UNIT 4. CONDITIONAL STATEMENTS
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Decision-Making Structure
Is the process of making a decision about which part of the code should be executed or not based on some condition.
Decision-Making Structure (2)
In C++ involves the usage of conditional statements to execute specific blocks of code primarily based on given situations and their results.
if structure
The _ _ is one of the selection structures that will execute the statement or block of statements following it when the comparison expression evaluates to true
if STATEMENT (2)
If the comparison expression evaluates to false, it will go out of the if structure without doing anything.
Syntax Statement (if STATEMENT)

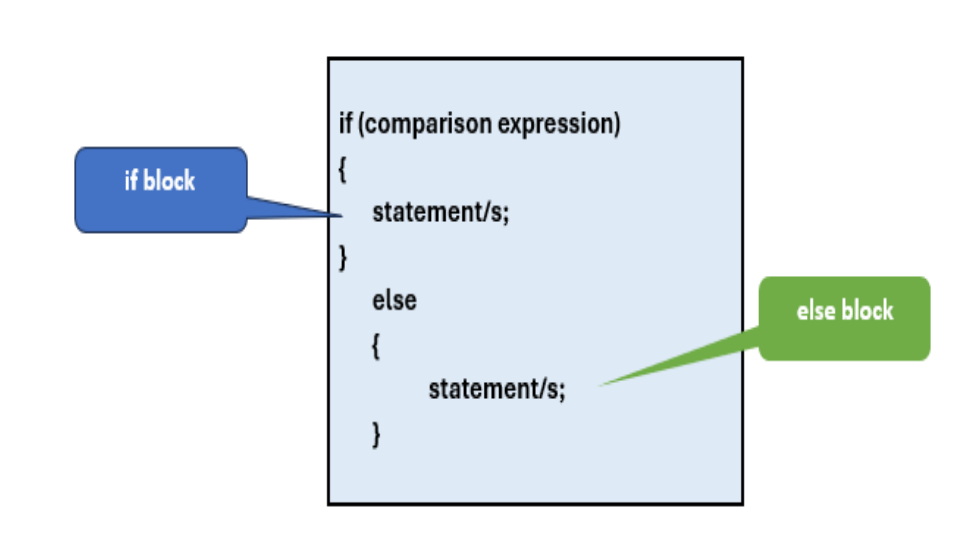
if-else STATEMENT
The if-else structure is a selection construct that will execute a statement or a block of statements when the condition evaluates to true or another series of instructions when the result of the comparison is false.
syntax statement (If-else STATEMENT)
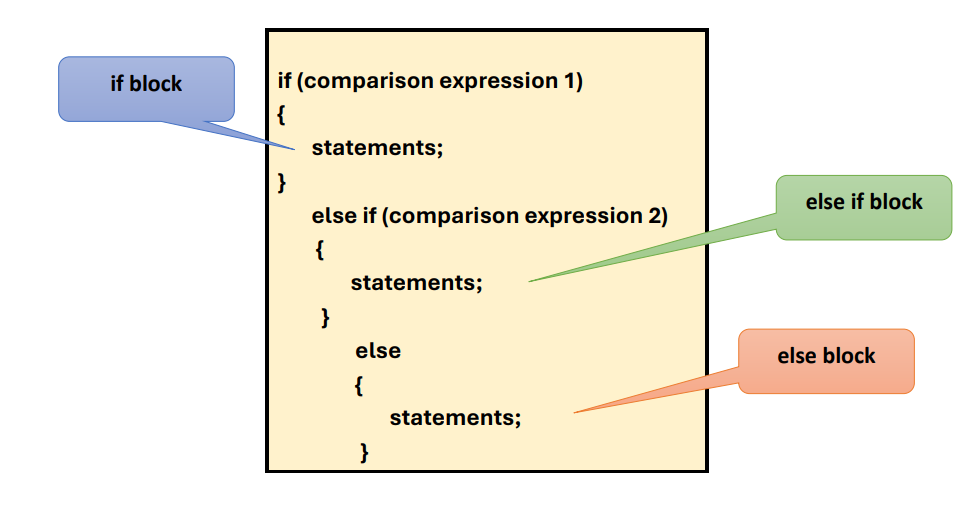
If-else-if ladder STATEMENT
helps the user decide from among multiple options. The C++ if statements are executed from the top down.
If-else-if ladder STATEMENT (2)
As soon as one of the conditions controlling the if is true, the statement associated with that if is executed, and the rest of the C++ _ _ _ is bypassed. If none of the conditions is true, then the next statement will be executed.
syntax statement (If-else-if ladder STATEMENT)
nested if-else STATEMENT
are those statements in which there is an if statement inside another if-else.
nested if-else STATEMENT (2)
when we want to implement multilayer conditions (condition inside another condition, inside another condition, and so on). C++ allows any number of nesting levels.
switch STATEMENT
is an alternative for the if else if ladder structure. It looks for a match among the cases and executes the statements inside the match. If no match is found, it will execute the default statements.