RCC Midterm
1/360
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
361 Terms
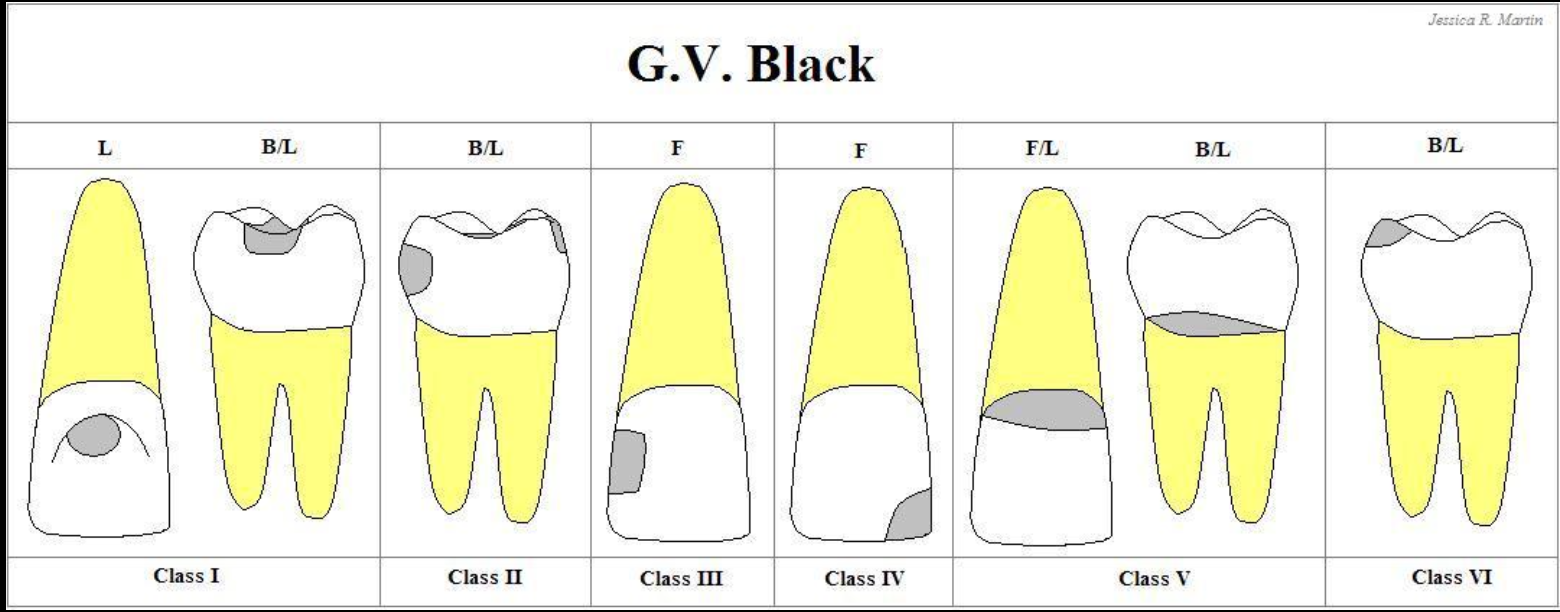
GV black class 1-6
Class 1: Pits and Fissures
Class 2: Proximal surfaces of posterior teeth
Class 3: Proximal surfaces of anterior teeth
Class 4: Proximal surfaces of anterior involving incisal edge
Class 5: Gingival 3rd of facial or lingual surface of all teeth
Class 6: Involving cusp tips
2 Internal Walls
_____ wall: Internal wall parallel with the long axis of the tooth
_____ wall: Internal wall that is perpendicular to the long axis of the tooth and occlusal of the pulp
Axial
Pulpal
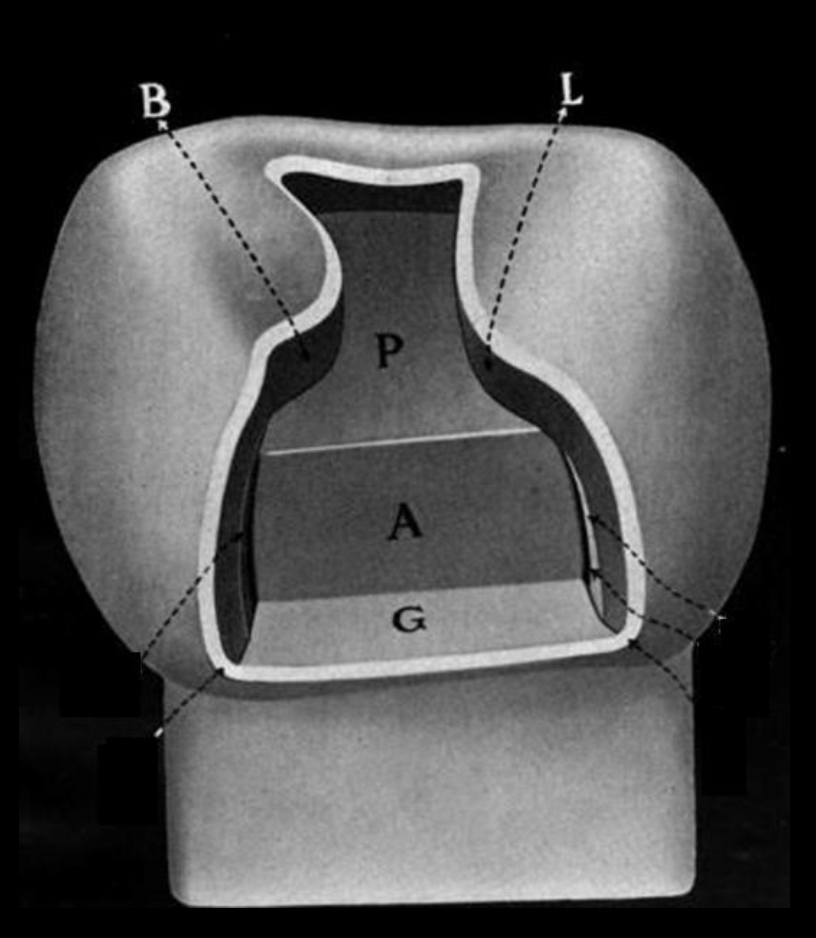
Line angle vs Point angle
Line angle is junction of two walls
Point angle is junction of three walls
Carbon steel is mainly used for
Stainless steel is mainly used for
Cutting instrument
Non-cutting such as shaping
Chisel and Excavator
Excavator is like spoon used close to dentin more control
Chisels are used to cut enamel
The working portion of a hand instrument is the ______
The handle is the ______
The portion of the instrument that connects the handle (shaft) to the blade is the
blade
shaft
shank
Instruments with longer blades require _____ complex angulation
more
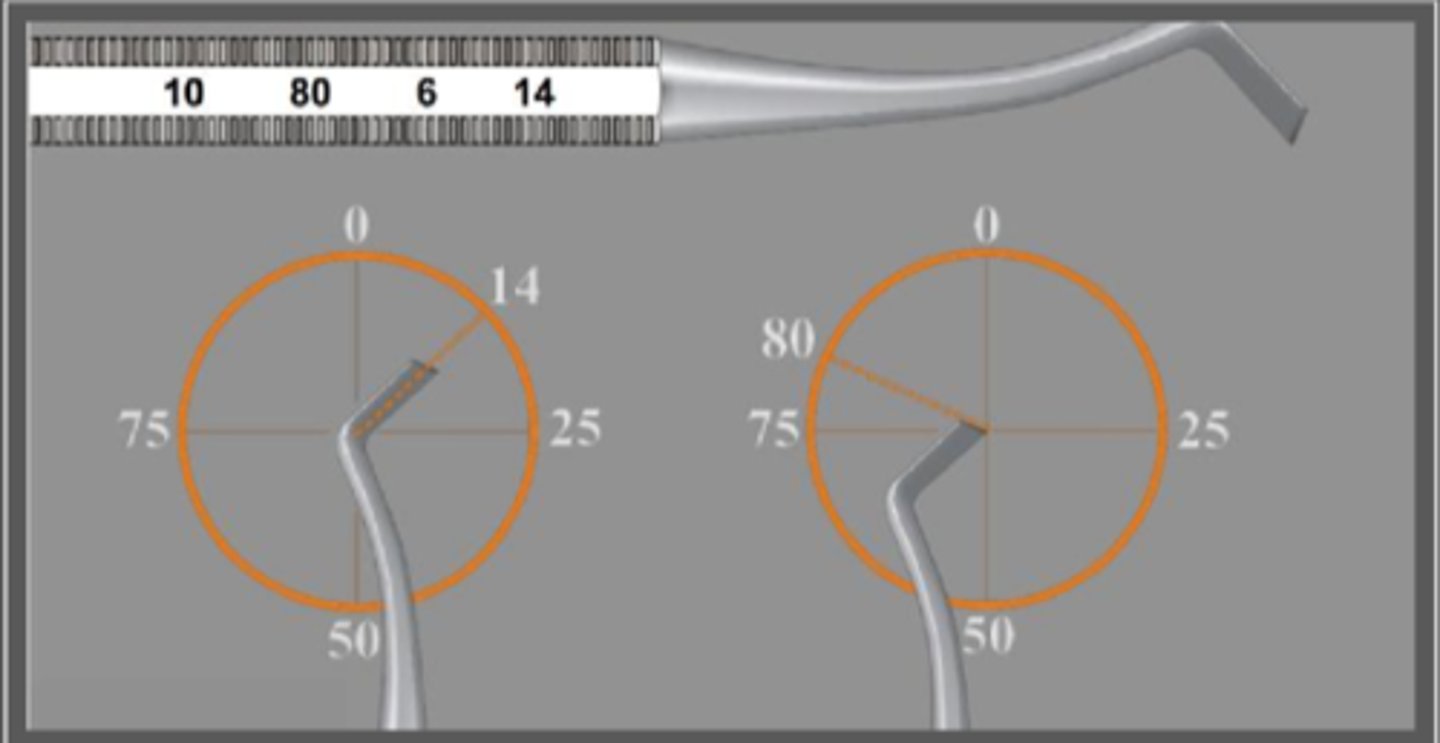
The first number on a hand cutting instrument represents the ____ of the blade in ____ of mm
The second number on a hand cutting instrument represents the ____ of the blade in _____.
The third number on a hand cutting instrument represents the ____ and is measured in _____
Width, tenths (10 = 1mm)
Length, mm
Angle, centigrades (circle in 100 pieces)
(Know this)

1 mm width
6 mm length
14 centigrades
If a hand cutting instrument has 4 numbers, the second number represents the angle of the ______ ______ in relation to the long axis of the handle and is measured in _____.
cutting edge
centigrade
The gingival margin trimmer is used for ______ and beveling margins. When the second number is <85 degrees, the instrument is for _____ surfaces.
When the number is >90 degrees, it is for _____ surfaces.
smoothing
mesial
distal
Hatchet CAL 29 and 28 for amalgam
29 for mesial
28 for distal
Spoon excavators is to remove carious _____
dentin
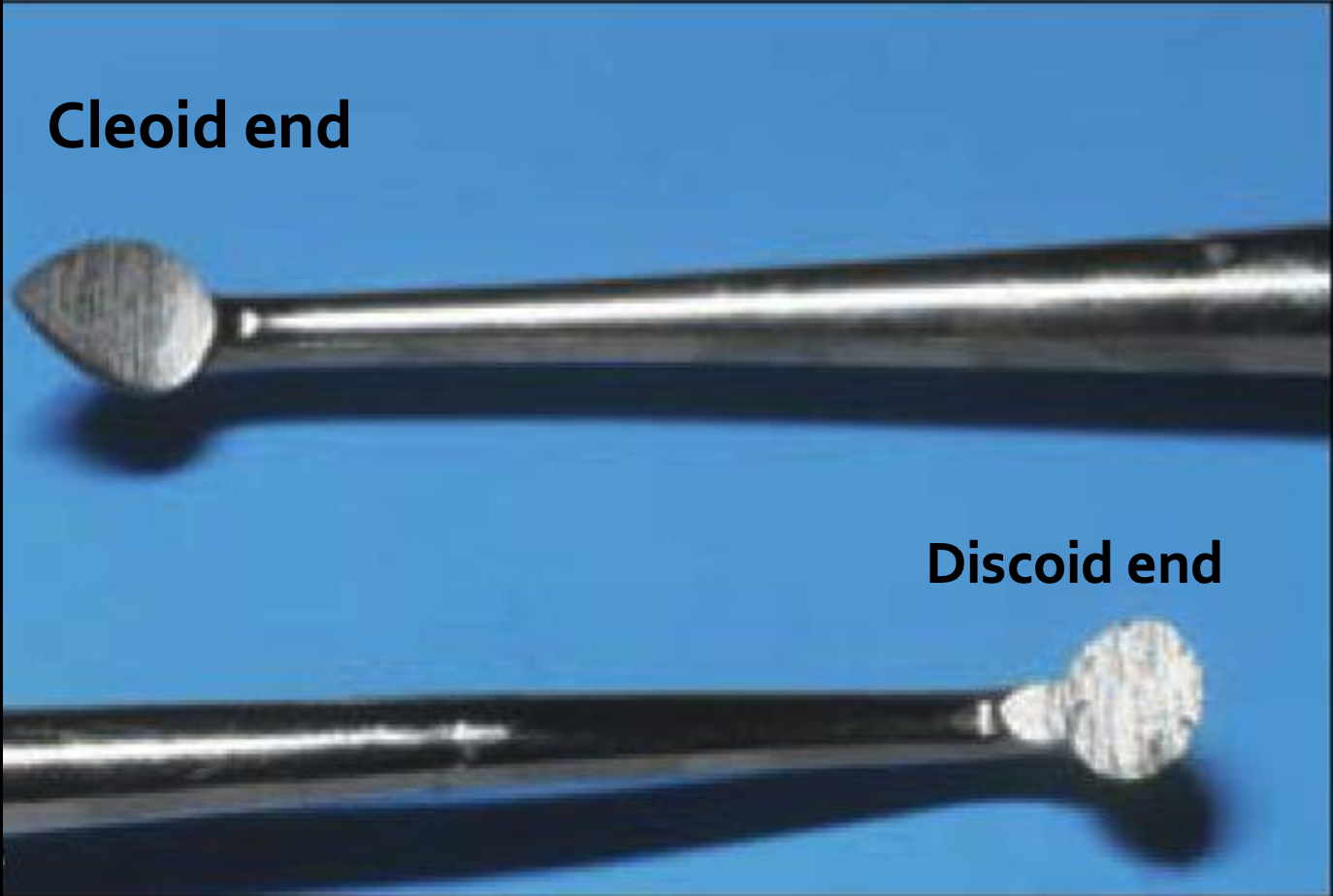
Cleoid discoid carver
Used to carve anatomy features in newly placed restorations or can be used to remove decay and tooth tissue during cavity preparations
Can you use explorer or probe to remove things when harden
No it will bend them
Cavo surface margin is the angle formed by the junction of the wall of the preparation and the _____ surface of the tooth
untouched
Straight Handpiece
A low-speed handpiece that may be used to hold rotary instruments most commonly used in the dental laboratory.
Contra-angle handpiece
2 types are
Head is angled to provide balance, used intra-orally
Low speed: 500-15,000 rpm
High speed: 160,000 most used for cutting
Air driven handpiece
Electric handpiece
Most common instrument for cutting teeth
An alternative to the air-driven handpieces becoming more popular
Electric handpieces operate up to 40,000 rpm, significantly less than 400,000 rpm (air driven), however they have attachments with ____ that increase the effective rotational speed.
multipliers
Zach and Cohen reported that with temperature increases of more than ____°C, dental pulp could not reverse inflammation in 40% of subjects tested; an increase of ____°C over normal temperature invariably resulted in necrosis.
5.5
11
Lasers are best used in the treatment of
soft tissues
Not for prep as impossible to make margin and heat
Which bur cut by milling
Which bur cut by grinding
Carbide
Diamond
Rake Face vs Clearance Face
Rake face is contact with tooth
Clearance face is contact away from bur rotation
Soft materials (acrylics) are best cut with ______ rake angle burs and hard/brittle materials (amalgam) are best cut with _____ rake angle burs.
positive
negative
ergo
nomos
work
natural laws or systems
Most common reason for early retirement among dentists
Musculoskeletal Disorder
Classes of movement
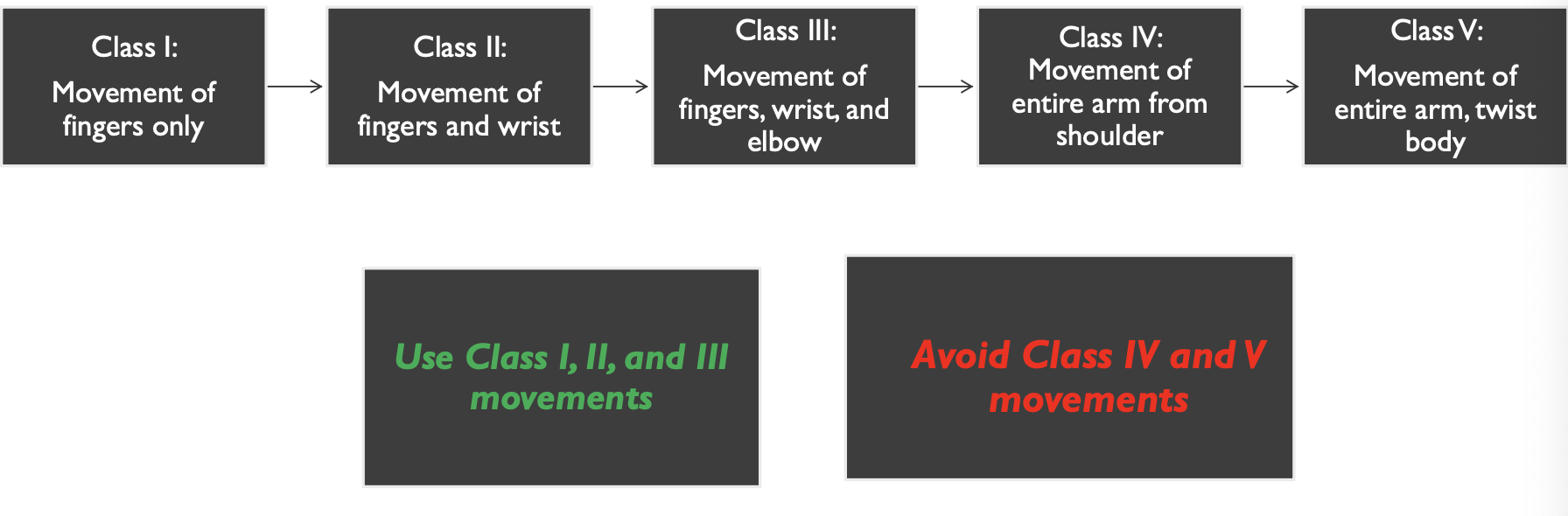
History of dental composites first started with acid-etching and _____ bonding then _____ bonding after
Original composite were self cured, then uv cured, and now is visible light cured
enamel, dentin
Dr. Oskar Hagger patented a monomer based on _______ acid dimethacrylate chemically cured with ______ acid, which led to development of the Sevitron commercial adhesive
glycerophosphoric, sulphonic
Monomers in composites _______ and form chains which take up less space. Using larger, fewer monomers results in less _______ which allows for a better bond.
polymerize
shrinkage
Polymer chains occupy _____ space than the total volume of the monomers before polymerization
smaller
3 Components of dental composite
Resin (Organic material Bis-GMA)
Filler (Inorganic silica and glass)
Coupling Agent (Silane that bond resin and filler together)
Monomers are ____ ____ of the resin
Curing systems are the ____ for polymerization
Fillers _______ composite
Coupling agent strengthens resin by bonding _____ to the resin matrix
building blocks, Ex. BisGMA
initiators, CQ and Tertiary Amine
Strengthen, quartz, silica, glasses
Filler, Silane
Radiopaque agents
Ex: Metal Oxides
Added so that composite materials would be visible in an x-ray
Chemical Curing uses (2)
Advantage and Disadvantage
Benzoyl Peroxide and Tertiary Amines
Advantage is curing occur and bulk packing used
Disadvantage is air bubbles when mixed and cannot control work time
Light Curing Material (2) and (2) new initiator
Advantage and Disadvantage
Camphorquinone and Tertiary Amine
TPO and Ivocerin
Advantage: unlimited work time, pore free material
Disadvantage: Limited depth of cure, shrink toward bond
Dual Curing (two paste)
Advantage and Disadvantage
Advantages: Cure in regions where light may not reach
Disadvantage: Discolors easier, require 2 component resulting porosities (empty space)
Bulk fill flowable composite allows for ______ passage of light due to _______ amounts of fillers.
greater
lower
Flowable
Packable
Bulk-Fill Composites
Less filler (more shrinkage and flow)
Packable (More resistance and less shrinkage)
Bulk-fill (Modified photoinitiators to allow high depth of cure)
______ composite should not be used on occlusal surface or proximal contact area because its resistance to occlusal forces is too low due to lack of fillers
Flowable
Traditional layering technique
2 mm increments forming several layers
Bulk Fill Layering Technique
Flowable at bottom and then packable on top
Or One layer of bulk fill
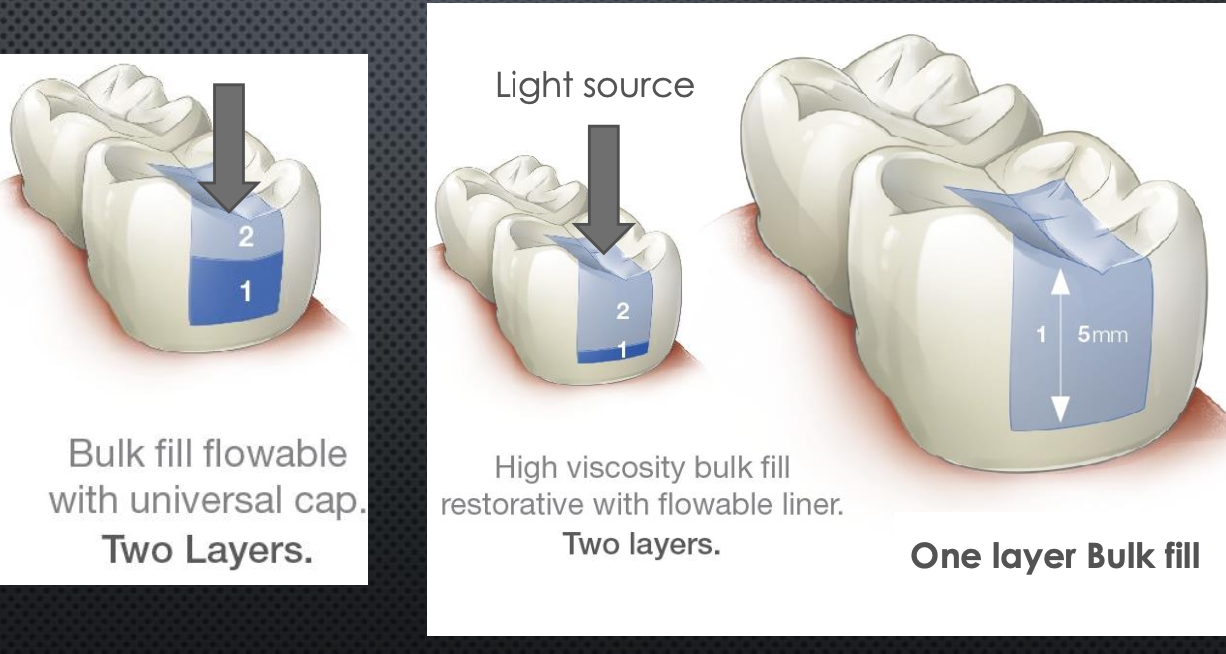
Shrinkage stress may cause ____ formation between resin and the walls of the preparation with the weakest bonds (usually _____)
Marginal ____ may result in microleakage, sensitivity, staining at the margins of the restoration, and recurrent caries
gap, dentin
gaps
Avoid by C-factor
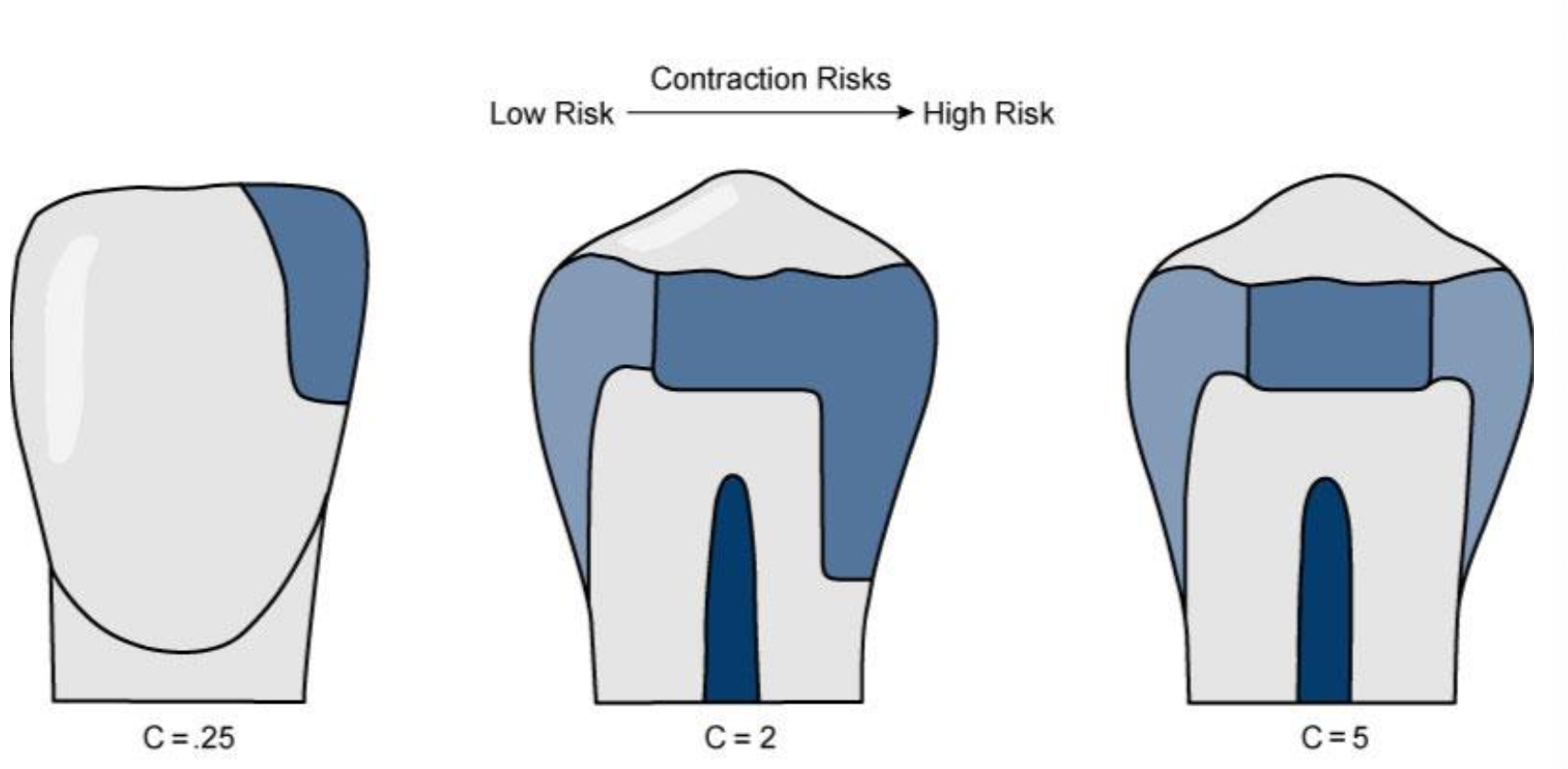
C-factor
# of bonded walls / unbonded walls ( total walls is 6)
the higher the C-factor the greater the negative effect of shrinkage
Too many bonded surface is bad
Fixed by Incremental placement
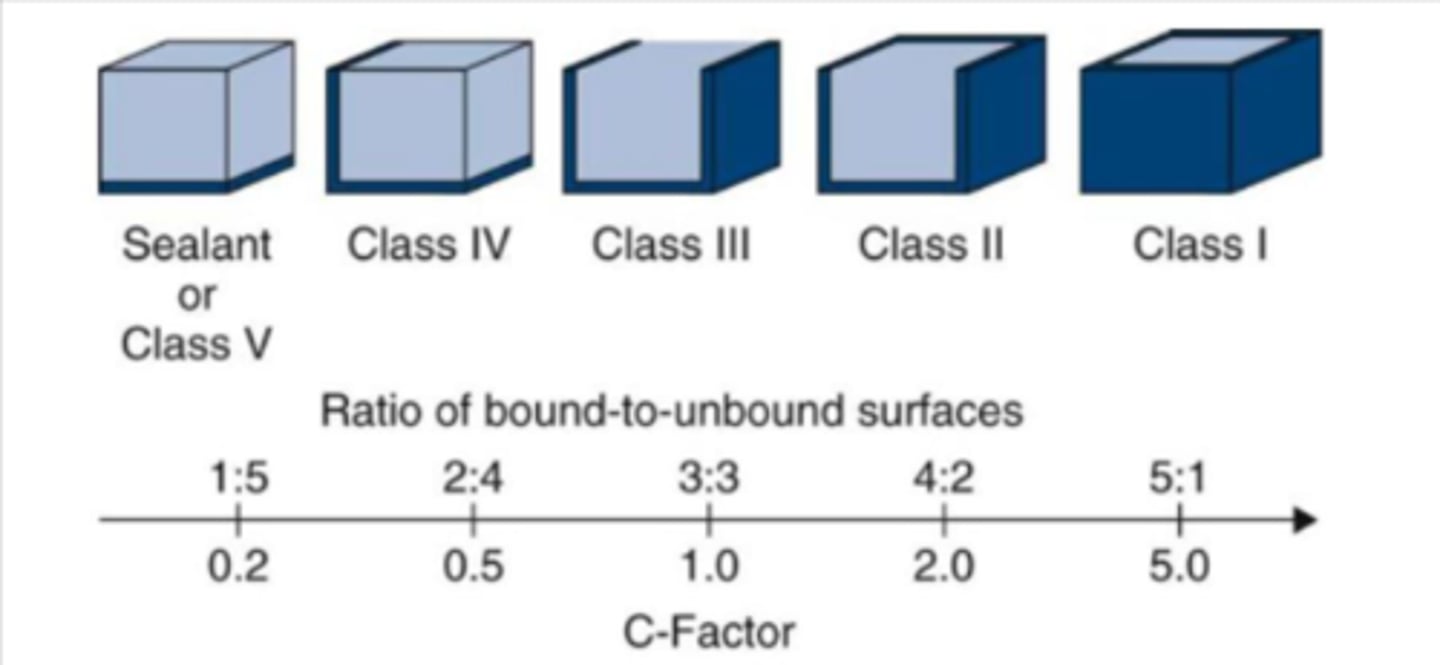
Incremental Placement of resin composites decreases the effect of _______ ______ by reducing the bulk of resin composite cured at a time; and reduces the _______, which helps relieve the stress developed at the bond between tooth and resin composite.
setting contraction
c-factor
Increments should be no thicker than
2 mm
Curing position
Cure at 90 degree angle and closer
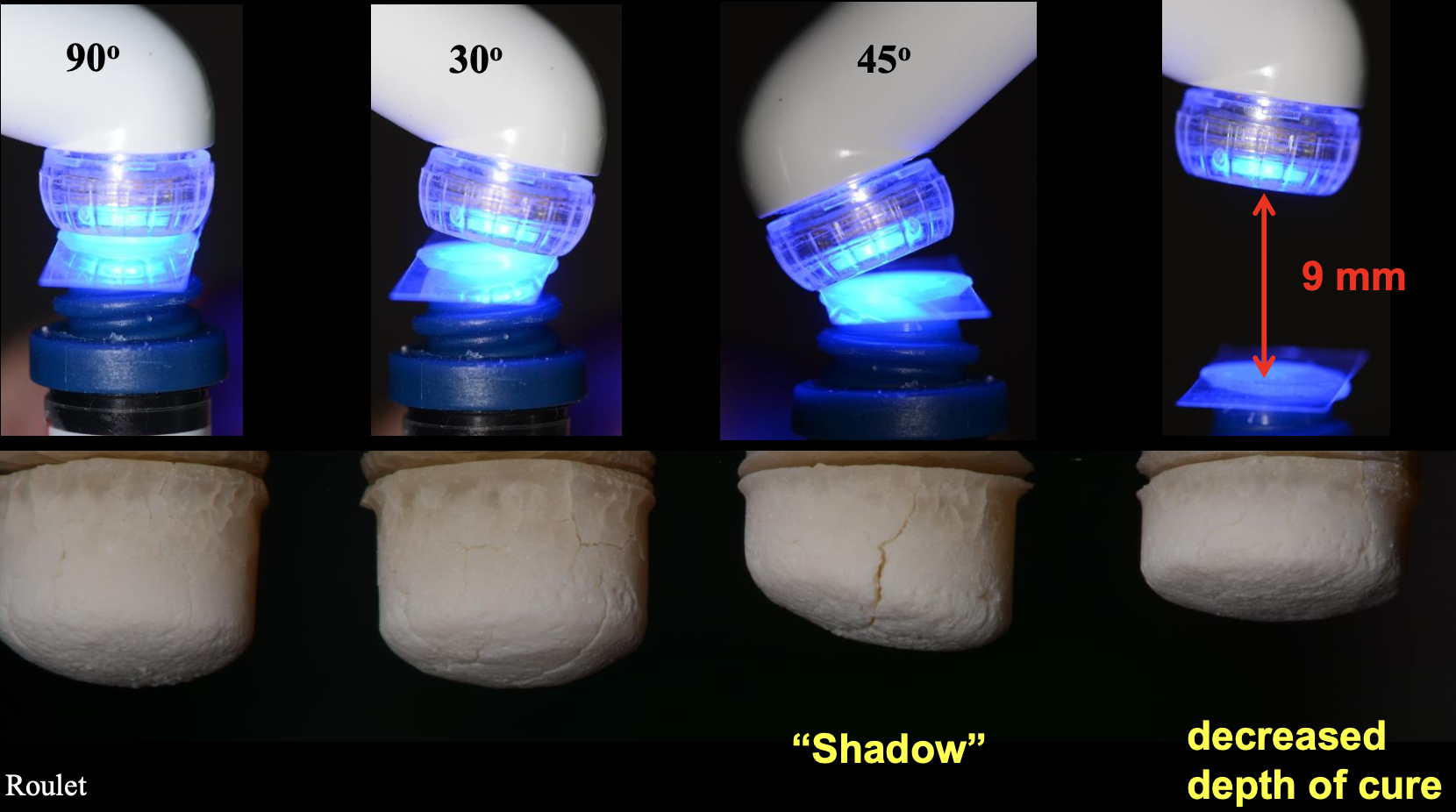
Light curing composite predominantly employ _______ which is sensitive to blue light (420-480nm)
Photoinitiator added to enhance ______ to violet spectrum
caphorquinone
sensitivity (ex. are Lucirin, PPD, and Ivocerin)
Types of curing light by intensity lowest to highest
LED
QTH
PAC (plasma)
Laser
LED lights are introduced in the late 1990s
Able to polymerize using _____
Ensured greater depth of cure compared to ____ lights
CQ
UV
CQ vs Alternative Photoinitiators
CQ has greater curing depth but yellow coloration
Alternative such as TPO, PPD, and Ivocerin avoid yellow discoloration but reduced depth of cure
Best is hybrid
_____- wavelength photoinitiators decrease depth of cure necessitating more layers
violet
Initiators contain _____ _____ that propagates polymerization by linking the monomers.
unpaired electrons
Autocure vs Light cure and Dual Cure
Autocure: Paste, benzoyl peroxide, and tertiary amine make free radical
Light cure: blue light and phoinitiator make free radical
Dual Cure: mix of both
Adequate light curing ______ the bond strength.
doubles
Before adhesion, dentists used a ______ ______ shape to create an artificial ______ to increase retention.
dove tail
undercut
Adhesive dentistry does not require that
Adhesion or Bonding is the attachment of one substance to another by _______ forces (valence, interlocking forces)
interfacial
Adhesive or bonding agent or adhesive system is a material, a viscous fluid, that joins two substrates together and solidifies and is able to transfer a _____ from one surface to another
load
________ adhesion is penetration of resin into demineralized tissues and formation of resin tags with the tooth structure
________ adhesion is chemical bonding to the inorganic (hydroxyapatite) or organic components (mainly type ___ collagen) of the tooth structure
________ adhesion is precipitation of substances on the tooth surfaces to which resin monomers can bond mechanically or chemically
mechanical
adsorption, 1
diffusion
Steps of applying bonding agent to enamel
1. acid etch
2. rinse
3. dry
4. apply hydrophobic resin
5. light cure
Resin binds to
Biological Substrates: Enamel and Dentin
Non-biological Substrates: Ceramic and Metal
Function of acid etch
Demineralizes bonding surface to increase binding surface area
Acid Etching uses ______ acid to change enamel surface
Concentration 30 to 40%
Surface free energy is ______
Increased capillary attraction allowing penetration of ____-viscosity fluid resins
phosphoric
doubled
low
Ideal Etching time is _____ seconds
Older teeth, fluorosis, and mottled may require _____ to achieve end point
Freshly cut enamel etches ____ than unprepared
15
longer
faster
Why is the use of a rubber dam necessary when applying bonding agents
the bonding agents are hydrophobic and cannot adhere to wet surfaces
Why is it necessary to apply a bonding agent before composite?
bonding agents are more flowable and will fill in irregularities more reliably
Appearance of properly etched enamel
frosted/chalky white
Insufficient washing after etching leaves debris that interferes with the flow of _____ into the enamel channels
resin
How long should you rinse after etching enamel?
at least as long as you etched
Usually 15-30 sec
Can you overdry after you etch
Yes and will cause post op sensitivity
Etching gel or liquid?
Smooth surfaces
Deep grooves
liquids and gels have similar results
liquid etch is recommended
Etching _____ can easily thicken through evaporation
gels
Enamel Bond strength is 80kg per _____ in
0.2362
Resin tag
Extension of resin that has penetrated into etched enamel or dentin.
Adhesives used on dentin require a _______ component (primers) to interact with the dentin surface and a _______ component (bonding agents) to interact with the composite.
hydrophilic
hydrophobic
Dentin ____ are composed of a mixture of hydrophilic monomers and solvents, aiming to improve the wettability and to permit substitution of the water retained
Dentin _____ contains hydrophobic part that allows coupling with the resin-based composite
primers
bond or bonding agents
Primer vs Bond
Primer: Hydrophilic prepare for bonding
Bond: Hydrophobic that bond composite to tooth
Dentin binding steps
1. acid etch (rinse) removes smear layer
2. primer infiltrates exposed collagen network links to adhesive
3. adhesive links to resin composite
Hybrid layer
Layer formed by dentin bonding agent and collagen fibrils exposed by acid etching. Excellent layer composite can be bonded
4th generation
separate etch, primer and bond
3 steps total
gold standard for minimal sensitivity and maximum bond strength
5th and 6th generation adhesive systems
5th: 1 bottle (prime and bond) weaker
6th: 2 bottle (etch prime) (bond) less sensitivity
7th generation
single bottle contains etching agent, primer, and bonding agent
decreased sensitivity and increased bond strength
Meese prefer anterior to etch first
Do self-etching systems require rinsing?
no
Which adhesive system creates a rougher surface?
total etch
however, it relies on operator to properly fill space
T or F: you should thoroughly dry dentin after applying acid etch.
false; gently dry but do not over-dry
removal of water form the dentin structure causes loss of structural integrity
this is why we use hydrophilic primer
Dentin enzymes, matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and cathepsins, are responsible for the __________ of the collagen matrix of the ____ layer.
leads to destruction of the hybrid layer and loss of dentin bond strength over time.
_______ inhibits this
hydrolysis/degradation
hybrid
Chlorhexidine
Which is harder to bond dentin or enamel
dentin
no open rod to bond to
Dentin enzymes, MMP and cathepsins, are responsible for the hydrolysis/degradation of the collagen matrix of the _____ layer
hybrid
Chlorohexidine helps that
Chlorohexidine inhibits MMP’s and cathepsins, which can cause _____ of the hybrid layer. It can therefore improve durability of the resin-dentin bodn formed by an etch and rinse adhesive
degradation
Contact pressure causes ______ stresses concentrated in the _____ of the occlusal surface, and their magnitude and area of interest reached its peak during _______ ______.
tensile
grooves
maximum intercuspation.
The force of the occlusal load, and the manner in which opposing teeth occlude strongly influence the selection of ______ _______, as well as the design of the preparation and restoration.
restorative materials
Objectives of tooth preparation
1. Conservative cutting
2. Remove defects
3. Protect the pulp
4. Allow for functional, resilient, and esthetic placement of restorative material
GV black steps in tooth preparation
Establish outline form
Obtain resistance form
Obtain retention form
Obtain convenience form
Remove carious dentin
Finish walls and margins
Clean the preparation
______ _____ is based primarily on the location and extent of the carious lesion, tooth fracture, or erosion.
The extent of carious _____ should be a primary determinant of the outline form of the preparation
Outline form
dentin
In carious teeth, the outline form is established before/after penetration into carious dentin and removal of the enamel overlying the carious dentin
after
The final outline is not established until the carious dentin and usually, its overlying ______ enamel have been removed
unsupported
Which of GV black's step of preparation are not usually necessary for composite fillings?
retention form due to use of adhesives
Resistance form provides resistance to the restoration from being _______ and both the restoration and tooth will be resistant to _____ during function
displaced
fracture
Retention form is obtained through ________ ________ to retain the restoration or through ________ that attaches the restoration to the tooth surface.
mechanical shaping
bonding
Not necessary for composite filling