Pathology of the ovaries
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
During early proliferative phase, many follicles develop and increase in size until about day ____ or ____ of cycle due to stimulation by both _______ and ________ hormone
8;9; FSH (follicle stimulating hormone); luteinizing hormone (LH)
Dominant follicles measures ____ cm at ovulation
2.0 - 2.5 cm
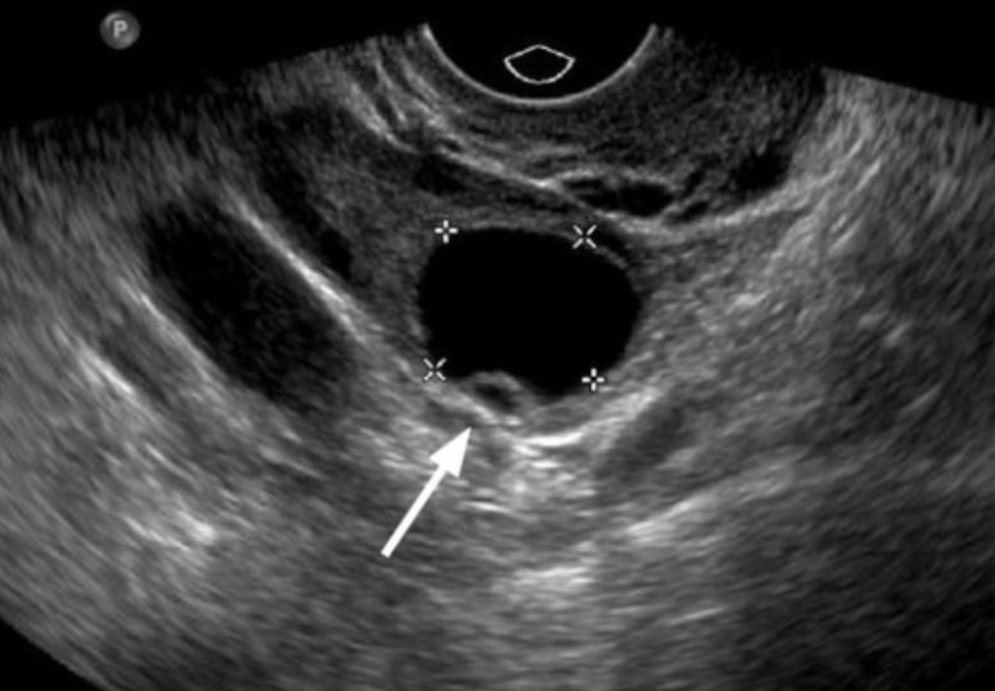
What may occasionally be detected as an eccentrically located, cyst-like, 1 mm internal mural protrusion in the ovary?
cumulus oophorus
Visualization of ______ indicates a _____ follicle and imminent _______ no reproducible sonographic sign reliable
cumulus; mature; ovulation
A ____ ____ develops if the fluid in the nondominant follicles is not reabsorbed
Follicular cyst
Usually, the dominant follicle disappears immediately after rupture at ovulation. Occasionally, the follicle decreases in size and develops a wall that appears _____
Crenulated (scalloped)
What are types of ovarian cysts?
Follicular
Corpus luteum
Hemorrhagic
Theca lutein cysts
Most ovarian cysts measure less than ____ in diameter and regress during next menstrual cycle
5 cm
What is the most common cause of normal ovarian enlargement?
Functional cysts
What can be used to treat ovarian cysts when necessary?
Birth control pills or cystectomy
A follicular ovarian cysts forms when a ______ _______ fails to ______ or ________ post-ovulation
Mature follicle; ovulate; involute
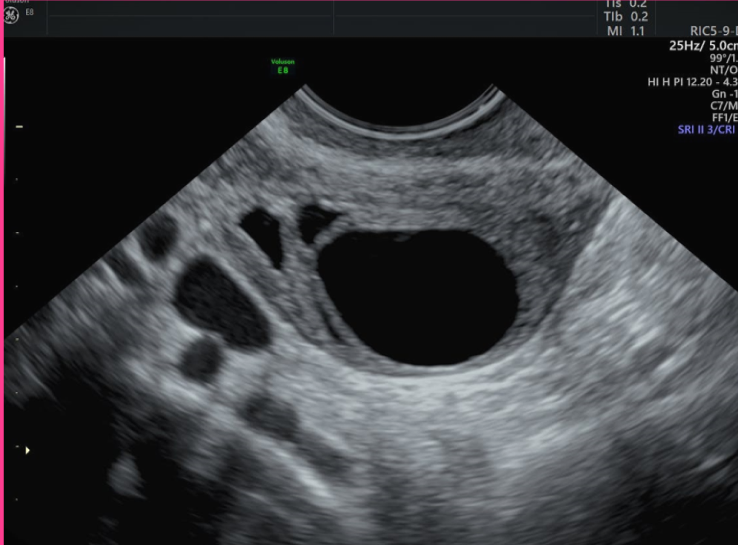
Follicular cysts are ______, ______ and less than _____ but can be as large as _____ in diameter
unilateral; asymptomatic; 2 cm; 20 cm
Corpus luteum cysts is the failure of ______ or excess ______ into the corpus luteum
resorption; bleeding
Corpus luteum cysts are less than _____ and ______
4 cm; unilateral
Corpus luteum cysts are prone to _____ and ______
hemorrhage; rupture
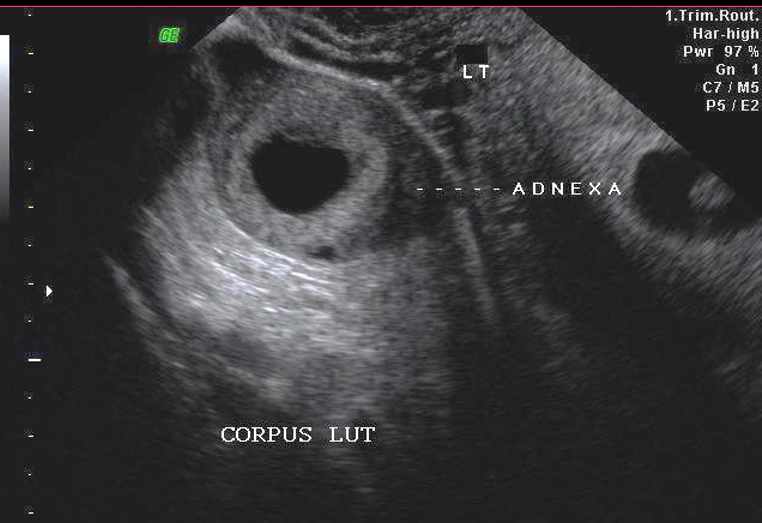
Corpus luteum cysts usually appear as _____ masses with central _____ _____ and _____
complex, blood clot, septations
Corpus luteum cysts are commonly seen up to _____ weeks of pregnancy
16
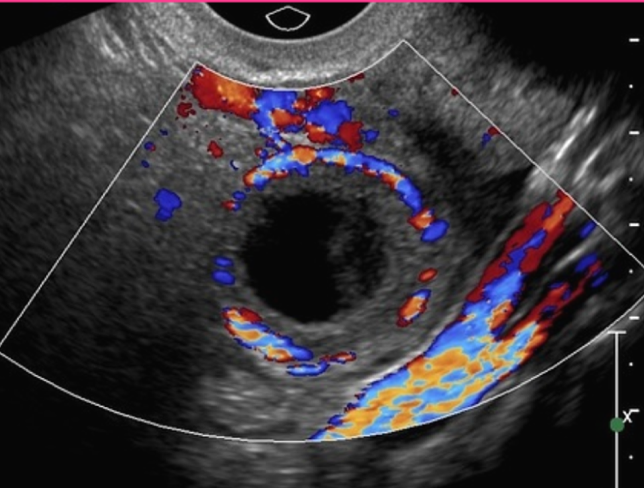
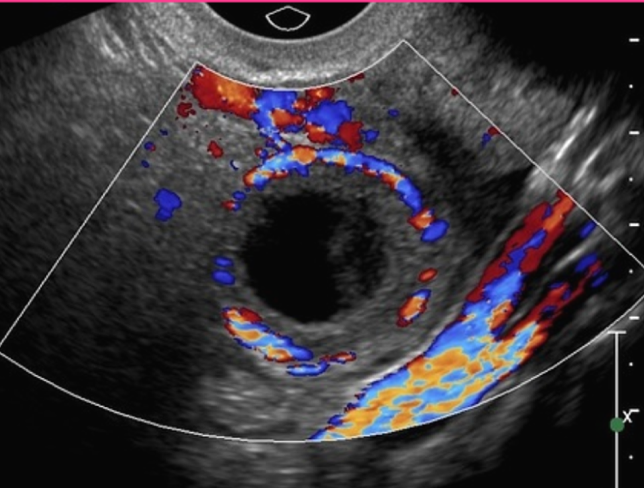
What sonographic appearance does a corpus luteum have with doppler?
Ring of Fire
Corpus luteum cysts have a similar appearance to ____
Ectopics
What is most commonly seen in corpus luteal cysts?
Hemorrhagic cysts
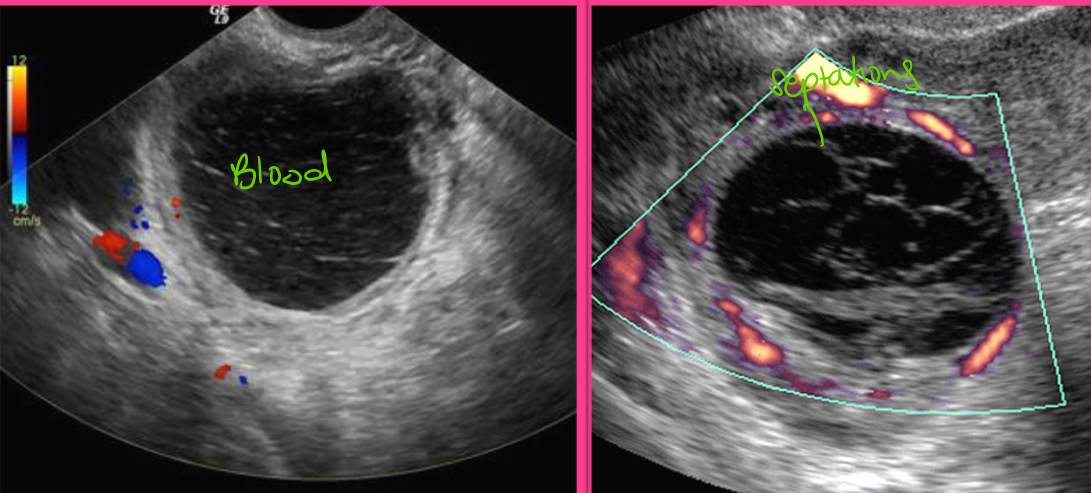
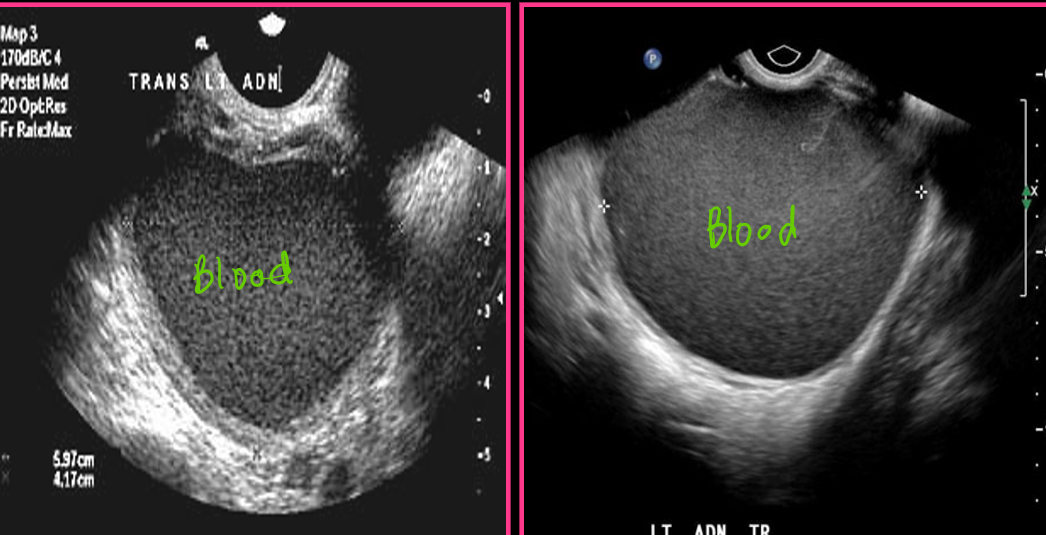
An acute hemorrhagic cyst is usually _______ and may mimic a ____ _____. It appears with a ______ posterior wall and ______
hyperechoic; solid mass; smooth; enhancement
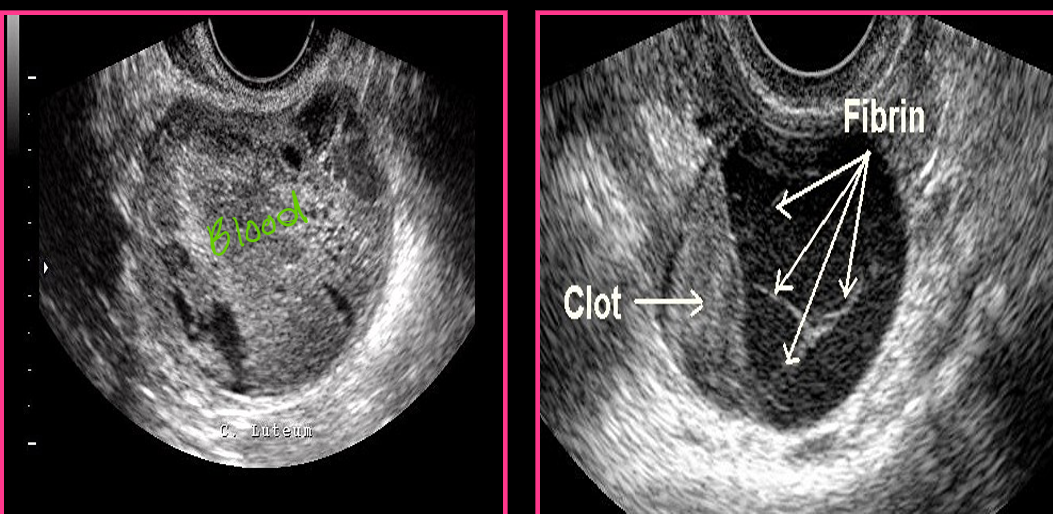
A chronic hemorrhagic cyst appears _____ with _____ clotted blood and _____ level
complex; echogenic; fluid
Intraperitoneal fluid results from _____ or ______ of the hemorrhagic cyst. This may mimic a ruptured ______
rupture; leakage; ectopic pregnancy
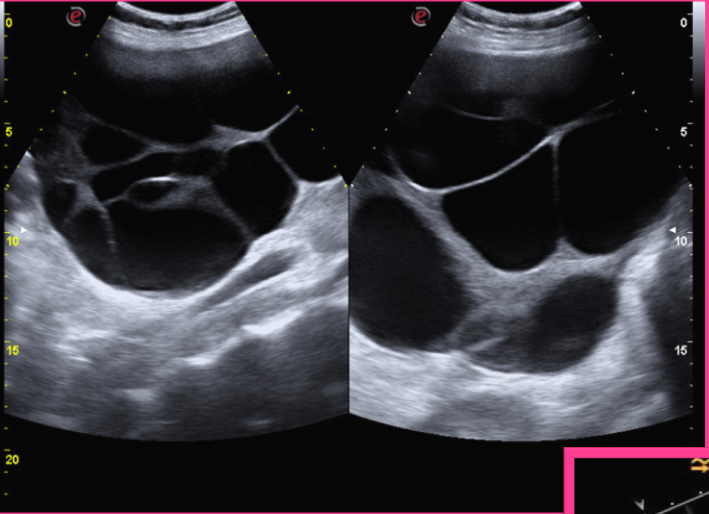
What is the largest functional cyst?
Theca-Lutein cysts
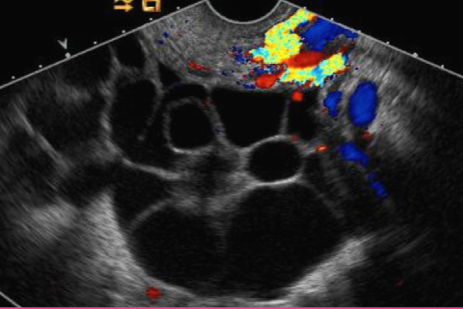
What is the sonographic appearance of a Theca-Lutein cyst?
Bilateral; Multiloculated cystic masses
Theca-Lutein cysts are associated with high levels of _____
hCG
_____ of Theca-Lutein cysts occur alongside gestational trophoblastic disease
30%
Theca-Lutein cysts may undergo _____, ______ and _____
hemorrhage, rupture, torsion
Patients with Theca-Lutein cysts may experience _____, _____ , ______
nausea; vomiting; pelvic fullness
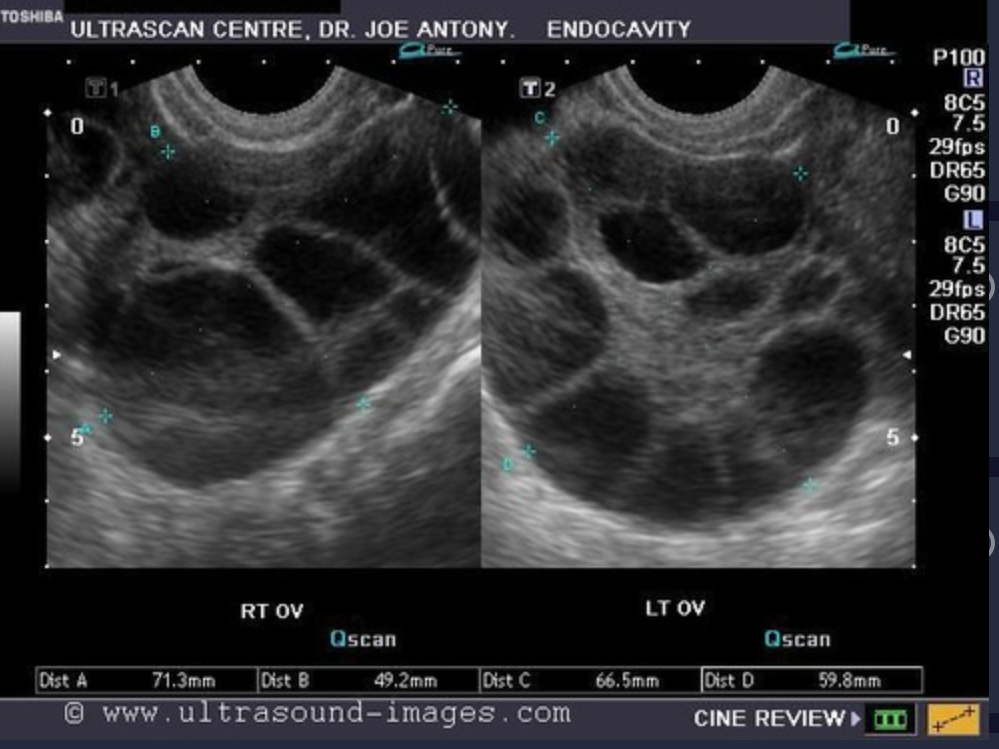
What is a frequent iatrogenic complication of ovulation induction?
Ovarian Hyperstimulation syndrome
Symptoms of mild OHSS are?
Pelvic discomfort; no weight gain; ovaries measure less than 5 cm
What are symptoms of severe OHSS?
Severe pelvic pain; abdominal distention; ovaries measuring greater than 10 cm
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome is associated with _____, _______, and numerous ______
ascites; pleural effusions; ovarian cysts
What was polycystic ovarian syndrome previously called?
Stein-Leventhal syndrome
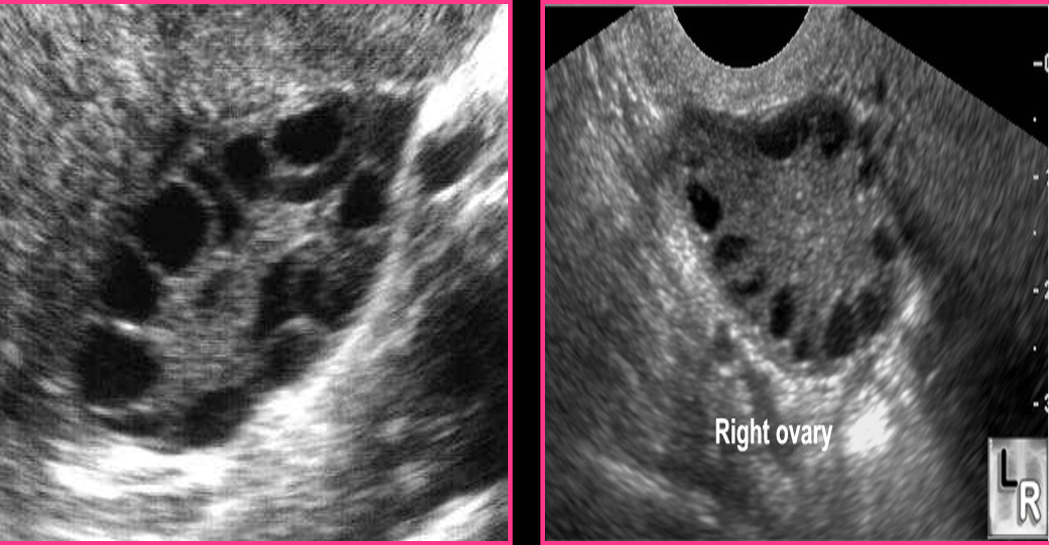
Polycystic ovarian syndrome has an increased number of _____ but __________
follicles; anovulation
PCOS affects ____ or ____ ovaries
one; both
PCOS occurs in late ____ through ____; common cause of ____ and early _______
teens; 20s; infertility; pregnancy loss
What are the clinical symptoms for PCOS?
Infertility
Oligomenorrhea - infrequent periods
Obesity
Hirsutism - Growing hair, high levels of testosterone
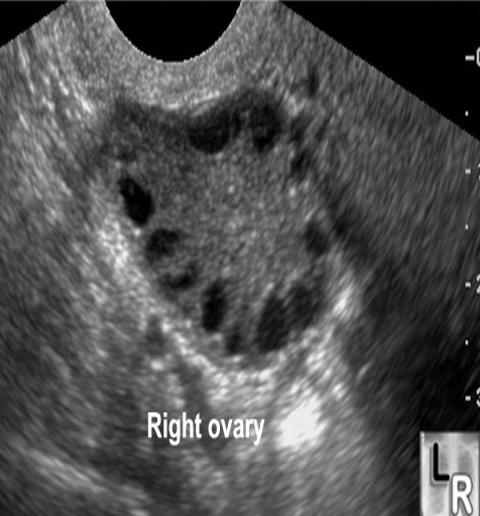
What are the sonographic findings for PCOS?
Normal or enlarged ovaries
“String of pearls”
What presents as a cystic mass after bilateral oophorectomy?
Ovarian remnant syndrome
Ovarian remnant syndrome results from _____ _____ _____ after a difficult surgery
residual ovarian tissue
With ovarian remnant syndrome, the ovarian tissue can become ______
functional
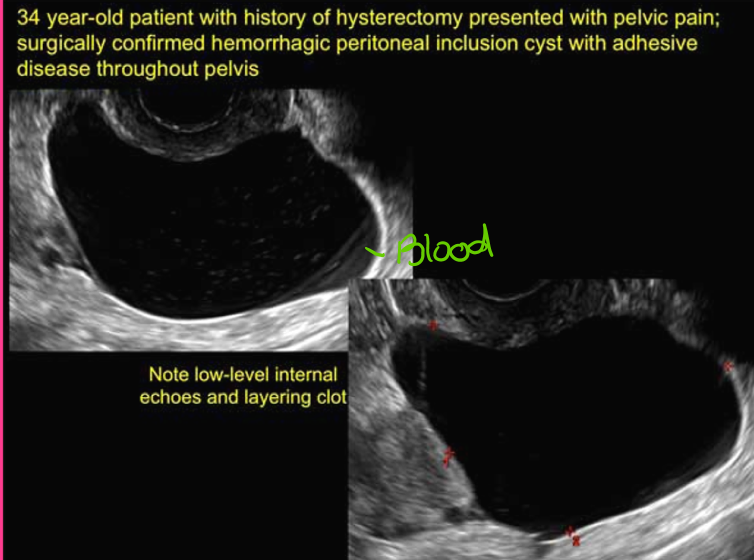
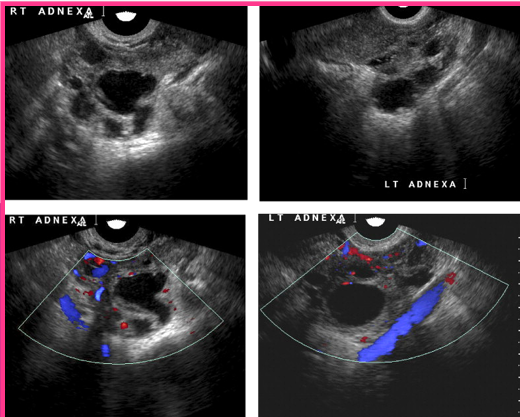
Peritoneal inclusion cysts are formed when _______ trap ________ ____ around the ovaries
adhesions; peritoneal fluid
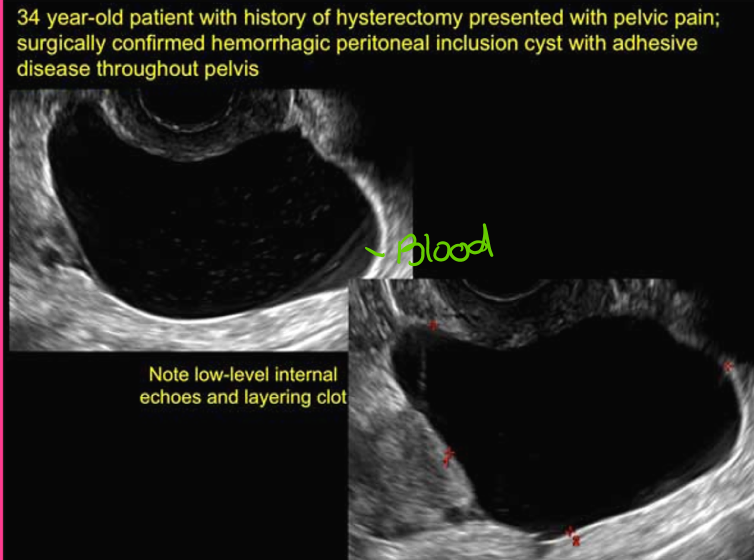
Peritoneal inclusion cysts are _____ ____ ______
Benign cystic mesothelioma
Peritoneal inclusion cysts occur in the _____ and cause _____ _____
adnexa; pelvic pain
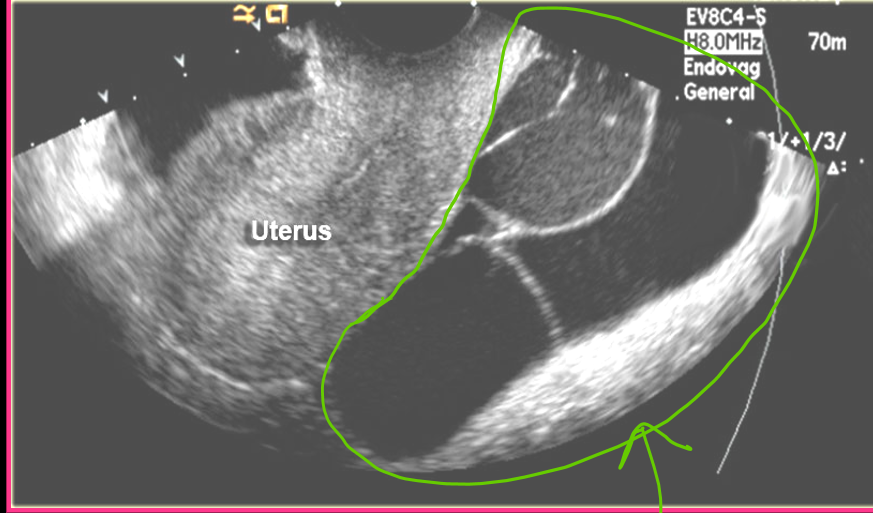
Peritoneal inclusion cysts are ______ cystic _____ masses
multiloculated; adnexal
Peritoneal inclusion cysts predominantly occur in _________ women, _____, _____, ______, ______
Premenopausal
abdominal surgery
history of trauma
PID
Endometriosis
Peritoneal inclusion cysts can reoccur up to ____ of the time
50%
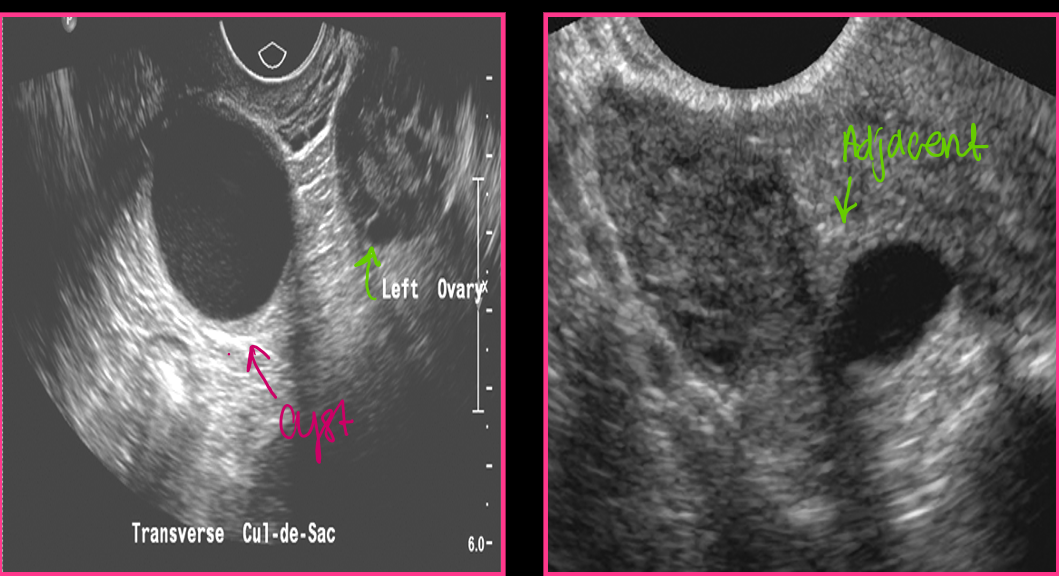
Paraovarian cysts account for approximately _____ of all adnexal masses
10%
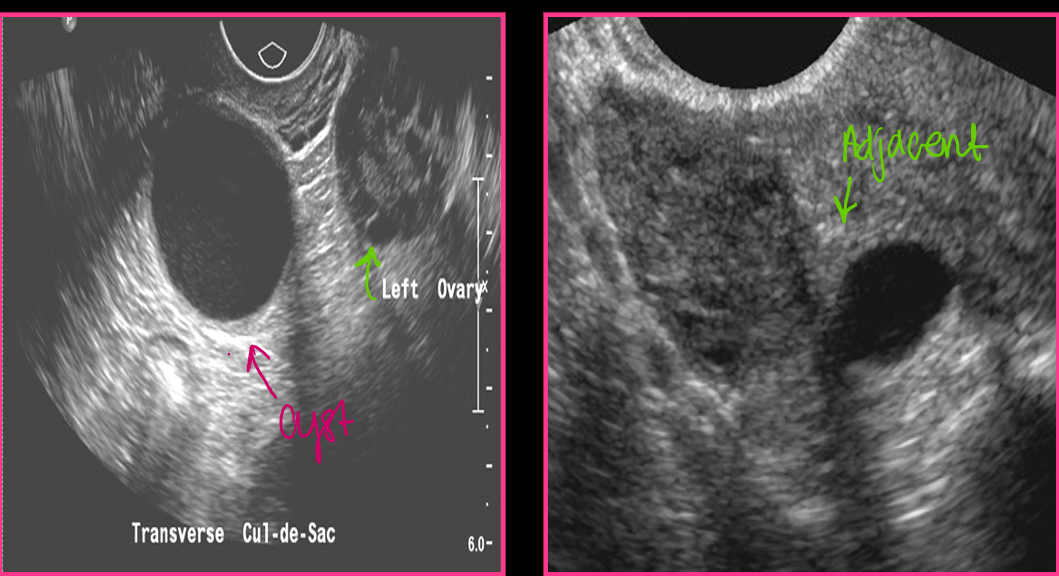
Paraovarian cysts arise from _______ ______ or _____ _____
fallopian tubes; broad ligament
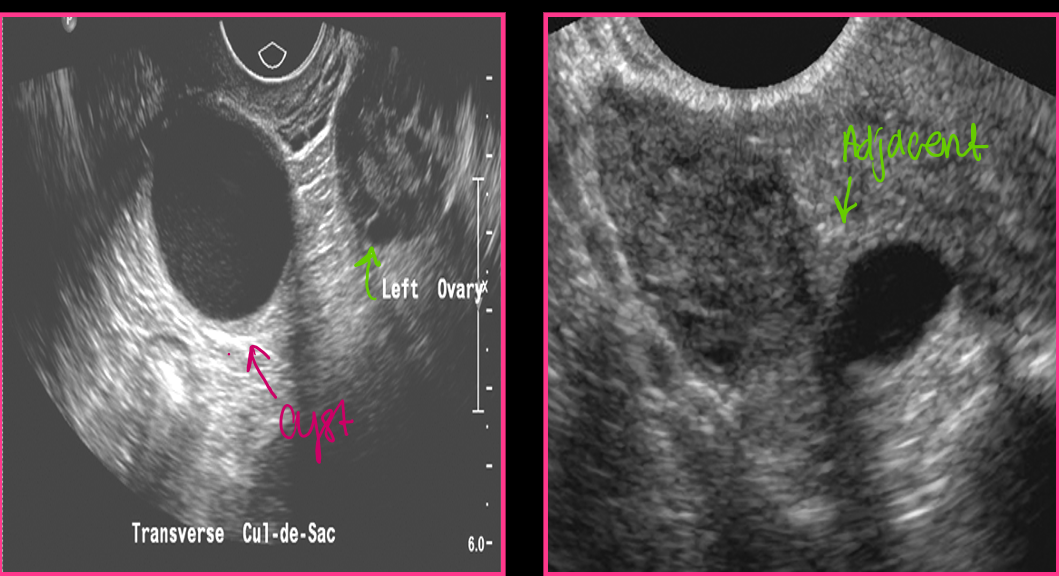
Paraovarian cysts are _____ from the ovary and ______ change in size with cycle
separate; do not
Paraovarian cysts are usually simple with _____, _____ walls _____ to the ovary
thin, deformable, adjacent
Fluid collections in adhesions create cystic structures with ____ shaped throughout the _____
odd; abdomen
Benign cysts in fetuses and adolescents are stimulated by _____ hormones and may cause ______ puberty
maternal; precocious
Simple cysts in postmenopausal women are considered normal if ______ but suspicious if CA-125 is _____
less than 5cm; elevated
Endometriosis is a common condition in which functioning endometrial tissue is present ______ the uterus
outside
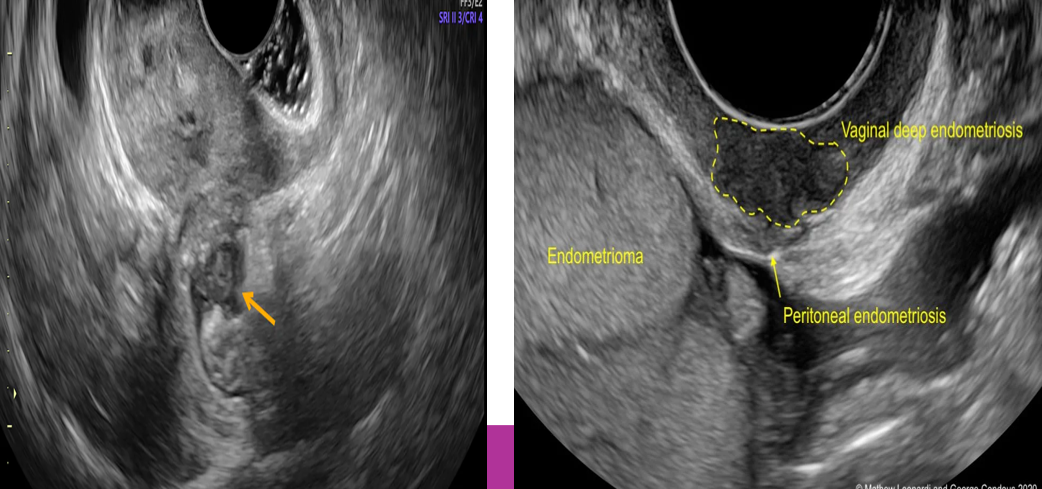
Focal endometriosis consists of a mass called ________ or _______
endometrioma; chocolate cyst
Diffuse form of endometriosis is more ____ but rarely diagnosed by sonography
common
Endometriosis can be found:
Ovaries
Uterus
Peritoneum
Bladder
Kidneys
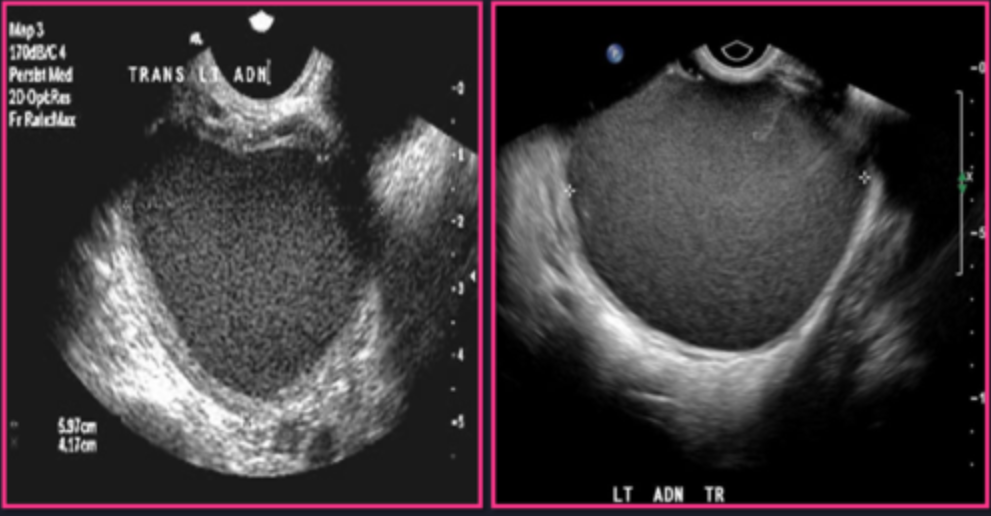
Chocolate cysts are “___” and _____ to the uterus, cul de sac, or rectosigmoid
sticky; adhere
Ovarian torsion is caused by _____ or _____ rotation of the ovarian pedicle on its axis
partial; complete
Ovarian torsion usually occurs in _____ or ______
childhood; adolescence
Once torsion has occurred, there is a ___ increased risk to occur in _________ ovary
10%; contralateral
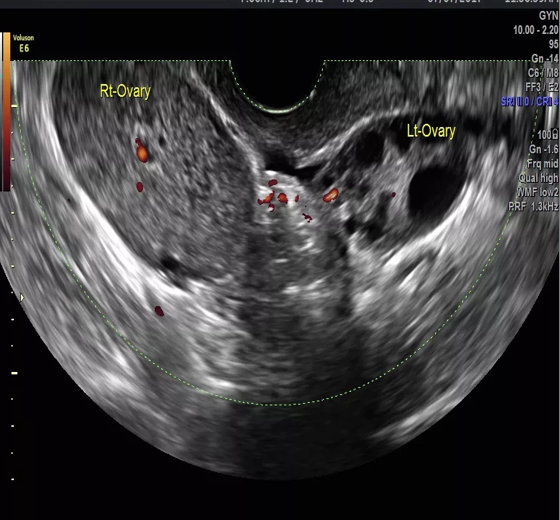
What are sonographic findings of ovarian torsion?
Enlarged ovary greater than 4cm
Solid adnexal mass
Free fluid
No flow
Ovarian torsion requires prompt _____ and _____ intervention
diagnosis; surgical
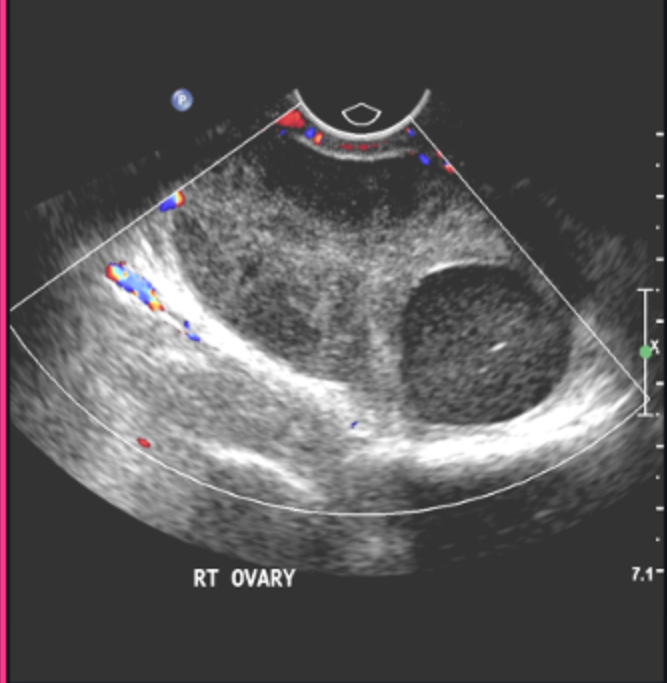
What is usually the cause of ovarian torsion?
Solid mass
The _____ ovary is 3 times more likely to torse than the _____
right; left
Only ____ of ovarian cysts less than ____ are malignant
3%; 5cm
Cysts greater than ____ are recommended for surgical removable
5cm
Any change in ovarian _______ or volume of more than ____ should be considered suspicious
echogenicity; 20ml
Abnormal ovaries suggestive of malignancy defined as _____ , _____ ovaries
enlarged; echogenic
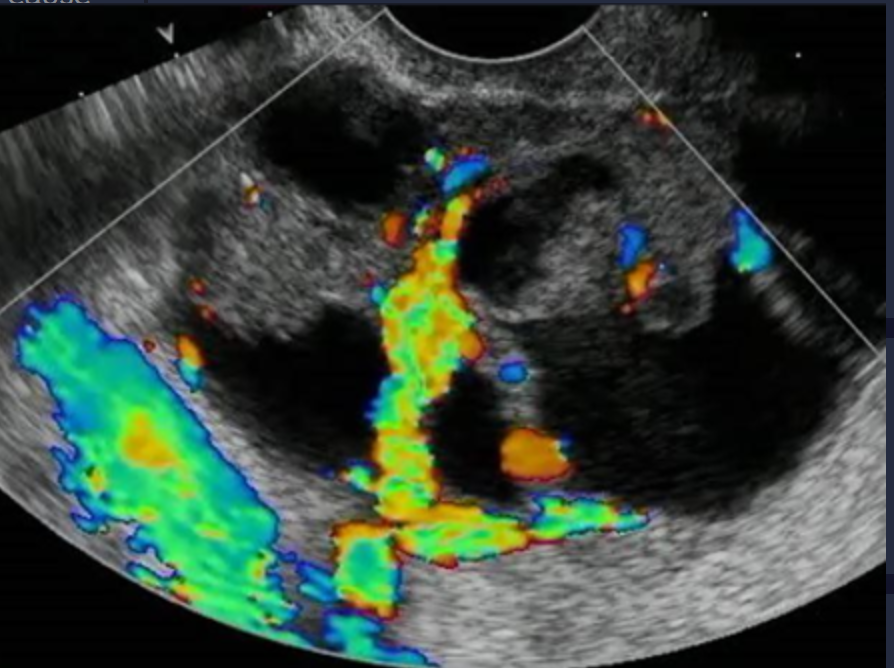
Ovarian ______ is the leading cause of death from gynecologic malignancy (____)
carcinoma; 25%
ovarian carcinoma is _____ in early stages
asymptomatic
_____ of ovarian carcinoma is detected at stage ___
50%; 3
Ovarian carcinoma is ______, 20% of the time
bilateral
Ovarian cancer can present as either a ____, ____, or _____ mass
complex; cystic; solid
Masses greater than _____ are more likely to be malignant.
10cm
Ovarian cancer incidence increases with history of _____ or ______ cancer
breast; colon
Ovarian carcinoma risk factors are:
Increasing age; nulliparity; infertility; uninterrupted ovulation; late menopause
Symptoms of ovarian cancer:
Abdominal pain; swelling; indigestion; frequent urination; constipation; weight change with ascites
Stage 1 ovarian cancer is limited to _____
ovary
Stage 2 ovarian cancer is limited to _____
Pelvis
Stage 3 ovarian cancer includes pelvis, _____, and ______
abdomen; small bowel
Stage 4 ovarian cancer includes pelvis, abdomen, small bowel, ____ and _______
liver; beyond
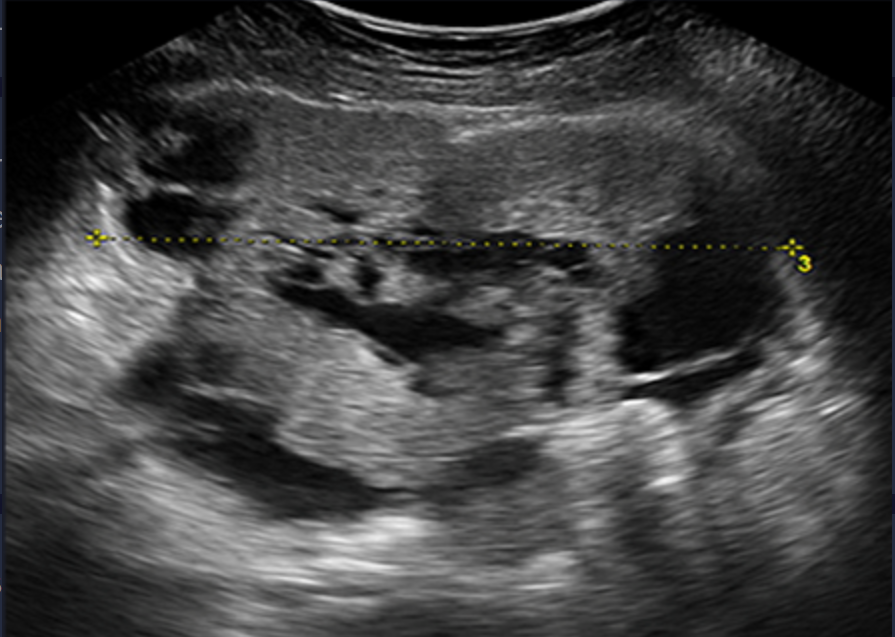
All stages of ovarian cancer have ____
ascites
CA-125 is a marker for _____ _____
Epithelial tumors account for ____ of all ovarian malignancies
90%
What tumor is more common and accounts for 30% of ovarian neoplasms?
Serous tumors
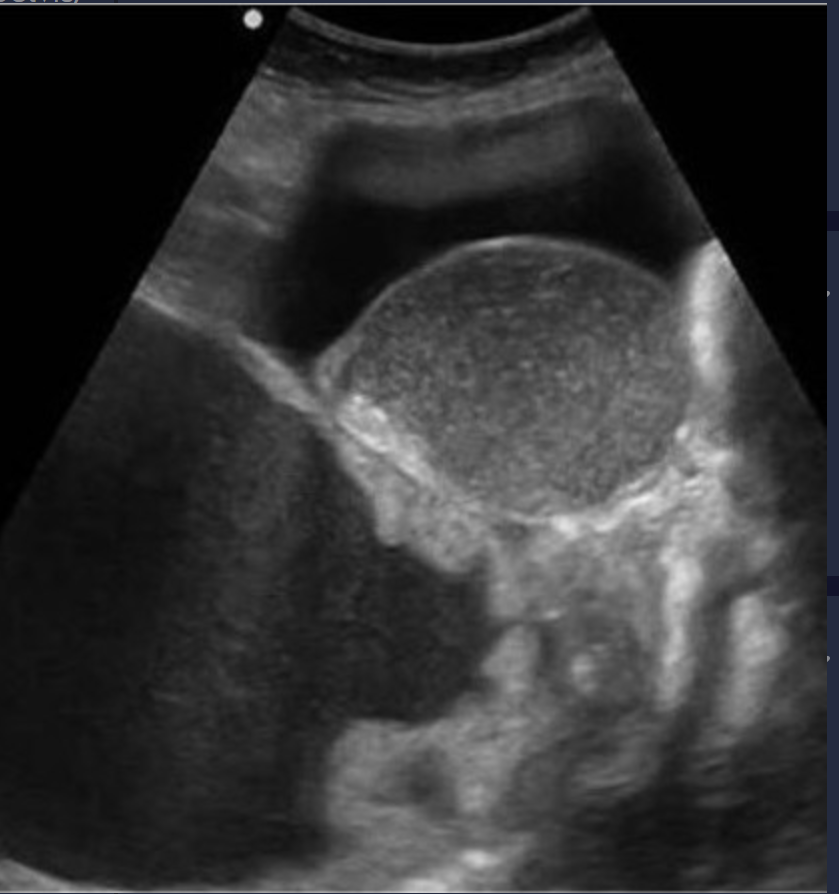
What is the most common cystic tumor measuring 15-30cm, thin-walled, filled with gelatin-like material and multilocular spaces?
Mucinous cystadenoma
Mucinous cystadenoma is found in women between the ages ___ - ___ years old
13-45
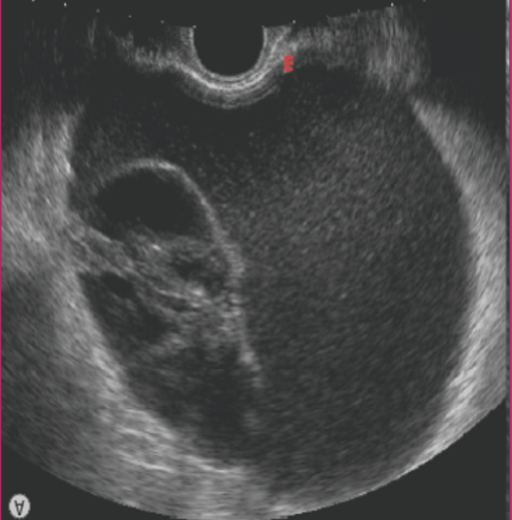
Mucinous cystadenoma is a benign tumor lined by the mucinous elements of the ______ and ______
endocervix; bowel
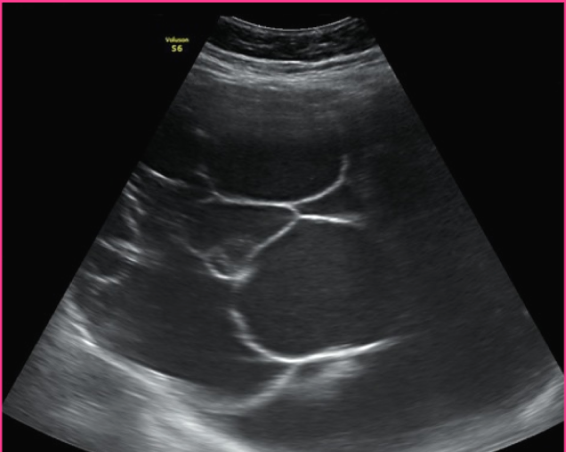
Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma is found in _____ women between the ages ___-____
older; 40-70
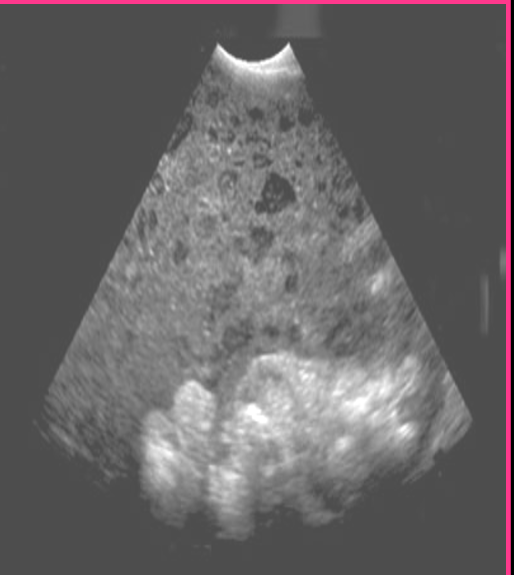
Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma is likely to rupture causing _______ ________ and _________ ________
Pseudomyxoma peritonei and loculated ascites
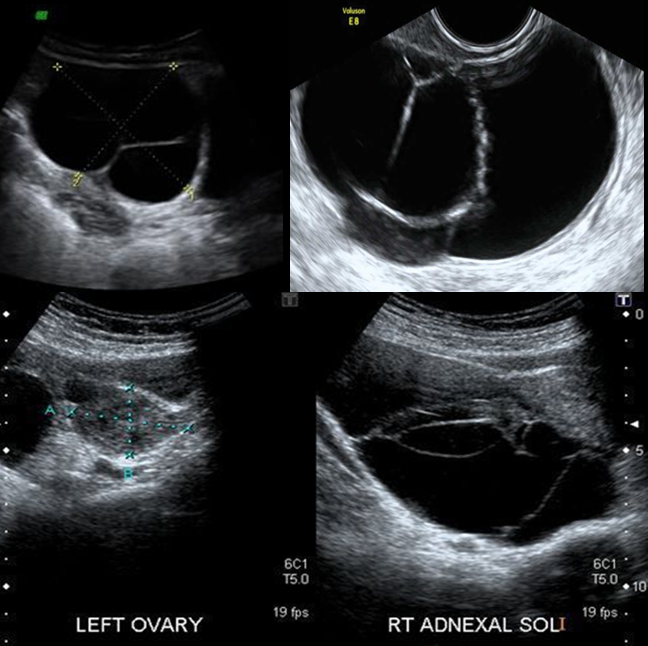
Serous cystadenoma is the _____ most common benign tumor of the ovary. Commonly seen in ______
second; pregnancy
What is the most common benign tumor of the ovary?
Dermoid
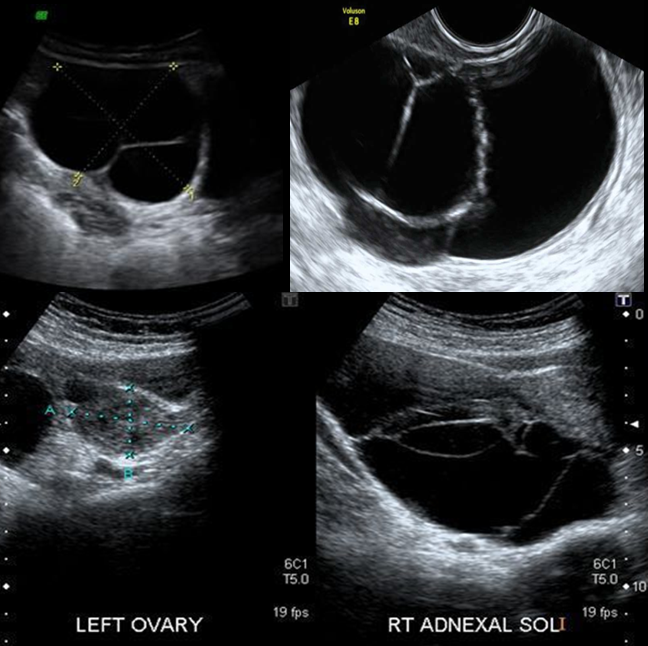
Serous cystadenomas are _____ than mucinous cysts, measuring up to ______
smaller; 20 cm
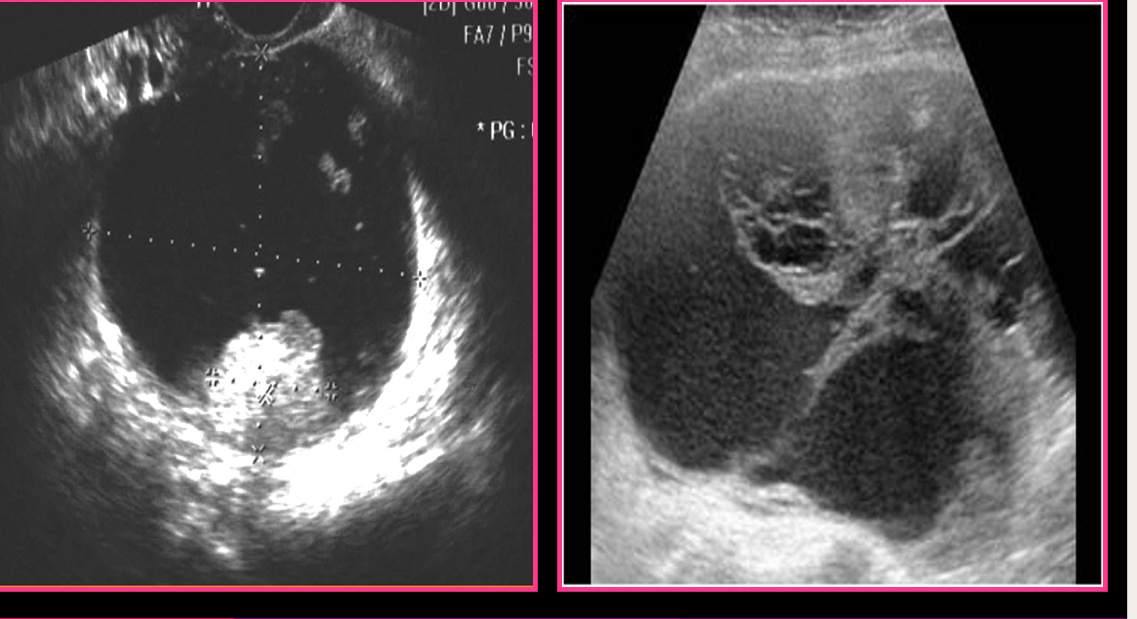
Serous cystadenocarcinoma is usually ______
bilateral
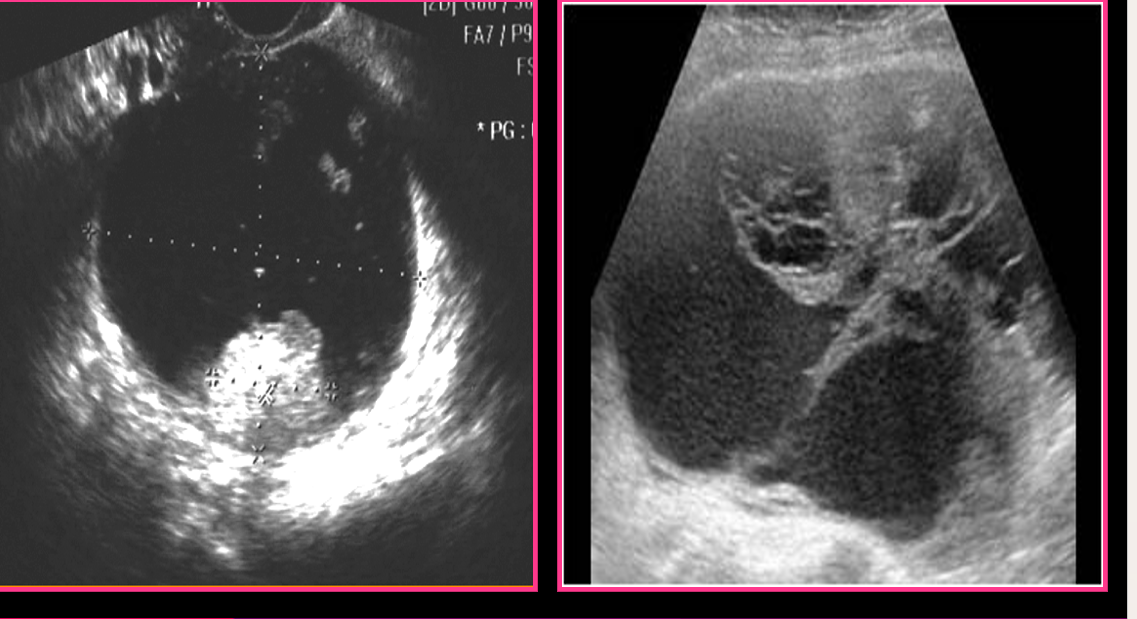
Serous cystadenocarcinoma can contain _____
calcifications
Endometrioid clear cell is the ____ most common epithelial malignancy.
second