UWORLD Renal Step 2 CK
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
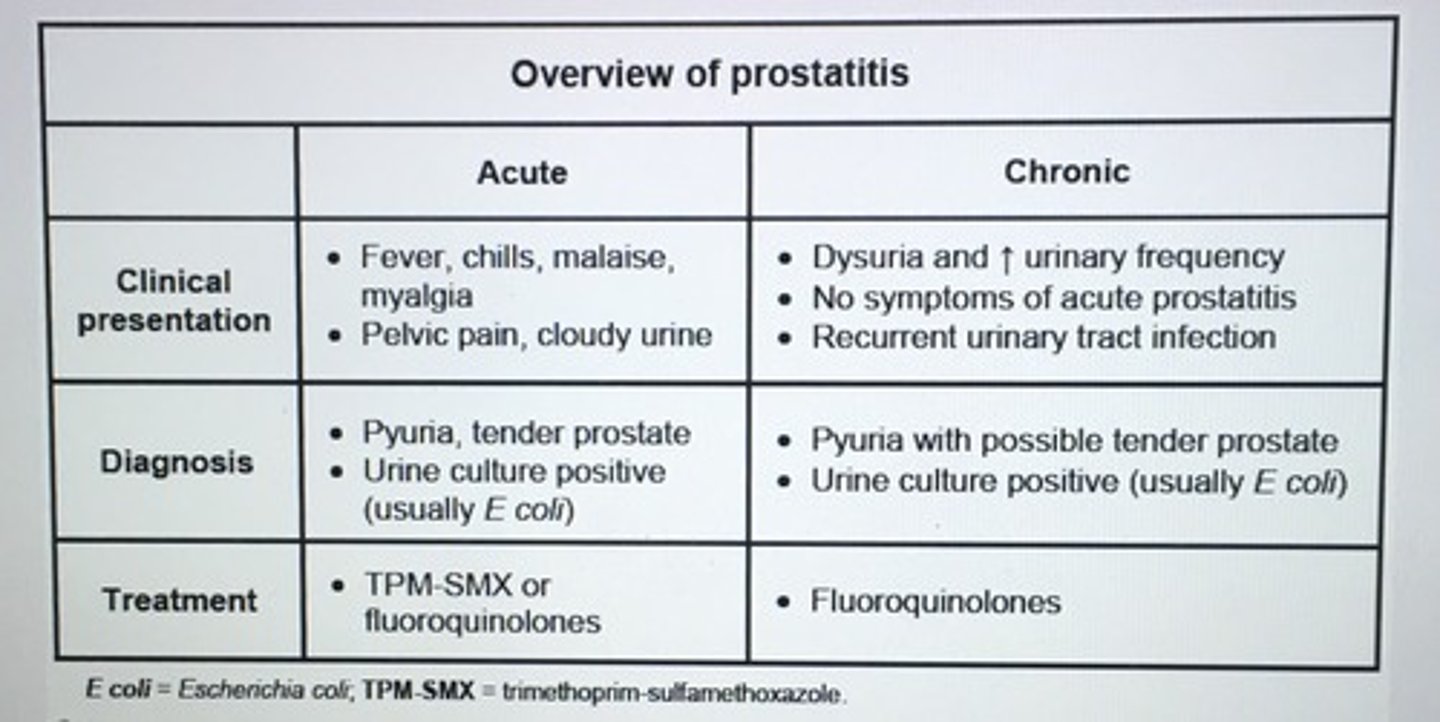
Next step in management pt with perineal pain, dysuria, fever, chills, acute illness, tender, boggy prostate.
Mid-stream urine sample
- empiric abx therapy with TMP-SMX or FQs and treatment continue for 4-6 weeks
Diagnostic criteria for SIADH.
1. Soms < 270
2. Uosm > Sosm
3. UNa > 20
4. Absence of hypovolemia
5. Normal renal. adrenal, and thyroid function
6. No obvious surgical, traumatic, or painful stimulus known to activate the neuroendocrine stress response, including ADH release
7. Absence of other known causes of hyponatremia
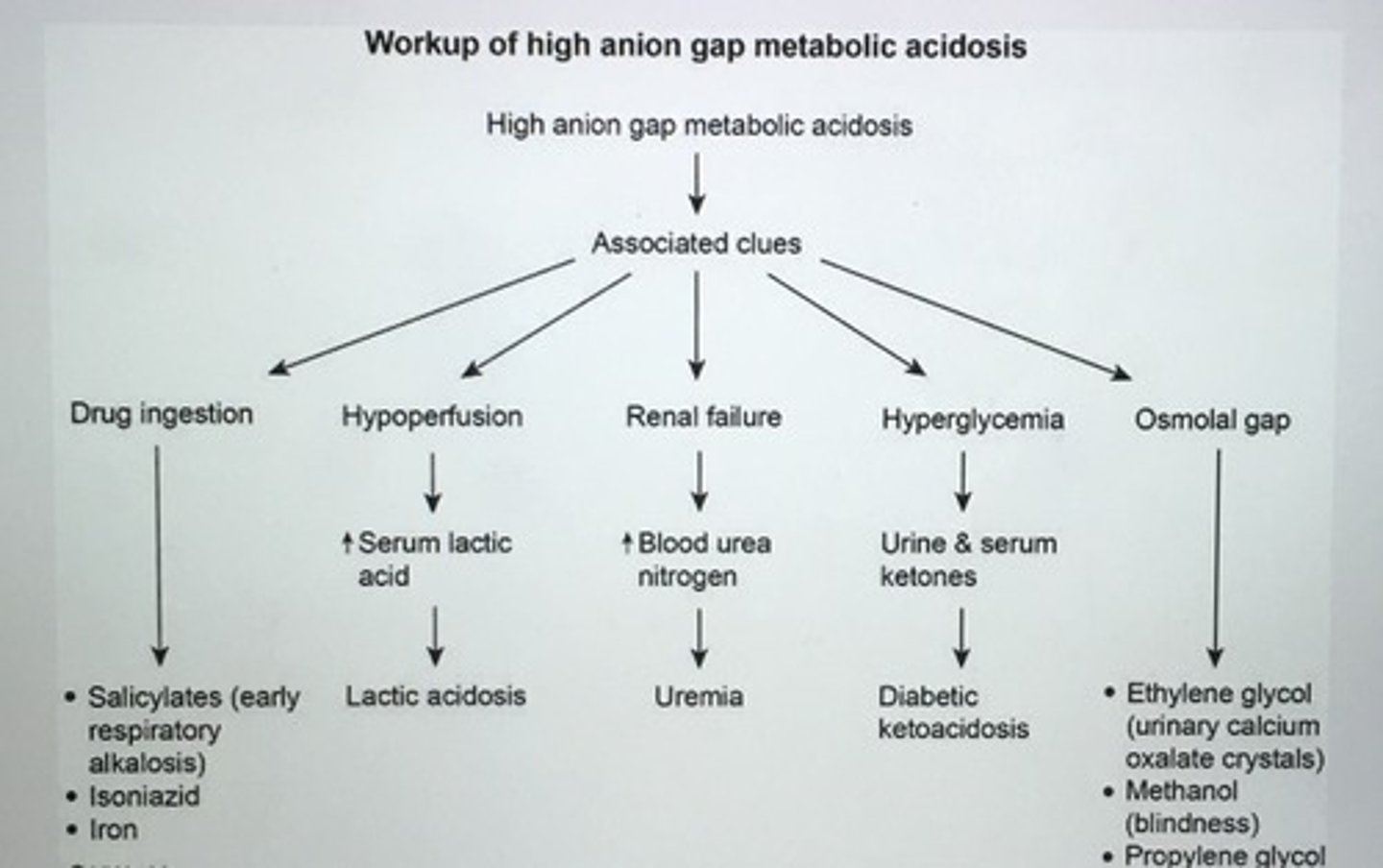
Most common causes of anionic gap metabolic acidosis (AGMA).
1. Lactic acidosis (lactate)
2. Ketoacidosis (beta-hydroxy butyrate, acetoacetic acid)
3. Methanol/formaldehyde ingestion (formic acid)
4. Ethylene glycol ingestion (glycol acid, oxalic acid)
5. Salicylate poisoning (salicylic, lactic, sulfuric, and phosphoric acid)
6. Uremia (ESRD) (impaired excretion of H+)
Current guidelines recommend evaluating all patients with probable BPH based on history and rectal examination with a ___.
Urinalysis
- assess for UTI and hematuria
- pts life expectancy > 10 years should have PSA to measured to screen for prostate cancer
Tx of severe hypernatremia.
0.9% saline isotonic with goal rate no more than 1mEq/L/h
___ caused by a mutation in calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR). Benign disorder with asx hypercalcemia, elevated or normal PTH, low urinary calcium excretion, urine calcium/creatinine clearance ratio < 0.01.
Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia
___ is a depolarizing neuromuscular blocker the can cause life-threatening ___. It should not be used in patients with or at high risk for ___ such as burn or crush injury patients or patients with prolong demyelination (Guillain-Barre).
Succinylcholine
- Hyperkalemia
better choice is non-depolarizing agents such as vecuronium or rocuronium
Medications that can cause hyperkalemia.
1. Nonselective BB
2. ACEi /ARBs
3. K+ sparing diuretics (amiloride, triamterene)
4. NSAIDs
5. Digoxin
6. Cyclosporine
7. Heparin
8. Succinylcholine
9. TMP-SMX
___ abuse leads to INC excretion of water and electrolytes by the kidneys, resulting in dehydration, wt loss, orthostatic hypotension, hyponatrmia, and hypokalemia.
Diuretic abuse
- urine Na+ and K+ are elevated
- pts may abuse diuretics for wt loss
Pt has HTN and palpable kidneys on exam.
ADPKD
- the enlarged right kidney is easier to palpate because it lies lower than the left kidney (liver may be enlarged due to cystic involvement)
- multiple cysts, intermittent flank pain, hematuria, UTIs, and nephrolithiasis
Tx of hypercalcemia.
Saline hydration to restore intravascular volume and calcitonin to inhibit bone resorption
Bisphosphonates further reduce calcium libels and are given after initial administration of saline
Chronic alcoholic presents with hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, and hypophosphatemia. ___ causes refractory hypokalemia.
Hypomagnesemia
- Mg cofactor for K+ uptake
Complications of nephrotic syndrome.
Nephrotic syndrome: hypercoagulable condition -> venous or arterial thrombosis -> PE
- Renal Vein thrombosis
- Protein malnutrition
- Iron-resistant microcytic hypochromic anemia
- INC susceptibility to infection
- vitamin D deficiency
- DEC thyroxin levels
HIGH YIELD: ___ is the most common cause of abnormal hemostasis in patient with chronic renal failure.
Platelet dysfunction
- uremic coagulopathy
- PT, PTT, platelet count normal
- BT prolonged
Tx for Chronic kidney disease with abnormal hemostasis.
DDAVP increased the factor VIII:vWF multimers from endothelial storage sites
Causes of normal anion gap metabolic acidosis.
- Diarrhea
- Fistulas (pancreatic, ileocutaneous)
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
- Renal tubular acidosis
- Ureteral diversion (ileal loop)
- Iatrogenic
One should suspect ___ whenever test results demonstrate a large amount of blood on urinalysis with a relative absence of RBCs on urine microscopy.
Myoglobinuria
- usually caused by rhabdomyolysis can be 2/2 seizures leads to acute renal failure
Patients with diabetes > 10 years can develop ____. Risk factors include poor glycemic control, elevate BP, smoking, INC age, and ethnicity (AA, Mexican america). Clinical findings include mild to moderate proteinuria and CKD with elevated creatinine.
Microangiopathy
Nephropathy
Glomerulosclerosis
The most common renal vascular lesions seen in hypertension are ____ lesions of afferent and efferent renal arterioles and glomerular capillary tufts.
Arteriosclerotic
- nephrosclerosis is characterized by hypertrophy and intimal medial fibrosis of renal arterioles
- glomerulosclerosis is progressive loss of glomerular capillary SA
- kidney size decrease
Hepatorenal syndrome is seen in patients with severe liver cirrhosis secondary to systemic and renal ___.
Hypoperfusion
- renal function does not improve with IV fluid resuscitation
- Acute renal failure (Cr > 1.5) with very low urine sodium < 10, absence blood, casts, or protein in urine
Postictal ___ commonly occurs following a tonic-clonic seizure. It is a transient anion gap metabolic acidosis that resolves w/o tx w/in 60-90 min. following the resolution of seizure activity
Lactic acidosis
- AGMA
___ presents with flank pain, low volume voids with or w/o occasional high-volume voids, and if B/L renal dysfunction.
Obstructive uropathy
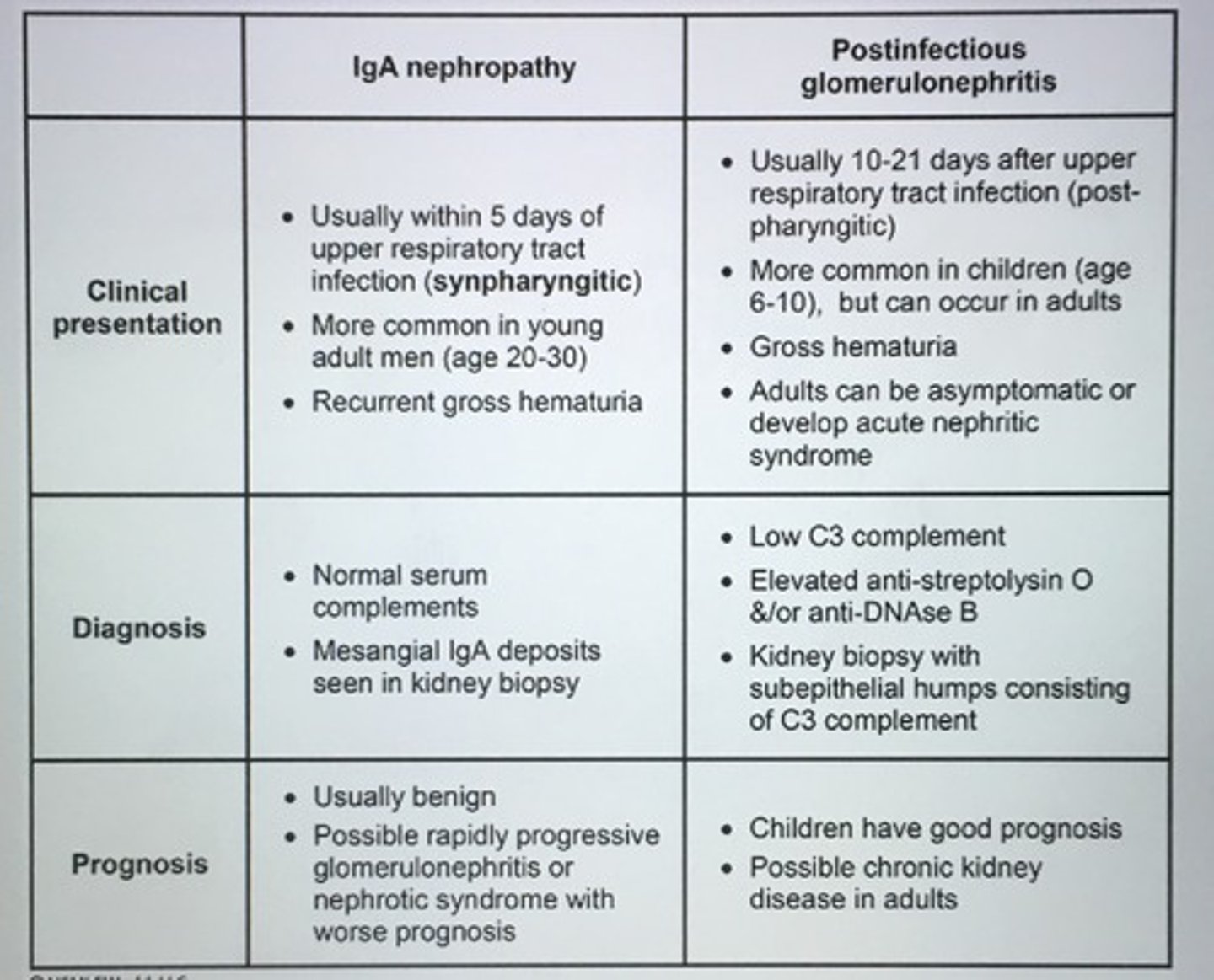
IgA nephropathy versus post infectious glomerulonephritis.
Analgesic nephropathy is the most common drug-induced chronic renal failure. ___ and ___ are the most common pathologies seen.
Papillary necrosis and chronic tubulointerstitial nephritis
- chronic analgesic abuse more likely to develop premature aging, atherosclerotic vascular disease, and urinary tract cancer
- WBC casts, polyuria
Muddy brown granular cast
Acute tubular necrosis
- prolonged hypotension
- hypovolemic shock
1. Urine osmolality 300-350
2. Urine Na > 20
3. FeNa > 2%
RBC casts
glomerulonephritis
WBC casts
pyelonephritis
interstitial nephritis
Fatty casts
nephrotic syndrome
Brown and waxy casts
chronic renal failure
__ should not be given to acutely ill patients with acute renal failure, liver failure, or sepsis as these conditions increase risk of lactic acidosis.
Metformin
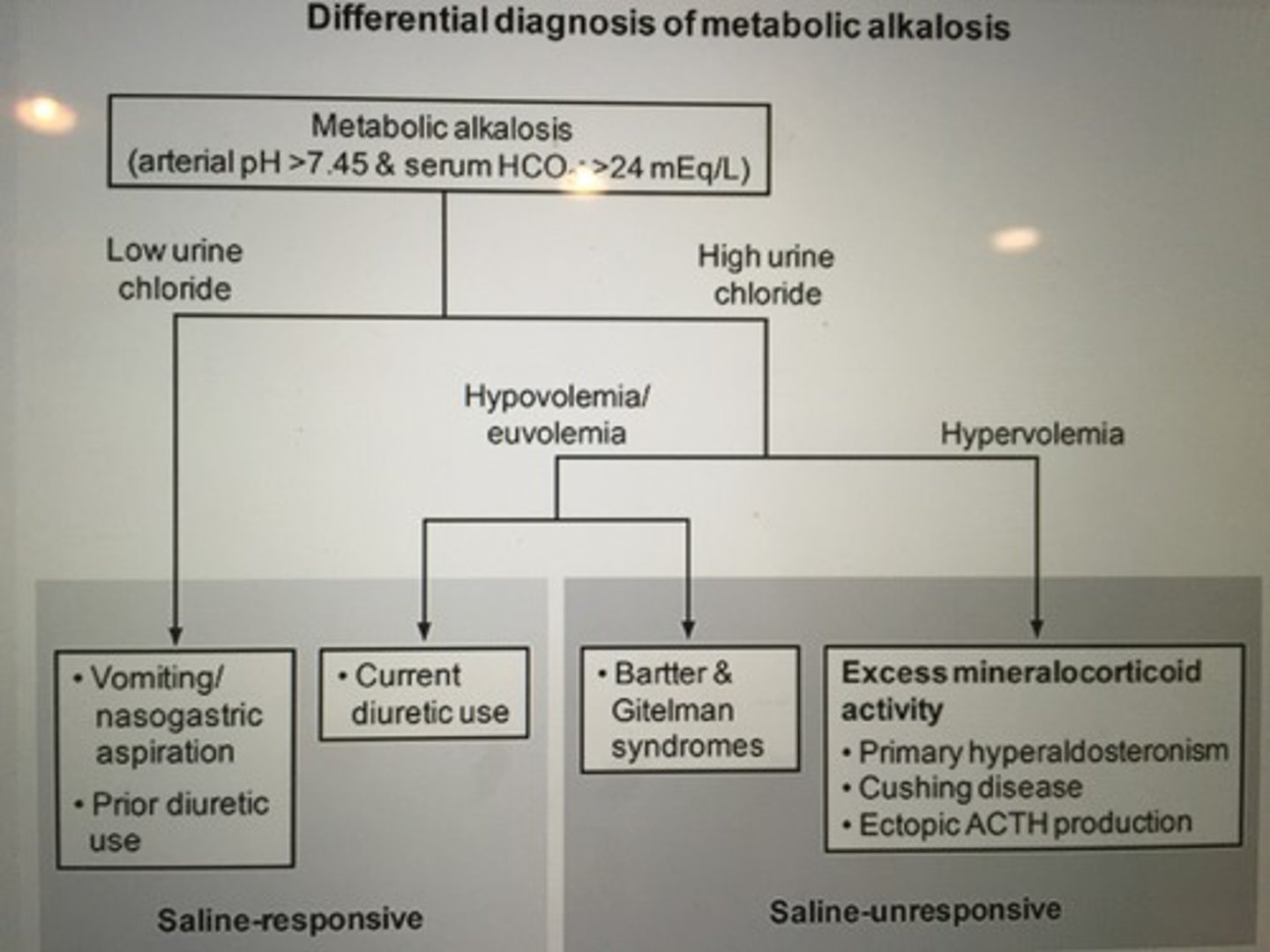
Differential diagnosis of metabolic alkalosis.
The common presentation of ____ included palpable purpura, glomerulonephritis, non-specific systemic sxs, arthralgias, hepatosplenomegaly, peripheral neuropathy, and hypocomplementemia. Most patients also have Hep C.
Mixed cryoglobulinemia
75% to 90% of kidney stones are made of ____.
Calcium oxalate
- small bowel disease
- surgical resection
- chronic diarrhea
lead to malabsorption of fatty acids and bile salts, predisposes to th formation of calcium oxalate stones
__ most common cause of death in dialysis patients.
CV disease
- 20% acute MI
- 60% sudden cardiac death
Pt has photosensitive skin, thrombocytopenia, glomerulonephritis with low complement C3 and C4. Dx.
SLE
Renal vein thrombosis is an important complication of all causes of nephrotic syndrome. However, it is more commonly associated with ____.
Membranous glomerulopathy
Flank pain, hematuria, and palpable abdominal renal mass, scrotal varicocele (L-sided).
Renal cell carcinoma
- paraneoplastic syndromes (anemia, thrombocytopenia, fever, hypercalcemia, cachexia)
- CT scan of abdomen
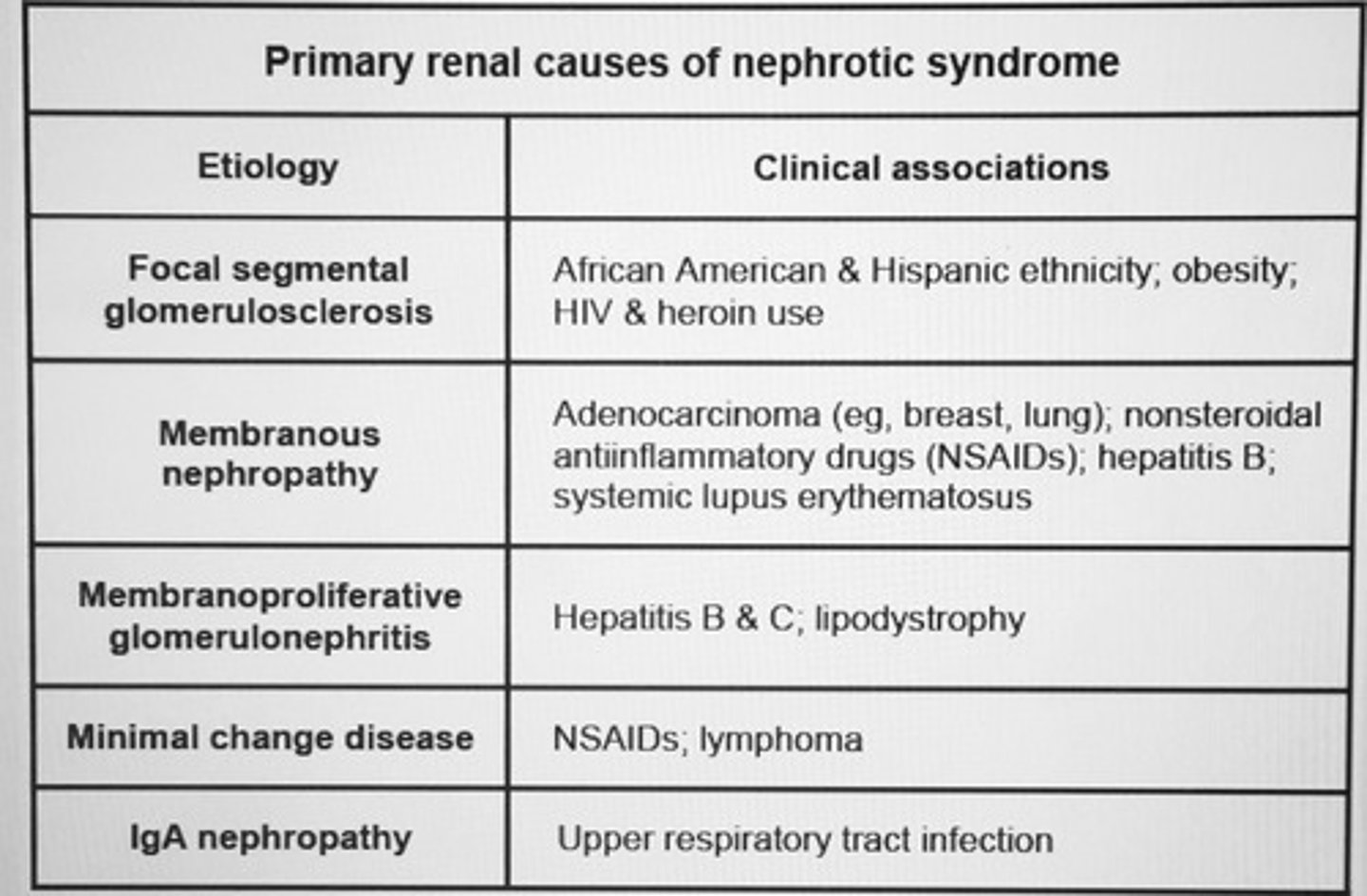
Primary renal causes of nephrotic syndrome
Major extra-renal complications of ADPKD.
1. Intracranial berry aneurysm (MC complication)
2. Hepatic cysts (most common extrarenal manifestation)
3. Valvular HD (MVP and AR)
4. Colonic diverticula
5. Abdominal wall and inguinal hernia
Indications for cystoscopy.
1. Gross hematuria with no evidence of glomerular disease
2. Microscopic hematuria with no evidence of glomerular disease or infection but increased risk of malignancy
3. Recurrent UTIs
4. Obstructive sxs suspicious for stricture, stone
5. Irritative sxs w/o urinary infection
6. Abnormal bladder imaging or urine cytology
___ is the most important risk factor for bladder cancer.
Cigarette smoking
Workup for high anion gap metabolic acidosis.
___ is the most common form of nephrotic syndrome in patients with Hodgkin lymphoma.
Minimal change disease
Ureteral calculi may cause flank or abd pain radiating to the perineum, often with N/V. ___ are the imaging modalities of choice to confirm the diagnosis.
U/S
Noncontrast spiral CT
U/S preferred in pregnant patient
Bladder pain with filling, relief with voiding. INC frequency and urgency, dyspareunia. Normal UA. More common in women. Associated with psych disorders (anxiety) and pain syndromes (fibromyalgia).
Interstitial cystitis (painful bladder syndrome)
- not curative, focus on quality of life
- behavioral modification and trigger avoidance
- amitriptyline
- analgesics for exacerbation
Nearly 20% of cocaine overdoses are complicated by ____, as indicated by marked elevations in serum creatine phosphokinase (CPK). The main danger associated with CPK levels greater than 20,000 U/L is ____.
Rhabdomyolysis
- Acute renal tubular necrosis due to myoglobunuria
Diabetes insipidus (DI) can be differentiated based on urine osmolality difference between Complete and Partial DI.
1. Complete DI - urine osmolality < 300mOsm/kg (often less than 100)
2. Partial DI - urine osmolality ranges from 300-600 mOsm/kg
Drugs that can cause Nephrogenic DI.
Lithium
Demeclocycline
Foscarnet
Cidofovir
Amphotericin
Tx of choice of uric acid stones.
Alkalization of the urine pH 6-6.6 with oral potassium citrate is the tx of choice
Hydration
Low-purine diet
HIGH YIELD: ___ is an inherited disease causing recurrent renal stone formation. Look for personal Hx of recurrent kidney stones from childhood and positive FHx. Hard and radiopaque stones. Hexagonal crystals. Urinary cyanide nitroprusside test is positive.
Cystinuria
- impaired amino acid transport (cystine, lysine, arginine, ornithine) at the brush border of renal tubular and interstitial epithelial cells
Hematuria at the end of urinary stream (terminal hematuria) with clots in urine. Dx.
Bladder or prostatic damage
- evaluate with cystoscopy
___ absorption is increased in Crohns disease and all other intestinal diseases causing fat malabsorption. Can lead to nephrolithiasis.
Oxalate
= hyperoxaluria + oxalate stone formation
____ is the most common cause of AA amyloidosis (inflammatory amyloidosis).
RA
- nephrotic syndrome
- amyloid deposits that stain with Congo red and demonstrate apple-green birefringent under polarized light
- abnormally folder proteins: beta-2 mcroglobulin, apolipoprotein or tranthyretin
___ is the most common cause of AL amyloidosis (amyloid light-chain amyloidosis).
MM
Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia
Light chains (lambda) composition of amyloid
Typical causes of respiratory alkalosis.
- Hyperventilation due to pneumonia
- High altitude
- Salicylate intoxication
___ can facilitate stone passage and reduce the need for analgesics.
Alpha-1 receptor blockers (tamsulosin) act on the distal ureter, lowering muscle tone and redding reflex ureteral spasm 2/2 stone impaction
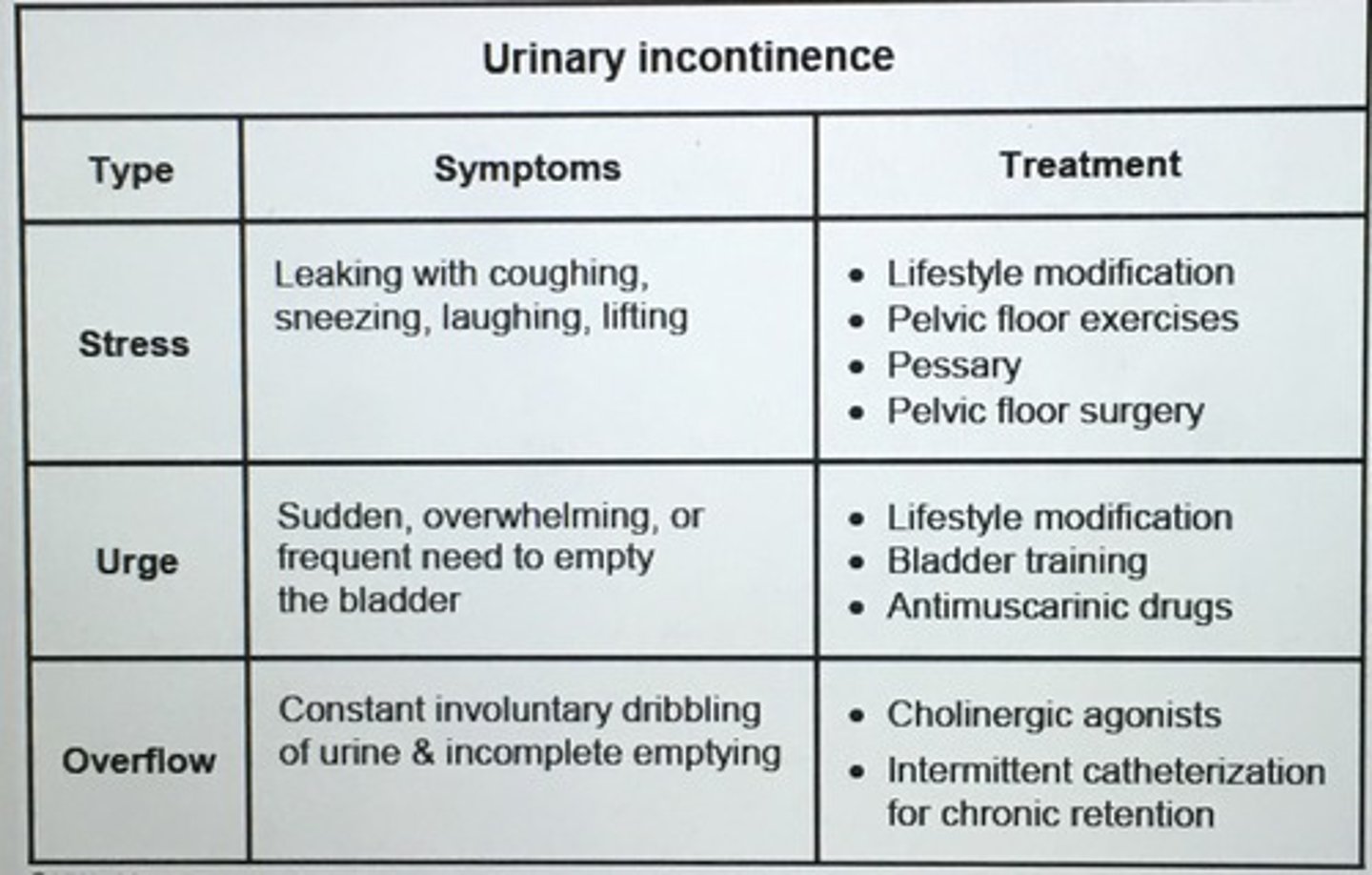
Urinary incontinence types.
Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis, type 2, is a unique glomerulopathy that is caused by persistent activation of the ____.
Alternative complement pathway
- nephrotic-range proteinuria, hematuria
- dense intramembranous deposits stain for C3
- caused by IgG antibodies (C3 nephritic factor) directed against c3 converts of the alternative complement pathway
__ are antibiotics used to treat serious gram negative infections. They are potentially nephrotoxic and drug levels and renal function must be monitored closely during therapy.
Aminoglycosides
HIGH YIELD: Acute renal transplant rejection is best treated with ___.
IV steroids
- renal transplant dysfunction in the early postoperative period can be due to ureteral obstruction, acute rejection, cyclosporine toxicity, vascular obstruction, acute tubular necrosis
- radioisotope scanning, renal U/S, MRI, and renal biopsy can help with DDx
___ is the earliest renal abnormality seen in diabetic nephropathy.
Glomerular hyperfiltration
- thickening of the glomerular basement membrane is the first change
Pt presents with maculopapular rash, fever, new drug exposure (PCN, TMP-SMX, cephalosporins, NSAIDs), and arthralgias. Pyuria, hematuria, WBC casts, eosinophilia, urinary eosinophils. Renal bx inflammatory infiltrate, edema.
Acute interstitial nephritis
- D/C offending drug, +/- systemic glucocorticoids
High doses IV acyclovir can cause cystalluria with renal ____.
Renal tubular obstruction
- give IV fluids with acyclovir reduce the risk of acute kidney injury
___ and __ should be performed in all patients with oliguria and acute renal failure due to suspected bladder outlet obstruction in the postoperative setting.
Urgent bladder scan and catheterization
The dietary recommendations for patients with renal calculi are?
1. Increase fluid intake
2. DEC sodium intake
3. Normal dietary calcium intake
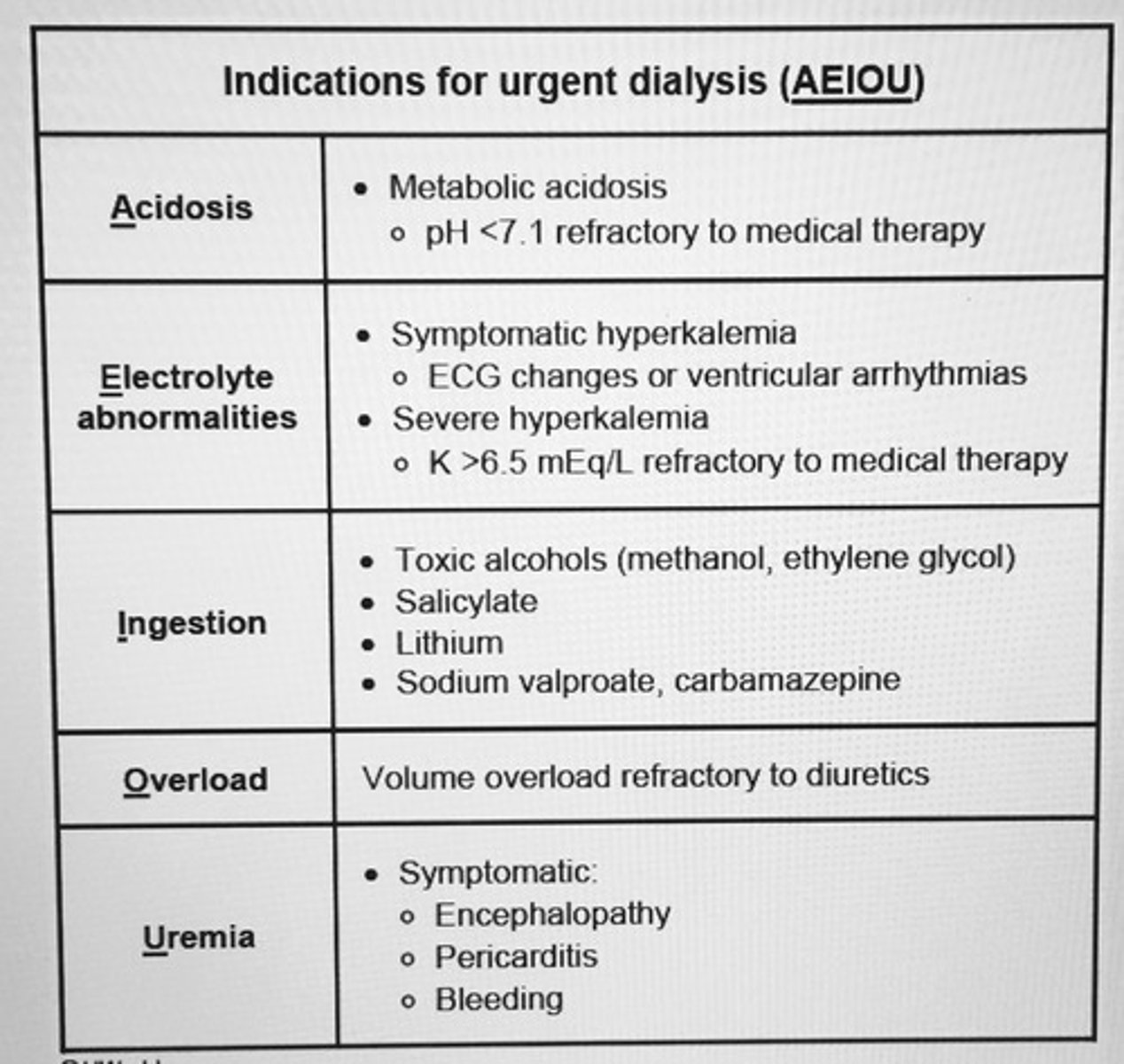
Indications for dialysis
PX
Pericarditis—friction rub
Encephalitis
Chest pain that changes w/ position
Pruritis
Benefit
Benefit becomes negligible in elderly patients
w/ sig. comorbidity & functional decline
Have prolonged fatigue
Increased hospitalizations ← catheter assc. Infections
Diminishes quality of life
Indications
Acidosis
Electrolytes— ↑ K+
Intoxications—Lithium, Aspirin, Methanol, Ethylene Glycol
Overload—CHF
Uremia—Uremic Pericarditis
MCC—Fanconi Syndrome
↓ K+
Risk Factors
NSAIDs
Sickle Cell Anemia
Urinary Tract obstruction
Diabetes
PX
Papillary sloughing
Back/ flank pain
Dark, cloudy urine
Fever
Urinary incontinence
↑ urinary frequency
PX
↑↑ proteinuria > 3.5 g/day
↓ albumin
Hyperlipidemia
Causes
Minimal change disease
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
Secondary
Diabetes mellitus
Amyloidosis
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Nephrolithiasis
Nephrolithiasis
Women > Men
← upper urinary infection
Proteus, Klebsiella
Nephrolithiasis
DX
on urinalysis
RBCs urinalysis
Drugs
Antibiotics
Allopurinol
Proton Pump inhibitors
Phenytoin
PX
Onset 10-14 days after starting a new medication
Fever
Rash
Arthralgias
↑ IgE—Eosinophilia
↑ Creatinine
U/A—↑ RBCs, WBCs
Wright or Hansel stain—detect eosinophilas