Vibrio, Aeromonas, Campylobacter
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Vibrionaceae
Gram negative
Oxidase positive
Fermenters
Straight to Curved rods
Motile by polar monotrichous flagella
Facultative anaerobic
Halophilic
Gram negative, Straight to Curved rods
Oxidase positive
Not H2S Producing
Indole Positive
Urea Negative
VP Variable
Fermenters: Lactose/Sucrose
String Test Positive
Motile by Polar Monotrichous Flagella
Facultative anaerobe
Halophilic (thrives in High Salt Concentrations)
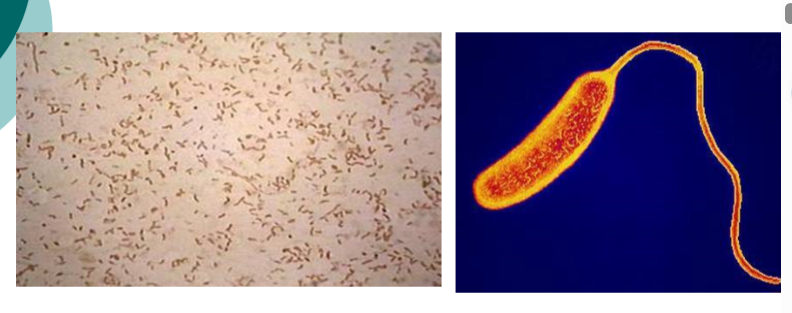
Vibrio gram stain
routes of transmission for vibriosis
Raw or undercooked shellfish, especially oysters
Drinking contaminated water
Exposing open wounds to salt water or brackish water
(including surgery, tattoo, piercing)
Handling raw seafood or seafood juices
Fishing in marine coastal waters and estuaries
specimens for vibrio
Stool Samples in Transport Media/Preservative (Cary-Blair)
o Collected during the Acute Stage of the Disease
o Tested at Guthrie
o BioFire Instrument - PCR
o Test TAT = 1hr 15 min
Vomit or Rectal Swabs in Transport Media (Amies Swabs)
o Acceptable if stool is unable to be collected
o Tested at Quest – Reference Lab - Culture
o Test TAT = 3 days
Blood Cultures
o Recommended if the patient is febrile, has hemorrhagic bullae, or
signs of sepsis
Other Samples include Wound swabs and Tissue samples
Vibrio is susceptible to drying and sunlight
o Making correct sample collection imperative for detection
culture media for vibrio
Vibrio is non-fastidious
o Do not have any special growth requirements
Standard Stool Culture Plating
o Blood, MacConkey, Hektoen, Brilliant Green, Campy
o TCBS Added if Vibrio is Suspected
Indicated by physician's order
thiosulfate-citrated-bile salts-sucrose agar (TCBS)
Selective and Differential media
Used for the Isolation of Vibrio, exclusively
o Increased pH enhances the growth of V. cholerae and inhibits the growth of
normal GI flora; Vibrio = alkaline loving
Bromothymol blue indicator
o AGAR turns yellow in presence of acid
o pH Indicator
H2S indicator
o H2S producing colonies have a black center
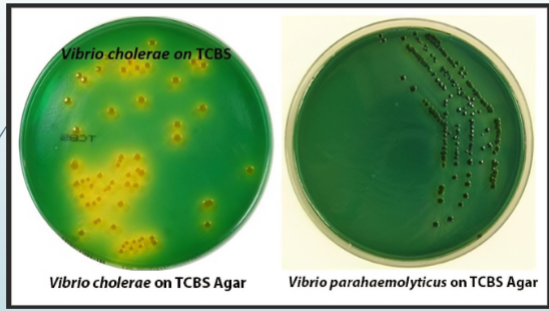
Sucrose Fermentation
o Fermenters: Colonies are YELLOW
(V. Cholerae and V. alginolyticus)
o Non-fermenters: Colonies are Blue/green
(V. parahaemolyticus and V. vulnificus)
growth characteristics on TCBS
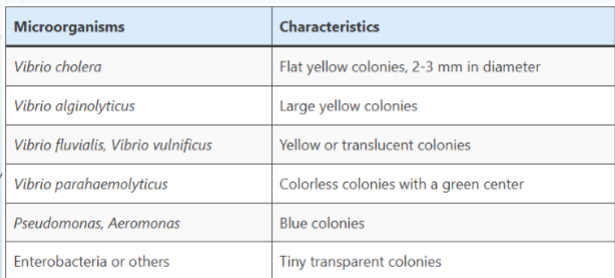
H2S production/sucrose fermentation
vibrio NaCl tolerance
vibrio cholerae
All strains share a common flagella H antigen
Further subdivided into serogroups by their somatic O
antigens
o At least 150 serogroups have been recognized
Two main groups:
o Toxigenic V. cholerae O1
Associated with epidemic cholera
o Non-O1 V. cholerae
Do not agglutinate with O1 antisera
V. cholera serotypes and biotypes
V. cholerae O1 biotypes
o Classic: Asiatic or epidemic cholera
o El Tor variant seen in recent cases
Non-O1
o V. cholerae 3 serotypes (Classic/El Tor)
Differentiated by LPS somatic antigens
Inaba (A & C antigens)
Ogawa (A & B )
Hikojima (A, B & C)
o V. cholerae O139
A.k.a. V. cholerae Bengal, 1992
Associated with epidemic outbreaks
Produces same cholera toxins as O1 biotypes
ferment glucose and other carbohydrates?
vibrio, aeromonas, plesiomonas
microaerophilic and do not ferment carbohydrates
Campylobacter spp
cholera: classic VS El Tor
Classic O1 Strain
o Non-hemolytic on Blood Agar
o Sensitive to Polymyxin B
o Non-agglutinating Chick RBCs
o VP -
El Tor O1 Strain
o Beta hemolytic on Blood Agar
o Resistant to Polymyxin B
o Agglutinates Chick RBC
o VP +
clinical disease spectrum
Epidemic cholera
o Mild to fatal illness
Extraintestinal infections
o Wounds and bacteremia
Gastroenteritis
o Cholera
Endemic or epidemic in areas with poor sanitation; it occurs
sporadically
Potentially life-threatening secretory diarrhea characterized by
numerous, voluminous watery stools, often accompanied by
vomiting, and resulting in hypovolemic shock and acidosis
Transmitted by the fecal-oral route
epidemic cholera outbreaks
o 1816-1826 - First Cholera pandemic – Bengal, India.
o 1829-1851 - Second Cholera pandemic
o 1849 - Second major outbreak in Paris, London, N.A., Mississippi River, New
Orleans, California & Oregon Trail.
o 1852-1860 - Third Cholera pandemic
o 1863-1875 - Fourth Cholera pandemic
o 1881-1896 - Fifth Cholera pandemic
o 1899-1923 - Sixth Cholera pandemic
o 1961-1970s -Seventh Cholera pandemic
o 1992 a new strain appeared in Asia, a non-O1, (NAG) named O139 Bengal.
o 2008-2009 Outbreak in Zimbabwe
o 2010-2011 Outbreak in Haiti; after earthquake
WHO Task Force Efforts:
o Reduce deaths & spread of Cholera by 2030
o Vaccinate in high-risk population
extraintestinal infections
Often caused by non-O1 strains
Usually in immunocompromised hosts
Bacteremia/Sepsis
Wound infections
Ear infections
gastroenteritis
Watery diarrhea
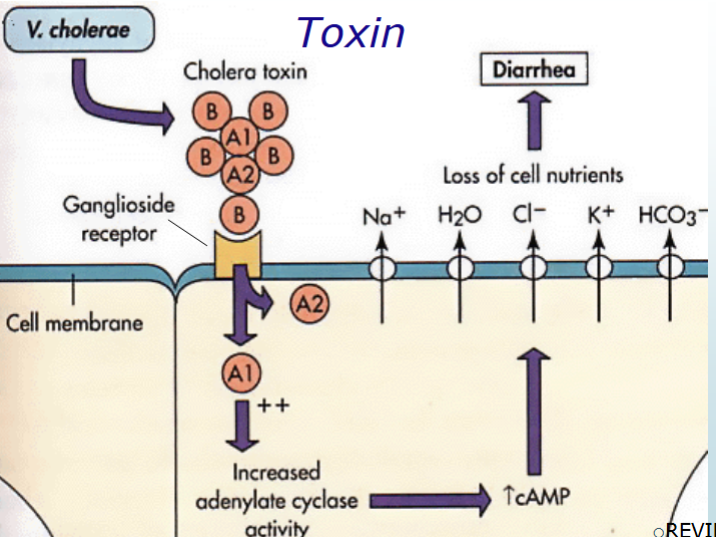
Caused by Choleragen (cholera toxin) CTX
CTX consist of two A subunits and 5 B subunit
B subunit binds to GM1 receptor on jejunal cells
Delivery of A2 subunit to cytosolic target
This facilitates entrance of A1 subunit into the cell
Activated A1 subunit stimulates the production of Adenylate cyclase
through inactivation of the G protein
This results in an accumulation of intracellular cyclic adenosine
monophosphate (cAMP)
Stimulates the Hypersecretion of electrolytes (Na+, K+, CL-)
out of the cell into the lumen of the intestine
Water passively diffuses out of the cell to maintain osmolality
Massive accumulation of water in the GI lumen
When the volume of fluid exceeds the capacity of the GI tract
to reabsorb it, results in massive outpouring of watery diarrhea
Fluid loss can be severe,
o up to 20 L per day
Stools may have “rice water” appearance
o colorless w/mucus flecks
Death can be caused by dehydration and low electrolyte levels
Cholera occurs as epidemics, pandemics, or sporadically
Cholera epidemics are usually caused by V. cholerae O1
Treatment:
o Administration of IV/oral fluids
o Antibiotics
mechanism of action of cholera toxin
vibrio cholerae O1 biochemicals/test results
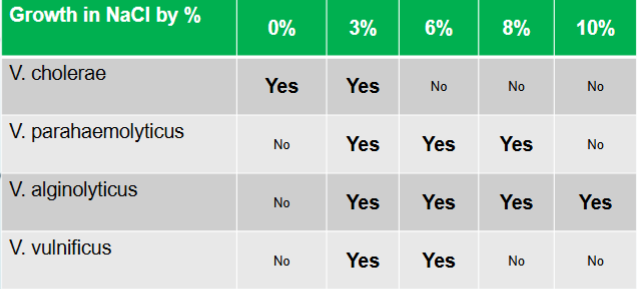
Does not require salt
o BUT will grow in media up to 3% NaCl
Sucrose Fermentation (Yellow on TCBS)
Non-Lactose Fermentation (Colorless on MacConkey)
Oxidase +
Motile
Nitrate +
Susceptible to O/129
Lysine +, ornithine +, arginine -
String test +
O1 agglutination +
V. parahaemolyticus biochemicals
Non-Sucrose Fermentation (Green on TCBS)
Lactose Fermentation (Pink on MacConkey)
H2S Producer (Black/Green on TCBS)
Requires 1-7% NaCl for growth
Oxidase +
Motile
Ornithine +
Sensitive to O/129
V. vulnificus biochemicals
Non-Sucrose Fermentation (Green on TCBS)
Lactose Fermentation (Pink on MacConkey)
Oxidase +
Requires 1-6% NaCl for growth
Motile
Underlying liver disease- Predisposition
Hepatitis, cirrhosis
V. alignolyticus biochemicals
Sucrose Fermentation (Yellow on TCBS)
Non-Lactose Fermentation (Colorless on MacConkey)
Strict Halophile
Growth 3-10% NaCl
Oxidase +
Motile
Sensitive to O/129
Ornithine +/-
differentiation of vibrio sp

aeromonadaceae
• Straight, gram negative bacilli
• Motile by polar flagella
• Glucose fermentation
• (Several) Sucrose and Lactose fermenation
• Oxidase Positive
• Catalase Positive
• H2S Producer
• Indole Positive
• Facultative Anerobe
• String Test Negative
• Urea Negative
• VP Positive
routes of transmission for aeromoniasis
Fecal/Oral transmission from contaminated food/water
Ubiquitous in terrestrial environments
Close association with humans and animals
Originally known to cause infections in fish and other cold-blooded
animals
Widely targets immunocompromised animals and human hosts,
resulting in wound infections, cellulitis, septicemia, and urinary tract
infections.
disease and specimens/culture media
Gastroenteritis
Wound infections
Bacteremia
UTI
Meningitis
Ear infections
Specimens/Culture Media
Same as Vibrio
complexes
Aeromonas sp are grouped into complexes:
o Aeromonas hydrophila complex
A. hydrophila, A.bestiarum, and A. dhakensis
o Aeromonas veronii complex
A. veronii, A. jandaei, A.trota, A.schubertii, A. diversa, and
A.encheleia
o Aeromonas caviae complex
A. caviae, A.media, A. riviopollensis, and A. eucrenophila
aeromonas hydrophila
Most strains are β-hemolytic
Oxidase +
Nitrate +
Resistant to O/129
No growth in 6.5 % NaCl
Indole +
Esculin +
TSI = K/A w/gas
Gel +
DNase +
Resistant to Amoxicillin and Ampicillin
aeromonas hydrophila growth on blood and Mac agar resembles pseudomonas aeruginosa
o Major Differences
Aeromonas = Indole Positive
Pseudomonas smells like Grapes
plesiomonaceae
Straight-to-rounded, short, Gram-negative rod
Motile
Have lophotrichous flagella
nonhemolytic on sheep blood agar
Glucose fermenter
Non-Lactose and Non-Sucrose fermenter
Oxidase Positive
Indole Positive
DNase Negative
VP Negative
Faculatative Anaerobe
routes of transmission for plesiomoniasis
Transmitted through the fecal-oral route
Consumption of infected seafood (especially oysters)
Contaminated water and contaminated vegetables
Exposure to amphibians and reptiles
Routes of Transmission for Plesiomoniasis
vibrio vs aeromonas vs plesiomonas
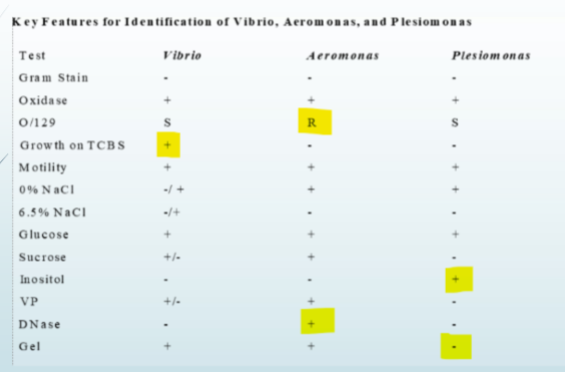
O/129 susceptibility testing for vibrio, aeromonas, and plesiomonas
O/129 disk is the vibriostatic agent
o 2,4-diamino-6,7-diisopropylpteridine phosphate
O/129 disks containing 10 and 150 μg are used in a method resembling disk susceptibility testing to
differentiate Vibrio species from Aeromonas species. Aeromonas species are resistant, with no zone
of inhibition at 24 hours, with both disks. Vibrio and Plesiomonas species will show susceptibility, with
a distinct zone of inhibition with the 150 μg disk; results for the 10 μg disk will vary among
the Vibrio and Plesiomonas species. Some Vibrio spp. require salt for growth. Therefore, the test is
run in duplicate on Mueller-Hinton agar (MHA) with low salt (0.5%) and with added NaCl (4%) to
ensure growth on at least one of the plates
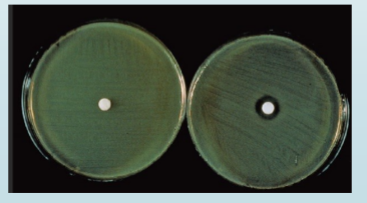
string test
Distinguishes Vibrio from Aeromonas
Mix a colony of test organism with 0.5 % deoxycholate
If a string forms as loop is lifted from the slide, the test is
positive
The string forms because bile lyses the organism and
releases DNA
Vibrio is string test positive (>60 seconds)
Aeromonas does not string

campylobacteraceae
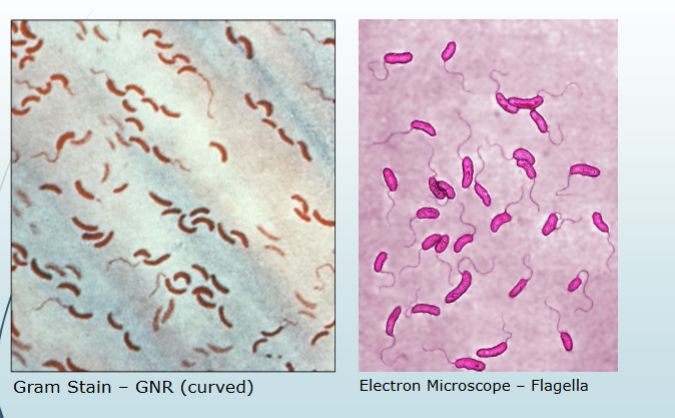
Curved, gram negative rod
Beard hairs in the sink
Catalase Positive
Non-H2S Producer
Non-hemolytic
Motile
Oxidase Positive
Urea Negative
DNase Negative
Hippurate Positive
Microaerophilic
Stain best with Safranin instead of Carbol Fuchsin
campylobacter gram stain
route of transmission for campylobacter
Route of Transmission for Campylobacter
Widely distributed in most warm-blooded animals
Prevalent in food animals such as poultry, cattle, pigs, sheep and
ostriches; and in pets, including cats and dogs
Has also been found in shellfish.
Main route of transmission is generally believed to be foodborne, via
undercooked meat and meat products, as well as raw or contaminated
milk
Contaminated water or ice is also a source of infection.
o Contact with contaminated water during recreational activities.
Campylobacteriosis is a zoonosis, a disease transmitted to humans
from animals or animal products.
o Most often, carcasses or meat are contaminated by Campylobacter from faeces during
slaughtering
o In animals, Campylobacter seldom causes disease
specimen and culture media for campylobacter
Same as Vibrio, Aeromonas, and Plesiomonas
campy agar
Developed for isolating C. jejuni and C. coli
Nutrient rich base
Contain several antimicrobial agents to inhibit normal GI
flora
Brucella agar base
with 10% sheep blood and antibiotics
Incubated in Microaerophilic Environment at 42o C
Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS)
o Low incidence potential Sequelae
o Reactive, self-limited, autoimmune disease
o Campylobacter jejuni most frequent antecedent pathogen
o Immune response to specific O-antigens cross-reacts with
ganglioside surface components of peripheral nerves
(molecular or antigenic mimicry)
Acute inflammatory demyelinating neuropathy (85% of
cases) from cross reaction with Schwann-cells or myelin
Acute axonal forms of GBS (15% of cases) from molecular
mimicry of axonal membrane
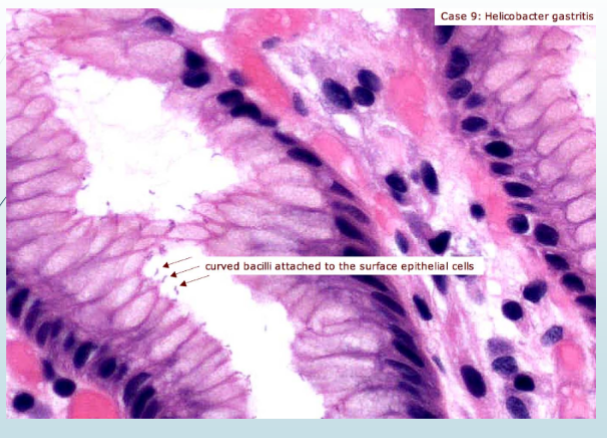
helicobacter pylori
Spiral, helical, curved or seagull shaped
Gram negative bacilli
Colonizes the epithelial cells of the stomach
Associated with type B gastritis
Most common cause of peptic (gastric) ulcers
Results from the excessive production of urease
With its flagella, the bacterium moves through the stomach
lumen and drills into the mucus gel layer of the stomach
Produces adhesins which bind to membrane-associated lipids
and carbohydrates and help its adhesion to epithelial cells
An example of this is the Lewis b antigen
additional helicobacter species
H. cinaedi
Hampsters primary host
H. fennelliae & CLO-3
Human primary host
helicobacter biochemicals
Microaerophilic
Oxidase +
Catalase +
Rapid urease Positive:
Place in Christensen’s media for 2 hours
A positive (pink color) within 15 minutes is
indicative of Helicobacter
Motile
specimen for helicobacter
Gastric biopsy specimen
Minced tissue: use touch preparation for
gram stain
helicobacter additional testing
CO2 Breath Test:
patients drinks 14C labeled urea
Urea is metabolized by urease
Measure liberated 14CO2 in breath
Other tests:
Enzyme immunoassays (EIA)-Anti H pylori IgG
Nucleic acid probes
Stool antigen tests
helicobacter treatment
Metronidazole
Amoxicillin
Clarithromycin
Proton pump inhibitors
Irreversibly blocking H+/K+ ATPase
Prilosec, Prevacid, Nexium
tests and colony reactions
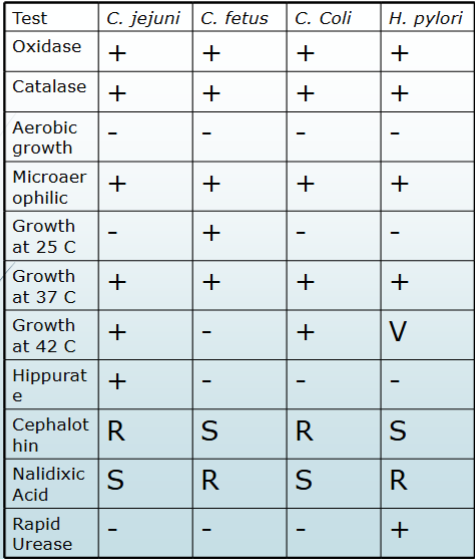
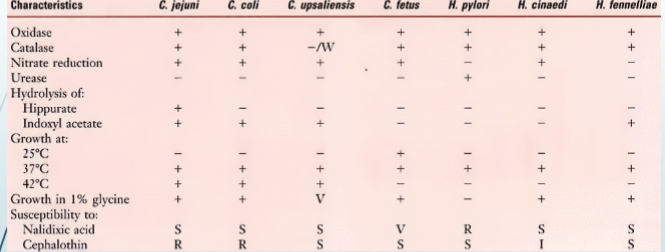
campy vs helicobactor