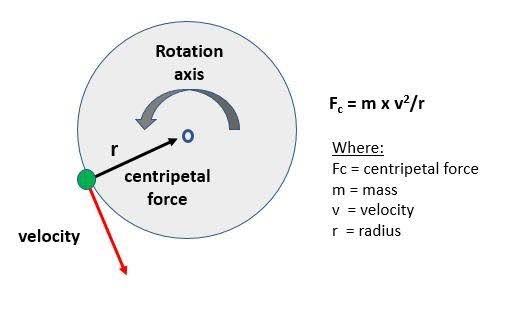
Centripetal Force
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
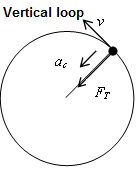
Centripetal Force (Fc)
Any center seeking force that causes an object to move in a circle
Newtons 2nd Law
An unbalanced force causes mass to accelerate
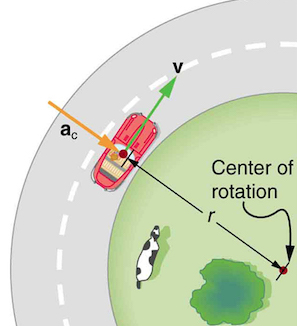
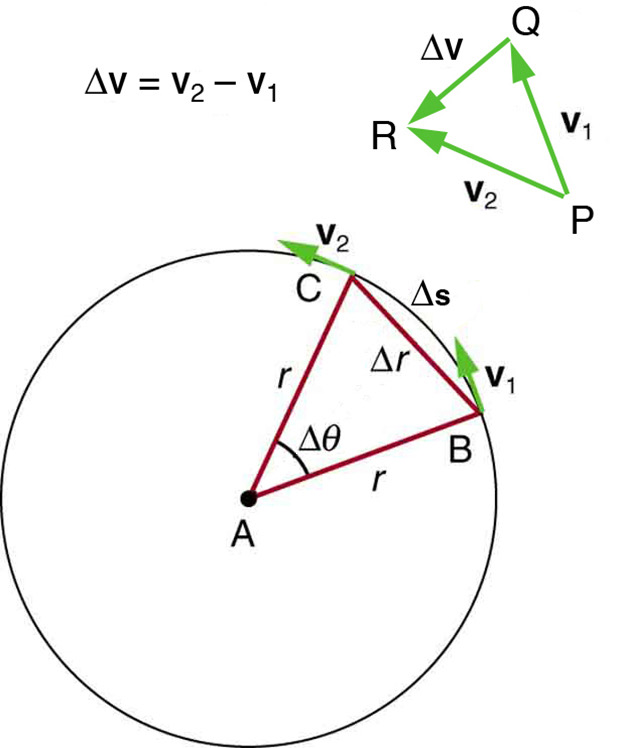
Centripetal Acceleration (Ac)
The acceleration that accelerates an object towards the center as it moves in a circle.
Circumference
Distance around a circle
Radius
The distance from the center of a circle to edge of circle
Inertial forces
Forces that want to accelerate an object in a straight line, Tangent to the curve.
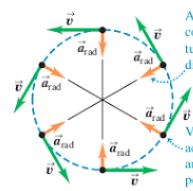
tangential velocity
is the linear speed of something moving along a circular path
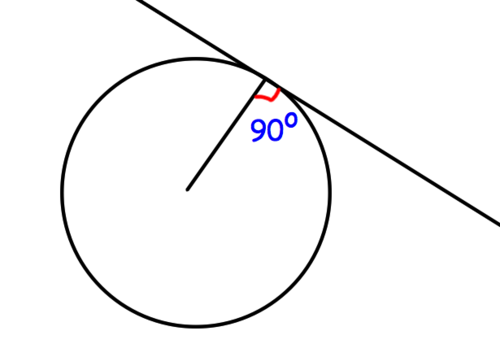
Circular motion
a movement of an object along the circumference of a circle.
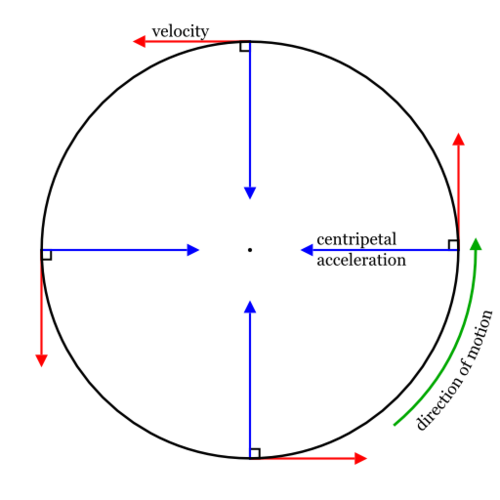
Newton's 1st Law
Newton's Law that dictates that an object will move at a linear (straight) direction when the centripetal force is absent

Directly Proportional
The relationship between the tangential velocity and the centripetal acceleration.
Inversely proportional
The relationship between centripetal acceleration and the radius
Tangential
Moving in a linear (straight) direction