ch 8 food safety (purchasing, storing, controls, HACCP, equiptment, sanitation, cleaning, waste
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
what is the ultimate goal of a food safety manager
assure that a safe food product is served to customers to protect them from foodborne illness
possibilities of food before it purchased include (5)
contaminated equipment, infected pests and animals, untreated sewage, unsafe water, and soil
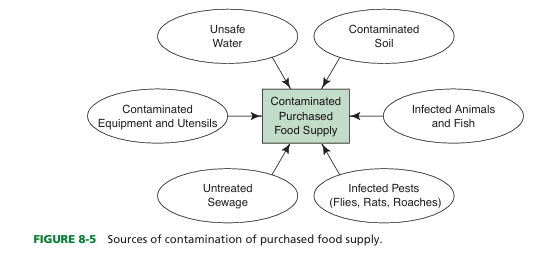
after purchase, possible contamination exist in (3) of food
purchase, storage, and service of food
possible transmission routes from infected persons
respiratory tract discharges, open sores, cuts, and boils, or through hands soiled with feces into food being prepared.
food should be purchased from suppliers that are
approved and reputable
suppliers should be using (2)
using Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) or Good Agricultural Practices (GAP)
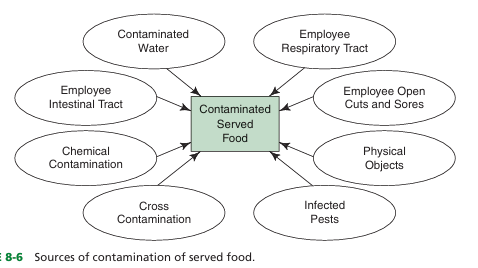
contaminated served food by (6)
contaminated water
employee respiratory tract
employee open cuts and sores
physical objects
infected pests
cross contamination
chemical contamination
employee intestinal trac
foodsafety starts in the _____ area of foodservice operation
receiving
meat food safety criteria
temp
color
texture
odor
packaging
41°F or below
bright red color
firm, nonslimy texture
no odor
intact and clean packaging
poultry food safety criteria
temp
color
texture
odor
packaging
41F or below
no discoloration
firm
no odor
frozen or packed in crushed, self draining ice
fish food safety criteria
temp
color
texture
odor
eyes
packaging
41°F or below
bright red gills and bright shiny skin
firm flesh; mild ocean or sea weed smell
bright, clear full eyes
frozen or packed in crushed, self-draining ice
shellfish food safety criteria
temp
odor
shells
packaging
Live on ice or at temperature of 45°F or below; shucked at internal temperature of 45°F or below
mild ocean or seaweed smell
unbroken shells; closed shells if alive
shellstock identification tags (packer’s name, address, and certification number) on container (manager must date when the last shellfish was served and then keep tags on file for 90 days from date)
shell eggs food safety criteria
temp
odor
packaging
Temperature of 45°F or below
no odor
clean and unbroken shells
liquid, frozen, dried food safety criteria
packaging
pausterization
Must be pasteurized
have a USDA inspection mark
dairy food safety criteria
temp
milk processes
cheese flavor, texture, color
Temperature of 41°F or below
milk must be pasteurized and comply with FDA Grade A standards
cheese with typical flavor, texture, and uniform color
canned goods food safety criteria
packaging
Can and seal in good condition (no swollen ends, leaks, dents)
dry goods food safety criteria
packaging
Intact packaging (no holes, tears, punctures, water stains
produce food safety criteria
temp
temperature of 41°F or below for fresh cut greens, melons, tomatoes, or other processed produce
define cold chain management
Temperature control throughout the supply chain delivery process of perishable foods.
focus is on maintaining a temperature-controlled environment throughout the distribution and storage stages of a food produce
Ex: for example, tracking the temperature of meat from the time it was initially processed at a meat packing plant through storage and transportation until it reached the foodservice operator to ensure that the temperature of the product was maintained at acceptable levels throughout the supply chain stages
define cross contamination
Transfer of microorganisms from one food product to another, by storing raw meat, poultry, and fish separate from cooked and ready-to-eat foods.
how should poultry, ground beef, meat, and RTE food and cooked meat be stored
Raw poultry should go on the lowest shelves
Raw ground meat should be placed on shelves above raw chicken but under raw whole meats and fish.
Raw meats should be placed above raw poultry and raw ground meat but under cooked and ready-to-eat foods
Ready-to-eat foods and cooked food items should be placed on upper shelves above any raw meat, fish, or poultry.
define temperature danger zone
Temperature range (41°F to 135°F) in which bacteria multiply rapidly
how quickly should TCS food be cooled
time/temperature control for safety (TCS) food, should be cooled within 2 hours from 135°F to 70°F; and within 6 hours from 135°F to 41°F or less
Safe temperatures are below 41F and 135F and above
when can cross contamination occur (like why)
Cross-contamination can occur in production and service when improper food-handling practices are used
Cutting board to cut raw meat and then using same uncleaned to cut produce
Handling raw meat or poultry and not washing hands well before handling RTE foods
why is employee hygiene and practices important
Employee personal hygiene and good food-handling practices are basics of a food safety program in a foodservice facility.
One major risk is that unsanitary employees can contaminate, or infect by bacteria, food products in production and service
A foodservice employee personal hygiene program should include three major components:
maintaining personal cleanliness
wearing proper work attire
following hygienic hand practices
basic rules for employee dress and rules
Proper attire (pulled back hair, closed toed shoes, proper clothes, no jewelry)
Proper handwashing
Nails short and clean, no false nails, no nail polish
Cuts and wounds on hands need be covered
No eating, chewing, drinking
how often to clean room temp food contact services
at least every 4 hours
for a food safety program, what 3 things must be put in place/ identified
critical control points (CCP) identified
standard operating procedure put in place
hazard critical control point (HACCP) model selected
define hazard analysis critical control points
systematic analysis of all process steps in the foodservice subsystems, starting with food products from suppliers and ending consumption of menu items by customers.
what are the critical points
those steps in production processing In which loss of control would result in a unacceptable safety risk
HACCP was crated as a what, for what
HACCP uses a preventive approach to quality control
HACCP was developed in 1971 for NASA to be sure food fed to astronauts in outer space is absolutely safe
3 phases of HACCP
Selection of control points
Identification of critical control points
Establishment of monitors for control
what are the 7 HACCP principles
Created in 1992 by NACMCF
Principle 1: conduct a hazard analysis
Principle 2: determine the critical control points
Principle 3: establish control limits
Principle 4: Establish monitoring procedures.
Principle 5: establish corrective actions
Principle 6: establish verification procedures
Principle 7: establish recordkeeping and documentation procedures
define hazard
Unacceptable contamination of food
define critical control points
Locations in the food product flow where mishandling of food is likely to occur
basis for a strong HACCP program is having the necessary prerequisite programs in place. What programs? (11)
Sanitation standard operating procedures
Quality management
Employee education and training
Personal hygiene
Safe food handling and storage practices
Temperature monitoring
Specifications and suppliers
Food recalls and disaster plans
Equipment monitoring and calibration
Preventive maintenance programs
Integrated pest management
define standard operating procedure (SOPs)
written, step-by-step instructions for routine tasks

what types of thermometers are need in foodservice operations (4 types)—> not specific names but like location and type
bimetallic stemmed or digital pocket test, refrigerator/freezer/dry storage, hot holding, and meat thermometers
what is the HACCP manager (type of thermometer)
is an electronic device for recording and transmitting temperature, time, and location for any food preparation process that requires accurate record keeping

infrared thermometer
not inserted into food; rather they use infrared technology to measure the temperature of the food on the surface
most commonly used thermometer
bimetallic stemmed thermometer

define calibrate
Process to assure temperature testing equipment is providing an accurate temperature reading.
Easiest way to calibrate is to place thermometer in glass of ice water for at least 30 seconds
what are T sticks
Many foodservice operations have supplemented the use of thermometers with a disposable product called T-Sticks.
T-Sticks are multipurpose sensor sticks used to monitor food temperatures and the temperature in the dishwasher’s final rinse section
define bioterrorism
Intentional use of biological agents or germs to cause illness.
Became a thing due to the sept 11 terrorist attacks
Food and water became a potential target for terrorist attacks
Strategic Partnership Program Agroterrorism (SPPA) Initiative
-what is
-formed by what agencies
Designed to protect nation's food supply
Is a DHS, USDA, FDA, and FBI collaboration
what is ALERT
FDA Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition developed food security preventive measures guidance for food processors and retailers
what does ALERT stand for
A- Assure products received are from safe sources,
L- Look (monitor) the security of productions in the operation
E- Employees know who should or should not be in the area
R- Report and keep information related to food defense accessible and
T- Threat
suggestions for food protection (7)
-awareness
-procurement
-access
-personnel management
-monitoring
-planning
-education
awareness
Awareness—be alert to unusual activity in and around your operation
procurement
Procurement—use reputable suppliers and inspect deliveries carefully
access
Access—control access to foodservice operation
personnel management
Personnel Management—screen applicants carefully and document, post, and enforce employee schedules
monitoring
Monitoring—observe employees and customers and check less used areas
planning
Planning—have detailed response plans in place that include call lists
education
Education—educate employees on the role they need to play in helping monitor and report unusual occurrences
procedure for complaints
have person complete a complaint report
Obtain all the pertinent information including names and addresses of all party members, the employee who served the meal, the date and time of customer's visit, and suspect meal
Remain concerned and polite, but do not admit liability of offer to pay medical bills
Never suggest symptoms, but let the complainant tell their own story
Record the time the symptoms started, which will help in identifying the disease

The first requirement for a sanitary design is
cleanability
which means the facility has been arranged so that it can be cleaned easily
define clean
Free of physical soil and with an outwardly pleasing appearance.
define sanitary
Free of disease-causing organisms and other contaminants
what 6 factors effect cleaning process
Type and condition of dirt—certain types of dirt require special cleaning methods
Water hardness—cleaning is more difficult with hard water as the minerals in the water react with the cleaning detergent and decrease its effectiveness
Water temperature—hot water aids in dissolving detergent and loosening dirt
Surface to be cleaned—some surfaces require special cleaning supplies and techniques
Agitation or pressure—additional pressure may be needed to remove dirt
Length of treatment—longer exposure to detergent makes cleaning easier
what are the 4 types of cleaners
detergents, abrasive cleaners, degreasers, delimers
detergents
detergents- used to remove dirt from surfaces (floors, walls, counters, equipment)
abrasive cleaners
Abrasive cleaners- contain abrasive agent(s) to help more difficult to remove dirt
degreasers
Degreasers- used to remove grease from surfaces (ovens, grills, hoods)
delimers
Delimers- used to remove mineral deposits (dishmachines, steam wells)
____________ is critical for any surface that comes in contact with food, which includes, of course, all dishes, utensils, pots, and pans
sanitation
most common chemicals used in sanitation
Chlorine
Iodine
quaternary ammonia
effective of sanitation agent is impacted by (5)
concentration of the sanitizer, the hardness, temperature, and pH of the water, and the contact time on a surface
define material safety data sheet (MSDS)
Sheet with use and safety information about a chemical.
how should receiving and storage area be designed
for easy cleaning
dry storage area design
Slip resistant floors, insulated walls and subfloors, insect and rodent proof, light colored walls, products never stored on floor--> dry storage area
fridge and freezer storage area design
Hard surfaces, easy clean floors, walls, fixtures, nonabsorbent material, drains, uniform ventilation and adequate lighting--> fridge and freezer storage
define ware washing machine
Process of washing and sanitizing dishes, glassware, flatware, and pots and pans either manually or mechanically.
dishmachine process consist of (5)
scrapping, prewashing, washing, sanitizing, and air drying
single tank dish machine (for what, has what)
For plates, cups, silverware, or glasses.
two doors that can be manually opened and one combined wash-and rinse tank. It holds a rack of dishes that does not move.

rack coveyor dishmachine (works how)
Dishes are still racked to be cleaned in the rack conveyor dishmachine. After dishes are scrapped and sorted, they are placed in racks and the racks with soiled dishes are put on a conveyor that moves the racks through the dishmachine.
Rack conveyor dishmachines have one, two, or three tanks.

2 tank vs 3 tank rack conveyor machine
The two-tank machine has prewash and power-wash tanks
the three-tank machine has a heavy-duty power prewash, power-wash, and power-rinse
flight type continous conveyor
This dishmachine is typically used in high-volume operations
rather than being placed in racks, plates and trays are placed between rows of plastic pegs on a conveyor; smaller items such as glasses, cups, and flatware are racked before sending them through the machine.

pot washing is done how
with power soak
Pot washing is quite different from dishwashing because pressurized hot water is sprayed directly on the soiled surface.
define power soak, what is it
Pot- and pan-washing equipment that capitalizes on the natural scouring abilities of high-turbulence, heated water
considered the easiest way to clean pots and pans
Maintaining an optimum cleaning temperature of 115°F loosens soil while powerful jets blast clinging particles away
proper plumbing is important to prevent mixing of what 2 things
potable and nonpotable water
potable water
water that is safe for human consumption
sanitation of kitchen and dining areas (plan)
-need regularly scheduled programs on proper cleaning procedures
-plan must be started when facility is being planned
procedure for cleaning floors
Spills should be wiped up promptly to avoid tracking and to eliminate a safety hazard.
Regular schedules for cleaning floors should be established. Floors subjected to heavy traffic and food spills, such as in the production areas, must be scrubbed at least daily and hosed, stripped, and steamed periodically for more thorough cleaning.
Floor care equipment, including brooms, mops, and vacuums, should be cleaned regularly.
dish storage
All dishes and utensils must be stored dry and in clean, dust-free areas above the floor and protected from dust, mop splashes, and other forms of contamination
Mobile equipment designed for various things is ideal
general rules to trash and garbage handling (5)
Garbage and trash containers must be leakproof, easily cleanable, pest-proof, and durable with tight-fitting lids. Today, plastic bags frequently are used for lining containers to facilitate disposal.
Garbage and trash should not be allowed to accumulate anywhere but in containers
Garbage and trash should be removed from production areas on a frequent basis for appropriate disposal.
Garbage storage areas should be easily cleanable and pest-proof. If long holding times for garbage are required, these areas should be refrigerated to prevent decomposition, odor, and infestation by vermin.
A garbage can washing area with hot water and a floor drain should be located away from food production and storage areas.
define pulper
Water-filled tank in which solid waste is broken down into a slurry by a shred ding device and then water is pressed out of it (water is then reused)
replacing garbage disposal units
require daily cleaning
define solid waste
Solid and semisolid products, such as foodwaste, paper, cardboard, metal, and plastic, that are being discarded from a foodservice
goal is what when it comes to food waste
prevent pollution before it occurs
An integrated solid waste management program includes the following:
Menu design and planning
Purchase specifications
Food production practices
Service methods
Portion control
Waste-product disposal methods
Consumer education
Employee training
how much of solid food waste is service related? from food production and prep areas?
-60-70%
-30-40%
define source reduction
Reducing the amount of waste going into the waste stream from a foodservice operation (source).
define recylcing
Act of removing materials from solid waste stream for reprocessing into valuable new materials and useful products.
Many of the traditional packaging materials, including paper, metals, plastic, and glass, can be recycled.
define composting
Controlled application of the natural process of organic degradation.
Any organic material, including food waste and paper or cardboard that has been contaminated with food, can be composted.
define combustion
Form of solid waste recycling in which the energy value of combustible waste materials is recovered
define biological solution
use bacteria to break down animal fats and food products that clog drains
employee facilities
-what should be provided for them
-type of flooring
-closeness to work area
Locker rooms should be provided for employees to change clothes
Individual lockers with locks are needed for storing street clothes and personal effects when employees are working
Floors should be tile laid in cement or other nonabsorbent materials
Employee facilities should be located near the work area
guest restrooms
should be easily accessible from the dining room
Keeping both employee and guest restrooms clean can be a major management problem
Employee restrooms should be maintained at the same quality as those for guests