VMCB 121 Demonstartion of Bacteria - Stains
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Advantage and Disadvantage of Unstained Bacteria
Adv: Bacteria is still alive
Disadv: Can be hard to detect with the light microscope
advantage and disadvantage of stained bacteria
adv: provides contrast in the structure
disadv: no mobility
classification: morphology and arrangement
what does fixation do
kill the pathogenic bacteria
attach bacteria firmly to the slide
improve staining
two types of fixation
HEAT FIXATION
gently flame heating an air-dried film of bacteria and adequately preserve overall morphology but not structures within the cells
CHEMICAL FIXATION
used to protect fine cellular substructure and the morphology of larger and more delicate microorganisms
types of stain/dyes
acidic dye
basic dye
neutral dye
acidic dye
anionic chromophore = negative charge
stains basic components
basic dye
cationic chromophore = positive charge
stains acidic component
neutral dye
eosinate of methylene blue
types of stain
simple stain = one dye = same color
differential stain = two stains = diff microorganisms
special stains = highlight specific cell structures
simple stain process
smear
fixing
stain
washing
air dry
observation
why does bacteria have an affinity to basic dyes?
due to the acidic nature if their protoplasm
differential stain process
smear
fixing
primary stain
decolorize
counter stain
air dry
observation
examples pf simple stai
methylene blue, crystal violet, safranin, carbol fuchsin
example of differential stain
gram stain, acid-fast stain
example of special stains
hansen’s, anthony’s, schaeffer-fulton
Gram Stain (by Hans Christian Gram 1884)
differentiate 2 groups: gram positive and gram negative bacteria
cell wall is composed of peptidoglycan
Gram + bacteria
thick layer (50-90%)
no/less lipid
purple
Gram - bacteria
thin layer (-10%)
takes up safranin
pink/red
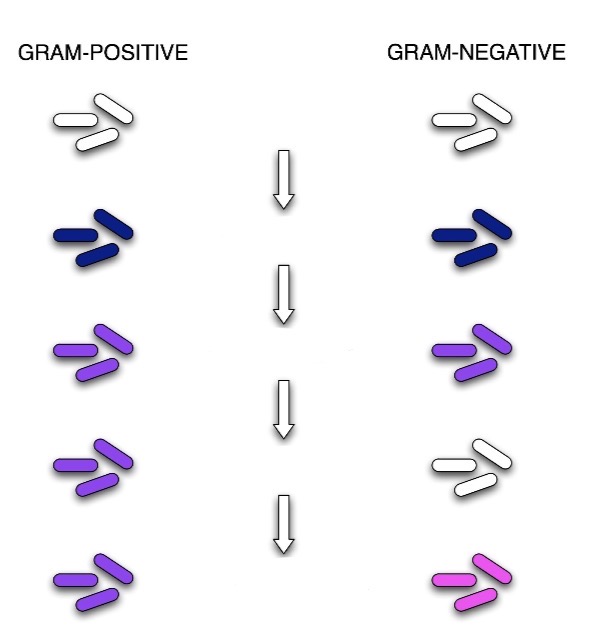
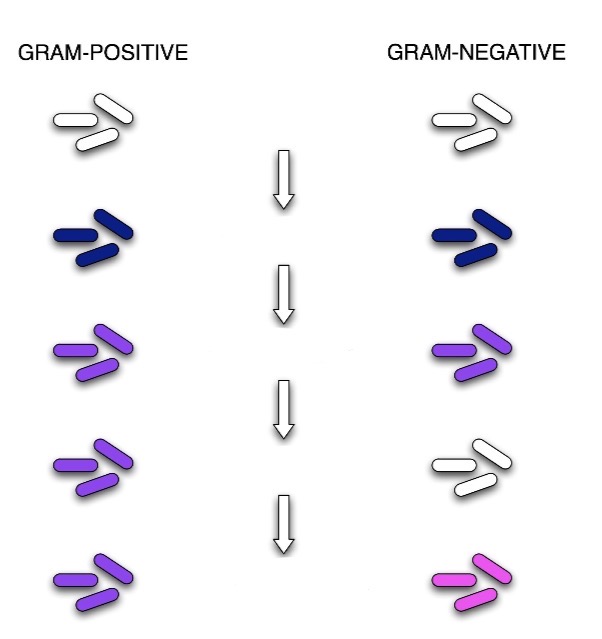
Gram Stain Process
Crystal Violet - primary stain added to the smear (1min)
Iodine - mordant makes dye less soluble = adheres to the cell wall (1min)
Alcohol - decolorizer washes away stain from G-cell walls (10secs)
Safranin - counterstain allows dye adherence to G-cell walls (30secs)
Acid Fast
cells that retain a basic stain in the presence of acid-alcohol
other term for acid stain
ZN, Ziehl-Neelsen’s Stain
used for those microorganisms that are not stained by simole or Gram staining methos
Myolic Acid
waxy material that composes the cell wall of acid fast materials. it does not allow the decolorizer into the cell wall
Myobacterium
why do acid-fast bacteria retain the color of carbon fuchsin
because of mycolic acid
acid-fast staining process
carbol fuchsin: primary stain
heat: mordant
acid-alcohol: decolorizer
methylene blue: counterstain
special stain
staining procedures used to identify specific external or internal structures that are not found in all bacterial species
example or special stains
capsule stain
flagella stain
capsule stain
the capsule is synthesized in the cytoplasm and secreted outside the cell, where it surrounds the bacterium
methods of capsule stain
india ink method
anthony’s stain method
india ink method
shows a halo around the cell
colorless bacteria against a colored background
cells are highly visible
why are the distortions of cell size and shape minimized in india ink method
because heat fixing is not necessary and the cells do not pick up stain
anthony’s stain method
uses specific reagents and avoids heat-fixing to properly highlight this structure
capsule appears as a faint blue halo around a purple cell
reagents used by anthony’s stain method
crystal violet: primary stain
20% of CuSO4: decolorizing agent and counterstain
endospore stain
schaeffer-fulton method
heat is required to drive the stain into the endospore
spores
endospore stain process
stained with malachite green
heat for stain penetration
decolorized
counter stained with safranin
flagella staining
demonstrates the number and arrangement of flagella, crucial for identifying motile bacteria
coats the thin bacterial flagella with heavy metals or other compounds to make them visible in the light microscope
what is the use of silver nitrate in flagella staining
to see bacterial flagella that are too slender
makes flagella appear larger
used to determine arrangement, location, number of flagella for identification