A. WOOD: 5 Veneers and Grains
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Inter-locked
A type of grain where grains are in successive layers and in opposite direction caused by each growth year
Diagonal grain
A type of grain when straight grained log is not sawn along its vertical axis
Spiral grain
A type of grain when trees grow twisted, spiral-grained logs and subsequent boards are produced. This twist happens either left or right-handed.
End grain
A type of grain when board is cut across the grain (perpendicular to the grain direction and the growth rings)
Quarter sawing
A type of sawing lumber when first, the sawyer cuts the log in quarters, then slices each quarter into boards, either by cutting boards from two flat sides alternately or by gang-sawing the quarter (parallel cuts)
Live saw
Sometimes called sawing through and through; produces much wider boards than other methods, and these boards show mostly mixed grain - flat grain near the centre of the face and quarter grain near the edges
veneer
A thin sheet of wood, rotary cut, sliced or sawn from a log or flitch.
stump veneer
Produced from the base of the tree. Here the grain pattern is always swirly twisted and often accompanied by cross fire and patches of burl. The sizes are normally small.
Crotch Veneer
Produced from the portion of the tree just below the point where it forks into two limbs. The grain is twisted, creating a variety of flame figures.
cathedral pattern
A grain appearance characterized by a series of stacked "V" and inverted "V". Pattern common in plain-sliced (flat-cut) veneer.
burl veneer
Produced from a large, wartlike growth on the trunk of the tree. The grain pattern typically resembles a series of eyes laid side by side. Obviously the veneers leaf sizes are generally small and additionally are defective
random match
The veeers are placed in a random order and orientation. This provides a completely random and unmatched look.
center match
where the leaves are all the same width and the grain pattern is centered on the panel. This is the most labor intensive and, therefore, is most expensive
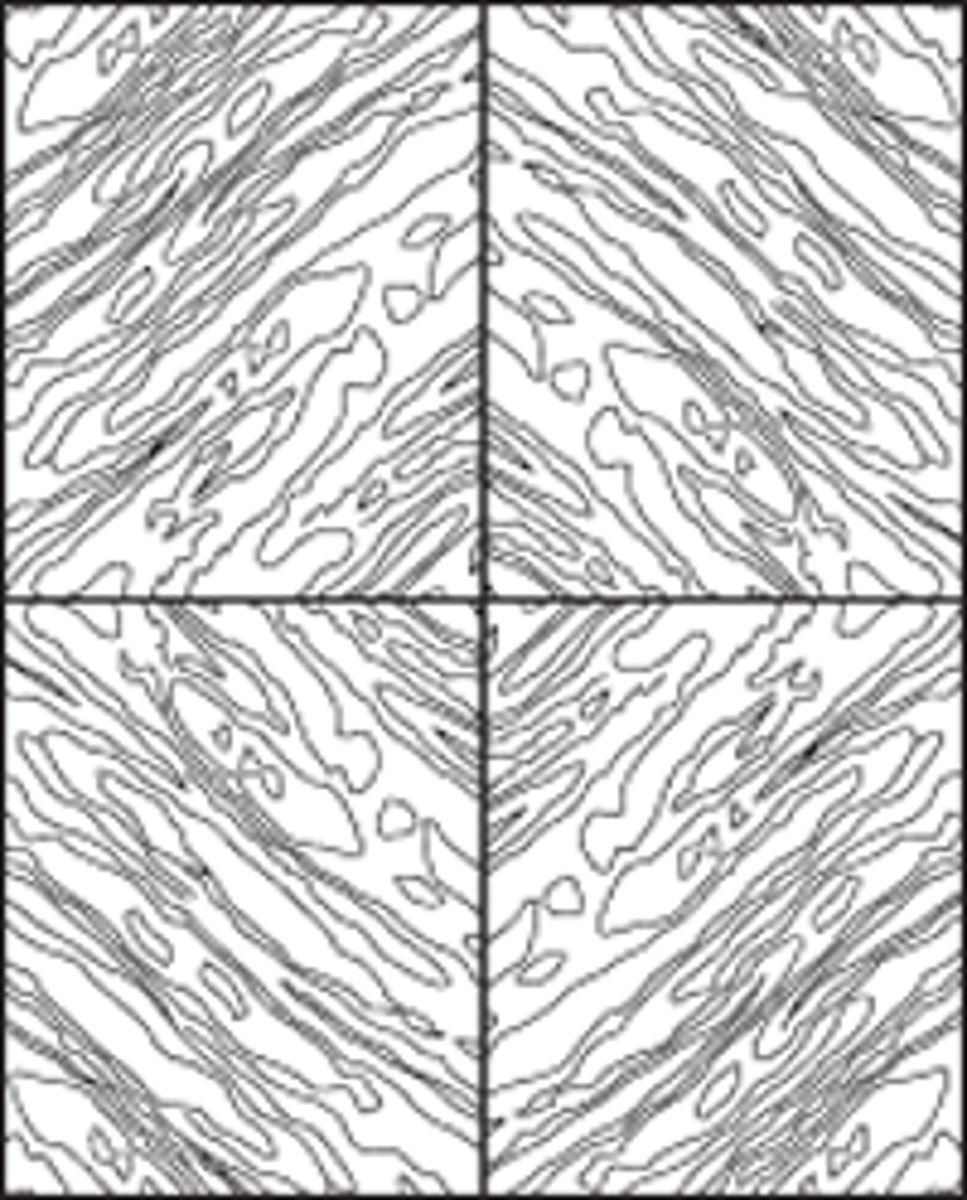
book match
practice of matching two surfaces, so that two adjoining surfaces mirror each other
diamond match
Leaves of veneer are oriented at an angle in a mirror image that forms a concentric diamond pattern.
slip match
The joining together of individual wood flitches, side by side, so as to provide a repetitive decorative pattern in the arrangement, but not necessarily continuous or symmetrical in the overall visual effect.
saw cutting
method of cutting veneer used for thick cut veneers that are 1/8" thick. These are cut using circular saws
rotary cutting
method of cutting veneer widely used for constructional and some decorative veneers such as bird's eye maple
off center cutting
method of cutting veneer with a combination of rotary cutting and flat slicing that produces a figure similar to a flat sliced veneer
half round cutting
method of cutting veneer similar to off center cutting and produces also a flat sliced veneer.
back cutting
method of cutting veneer where a rotary method is used for cutting decorative butt and crotch veneers
flat slicing
method of cutting veneer common for producing traditional crown cut veneer
book match veneer
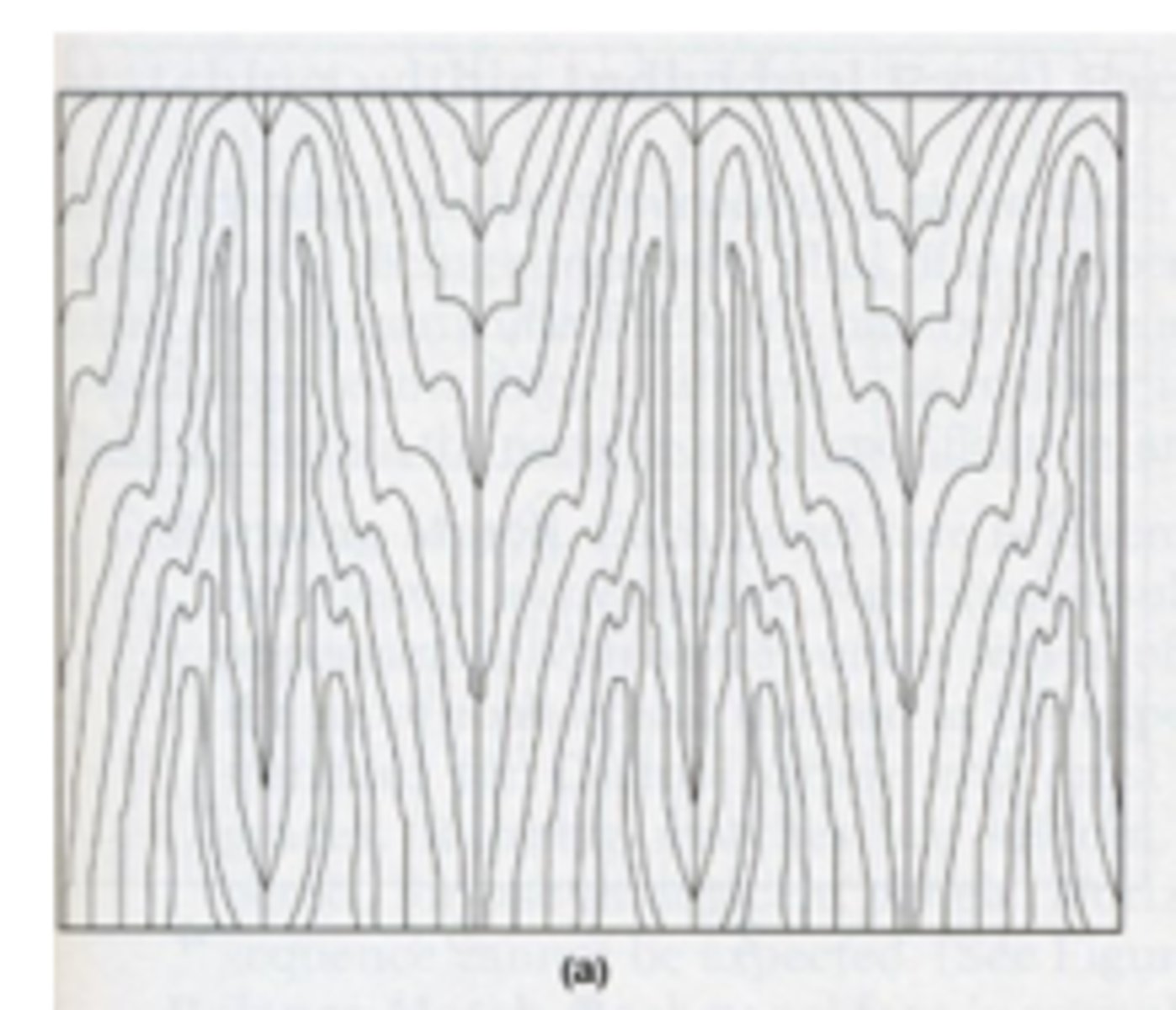
slip match veneer
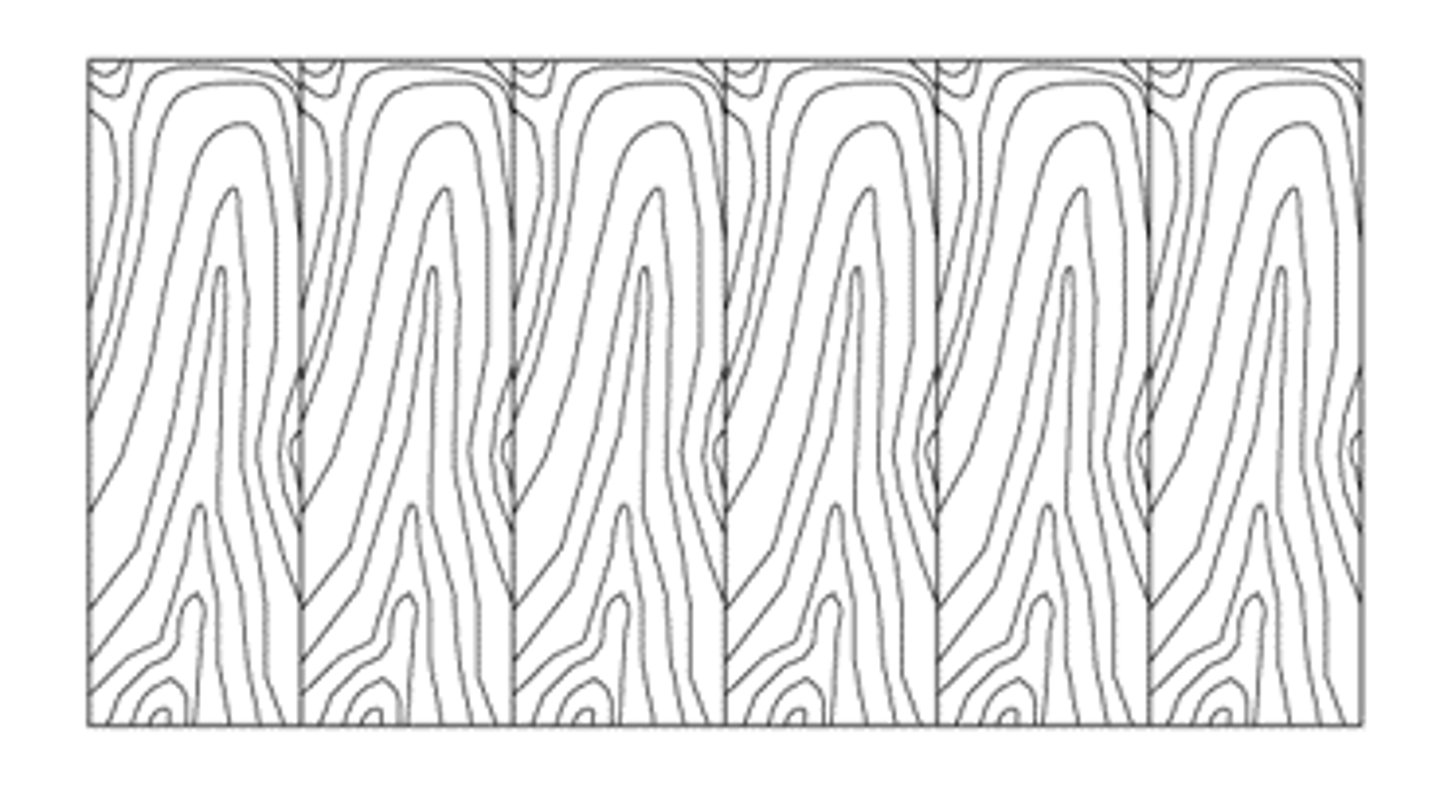
diamond match veneer