Global Diagrams, gvy policy eval.
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
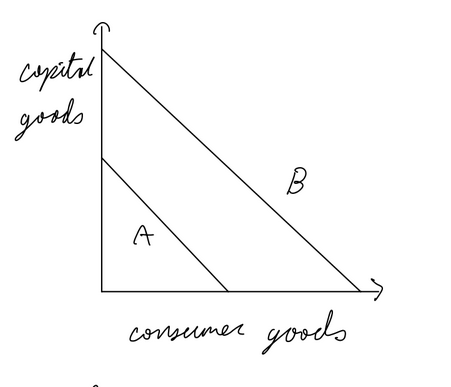
Absolute advantage
can produce a good with fewer resources, countries should specialize
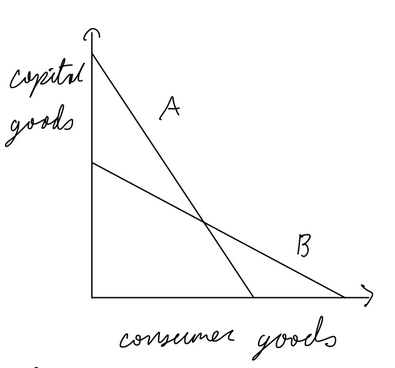
Comparative Advantage
a country can produce a good with lower opportunity cost
Limitations of theory:
unrealistic assumptions (free trade, fixed fop, full employment, perfect comp, no transport costs)
risk of excessive specialization
inability of developing countries to diversify manufacturing
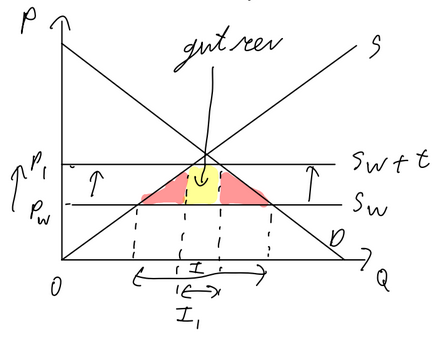
Import Tariff
Pros:
domestic producers gain revenue
workers gain as domestic production increases
gvt revenue
Cons:
price goes up
wellfare loss
imported goods more expensive, domestic productions more expensive
loss of export competitiveness as production price increases
foreign producers lose
global economy lose
risk of retaliation
potential corruption
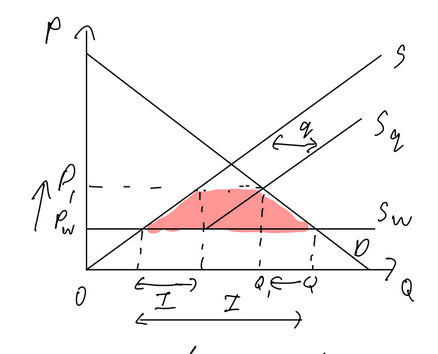
Import Quota
Pros:
domestic producers gain revenue
workers gain as domestic production increases
Cons:
price goes up
wellfare loss
imported goods more expensive, domestic productions more expensive
loss of export competitiveness as production price increases
foreign producers lose
global economy lose
risk of retaliation
potential corruption
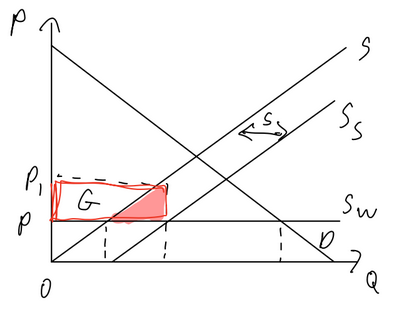
Subsidy (global)
Pros:
domestic producers gain revenue
workers gain as domestic production increases
Cons:
gvt debt
wellfare loss
imported goods more expensive, domestic productions more expensive
loss of export competitiveness as production price increases
foreign producers lose
global economy lose
risk of retaliation
potential corruption
Trade protection
Pros
protect infant industries
diversification of developing countries
national security
health, safety, env. standards
gvt revenue
overcoming trade deficit
anti-dumping
protect domestic jobs
cons
difficult to select what industry to protect
can be used to “protect’ unrelated industries
when relying on tariffs for gvt rev. probabluy means theres a problem w the tax system
retaliation is possible
hard to prove dumping
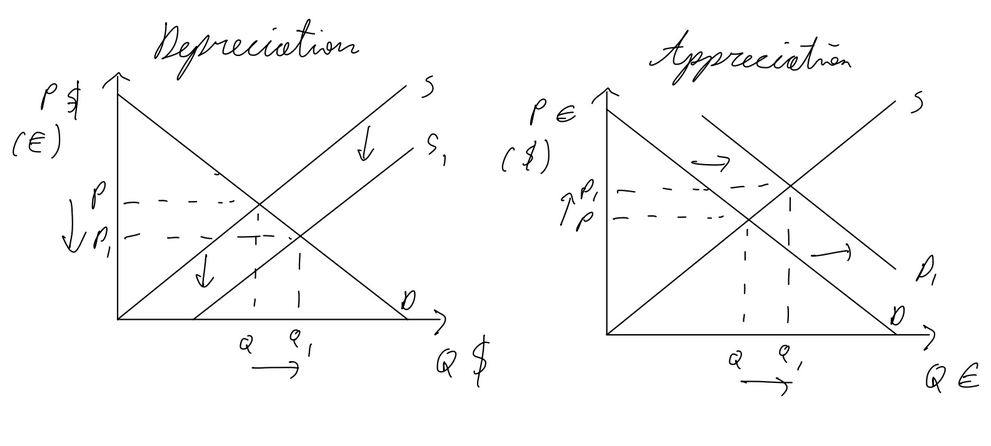
Freely Floating Exchange Rate
Appreciation: occurs with excess demand. if Americans buy euros w dollars, the demand for euros increases, appreciating the currency
Deppreciation: osccurs with excess supply. the americans buying euros means theyre selling dollars, increasing supply of dollars, leading to depreciation
pros:
allows for greater flexibilty in monetary policies
allows for automatic adjustments to external shocks
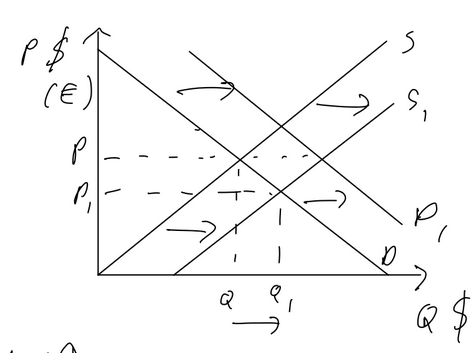
Fixed Exchange Rate
fixed at partiy: 1 to 1 ratio, usually doesn’t happen
Appreciation: CB buys it on forex market to increase demand
deppreciation: CB sells it on forex, increase supply
revaluation: change where the exchange rate is fixed to higher price
devaluation: change where the exchange rate is fixed to lower price
pros:
provides stability and predictability
lowers speculative trading and currency volatility
cons:
limits a country’s ability to conduct monetary policies as focus is on exhcange rate and not interest rate
Managed Exchange Rate
allowed to fluctuatie within a specific band, CB intervenes when exchange rate leaves band
Appreciation: CB buys it on forex market to increase demand
deppreciation: CB sells it on forex, increase supply
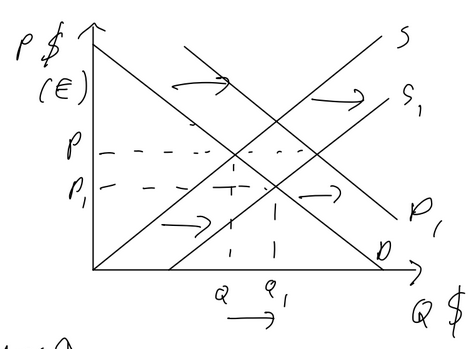
Consequences of curency depreciation
imports are more expensive, exports are cheaper. therefore net exports increase, shifting AD right
cose push inflation as imported raw materials are more expensive
demand pull inflation as AD increases
unemployment falls as exports increase
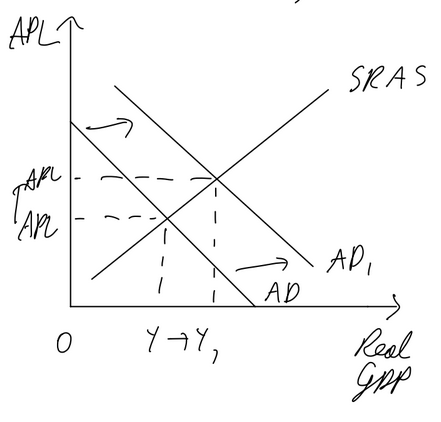
Consequences of currency appreciation
imports are cheaper, exports are more expensive. net exports decrease, AD shifts left
cost push deflation as imported raw materials are cheaper
demand pull deflation as net exports fall
unemployment may increase as less is exported
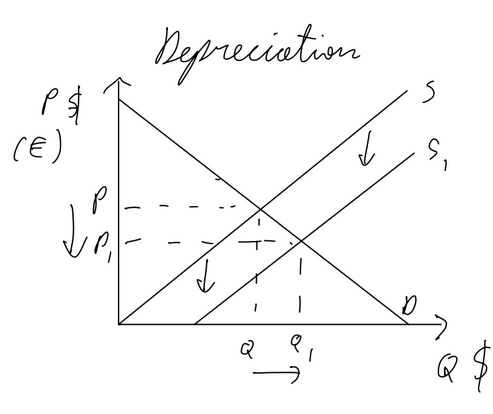
impact of currenccy depreciation on current account
depreciation → net exports increase → current account balance improves
the extent to which depends on Marshall-Lerner condition
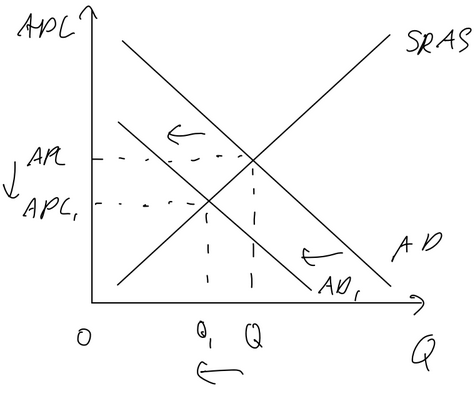
impact of currency appreciation on current account
appreciation → net exports decrease → current account balance worsens
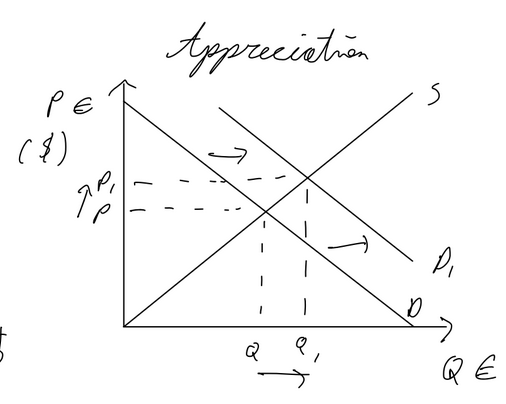
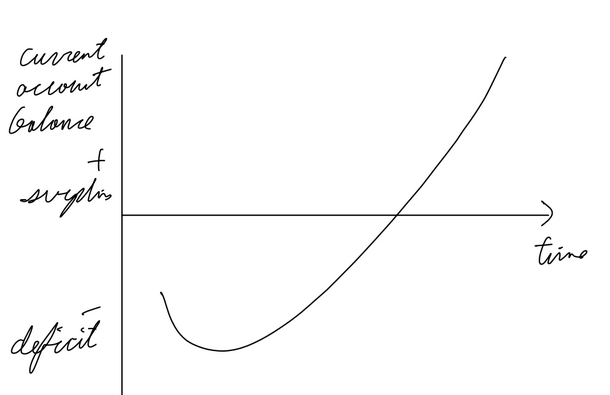
Marshall-Lerner condition / J-Curve
ML condition: extent to which a currency depreciation improves the current account balance, PED imports + PED exports > 1
Time lag between depreciation of a currency and an improvement in current account balance explained by J curve.
If a country’s currency depreciates, its good will become cheaper for other countries. However, it will take time before the other countries switch to that country’s goods as they aren’t sure whether the exchange rate my return in the short run
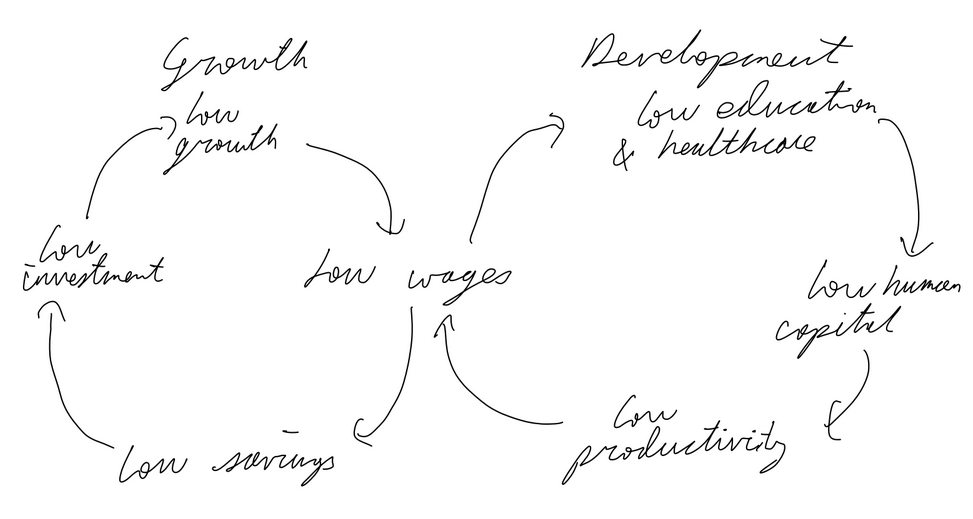
Poverty Cycle
A situation where poverty tends to perpetuate itself from one generation to the next.