XVI - Citric Acid Cycle
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
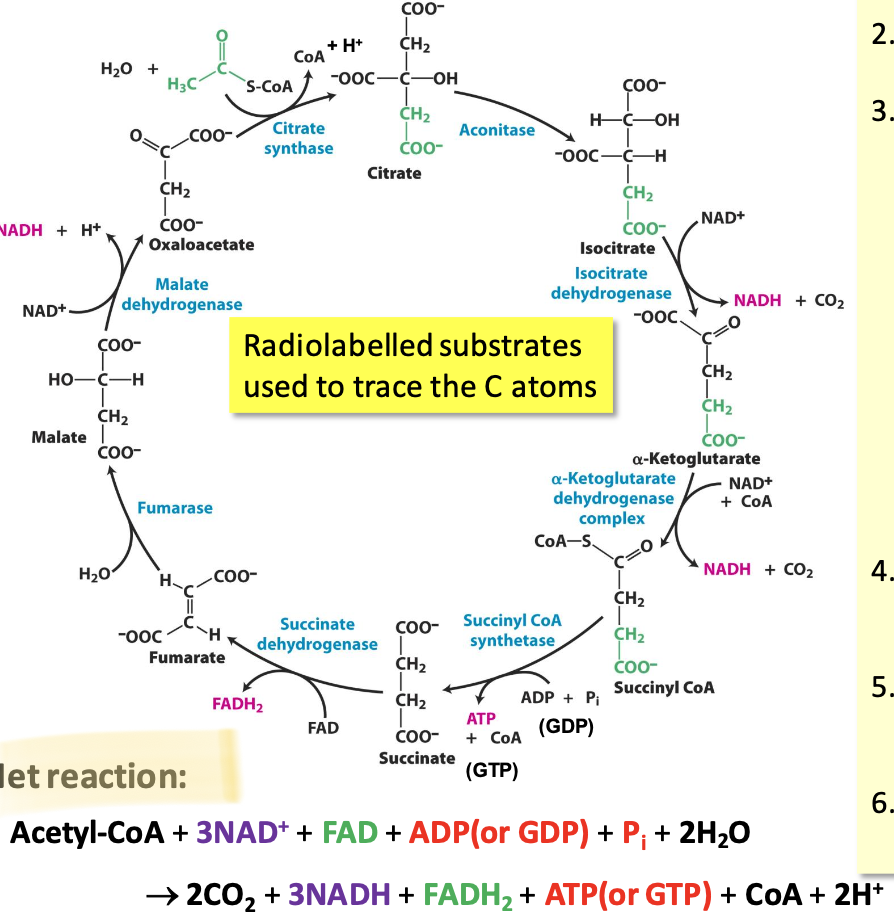
Citric acid cycle
A series of 8 enzyme-catalyzed reactions in the mitochondrial matrix that oxidize acetyl CoA to CO₂ while generating NADH, FADH₂, and GTP (or ATP). It takes place in the mitochondrial matrix
Why is the citric acid cycle amphibolic?
It serves both catabolic (energy production) and anabolic (precursor synthesis) functions.
Net reaction of the CAC
Acetyl-CoA + 3NAD⁺ + FAD + ADP (or GDP) + Pᵢ + 2H₂O → 2CO₂ + 3NADH + FADH₂ + ATP (or GTP) + CoA + 2H⁺
∆Gº’ = -41 kJ/mol
Why is the mitochondrion crucial for the CAC?
It houses the enzymes for the CAC and provides compartments for oxidative phosphorylation to regenerate NAD+ and FAD.
✧ muscle cells have more mitochondria because they require higher energy production to sustain contractions
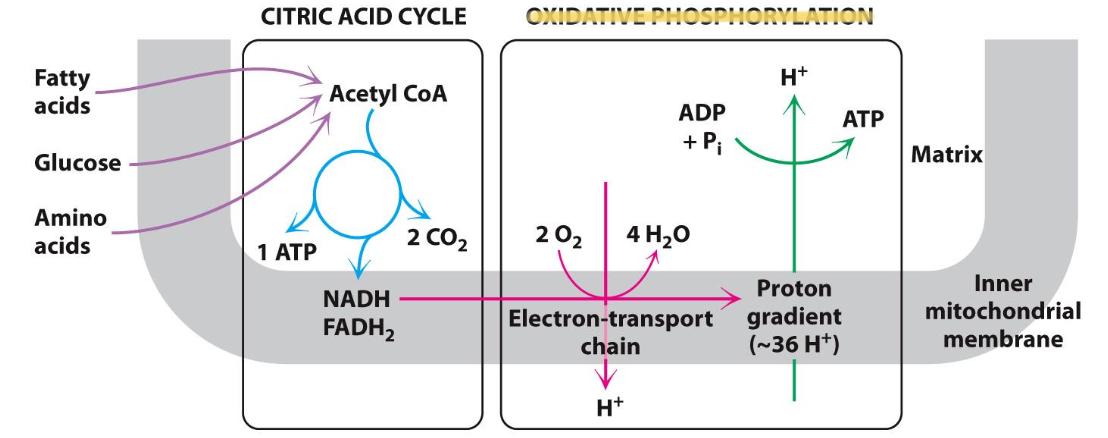
Cellular respiration
Molecular process where O₂ is consumed and CO₂ is released from the oxidation of nutrients
✦ CAC: high-energy e⁻ derived from C fuels are used to reduce NAD⁺ and FAD, generating NADH and FADH₂
✦ Oxidative Phosphorylation: electrons carried by NADH and FADH₂ reduce O₂, generating a proton gradient used for ATP synthesis
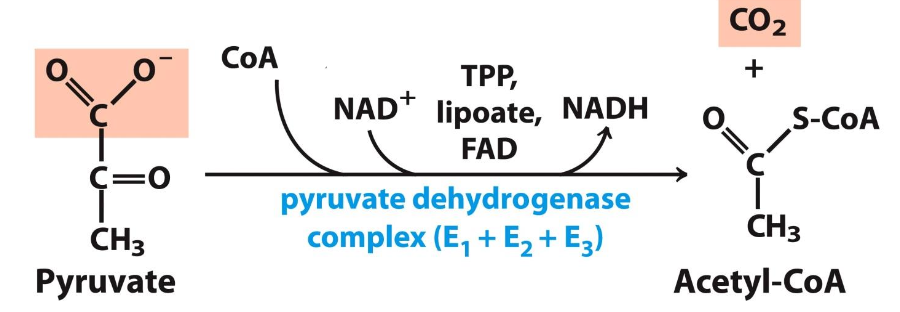
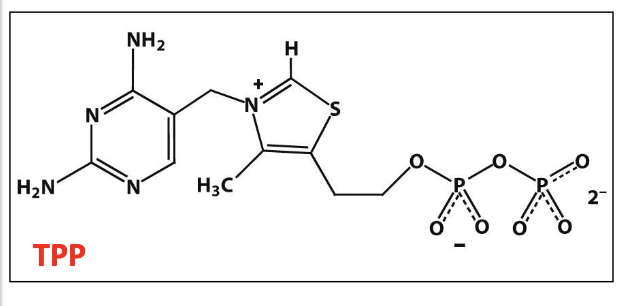
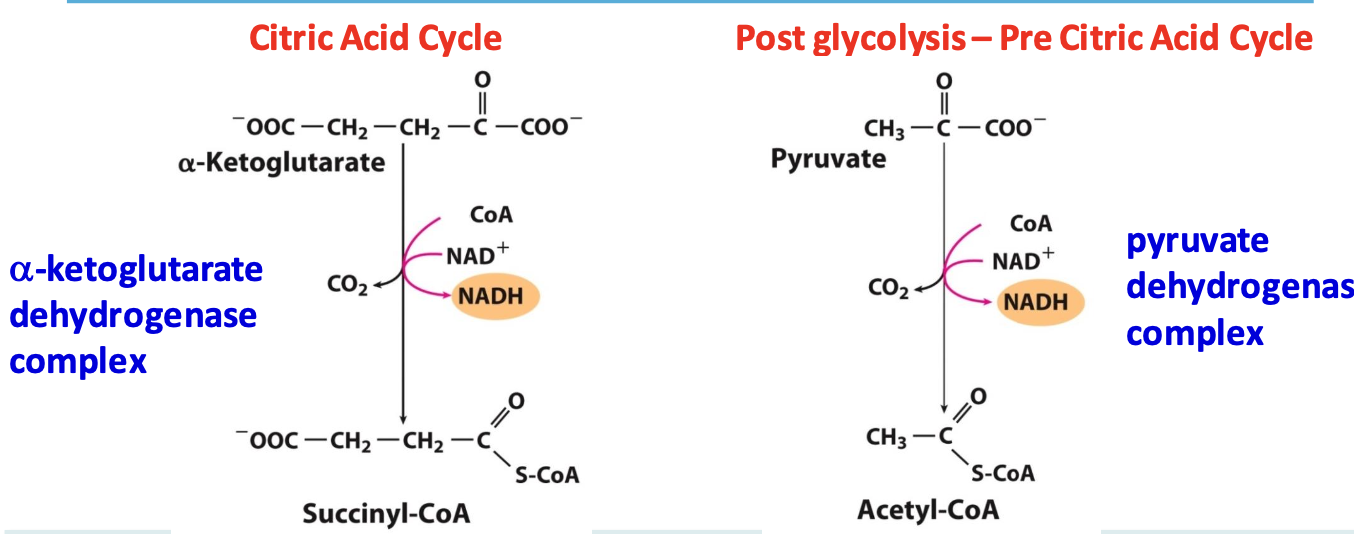
Cofactors and enzymes used in the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
Cofactors: Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP), Lipoic acid, FAD, CoA, NAD⁺
Enzymes: Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDH) composed of 3 enzymes E₁-E₃
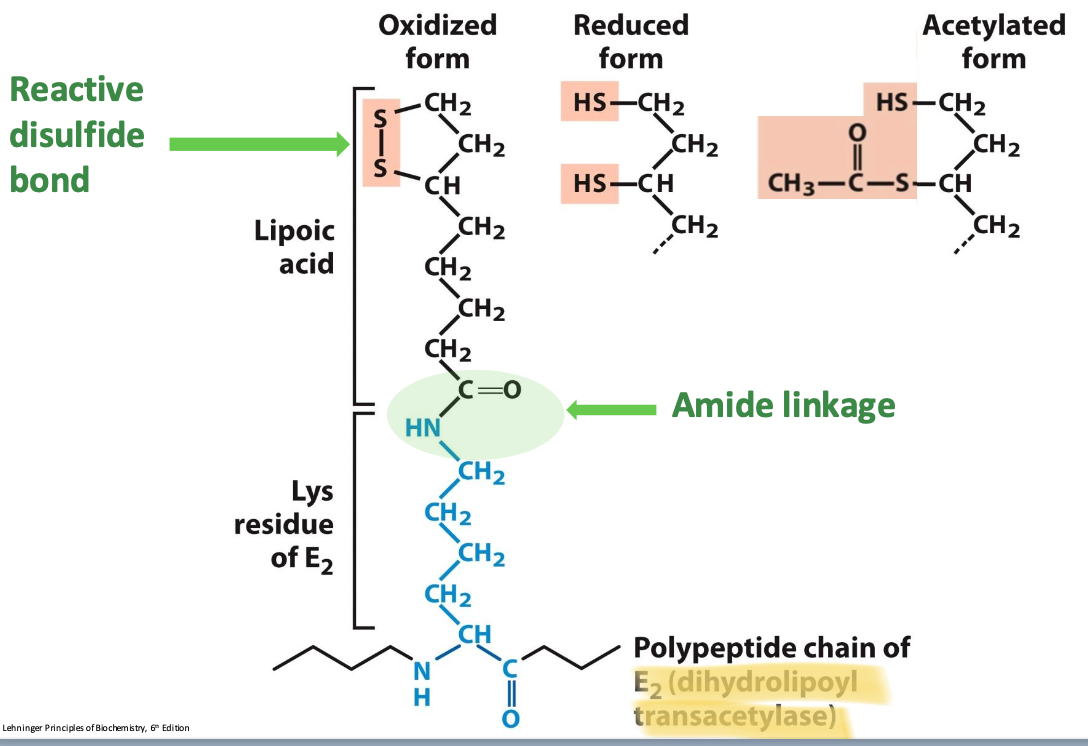
Structure of lipoamide
Lipoamide = lipoic acid covalently bound to E₂ via amide bond to a Lys side chain.
✧ Oxidized/reduced form dihydrolipoamide & acylated form acetyl-lipoamide
✧ Arm of E₂ subunit carries substrate from active site to active site = increase in rx rate, minimizes side rxs
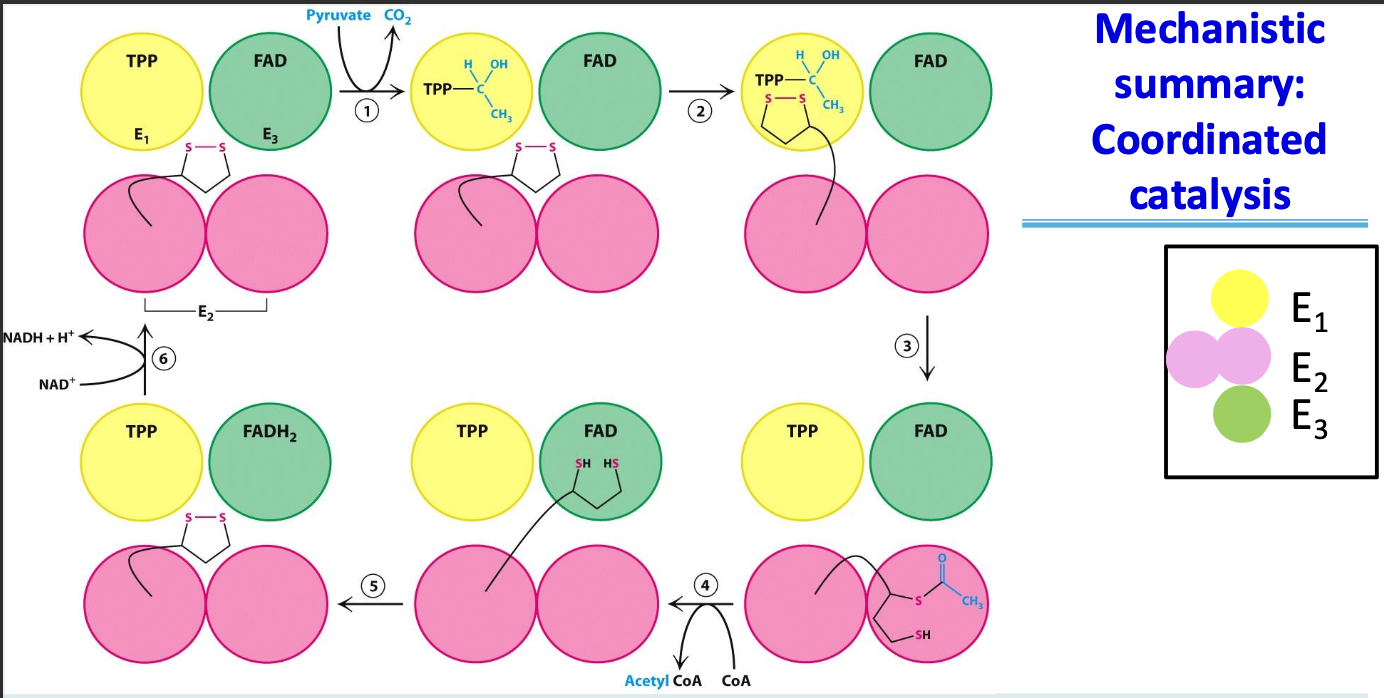
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
✦ E₁ - pyruvate dehydrogenase component, TPP, catalyzes oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate
✦ E₂ - dihydrolipoyl transacetylase, lipoamide, transfer of acetyl group to CoA
✦ E₃ - dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase, FAD, regen of dihydrolipoamide (oxidized)
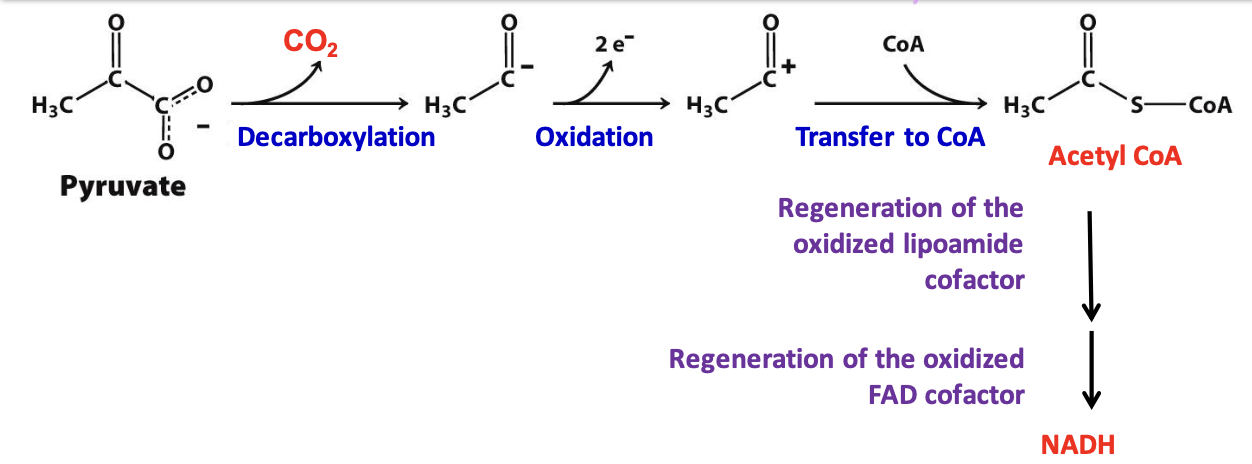
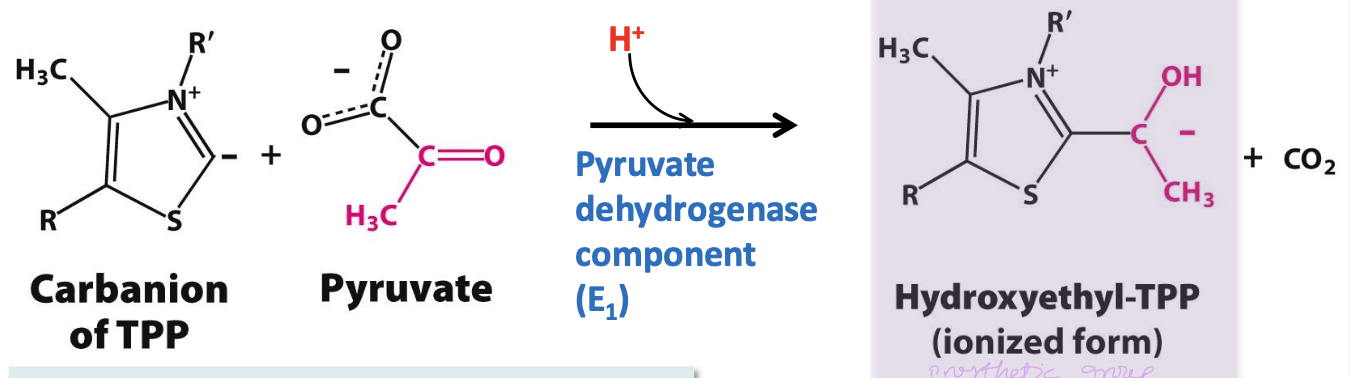
Decarboxylation step
First step in acetyl CoA formation (rate determining).
✧ Pyruvate + ionized TPP ( carbanion of thiamine pyrophosphate) is decarboxylated = hydroxyethyl-TPP
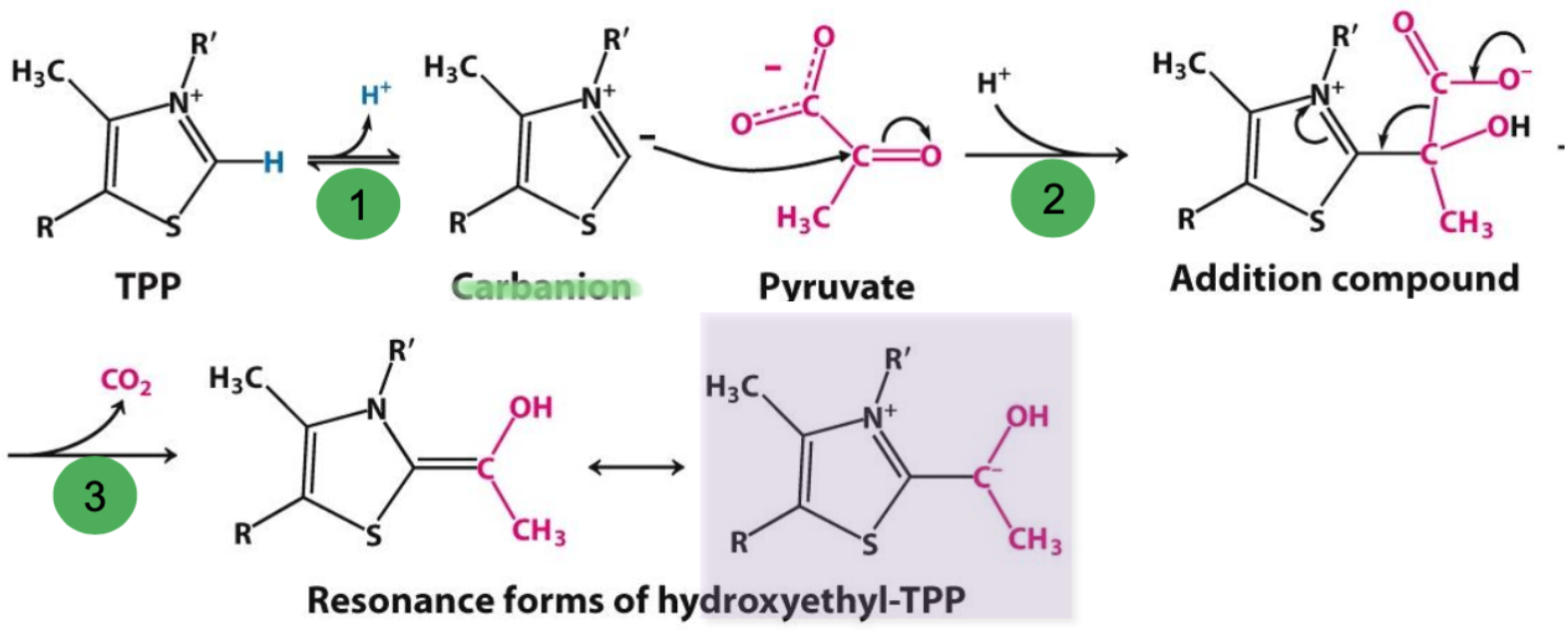
Decarboxylation mechanism
✧ deprotonation of TPP forms a carbanion that attacks pyruvate’s C=O group
✧ TPP’s + charge acts as an electron sink that stabilizes transferred neg. charge → + charge makes TPP carboxylation favourable
✧ resonance forms of hydroxyethyl-TPP exit
Oxidation step
E₁ catalyzes oxidation of ionized TPP & the transfer of the acetyl group to lipoamide (E₂) generating acetyl-lipoamide
✦ lipoamide disulfide is reduced while hydroxyethyl group is oxidized
✦ Produces high energy thioester compound acetyl-lipoamide and regenerates TPP carbanion
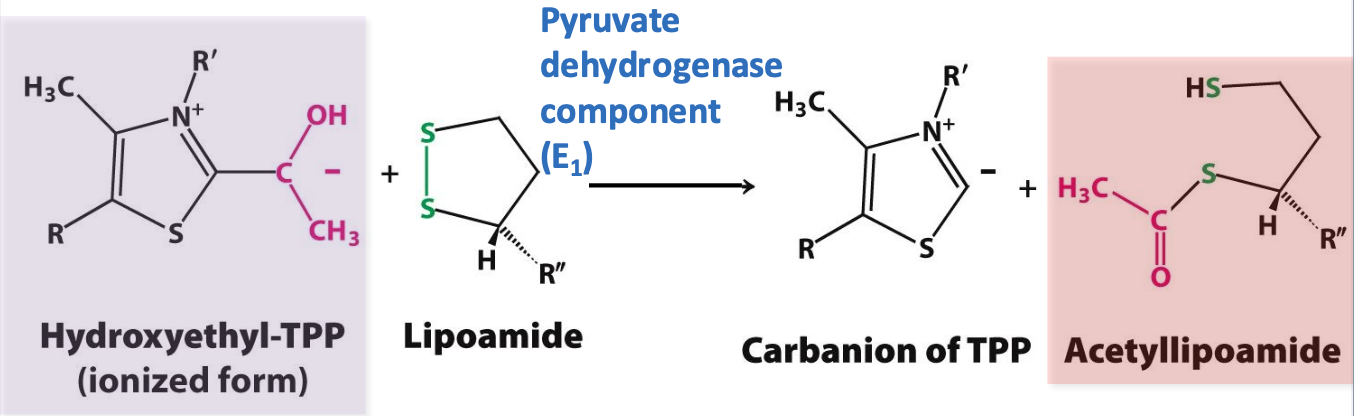
Formation of acetyl CoA
E₂ (dihydrolipoyl transferase) catalyzes the transfer of acetyl group from acetyl-lipoamide to CoA = acetyl CoA + dihydrolipoamide
✦ thioesterification rx
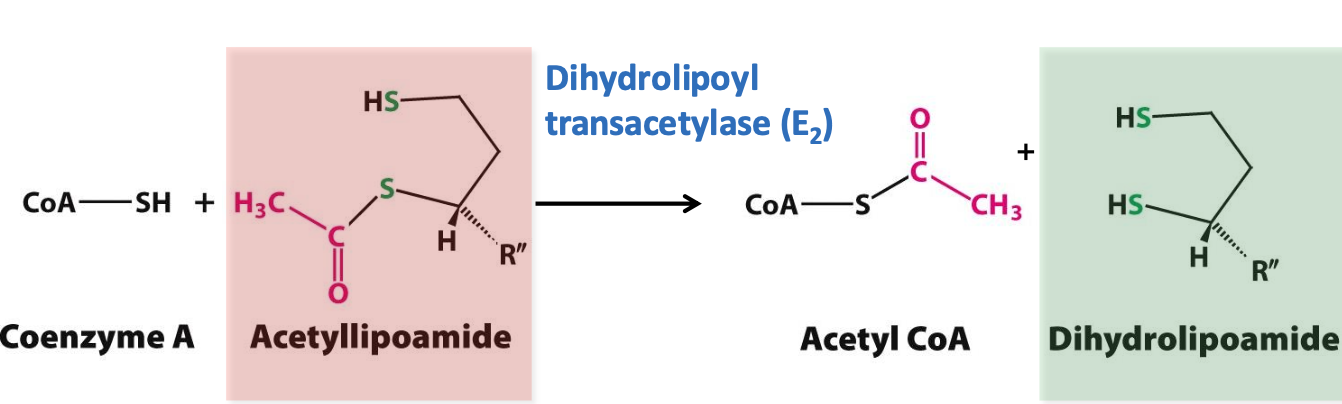
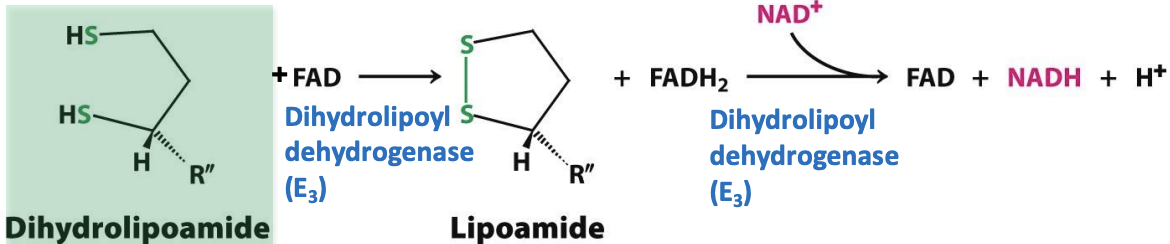
Regeneration of lipoamimde
Fourth step catalyzed by E₃ (dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase) to regenerate lipoamide needed for step 2 of acetyl CoA formation
✦ 2 e⁻ and 2 H⁺ are transferred to FAD group on the enzyme = cofactor lipoamide + FADH₂
✦ 2 e⁻ and 1 H⁺ from FADH₂ transferred to NAD⁺ = FAD and NADH
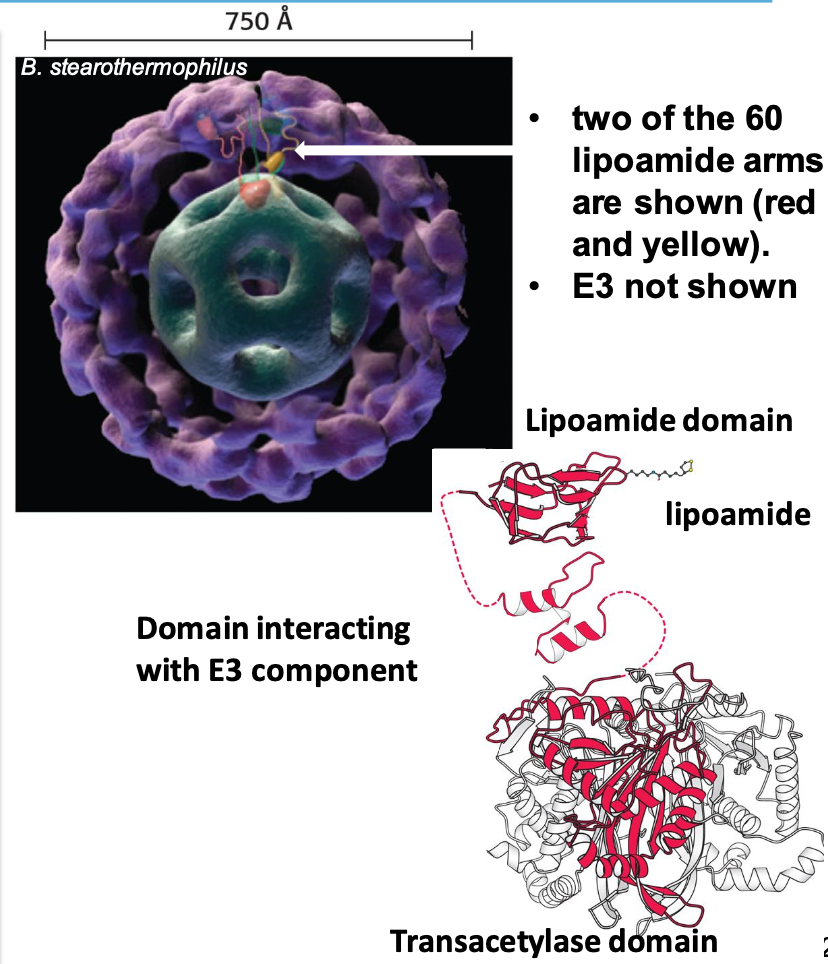
Quaternary structure of PDH complex
Composed of 20 trimers forming a hollow cube. Core of PDH complex is E₂ (surrounded by ∼45 copies of E₁, ∼10 copies of E₃) Each subunit of the trimer has 3 domains:
✦ lipoamide domain (bound flexible lipoamide arm attached to Lys)
✦ small domain interacting w/ E₃ (dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase)
✦ transacetylase domain (w/ 3 domains)
Coordinated catalysis
The integration of enzymatic activities within the PDH complex, where intermediates are transferred between enzyme active sites without dissociating. In the PDH, this is made possible by the lipoamide arm of E₂ moving between the active sites
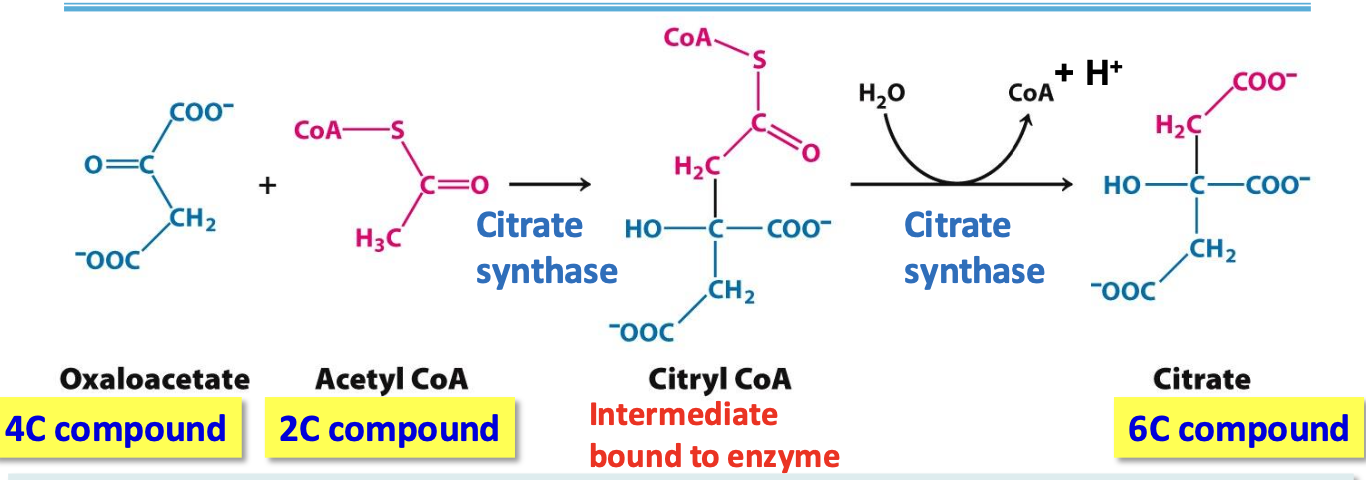
Step 1: Citrate
Citrate synthase: condensation of oxaloacetate (4C) w/ acetyl CoA (2C) = citryl CoA thioester intermediate hydrolysed into citrate (6C)
✦ irreversible, no ATP needed
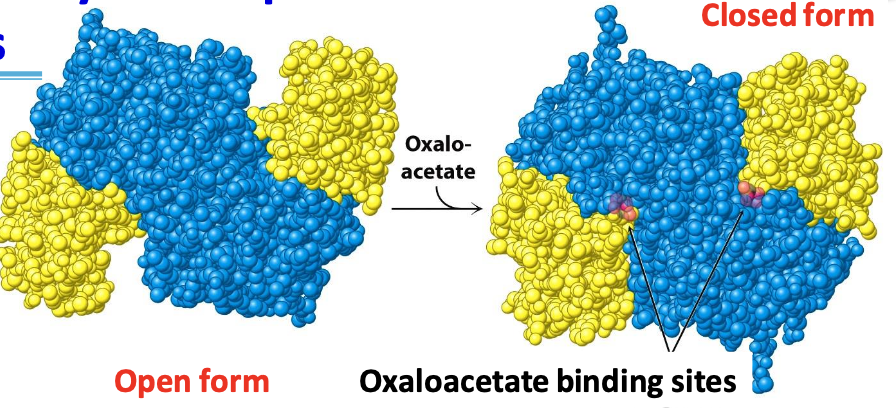
Mechanisms of citrate synthase
Sequential ordered kinetics: acetyl CoA can’t bind until oxaloacetate is ready for condensation
✧ oxaloacetate binds to the open form = conformational changes = formation of acetyl CoA binding site in closed form
✧ formation of citryl CoA (intermediate) = structural change completing the active site = hydrolysis of thioester linkage = formation of citrate
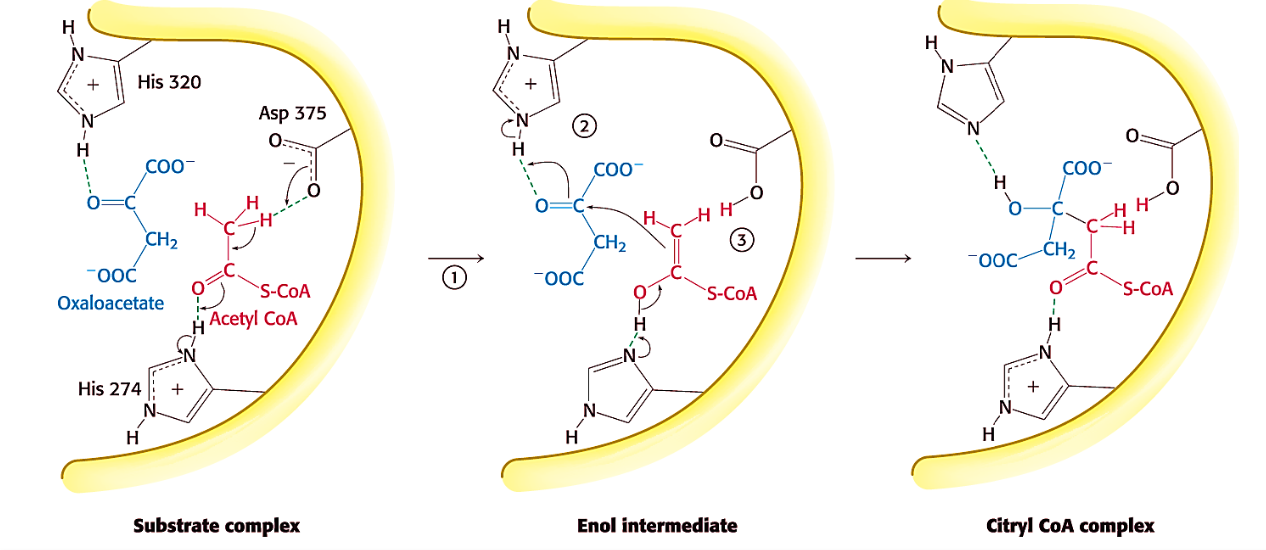
Formation of citryl CoA
✧ citrate synthase orients substrates closer (catalysis by approximation)
✧ His274 donates H⁺ to C=O of acetyl CoA in order to deprotonate its CH₃ by Asp375 = enol intermediate formed
✧ His320 donates H⁺ to C=O of oxaloacetate to activate it WHILST enol attacks C=O to generate C-C and citryl CoA (concerted rx)
✧ His274 hydrolyzes thioester bond
Step 2: Isocitrate
For step 3 to occur (oxidative carboxylation), OH must be moved to C2: aconitase isomerizes citrate to isocitrate
✦ cis-aconitate intermediate formed by dehydration, H₂O eliminated to give a cis-dble bond
✦ reversible, but product is quickly pulled into step 3
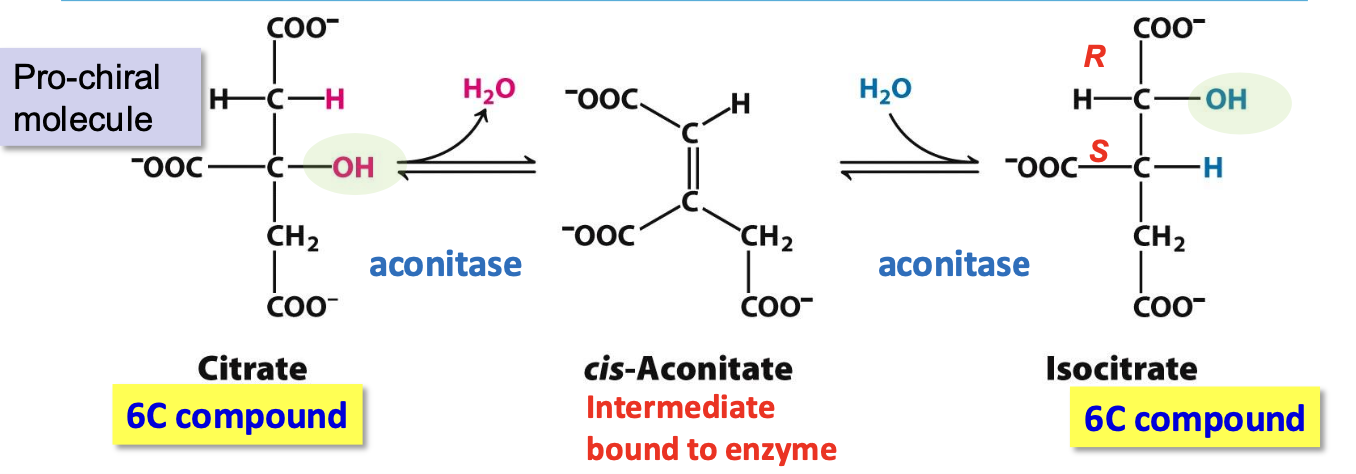
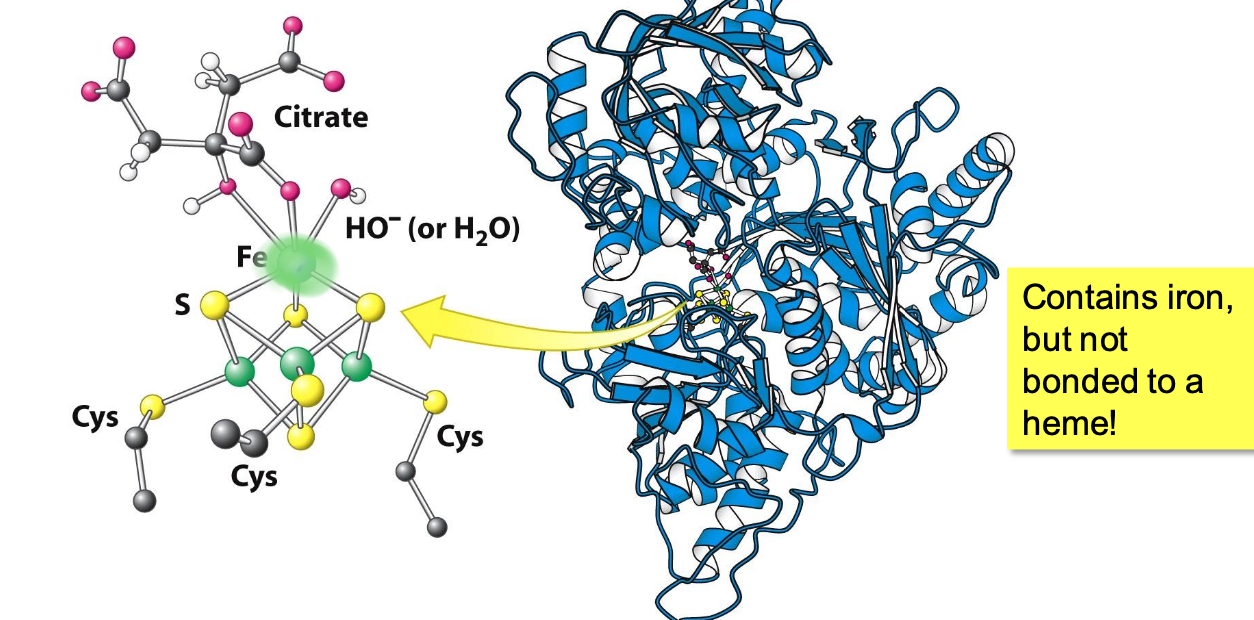
Aconitase
Iron-sulfur protein containing a 4Fe-4S cluster in its active site. Fe atoms are complexed to 4 Sᵢ and 3 Cys
✧ the 1 Fe not bound to Cys binds citrate in order to mediate the rx
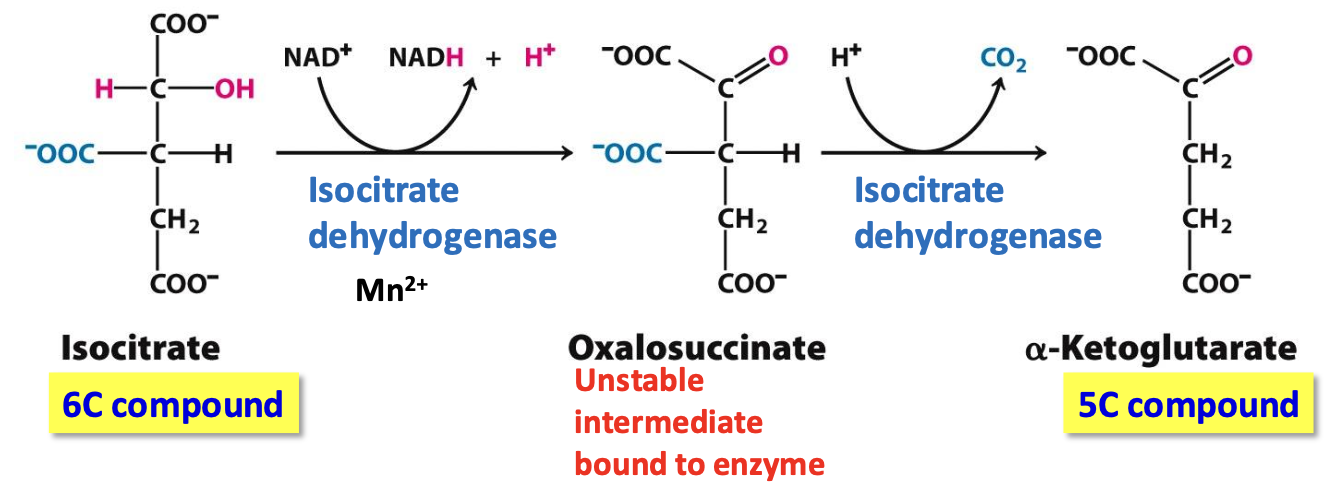
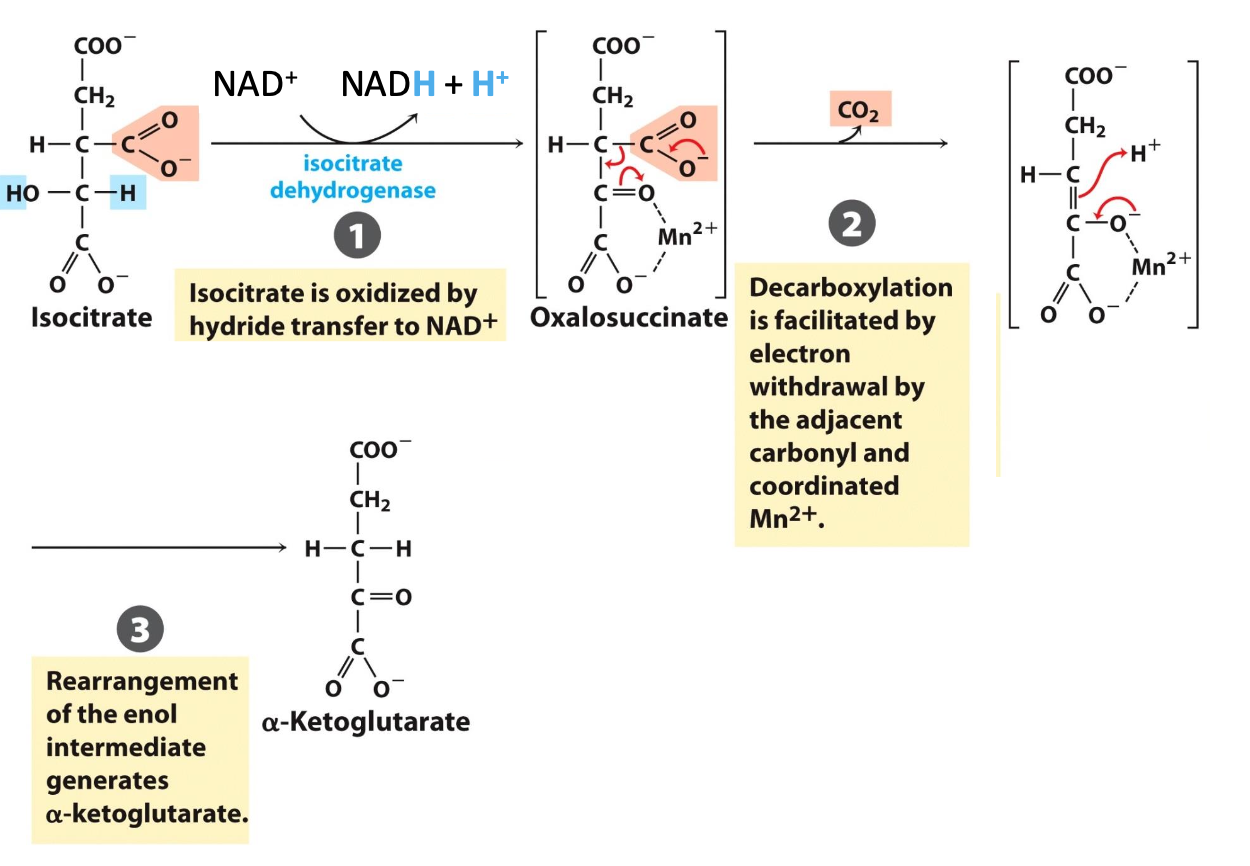
Step 3: 𝛼-Ketoglutarate
Isocitrate dehydrogenase catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate → 𝛼-ketoglutarate
✦NAD⁺ reduced into NADH when unstable intermediate oxalosuccinate is formed → CO₂ readily lost
✦ irreversible, first CO₂ release & NADH generated
Step 4: Succinyl CoA
𝛼-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex catalyzes oxidative decarboxylation of 𝛼-ketoglutarate to succinyl CoA
✦ irreversible, CO₂ removed, NAD⁺ reduction into NADH
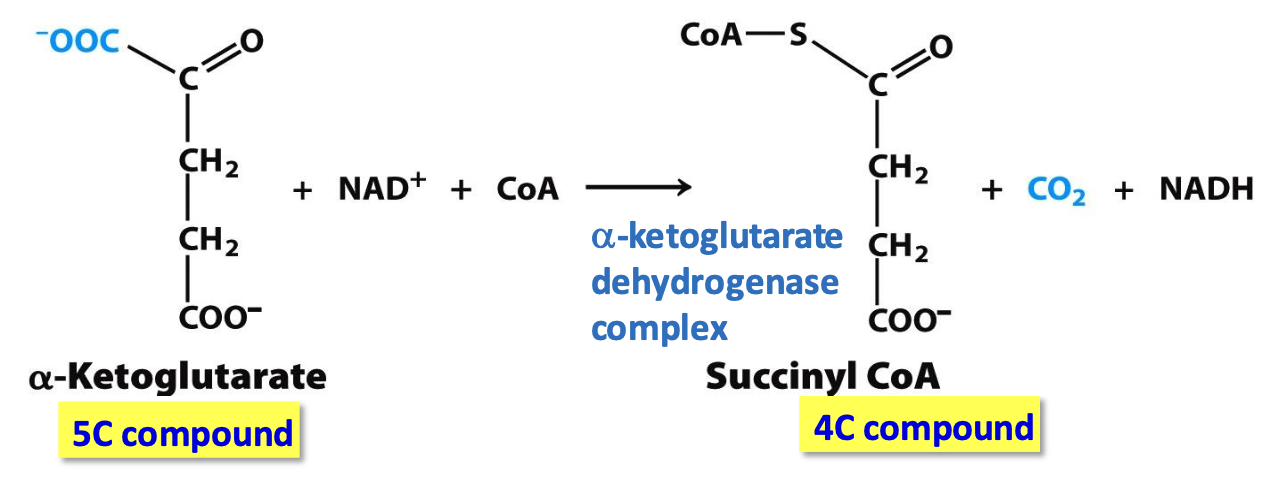
𝛼-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex & pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
These 2 complexes are homologous: same 3 enzyme assembly; similar enzymatic activities; same 5 cofactors (TPP, lipoamide, FAD, CoA, NAD⁺); similar mechanisms
The active sites have diff binding specificities as they accommodated differently sized molecules
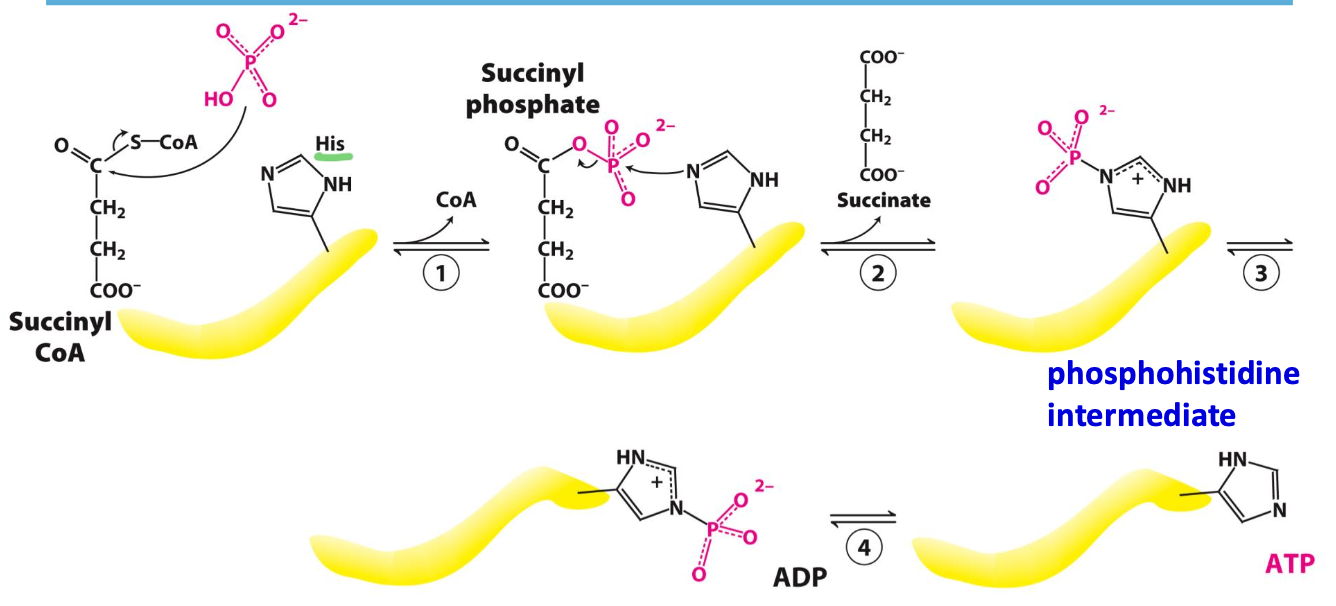
Step 5: Succinate
Succinyl CoA synthase catalyzes cleavage of thioester bond on succinyl CoA coupled to phosphorylation of ADP/GDP → succinate
✦ reversible, only generation of ATP/GTP by substrate-level phosphorylation
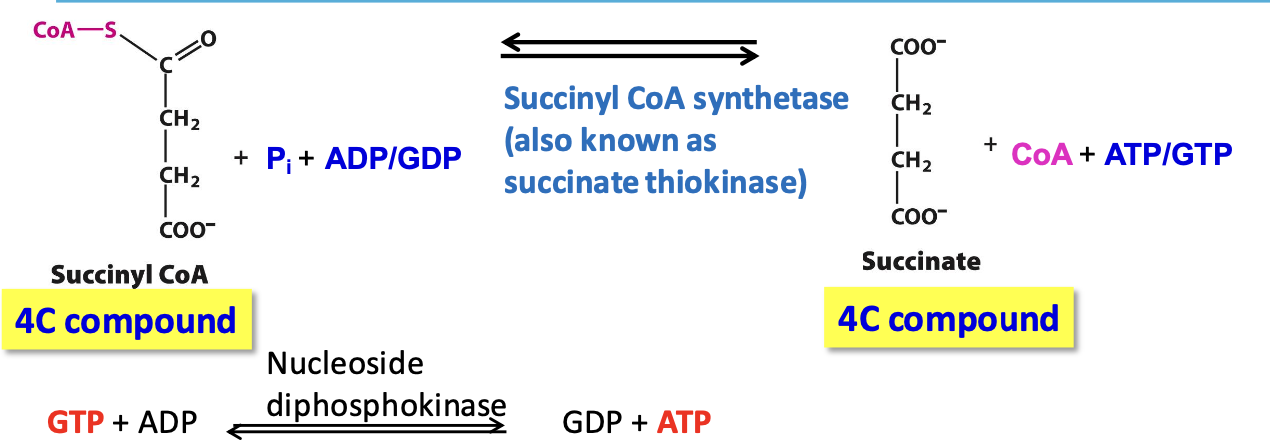
Isozymes of succinyl CoA synthase
✦ requires ADP (muscles, heart, tissues that perform a lot of cellular respiration)
✦ requires GDP (liver, tissues that perform many anabolic rxs)
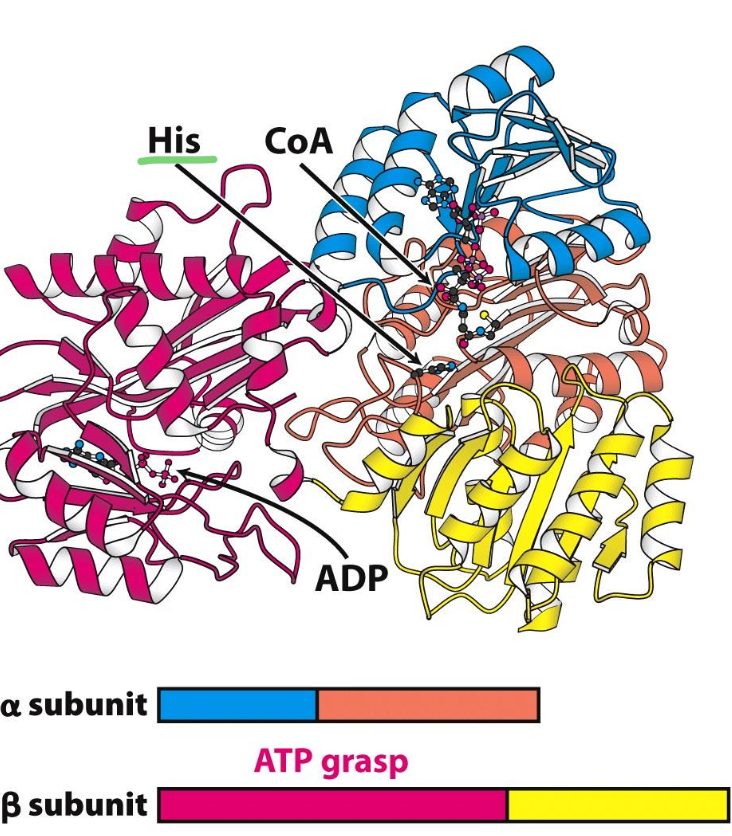
Structure of succinyl CoA synthase
An 𝛼₂𝛽₂ heterodimer:
✦ 𝛼 subunit binds CoA
✦ 𝛽 subunit contains ATP-grasp domain (binds activates ATP)
✦ His residue between CoA (𝛼) and ADP (𝛽) presents the P to the bound ADP in 𝛽 = ATP generated
Mechanism of succinyl CoA synthase
✦ Pᵢ attacks thioester = CoA + succinyl phosphate
✦ His in active site removes P = succinate + phosphohistidine intermediate
✦ intermediate swings and presents P to bound ADP → ATP formed (substrate-level phosphorylation)
What is the purpose of the last 2 steps of the CAC?
Steps 6-8 regenerate oxaloacetate so the cycle can renew
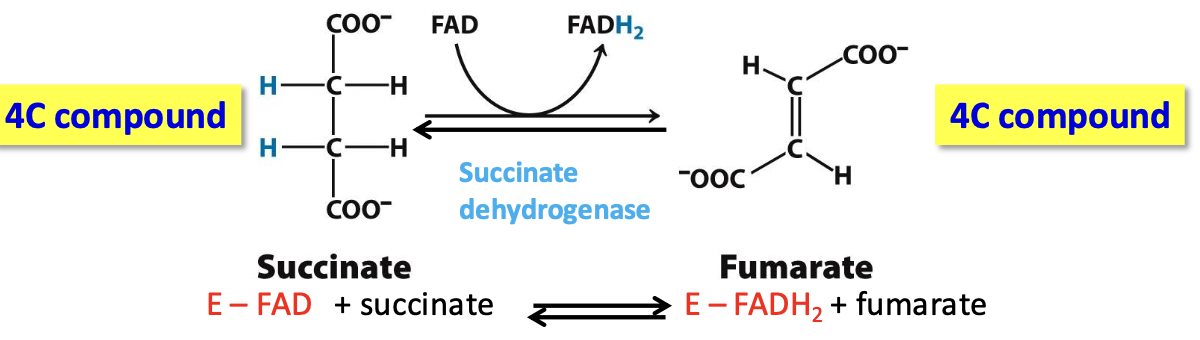
Step 6: Fumarate
Succinate dehydrogenase catalyzes reversible oxidation of succinate to fumarate (alkane to alkene)
✦ Enzyme (Fe-S protein in the inner mito membrane) requires FAD, an strong oxidizing agent that can reduce succinate (alkane, poor reducing agent)
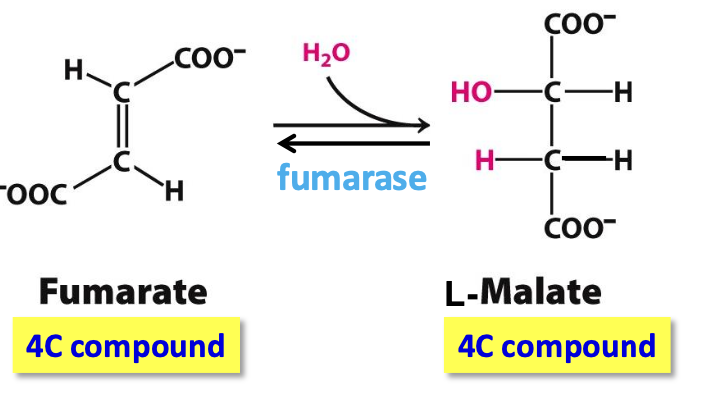
Step 7: Malate
Fumarase catalyzes reversible stereospecific hydration of fumarate → L-malate
✦ trans addition of H⁺ and OH⁻ across C=C
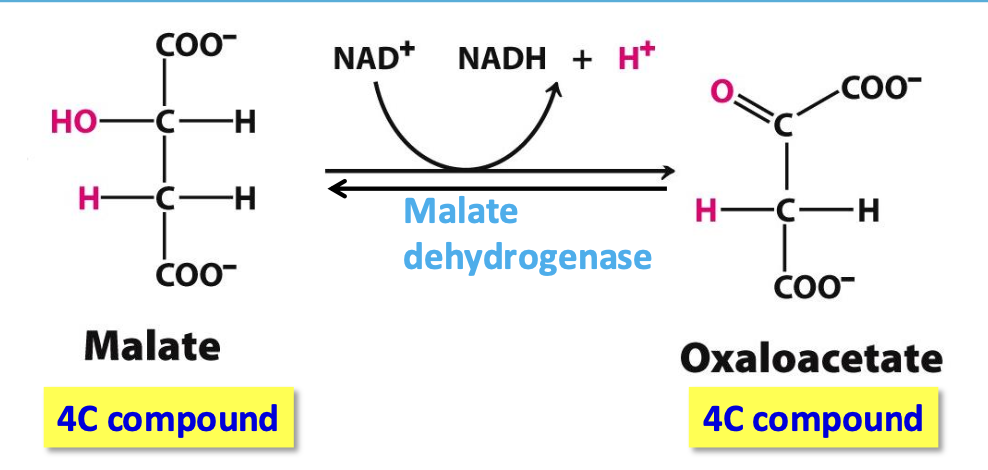
Step 8: Oxaloacetate
Malate dehydrogenase catalyzes reversible oxidation of malate to oxaloacetate
✦ ∆Gº’ = +29.7 kJ mol but using the products (oxaloacetate in step 1 & ETC NADH), the rx is driven forward
One turn of the CAC
✦ Oxaloacetate used and regenerated
✦ The 2 C atoms that entered as acetyl CoA DO NOT leave as 2 CO₂ -their identity is lost in symmetrical succinate and incorporated in oxaloacetate
✦ Mol w/ high phosphoryl-transfer potential (ATP) generated a
✦ 4 oxido-redox rxs = 3 NADH, 1 FADH₂
Where in the CAC are oxido-reductions?
NADH: steps 3, 4, 8
FADH₂: step 6
ATP/GTP: step 5
Why does the CAC operate under aerobic conditions?
The CAC doesn’t require oxygen, but FAD and NAD⁺ can only be regenerated in the mitochondria by the transfer of electrons to O₂
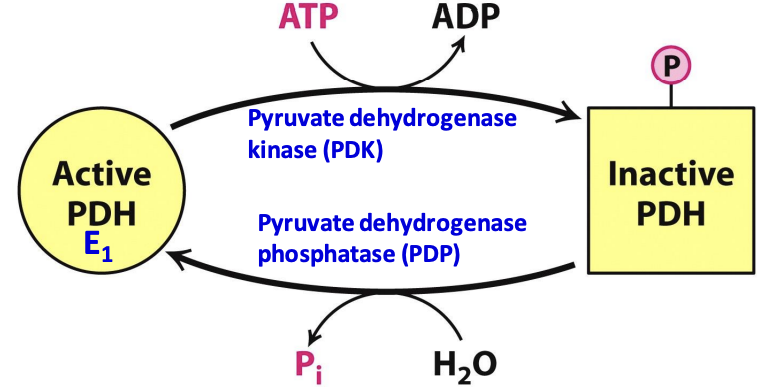
How is the PDH complex regulated?
By reversible phosphorylation (under hormonal control)
Phosphorylation of E1 by specific isozyme of PDK (pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase) inactivates PDH, while PDP (pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase) removes the P and activates PDH
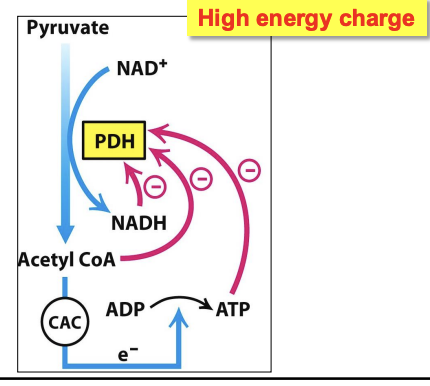
Regulation of the PDH complex in muscles at rest
Allosterically inhibited by its products (acetyl CoA on E₂, NADH on E₃) & high energy charge (ATP)
✧ these molecules signal that no more pyruvate needs to be metabolized to acetyl CoA as the energy needs are met
✧ at rest, energy demand is low (products are not being used up fast) = high ratios of NAD⁺/NADH, ATP/ADP = activation of PDK = inactive PDH and less acetyl CoA produced
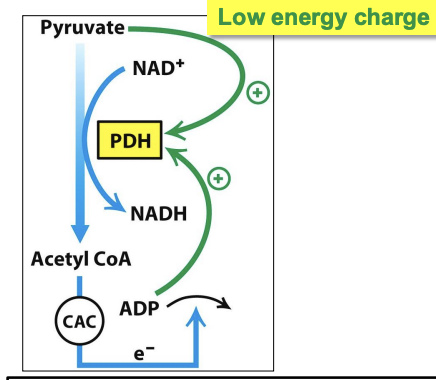
Regulation of the PDH complex in muscles during exercise
Higher demand for pyruvate to fuel muscles = increase in ADP + [pyruvate] as ATP is used up and glucose is converted
✧ high [ADP] and [pyruvate] inactivate PDK = active PDH complex = more acetyl CoA production
✧ Ca²⁺ released when muscle contracts stimulates PDP = enhances PDH activity
Regulation of the CAC
The rate of CAC is allosterically regulated by isocitrate dehydrogenase and 𝛼-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, which are inhibited by the pathway products NADH, ATP, succinyl CoA (for 𝛼-keto) which signal high energy charge
✧ high [NADH] will compete with NAD⁺ for the binding site = inhibition
✧ ADP (low energy charge) enhances the enzymes’ affinity for their substrates
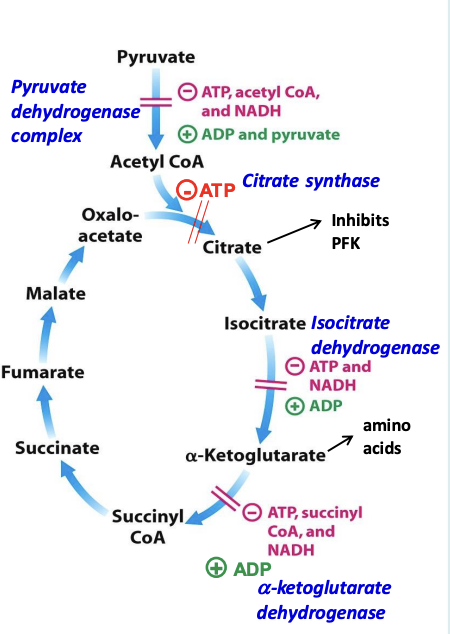
Prolonged inhibition of the CAC’s regulatory enzymes
✦ inhibition of 𝛼-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase = build up of 𝛼-ketoglutarate = generation of AAs & nucleotides
✦ inhibition of isocitrate dehydrogenase = increase of citrate = inhibition of glycolysis/PFK (F-6P → F-1,6-BP)
How are the CAC, glycolysis, and gluconeogenesis coordinated?
These cycles are regulated to meet the energy needs of the cell. Inhibition of isocitrate dehydrogenase = accumulation of isocitrate, which is in equilibrium with citrate (reversible rx)
✦ accumulated citrate transported from mito. → cytoplasm = inhibition of PFK (glycolysis) and activation of F-1,6-BP (gluconeogenesis)
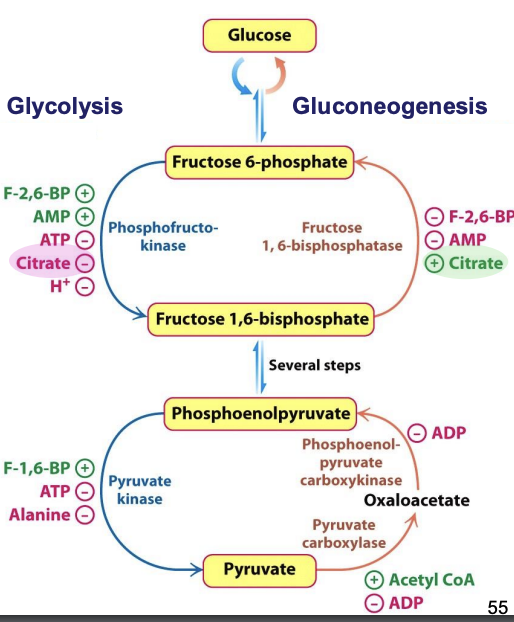
Role of the CAC in biosynthesis
Amphibolic!
✦ production of energy and biosynthesis intermediates that can be removed from the cycle when energy needs are met (e.g. 𝛼-ketoglutarate → glutamate)
✦ oxaloacetate replenished from pyruvate by pyruvate carboxylase (gluconeogenesis)
Anaplerotic reactions
Reactions that replenish CAC intermediates when they are drawn off for biosynthesis.
✦ pyruvate carboxylase rx (pyruvate → oxaloacetate) which is only active when acetyl CoA is present (which signals more oxaloacetate is needed).
✦ If high energy, converted to glucose (gluconeogenesis). If low energy, replenished for CAC
Glyoxylate cycle
A metabolic pathway in plants, bacteria, and fungi that bypasses the two CO₂-producing steps of the citric acid cycle, allowing acetyl CoA → glucose precursors.
✦ enzymes isocitrate lyase and malate synthase as well as intermediate glycoxylate
✦ 2 acetyl CoA + NAD + 2H₂O → succinate + NADH + 2CoA-SH
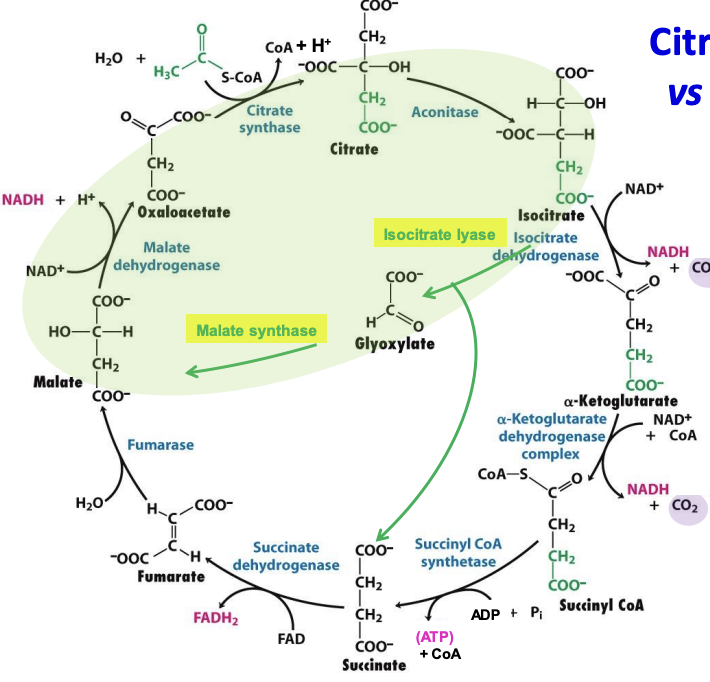
Roles of glyoxylate cycle
✦ Seed Germination in oil-rich seeds (sunflower seeds): convert stored lipids into carbohydrates into fuel until photosynthesis begins.
✦ Compartmentalization: occurs in glyoxysomes (plant organelle) → succinate (can enter CAC in mitochondria) → malate (brought to cytoplasm for gluconeogenesis)