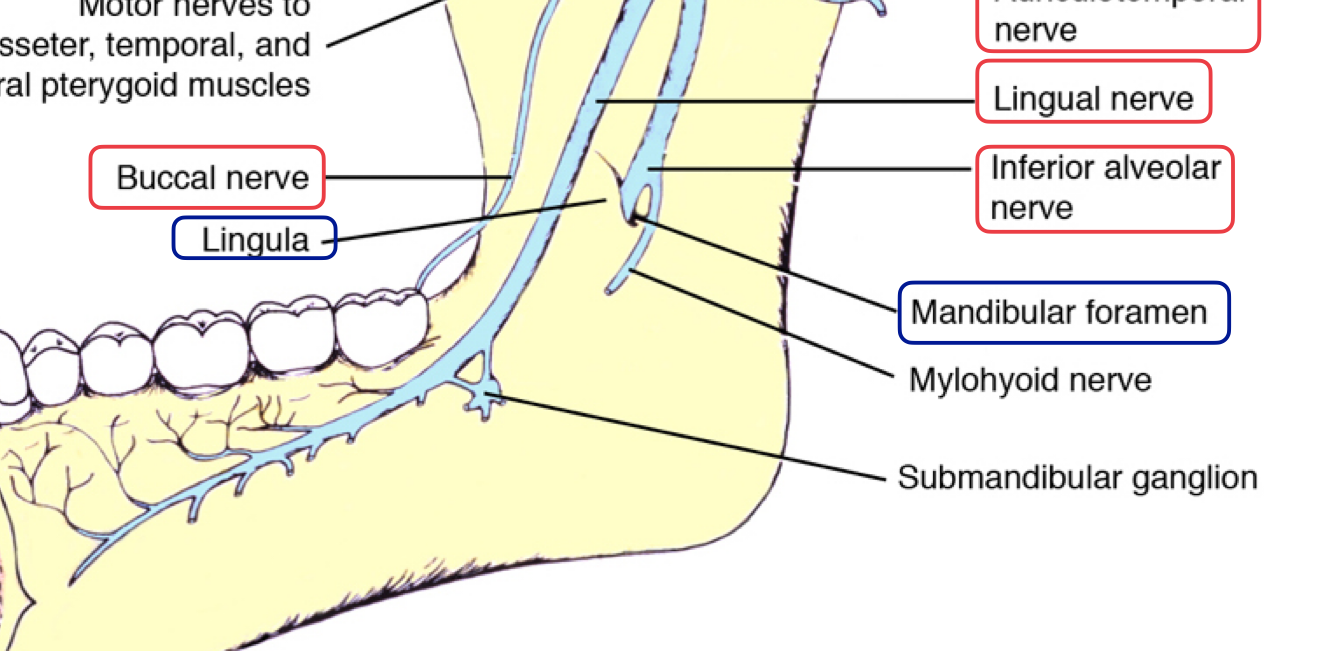
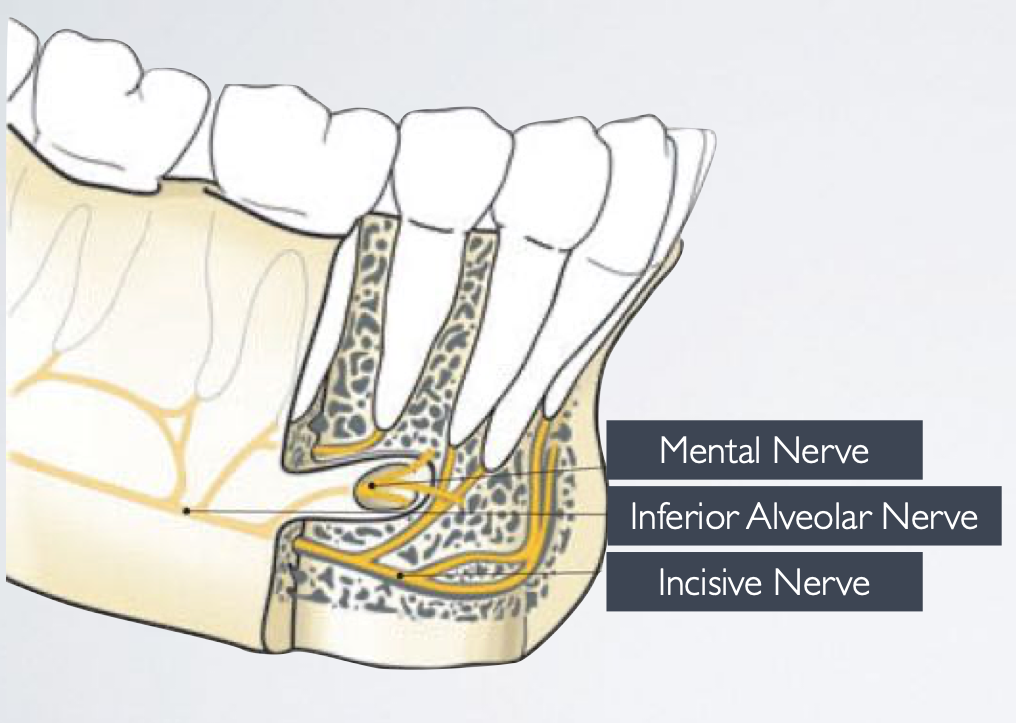
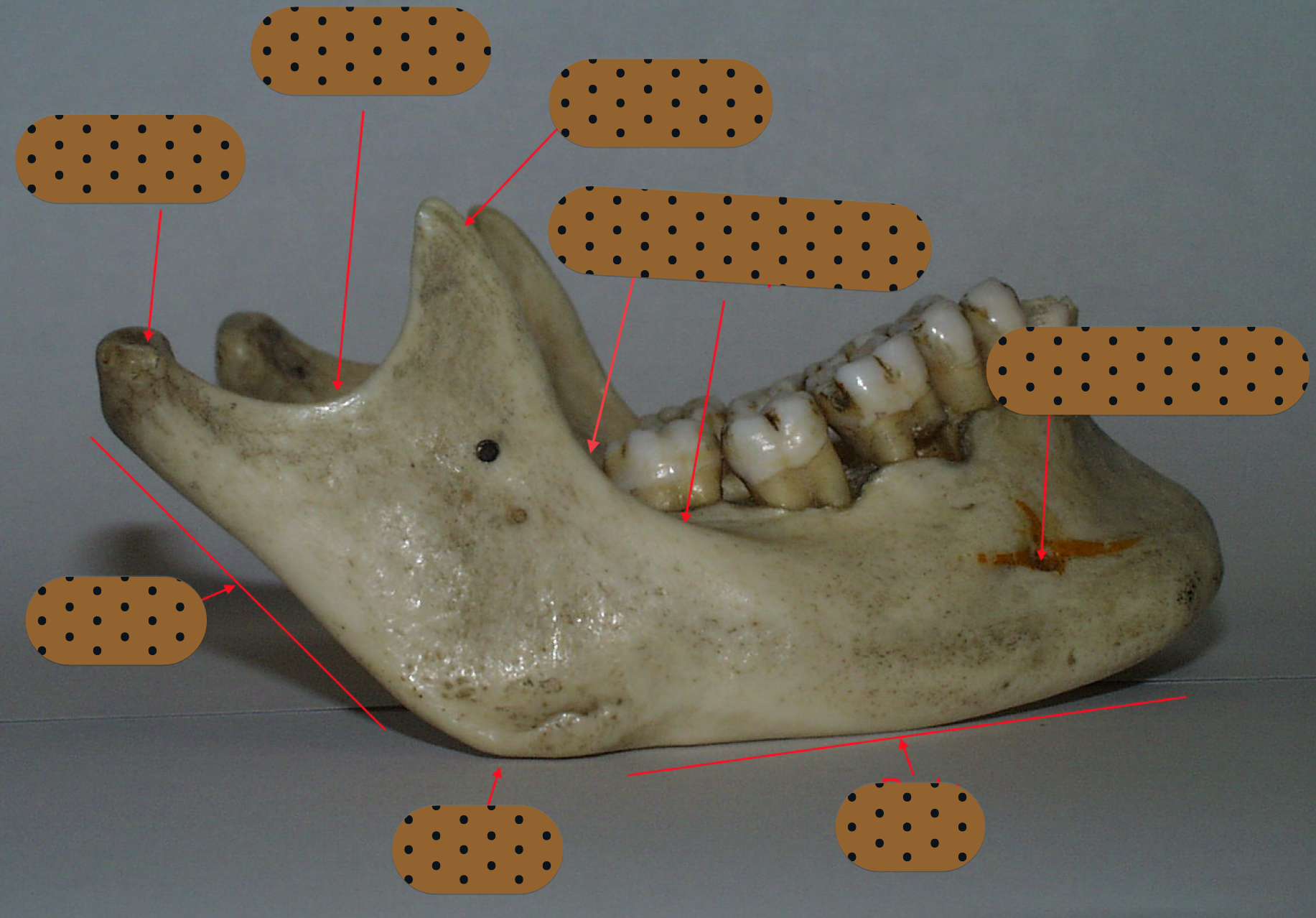
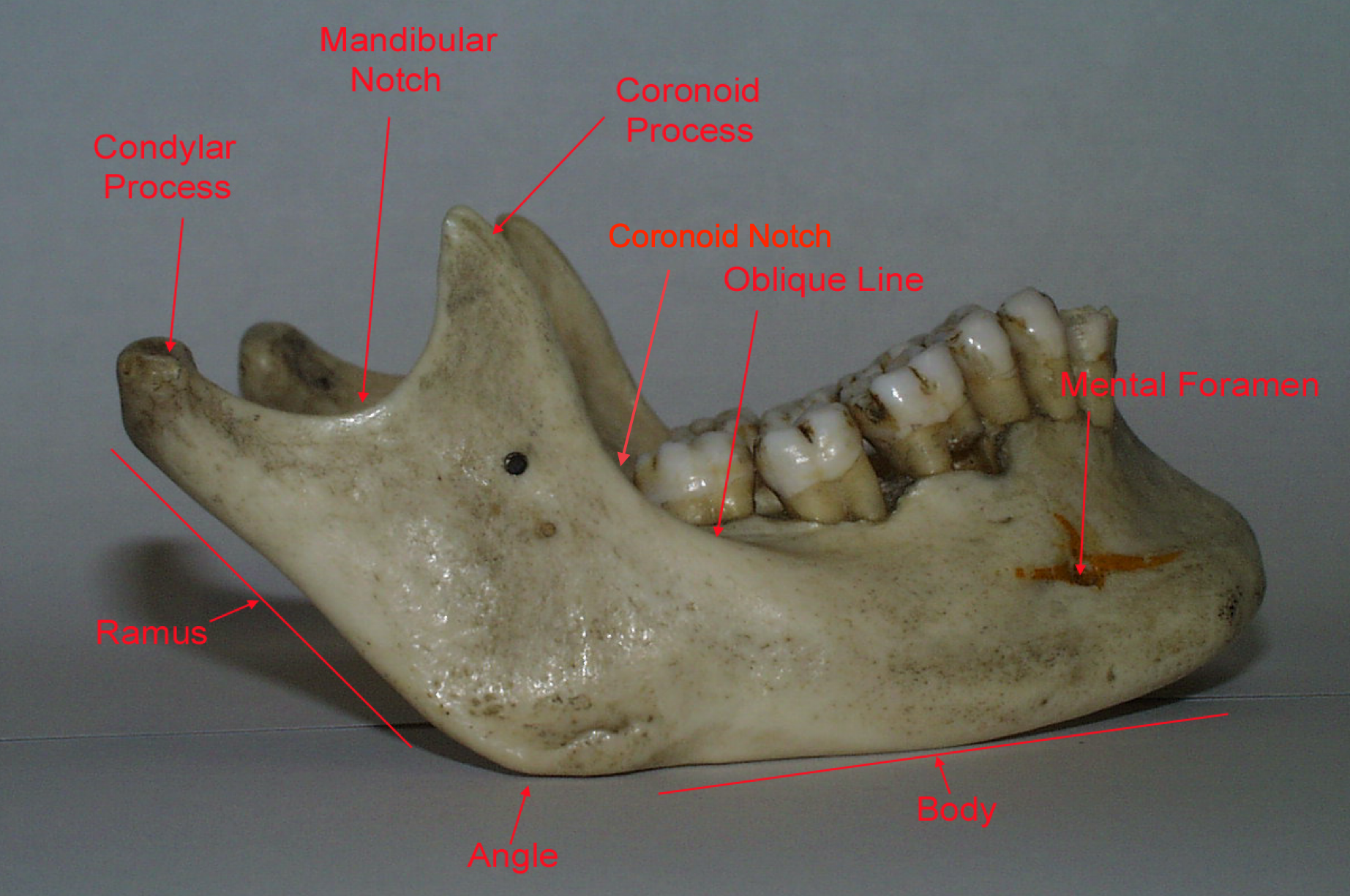
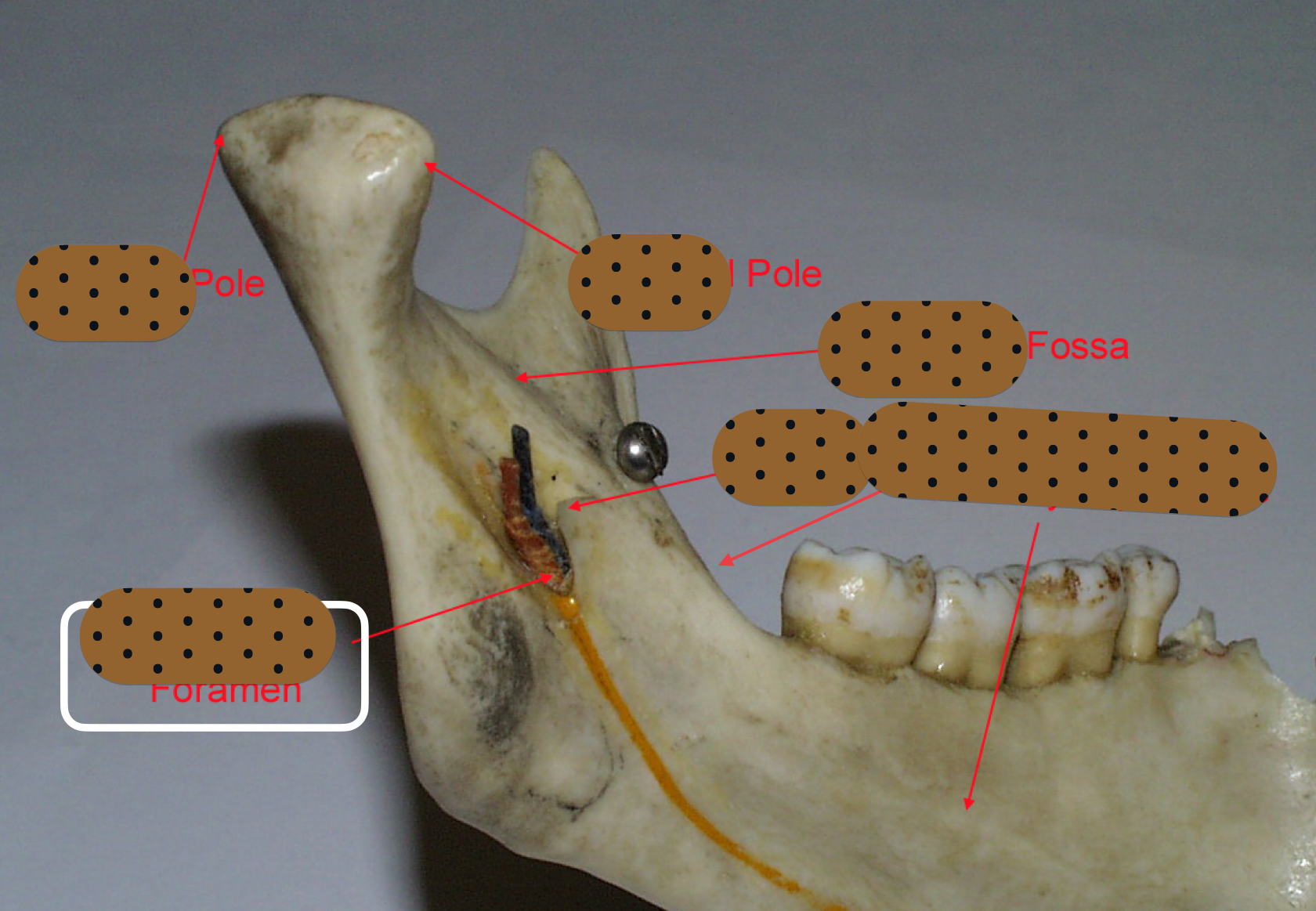
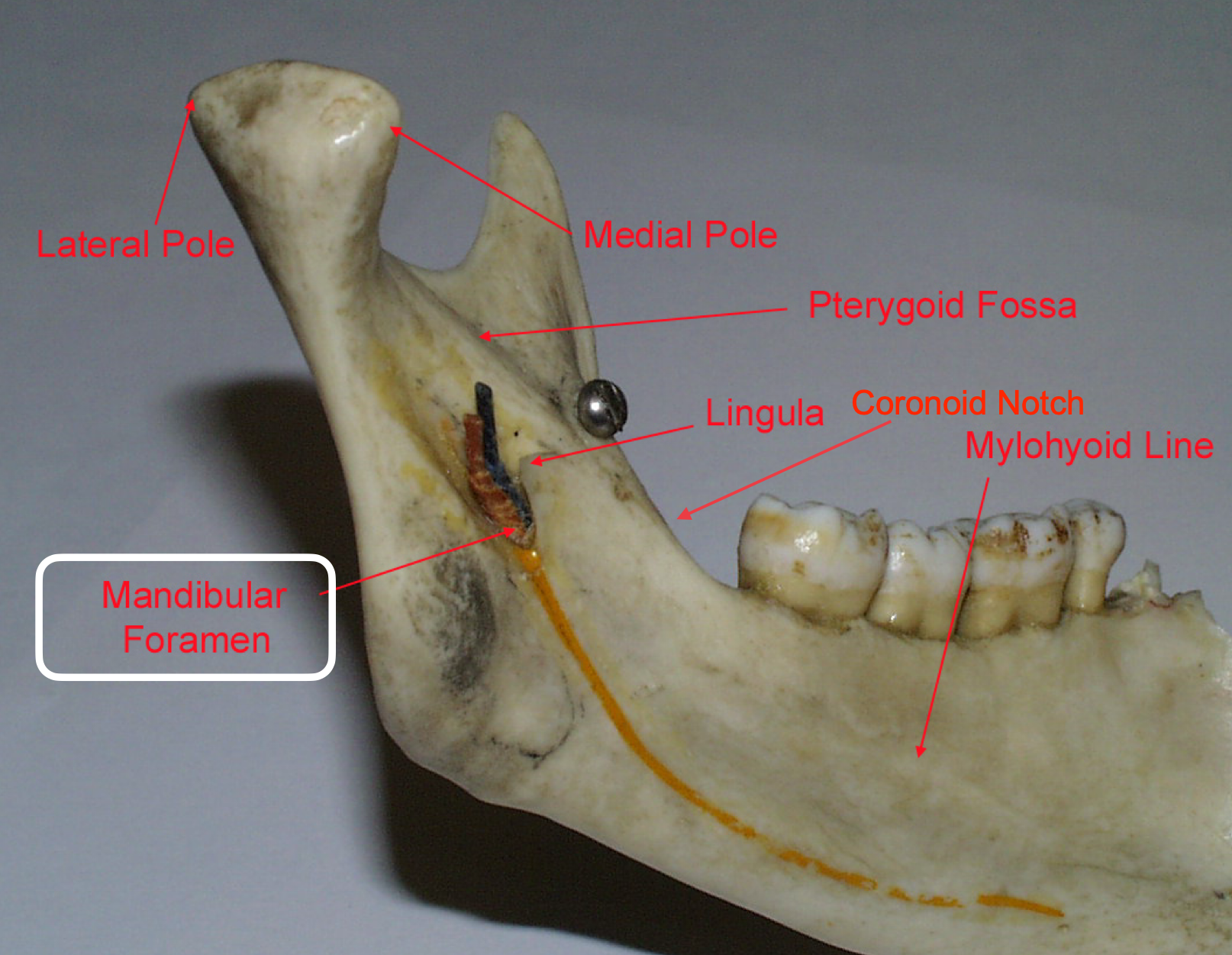
lingula = bony prominence of mandibular foramen where IAN enters, protects nerve
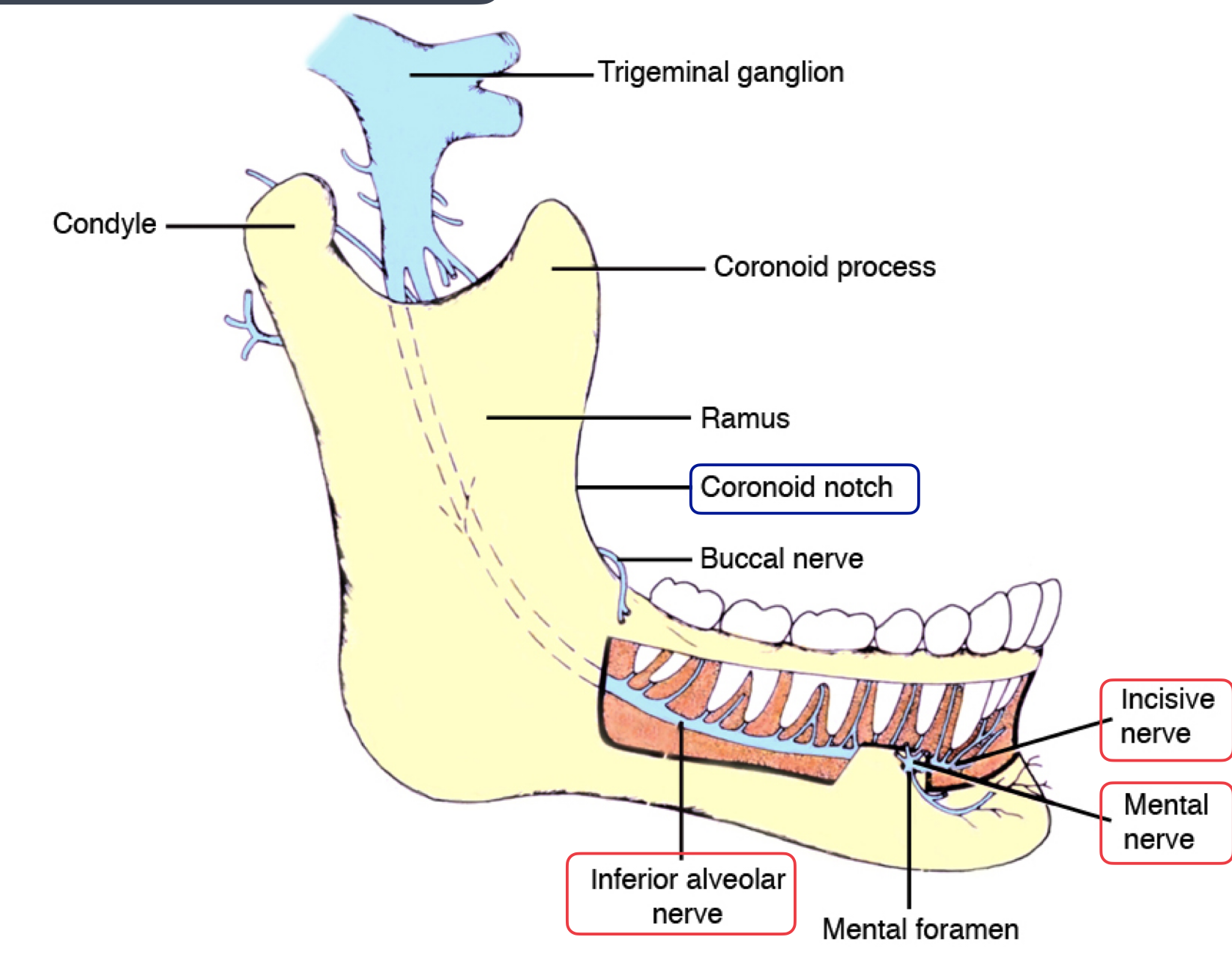
innervates the skin of the chin, lower lip, and buccal mucosa
mental n
continues within the mandible to supply sensory innervation to the mandibular canine, premolars, and their associated gingiva and pulps, originating from the inferior alveolar nerve
incisive nerve
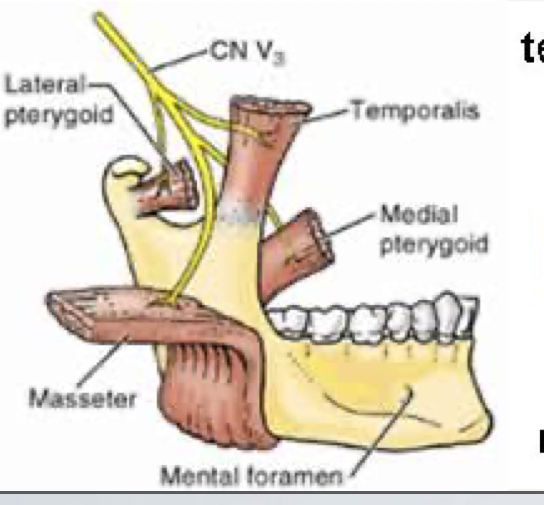
innervates medial pterygoid, tensor veli palatini of palate and tensor tympani of ear
medial pterygoid
innervates masseter
masseteric
innervates temporalis muscle
deep temporal
innervates lateral pterygoid
lateral pterygoid
innervates mylohyoid muscle and anterior belly of digastric m
mylohyoid
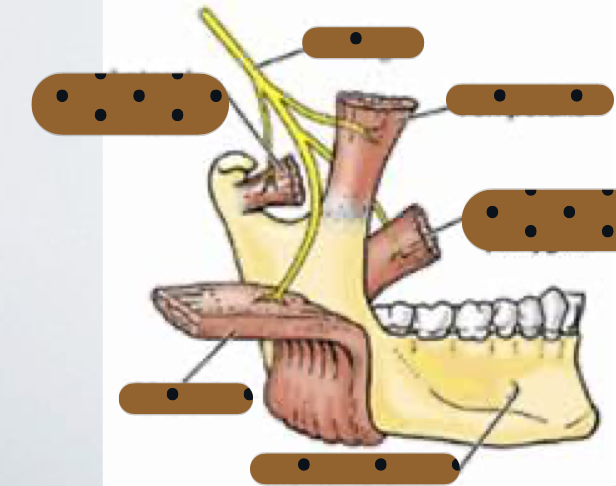
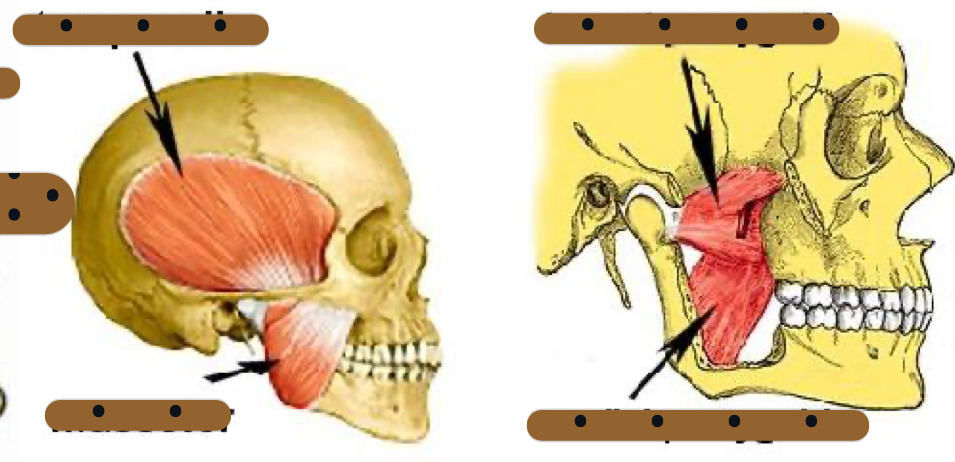
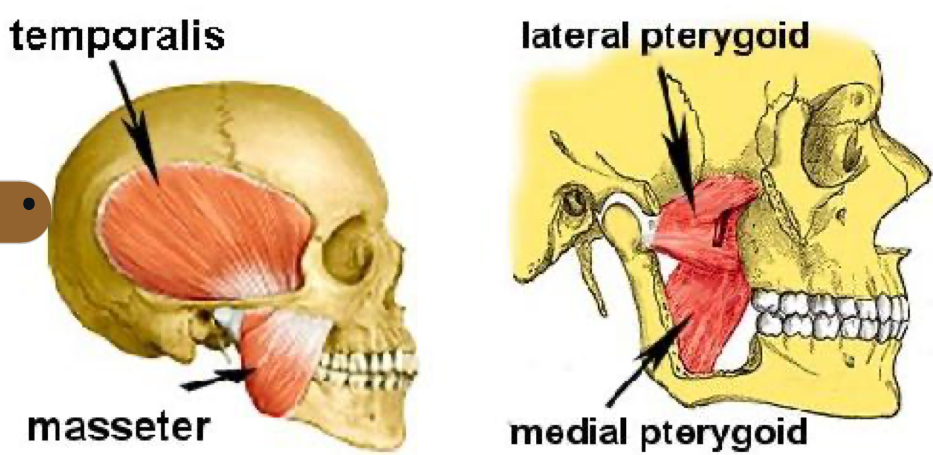
sensory root of V3 innervates skin of
Temporal region
Auricular
External auditory meatus
Cheek
Lower lip
lower part of the face (chin region)
sensory of V3 also innervates
Mucous membranes of cheek
Tongue (anterior two thirds)
Mucous membrane of mastoid cells and
parotid glands
Mandibular teeth and periodontal tissues
Mandibular bone and TMJ
describe dermatomes
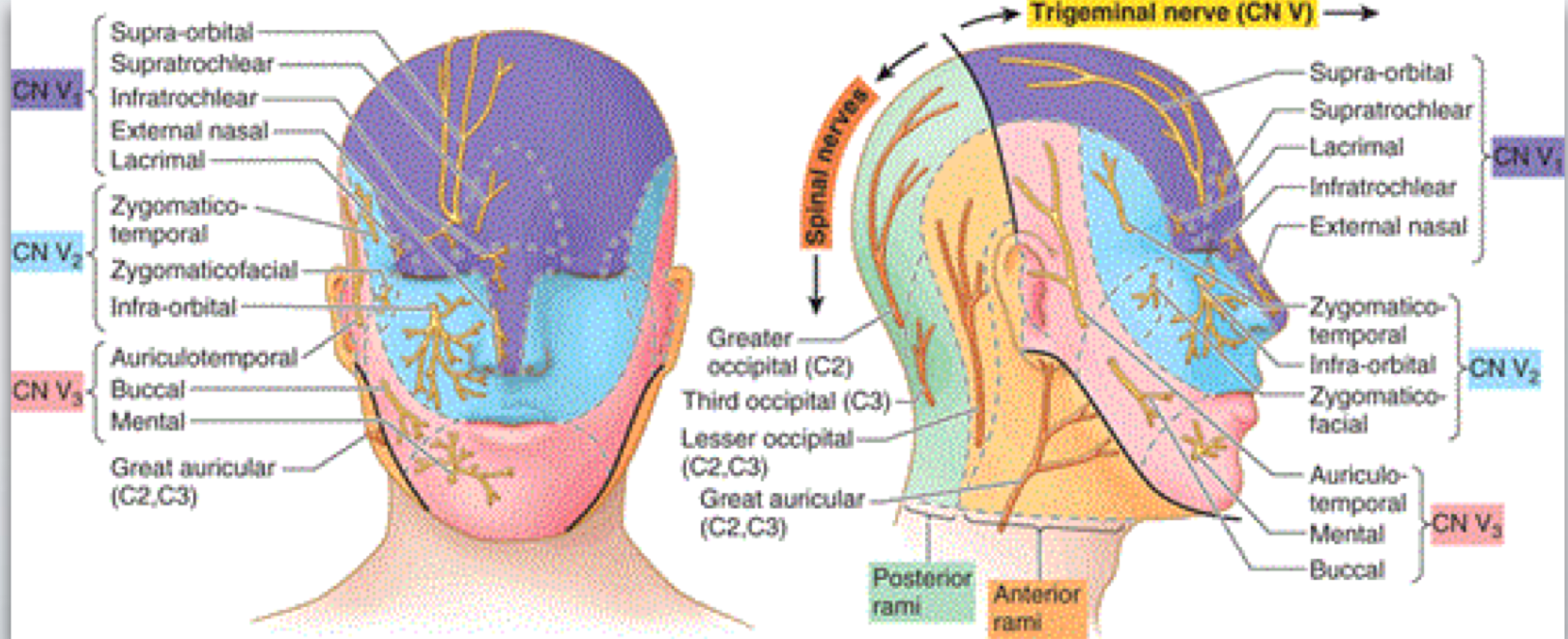
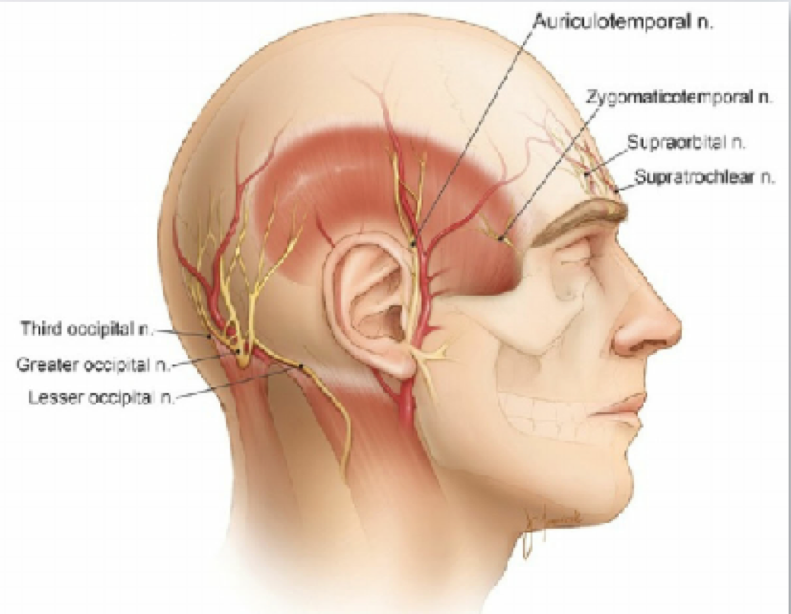
sensory innervation to:
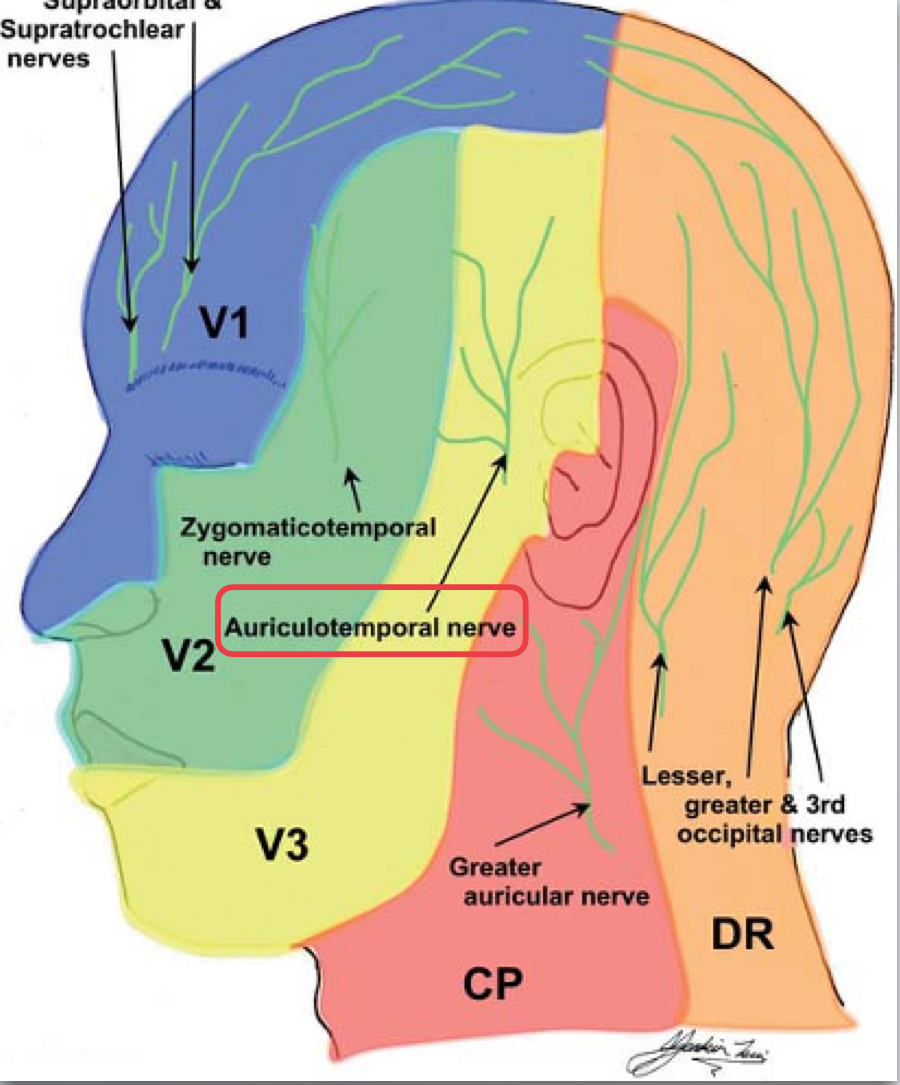
External auditory meatus
Skin of anterior aspect of temple
Skin of the auricle
auriculotemporal
dermatome for auriculotemporal
Location:
Runs from the medial side and cross the anterior border of the ramus
Runs anterior to inferior alveolar nerve
Enters the cheek
(long) buccal
Sensory Innervation :
Buccal gingival tissue of the molars to the second premolar region
Skin of the cheek
(long) buccal
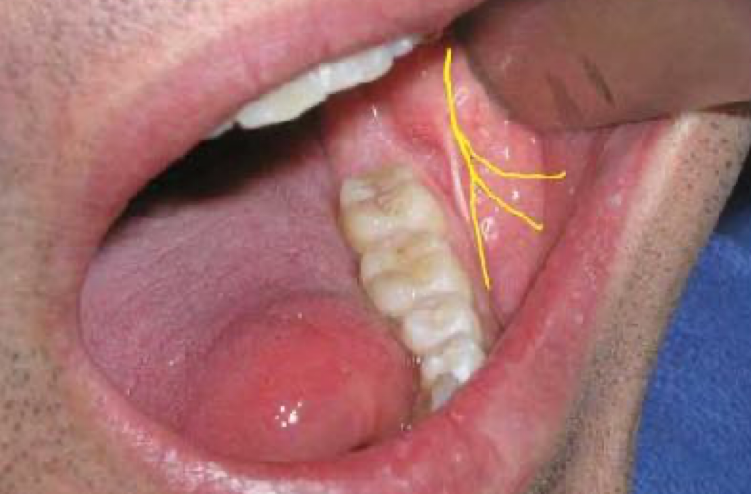
(long) buccal
Sensory Innervation:
Mandibular dentition to midline
Lingual hard and soft tissue
Buccal gingiva anterior to mandibular first molar
IAN
Terminal Branches: mental and incisive nerves
IAN
Location: Emerges from the mental foramen
Sensory Innervation: Buccal gingiva from second premolars to midline Lower lip and skin of the chin to midline
mental nerve
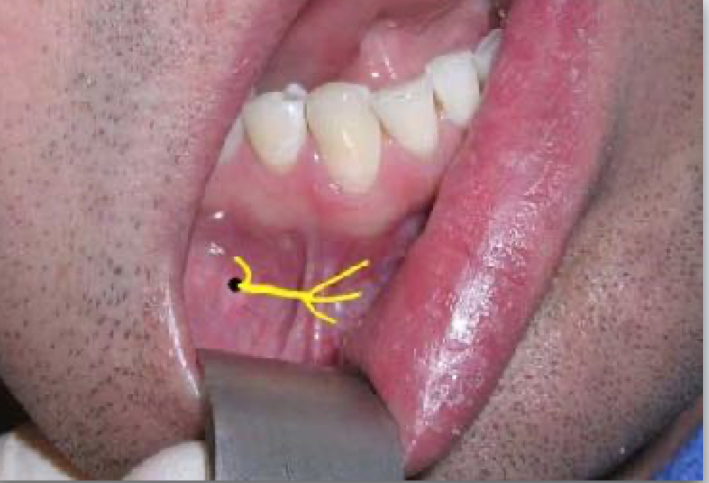
mental nerve
Location:
Remains within the mandibular canal
Sensory Innervation:
Buccal mucosa anterior to mental foramen from second premolar to midline
Lower lip and skin of chin to midline
Dental pulps of premolars, canine, lateral and central incisors
incisive nerve
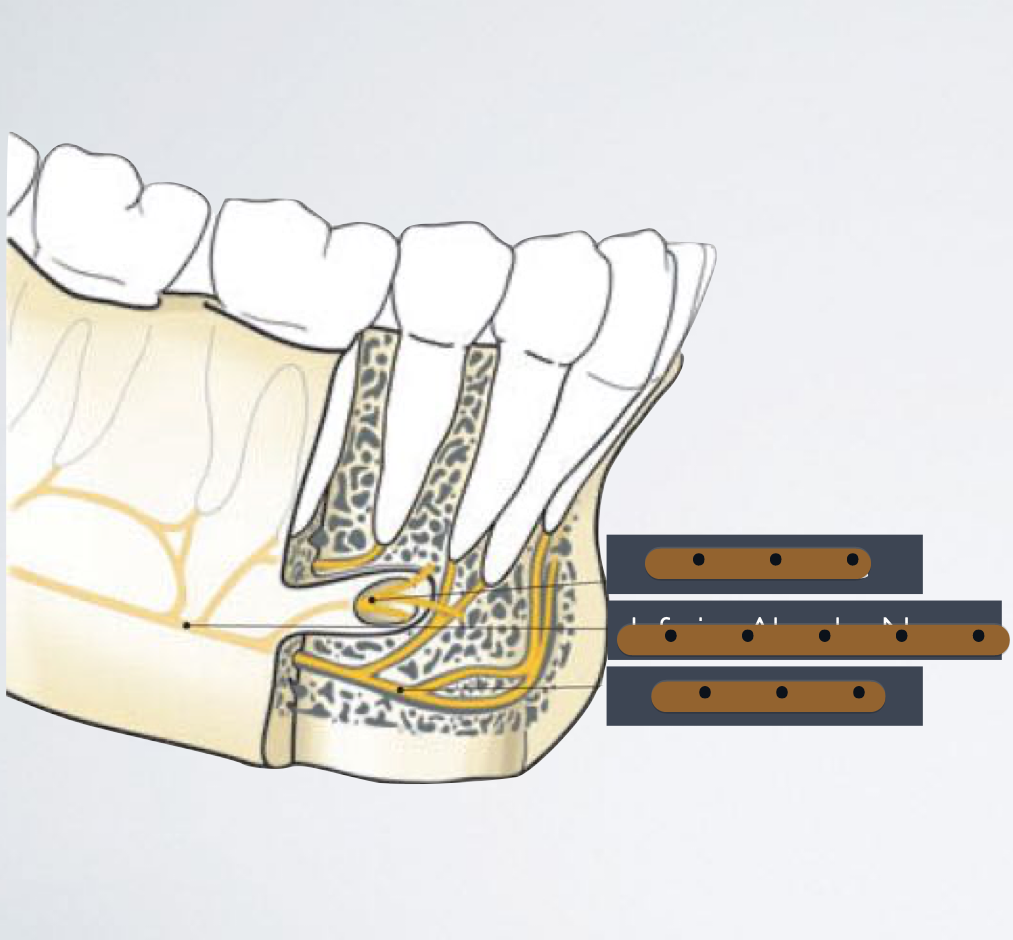
mostly motor innervation
Sensory Innervation: Mandibular dentition accessory innervation
mylohyoid
Communicates with Chorda Tympani (Facial Nerve)
Parasympathetic fibers to the submandibular/sublingual gland
Special taste sensory fibers to taste buds on the anterior two thirds of the tongue
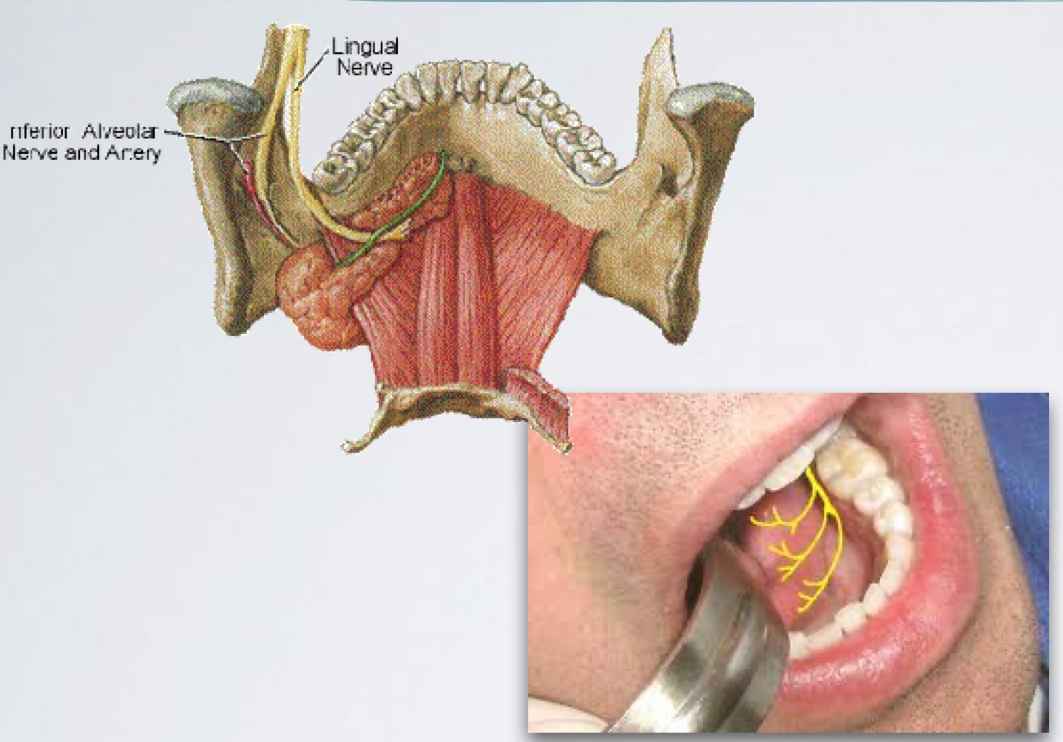
lingual nerve
Sensory Innervation :
Lingual gingiva of lower dentition
Mucosa of floor of the mouth
Anterior two thirds of the tongue - general sensation
lingual
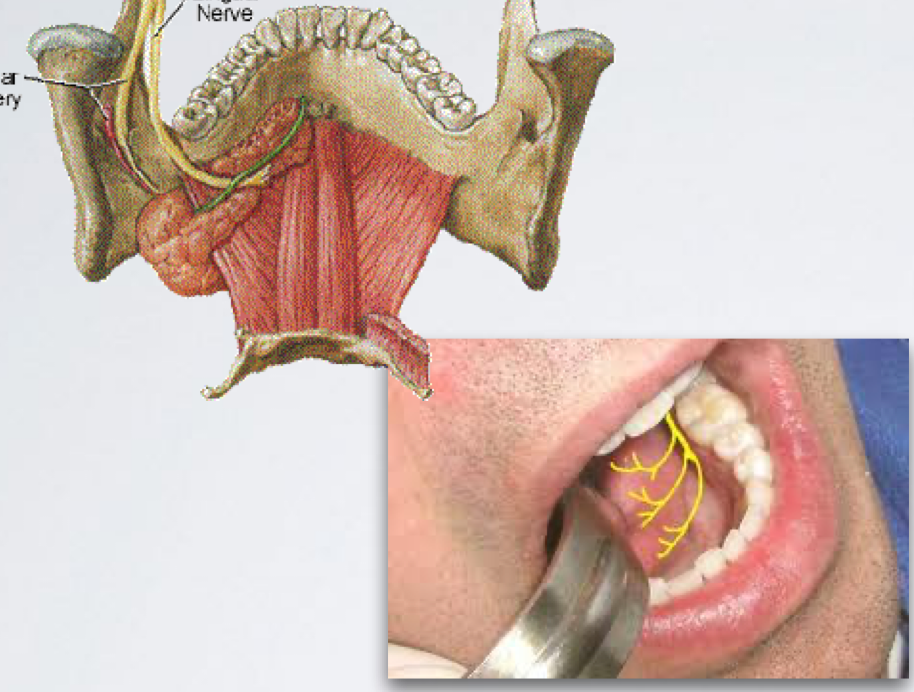
lingual
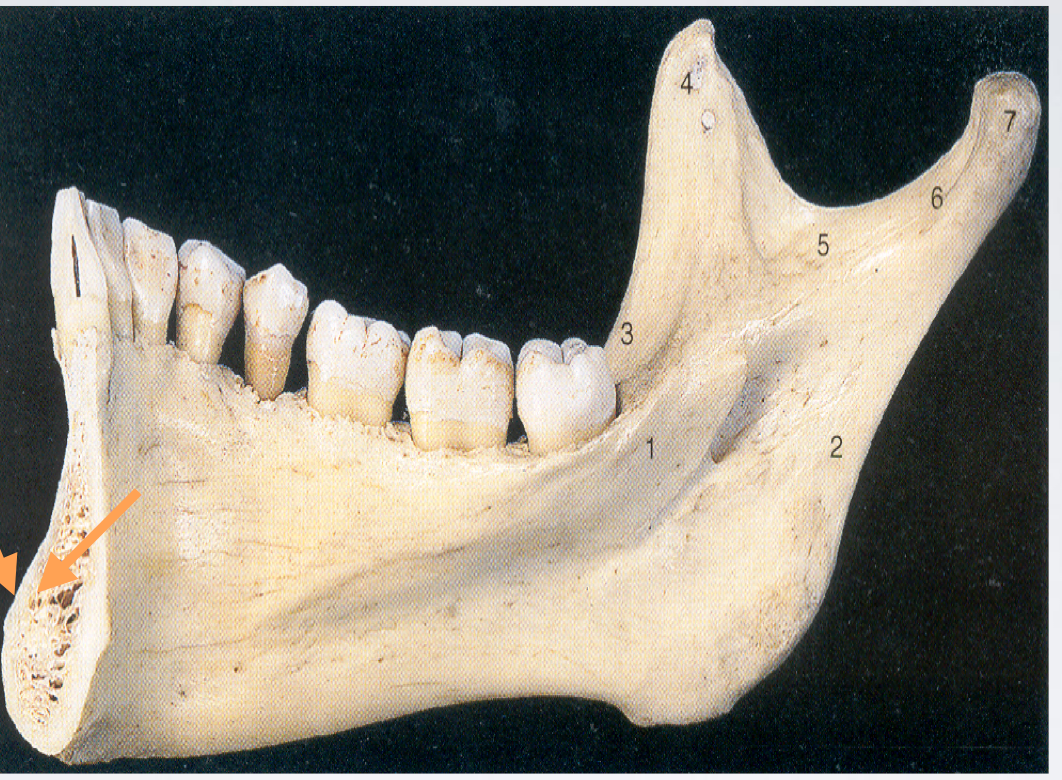
The problem with mandibular anesthesia, in adults, is the density of the cortical plate of the mandibular bone
It precludes the successful administration of supraperiosteal anesthesia
MOM attachments
hat are six mandibular injections?
Supraperiosteal Injection
Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block: Standard “classic” technique, Gow-Gates Mandibular technique Akinosi “closed mouth” technique
Lingual Nerve Block
(Long) Buccal Nerve Block
Mylohyoid Nerve Block
Mental/Incisive Nerve Block
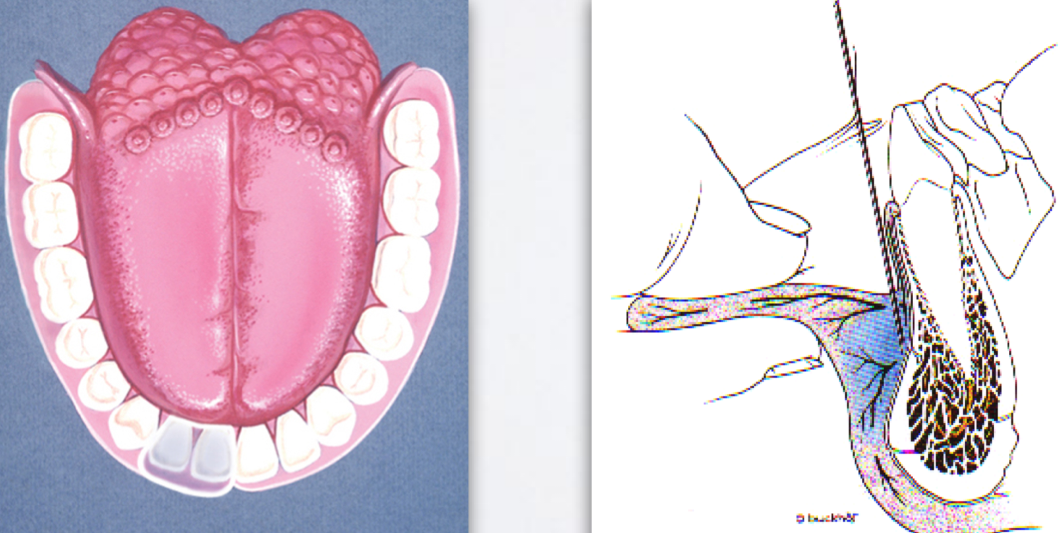
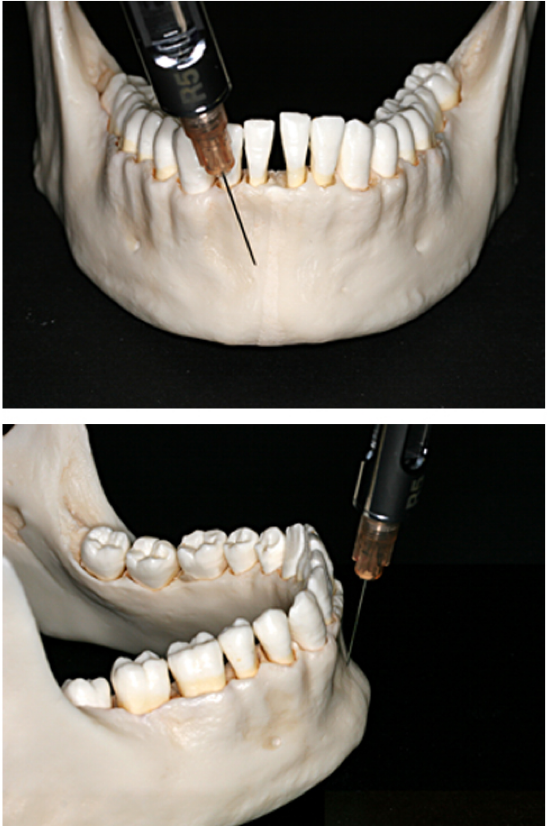
Indication: Pupal and buccal soft tissue anesthesia for a limited area (single tooth)
Contraindication: Infection, dense bone covering the apices of teeth
Nerve Anesthetized: Large terminal branches of the dental plexus
supraperiosteal injection
supraperiosteal injection
supraperiosteal injection
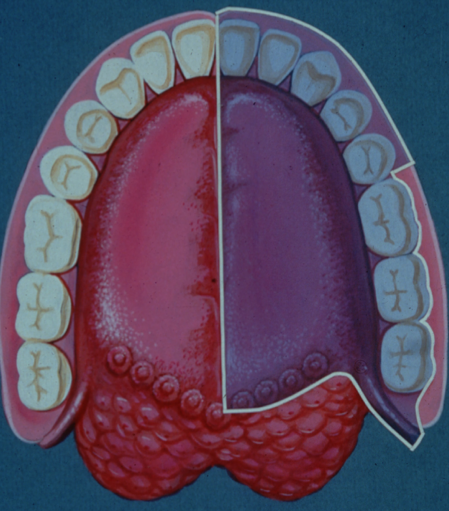
Area of Anesthesia
All mandibular teeth to midline and surrounding periodontium and alveolar
Buccal and labial soft tissue anterior to mandibular 1st molar (served by mental nerve)
All lingual soft tissue, floor of the mouth,anterior two thirds of the tongue
IAN nerve block - standard/Halstead
Nerves Anesthetized
Inferior alveolar nerve
Incisive nerve and mental nerve
Lingual nerve (very commonly)
IAN nerve block
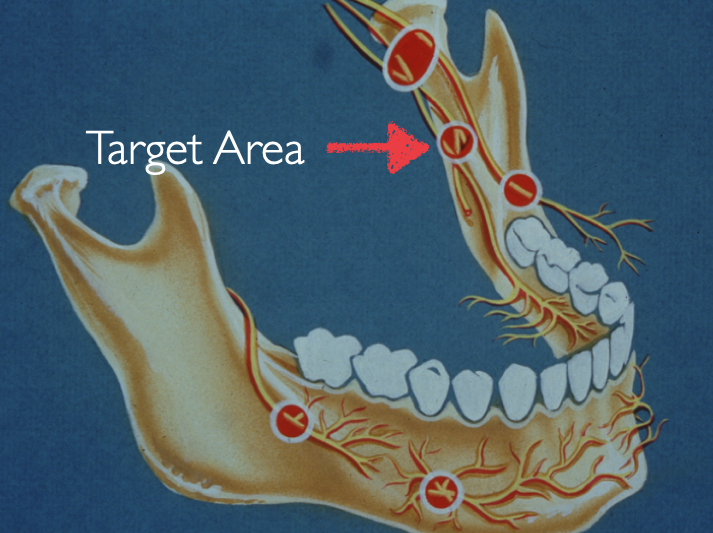
(before mandibular foramen)
IAN nerve block
Indication:
Procedure on multiple mandibular teeth in one quadrant
When buccal (anterior to 1st molar) and lingual soft tissue anesthesia is required
Contraindication:
Infection/acute inflammation in area of injection
Patient who might bite either the lip or tongue (young pediatric or special needs patients)
IAN nerve block
Advantage:
One injection provides a wide area of anesthesia - useful for quadrant dentistry
Bony contact
Disadvantage:
Lower success rate than maxillary anesthesia (80-85%)
Density of bone
Anatomical variations
Greater distance to target area
Positive aspiration: 10-15%
Wide area of anesthesia (vs localized procedure)
Lingual and lower lip anesthesia, which causes discomfort for many patients
Inadequate/partial anesthesia (supplemental buccal nerve block or supraperiosteal injections may be needed)
IAN nerve block
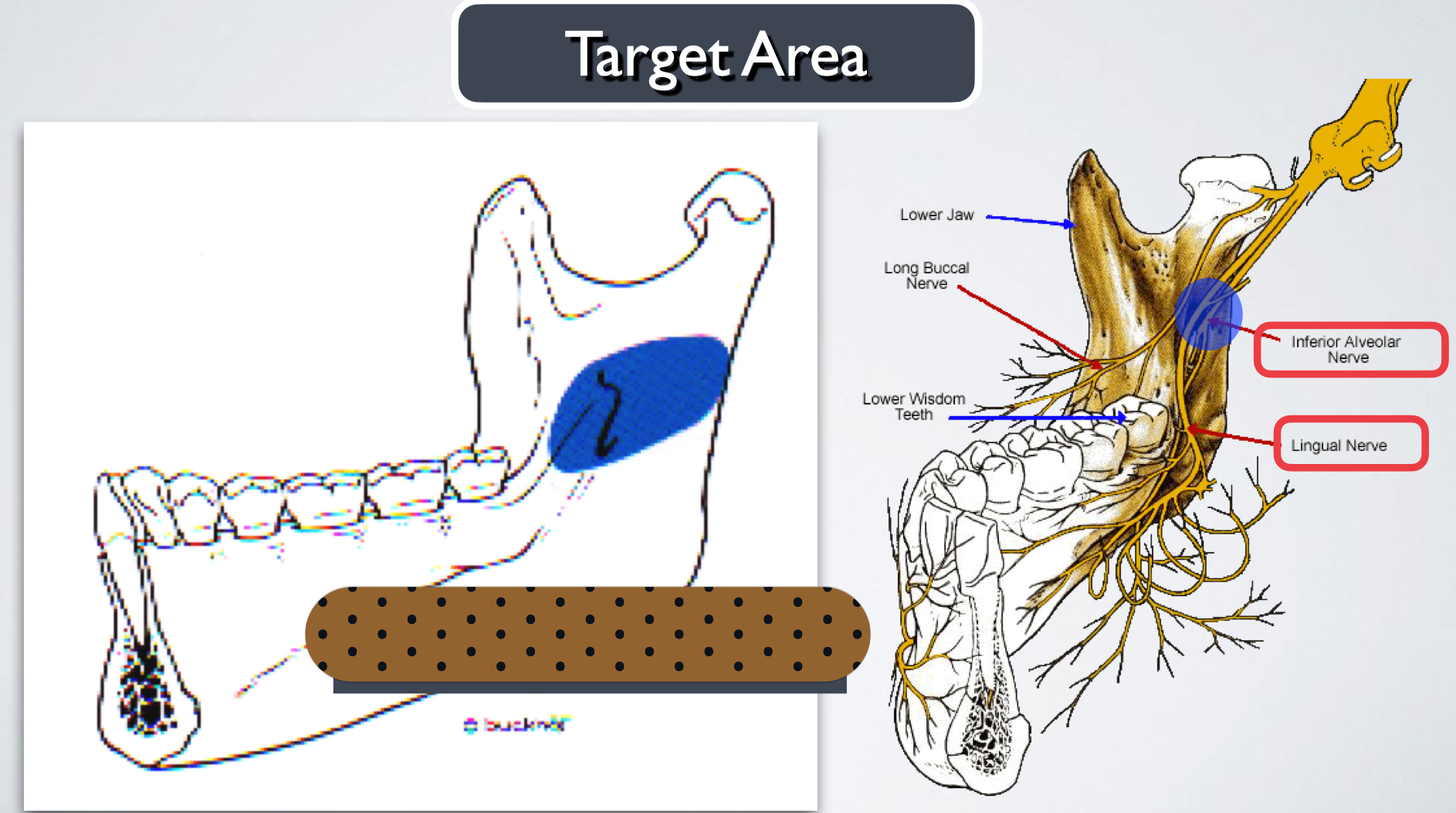
IAN nerve block- standard/Halstead
three steps of the IAN standard/classic technique
find lamarks
establish height of injection
determine direction/angulation of injection
what landmarks are you looking for with standard/halstead IAN nerve block technique?
coronoid notch and pterygomandibular raphe
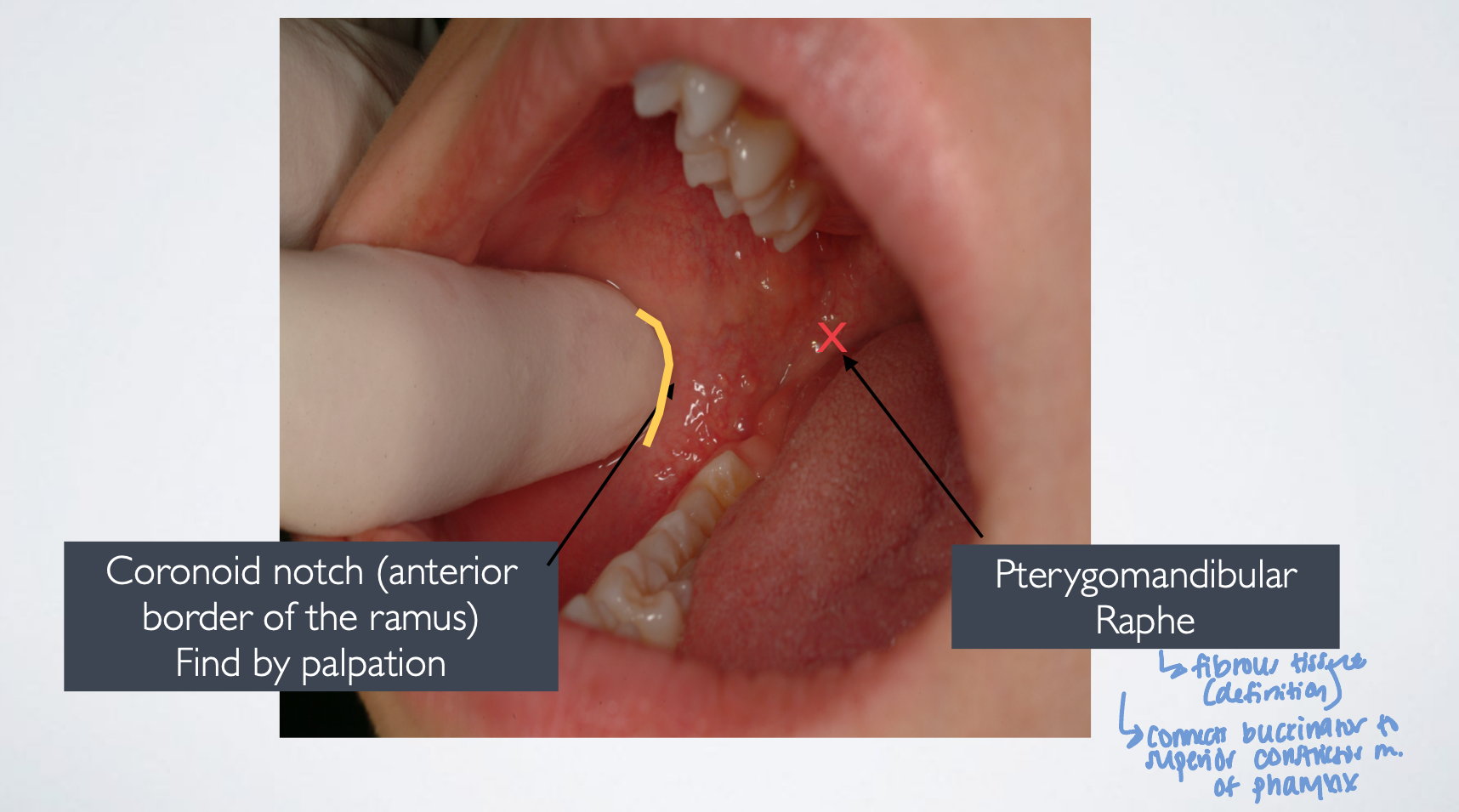
what does the pterygomandibular raphe connect?
superior connector muscle and buccinator muscle
for standard/halstead technique for IAN nerve block needle insertion is slightly (medial/lateral) to the pterygomandibular raphe
lateral
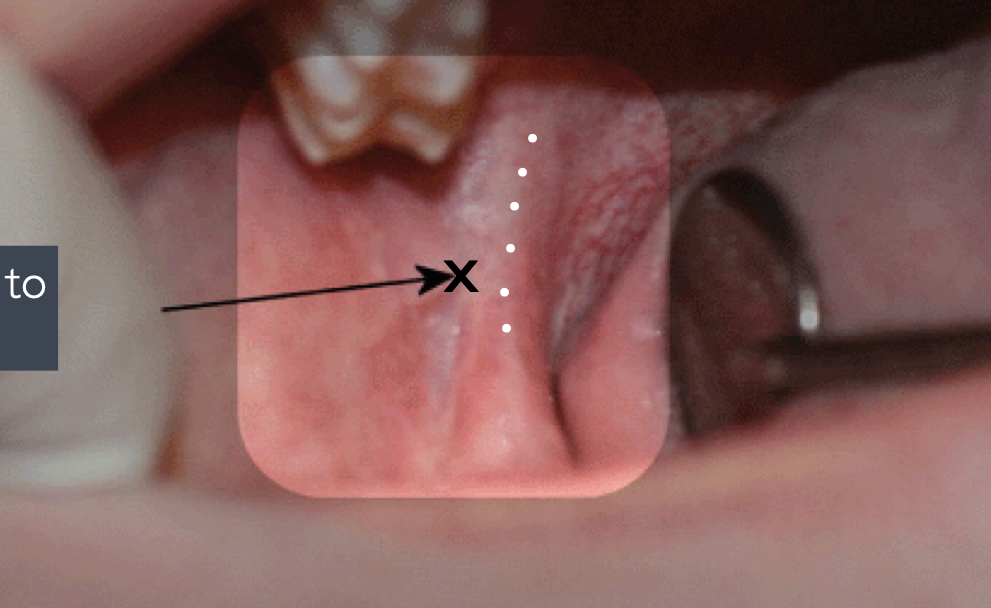
IAN standard/classic/halstead technique
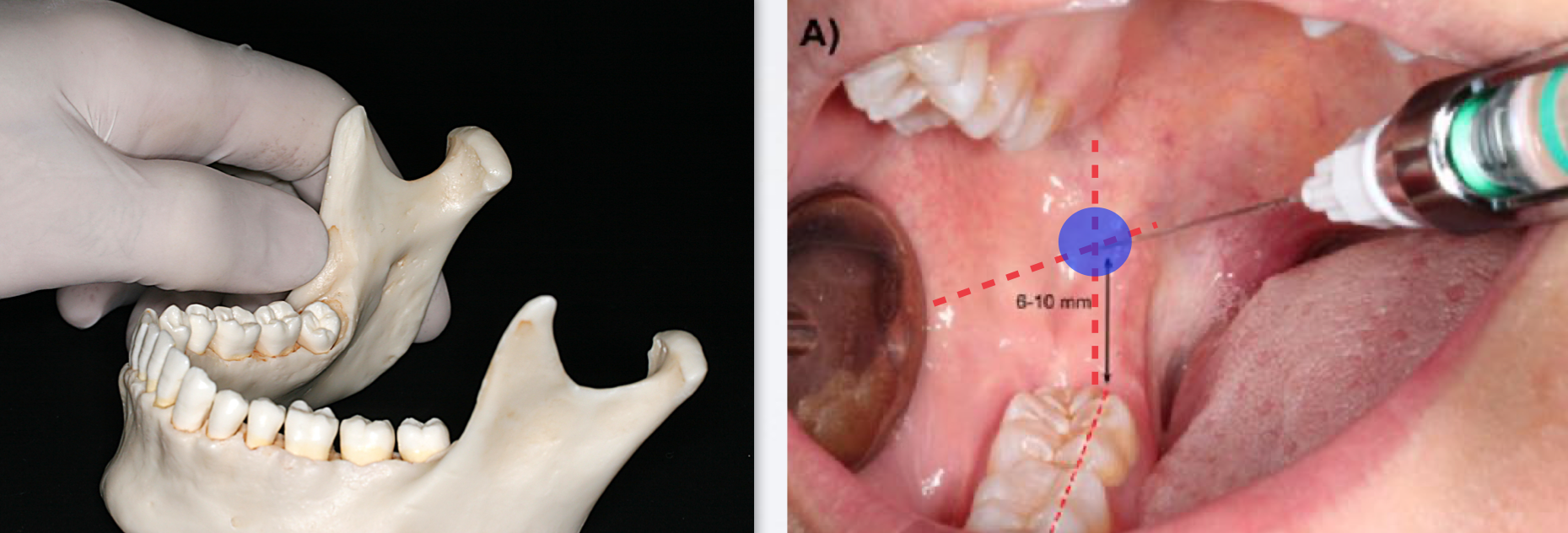
how to establish height for IAN nerve block classic/standard/halstead injection?
Place thumb at the coronoid notch, parallel to the plane of occlusion
The imaginary line begin at the midpoint of the notch and terminate at the deepest part of the pterygomandibular raphe
Place finger in the coronoid notch (greatest concavity on anterior border of the ramus)
Continue the imaginary line to the deepest part of the pterygomandibular raphe. (In most patients, this line lies 6-10 mm above the mandibular occlusal plane)
Needle insertion lies 3/4th of the anteroposterior distance of this line
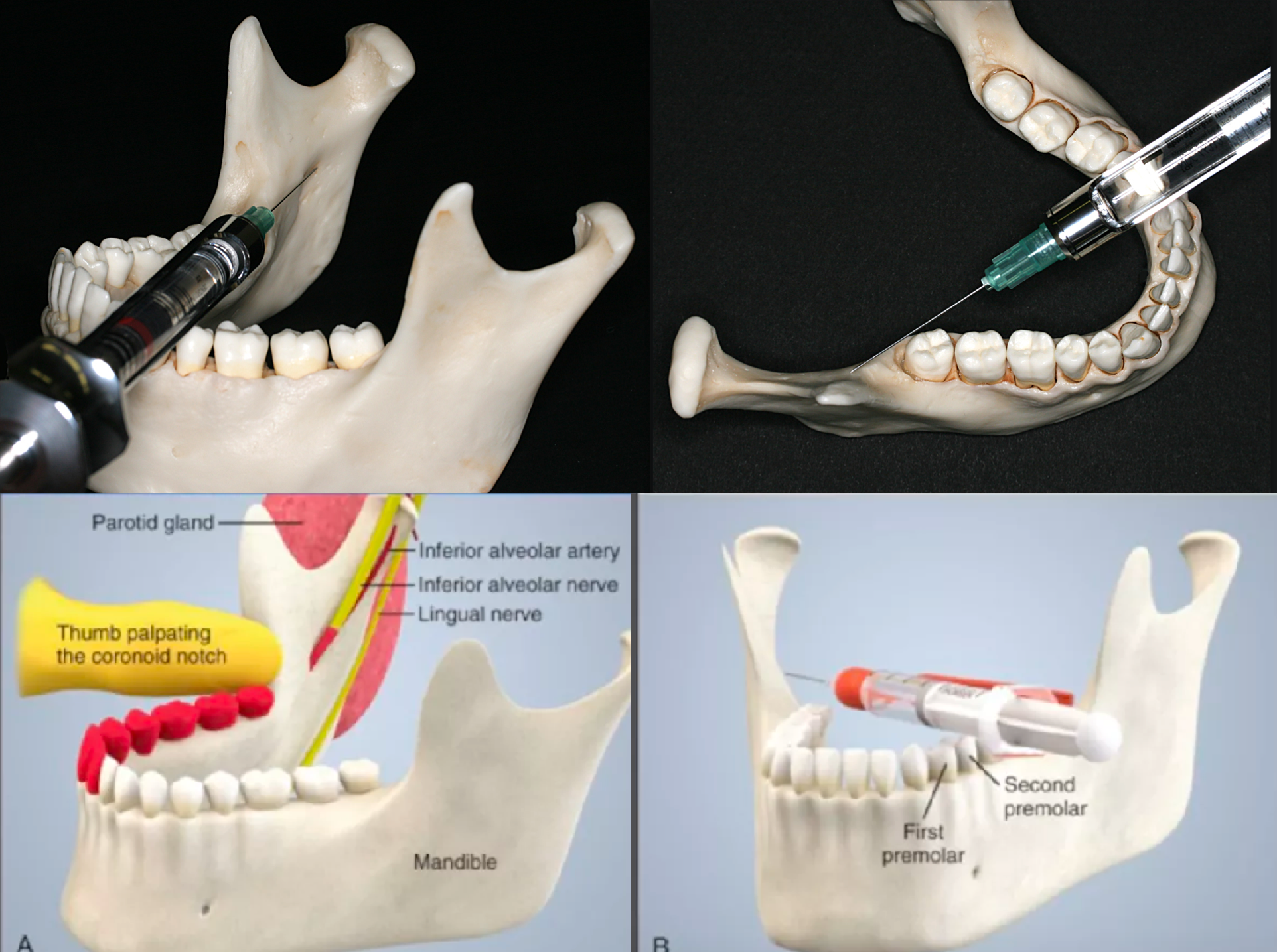
how to determine direction/angulation for IAN nerve block classic/standard/halstead injection?
Come in from the contralateral side between the premolar area
Slowly advance until bone is contacted
Average depth of insertion: 20-25 mm ~ 2/3rd needle size
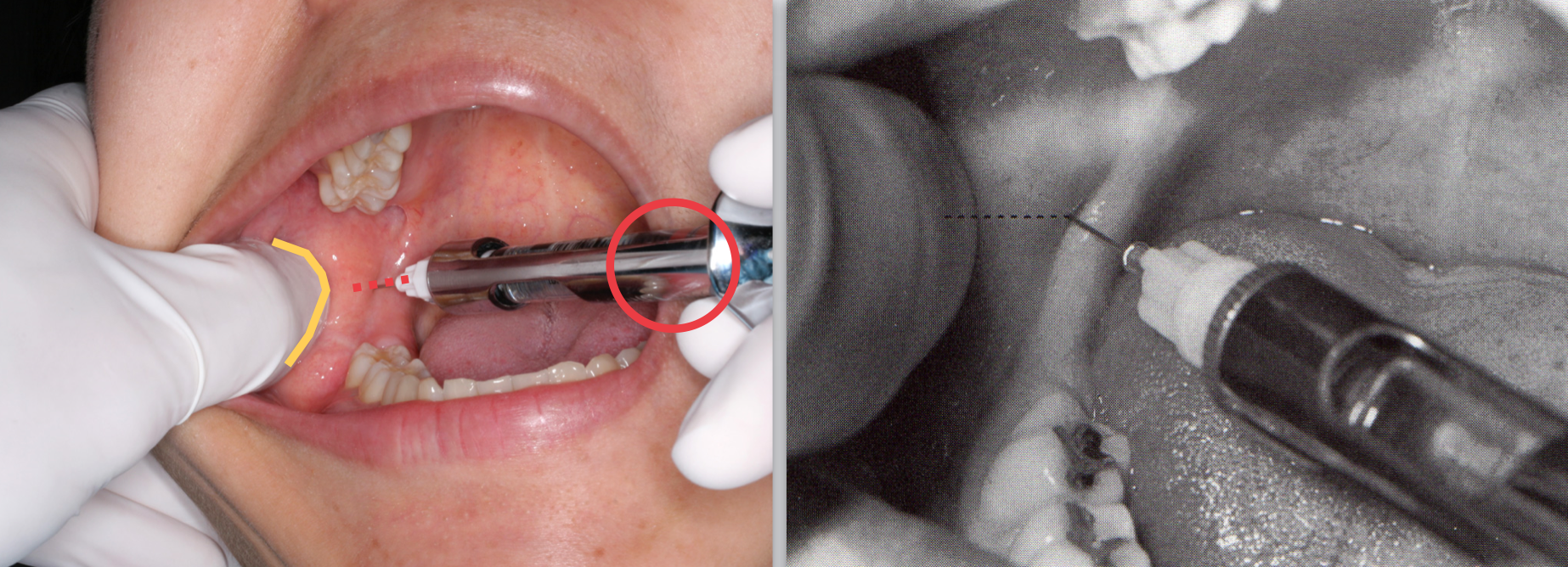
IAN standard/halstead technique
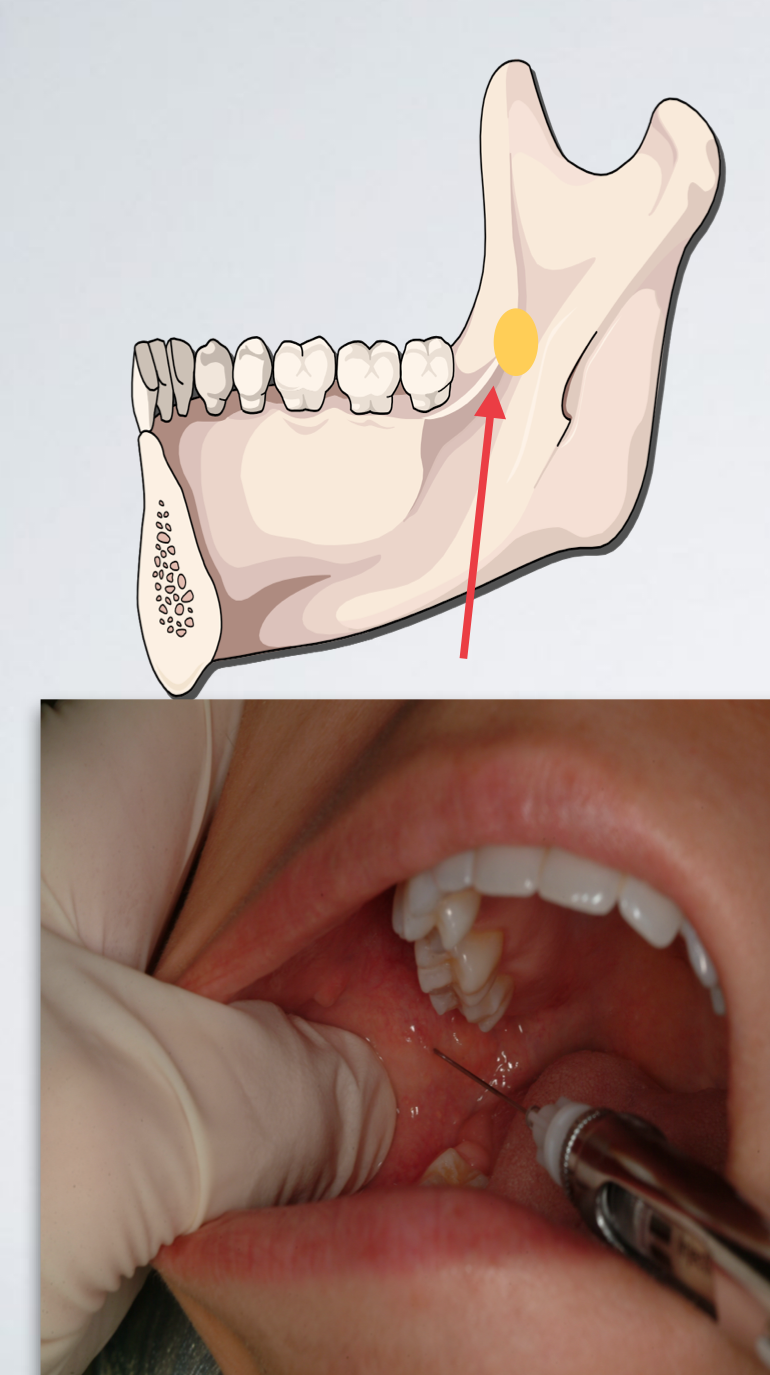
which IAN standard/halstead issue?
Needle tip is located too anteriorly
Withdraw slightly
Angulate the needle tip more posteriorly (syringe barrel more anteriorly)
Re-advance to correct depth (20-25 mm)
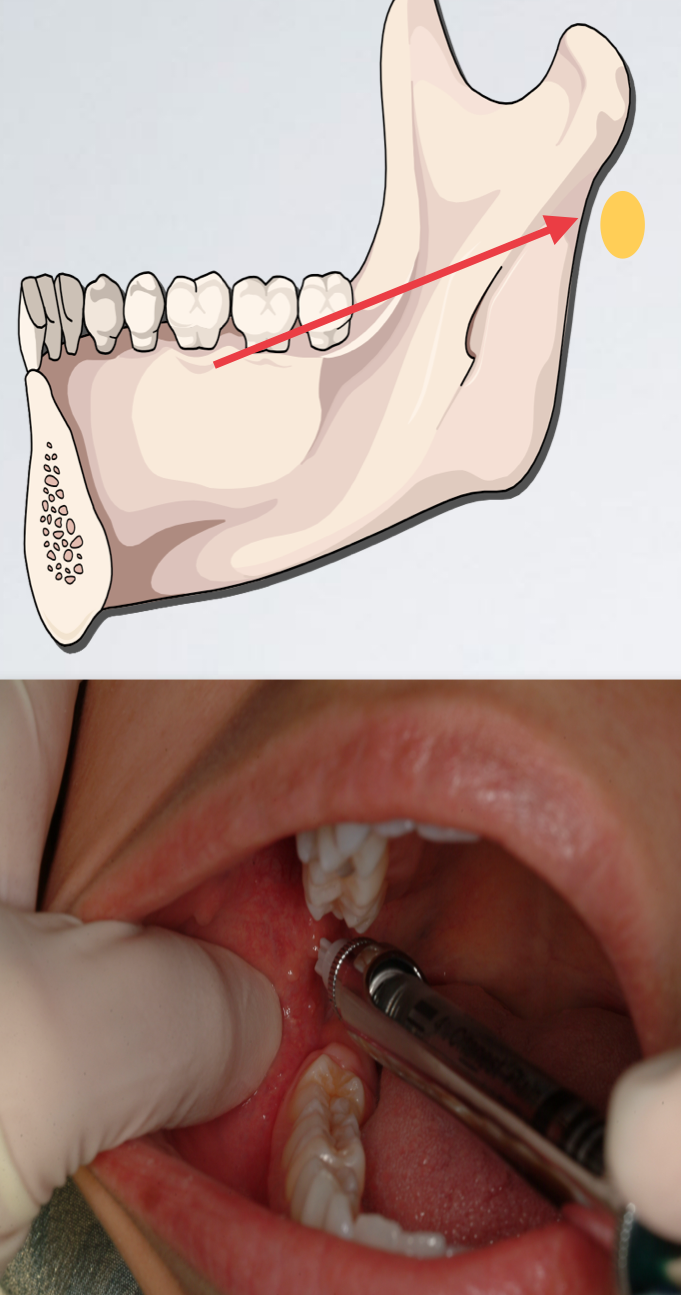
bone contacted too soon
which IAN standard/halstead issue?
Needle tip located too posteriorly
Withdraw slightly
Angulate the needle tip more anteriorly (syringe barrel more posteriorly)
Re-advance to correct depth (20-25 mm)
no bony contact
what two nerves are anesthetized with IAN standard/halstead technique?
lingual and IAN
what is in the pterygomandibular space? what if you hit no bone
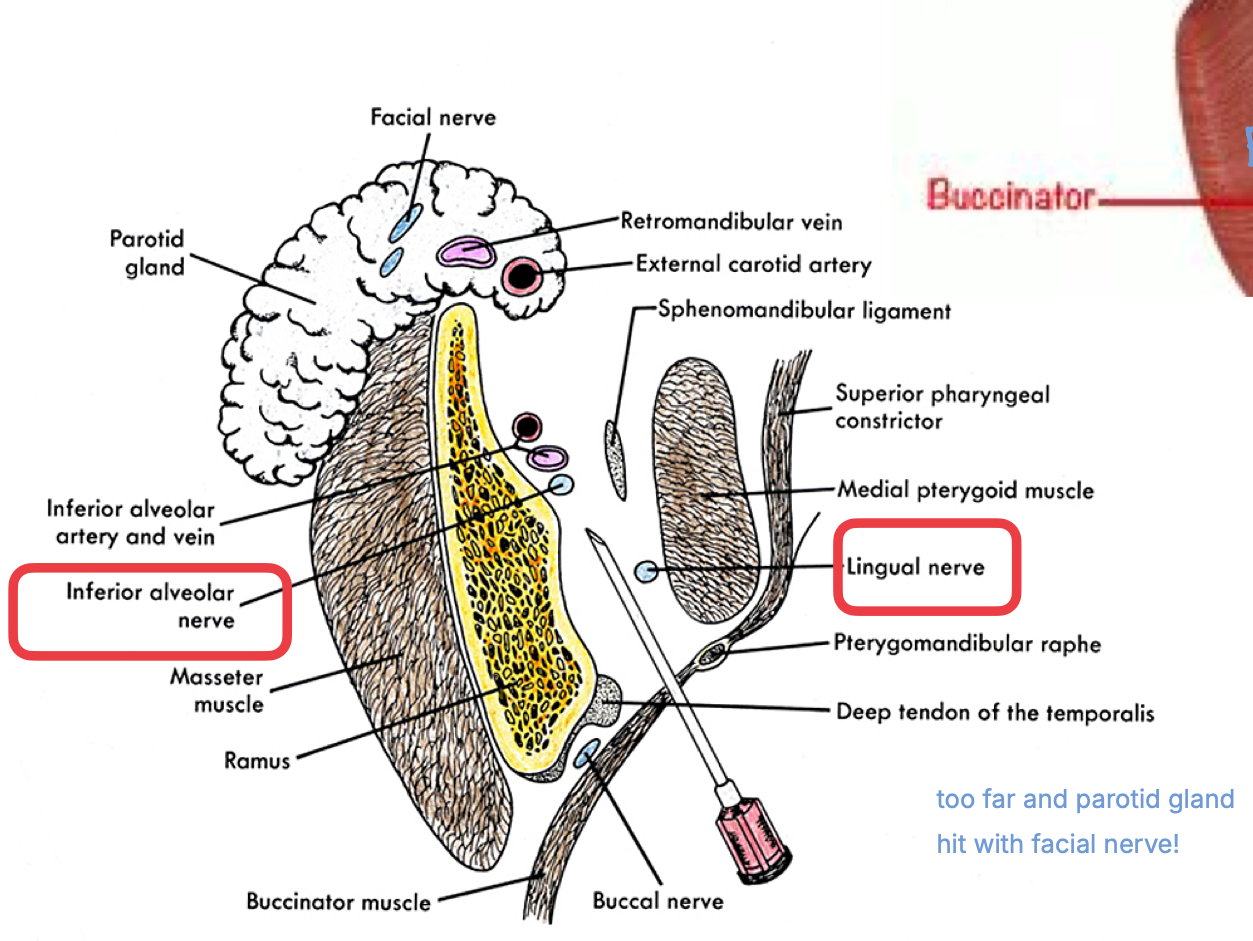
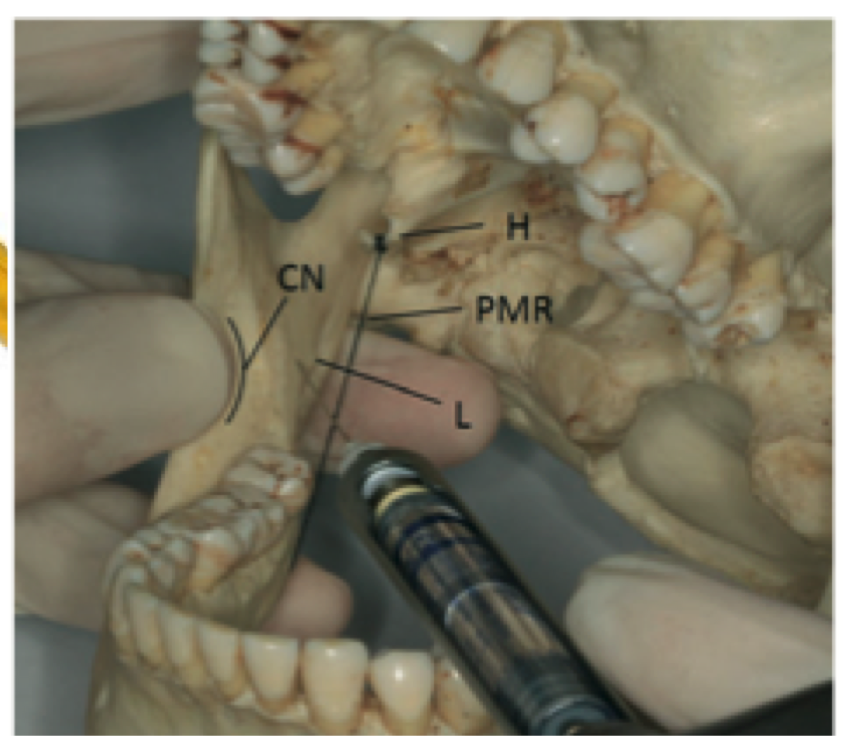
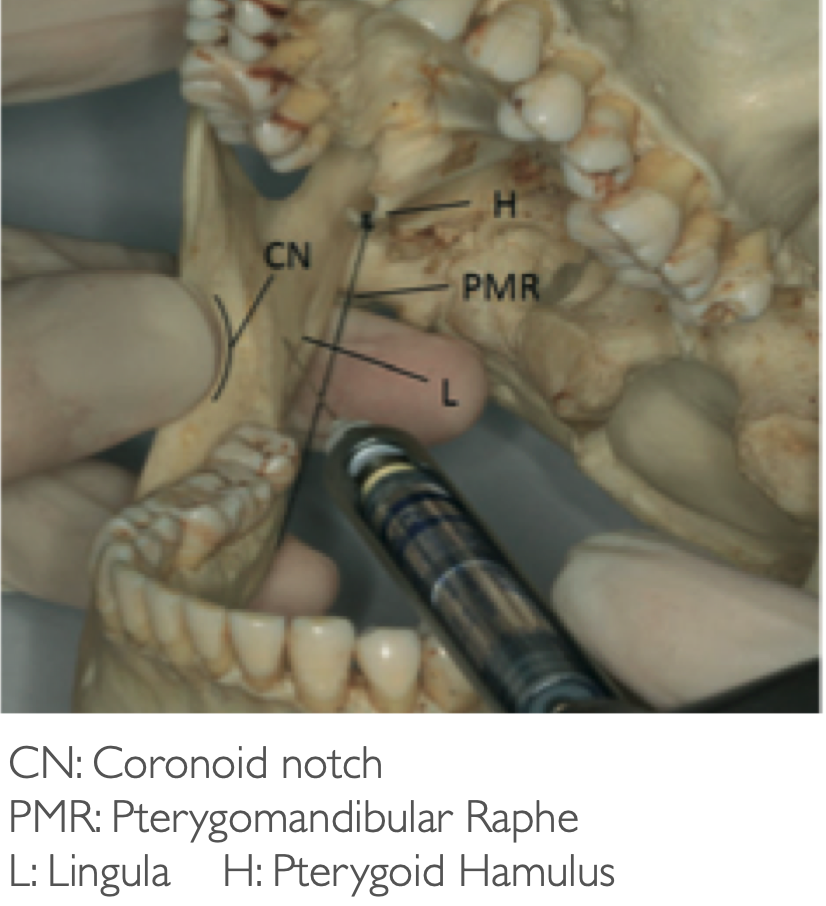

standard IAN technique
what are the signs and symptoms of a successful IAN nerve block? think tingling and numbness of lower lip and tongue
Tingling or numbness of lower lip
Mental nerve - good indication
But not a reliable indicator of pulpal anesthesia depth - means you got mental nerve but maybe not IAN
Tingling or numbness of tongue
Lingual Nerve
May be present without anesthesia of the inferior alveolar nerve
Objective: no pain is felt during dental therapy