Replication
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
continuity
DNA replication exists to ensure the ? of hereditary info
Synthesis
DNA replication occurs before cell division, specifically during the ? phase of the cell
Semiconservative
DNA is ? because it contains one original strand and one newly synthesized compliment (from replication)
5’ End
The end of DNA that has the phosphate terminus
3’ End
The end of DNA that has the hydroxyl terminus
Antiparallel
The feature of DNA where two strands run opposite to each other
one is 5’-3’ while the other is 3’-5’
added, 3’
When new nucleotides are ?, it can only happen to the ? end
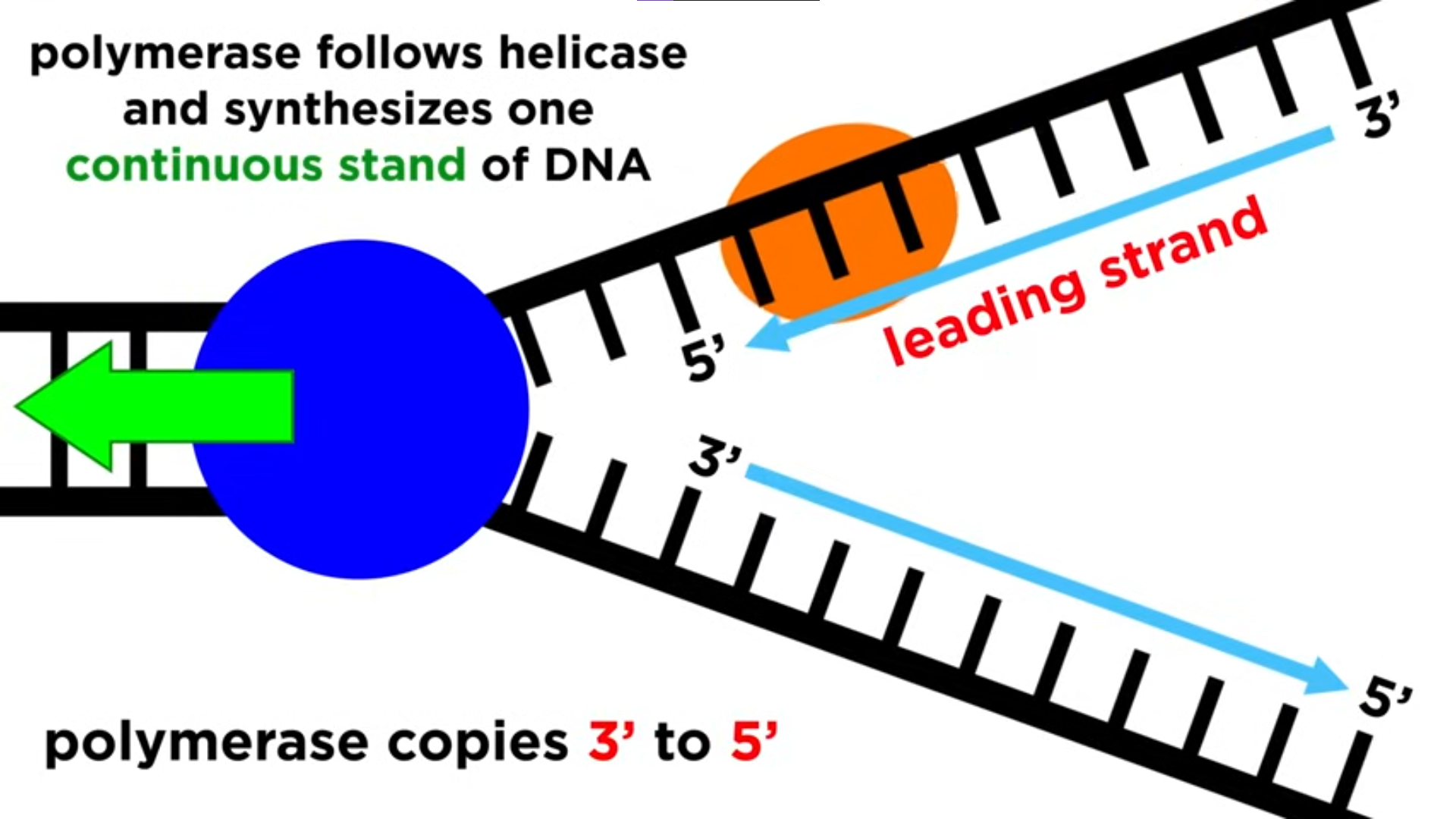
Leading Strand
strand of DNA that is synthesized continuously
towards the fork
Lagging Strand
strand of DNA that is synthesized in fragments
away from the fork
it’s harder to work backwards so it must be done in fragments
this strand of DNA occurs because DNA polymerase can only add bases on the 3’ end, meaning it must wait for helicase to finish unzipping every time it adds a new set of fragments

directionality
? is based on the strand being made, not the template strand
DNA Polymerase
enzyme that synthesizes new strands by attaching to the 3’ end of the template strand and adds new bases from 5’ to 3’
needs primase to create short RNA segments before this enzyme can work
Ligase
enzyme that joins DNA fragments on the lagging strand
Topoisomerase
Enzyme that relaxes the supercoil of DNA and helps form the replication fork
comes before helicase
Helicase
enzyme that unwinds DNA by breaking hydrogen bonds
Okazaki Fragments
sections of copied DNA created on lagging strand
Primase
enzyme that initiates synthesis of DNA by creating a short RNA segment before polymerase