Equine Disease and Lameness Exam 4
1/420
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
421 Terms
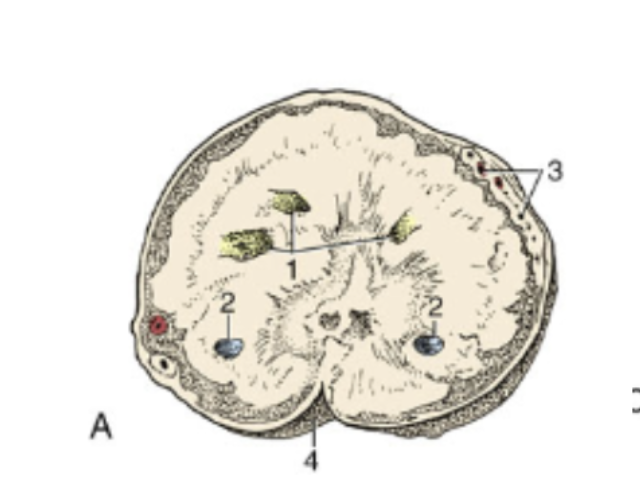
What type of ovary is this
quiet functional ovary
What type of ovary is this
ovary with corpus luteum
What type of ovary is this
ovary with follicle
What is made up of many fimbriae that surround the ovary collecting the ovulated egg
infundibulum
What is the “tortuous” narrow tube that the ovulated egg travels through to get to the uterus where fertilization occurs
isthmus
What is the structure made up of the infundibulum and isthmus
oviduct
What does the junction of the isthmus and uterus allow
only fertilized eggs can enter the uterus
When does the fertilized egg make it to the cuterus
approximately 6 days after fertilization
Is the conceptus very mobile or immobile
mobile
Due to the mobility of the conceptus, what is the movement and frequent contact with the endometrium thought to aid in
maternal recognition of pregnancy
What is the inner lining of the uterus
endometrium
What does maternal recognition of pregnancy prevent
regression of the corpus luteum on the ovary - which maintains pregnancy
Why is the equine conceptus highly unusual
takes a long time to form a blood connection with the mare
How long does it take for the conceptus to form a blood connection with the mare
40 days until about 150 days to complete
What is the placental attachment to the uterine wall
epitheliochorial and diffuse
What does it mean for the placenta to have an epitheliochorial attachment
the chorion portion of the fetal membranes is in contact with the mare’s uterine lining
What does it mean for the placental attachment to the uterine wall to be diffuse
the chorion has contact with the uterine lining all over, not just in specific locations
How is pregnancy diagnosed
by hand via rectal palpation or ultrasound
When can pregnancy be diagnosed by hand
25-30 days
When can pregnancy be diagnosed by ultrasound
11-14 days
By what point does the fetus have a heartbeat
day 28
How long are mares pregnant
335-340 days (can range from 300-385)
What are reasons that gestation be longer
mare has low plane of nutrition, cooler weather, or carrying a mule
What is the act of giving birth called
parturition/foaling
What are signs of foaling within the udder
distention 2-6 weeks prior
What are signs of foaling within the muscles and ligaments
relaxation of muscles and ligaments around the pelvis 7-10 days prior
What happens in the hours prior to foaling
separation from the herd
What happens 2-4 days prior to foaling
waxing
What happens during the first stage of parturition
fetal positioning
What are symptoms of fetal positioning
abdominal discomfort, restlessness, uterine contractions
What happens during the second stage of parturition
fetal membrane rupture, contractions, birth of the foal
What is the third stage of parturition
passing of fetal membranes
How soon after parturition should fetal membranes be passed
within 3 hours
What is waxing
pre-colostrum mucous plug at the tips of the teats
What should break when the foal is born
amniotic membrane
How long can the first stage of labor last
variable - a few hours to a day
How long is the second stage of parturition
15-30 minutes after the fetal membrane ruptures
What happens shortly after the water breaks
abdominal contractions, birth of foal
What is the inflamation/infection of the placenta
placentitis
What is the way placentitis occurs, where infectious organisms travel up the reproductive tract
ascending infection
What are the clinical signs of placentitis
vaginal discharge and premature “bagging up”
What is an ascending placentitis infection sometimes due to
poor vulvar conformation
What is the cause of placentitis where bacteria circulate through the bloodstream
hematogenous
Where does placentitis occur
diffusely across the placenta or localized infection
What can placentitis lead to
detaching of the placenta or issues at parturition and can be difficult to break
How can placentitis be prevented
check routinely throughout pregnancy via ultrasound
What is the pathology where there are amorphous pieces of allantoic material often delivered along with the fetus
hippomanes
How do hippomanes form
fluid and particulates collect around a central nidus
What are hippomanes mostly comprised of
mucoproteins and calcium phosphate
What do hippomanes look like
beige-brown-green color, firm, several cm in diameter
Are hippomanes pathologic (related to disease)
no
What are the issues with twins
rarely born full term and alive, often retained membranes and a dystocia
What is recommended when finding twins
terminate one or both (can pinch one)
When should twins be terminated
35 days or less
What is the pathology where the outer fetal membranes (chorion and allantois) separate from the uterine lining before the amnion ruptures
premature chorioallantois separation “red bag”
What can premature chorioallantois separation quickly result in
foal not getting enough oxygen and dying via suffocation
Is premature chorioallantois separation an emergency
yes
What is premature chorioallantois separation caused by
placentitis, twins, fescue toxicity, or no reason at all
What is the foaling problem that does not allow the mare to give birth on her own
dystocia
Is dystocia caused by the mare or fetus
either
Why is dystocia a serious problem
often fatal for the mare and/or foal
What must be considered when assisting a mare with a dystocia
cleanliness and gentleness to prevent trauma of vulva, vagina, or uterus
Whom should dystocia be addressed by
veterinarian or experienced caretaker
What are the mare causes of dystocia
uterine atony, uterine torsion
What is the mare cause of dystocia which is failure of the uterine muscles to contract
uterine atony
What is the mare cause of dystocia where the uterus has twisted on its axis - cranial or caudal to the cervix
uterine torsion
What are the foal causes of dystocia
malposition, fetal malformation
What should be cleaned well when addressing a dystocia
external vulva and surrounding tissue with iodine and warm water
Why is cleanliness essential when addressing a dystocia
to prevent infection of the mare’s reproductive tract
What is there never too much of when addressing a dystocia
too much lubrication
What is the general rule of traction when addressing a dystocia
if traction (pulling) requires more strength than two strong men, consider alternative method
What is often required to aid in grip and traction when addressing dystocia
obstetrical chains
What are the secondary options for addressing dystocia
controlled vaginal delivery, casarean section, fetotomy
What is the way to address dystocia where the mare’s hindquarters are hoisted to push the GI tract cranially
controlled vaginal delivery
What is required for a controlled vaginal delivery
mare must be anesthetized
What is the way to address a dystocia that is delivery of the foal by an abdominal and uterine incision
cesarean section
What is the option of addressing dystocia where the fetus is cut into manageable pieces within the uterus to be delivered vaginally with assistance
fetotomy
When is a fetotomy done
when cesarian section is not an option
What must be examined after every delivery
fetal membranes
Where are the fetal membranes ruptured in a normal birth
the cervical star
What is the weakened area of the chorioallantois where the fetal membranes rupture
cervical star
What should the fetal membranes appear as
the letter F
What is included in the fetal membrane’s “letter F”
two uterine horns and the uterine body
What is the condition where missing pieces or the entirety of fetal membranes have not passed within three hours called
retained placenta
How is a retained placenta treated in early cases
oxytocin to promote uterine contractions
How is a retained placenta treated in cases over 8 hours
antibiotics and anti-inflammatories
What does a retained placenta predispose the mare to
laminitis
What is the loss of pregnancy during the first 42-50 days of pregnancy called
early embryonic death
What is the most common time to lose a fetus
during the first 42-50 days (early embryonic dreath)
What is a loss of pregnancy after 50 days of pregnancy called
abortion
What condition causes abortions, especially in the third trimester
equine herpes virus (EHV)
What type of pathogen is equine herpes virus
airborne
How is equine herpes virus transmitted
easily - shared water, nose-to-nose contact, neighboring stalls
When should a horse be vaccinated to equine herpes virus
3, 5, 7, and 9 months of pregnancy
Who should be vaccinated for equine herpes virus other than the pregnant horse
other horses in the barn
What are the symptoms of EHV-1 in the mare
no disease, can have normal placenta or edematous (thickened with intercellular fluid)
What are the EHV-1 symptoms in the fetus
fetal lesions - swelling and fluid accumulation under the skin, jaundice, enlarged liver with pale lesions, large amounts of intrathoracic fluid
What can twinning cause
abortion
When does the mare typically lose the fetus when twinning
8-9 months
What symptom will the mare usually experience when abortion due to twinning
premature lactation