Diagram of OCR A-Level Chemistry A Organic Synthesis, 28.3: Synthetic Routes | Quizlet
1/214
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
215 Terms
Alkene + hydrogen /nickel catalyst/423K=
alkane
Alkene + bromine /room temperature=
dihaloalkane
Alkene + HCl(g/aq) /room temperature=
haloalkane (mixed products)
Alkene + H2O(g) /H3PO4=
alcohol (mixed products)
Primary alcohol + 2[O] /excess K2Cr2O7/H2SO4/reflux=
carboxylic acid
Primary alcohol + [O] /K2Cr2O7/H2SO4/distil=
aldehyde
Secondary alcohol + [O] /K2Cr2O7/H2SO4/reflux=
ketone
Alcohol + H3PO4 or H2SO4/reflux=
alkene + H2O
Alcohol + HBr /H2SO4/reflux=
haloalkane + H2O
Haloalkane + NaOH(aq)=
alcohol + sodium halide
Haloalkane + H2O=
alcohol + halide acid
Haloalkane + NH3=
primary amine + halide ion
Benzene + HNO3 /Conc. H2SO4/50C=
nitrobenzene + H2O
Benzene + 2HNO3 /Conc. H2SO4/70C=
dinitrobenzene + 2H2O
Benzene + Br2 /FeBr3 or AlBr3/room temperature & pressure
bromobenzene + HBr
Benzene + Cl2 /FeCl3 or AlCl3/room temperature & pressure
chlorobenzene + HCl
Benzene + haloalkane /AlCl3=
ethylbenzene + Hcl
Benzene + acyl chloride /AlCl3=
aromatic ketone + Hcl
Phenol + NaOH=
sodium phenoxide + H2O
Phenol + 3Br2 /room temperature=
2,4,6-tribromophenol + 3HBr
Phenol + dilute HNO3 /room temperature
2-nitrophenol or 4-nitrophenol
Aldehyde + [O] /K2Cr207/H2SO4/reflux=
carboxylic acid
Aldehyde + 2[H] /NaBH4/H20=
primary alcohol
Ketone + 2[H] /NaBH4/H2O=
secondary alcohol
Aldehyde + HCN(H2SO4/NaCN)=
hydroxynitrile
Carboxylic acid + metal=
carboxylate salt + H2
2Carboxylic acid + metal oxide=
carboxylate salt + H2O
Carboxylic acid + alkali=
carboxylate salt + H2O
2Carboxylic acid + carbonate=
carboxylate salt + H2O + CO2
Carboxylic acid + alcohol /Conc. H2SO4=
ester + H2O
Ester + H2O /dilute aqueous acid/reflux=
carboxylic acid + alcohol
Ester + OH-(aq) /reflux=
carboxylate ion + alcohol
Ester + SOCl2=
acyl chloride + SO2(g) + Hcl(g)
Acyl chloride + alcohol=
ester + HCl
Acyl chloride + phenol=
phenyl ester + HCl
Acyl chloride + 2NH3=
primary amide + ammonium chloride
Acyl chloride + 2amine
secondary amide + methyl ammonium chloride
Acid anhydride + H2O=
2carboxylic acid
Acid anhydride + alcohol=
carboxylic acid + ester
Acid anhydride + phenol=
carboxylic acid + ester
Acid anhydride + NH3=
primary amide + carboxylic acid
Acid anhydride + amine=
secondary amide + carboxylic acid
Amine + acid=
ammonium salt
1) Haloalkane + excess NH3=
2) Ammonium salt + NaOH=
1) ammonium salt
2) primary amine + sodium chloride + H2O
1) Haloalkane + primary amine=
2) Diammonium salt + NaOH=
1) diammonium salt
2) secondary amine
1) Haloalkane + secondary amine=
2) Triammonium salt + NaOH=
1) triammonium salt
2) tertiary amine
1) Nitrobenzene + 6[H] /tin/conc. HCl=
2) Phenylammonium chloride + excess NaOH=
1) phenylammonium chloride
2) phenylamine + water
Amino acid + HCl=
salt(NH3+) + Cl-
Amino acid + NaOH=
salt(COO-Na+) + H2O
Amino acid + alcohol /Conc. H2SO4=
ester
Amino acid at isoelectric point=
zwitterion (COO- and NH3+)
diester + diester=
polyester + H2O
Dicarboxylic acid + diol=
polyester + H2O
diamino acid + diamino acid=
polyamide + H2O
Diamine + diacyl chloride=
polyamide + HCl
Polyester + H+ /H2O=
dicarboxylic acid + diol
Polyester + NaOH /H2O=
diol + dicarboxylate(COO-Na+) salt
Polyamide + H+ /H2O=
dicarboxylic acid + diammonium(NH3+) salt
Polyamide + NaOH /H2O=
diamine + dicarboxylate(COO-Na+) salt
how do alkanes produce CO2 + H2O
- complete combustion
- via excess O2

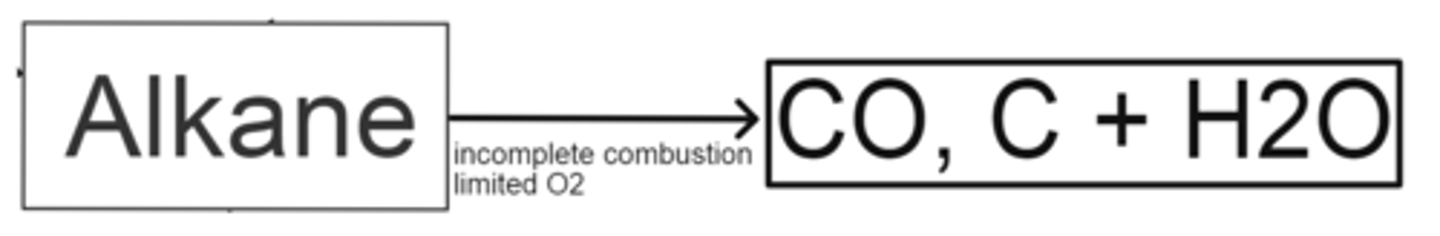
how do alkanes produce CO, C + H2O
- incomplete combustion
- limited O2
how do we get from an alkane to a haloalkane
- via mechanism called
- free radical substitution:
- step 1:
=== turning halogen into halogen free radical
=== via in the presence of UV light
- step 2:
=== propagation step
- step 3:
=== termination step
how do we get from an alkene to an alkane and name the mechanism
- Hydrogen
- Ni Catalyst
- 150°C temp
- electrophilic addition
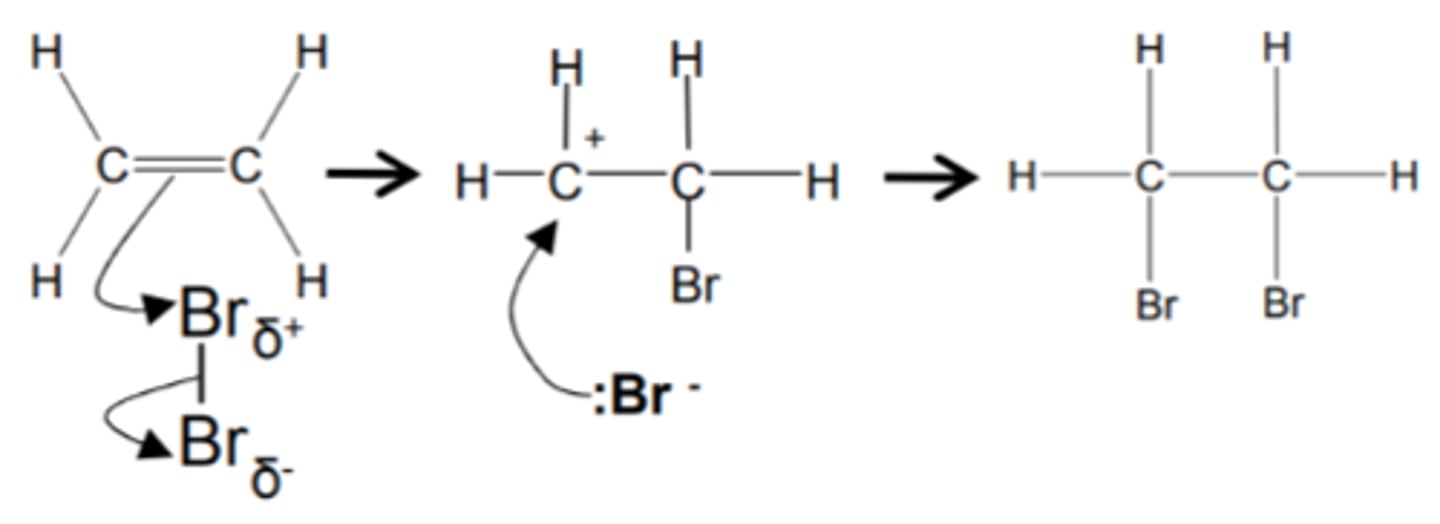
how do we get from an alkene to a dihalogenoalkane and name the mechanism
- halogen
- Cl2, Br2, I2 for example
- at room temperature
- Electrophilic addition
show and name the mechanism for alkene to dihaloalkane
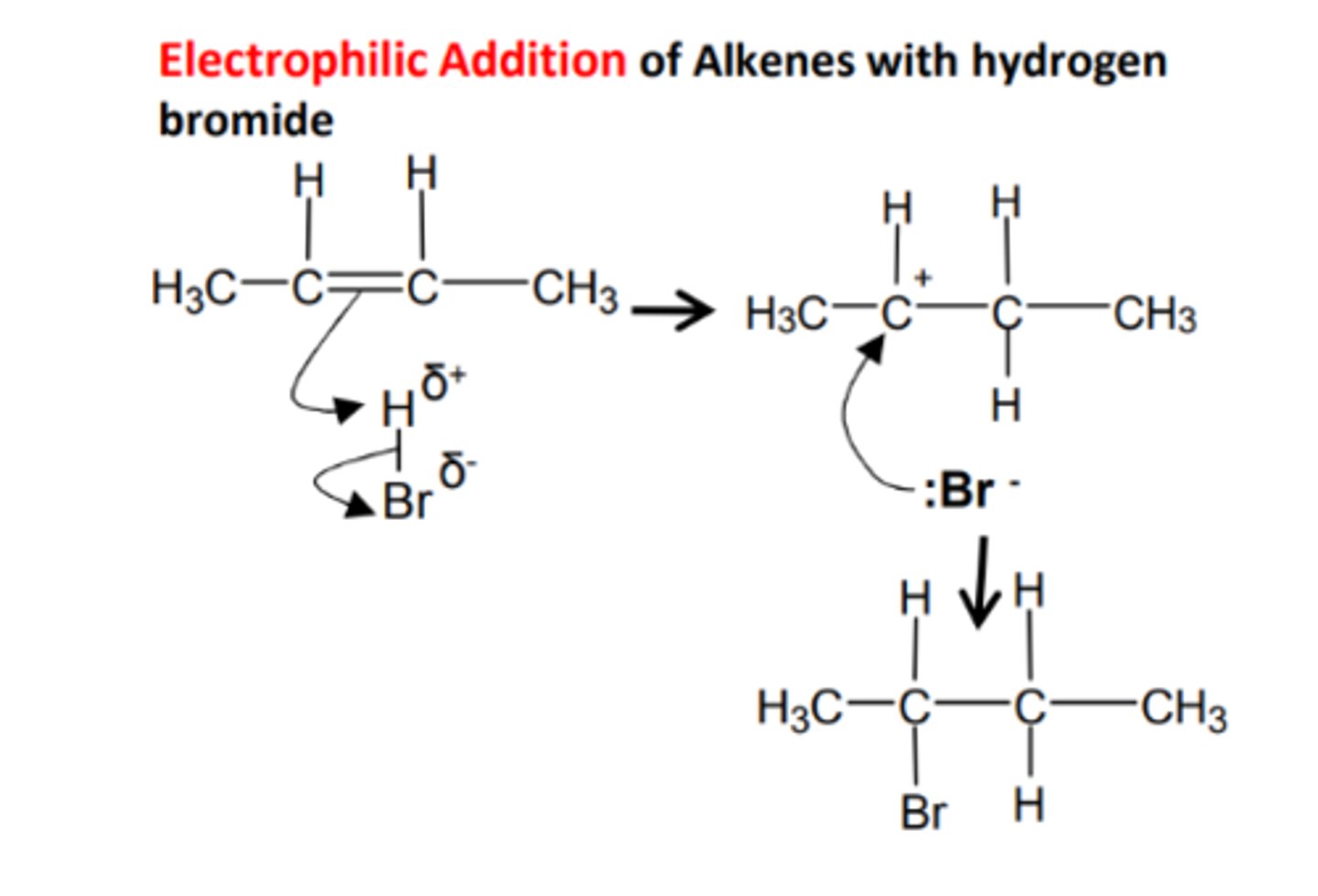
how do we get from an alkene to a halogenoalkane and name the mechanism
- hydrogen halide
- at room temperature
- Electrophilic addition
show and name the mechanism for alkene to haloalkane
Electrophilic addition
name two ways to get from an alkene to an alcohol
- directly
- indirectly using H2SO4
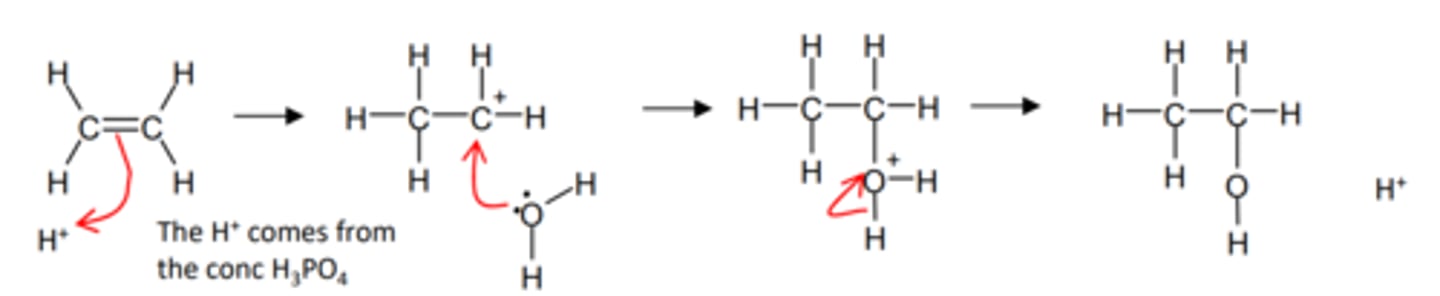
how do we get from an alkene to an alcohol directly and name the mechanism
- hydration reaction
- Electrophilic addition
- 300°C
- 70 atm
- H3PO4 acid
- which acts as a catalyst
- by providing the H+ ion
show and name the mechanism for alkene to alcohol directly
Electrophilic addition
how do we get from an alkene to an alcohol indirectly using H2SO4 and name the mechanism
IN 2 STEPS:
step 1:
=== concentrated H2SO4
=== room temp
=== producing alkyl hydrogen sulphate
=== Electrophilic addition
step 2:
=== alkyl hydrogen sulphate to alcohol
=== hydrolysis via warm water
show and name the mechanism for first step in making alcohol from alkene indirecty, where alkene is converted to alkyl hydrogen sulphate
Electrophilic addition
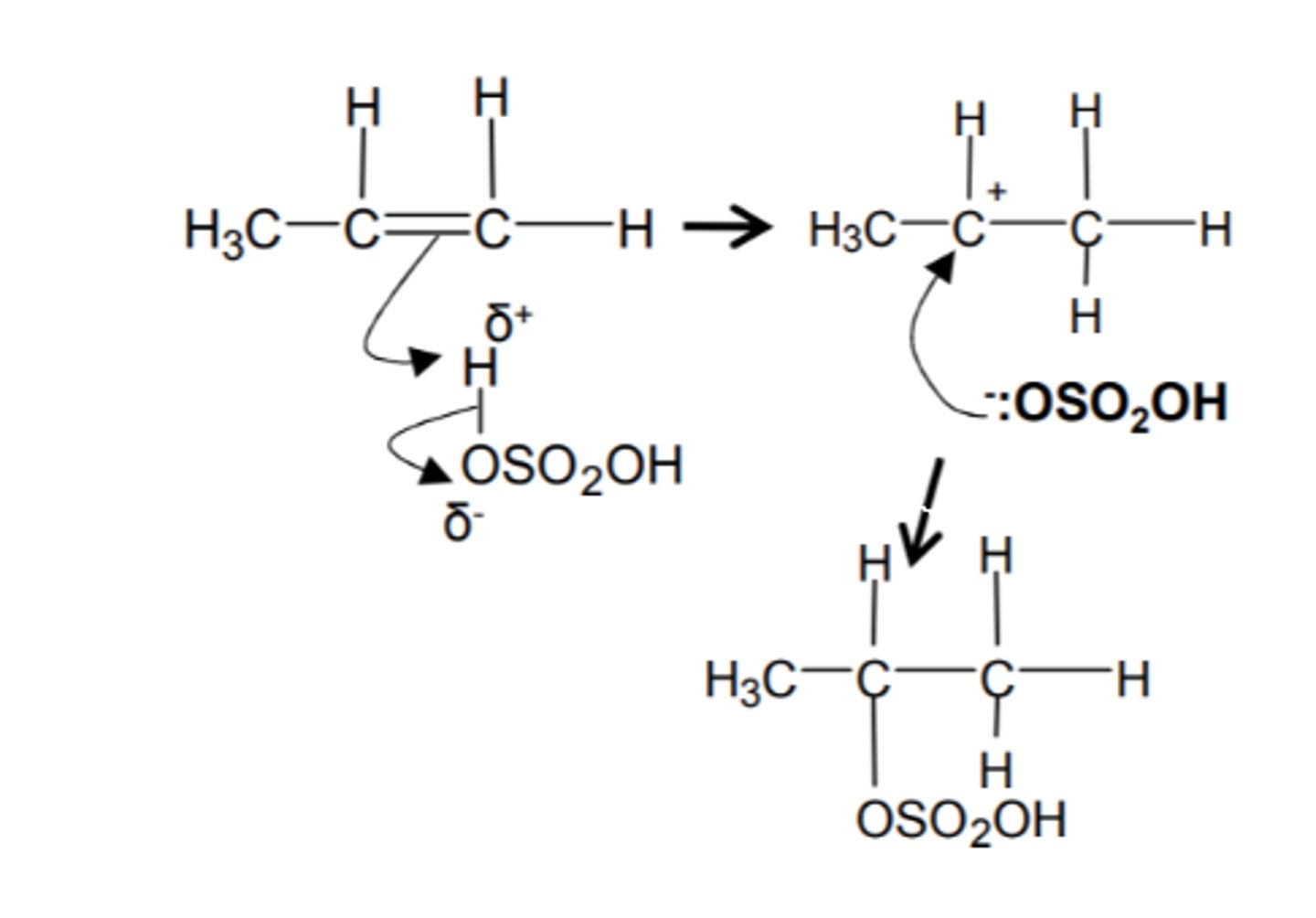
how do we make a large number of smaller alkenes to 1 large alkene and name the mechanism
- radial initiator
- addition polymerisation
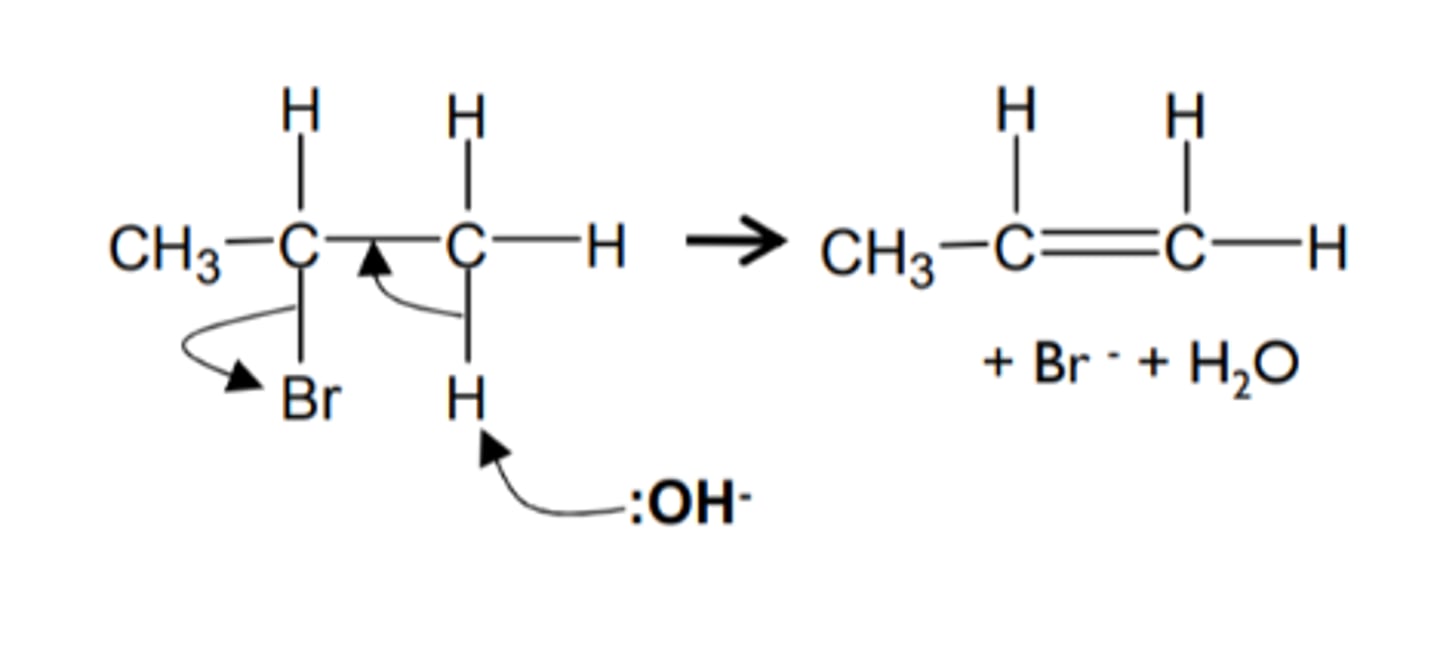
how do we get from a haloalkane to an alkene and name the mechanism
- KOH (ethanolic) reagent
- heat under reflux
- elimination
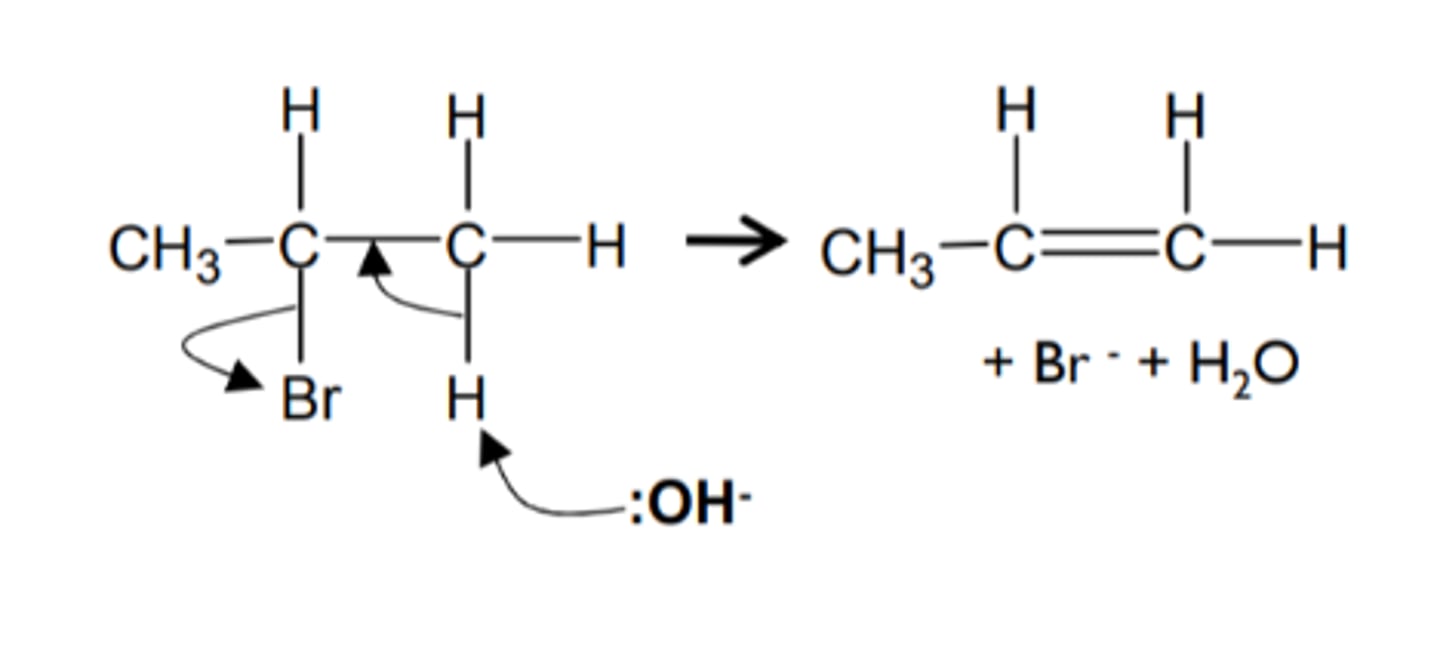
show and name the mechanism for a haloalkane to an alkene and name the mechanism
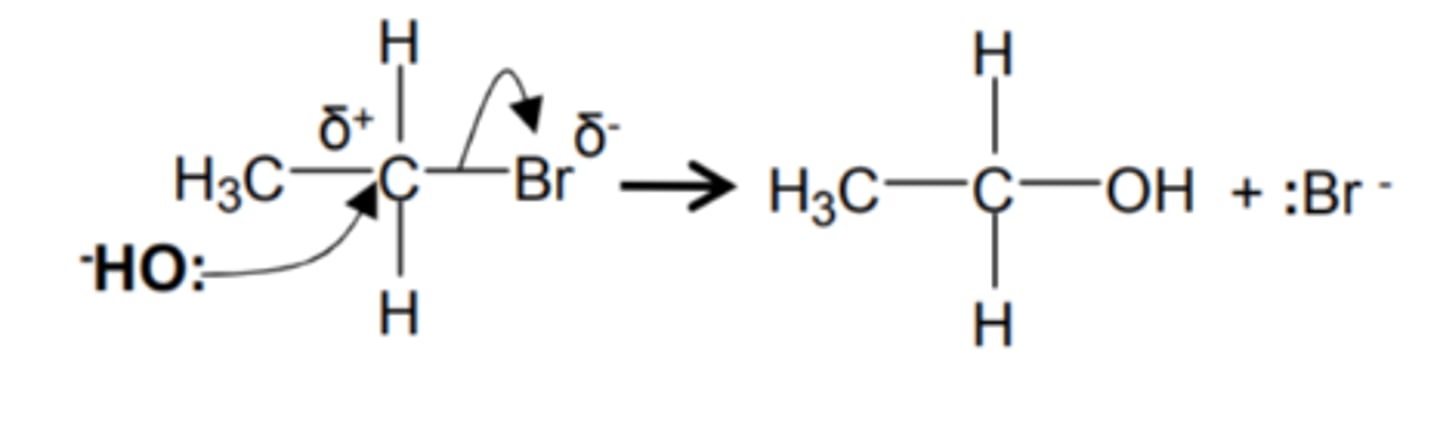
how do we get from a haloalkane to an alcohol and name the mechanism
- KOH (ethanolic) reagent
- heat under reflux
- nucleophilic substitution
show and name the mechanism for a haloalkane to an alcohol and name the mechanism
nucleophilic substitution
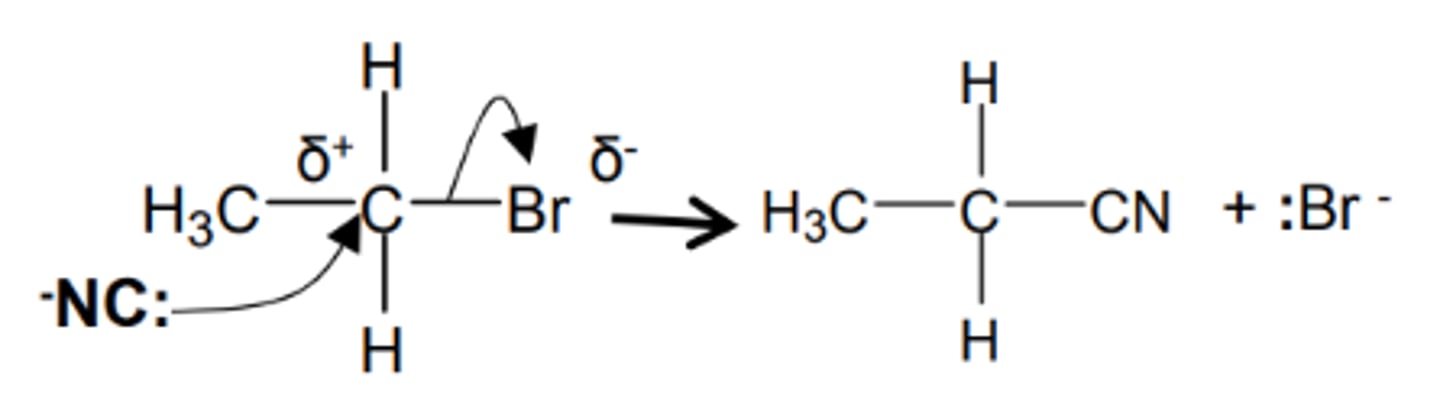
how do we get from a haloalkane to an nitrile and name the mechanism
- KCN dissolved in ethanol
- heat under reflux
- nucleophilic substitution
show and name the mechanism for a haloalkane to an nitrile and name the mechanism
nucleophilic substitution
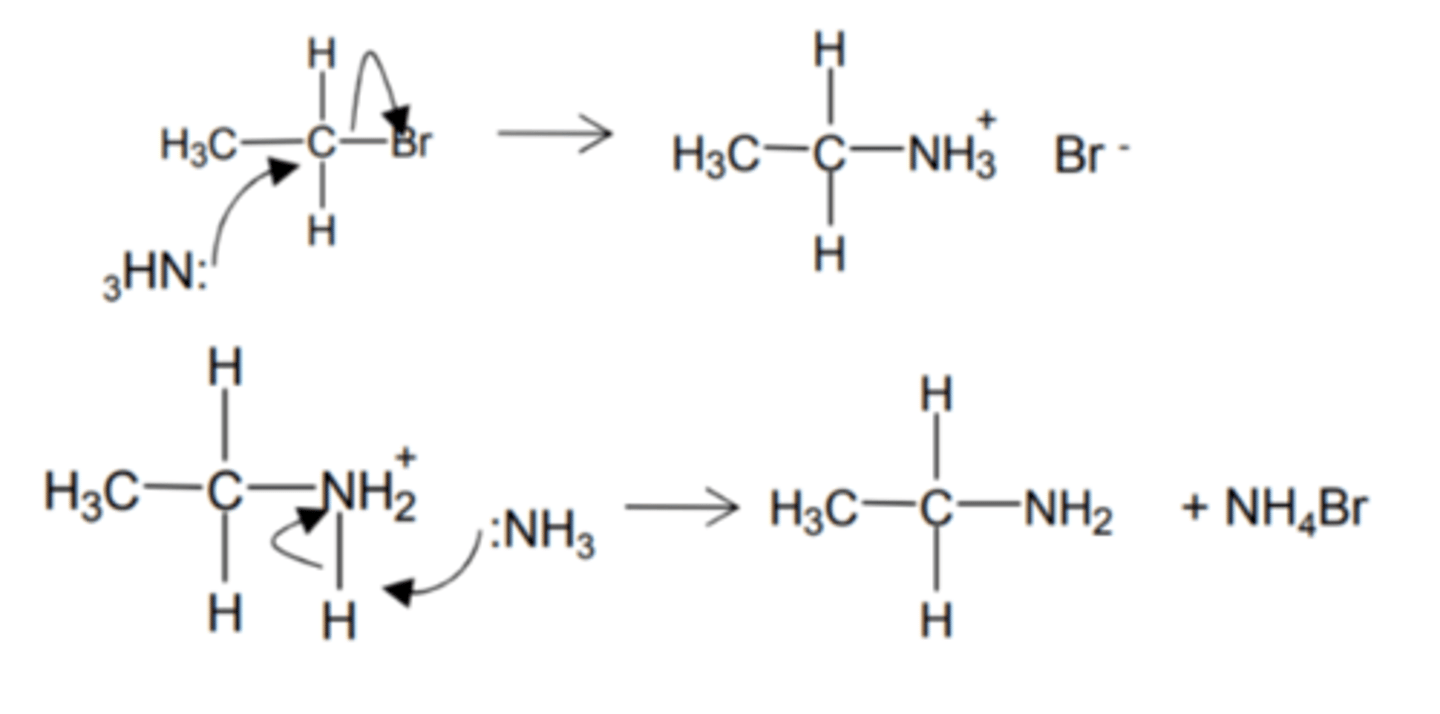
how do we get from a haloalkane to an 1° Amine and name the mechanism
- NH3 ethanolic
- heat in a sealed tube
- under pressure
- nucleophilic substitution
show and name the mechanism for a haloalkane to an 1° Amine and name the mechanism
nucleophilic substitution
how do we get from a 1° alcohol to an aldehyde and name the type of reaction
- acidified K2Cr2O7
- distill out aldehyde
- as it forms
- using simple distillation apparatus
- oxidation
how do we get from a 1° alcohol to a Carboxylic acid and name the type of reaction
- excess acidified K2Cr2O7
- heat under reflux
- oxidation
how do we get from a 2° alcohol to a ketone and name the type of reaction
- excess acidified K2Cr2O7
- heat under reflux
- oxidation
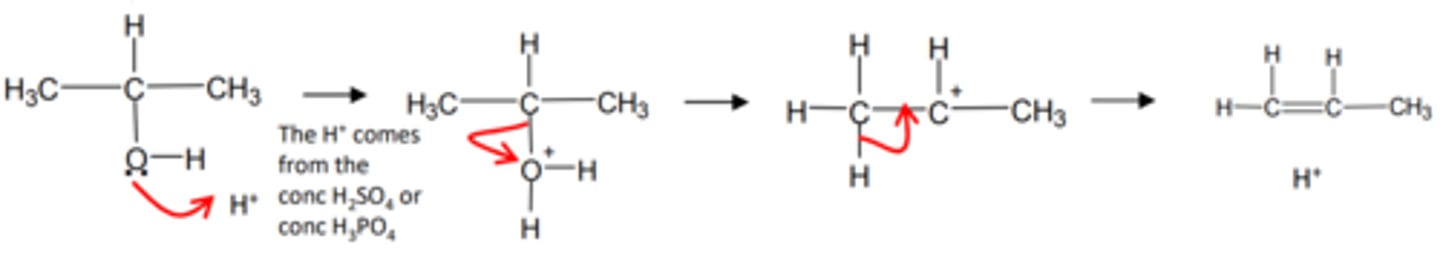
how do we get from an alcohol to an alkene and name the mechanism
- conc H2SO4/ conc H3PO4
- dehydration
- elimination
show and name the mechanism for a alcohol to an alkene and name the mechanism
elimination
how do we get from an aldehyde to a 1° alcohol and name the type of reactions
- Method 1: Reduction
=== the addition of LiAlH or NaBH
=== at room temp and pressure
=== with a weak acid
=== which will supply the H+ ion.
- Method 2: Catalytic hydrogenation
=== where H+ and a Nickel catalyst
=== are added at HIGH PRESSURE
show and name the reduction mechanism for an aldehyde to a 1° alcohol
nucleophilic addition
how do we get from an aldehyde to a hydroxynitrile and name the mechanism
- KCN
- HCl aqueous
- nucleophilic addition
show and name the reduction mechanism for an aldehyde to a hydroxynitrile
nucleophilic addition
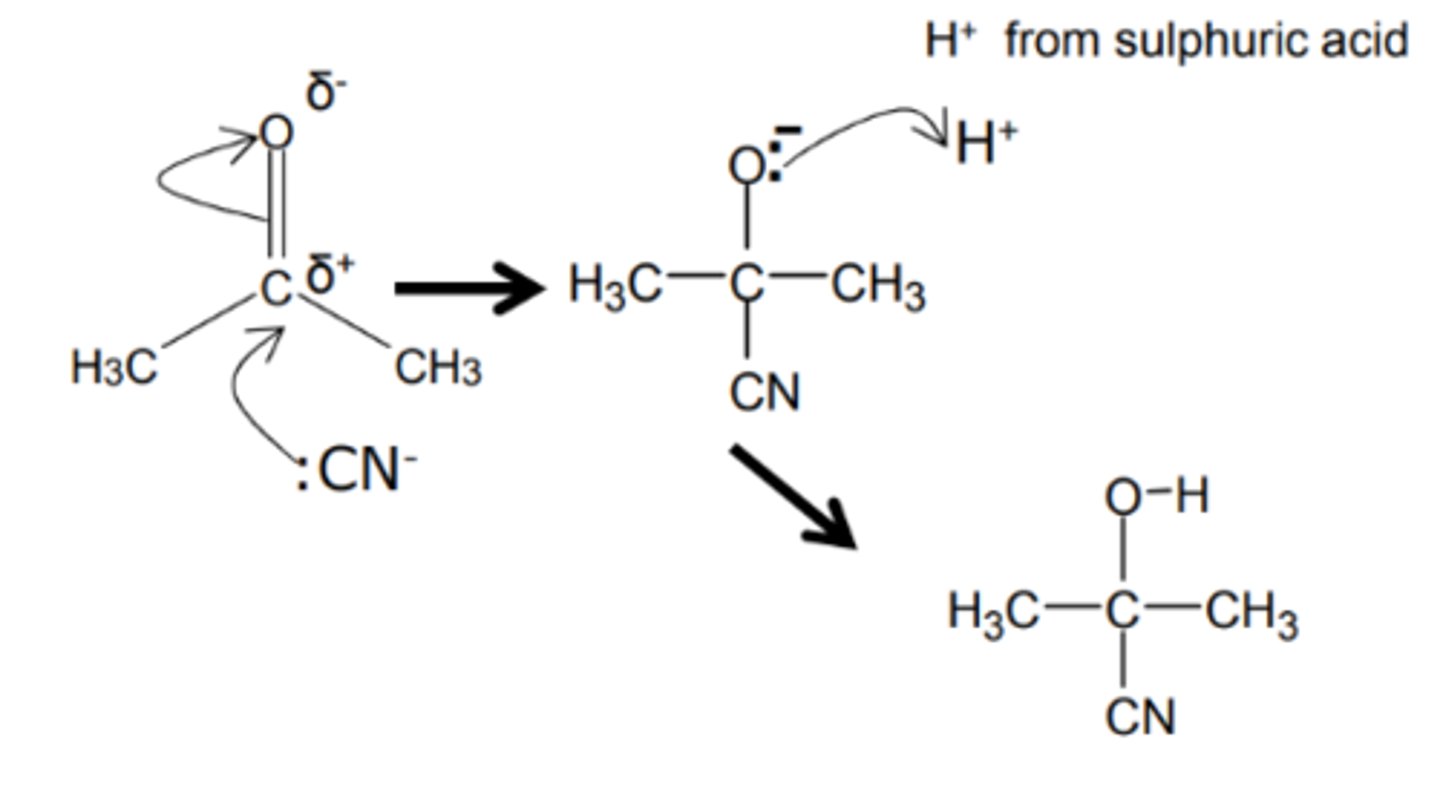
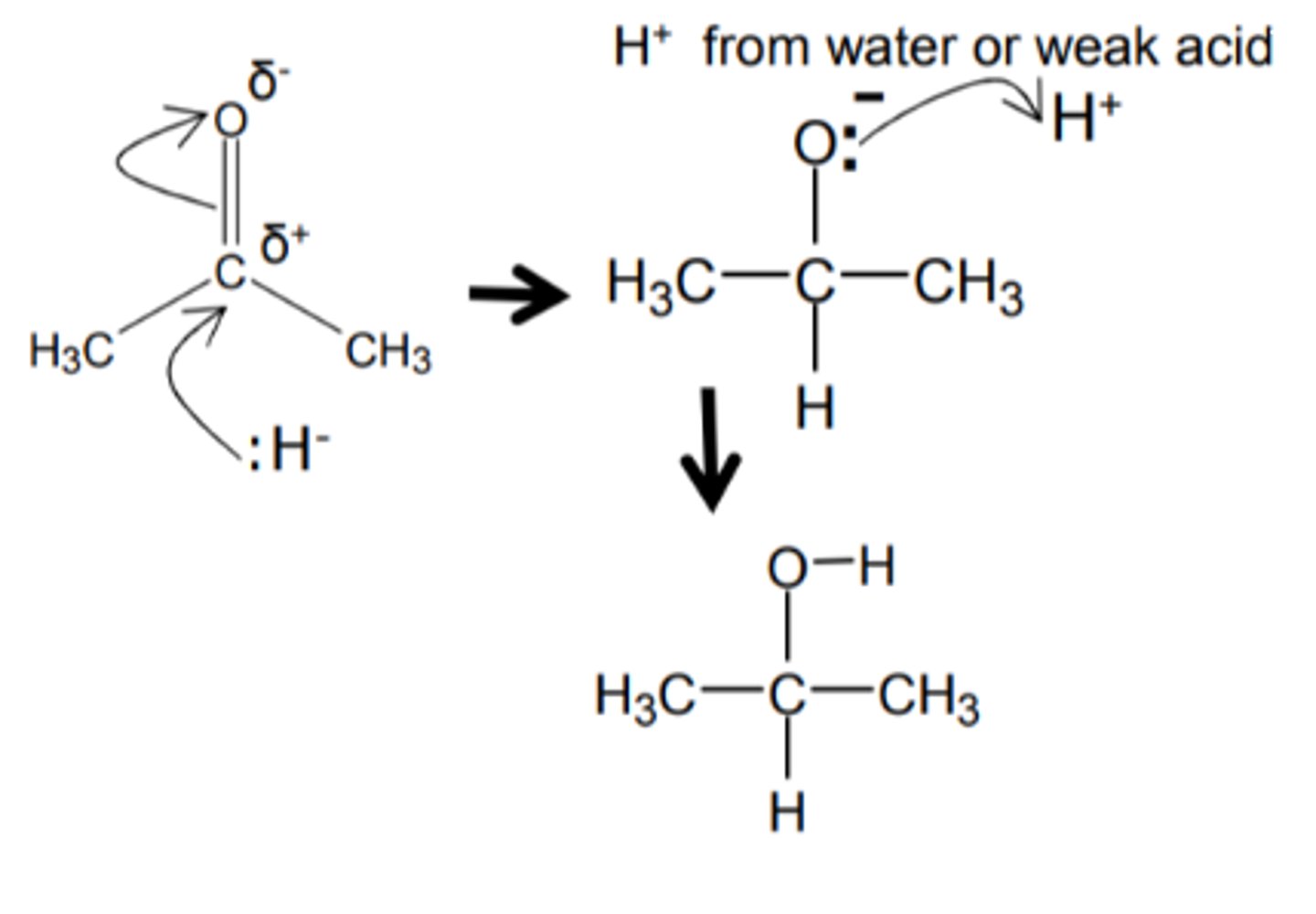
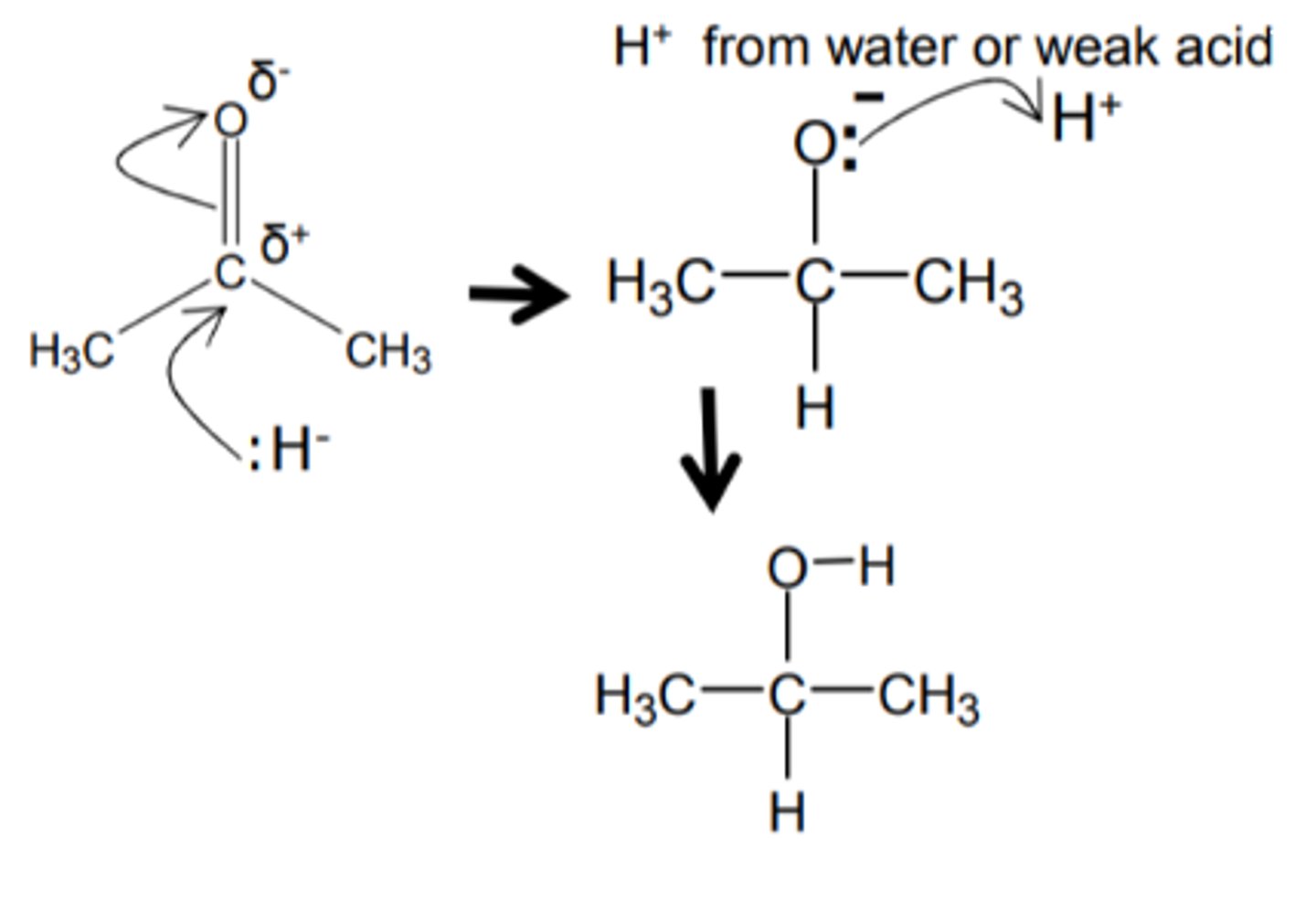
how do we get from a ketone to a 2° alcohol and name the type of reaction
- Method 1: Reduction
=== the addition of LiAlH or NaBH
=== at room temp and pressure
=== with a weak acid
=== which will supply the H+ ion.
=== nucleophilic addition
- Method 2: Catalytic hydrogenation
=== where H+ and a Nickel catalyst
=== are added at HIGH PRESSURE
show and name the reduction mechanism for a ketone to a 2° alcohol and name the mechanism
nucleophilic addition
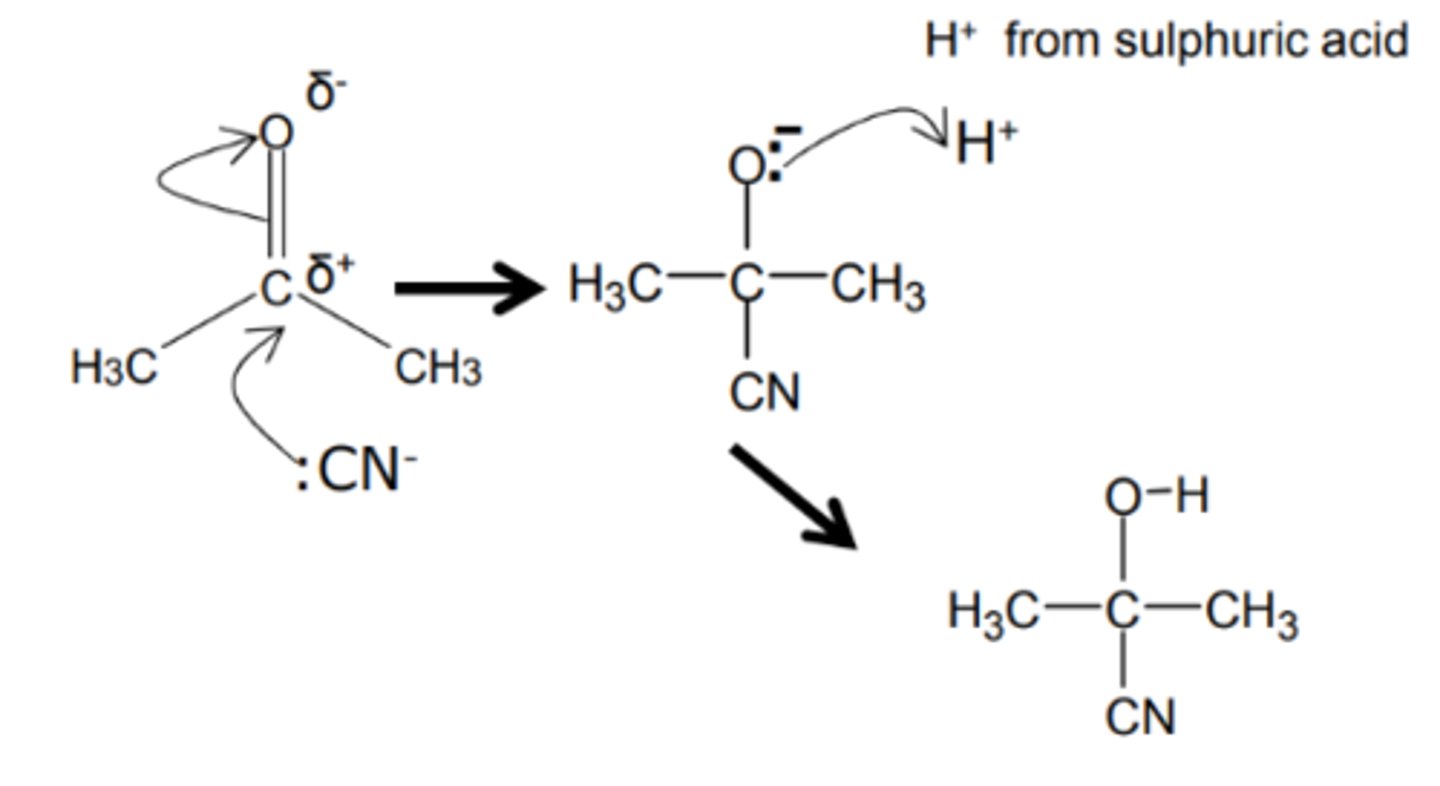
how do we get from an ketone to a hydroxynitrile and name the mechanism
- KCN
- HCl aqueous
- nucleophilic addition
show and name the reduction mechanism for an ketone to a hydroxynitrile
nucleophilic addition
how do we get from a nitrile to a COOH and name the type of reaction
- dilute HCl (aq)
- Acid Hydrolysis
how do we get from a nitrile to a sodium carboxylate salt and name the type of reaction
- dilute NaOH (aq)
- Alkaline Hydrolysis
how do we get from a nitrile to an amine and name the type of reaction
- Hydrogen
- Ni Catalyst
- Reduction
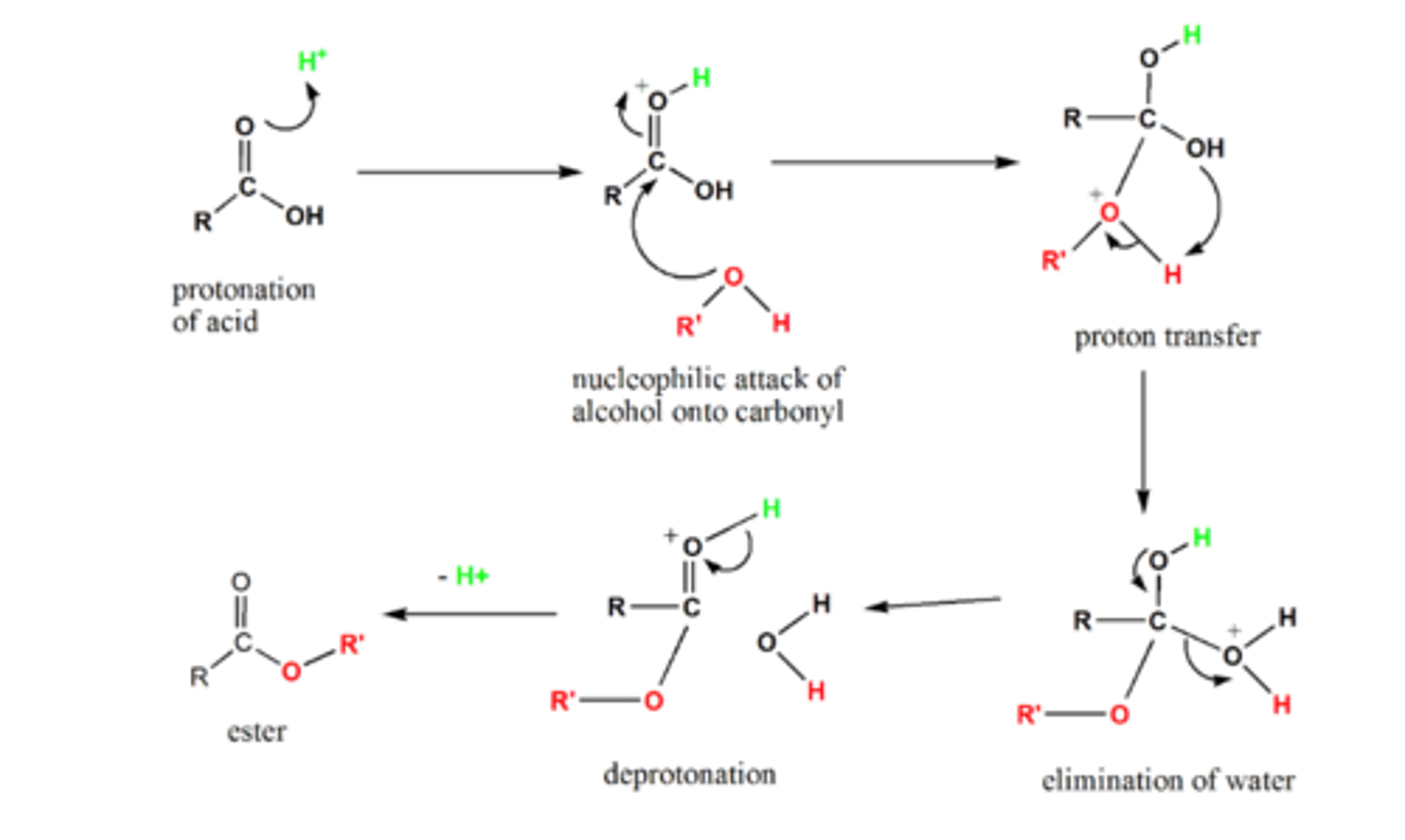
how do we get from an COOH to an ester and name the mechanism
- add any OH
- add conc H2SO4
- which acts as a catalyst
- nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction
show and name the reduction mechanism for an COOH to an ester
nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction
how do we get from a 1° amine to 2° amide and name the mechanism
- Acyl chloride/ Acid anhydride
- room temp
- Nu add/elim