Class 13: Constipation & diarrhea & incontinence
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
risks for constipation
activity and diet
metabolic
neurogenic
medication
somatic (emotional issues that a expressed with physical issues)
depression
constipation
Hard, slow stools that are difficult to eliminate; often a result of too little fiber in the diet
chronic use of laxatives can cause
the body to become dependent
constipation is less then_____ per week
3
barium enema (BE)
series of radiographic images taken of the large intestine after the contrast agent barium has been administered rectally
(also called lower GI series)
Valsalva maneuver
forceful exhalation against a closed glottis, which increases intrathoracic pressure and thus interferes with venous blood return to the heart
aka straining
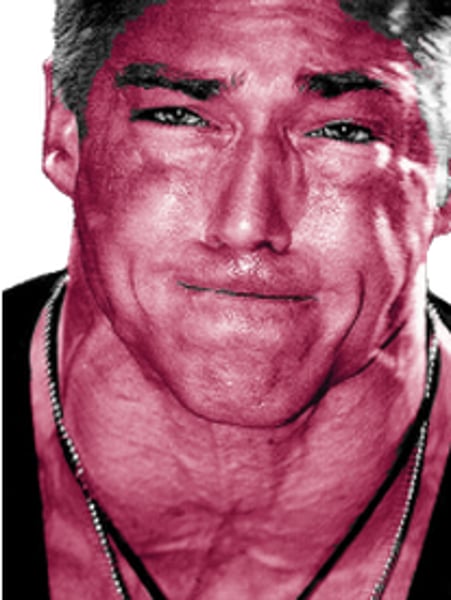

fecal impaction
the prolonged retention and buildup of feces in the rectum
hemorrhoids
swollen, twisted, varicose veins in the rectal region
dilated portions anal veins
Fissures
normal or abnormal folds, grooves, or cracks in body tissue
rectal prolapse
rectal walls have prolapsed and can be seen outside of the body
if someone is constipated, small bowel movements
do not get rid of constipation
fiber rich foods
Beans, peas, bran, whole grain foods, and fruits and vegetables
prune juice is a
natural laxative
manual removal of stool can only be done by
trained professionals
diarrhea is more then
3 loose BM a day or more
inflammatory diarrhea
A diarrhea associated with pathogen invasion of the intestinal mucosa characterized by dysentery.
inflammatory bowel disease
inflammation of the colon and small intestine
s/s for diarrhea
a lot of loose stools
abdominal cramps
abdominal distension
anorexia and thirst
diarrhea is most commonly from
infections of the GI tract
a Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP) test for diarrhea is necessary to
make sure eletroclyte and water balance is ok
what is the most concerning complications of diarrhea
dehydration
urine output after diarrhea would be
less then normal
if you have diarrhea you should avoid
caffeine
alcohol
foods low in bulk
fatty foods
oil
bowel incontinence usually is caused by
impaired functioning of anal sphincter or nerve supply
bowel incontinence is usually a s/s of
another disorder
Partial Bowel Incontinence
inability to control flatus or to prevent minor soiling
Major Bowel Incontinence
inability to control feces of normal consistency
risk factors for bowel incontinence
nerve damage
older age- weak muscles
female- after birth
dementia
physical disability
s/s of bowel incontinence
loss of voluntary bowel control
urgency and loss of control of stool
mucous leak out of anus at unwanted times
can be accompanied by constipation, diarrhea, gas, bloating, cramping, etc
embarrassment
anorectal manometry
measures the pressure activity of internal and external and sphincters and reflexes during rectal distention, relaxation during straining, and rectal sensation
interventions that are non pharmacological
pelvic floor muscle exercises
skin integrity maintenance
fecal incontinence devices
laxative foods
fruits and vegetables, bran, chocolate, alcohol, coffee
which of the following would be a common nursing problem for a client with a colostomy?
A. constipation
B. Bowel incontinence
C. negative body image
D. excess fluid volume
C. negative body image
a client has constipation. what is included in the education to treat and prevent constipation? Select all that apply.
a. hold urge to defecate for 30 minutes then go
b. drink 1000 to 2000 ml of water a day
c. increase fiber in ur diet
d. take etc laxatives as long as u need to
e. increase daily activity
C. increase fiber
E. increase daily activity
you should drink
2-3 L of water daily
how long can you take laxatives for
MAX a week