CSE 4830 - Computer Vision
1/166
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
167 Terms
computer vision is an ____ field whos goal is to enable machines to automatically ____ and ____ visual information
multidisciplinary, interpret, understand
Computer vision focuses on visual information from the _____ world.
real
Computer vision aims to help computers _____ visual data rather than just ____ it.
interpret, display
In computer vision, understanding is NOT just seeing _____.
____ _____ in images is a key part of visual understanding.
Understanding how things move involves interpreting _____.
pixels, recognizing objects, motion
Interpreting the overall environment of an image is called ____ _____.
scene understanding
Computer vision systems can make decisions based on ____ ____
visual input
Extracting physical information from images often involves _____ and ____ .
geometry, motion
Determining where an object is over time is called ____ _____.
object tracking
Estimating how fast and in what direction an object is moving is called _____ _____.
motion estimation
Determining how far away objects are is called _____ _____.
depth estimation
Computer vision attempts to infer _____ structure from _____ images.
3d, 2d
Identifying whether something is a person, dog, or chair is an example of ____ _____.
object recognition
Recognition uses _____ and _____ to interpret images.
algorithms, representations
Mining visual data involves working with large image or video _____.
datasets
Vision is considered an _____ problem.
inverse
In an inverse problem, we try to infer the _____ from the ____ ____.
cause, observed result
What are the steps in the computer vision pipeline?
image acquisition, preprocessing & enhancement, feature extraction, object recognition, interpretation & decision making
We can think of a greyscale image as a function:
f: {R}² → {R}
input= ___ ___ ___
output = ____
spatial location (x,y), intensity
A digital image is a ____ version of the continuous image where..
image plane = a ____
each entry = ____ ____
discrete, matrix, pixel intensity
pixel values:
0 is ___ and 255 is ___
black, white
a scalar is just a ____
number
how do you denote a scalar?
lowercase, italics
a vector is a ____ ____ of numbers
1d array
how do you denote a vector?
lowercase, italics, bold
a matrix is a ___ ___ of numbers
2d array
how do you denote a matrix?
uppercase, italics, bold
a 0D tensor is a ____. a 1D tensor is a ____, a 2D tensor is a ____, a 3D+ tensor is a ____
scalar, vector, matrix, tensor
a grayscale image is a ____ tensor
2d
a RGB image is a ____ tensor
3d
whats the transpose of a scalar?
itself
a transpose swaps ___ and ___
rows, columns
matrix addition (element wise) the matrices must be the ___ ___
same size
what do you do when you multiply a MATRIX by a SCALAR?
scale all entries
what do you do when you add a SCALAR to a MATRIC
shift all entries
matrix times a matrix: row of ___ times the column of ___ AND ___ ____ ___
1st, 2nd, dimensions must align
the result of the inner product (dot product) of two vectors is a….
scalar
the outer product of two vectors is a….
matrix
norms are functions that measure how __ a __ is
large, vector
norms are the distance from the ___ ___ to the ___
zero vector, vector
positive definiteness: the unit vector with size 0 is the __ ___, and NO OTHER VECTOR can have ___ ___
zero vector, zero length
absolute scalability: scaling a vector scales its length by the __ __ of a scalar, _ doesnt matter only _
absolute value, direction, magnitude
unit vector: vector with a norm equal to _
1
unit vector represents _ only, not _
direction, magnitude
orthogonal vectors: two vectors whose __ ___ is __
dot product, zero
orthogonal vectors: vectors are _
perpendicular
symmetric matrix: a matrix equal to its _
transpose
symmetric matrices are only possible for __ matrices
square
orthogonal matrix: the __ of a square matrix equals its _
transpose, inverse
orthogonal matrix: columns and rows are _
orthonormal
diagonal matrix: all __ ___ entries are __
off diagonal, zero
diagonal matrix: diagonal entries cant be _
zero
eigendecomposition is a way to break a matrix into:
__ it acts along (eigenvectors)
__ ___ it acts along each __ (eigenvalues)
directions, how strongly, direction
A non-zero vector v is an eigenvector of matrix A if:
___
Av = lambda v
The scalar λ\lambdaλ represents the __________ factor applied to the eigenvector.
scaling
Multiplying a matrix by its eigenvector does not change the ___, only the ___
direction, magnitude
Geometric Meaning
eigenvectors are __ that stay the same after transformation
eigenvalues tell how much — or —- occurs
directions, stretching, compressing
eigenvectors must be __
eigenvalues are __
non-zero, scalars
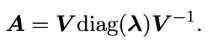
A ___ matrix can be written as.
V = matrix of __________
Λ\LambdaΛ = diagonal matrix of __________
diagonalizable, eigenvectors, eigenvalues
Real Symmetric Matrix:
A = A^T
Eigenvalues are __
Eigenvectors can be __
real, orthonormal
SVD works for —- — matrices
any size
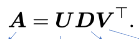
SVD equation:
U = output __
V = input __
D = __ values
directions, directions, singular
pseudoinverse is used when the normal inverse — — —
does not exist
trace is a — of — —
sum, diagonal elements
trace equals sum of —
eigenvalues
determinant = product of —
measure — —
eigenvalues, volume scaling
If det(A) ≠ 0 → matrix is __________
If det(A) = 0 → matrix is __________
invertible, not invertible
orthonormal vectors are — to eachother and — —
perpendicular, unit length
unit length is a length of —
1
probability theory allows us to — in the presence of —
reason, uncertainty
information theory allows us to — the amount of —
quantify, uncertainty
There are - interpretations of uncertainty
two
frequentist interpretation (of probability)
probability is defined as a - - -
P(a) is the - of an - a in the limit
Example: coin toss, probability based on how often heads appears over many trials
long run frequency, frequency, event
subjective interpretation (Bayesian, of probability)
probability represents a - - -
P(a) reflects how strongly we - a will occur
Example: - -
degree of belief, believe, doctors diagnosis
a probability space describes a - - or - and consists of 3 components
Sample space
Ω is the set of - - -
Set of events (S)
an event is a subset of the - -
An event may include: 0 to - outcomes
Probability Distribution(D)
P is a function that assigns - to - or -
Probabilities are real numbers between - and -
The probability of an event is the sum of the probabilities of its -
random process, event, all possible outcomes, sample space, N, probabilities, outcomes, events, 0, 1, outcomes
what are the 3 components of a probability space?
sample space, set of events, probability distribution
what are the two types of probability space
discrete probability space, continuous probability space
types of probability space:
discrete:
Ω is -
analysis involves -
continuous:
Ω is -
analysis involves -
finite, summation, infinite, integrals
Ω is the number/set of all - -
possible outcomes
A random variable - is a function that assigns a - value to each - of a random process
X, numerical, outcome w
how many types of random variables?
two
types of random variables:
categorical (discrete): takes values from a - -
continuous (real-valued): takes values from a - -
countable set, continuous range
a probability distribution describes how - each possible - of a - - is
likely, outcome, random process
PROPERTIES OF A PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION
probabilities cant be -
normalization means that something must -
additivity: if two events cant both happen, — their —
negative, happen, add, probabilities
a probability mass function is used when outcomes are -
countable
the PMF is written as:
P(X=x)
PMF assigns a probability to each - - of a - - -
possible value, discrete random variable
PMF:
must be between - and -
the sum must equal -
0, 1, 1
a probability density function is used when outcomes are -
continuous
PDF is defined as:
p(x)
must be - than -
integral must equal -
does NOT have to be - - or equal to -
greater, 0, 1, less than, 1
for continuous variables. probability is computed as the - under the -
area, curve
a PMF assigns probability to - values, while a PDF assigns density to - values
discrete, continuous
multivariate probability distributions are used when more than one - - are involved
random variable
X = car model type
y = manufacturer
- - tells us how likely each combination is
joint probability
marginal probability asks: “What is the probability of - - of what - is?”
X regardless, Y
marginal probability: discrete case:
fix -
add up - over all - -
x, probabilities, possible y
to compute a marginal probability we - the other variable
ignore
marginal probability removes the - of other -
effect, variables
conditional probability answers: “What is the probability of -, - that - has already -?”
Y, given, X, happened
relationship between marginal & conditional probability:
marginal uses the - -
conditional uses - by a -
sum rule, division, marginal