Unit 4 Test
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What is the apparent force rotation of the Earth?
The Coriolis Effect
What is the best scenario for divergence and convergence to strengthen a mid-latitude low pressure system?
Source of upper-level divergence aloft, removes mass from the column of air, causing surface pressure to fall
Surface convergence that draws warm, moist air into the low-pressure system
A large surface temperature gradient/front
What is geostrophic wind and what forces are balanced to achieve this?
The pressure gradient force and Coriolis force are balanced to create geostrophic winds.
Winds move parallel to the isobars with the low to the left and the high to the right of its path
Nearly straight isobars
500 mb chart, what do the contour lines represent?
They represent the height/altitude above sea level (isohypses)
What wind pattern can be described as a zonal wind flow?
When wind blows west to east.
Where can you find the warm sector?
The warm sector is an area of warm air between the warm and cold front
On an upper-level map (lower pressure mb), how do the winds generally flow?
They tend to flow along contour lines of constant pressure, primarily from west to east in the mid latitudes.
If the contour lines are wave like the winds are more meridional (north-south)
How does the height of an isobaric surface relate to temperature in that column below it
how does a cold air mass vs a less dense warm air mass vary in height
Warm air has a higher isobaric surface because it is less dense and pressure drops slowly with height
Cold air has lower isobaric surface because it is denser and pressure drops rapidly with height
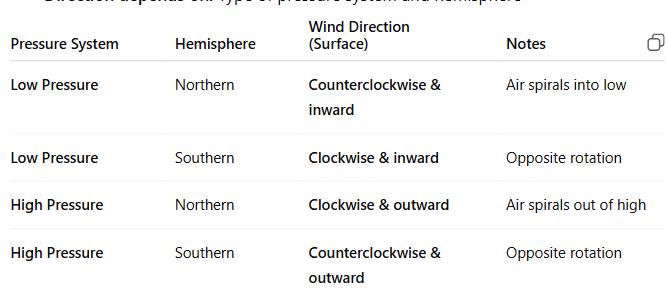
Wind around _____ pressure system in the _____ hemisphere blows which way?
Wind around LOW pressure system in the NORTHERN hemisphere blows counterclockwise and into the low
Wind around LOW pressure system in the SOUTHERN hemisphere blows clockwise and into the low
Wind around HIGH pressure system in the NORTHERN hemisphere blows clockwise and outward of the high
Wind around HIGH pressure system in the SOUTHERN hemisphere blows counterclockwise and outward of the high
Which way does the pressure gradient force work/act?
It moves from high to low pressure
(points out of highs and into lows)
What is the most commonly used unit of air pressure on a surface level map?
Millibars
1 bar = 1000 mbar
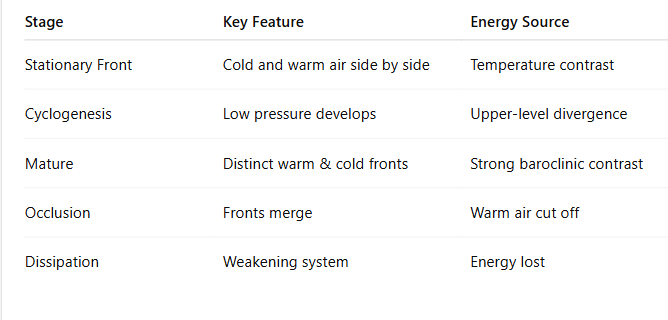
What are the general features of the mid latitude cyclone life cycle.
1) stationary front, 2) frontal wave, 3) open wave, 4) mature (initial occlusion) 5) advanced occlusion, 6) cut-off cyclone
An upper-level disturbance (divergence) reduces weight of local air columns, there is a large surface gradient/front, a weak low is created that induces rotation, turning a stationary front into separate cold and warm fronts called a frontal wave.
The cold front advances southward faster than the warm front moving northward. The entire system moves east.
Temperature advection increases and area of divergence aloft is created.
Cyclone becomes most intense at occlusion and begins to weaken when the cold front catches up to the warm front.
Low detaches and forms an occluded front
If I have a ____ pressure system on a surface map, what kind of corresponding feature will be seen on an upper level (500 mb) map at the same time?
a LOW PRESSURE system will show troughs on an upper level map, because the air is converging due to areas of lower heights. (air is rising at surface)
a HIGH PRESSURE system will show ridges on an upper level map, because the air is diverging above it, due to areas of higher heights. (air is sinking at the surface)
Surface wind at my home is blowing from ____ the high pressure is on the ___ and the low pressure is on the _____
Winds aloft to your back, L is to the left and H is to the right
Arms straight out with surface winds to your back, L is to your left a 10 o’clock and H is to your right at 4 o’clock
Surface wind at my home is blowing from SOUTH the high pressure is on the RIGHT and the low pressure is on the LEFT
Surface wind at my home is blowing from NORTH the high pressure is on the LEFT and the low pressure is on the RIGHT
Surface wind at my home is blowing from the EAST high pressure is on the LEFT and the low pressure is on the RIGHT
Surface wind at my home is blowing from WEST the high pressure is on the RIGHT(not the southeast) and the low pressure is on the LEFT
Which form of precipitation is most damaging?
Either freezing rain or hail
What is the purpose of mid-latitude cycles?
Their purpose is to transport and circulate air of different temperatures to and from the poles.
Warm air from the equator northward
Cold air from the poles outward
They help balance large temperature gradients.
Why might mid latitude cyclones occur one time in the year over the other?
There is usually a large temperature gradient near the east coast and a lot of temperature changes.
How to convert between station pressure and sea level pressure?
For every 100 meters of elevation above sea level, add 10 mbar to station pressure
example: if the station pressure is 960 mb at 450 m elevation, the sea level pressure would be around 1005 mb.
Mid latitude cyclone in relation to warm/cold air advection?
Warm air advection occurs to the east of the low pressure center along and ahead of the warm front, while cold air advection happens to the west of the low pressure center behind the cold front.
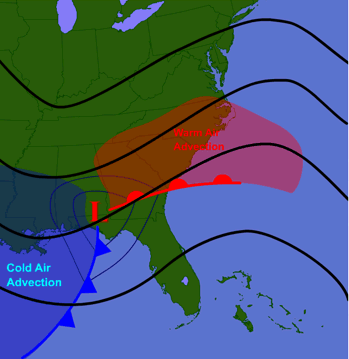
How does a mid-latitude cyclone form?
Amid-latitude cyclone is born when an upper-level disturbance passes over a surface stationary front, creating a weak area of low pressure along it as divergence aloft reduces the weight of local air columns.
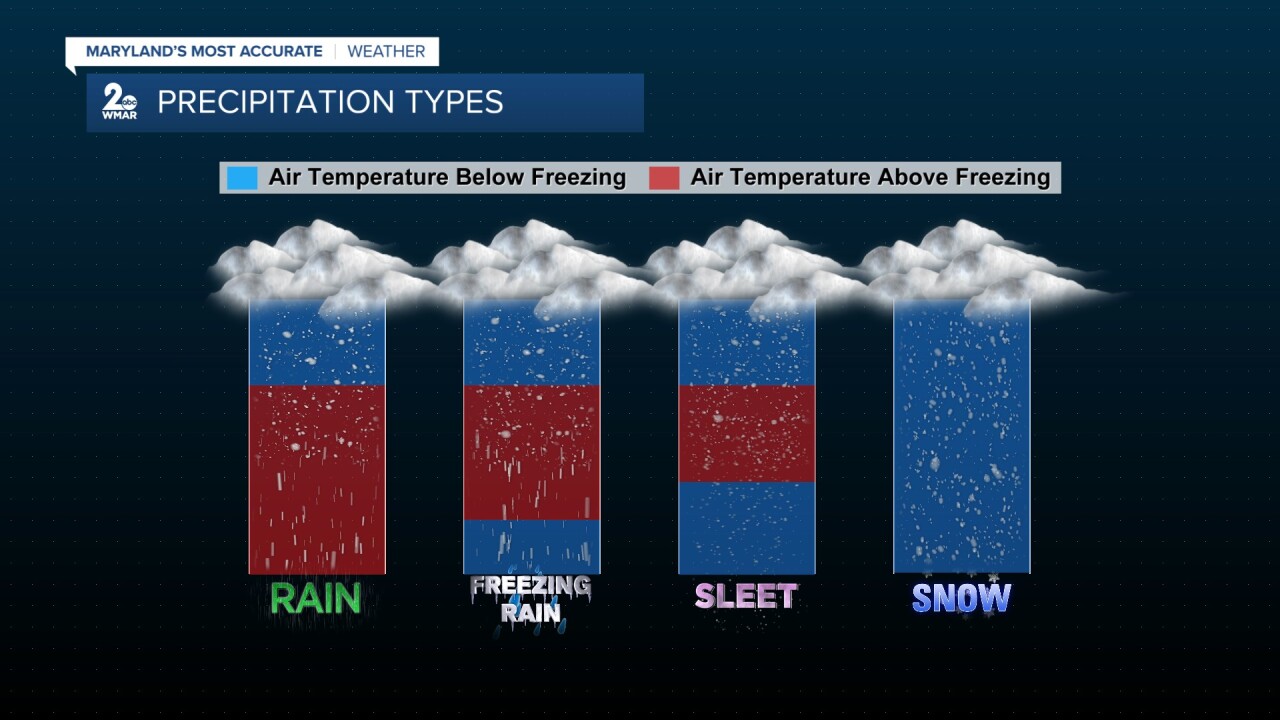
precipitation types
…
Which side of a mid-latitude cyclone would you find warm air advection?
NOT IN FRONT OF A WARM FRONT