3.1.1-2 - Monomers and polymers + Carbohydrates
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Polymers
Large, complex molecules made of long chains of monomers

Monomers
Small, basic molecular units
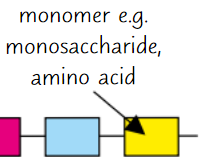
Monomer examples
Monosaccharides, amino acids, nucleotides
Carbohydates contain ____
C, H, O
Monosaccharide examples
Glucose, fructose, galactose
Carbohydrates are (mono/polysaccharides)
Polysaccharides
Glucose
Hexose sugar - 6 C atoms per molecule
Has 2 isomers - alpha (α) and beta (β)
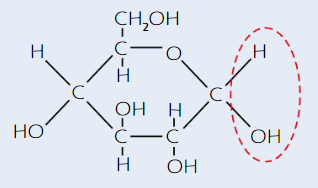
α-glucose structure
(alpha - H is on top)
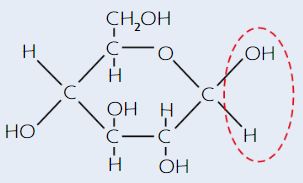
β-glucose structure
(beta - H is on bottom)
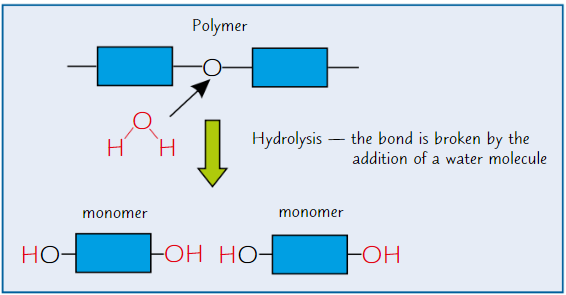
Condensation reaction
Two molecules join with formation of new chemical bond
+ water molecule released
Monosaccharides are joined by ____
condensation reactions
Glycosidic bond
Bond between two monosaccharides
Sucrose
Disaccharide formed by glucose + fructose (via condensation reaction)
Lactose
Disaccharide formed by glucose + galactose (via condensation reaction)
Maltose
Disaccharide formed by glucose + glucose (via condensation reaction)
Hyrolysis reactions
Breaking of chemical bond between monomers using water molecule
What is starch made of?
Mixture of amylose + amylopectin - polysaccharides of α-glucose
Plants store excess glucose as ____
starch
Why is starch good for storage?
Insoluble in water → doesn’t affect water potential
→ doesn’t cause water to enter cells by osmosis
→ good for storage
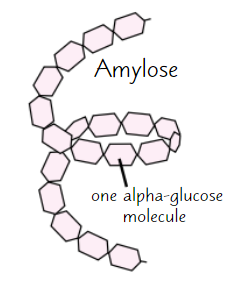
Amylose
Long, unbranched chain of α-glucose
Angles of glycosidic bonds → coiled structure
→ compact
→ good for storage
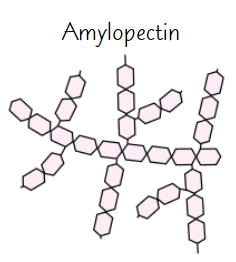
Amylopectin
Long, branched chain of α-glucose
Side branches allow enzymes that break down molecule to reach glycosidic bonds easily
→ glucose can be released quickly
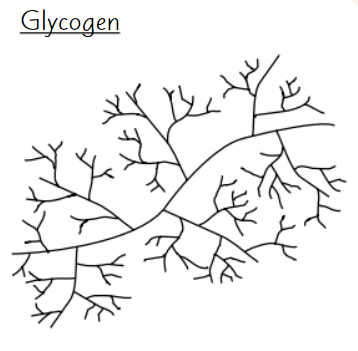
Glycogen
Polysaccharide of α-glucose
Animals store excess glucose as glycogen
Glycogen structure
Highly branched structure
→ stored glucose can be released quickly
Compact
→ good for storage
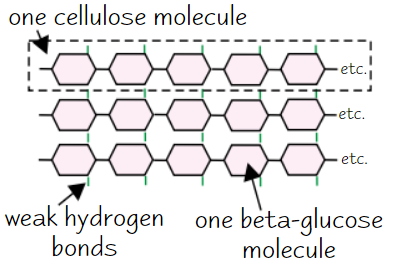
Cellulose
Made of long, unbranched chains of β-glucose
When β-glucose molecules bond, they form straight cellulose chains
Cellulose chains linked by H bonds to form microfibrils (strong fibres)
→ strong fibres make cellulose a good structural support for cells
Which sugars are reducing sugars?
All monosaccharides + some disaccharides (e.g. maltose, lactose)
Test for reducing sugars
Add Benedict’s reagent (blue) to sample + heat in water bath at 100ᵒC
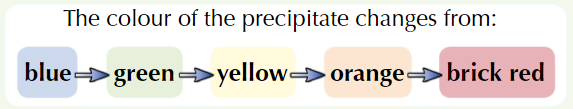
If positive test, coloured ppt forms
Higher conc. of reducing sugar = further colour change
Test for non-reducing sugars
If reducing sugar test negative, must do non-reducing sugar test
Get new sample of test solution, add dilute hydrochloric acid + heat in water bath at 100ᵒC
Add sodium hydrogencarbonate to neutralise
Carry out Benedict’s test (reducing sugar test)
If positive test, coloured ppt forms
If negative, solution stays blue → no sugar in solution
Test for starch
Add iodine dissolved in potassium iodide solution to sample
If positive test, sample changes from browny-orange → blue-black