Unit 5 Part 2
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
deinstitutionalization
moving people with psychological or developmental disabilities from highly structured institutions to home- or community-based settings

evidence based intervention
a treatment that has been found to be effective on the basis of valid and reliable research studies
biomedical approach
focuses on biological causes and medical treatment; offers medications and other biological treatments that act directly on a person's physiology
psychotherapy
treatment involving psychological techniques; consists of interactions between a trained therapist and someone seeking to overcome psychological difficulties or achieve personal growth

Eclectic approach
an approach to psychotherapy that, depending on the client's problems, uses techniques from various forms of therapy
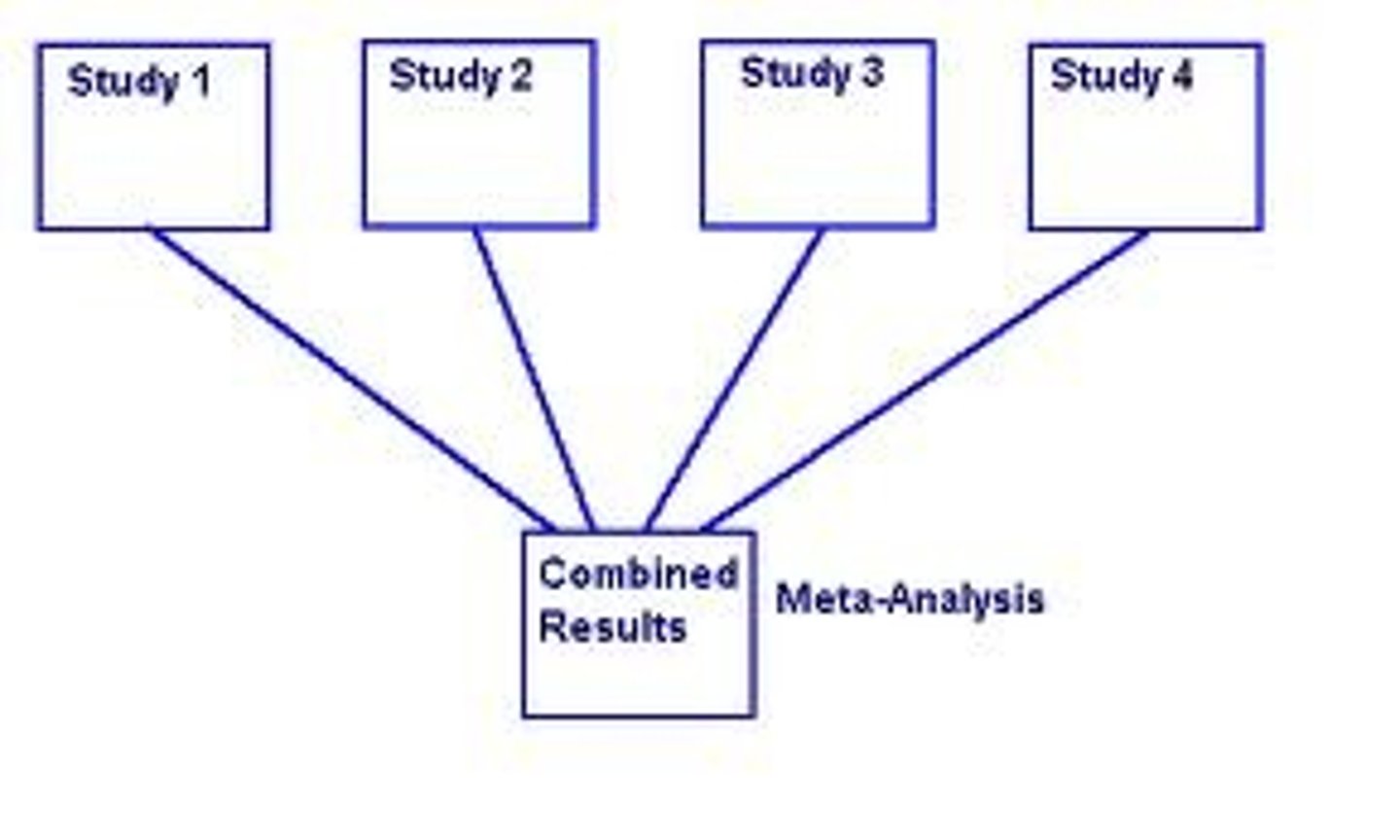
meta analysis
a procedure for statistically combining the results of many different research studies
therapeutic alliance
a relationship between client and therapist that is caring, genuine, and empathetic

positive expectations
the belief that things can and will get better through therapy

cultural humility
which involves striving to understand and respect different cultural groups values, beliefs, and traditions
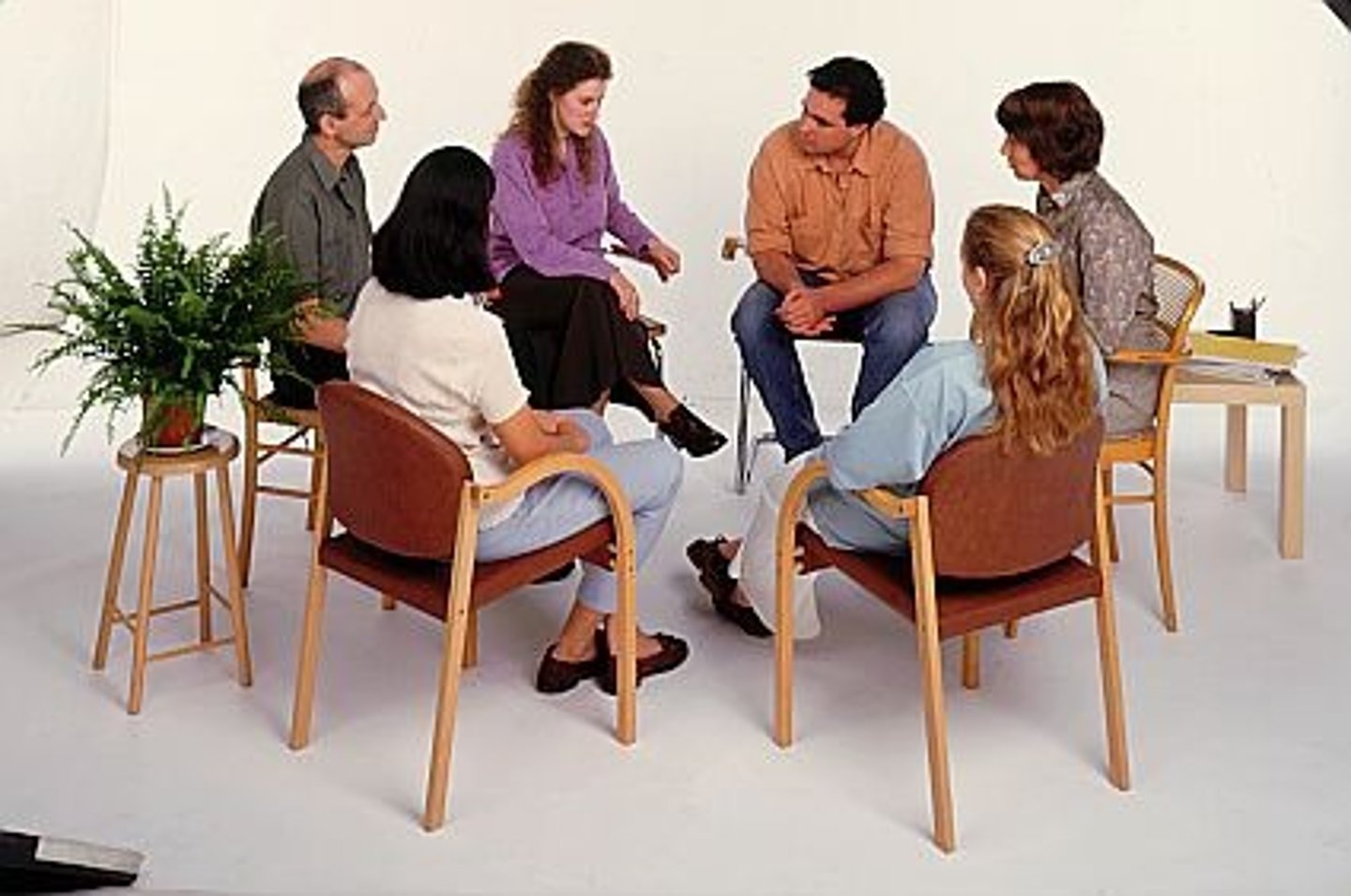
group therapy
therapy conducted with groups rather than individuals, permitting therapeutic benefits from group interaction

Nonmalefience
do no harm
fidelity
establish and maintain trustworthy relationships with clients, colleagues, and the public
integrity
honesty, high moral standards; an unimpaired condition, completeness, soundness
respect for people's rights and dignity
Psychologists respect the dignity and worth of all people, and the rights of individuals to privacy, confidentiality, and self-determination.
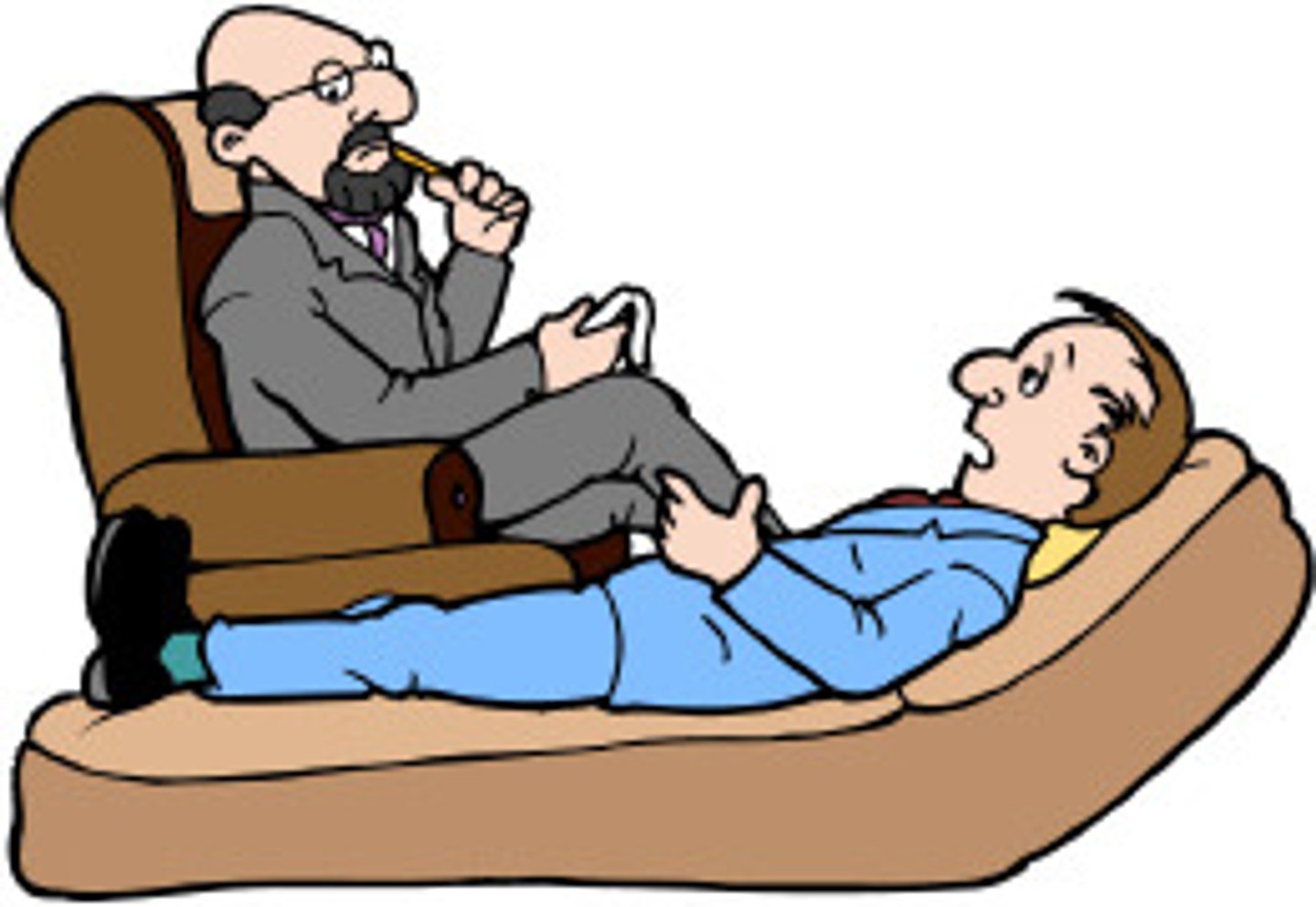
free association
in psychoanalysis, a method of exploring the unconscious in which the person relaxes and says whatever comes to mind, no matter how trivial or embarrassing

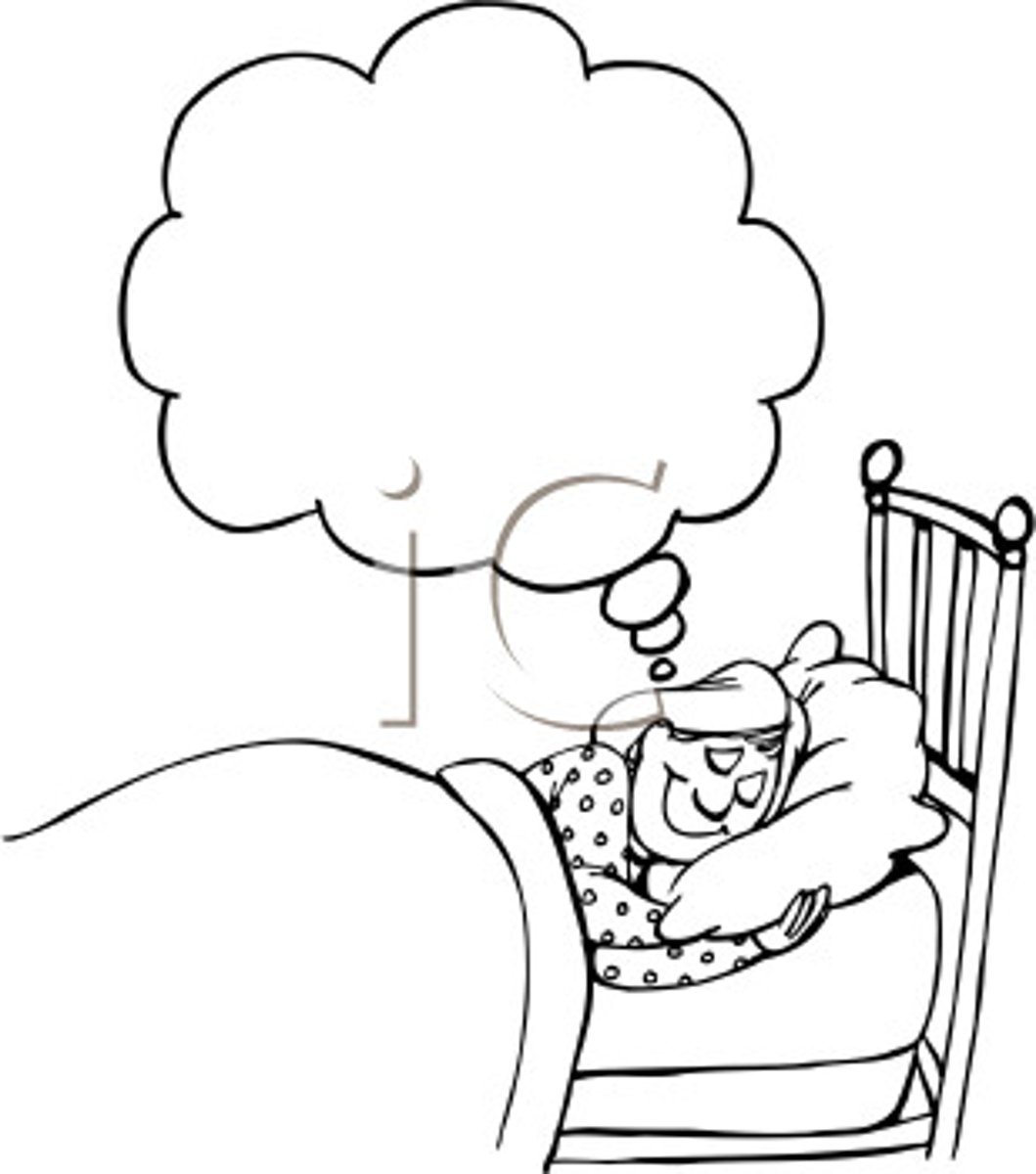
dream analysis
the therapist interprets the symbolic meaning of the client's dreams

interpretations
a psychoanalytic method that uses suggestions of underlying wishes, feelings, and conflicts
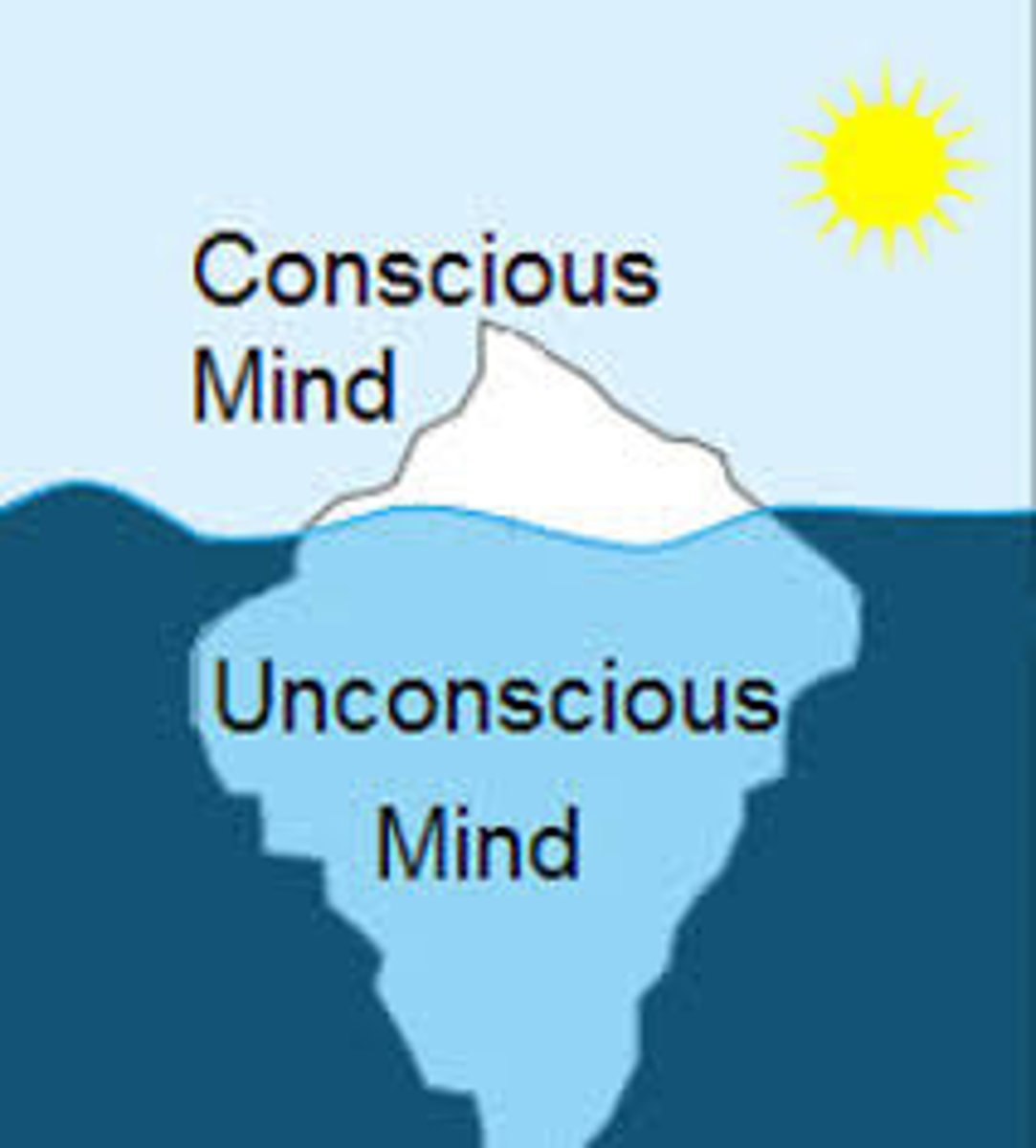
unconscious
influences on the mind
Person centered therapy
a nondirective insight therapy based on the work of Carl Rogers in which the client does all the talking and the therapist listens

token economy
a form of behavior therapy in which clients are given "tokens" for desired behaviors, which they can later trade for rewards

aversion therapy
A behavior therapy in which an aversive stimulus is paired with a stimulus that elicits an undesirable response.

biofeedback
a system for electronically recording, amplifying, and feeding back information regarding a subtle physiological state, such as blood pressure or muscle tension

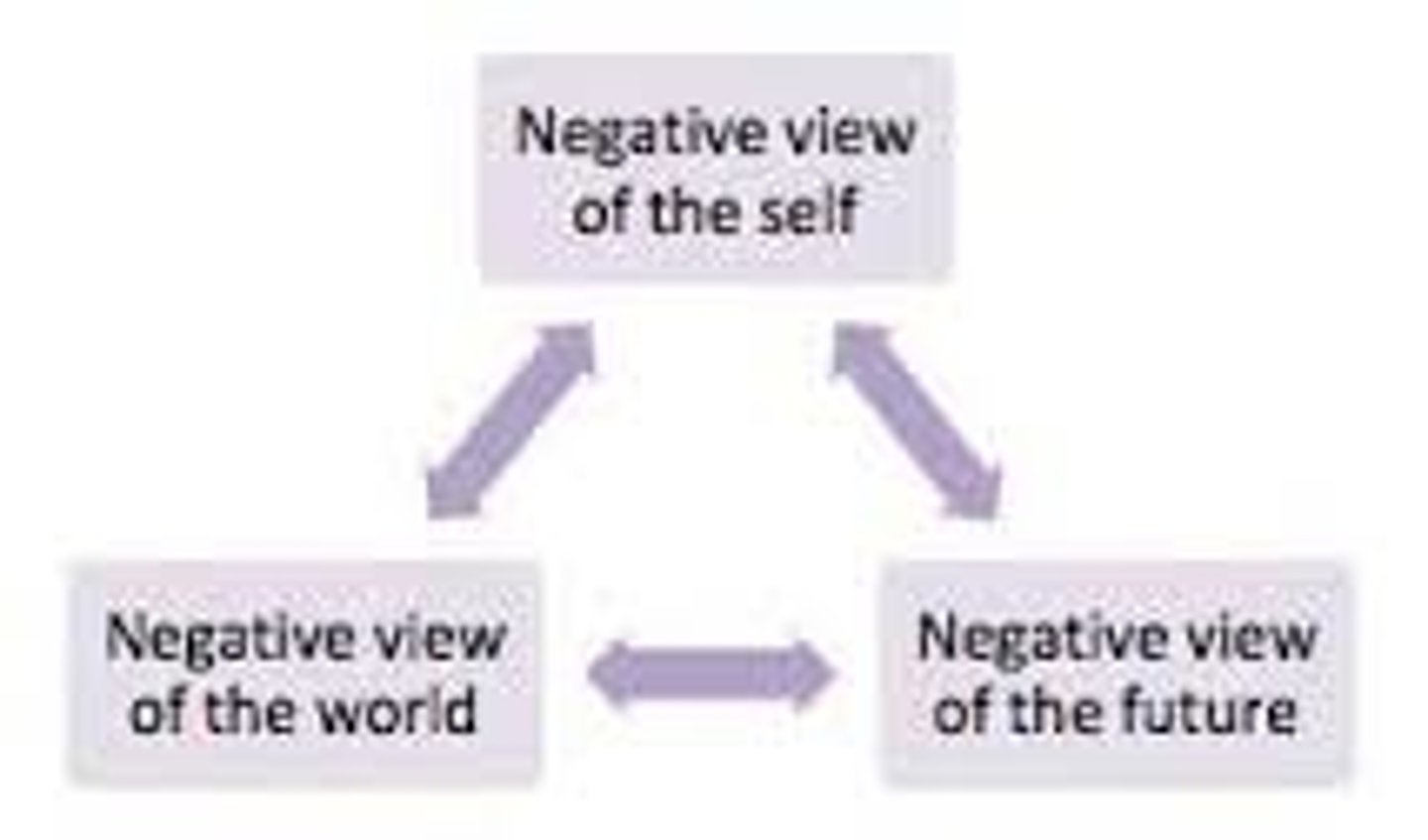
Cognitive triad
negative thoughts about self, world, and the future
cognitive restructuring
a therapeutic approach that teaches clients to question the automatic beliefs, assumptions, and predictions that often lead to negative emotions and to replace negative thinking with more realistic and positive beliefs
Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy
a confrontational cognitive therapy, developed by Albert Ellis, that vigorously challenges people's illogical, self-defeating attitudes and assumptions
dialectical behavior therapy (DBT)
A treatment often used for borderline personality disorder that incorporates both cognitive-behavioral and mindfulness elements.
hynosis
state of consciousness in which the person is especially susceptible to suggestion
psychoactive medications
used to treat psychological disorders
anti-anxiety drugs
drugs used to treat and calm anxiety reactions, typically minor tranquilizers

Antidepressants
drugs that combat depression by affecting the levels or activity of neurotransmitters in the brain (serotonin)
Mood Stabilizers
drugs used to control mood swings in patients with bipolar mood disorders (lithium)
Antipsychotic medications
Prescription drugs that are used to reduce psychotic symptoms; frequently used in the treatment of schizophrenia (dopamine)
tardive dyskinesia
involuntary movements of the facial muscles, tongue, and limbs; a possible neurotoxic side effect of long-term use of antipsychotic drugs that target certain dopamine receptors
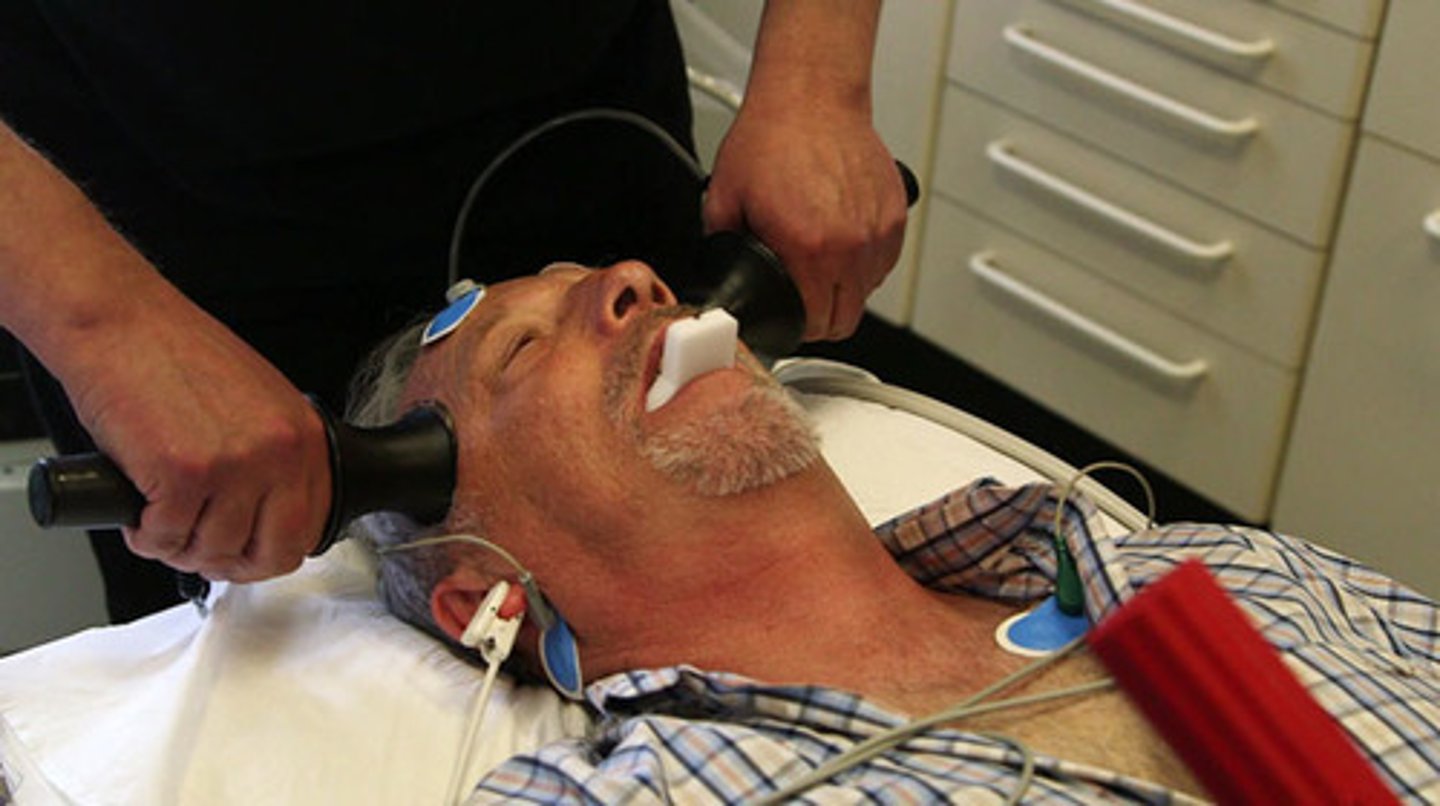
electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)
a biomedical therapy for severely depressed patients in which a brief electric current is sent through the brain of an anesthetized patient
psychosurgery
surgery that removes or destroys brain tissue in an effort to change behavior
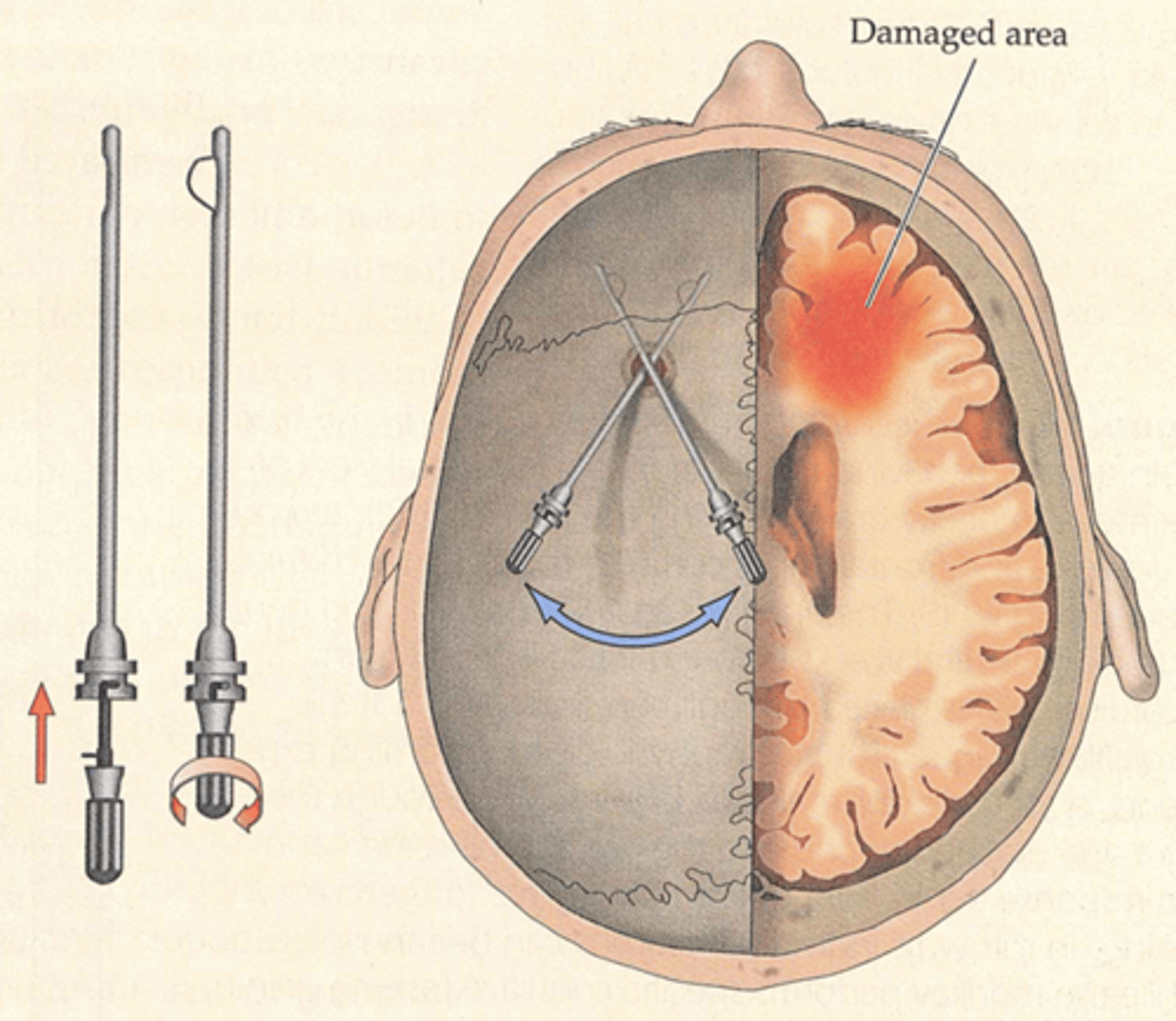
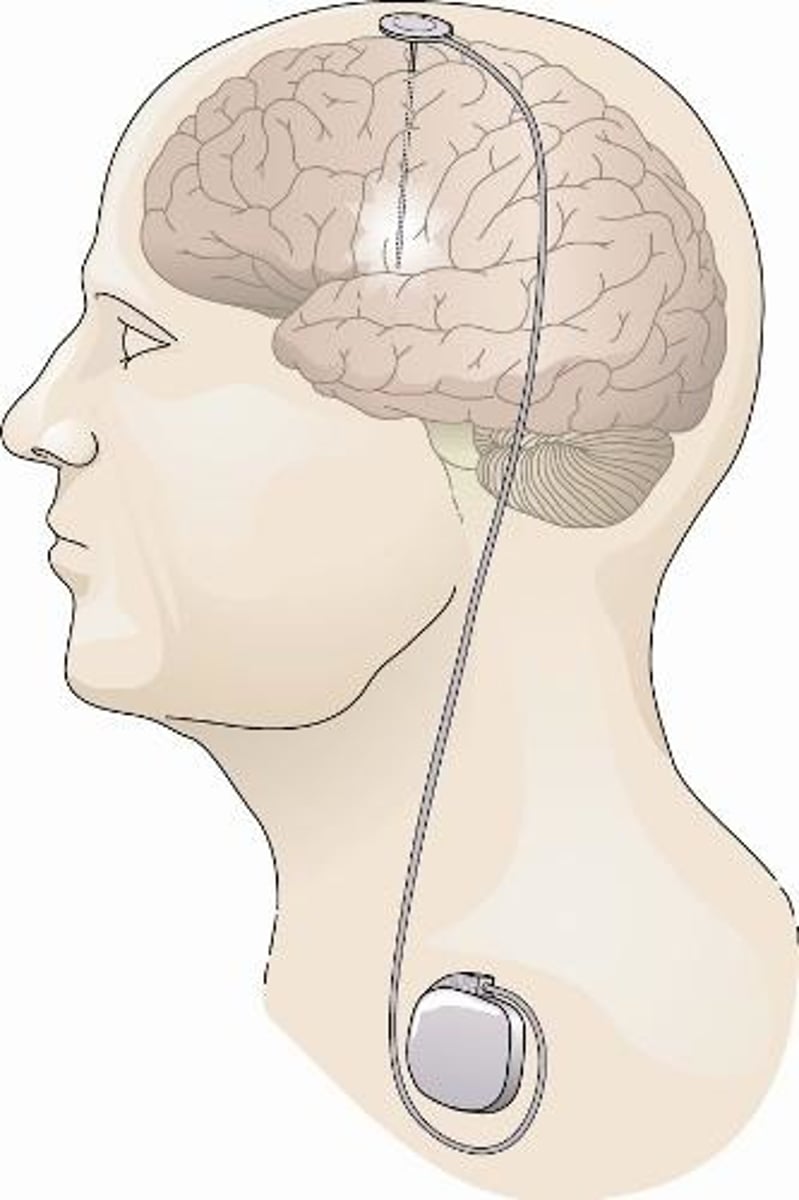
deep brain stimulation
electrical stimulation applied through surgically implanted electrodes; used to treat severe cases of depression
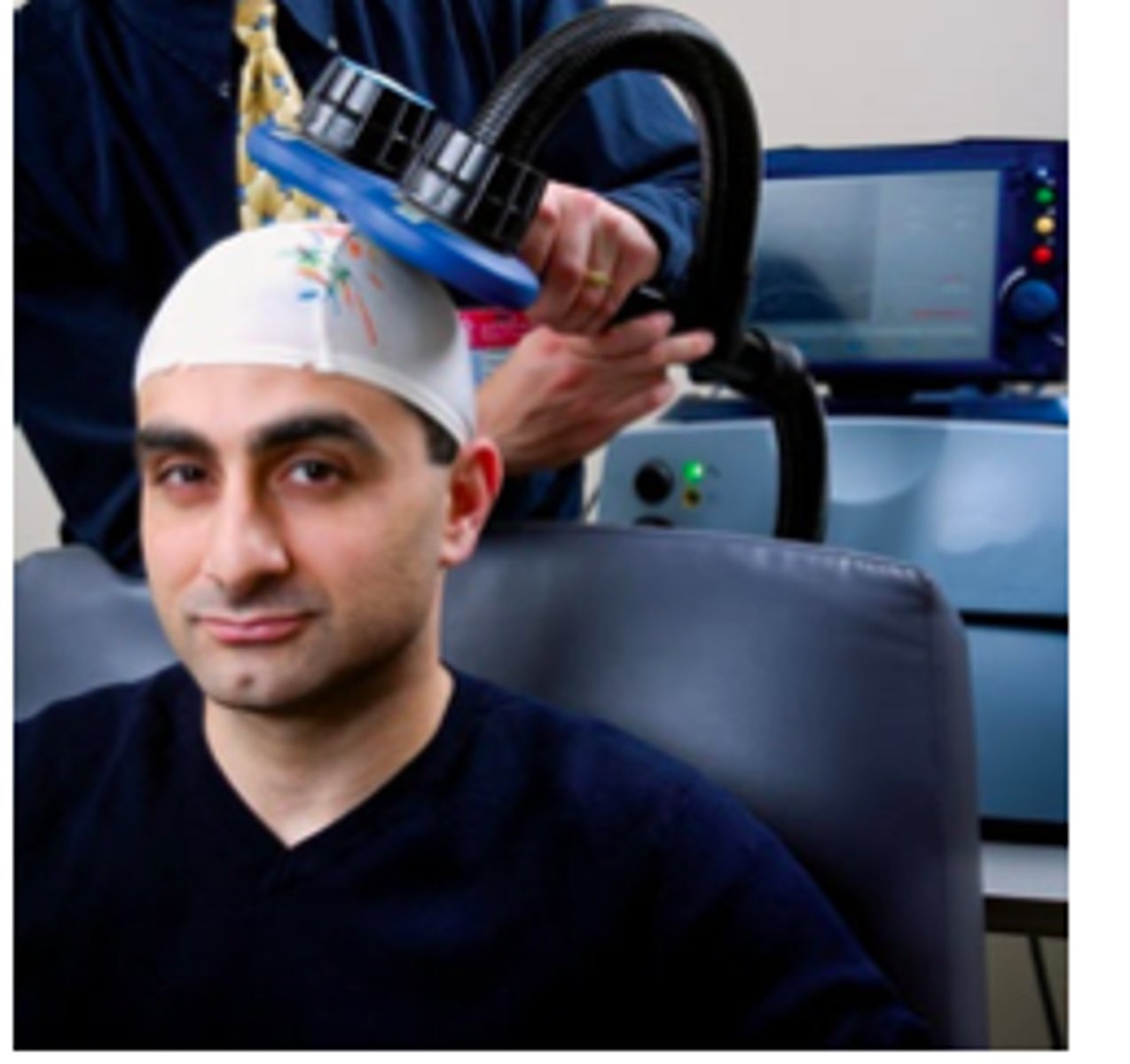
transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)
electrified coil placed very near the skull delivers and electric shock to a specific area of the brain
What is Person-Centered Therapy?
Person-Centered Therapy is a type of therapy that helps people grow and heal by focusing on their needs and feelings, developed by Carl Rogers.
What is Classical Conditioning?
learning by connection.
What is Operant Conditioning?
Operant Conditioning is learning where behaviors are influenced by rewards or penalties.