Health Test
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/505
Last updated 8:23 AM on 3/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
506 Terms
1
New cards
Part 1: Infectious Disease
2
New cards
Bacteria
Bacteria are single-celled organisms that are pretty much everywhere: in the ground, in the ocean, on your hands and in your gut. While some are harmful, most are not — and some are even beneficial to human health. In many cases, humans live in symbiosis with bacteria, maintaining a mutually beneficial relationship without even knowing it. Ex. Salmonella bacteria
3
New cards
Infectious Disease
Communicable disease caused by microorganisms in or on humans, plants or animals ex. Salmonella
4
New cards
Parasite/protozoa
One celled organisms that can live freely or be a parasite in nature ex. Giardia
5
New cards
Virus
Microorganisms that infect cells and may cause disease ex. Cold

6
New cards
Fungi
Spore-producing organisms ex. Athlete's Foot
7
New cards
Disease
An illness/sicknes characterized by specific signs and symptoms
8
New cards
Methods of Transmission, Direct
Exchange of infectious material from its origin to susceptible individual ex. Sneezing, Coughing, Sharing Drinks
9
New cards
Methods of Transmission, Indirect
Exchange of infectious material by source that acts as carrier ex. Animals, Airborne, Contaminated objects
10
New cards
How do you prevent the spread of infectious diseases? Give at least 4 examples
Cover nose/mouth when sneezing or coughing. Vaccinations. Wash your hands. Food Sanitation.
11
New cards
Part 2: STI and HIV/AIDS
12
New cards
How are STI’s contracted? Can you get one from casual contact?
By engaging in sexual activity with an infected partner. Cannot get by casual contact. Treatment: Antibiotics
13
New cards
How are HIV and AIDS contracted?
By having sex, sharing needles or syringes
14
New cards
What treatment are available for STIs?
STI’s are treated by antibiotics
15
New cards
What treatment is available for HIV/AIDS?
antiretroviral therapy, NOT a cure
16
New cards
How can you prevent STI’s?
Abstinence, Limited number of partners, Both partners tested, condoms
17
New cards
Part 3: Chronic Disease/Non-communicable Disease
18
New cards
\--Key Terms - Define all terms with examples--
19
New cards
Diagnosis
Identifies type of disease that person has and treatment ex. Pneumonia
20
New cards
Complications
A new problem or related disease occurs ex. Sepsis (infection of the blood) may occur as a complication of a bacterial, viral, or fungal infection
21
New cards
Prognosis
Probable outcome of the disease, including duration and severity ex. Cancer→Death
22
New cards
Allergens
Substance that causes an allergic reaction ex. A food
23
New cards
Cancer
An abnormal development of cells that divide uncontrollably ex. Malignant Tumor
24
New cards
Stroke
Blood supply to brain is interrupted or reduced, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients ex. Drooping mouth
25
New cards
Hypertension
Long term force of blood against artery walls that is higher than normal ex. Too high blood pressure reading
26
New cards
Heart Disease
Range of conditions of heart that prevent it from functioning normally ex. Heart failure
27
New cards
Diabetes
Affects the way the body processes glucose ex. Type 1(where the body's immune system attacks and destroys the cells that produce insulin.) , Type 2(where the body does not produce enough insulin, or the body's cells do not react to insulin.)
28
New cards
Chronic Disease
Diseases that can’t be spread from person to person that develop over time ex. Obesity
29
New cards
What are the risk factors that contribute to chronic diseases?
1. Smoking 2. Poor Nutrition 3. Drug/Alcohol use
30
New cards
What are 3 ways to prevent chronic diseases?
1. Eat healthy 2. Don’t Smoke 3. Don’t use drugs
31
New cards
Unit 4: Injury Prevention
32
New cards
Unintentional Injuries/Accidents vs. Intentional Injuries
UI Injury: Can be predicted + prevented I Injury: Caused by violence, destructive behaviors
33
New cards
Different Factors that Affect Injuries
34
New cards
Individual Behaviors
Choices made by you, no matter your environment
35
New cards
Access to Services
Such as health care, doctors office, hospitals
36
New cards
Physical Environment
Choices made at home or in community ex. falls, fires, burns
37
New cards
Social Environment
Choices made with peers ex. Peer pressure, social norms
38
New cards
Cautious Risk Taker vs. Reckless Risk Taker
Recognize potential risk vs act impulsively
39
New cards
First Aid
First help given to injured/sick person
40
New cards
Lay Responder
Non-professional person who provides first aid and helps ex. “me”
41
New cards
Good Samaritan Laws
Laws that protect individuals who willingly give care to others in an emergency situation
42
New cards
Check, Call, Care
Checking scene for safety, Call 911, Care providing treatment within area of training
43
New cards
D.E.C.I.D.E. Decision Making Model- know what each letter stands for
44
New cards
D of Decision Making Model
Define Problem
45
New cards
E of Decision Making Model
Establish criteria
46
New cards
C of Decision Making Model
Consider all alternatives
47
New cards
I of Decision Making Model
Identify the best alternative
48
New cards
D #2 of Decision Making Model
Develop and implement a plan of action
49
New cards
E of Decision Making Model
Evaluate and monitor
50
New cards
What are Barriers to helping someone in an emergency and ways to overcome those barriers?
Barriers: Not knowing CPR, not having correct Equipment, Not sure if you can help How to overcome: Get First Aid/CPR/AED certified, use personal protective equipment, Be familiar with Good Samaritan Law
51
New cards
Signs of a heart attack
Chest pain, Pain spreading to all body parts, mainly left-side, Nausea, Vomiting, Grayish-blue skin color
52
New cards
Signs of a stroke
Trouble speaking/slurred speed , Confused, Numbness, Vision issues
53
New cards
Cardiac Chain of Survival- Define all steps
Early Access, Early CPR, Early Defibrillation, Early advanced care
54
New cards
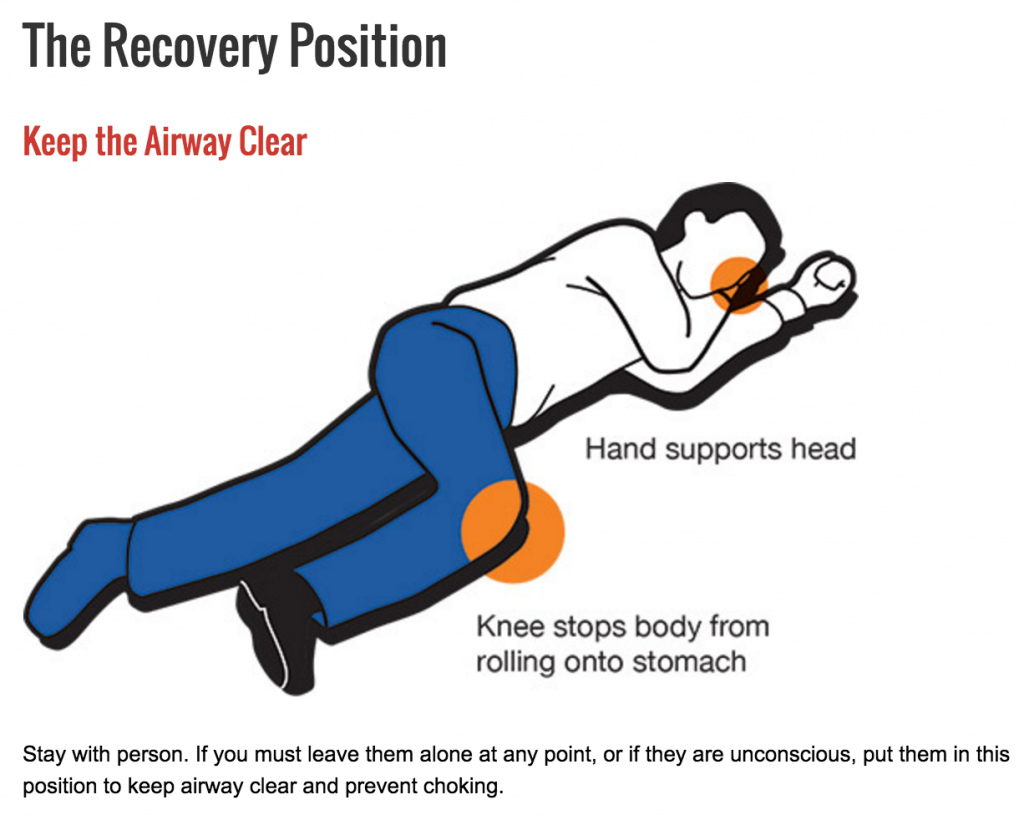
What is the recovery position?
In first aid, the recovery position is one of a series of variations on a lateral recumbent or three-quarters prone position of the body, often used for unconscious but breathing casualties.
55
New cards
psychology
the science of behavior and mental processes
56
New cards
nature-nurture issue
the long-standing controversy over the relative contributions that genes and experience make to the development of psychological traits and behaviors
57
New cards
natural selection
the principle that, among the range of inherited trait variations, those contributing to reproduction and survival will most likely be passed on to succeeding generations
58
New cards
neuroscience
the perspective of psychological science that deals with how the body and brain create emotions, memories, and sensory experiences
59
New cards
evolutionary
the perspective of psychological science that deals with how nature selects traits that promote the perpetuation of one's genes
60
New cards
behavior genetics
the perspective of psychological science that deals with how much our genes, and our environment, influence our individual differences
61
New cards
psychodynamic
the perspective of psychological science that deals with how behavior springs from unconscious drives and conflicts
62
New cards
behavioral
the perspective of psychological science that deals with how we learn observable responses
63
New cards
cognitive
the perspective of psychological science that deals with how we encode, process, store, and retrieve information
64
New cards
social-cultural
the perspective of psychological science that deals with how behavior and thinking vary across situations and cultures
65
New cards
basic research
pure science that aims to increase the scientific knowledge base
66
New cards
applied research
scientific study that aims to solve practical problems
67
New cards
clinical psychology
a branch of psychology that studies, assesses, and treats people with psychological disorders
68
New cards
psychiatry
a branch of medicine dealing with psychological disorders, practiced by physicians who sometimes provide medical (for example, drug) treatments as well as psychological therapy
69
New cards
hindsight bias (I-knew-it-all-along phenomenon)
the tendency to believe, after learning an outcome, that one would have foreseen it
70
New cards
critical thinking
thinking that does not blindly accept arguments and conclusions. Rather, it examines assumptions, discerns hidden values, evaluates evidence, and assesses conclusions
71
New cards
theory
an explanation using an integrated set of principles that organizes and predicts observations
72
New cards
hypothesis
a testable prediction, often implied by a theory
73
New cards
operational definition
a statement of the procedures (operations) used to define research variables. For example, intelligence may be operationally defined as what an intelligence test measures
74
New cards
replication
repeating the essence of a research study, usually with different participants in different situations, to see whether the basic finding generalizes to other participants and circumstances
75
New cards
case study
an observation technique in which one person is studied in depth in the hope of revealing universal principles
76
New cards
survey
a technique for ascertaining the self-reported attitudes or behaviors of people, usually by questioning a representative, random sample of them
77
New cards
false consensus effect
the tendency to overestimate the extent to which others share our beliefs and behaviors
78
New cards
population
all the cases in a group, from which samples may be drawn for a study
79
New cards
random sample
a sample that fairly represents a population because each member has an equal chance of inclusion
80
New cards
naturalistic observation
observing and recording behavior in naturally occurring situations without trying to manipulate and control the situation
81
New cards
correlation coefficient
a statistical measure of the extent to which two factors vary together, and thus of how well either factor predicts the other
82
New cards
scatterplot
a graphed cluster of dots, each of which represents the values of two variables. The slope of the points suggests the direction of the relationship between the two variables. The amount of scatter suggests the strength of correlation (little scatter indicates high correlation).
83
New cards
illusory correlation
the perception of a relationship where none exists
84
New cards
experiment
a research method in which an investigator manipulates one or more factors (independent variables) to observe the effect on some behavior or mental process (the dependent variable). By random assignment of participants the experimenter controls other relevant factors)
85
New cards
placebo
an inert substance or condition that may be administered instead of a presumed active agent, such as a drug, to see if it triggers the effects believed to characterize the active agent
86
New cards
double-blind procedure
an experimental procedure in which both the research participants and the research staff are ignorant (blind) about whether the research participants have received the treatment or a placebo. Commonly used in drug-evaluation studies.
87
New cards
placebo effect
any effect on behavior caused by a placebo
88
New cards
experimental condition
the condition of an experiment that exposes participants to the treatment, that is, to one version of the independent variable
89
New cards
control condition
the condition of an experiment that contrasts with the experimental condition and serves as a comparison for evaluation the effect of the treatment
90
New cards
random assignment
assigning participants to experimental and control conditions by chance, thus minimizing preexisting differences between those assigned to the different groups
91
New cards
independent variable
the experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect if being studied
92
New cards
dependent variable
the experimental factor--in psychology, the behavior or mental process--that is being measured; the variable that may change in response to the manipulations of the independent variable
93
New cards
mode
the most frequently occurring score in a distribution
94
New cards
mean
the arithmetic average of a distribution, obtained by adding the scores and then dividing by the number of scores
95
New cards
median
the middle score in a distribution; the scores are above it and half are below it
96
New cards
range
the difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution
97
New cards
standard deviation
a computed measure of how much scores vary around the mean score
98
New cards
statistical significance
a statistical criterion for rejecting the assumption of no differences in a particular study
99
New cards
culture
the enduring behaviors, ideas, attitudes, and traditions shared by a large group of people and transmitted from one generation to the next
100
New cards
Biological psychology
concerned with links between biology and behavior