Body Systems
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/99
Last updated 8:19 PM on 5/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
1
New cards
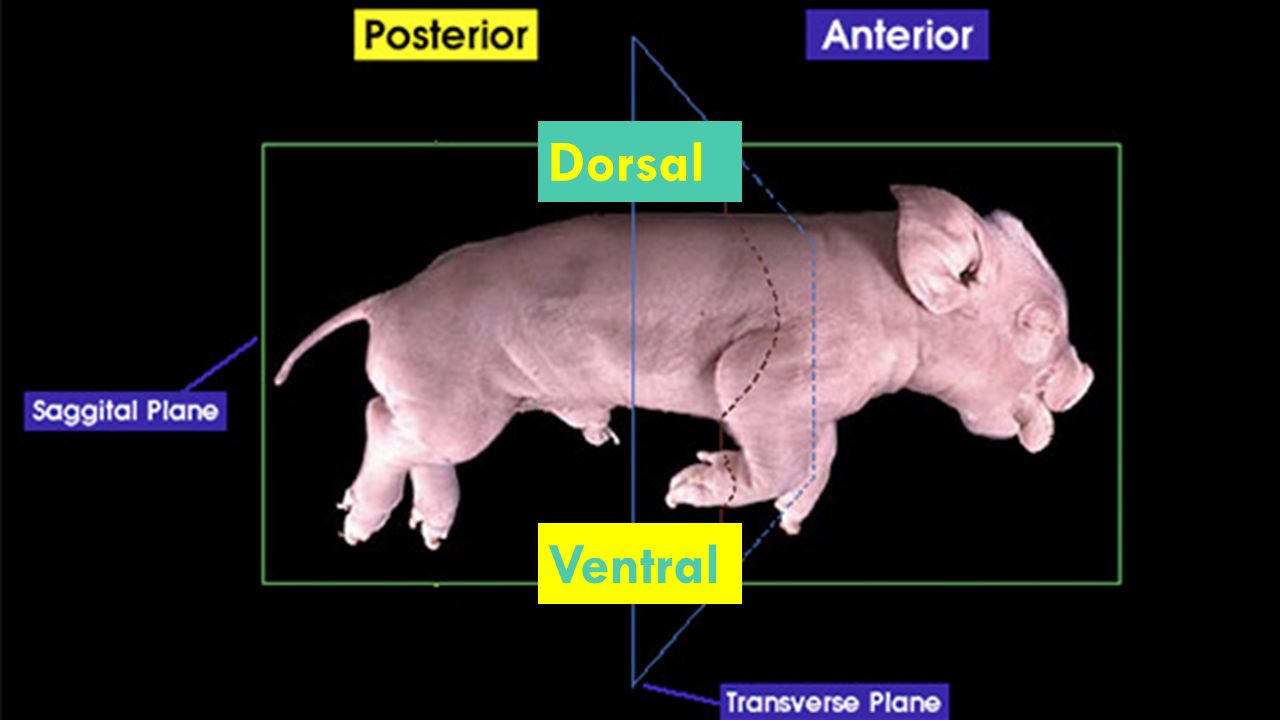
Dorsal side
The top side or above
2
New cards
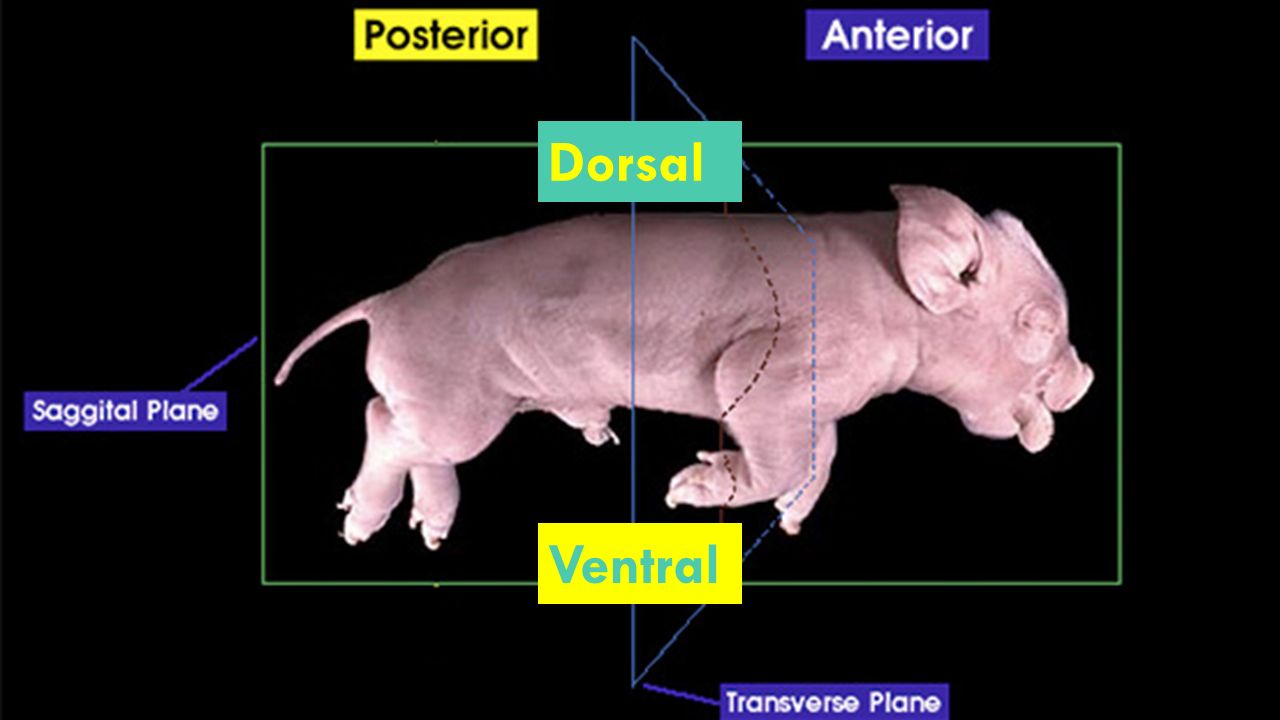
Ventral Side
The lower side
3
New cards
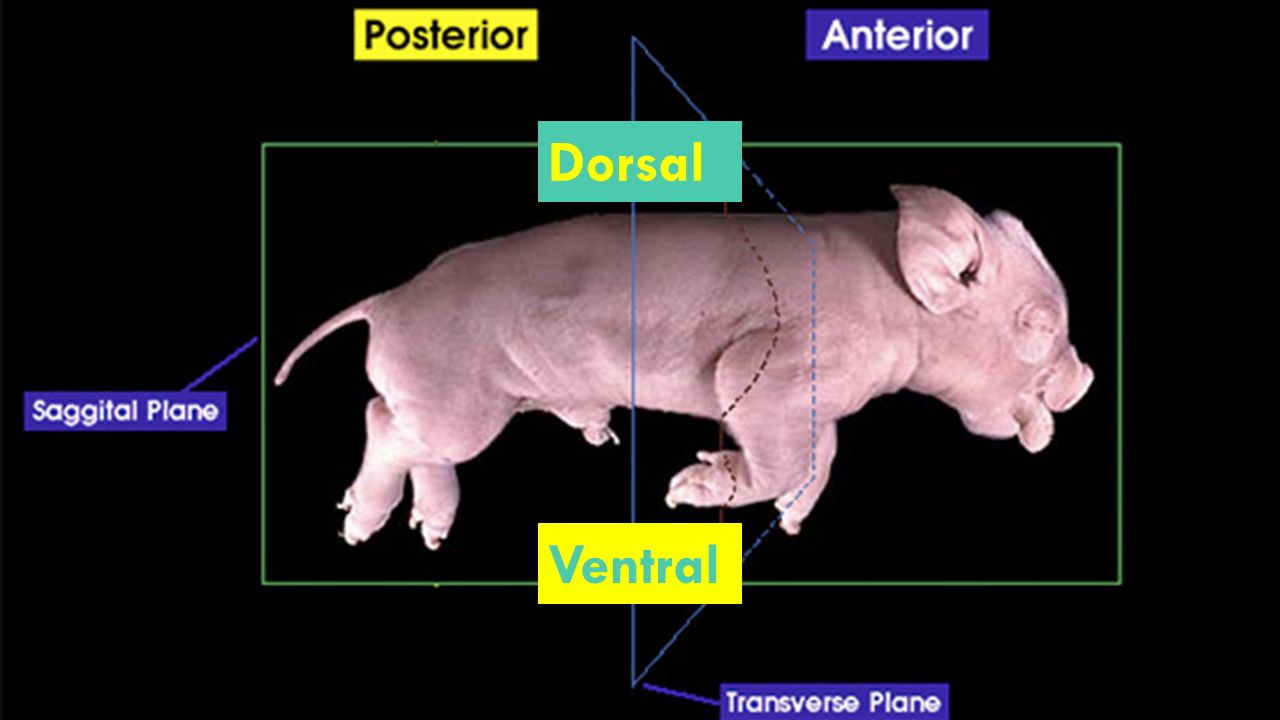
Anterior
Toward the head or front
4
New cards
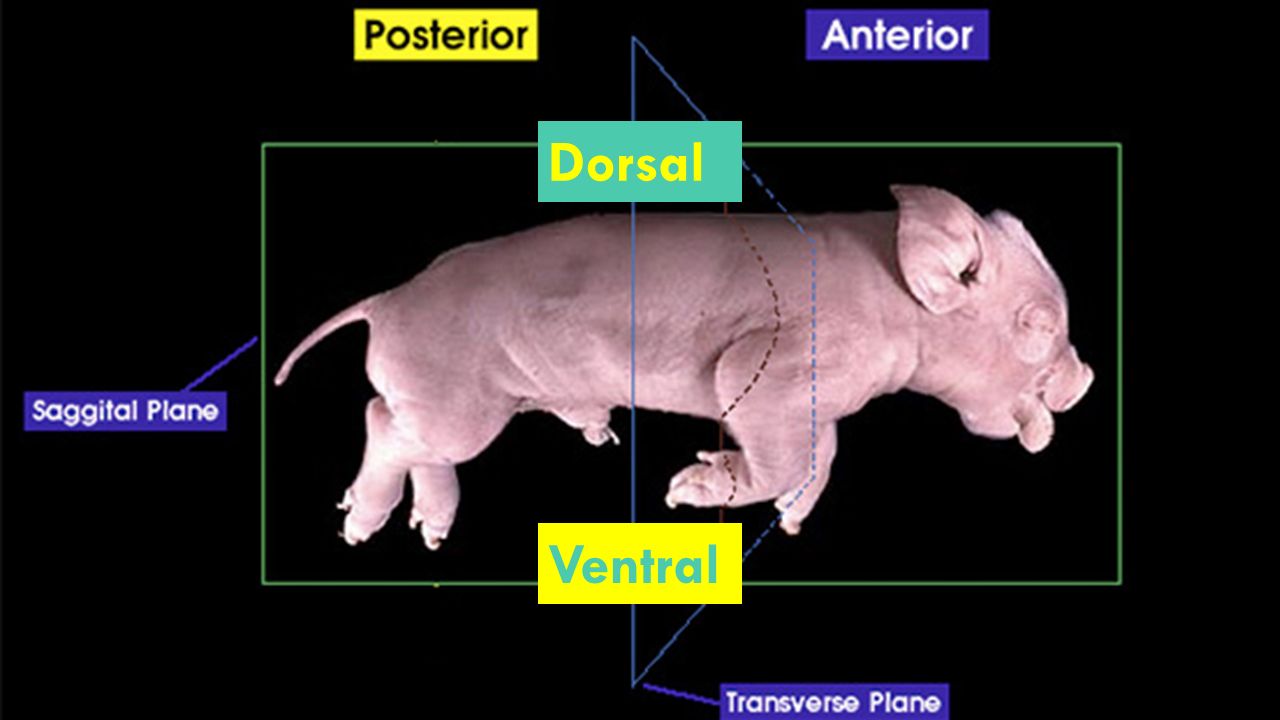
Posterior
Toward the tail or rear
5
New cards
Lateral
Toward the side
6
New cards
Medial
Toward the midline
7
New cards
Proximal
Near a point of reference
8
New cards
Distal
Away from a point of reference
9
New cards
Right
Structures to the right of the “dorsal” midline
10
New cards
Left
Structures to the left of the “dorsal” midline
11
New cards
Pinna
The outer ears
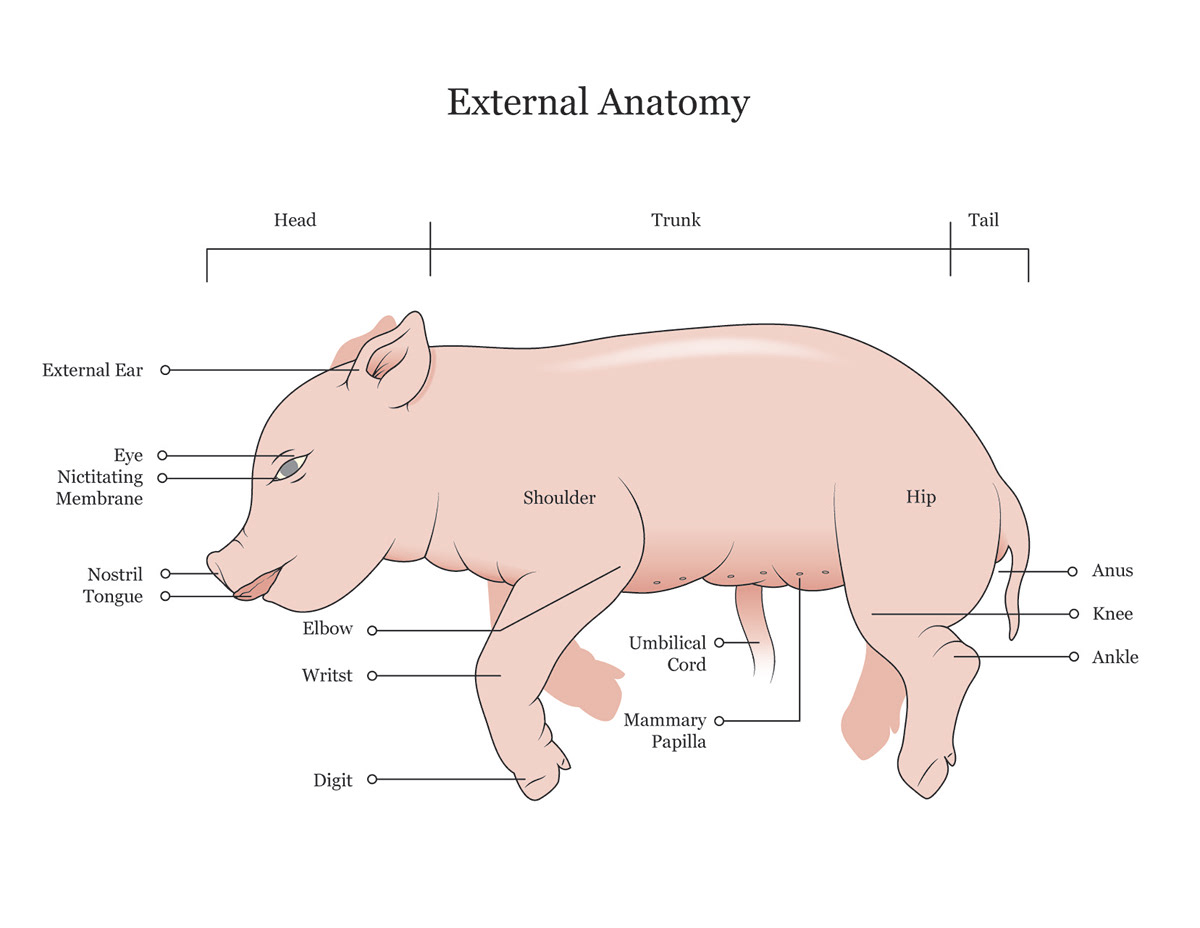
12
New cards
Nostrils
Also known as the nares
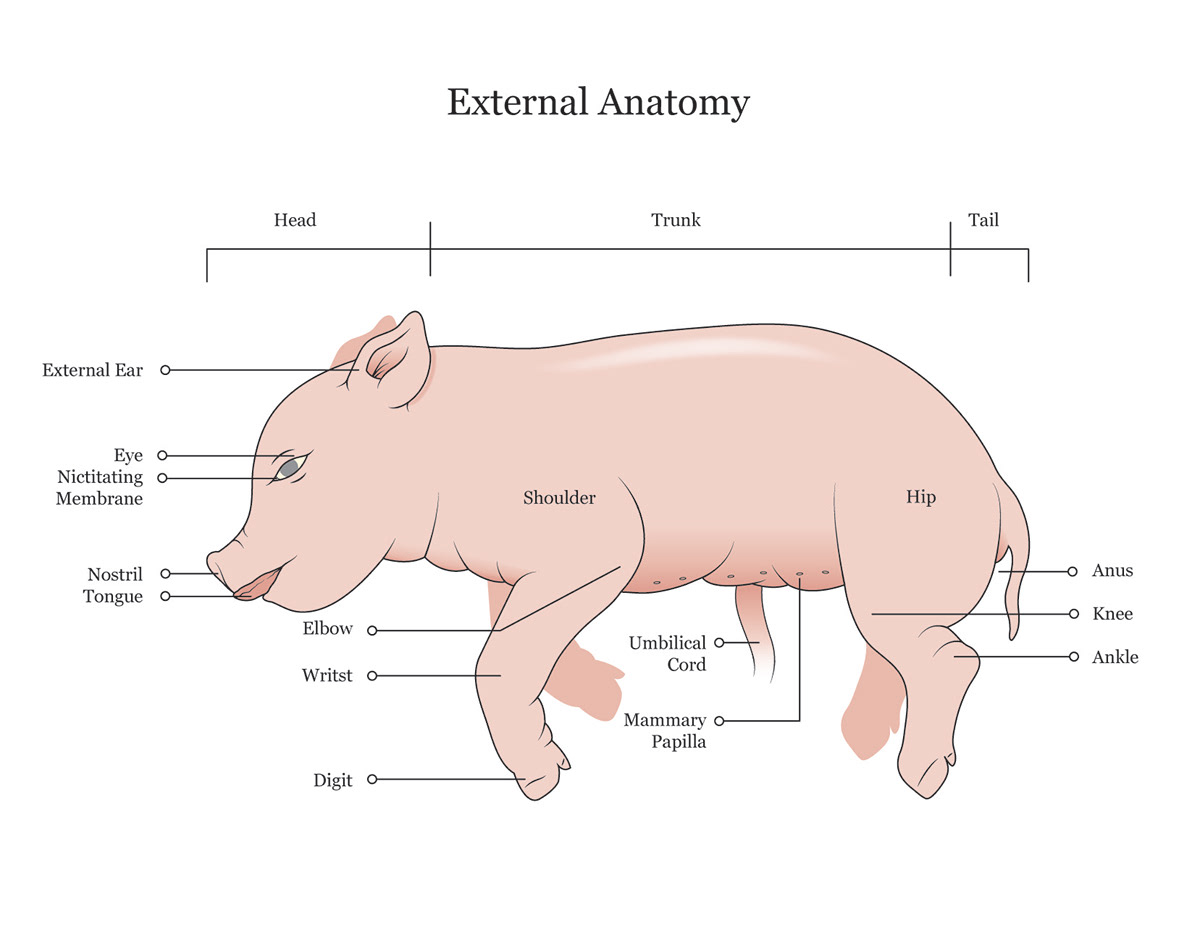
13
New cards
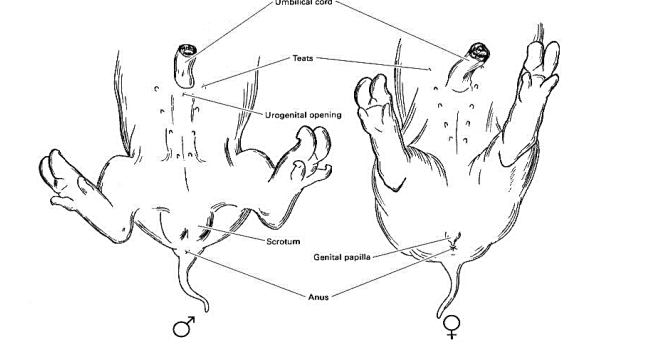
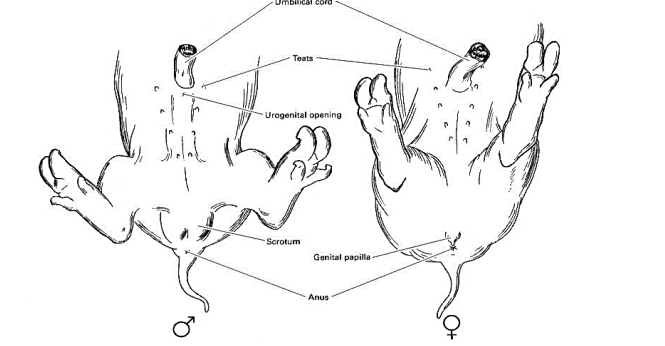
Umbilical Cord
Tube connecting the fetus with the placenta
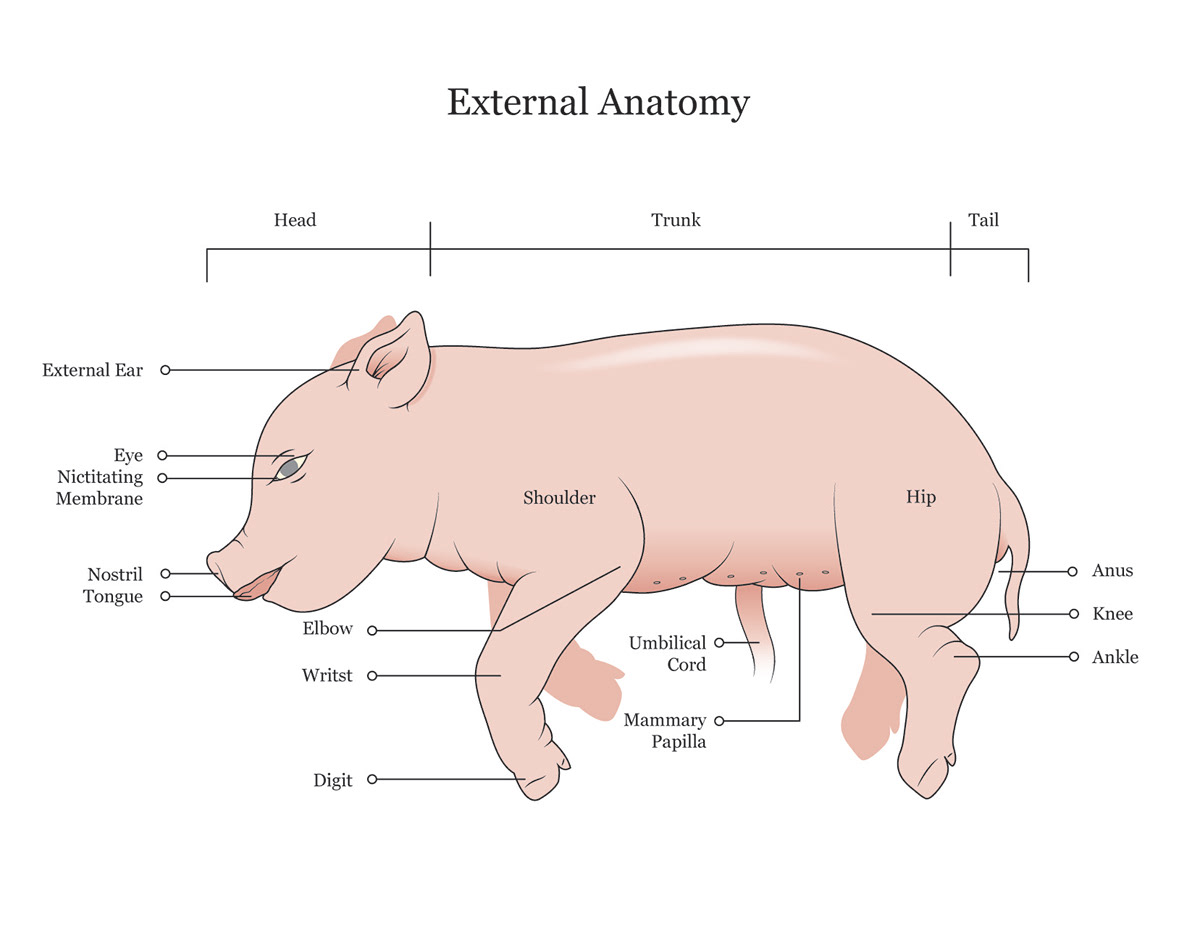
14
New cards
Mammary Papillae
also known as the teats
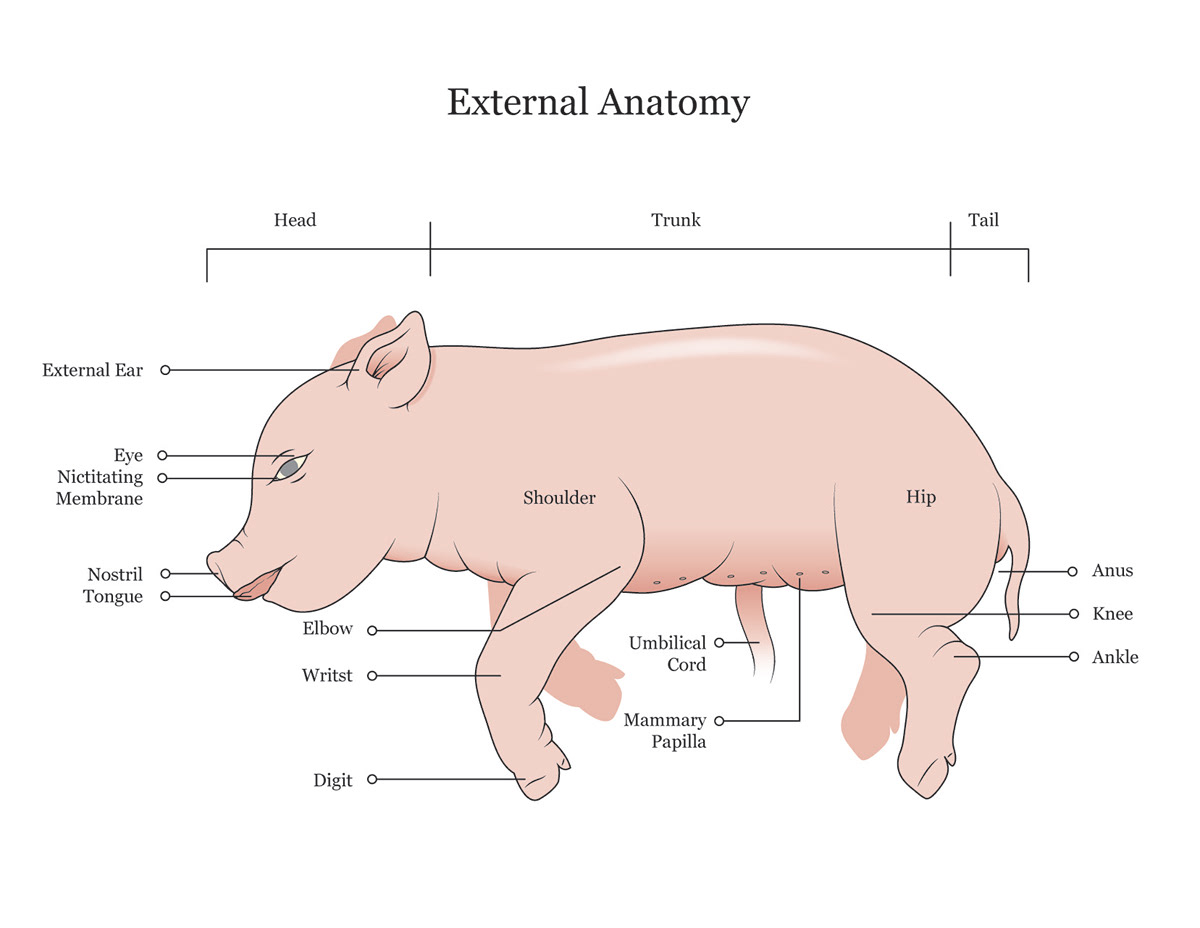
15
New cards
Scrotum
External sac containing the testes
16
New cards
Genital Papilla
\
17
New cards
Urogenital Opening
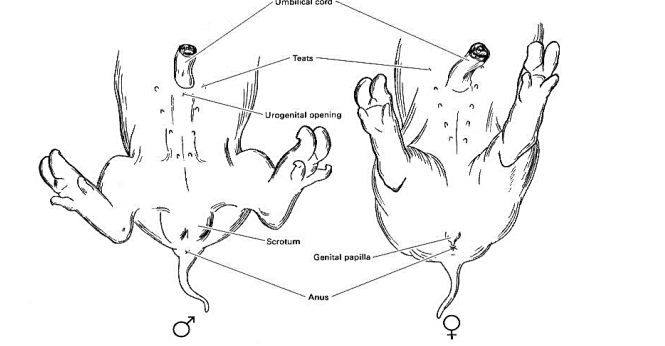
18
New cards
Define Hormone
A chemical released in 1 part of the body and affects cells of a different part of the body, a “messenger”.
19
New cards
What is the function of the endocrine system?
To deliver "messages” throughout the body.
20
New cards
What is the difference between exocrine and endocrine glands?
Exocrine: releases secretions through ducts.
Endocrine: releases secretions through the bloodstream.
Endocrine: releases secretions through the bloodstream.
21
New cards
Give one example of an exocrine gland.
Sweat glands, tear glands.
22
New cards
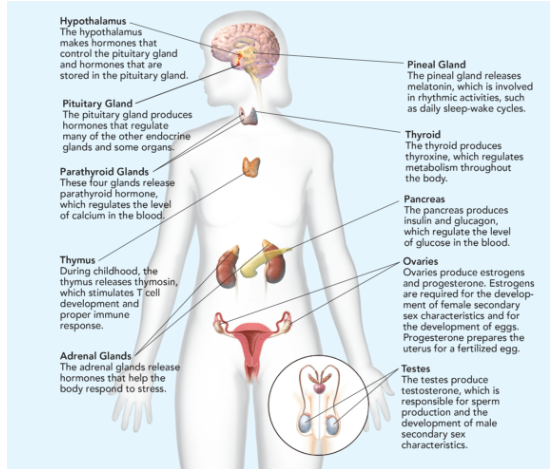
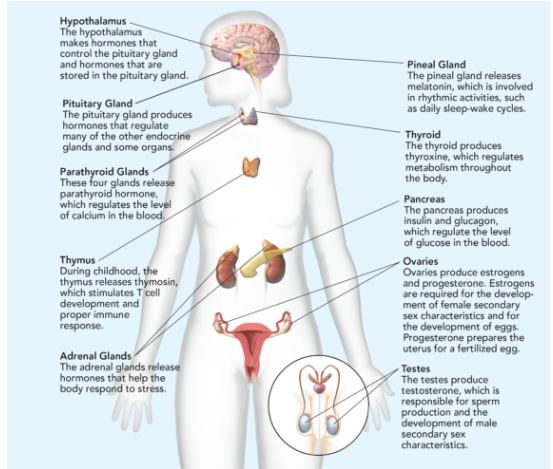
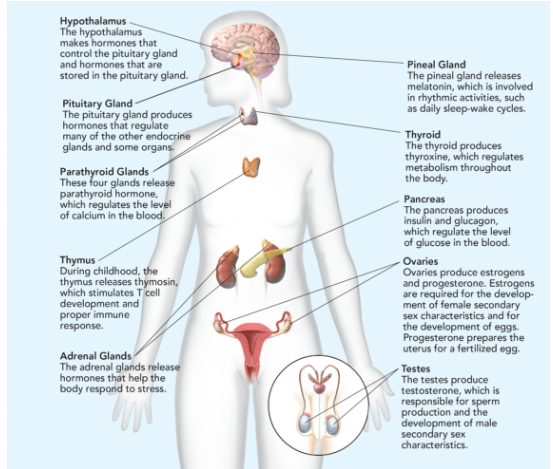
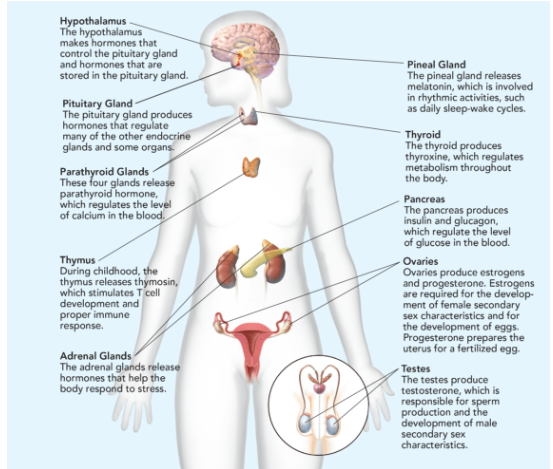
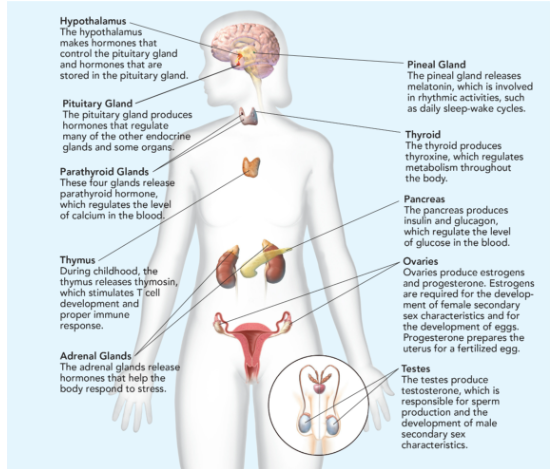
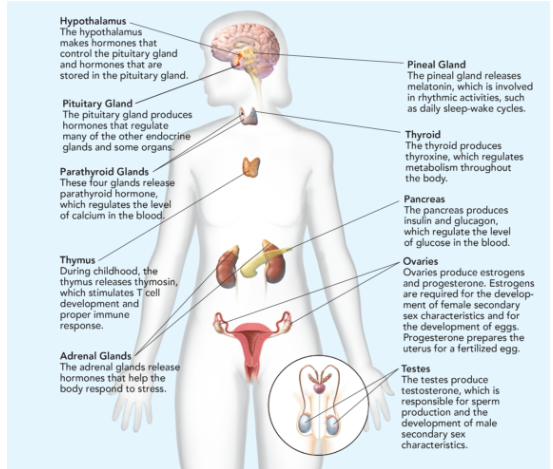
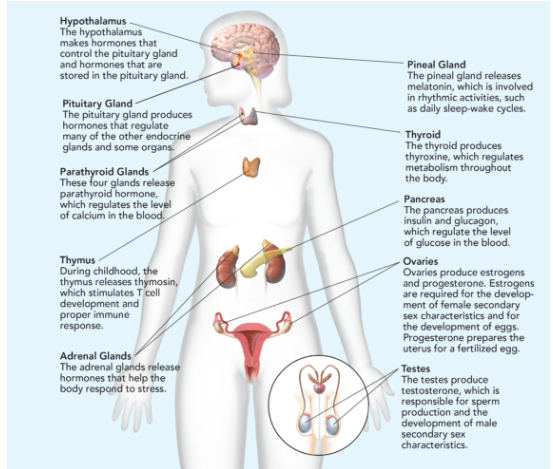
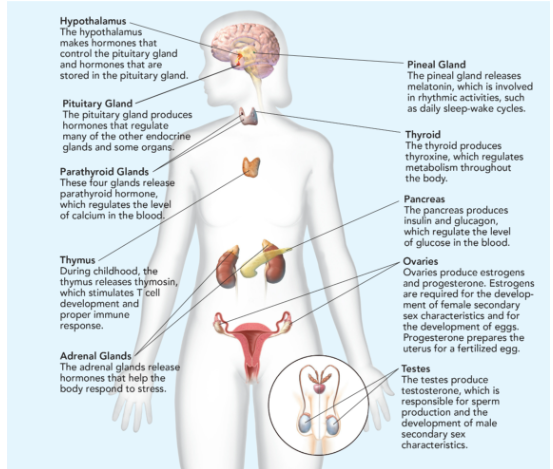
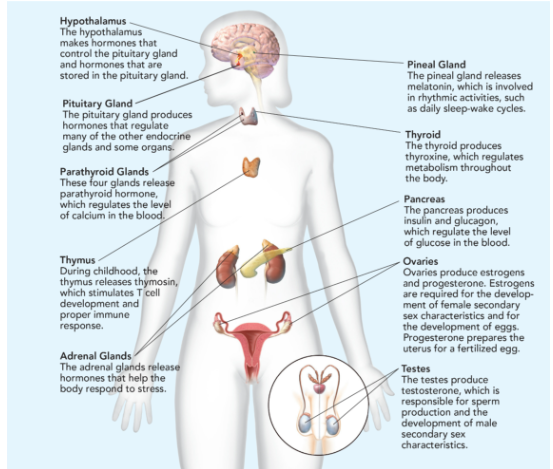
Hypothalamus
makes hormones that control the pituitary gland and hormones that are stored in the pituitary gland.
23
New cards
Pituitary Gland
Makes hormones that controls the function of other endocrine glands; called “the master gland”; releases 9 hormones; smaller than the tip of little finger.
24
New cards
Parathyroid Glands
These four glands release parathyroid hormone, which regulates the level of calcium in the blood.
25
New cards
Thymus
During childhood, the thymus releases thymosin, which stimulates T cell development and proper immune response.
26
New cards
Adrenal Glands
The adrenal glands release hormones that help the body respond to stress.
27
New cards
Pineal Gland
releases melatonin, which is involved in rhythmic activities, such as daily sleep-wake cycle.
28
New cards
Thyroid
produces thyroxine, which regulates metabolism throughout the body.
29
New cards
Pancreas
produces insulin and glucagon, which regulate the level of glucose in the blood.
30
New cards
Ovaries
produces estrogen (responsible for egg development and the formation of the physical characteristics associated with puberty) and progesterone (prepares uterus for pregnancy.
31
New cards
Testes
produces testosterone (sperm production and the formation of the physical characteristics associated with puberty).
32
New cards
Which gland is considered part of both the endocrine and digestive system?
pancreas
33
New cards
Explain how the thyroid gland maintains homeostasis.
the hypothalamus senses low thryoxine levels in the body and then releases thryoxine.
34
New cards
Explain how the pancreas maintains homeostasis.
When blood sugar levels are too high, the pancreas secretes insulin. Insulin stimulates liver and muscles to store excess glucose as glycogen. When blood sugar levels are too low, the pancreas secretes glucagon. Glucagon stimulates liver and muscles to break down glycogen and release glucose back into the blood.
35
New cards
What is the function of the respiratory system?
Exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide between blood, air, and tissues.
36
New cards
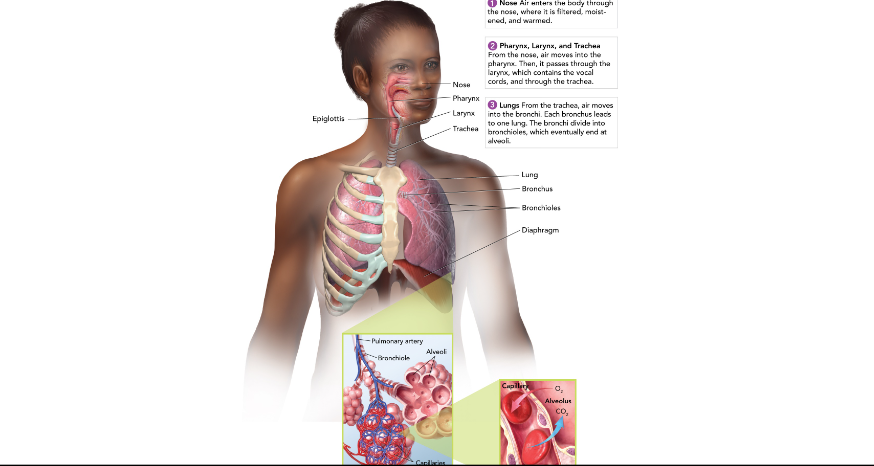
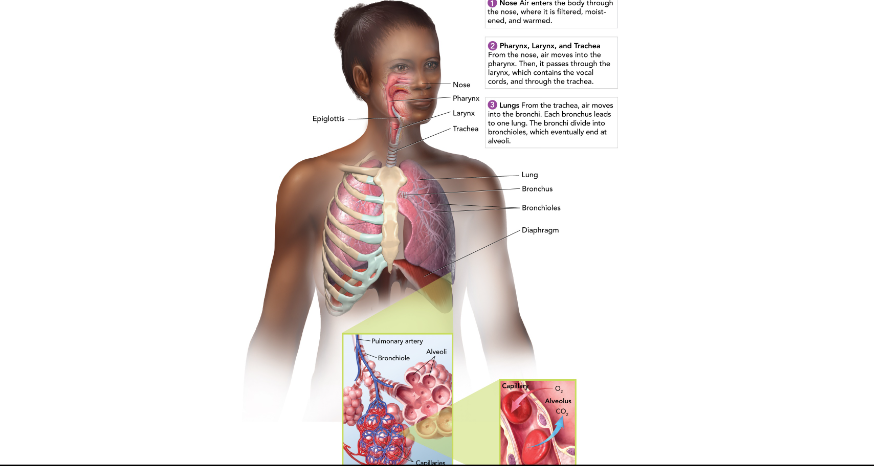
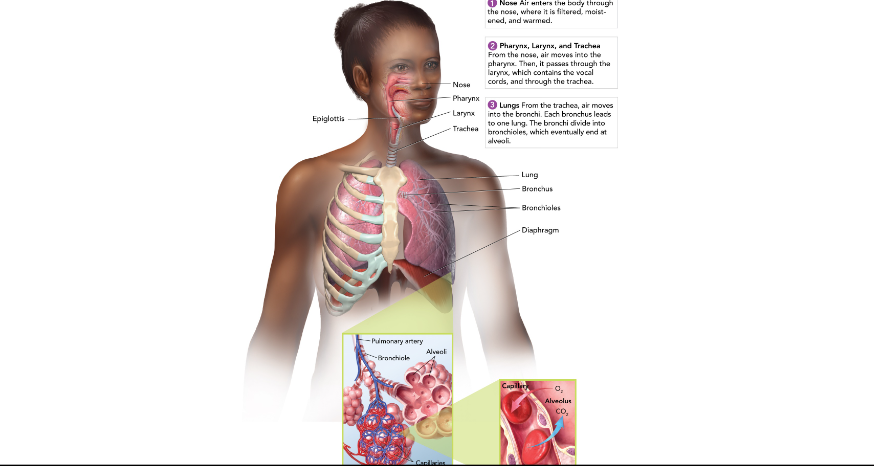
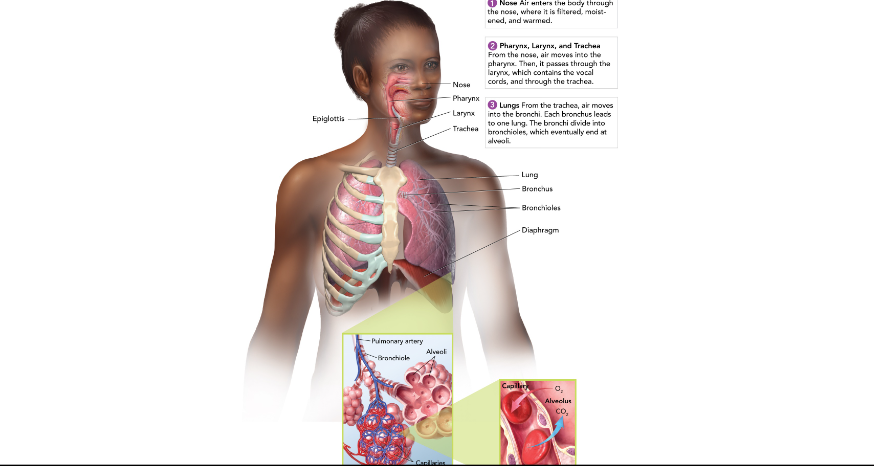
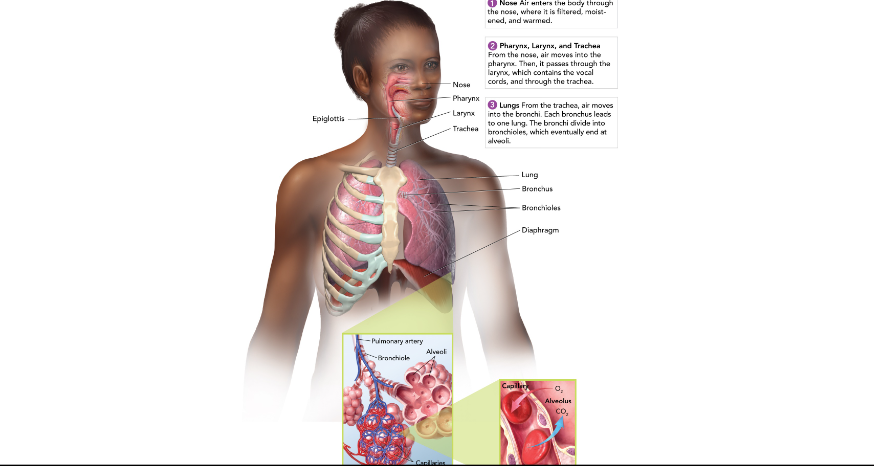
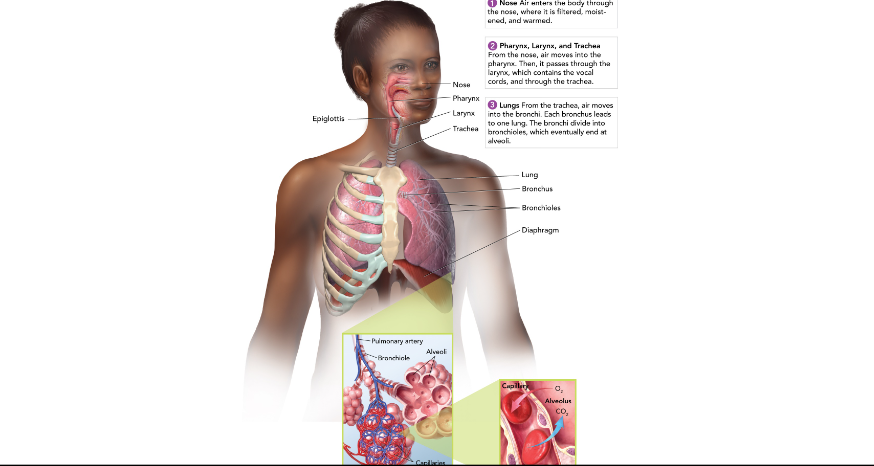
Nose and Mouth
warms, moistens, and filters the air we breathe in.
37
New cards
Epiglottis
covers the entrance to the trachea where we are swallowing.
38
New cards
Pharynx (throat)
passageway for food and air
39
New cards
Larynx (voicebox)
Muscles pull vocal cords together and air moving between them producing sound.
40
New cards
Trachea (windpipe)
Connects larynx to bronchi; has cells with cilia to filter air.
41
New cards
Lungs
made up of many tiny air sacs that are lined with capillaries for gas exchange with the blood.
42
New cards
Bronchioles
Leads into the lungs from the trachea; branches out until it reaches alveoli.
43
New cards
Diaphragm
large, flat, thin muscle that is between the heart and liver and is involved in breathing.
44
New cards
Where does gas exchange take place?
between capillaries and the alveaoli, which are grouped into clusters that look like grapes; a delicate network of thin-walled capillaries surround each alveolus.
45
New cards
What organs does the circulatory system include?
heart, blood vessels, and blood
46
New cards
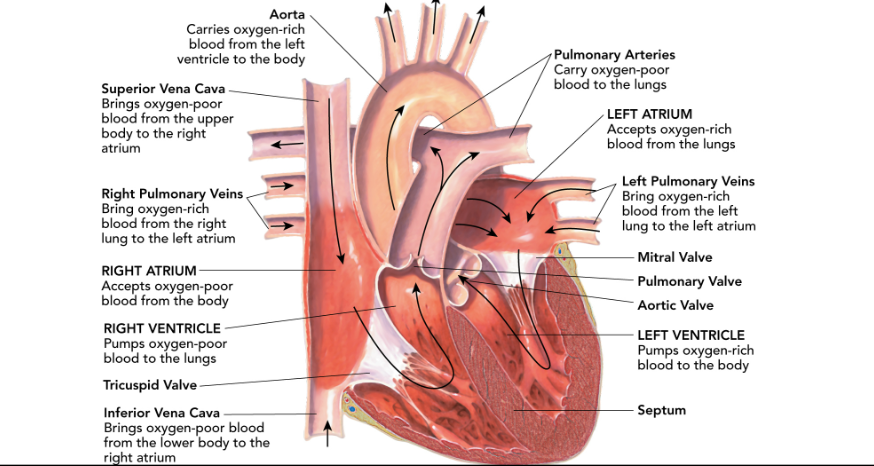
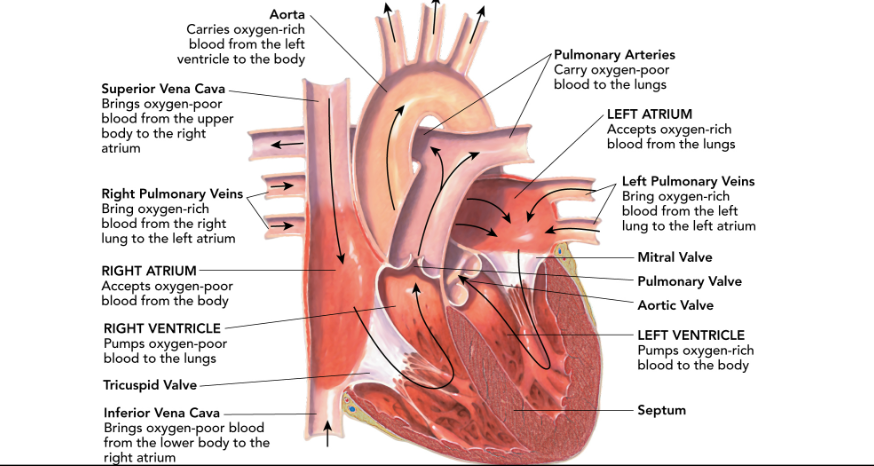
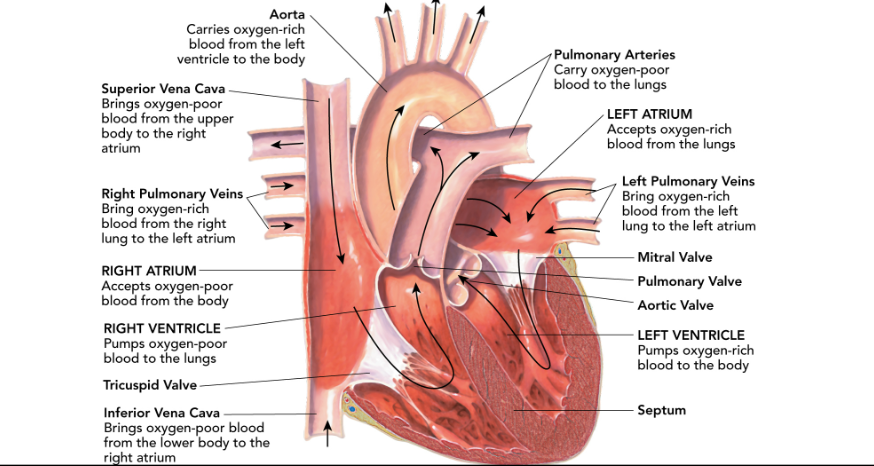
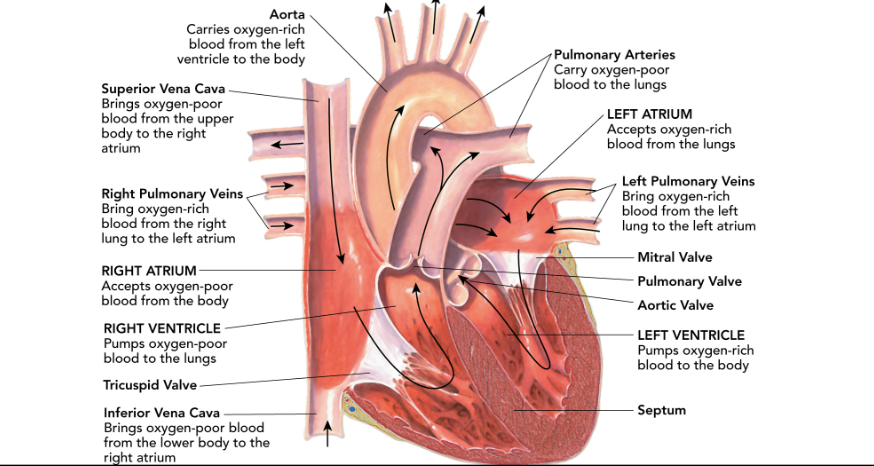
Pericardium
the protective sac of tissue that the heart is enclosed in.
47
New cards
This thing divides the left side of the heart from the right side of the heart.
septum
48
New cards
how many chambers does a human heart have?
4
49
New cards
What are the upper chambers of the heart called?
atria
50
New cards
What are the bottom chambers of the heart called?
ventricles
51
New cards
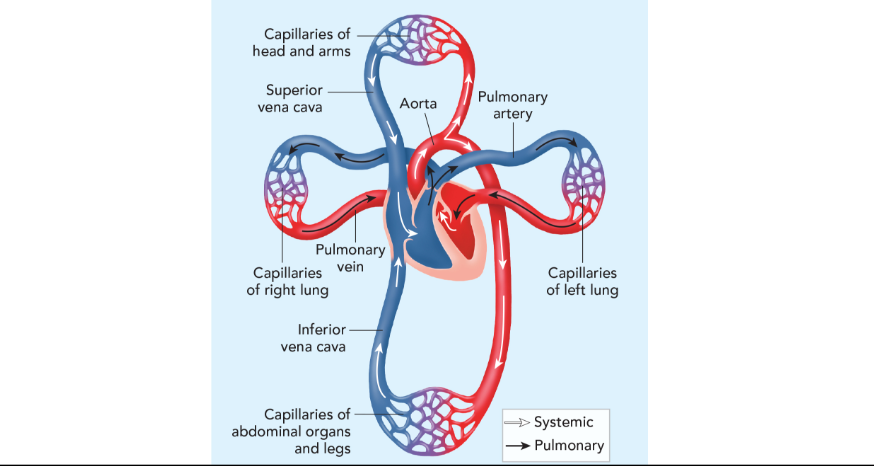
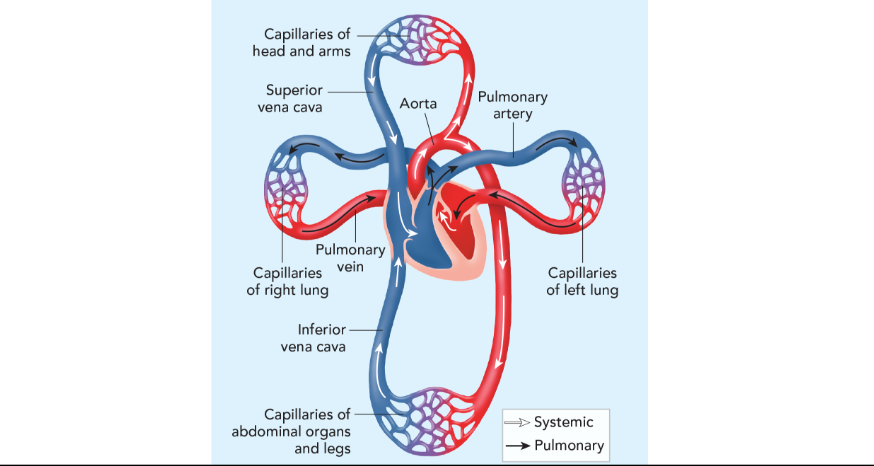
Pulmonary circulation pathway
the right side of the heart pumps blood from the heart to the lungs.
52
New cards
Systemic circulation pathway
o2 rich blood from the lungs flows into the left side of the heart and is pumped to the rest of the body.
53
New cards
Why are valves important in the heart?
they keep blood moving through the heart in only one direction.
54
New cards
What are the three types of blood vessels in the circulatory system?
arteries, capillaries, and veins.
55
New cards
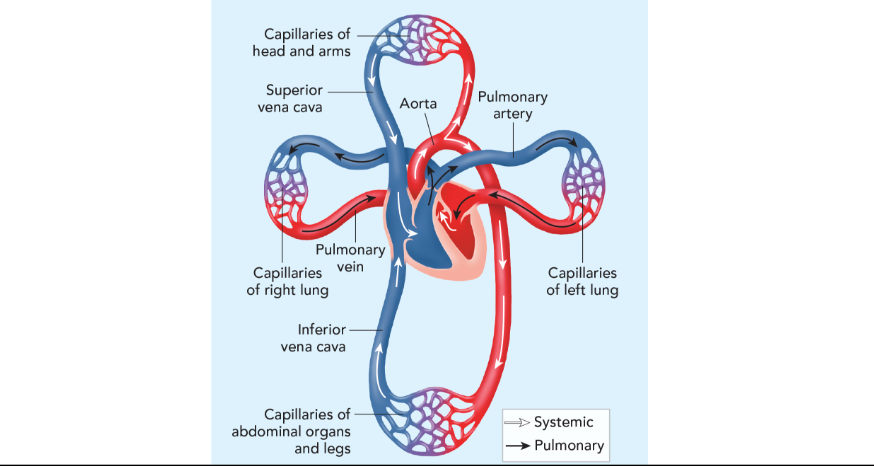
Artery
carries o2 rich blood away from the heart to the rest of the body; largest vessel; has thick walls; are bright red because blood is o2 rich.
56
New cards
Capillaries
brings nutrients and o2 to cells; removes CO2 and waste from cells; smallest vessel; one cell thick; connects arteries to veins.
57
New cards
Veins
returns o2 poor blood back to the heart from the body; contains valves to keep blood flowing toward heart; are “blue” because blood is o2 poor.
58
New cards
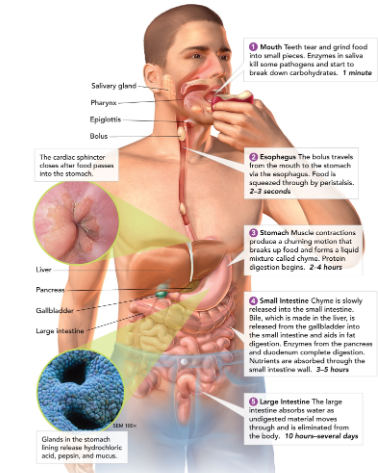
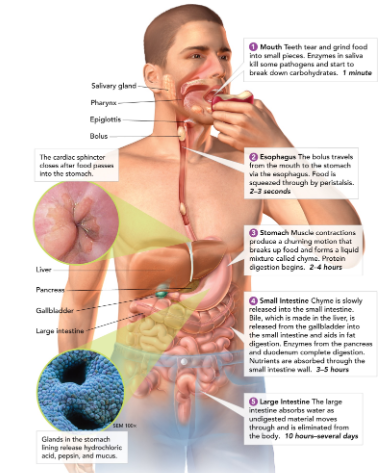
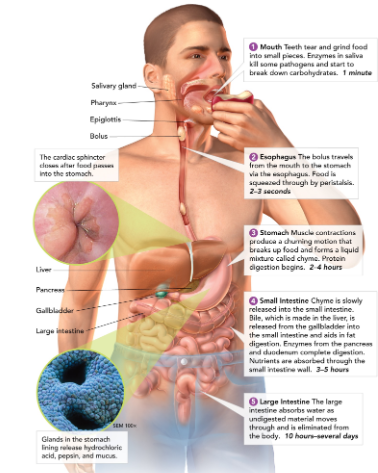
What is the function of the digestive system?
convert food into simpler molecules that the cells can use.
59
New cards
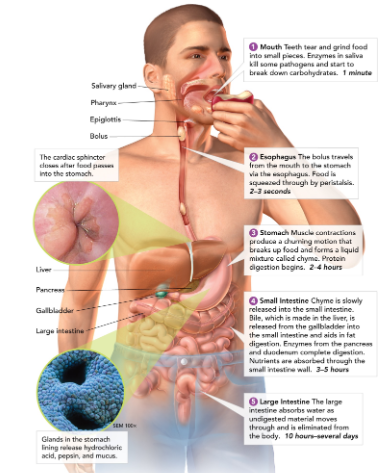
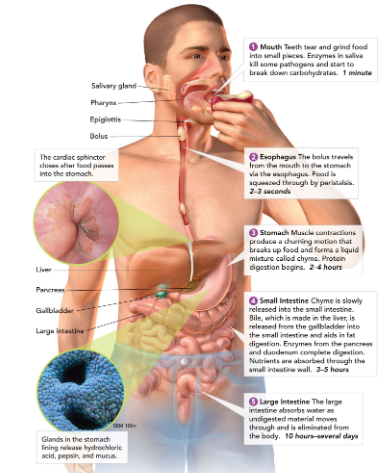
Salivary glands
create saliva, which contains enzymes to start breaking down food in the mouth.
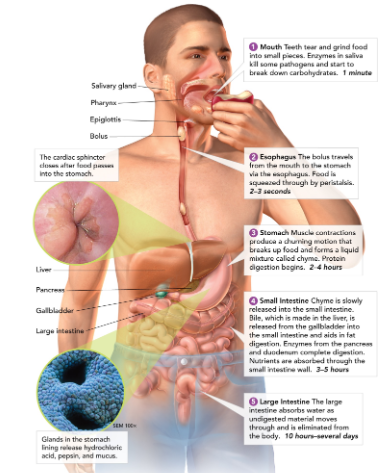
60
New cards
Esophagus
connects the mouth to the stomach (contracts to help guide food down to stomach - this is called peristalsis).
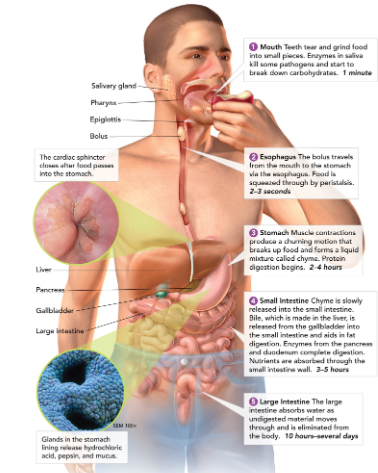
61
New cards
Stomach
a large muscular sac that contains digestive enzymes to break down food.
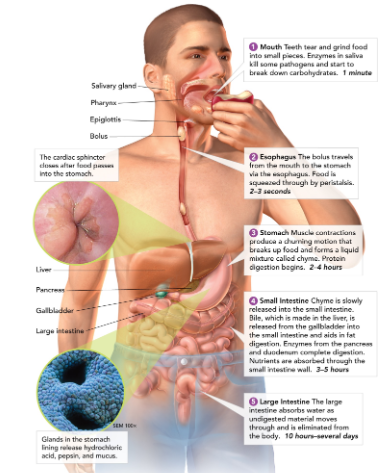
62
New cards
Small intestine
most chemical digestion takes place here; where nutrients are absorbed from food.
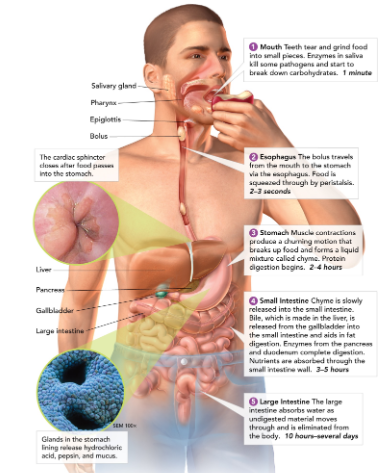
63
New cards
Large intestine (colon)
retains excess water; develops feces; make and absorbs vitamins.
64
New cards
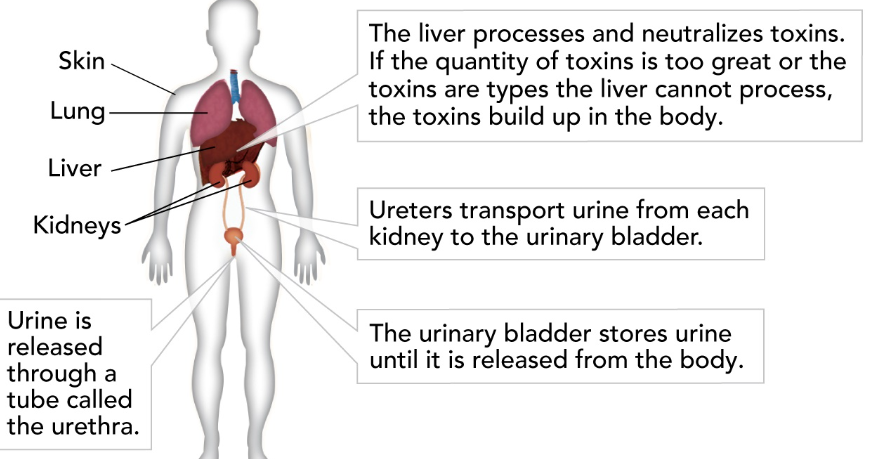
Liver
detoxifies blood, produces bile (which breaks down, or emulsifies, fats)
65
New cards
Gallbladder
stores bile
66
New cards
Spleen
destroys and makes red blood cells; produces antibodies for the immune system.
67
New cards
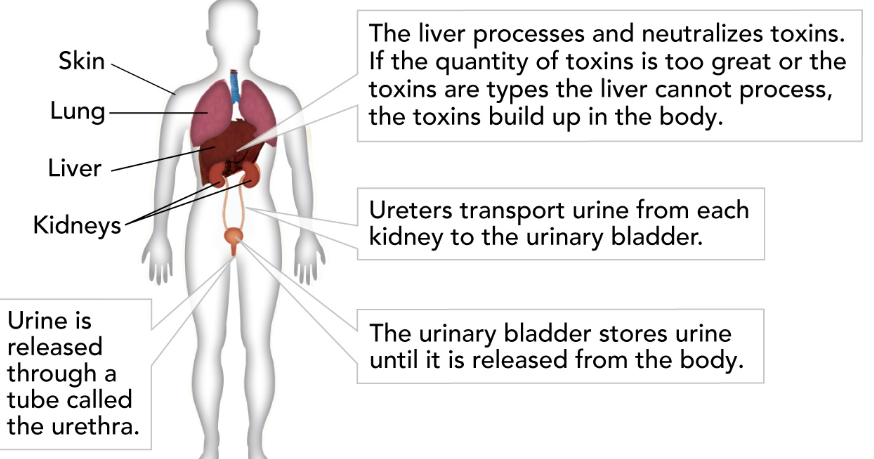
What is the function of the excretory system?
removes waste from the body
68
New cards
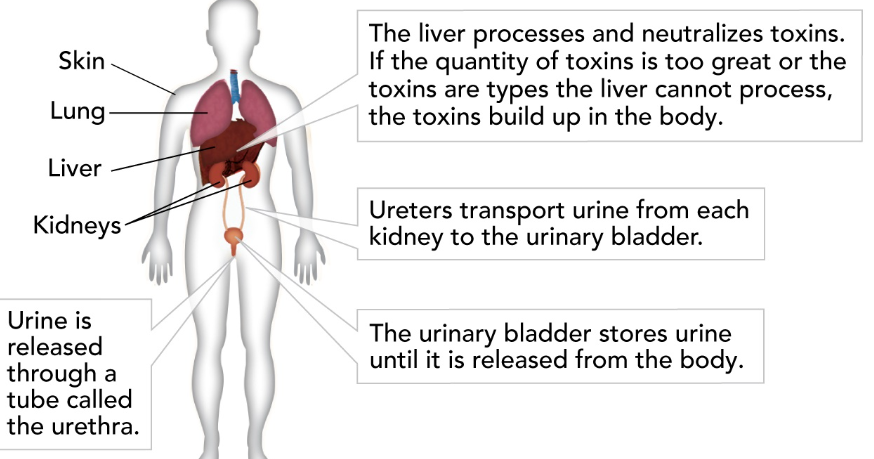
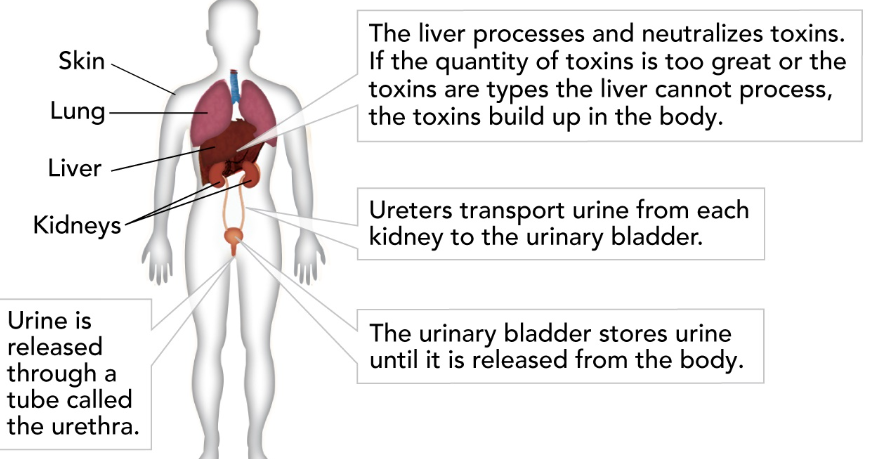
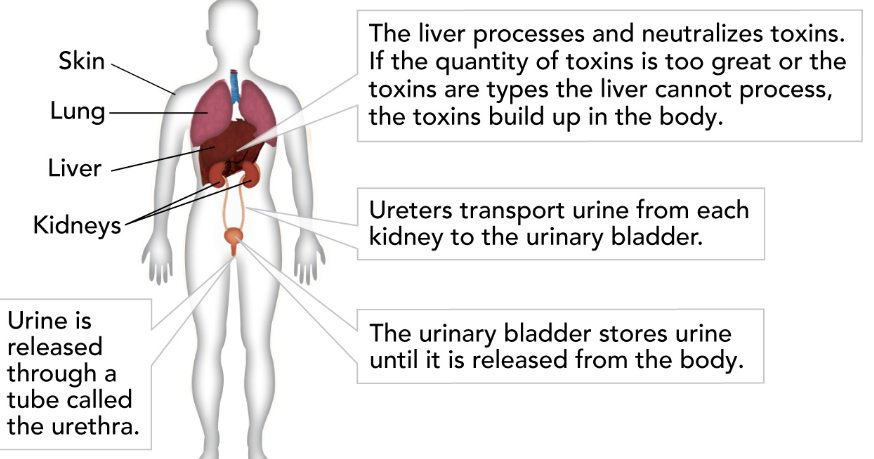
Kidney
removes waste products from the blood; maintains blood pH, regulates the amount of water in the blood.
69
New cards
Ureter
tube that carries urine from the kidney to bladder
70
New cards
Bladder
stores urine
71
New cards
Urethra
tube that carries urine from the bladder to outside of the body.
72
New cards
Which two processes are used for blood purification?
filtration and reabsorption
73
New cards
Filtration
removes waste from the blood
74
New cards
Reabsorption
water and nutrients are reabsorbed by the blood.
75
New cards
The kidneys filter all of the blood in the body every ___ minutes.
45
76
New cards
True or False? A person can live without one of their kidneys.
true
77
New cards
Puberty
period of time where adolescents reach sexual maturity and are capable of reproduction.
78
New cards
Approximately what age does puberty occur?
Females: 10-14
Males: 12-16
Males: 12-16
79
New cards
Explain how the onset of puberty begins.
the hypothalamus stimulates the pituitary gland to release luteinizing hormone and follicle stimulating hormone.
80
New cards
What is the primary function of the male reproductive system?
produce sperm
81
New cards
Seminiferous tubules
hundred of tiny tubes where the sperm are produced.
82
New cards
Epididymis
where the sperm mature and are stored before ejaculation
83
New cards
What is the primary reproductive organ in a female?
ovaries
84
New cards
What are the primary functions of the female reproductive system?
produce mature eggs every 28 days and prepare the body for pregnancy.
85
New cards
About how many eggs are released in a females body in her life?
400
86
New cards
Ovulation
the process in which an egg or eggs are released from one or both ovaries
87
New cards
Fallopian tubes
have cilia that sweep eggs into the uterus and there the sperm find the egg for conception.
88
New cards
Uterus
where the fertilized egg implants and grows and develops for 40 weeks.
89
New cards
Placenta
develops in uterus during pregnancy and allows for mom’s blood vessels and fetal blood vessels to be close together for transfer of carbon dioxide and oxygen, nutrients and waste between mother and baby.
90
New cards
What is the function of the nervous system?
collects sensory input and conducts impusles around body so body can respond to external and internal environmental changes.
91
New cards
What are the cells that transmit impulses within the nervous system called?
neurons
92
New cards
What does the central nervous system consist of?
the brain and spinal cord
93
New cards
What are the layers that surround the brain called?
meninges
94
New cards
Cerebrospinal spinal fluid
bathes the brain and spinal cord and acts as a “shock absorber”.
95
New cards
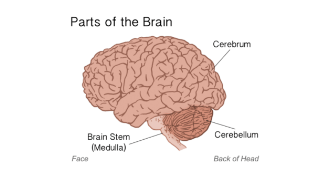
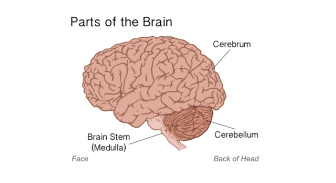
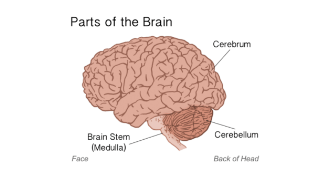
Cerebrum
largest part of brain; involved in thinking, logic, learning, judgement, intelligence, emotions, conscious though and conscious movement.
96
New cards
Cerebellum
Coordination of muscle movements such as posture and balance.
97
New cards
Medulla oblongata
part of the brain stem; regulates INVOLUNTARY survival functions such as blood pressure, heart rate, breathing, digestion, vomiting, swallowing, defecation and blinking.
98
New cards
Auricles
external, earlike flaps composed of muscle from the atria.
99
New cards
Meconium
amniotic fluid that the fetal pig has swallowed
100
New cards
Mesenter
The mesentery attaches the intestines to the abdomen and contains blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatics. It keeps the intestines in place and allows them to move during digestion.