Week 7-Organic Functional Groups, Carbohydrates and their Biological Importance
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Biological macromolecules (big molecules), also known as macro biomolecules
are large molecules that are built from smaller organic molecules (molecules that contain carbon
are necessary for life
Four Major biomolecules (make up the majority of a cell’s mass;
Carbohydrates
lipids
proteins
nucleic acids
Hydrocarbons
Organic molecules are a class of molecules that contain carbon, in which one or more atoms of carbon are covalently linked to atoms of other elements, most commonly with hydrogen, oxygen, or nitrogen.
Organic molecules are important because all biological macromolecules are made of Carbon.
These organic molecules, also known as macromolecules, are made up of long chains of carbon atoms bonded with hydrogen atoms.
Chains of carbon and hydrogen are known as hydrocarbon.
These long hydrocarbon chains are referred to as the carbon backbone or the carbon side chains of the molecules.
These chains of hydrocarbon range from one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms, to polymers like polystyrene, which consist of thousands of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
Organic molecules (hydrocarbons)
are a class of molecules that contain carbon, in which one or more atoms of carbon are covalently linked to atoms of other elements
most commonly with hydrogen, oxygen, or nitrogen.
Organic molecules are important because all biological macromolecules are made of carbon
known as macromolecules, are made up of long chains of carbon atoms bonded with hydrogen atoms
hydrocarbon Chains of carbon and hydrogen
Chains of carbon and hydrogen
These long hydrocarbon chains are referred to as the carbon backbone or the carbon side chains of the molecules.
range from one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms, to polymers like polystyrene, which consist of thousands of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
Saturated Hydrocarbons (Alkanes)
have only single bonds between carbon atoms.
Alkanes are a type of saturated hydrocarbons.
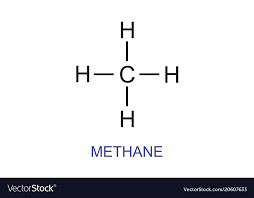
Cycloalkanes
Single bonded hydrocarbons, when arranged in a cyclic manner
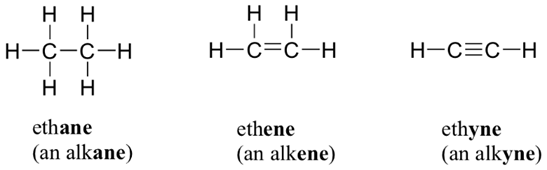
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons (
These hydrocarbons have double or triple bonds between carbon atoms.
Alkenes and Alkynes are types of unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Alkenes
are unsaturated hydrocarbons that have a double bond between the carbon atoms.
Their names end with-ene.
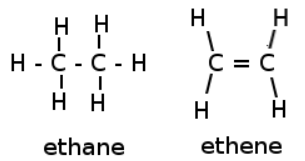
Alkynes
Alkynes are unsaturated hydrocarbons that have a triple bond between the carbon atoms.
Their names end with -yne.
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
are unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbons with alternating double and single bonds between carbon atoms.
These compounds are called aromatic because of their pleasant smell.
These cyclic hydrocarbons are also referred to as benzene rings.
Benzene is the simplest cyclic hydrocarbon with a formula of C6H6.
A functional group
is an atom, group of atoms or a bond where, when attached to a carbon side chains of an organic molecule, gives the molecule a particular set of chemical and physical properties.+
Atoms of functional groups are linked together within the molecule by covalent bonds
play an important role in the formation of molecules like
DNA, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids.
Also in all medicinal drugs, it is the functional group that gives the chemical its physiological activity.
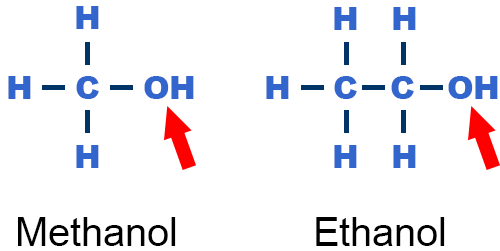
Hydroxyl Group
R−OH
one hydrogen atom paired with one oxygen atom
The OH group is attached to the hydrocarbon side chains
readily form hydrogen bonds
contribute to making molecules soluble in water
They are named alkanol, where the ending “ol” indicates alcohol.
Carbonyl Group
have one Oxygen atom double-bonded with a carbon atom
presented as C=O
contribute to making molecules that are water-soluble
Depending on the position of the C=O group in the carbon chain and the atoms it is attached to, the Carbonyl group has two forms namely
Aldehyde group
Keto group (sometimes referred to as Ketones).
Aldehydes
the Carbonyl group (C=O) is attached by a single bond with a hydrogen atom.
The carbon atom is also attached to a hydrocarbon chain represented by R.
he Carbonyl group (C=O) of the Aldehyde is polar, which makes aldehydes water-soluble
are powerful disinfectants.
Examples
Formaldehyde
Acetaldehyde
Glutraldehyde
Note that the ending of “aldehyde” in the name indicates an aldehyde functional group.
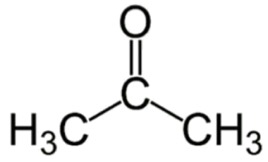
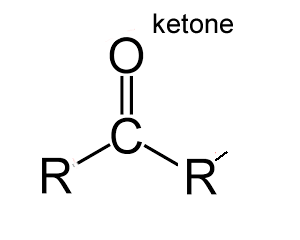
Ketones
the carbonyl group (C=O) is located within an organic molecule.
his means that the C=O group is not at the end of the carbon chain,
but it is next to 2 other carbon atom chains.
As with Aldehydes, the polar carbonyl group (C=O) makes ketones water-soluble.
ending of “one” in in the name of compounds indicates a ketone group.
e.x Acetone
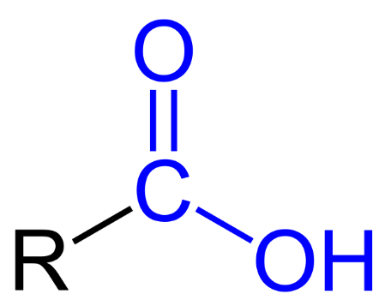
Carboxyl Group
has both a Hydroxyl group (OH) which is attached to the carbon atom of a Carbonyl (C=O) group, resulting in new properties.
is presented as R -COOH, where R represents the hydrocarbon side chain.
has to be at the end of the hydrocarbon chain.
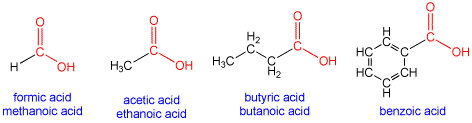
are called Carboxylic acids
dissociate partially into H+ and COO−
common in many biological molecules,
including amino acids and fatty acids
ending of “noic” in in the name of compounds indicates a carboxylic acid.
Examples are
Methanoic acid also known as Formic acid
Ethanoic acid also known as Acetic acid.
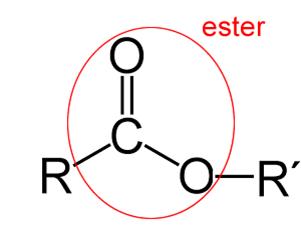
Ester Group
are derived from the Carboxylic acids.
In an Ester group, the Hydrogen in –COOH is replaced by a hydrocarbon side chain
as presented by –R’ in the following image
The ending of “noate” in in the name of compounds indicates an ester.
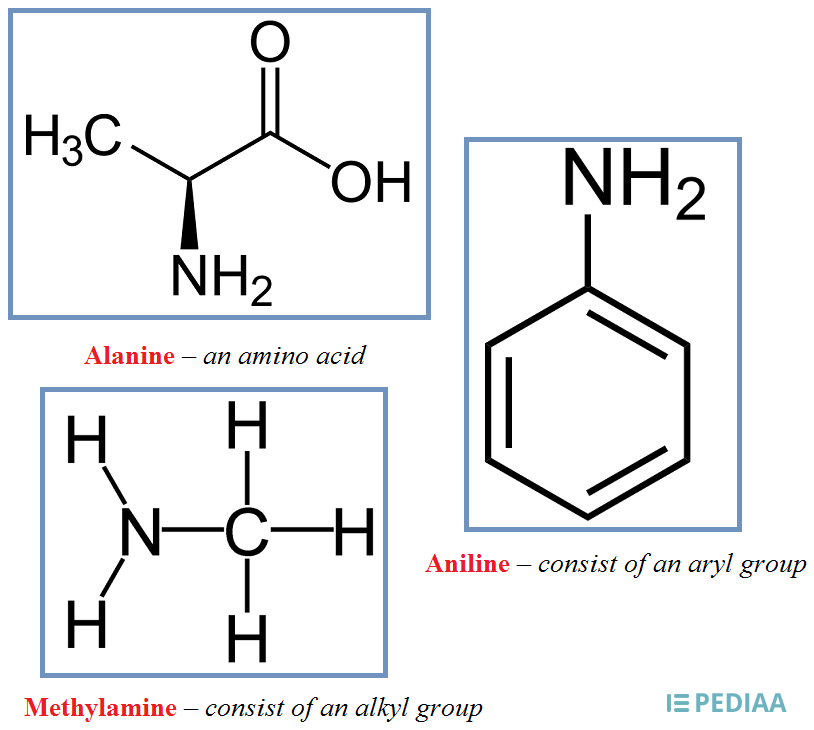
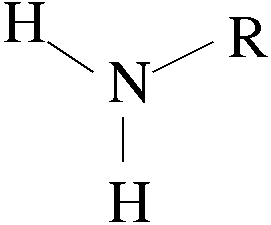
Amine Group
Amine group has one nitrogen atom attached to two hydrogen atoms with single bonds (NH2).
a general formula of R–NH2 where NH2 is the amine group attached to the end of the hydrocarbon side chain R.
The ending of “amine” in the name of compounds indicates an amine group.
examples
Alanine
Methylamine
Aniline
Carbohydrates
are large organic molecules, consisting of
sugars
starch
fibres
found in
fruits
grains
vegetables
milk products
They are a major food source and energy supply for the body.
Carbohydrates are also referred to as sugars.
The main atoms in the molecule of carbohydrates are
Carbon (C)
Hydrogen (H)
Oxygen (O) atoms.
may have other functional groups like
an aldehyde (-CHO)
ketone (C=O)
are stored in the liver and muscle glycogen as fats
the primary way for cells to get energy is through the breakdown of carbohydrates.
Basic Structure of a Carbohydrate
The general formula
Cn(H2O)n
n is the number of Carbon atoms.
the ratio of C to H to O atoms is 1:2:1.
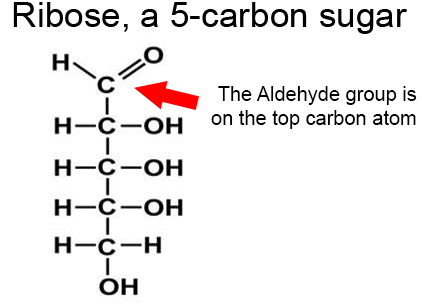
example Ribose
C5 (H2O)5 which is C5H10O5
and has an aldehyde group
Monosaccharides
glucose,
can be linear or cyclic
6 carbon sugar
fructose
linear/non-cyclic
6 carbon sugar
galactose
are one sugar (saccharide) molecules.
as simple sugars as they cannot be broken down into simpler chemical compounds.
A single molecule of a monosaccharide is also referred to as a monomer.
These sugars are named on the basis of functional groups:
If there is a Ketone carbonyl group in the
called a Ketose.
If there is an Aldehyde carbonyl group in the molecule,
it is called an Aldose.
can be 3, 4, 5 or 6 carbon atoms
can be
Non-cyclic Structures
the linear structures, the structural formula of the sugar is in a linear form, showing the carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms, as well as the functional groups.
Cyclic Structures (ring structures)
if has contain five or more carbon atoms can (not must) form cyclic structures
the carbon atoms in the compound are connected to form a ring
Glucose
an aldohexose sugar, which means
a molecule with 6 carbon atoms and an Aldehyde group.
It is one of the most biologically important sugars.
Glucose is the sugar that circulates in the human body, hence referred to as blood sugar.
The glucose molecule exists as 2 ISOMERS
Alpha (α)
OH facing downward
Beta (β) isomers,
OH facing upward
Based on OH on carbon 1
which means they have the same atoms, but differ in the arrangement of the O and H atoms at one of their carbon atoms
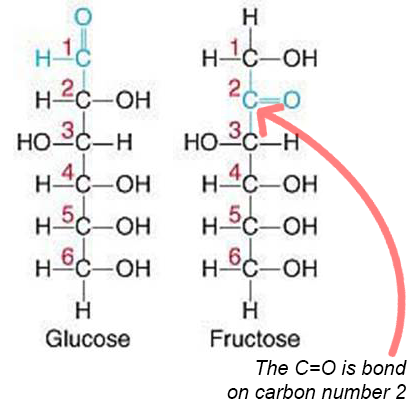
Fructose
is a ketohexose sugar
6 carbon atoms
Ketone group
also has OH bonded on diff carbon
It is also called fruit sugar and is found in large amounts in fruits, honey and corn syrup, and is the sweetest of all sugars!
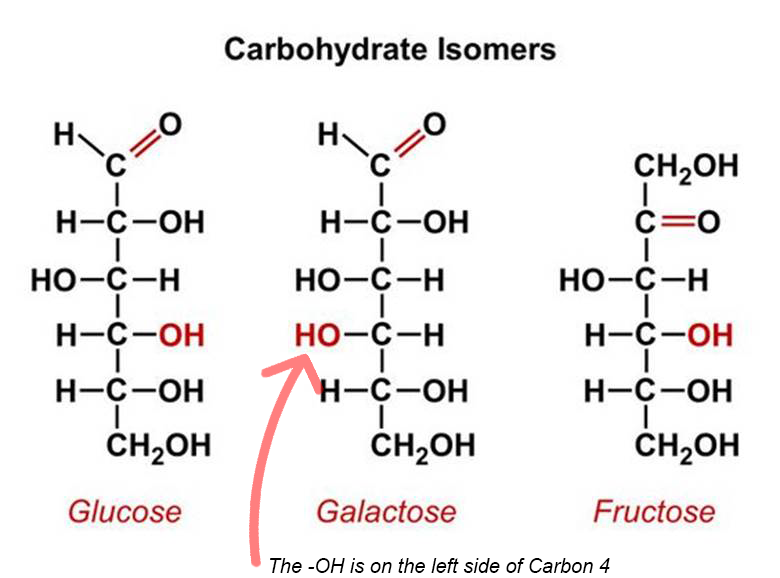
Galactose
aldohexose sugar and is the principal sugar found in mammalian milk (milk produced by mammals).
Galactose is very similar to glucose.
However, glucose and galactose cannot be easily converted into one another.
2 OH groupds
1 Aldehyde group
Pentose: 5 Carbon Sugars
Pentose molecules contain 5 carbon atoms and so the chemical formula is C5 H10 O5 .
Some common examples are Arabinose, Xylose and Ribose.
Ribose is the pentose sugar component of the nucleotides of the RNA (Ribo Nucleic acid).
Deoxyribose which is a type of Ribose, is the sugar component of the nucleotides of DNA (De Oxy Ribonucleic acid).
RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, which we will learn about in the later lessons.
Deoxyribose C5H10O4
Ribose C5H10O5
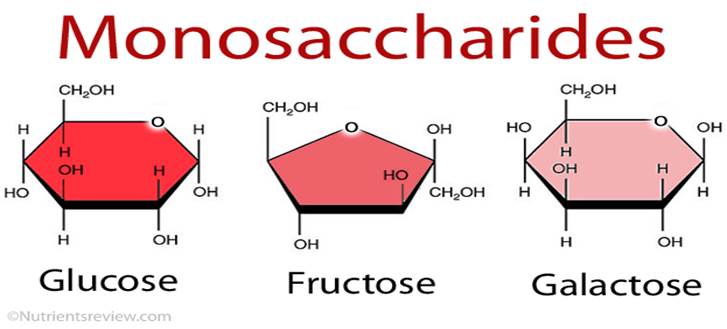
Hexose: 6 Carbon Sugar
Hexose molecules contain 6 carbon atoms and so the chemical formula is C6 H12 O6
Some common examples are
glucose
fructose,
galactose, as shown in the following image.
Disaccharides
sucrose
glucose and fructose
lactose
maltose
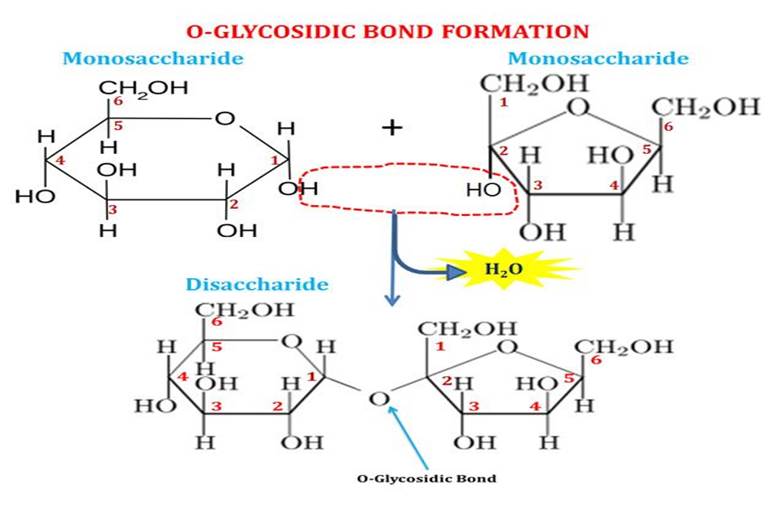
are two monosaccharides linked together.
bonded with Glycosidic Bond (the oxygen bridge)
a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another carbohydrate molecule or another group.
eOH (Hydroxyl group) of Carbon 1 containing the aldehyde or ketone group of the sugar, forms the bond with the OH (hydroxyl group) of the other sugar molecule, and it involves the removal of water molecule during the reaction.
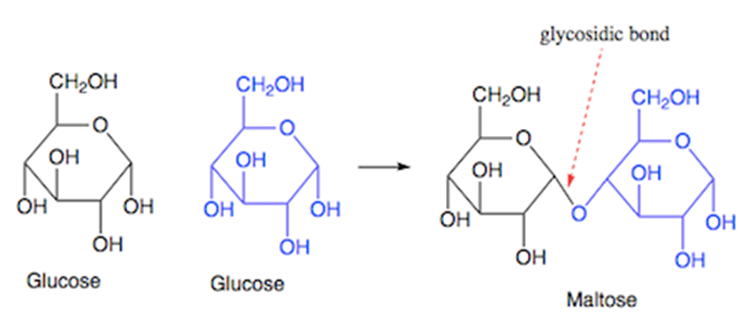
Maltose
a disaccharide formed by joining of two glucose molecules via a glycosidic bond, as shown in the following diagram.
known as malt sugar
is formed as an intermediate in the intestinal digestion (inside the intestines) of starch and glycogen.
It is also found in germinating grains and some other vegetables.
Lactose
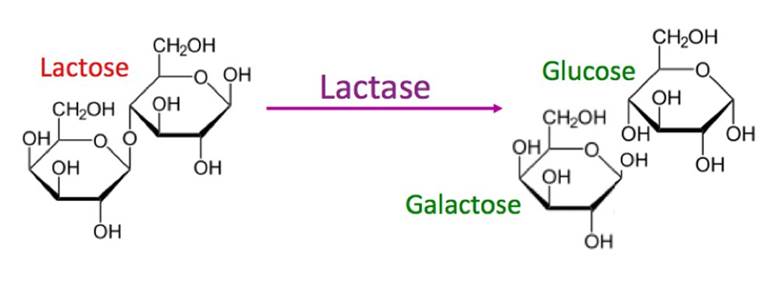
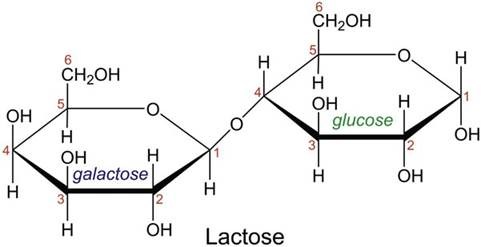
s disaccharide composed of a galactose and a glucose molecule, joined by a glycosidic bond, as shown in the following diagram.
Lactose is a sugar found in milk.
For it to be used as a source of energy, the glycosidic link must be broken (hydrolysed) forming glucose and galactose.
This link is broken in the presence of the enzyme Lactase.
As seen in the diagram below, lactose is broken down into Galactose and Glucose in the presence of the lactase enzyme.
People who lack the enzyme lactase (by approximately 20%) are unable to digest lactose and have the lactose intolerance condition.
Lactose intolerance results from lack of lactase that is needed to hydrolyze the glyosidic link of lactose.
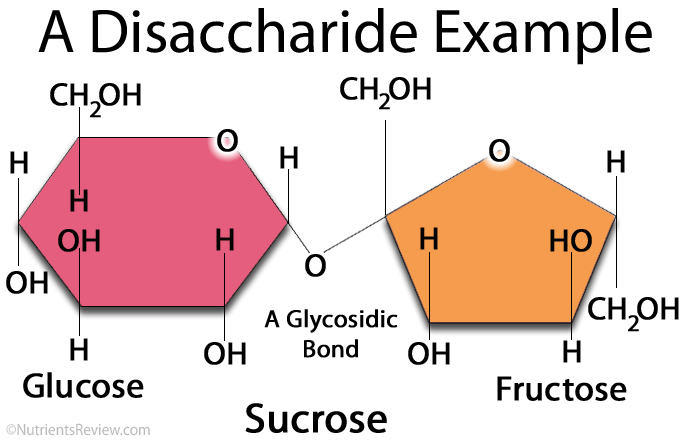
Sucrose
is a disaccharide formed by joining of a glucose molecule and a fructose molecule, via a glycosidic bond, as shown in the following diagram.
Sucrose is a very important plant carbohydrate.
It is water-soluble and is easily transported in the plant circulatory system.
This sugar cannot by produced by animals.
It is commonly known as “Table sugar”
The plant sources of sucrose are cane sugar and beet sugar.
Reducing Sugars
When sugars have a free hydroxyl group on Carbon 1 in the sugar structure, they are called reducing sugars.
All monosaccharides are reducing sugars because they have a free hydroxyl group on Carbon 1.
All disaccharides, except sucrose, are also reducing sugars.
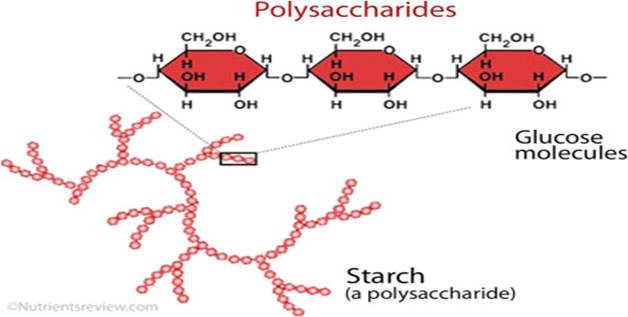
Polysaccharides
starch, glycogen, cellulose
Names of most sugars end in ‘ose”.
are chains of more than 10 monosaccharide units linked together
forming polymers of monosaccharides.
The type of polymer formed depends
on the monosaccharide sugars involved
the bonding arrangement between the monosaccharide monomers (single units).
an have linear (unbranched) chains of monomers or they can have branched chains of the monomers.
In the image to the right, hexagonal shapes represent the monosaccharide monomers (single units).
The three important polysaccharides formed from glucose monosaccharides are
Starch (present in plants)
Cellulose (present in plant cell wall)
Glycogen (present in animals)
Another polysaccharide which is a non-glucose polysaccharide is Chitin.
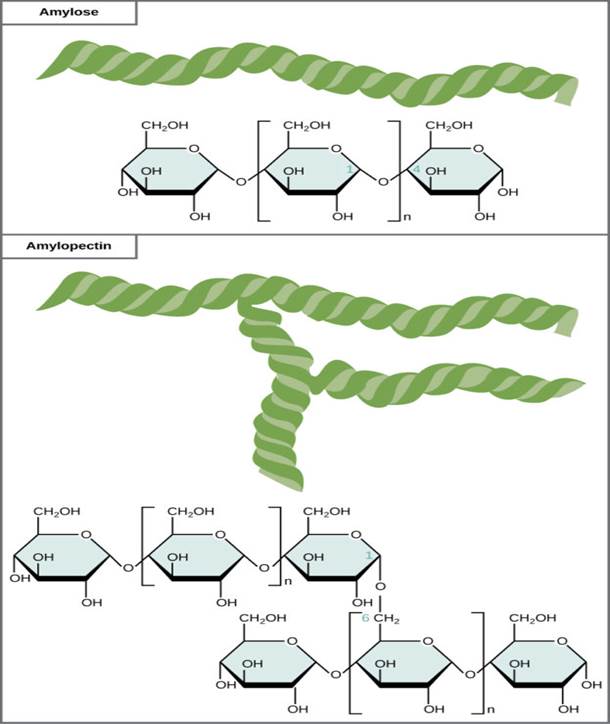
Starch
is the storage forms of glucose found in plants.
They are polymers of glucose molecules linked by the glyosidic bond., which has branches.
is a mixture of two polysaccharides: Amylose and Amylopectin.
Amylose is a linear (unbranched) chain of glucose molecules. It is not very soluble in water and is slowly digestible.
Amylopectin is a branched chain of glucose molecules. It is more soluble in water and more easily digestible than amylose.
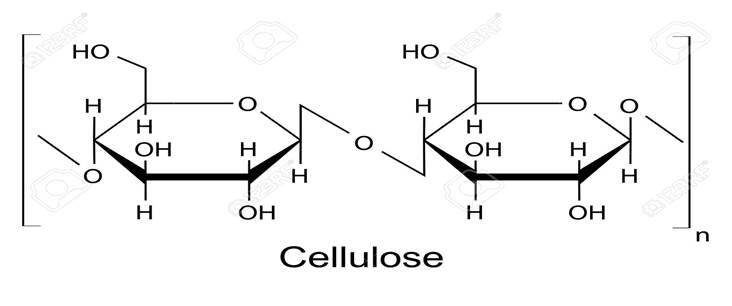
Cellulose
is the major structural polymer found in cell walls of plant stems and leaves.
It is a linear polymer composed of glucose units linked by glycosidic bond.
made up of a long chain of glucose monomers, where n represents the number of monomers of glucose.
Note that n can be anywhere between 7,000 and 15,000.
Animals lack the enzymes necessary to hydrolyze (breakdown) cellulose.
Animals like cow have a bacteria in their gut that can digest cellulose so that they can eat grass.
Humans cannot digest cellulose.
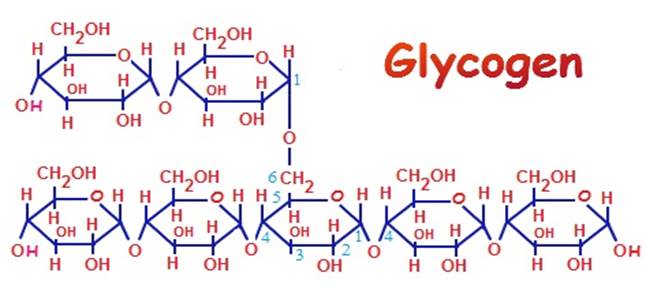
Glycogen
is a polymer of glucose monomers.
linked by glyosidic bonds.
Glycogen is the major storage of carbohydrate in animals.
The diagram shows monomers of glucose linked together by glycosidic bond to form a polymer of glycogen.
As Glycogen is the major storage of carbohydrate in animals,
it is stored in their liver and muscles.
Humans get energy by hydrolyses (breakdown) of glycogen to glucose.
Chitin
a non-glucose polysaccharide
made of polymers of N-acetylglucosamine, monomers,
a derivative of glucose.
Chitin is found in the cell wall of
fungi
outer skeletons of insects like cockroaches and scales of fish.
simple sugars
mono and di sachrides
complex
polysachirides
Clinical Significance of Carbohydrates
Glucose is one of the most important carbohydrate in the body as it is the primary way to obtain energy in the body.
Most of the dietary carbohydrates (starch) are digested and finally absorbed as glucose in the body.
Glucose is also called blood sugar as it circulates in the blood
at a normal concentration of less than 7.8 mmol/L (milimoles per litre) of blood.
Fructose is found in the semen
utilized by the sperms for energy.
A mucopolysaccharide by the name of Hyaluronic acid
works as a lubricant and shock absorbent in the joint.
Several diseases are associated with carbohydrates such as
Diabetes Mellitus, commonly known as Type II Diabetes
which is associated with glucose metabolism.
insulsin sensitivity disorder
Galactosemia, which is a genetic disorder (inborn error), is associated with galactose metabolism.
the body is not able to process galactose and use the energy from it
when people ingest food or liquid having galactose, it is not utilized but it gets accumulated in the body.
This is one of the most common inborn errors of carbohydrate metabolism.