Unit 2: Newton's Laws of Motion
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Physics
Newton's Laws
AP Physics C: Mechanics
Unit 2: Newton’s Laws of Motion
Newton's Laws of Motion
law of inertia
law of acceleration
Friction Force
The Normal Force
The Normal Force
Uniform Circular Motion
centripetal force
Centrifugal force
Newton's Third Law of Motion
Pulleys
Inclined Planes
University/Undergrad
Last updated 5:45 AM on 4/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
1
New cards
Inertia
An object's tendency to resist changes in its state of motion.
2
New cards
Force
A push or pull on an object that causes it to accelerate or change its state of motion.
3
New cards
Net force
The total force acting on an object, taking into account all the individual forces acting on it.
4
New cards
Mass
A measure of an object's resistance to acceleration, based on its amount of matter.
5
New cards
Acceleration
The rate at which an object's velocity changes over time, either in magnitude, direction, or both.
6
New cards
Velocity
A vector quantity that describes an object's speed and direction of motion.
7
New cards
Circular motion
A type of motion in which an object moves in a circular path around a central point.
8
New cards
Centrifugal force
a fictitious force that appears to act on an object moving in a circular path. It is not a real force, but rather an apparent force that arises from the fact that the object is moving in a curved path.
9
New cards
Centripetal force
A force that is directed toward the center of a circular path and is responsible for keeping an object in circular motion.
10
New cards
Action and reaction
The concept that every force is part of a pair of forces that act on two different objects, and are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.
11
New cards
Newton's laws of motion
Three fundamental principles that describe how objects move and interact with each other, developed by Sir Isaac Newton in the 17th century.
12
New cards
Static Friction
It is the friction that exists between two surfaces that are not moving relative to each other.
13
New cards
Kinetic Friction
It is the friction that exists between two surfaces that are moving relative to each other.
14
New cards
Rolling Friction
It is the friction that exists between a rolling object and the surface it is rolling on.
15
New cards
Uniform circular motion
the motion of an object moving in a circular path at a constant speed.
16
New cards
Newton's First Law of Motion/Law of Inertia
States that an object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will remain in motion with a constant velocity, unless acted upon by an external force
17
New cards
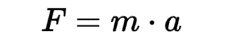
Newton's Second Law of Motion/Law of Acceleration
states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the force applied to it and inversely proportional to its mass.
18
New cards
Newton's Third Law of Motion
States that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.