Market power
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Market power
The degree to which a firm is able to raise their prices without losing a significant amount of consumers. The amount of power a firm has determines their power
Perfect competition
Market structure where there is an incentive degree of competition, with no individual firm having enough power to control the market
Perfect competition characteristics
Price takers
Homogenous products
Many firms
No barriers to entry and exit
Perfect information
Perfect resource mobility
Monopoly
A market structure where one large firm is controlling the supply and price of one particular good.
Monopoly characteristics
Price makers
Single/dominant firm
No close substitutes
Control of resources
Inelastic demand
High barriers to entry (BLADE)
Oligopoly
Market structure where a few large firms dominate the industry
Oligopoly characteristics
Few large firms
High barriers to entry
Interdependence
Price rigidity
Monopolistic competition
Market structure in which many firms exist but each firm has a small degree of power
Monopolistic competition characteristics
Large number of firms
Product differentiation
No barriers to entry
Total cost
Total fixed cost + total variable cost
Average fixed cost
Total fixed cost/ quantity
Average total cost
Total cost/ quantity
Average variable cost
Total variable cost/ quantity
Marginal cost
change in total cost/ change in quantity
Profit
Total revenue - Total cost
Why is market power considered a type of market failure?
They don’t need to produce at their allocatively efficient levels rather they will produce at a level that maximizes profits. This means they will always produce at a level lower than their efficient level/ underproduce
How does the level of competition and product differentiation relate to market power?
The higher the competition the lower the market power. For example, in perfect competition there are a large number of firms meaning there will be high competition. However the higher the market power the more product differentiation.
For any type of market, what is the profit maximizing quantity
MR=MC
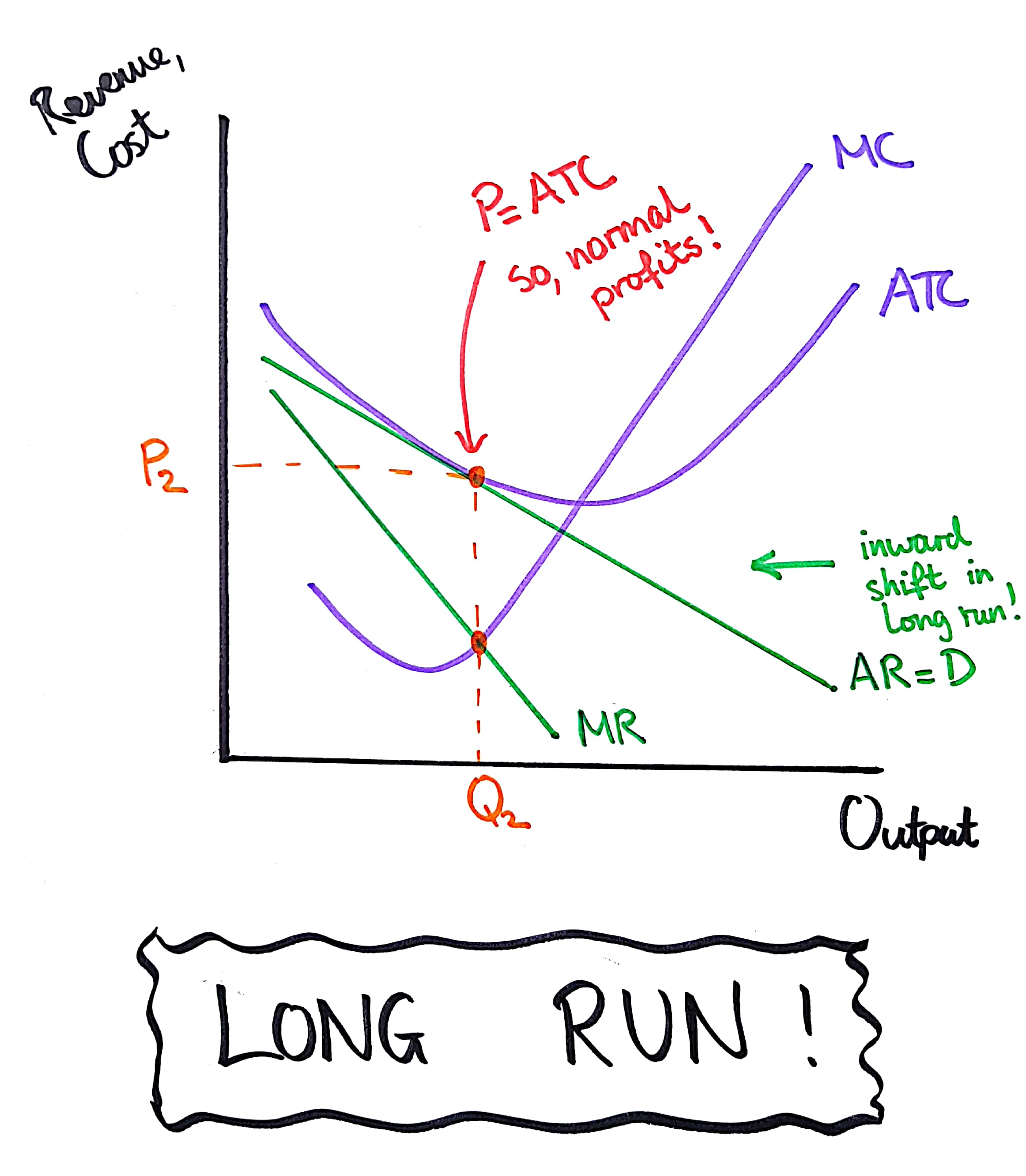
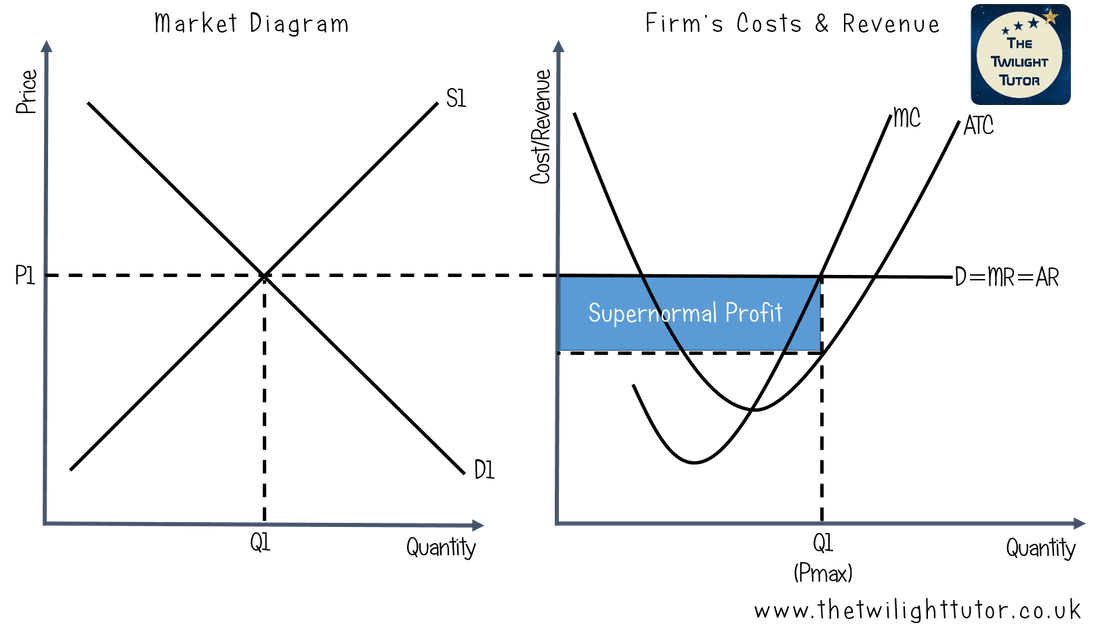
Perfect competition making abnormal profits
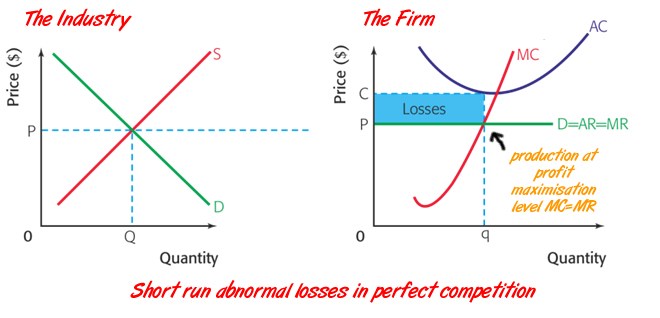
Perfect competition making losses
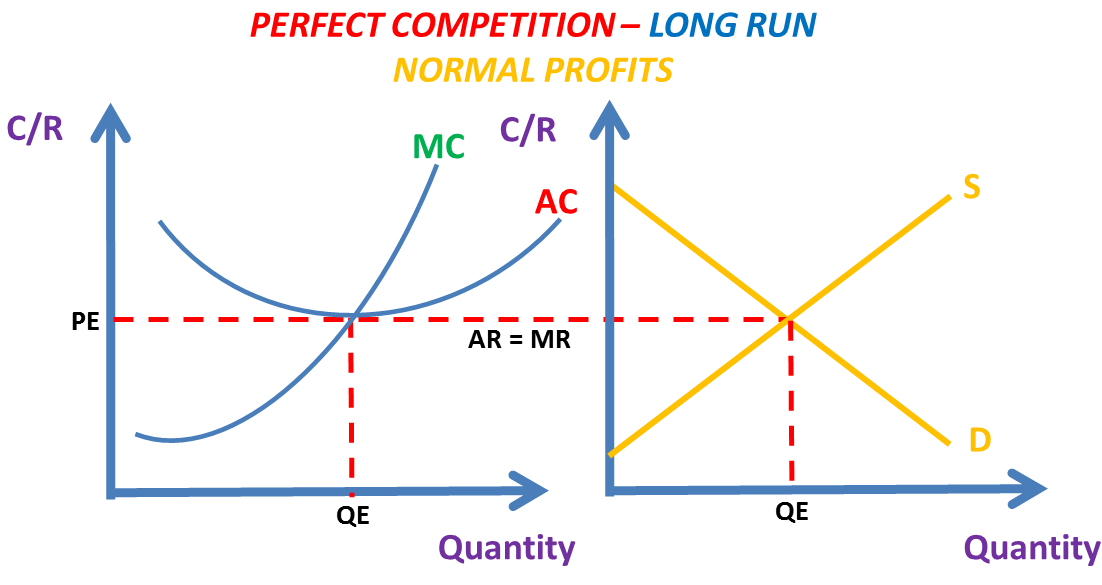
Perfect competition breaking even
Limitations of perfect competition
Unrealistic assumptions
Firms are too small to take advantage of economies of scale, which means they can’t lower their average costs.
All products are the same, there is no product variety
They are unable to engage in research and development to make new product
Advantages of perfect competition
Always allocatively efficient because the profit maximizing quantity is always MC=AR
Lower prices for consumers in the long run
No inefficient firms because all high cost firms are forced to leave the market
Monopoly making abnormal profit
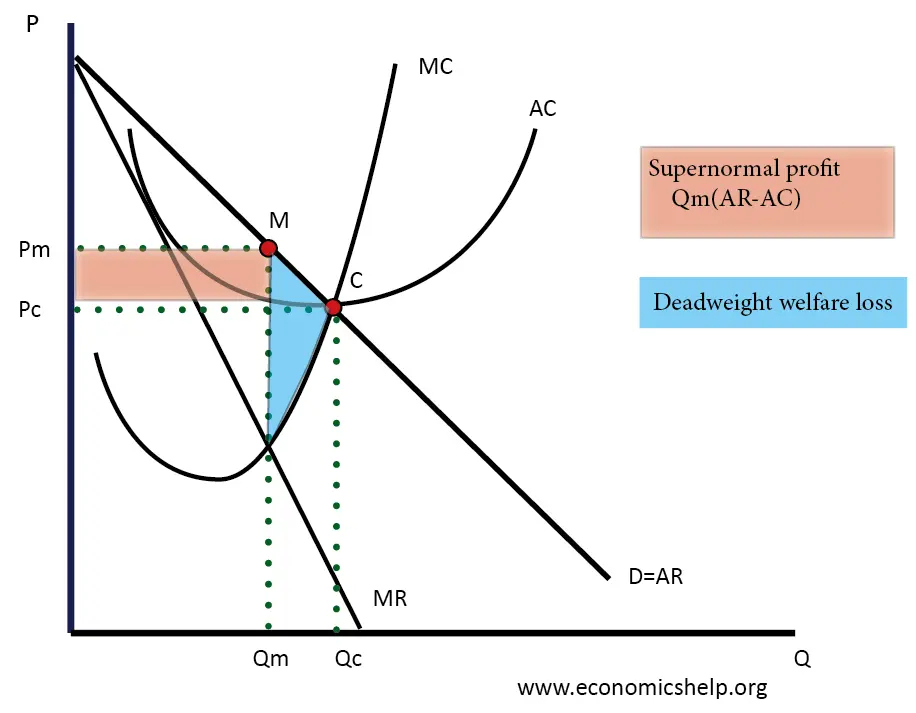
Monopoly making normal profit
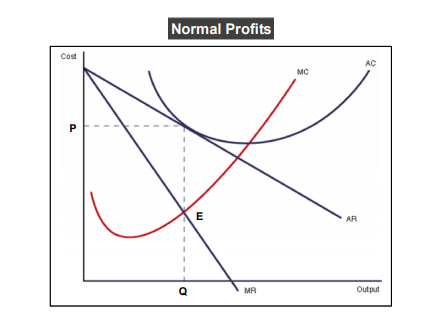
Monopoly making losses
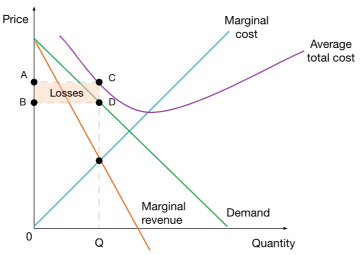
Does the monopoly change from the short run to the long run?
No, because they are the only firm in the market
Is the monopoly allocatively efficient?
No because the underproduction results in a deadweight loss
Disadvantages of monopoly
Allocative inefficiency
Productive inefficiency
Deadweight loss
Advantages of monopoly
Finance in R&D
Economies of scale
Incentive to innovate
Monopolistic competition making abnormal profits in the short run
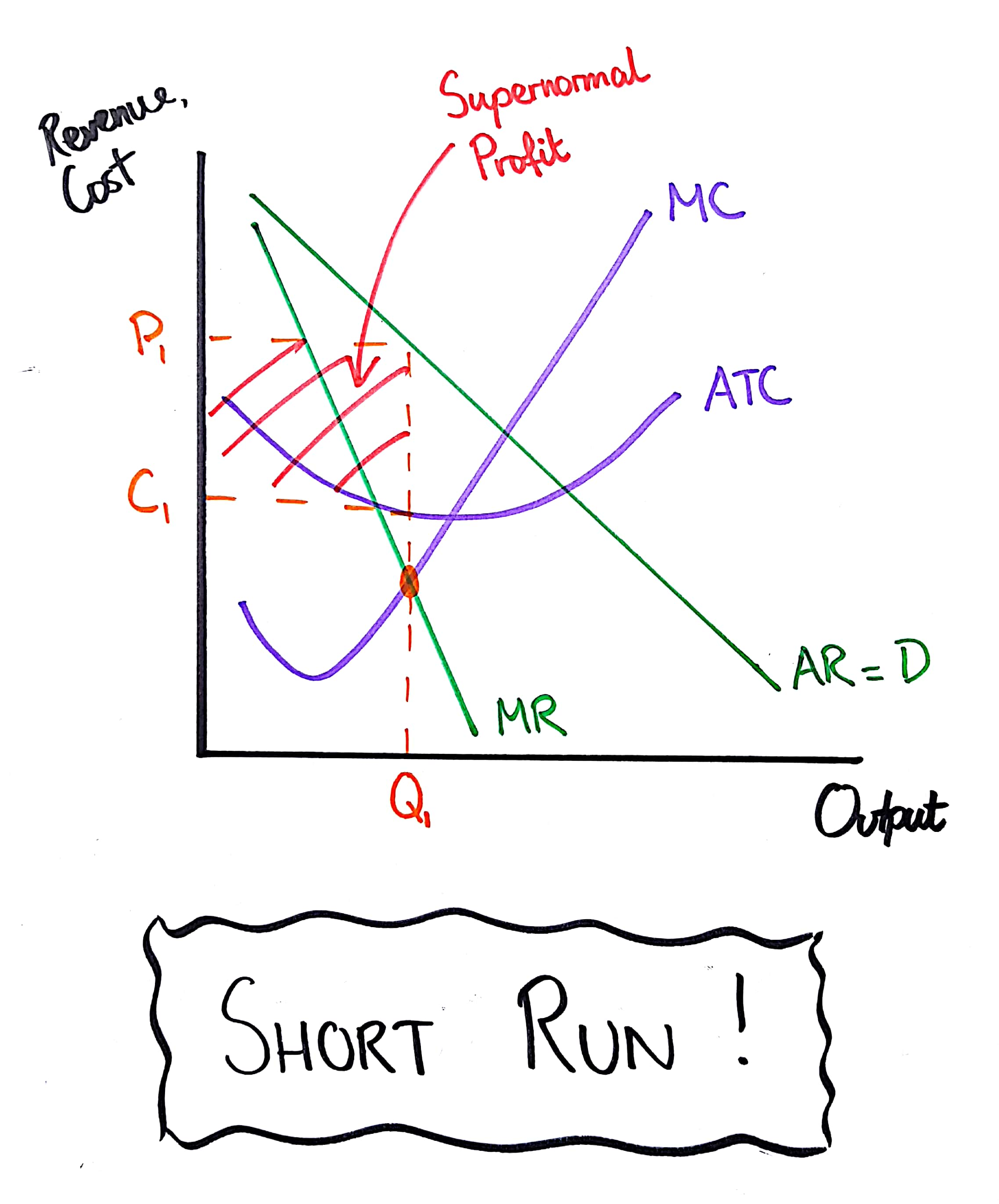
Monopolistic competition making short-run losses
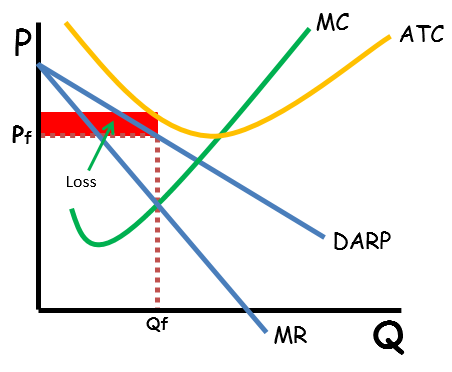
Monopolistic competition making normal profits