Geography CGC1W exam flashcards
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
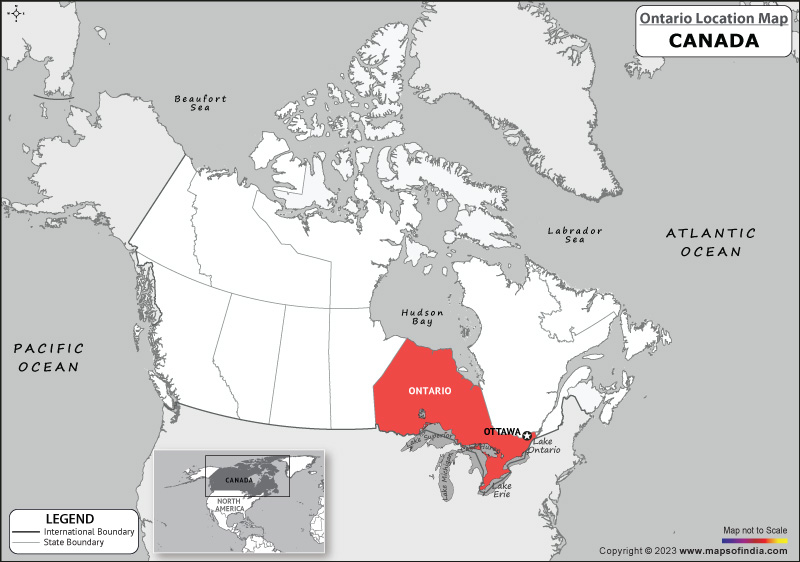
Where is Ontario located?
It is located…
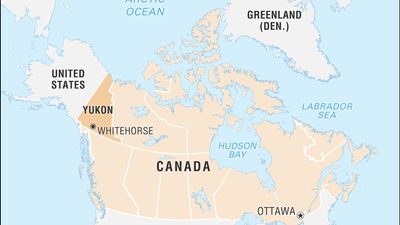
Where is Yukon located?
It is located…
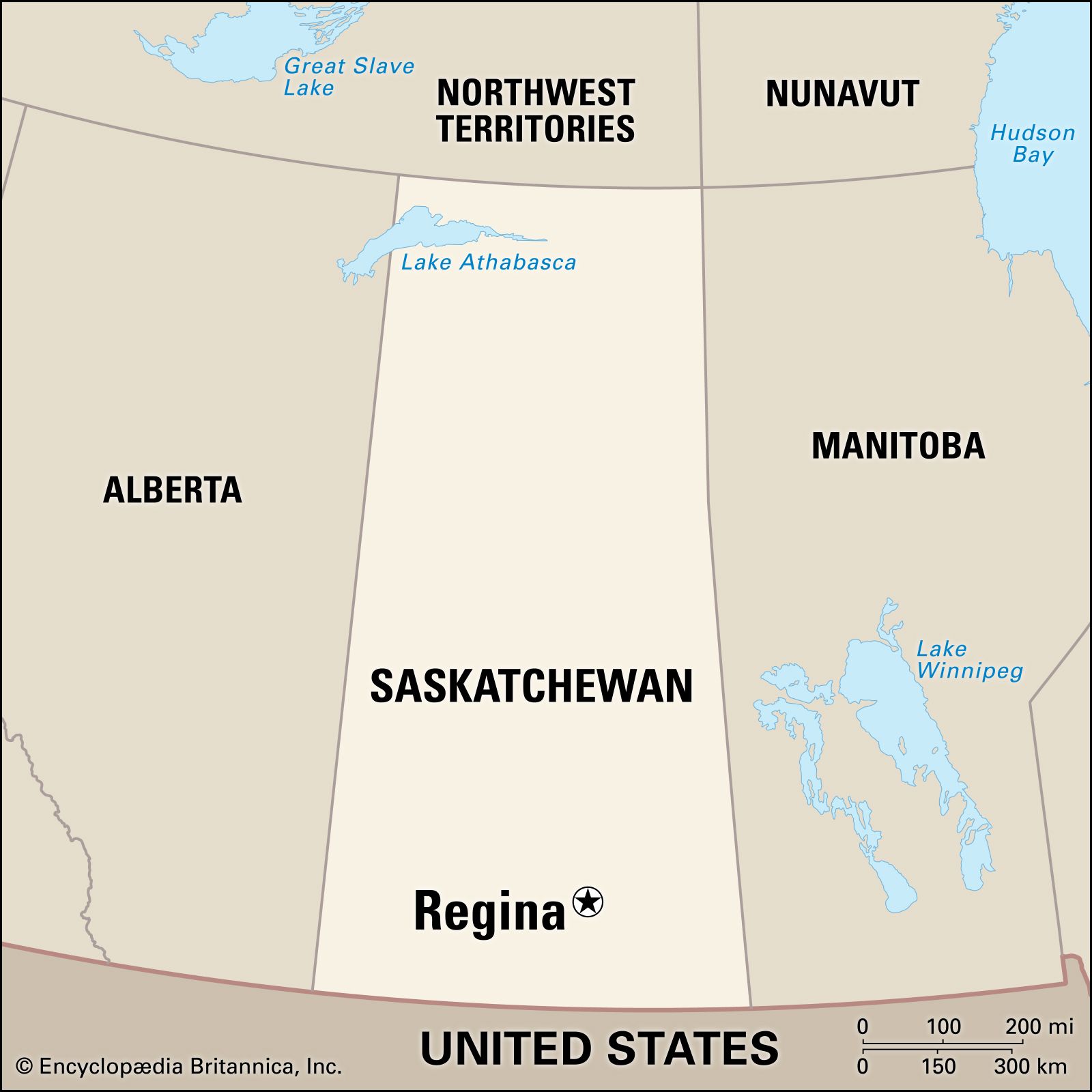
Where is Saskatchewan Located?
It is located…
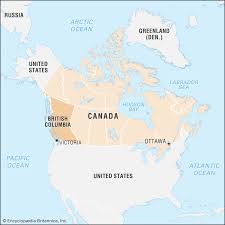
Where is British Columbia located on a map?
It is located…
Where is Northwest Territories located?
It is located…
Where is Prince Edward Island located?
It is located…
Where is Alberta located?
It is located…
Where is Nova Scotia located?
It is located…
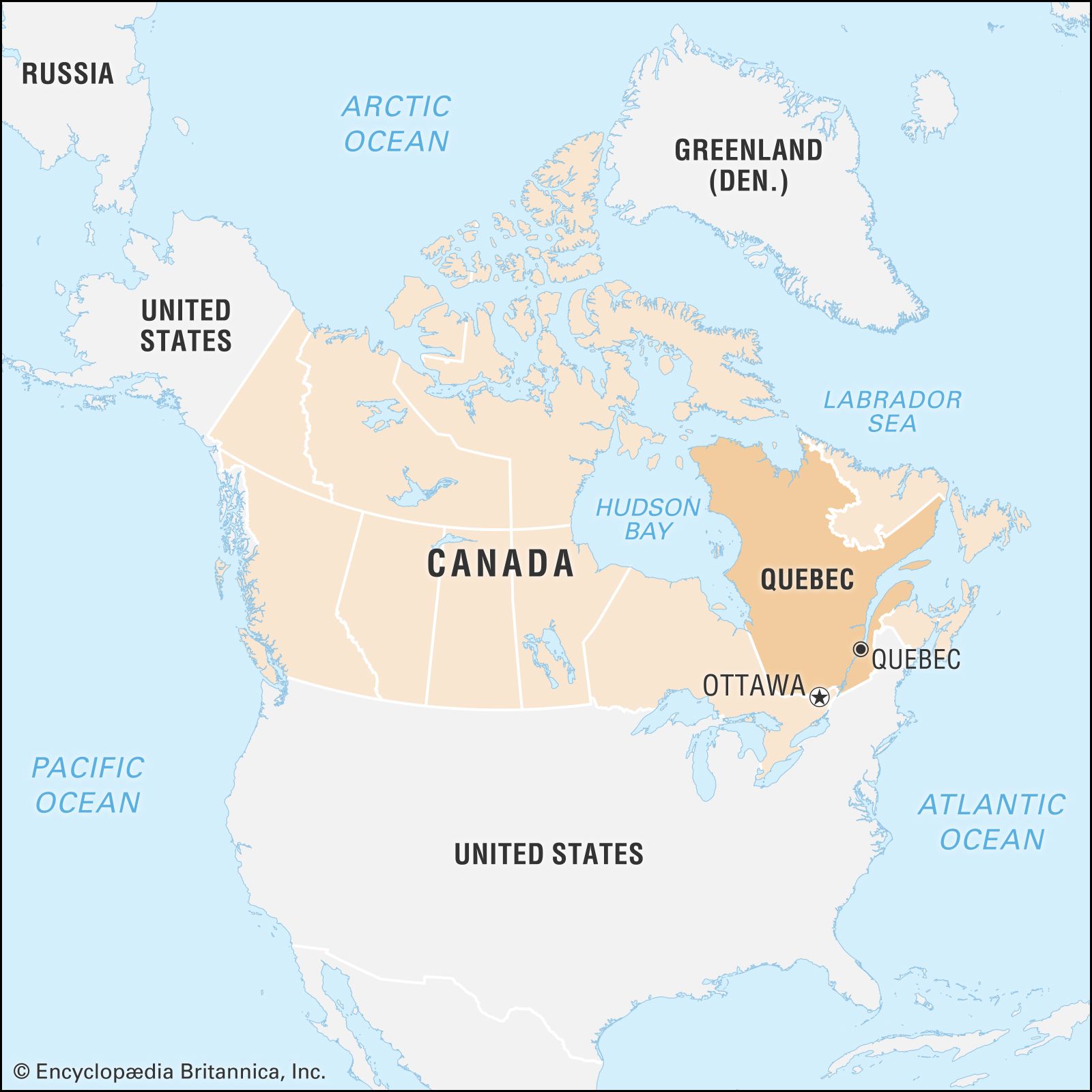
Where is New Brunswick located?
It is located…
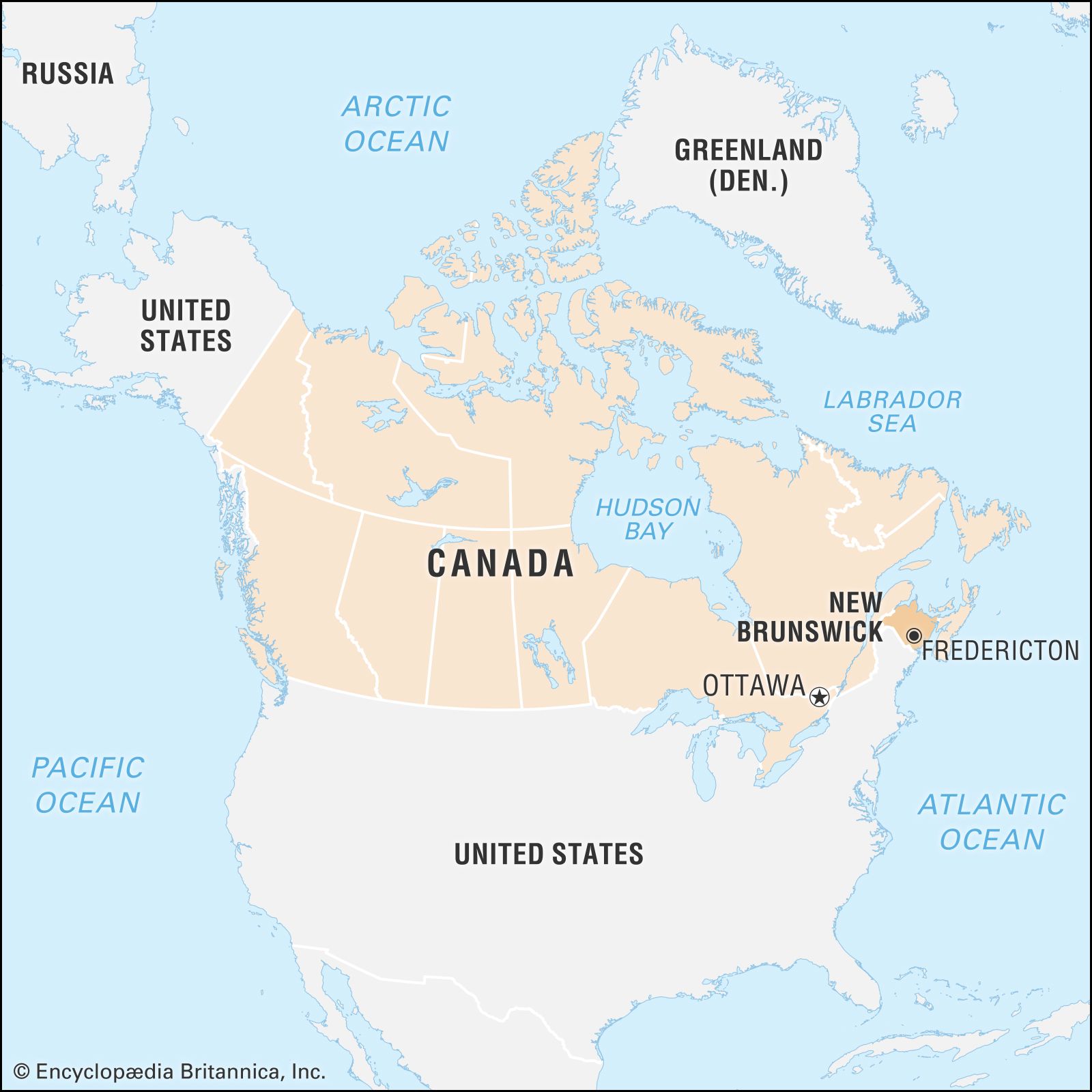
Where is Manitoba located?
It is located…
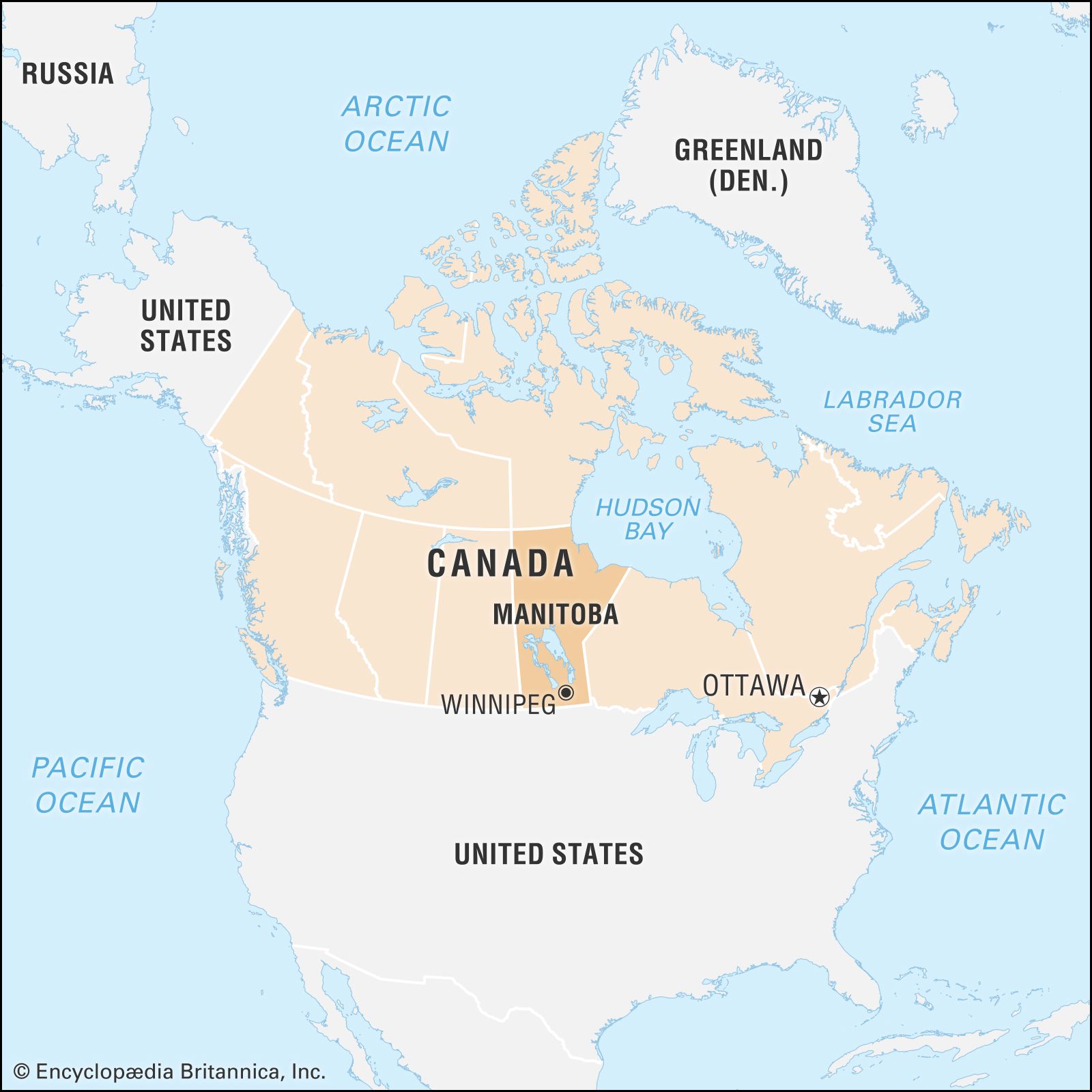
Where is Newfoundland And Labrador located?
It is located…
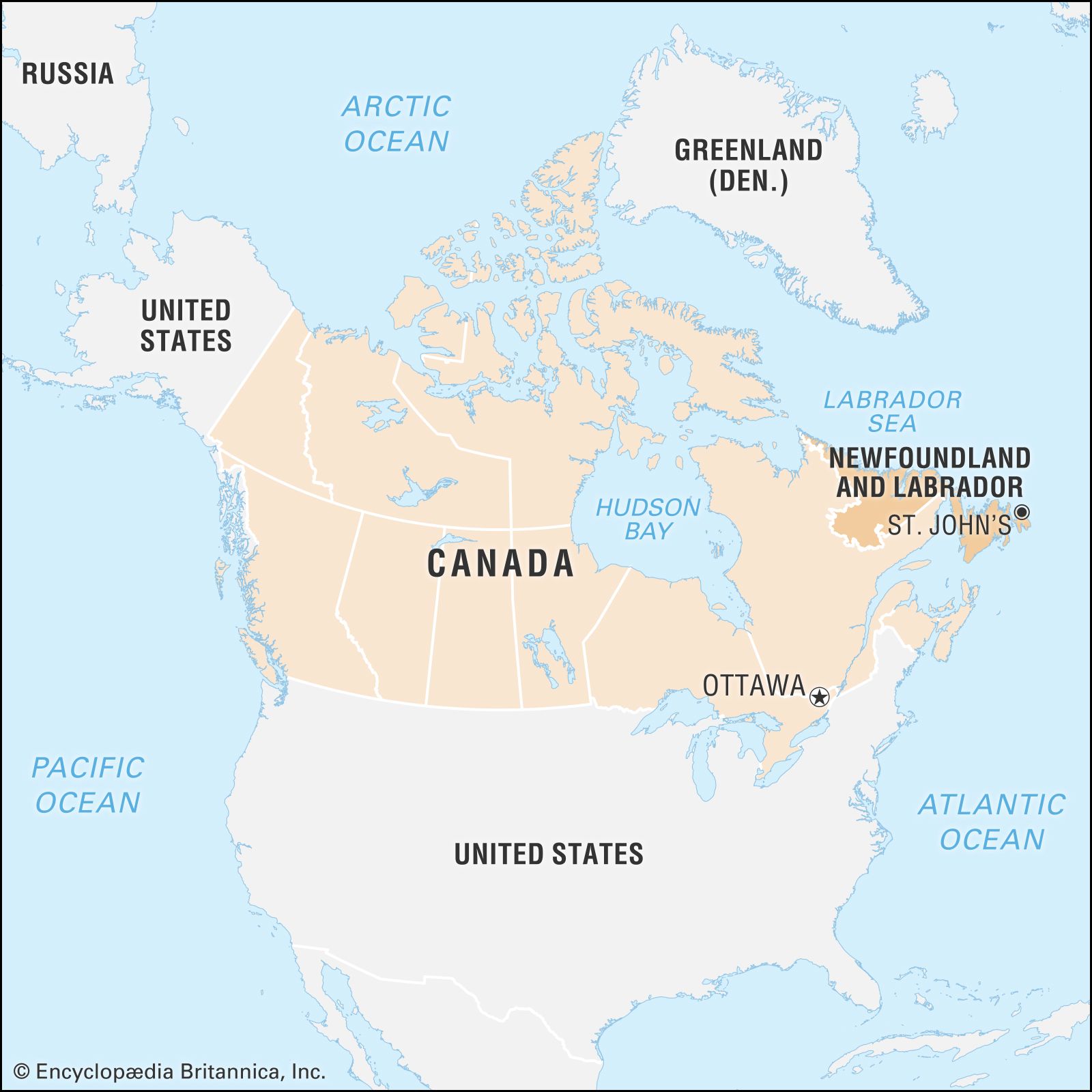
Where is Quebec located?
It is located…
Where is Nunavut located?
It is located…
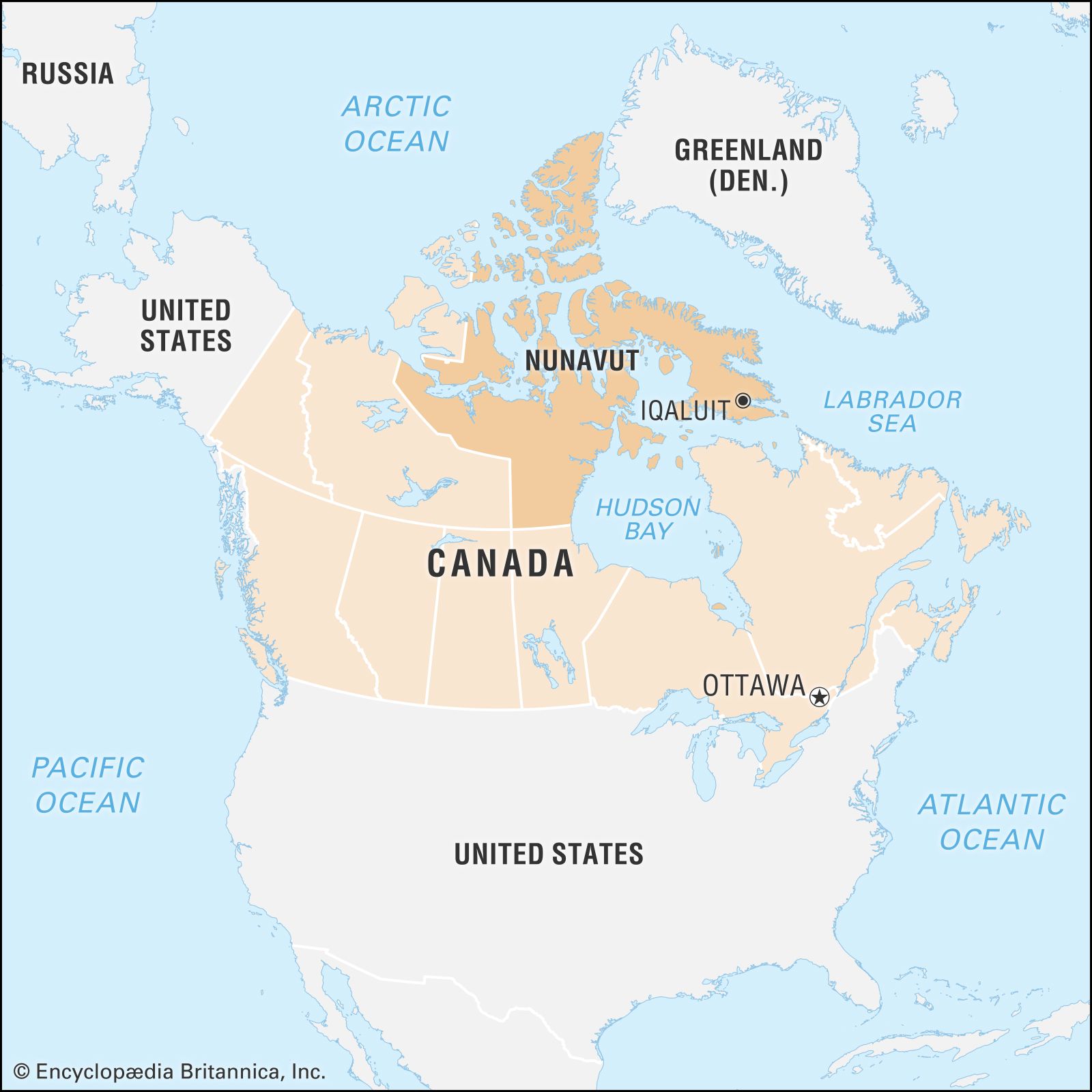
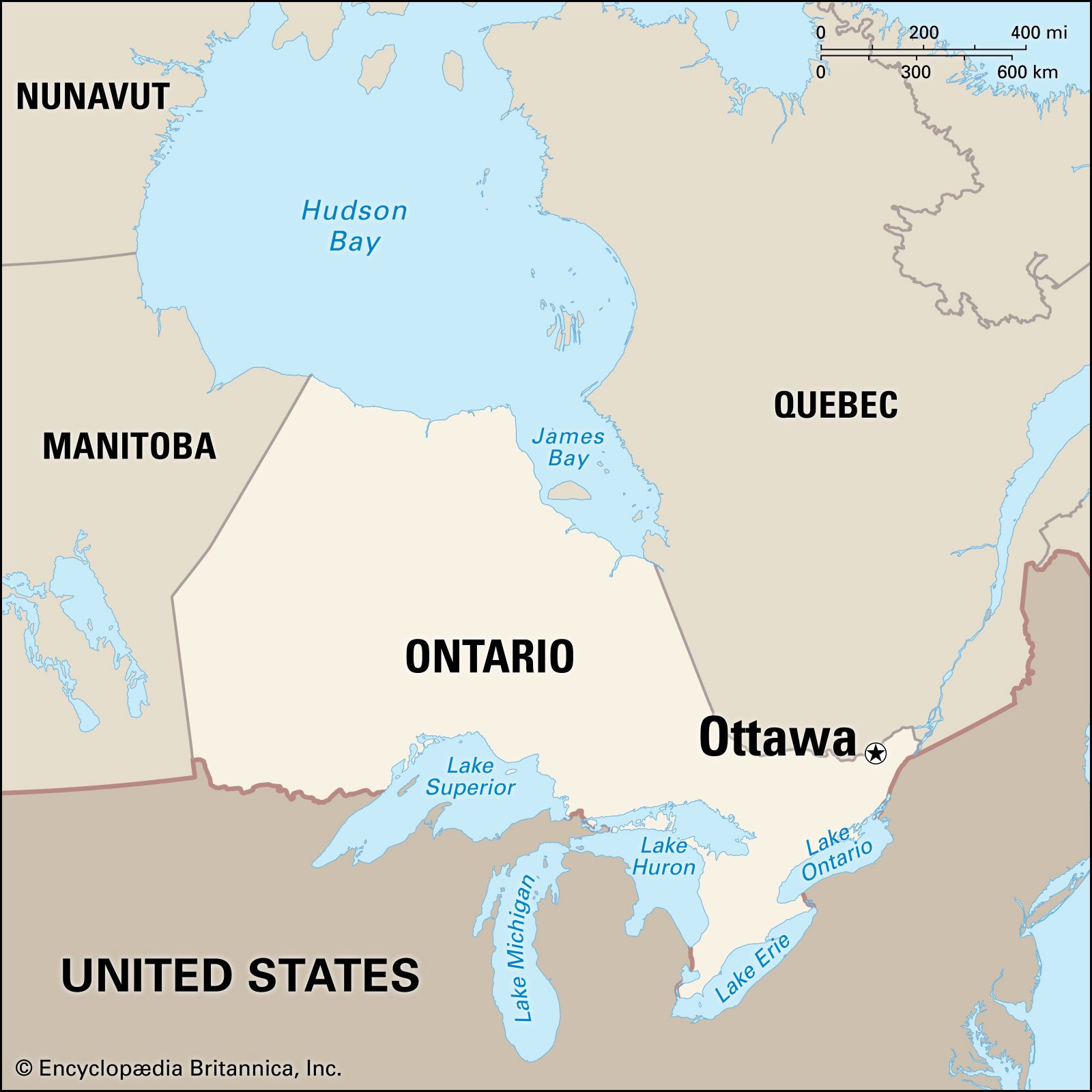
Where is Ottawa located?
It is located…
What is latitude mean?
Latitude indicates location either north or south of the equator
What is longitude?
Longitude indicates locations either east or west of the prime meridian
What are angular bearings?
angular bearings are when an angle is less than 90 degrees within a quadrant defined by the cardinal points.
What is a Compass Rose?
It helps us find directions such as north, south, east and west. It also helps us find anything in between such as ordinal points and additional ordinal points such as NNW (north, northwest) , and NE (north east).
What is continental drift?
Continental drift is the belief that earth’s continents are moving (very slowly) and this theory was made by Alfred Wegener in 1912.
What is plate tectonics?
Plate tectonics are the belief that convection currents in the earths mantle provided adequate energy to displace landmasses. This theory was made by John Tuzo Wilson.
What are convection currents?
Convection currents are like giant conveyer belts, their movement pushes and pulls the earth’s crust by 2 to 10 centimetres a year.
What are the layers of the earth?
The mantle, the outer core, the inner core, and the crust
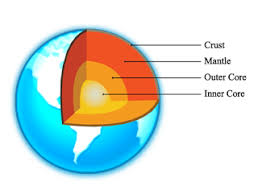
What is the Mantle made of?
The mesosphere (rigid lower part of the mantle) , the asthenosphere (plastic like layer that the lithosphere floats on) and the lithosphere (solid and rigid outer layer of the earth made up of crust and upper mantle)
What is the mantle?
The solid layer of rock that sits below the crust and above the core.
What is the core made of?
The inner core (the hot solid layer of the core made of nickel and iron) and the outer core (the hot liquid layer of the core made of nickel and iron.)
What is the core?
The hot dense centre of the earth.
What is the crust made of?
Oceanic crust (heavier/denser crust in the ocean floor) and the continental crust (less dense, on major land masses such as continents.)
What is the crust?
The rocky brittle outer layer of the earth
What is folding?
The bending or curving of rock layers due to compressional forces within the earth’s crust
What are the plate boundaries?
The interface where two tectonic plates meet. The types of plate boundaries are : divergent boundaries (where plates move apart, creating new oceanic crust as magma rises to the surface.) then the convergent boundaries ( where plates collide from sub-ducting beneath another or by colliding which can cause mountain building) and then there is the transform boundary ( where plates slide horizontally past each other often causing earthquakes from the friction)
What is igneous rock?
Igneous rocks are formed from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. Examples are : obsidian , granite, and basalt are all igneous rocks.
What are metamorphic rocks?
metamorphic rocks are created from igneous rocks through heat and or pressure. Examples of this type of rock include : slate, marble , quartzite, and more.
What are sedimentary rocks?
Sedimentary rocks are formed by compaction of sediments (particles of rocks, minerals, or organic matter) and examples of this rock include : sandstone , shale , limestone, coal, etc.
What is weathering?
The breaking down of rocks. Weathering agents include water, wind, ice , animals, and growing plants.