Chapter 7; Photosynthesis: Light Reactions and the Calvin Cycle
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
Photosynthesis
Process converting CO2 and H2O to sugars.
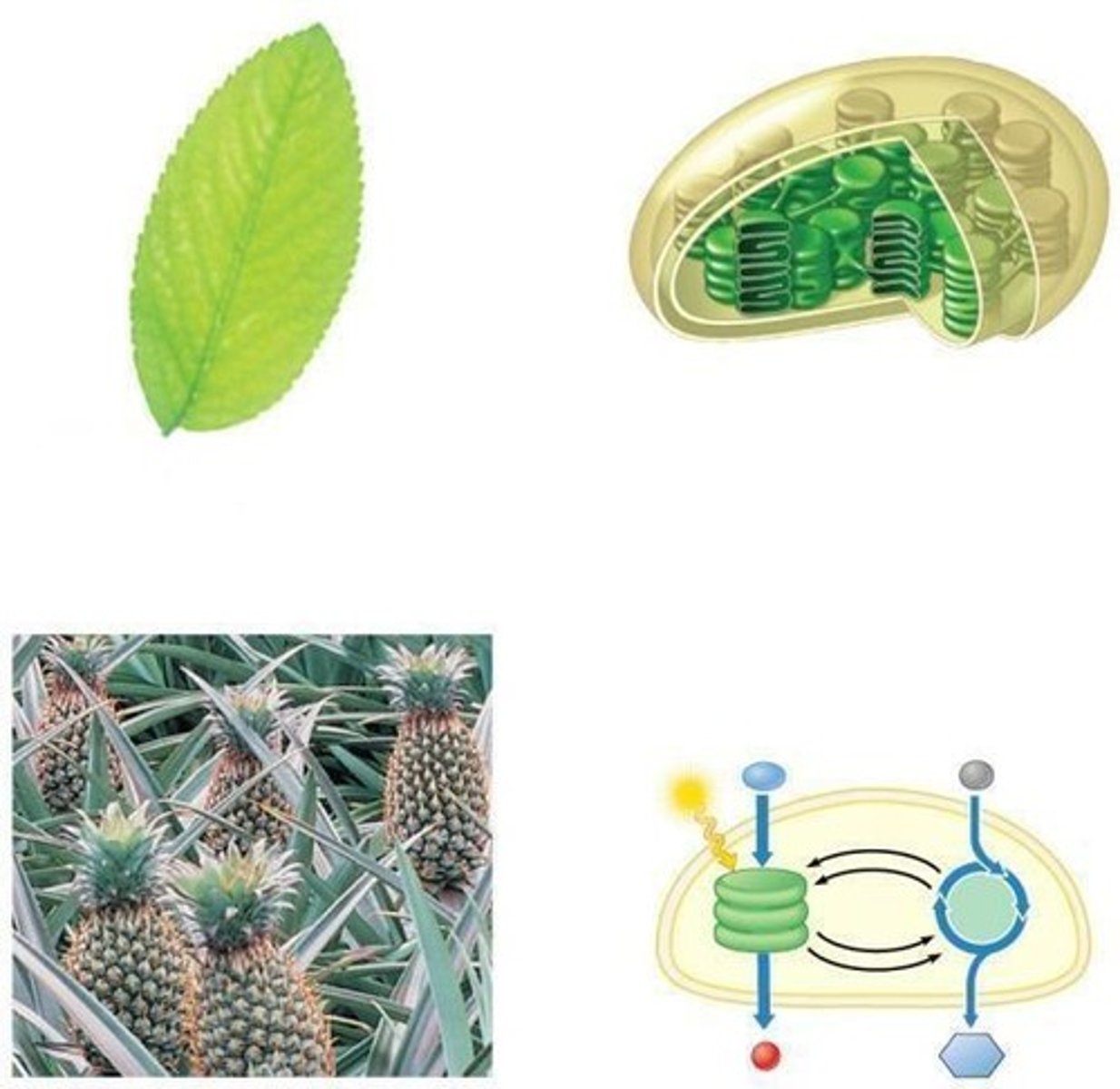
Autotrophs
Organisms that produce their own food.
Photoautotrophs
Use light energy to produce organic molecules.
Chemoautotrophs
Prokaryotes using inorganic chemicals for energy.
Heterotrophs
Organisms that consume other organisms for energy.
Light-dependent reactions
Capture sunlight energy to produce ATP and NADPH.
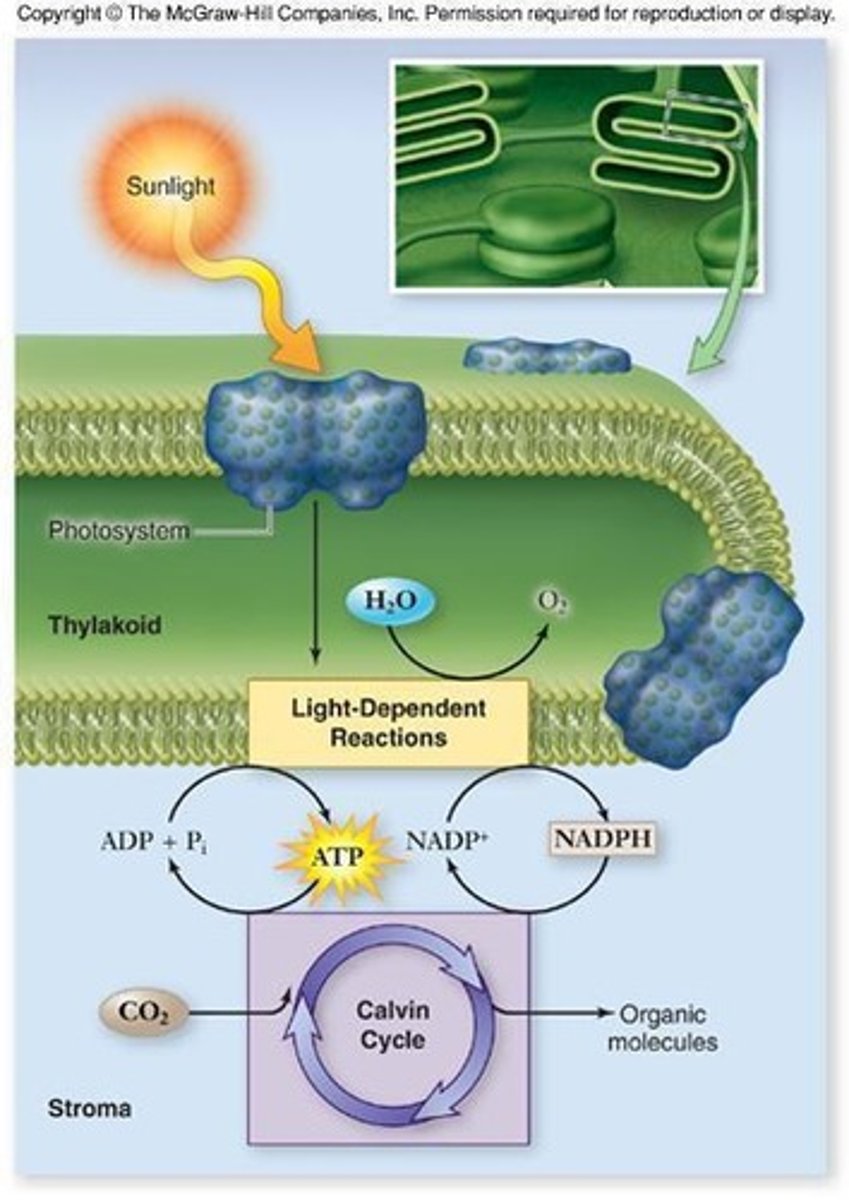
Calvin Cycle
Uses ATP and NADPH to synthesize sugars.
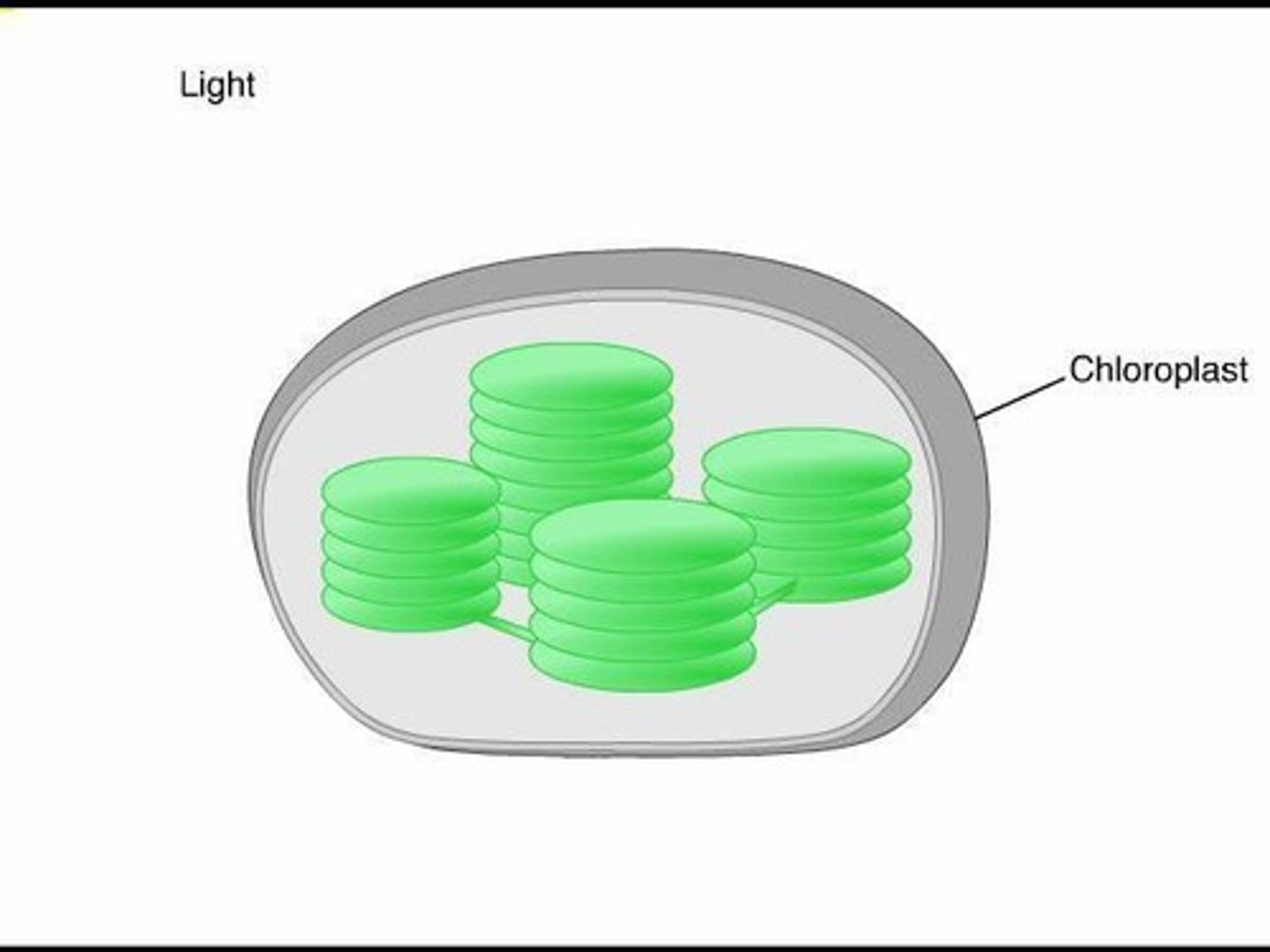
Chloroplasts
Organelles where photosynthesis occurs in plants.
Mesophyll
Green tissue in leaves containing chloroplasts.
Stomata
Pores allowing gas exchange in leaves.
Thylakoids
Membranous sacs in chloroplasts for light reactions.
Stroma
Thick fluid inside chloroplasts surrounding thylakoids.
Chlorophyll
Pigment in thylakoids capturing light energy.
Redox process
Involves oxidation and reduction reactions.
Oxygen production
O2 produced from H2O during photosynthesis.
Isotopes in research
Used to trace oxygen source in photosynthesis.
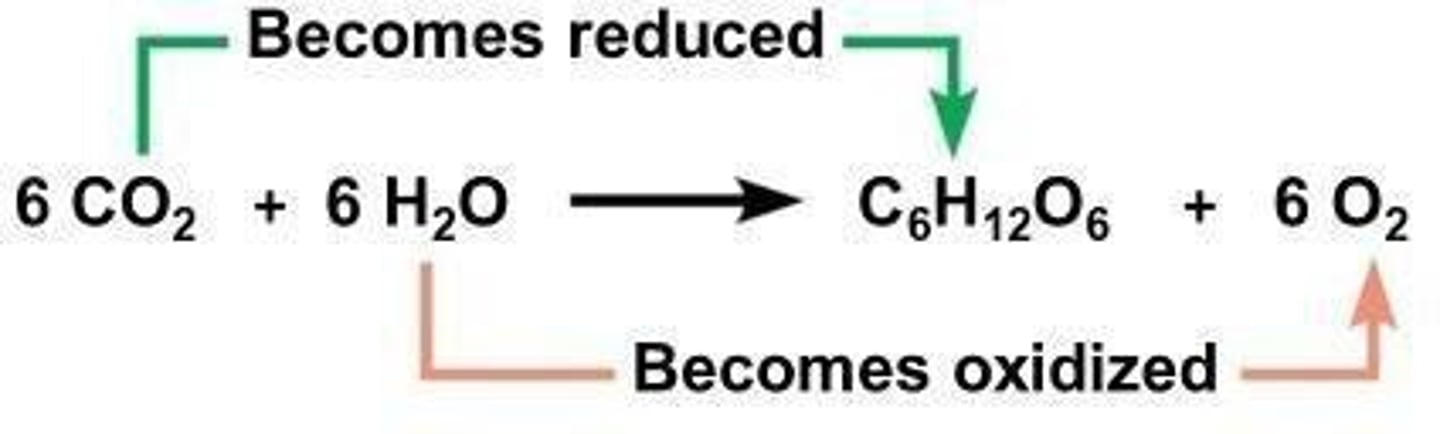
Chemical equation
6CO2 + 12H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2.
Electron transport chain
Pathway for electrons during cellular respiration.
Oxidation
Loss of electrons from a molecule.
Reduction
Gain of electrons by a molecule.
Energy conversion
Light energy converted to chemical energy.
ATP
Energy currency produced during light reactions.
NADPH
Electron carrier produced in light-dependent reactions.
Light Reactions
Convert solar energy to chemical energy.
Calvin Cycle
Cyclic reactions assembling sugars from CO2.
Water Splitting
Provides electrons and releases oxygen.
ATP Generation
Produced from ADP and phosphate group.
NADPH Production
Reduces NADP+ using electrons from water.
Carbon Fixation
Incorporates CO2 into organic compounds.
Chlorophyll
Main pigment absorbing blue-violet and red light.
Accessory Pigments
Absorb different wavelengths, enhancing photosynthesis.
Carotenoids
Broaden light spectrum and provide photoprotection.
Photons
Discrete packets of light energy.
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Full range of electromagnetic wavelengths.
Wavelength
Distance between crests of adjacent waves.
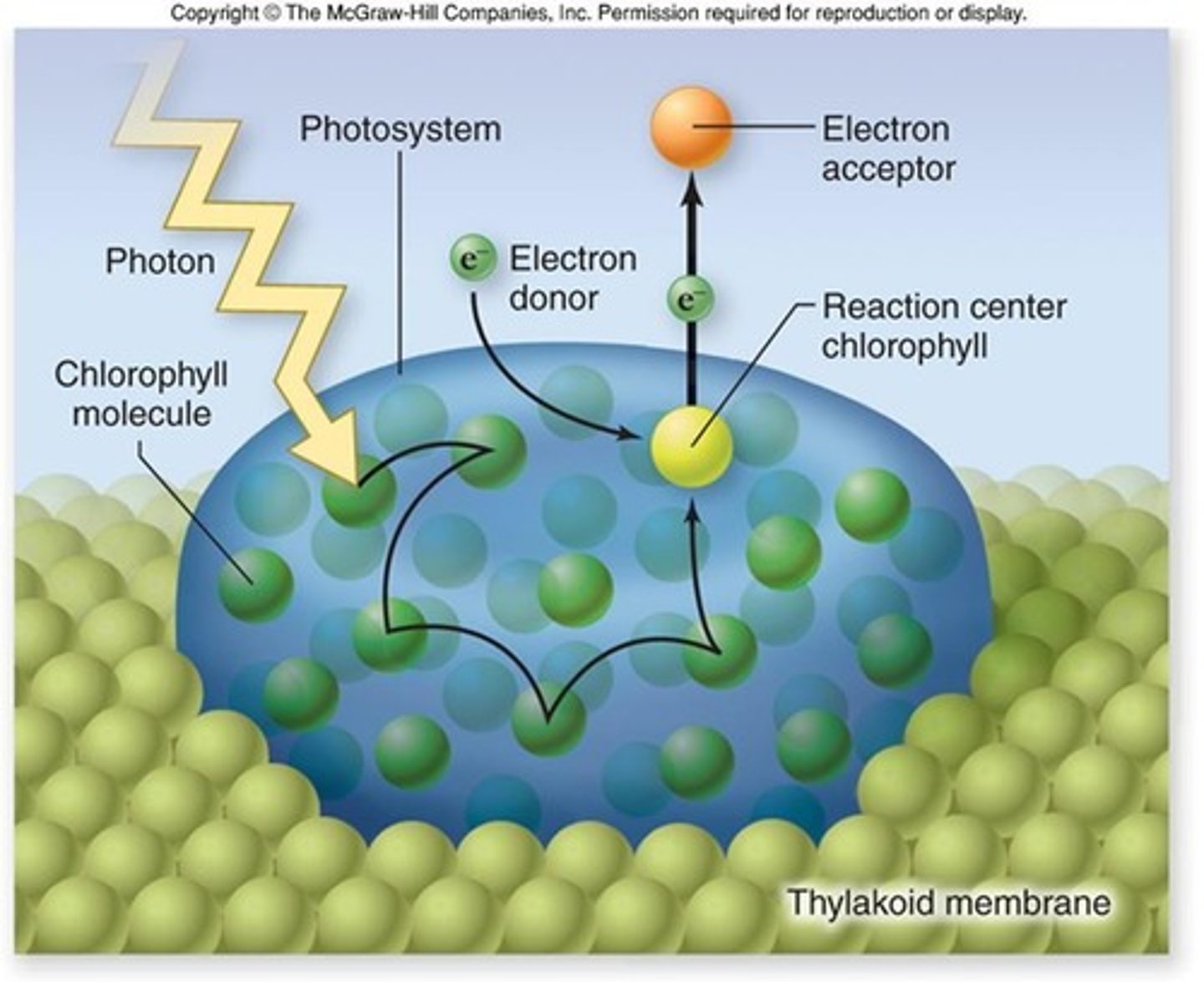
Photosystem
Complex of pigments capturing solar energy.
Antenna Complex
Hundreds of accessory pigments in photosystems.
Reaction Center
Contains chlorophyll a for energy transfer.
Thylakoid Membrane
Location of light-dependent reactions in chloroplasts.
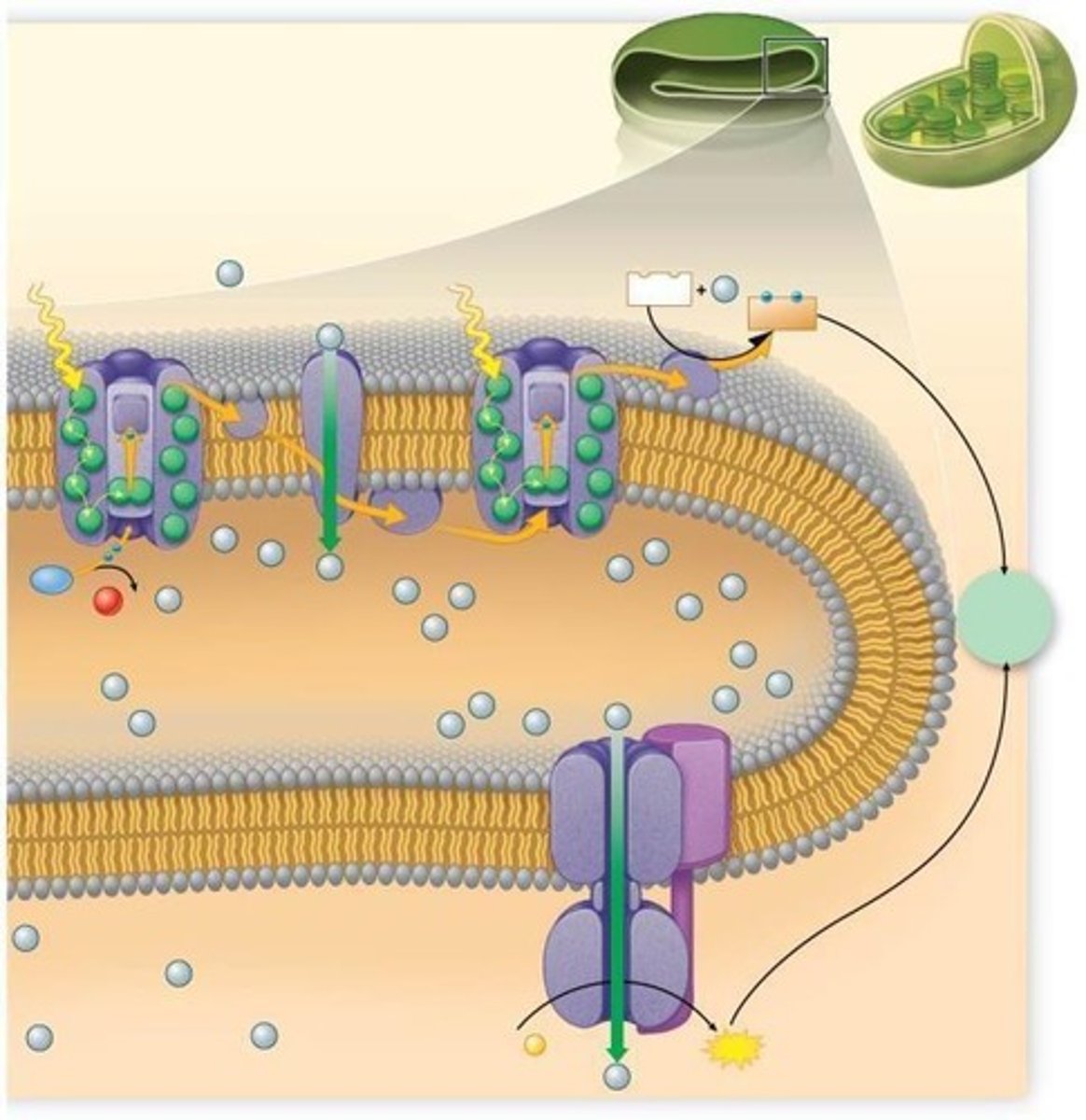
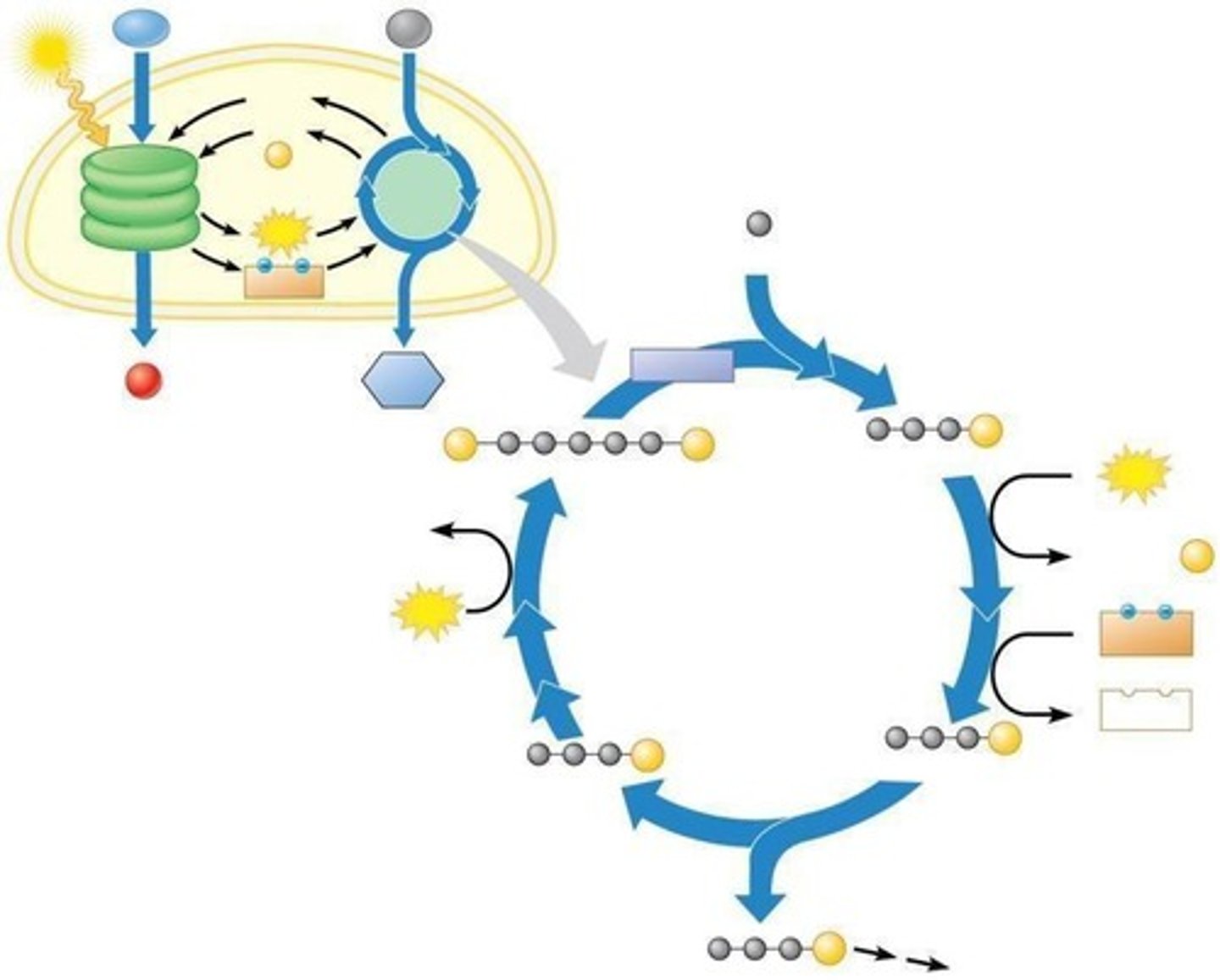
Noncyclic Photophosphorylation
Uses two photosystems for ATP and NADPH.
Photosystem I
Reaction center pigment P700, absorbs at 700nm.
Photosystem II
First photosystem in light reactions.
Light-Dependent Reactions
Require light to produce ATP and NADPH.
Reducing Power
NADPH provides energy for Calvin cycle.
Heat Release
Excess energy from excited electrons dissipated as heat.
Visible Light
Small part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Chloroplast
Organelles where photosynthesis occurs.
Photosystem II
First photosystem with P680 pigment, absorbs at 680nm.
Electron Transport Chain
Connects two photosystems, generates ATP and NADPH.
Light Reactions
Convert light energy into ATP and NADPH.
Water Splitting
Electrons are removed from water during light reactions.
NADP+
Electron acceptor, reduced to NADPH in photosynthesis.
Thylakoid Membrane
Site of ATP synthesis via chemiosmosis.
Photophosphorylation
ATP production driven by light energy.
H+ Gradient
Created across thylakoid membrane, drives ATP synthase.
G3P
Three-carbon sugar produced in the Calvin cycle.
Carbon Fixation
First phase of Calvin cycle, incorporates CO2.
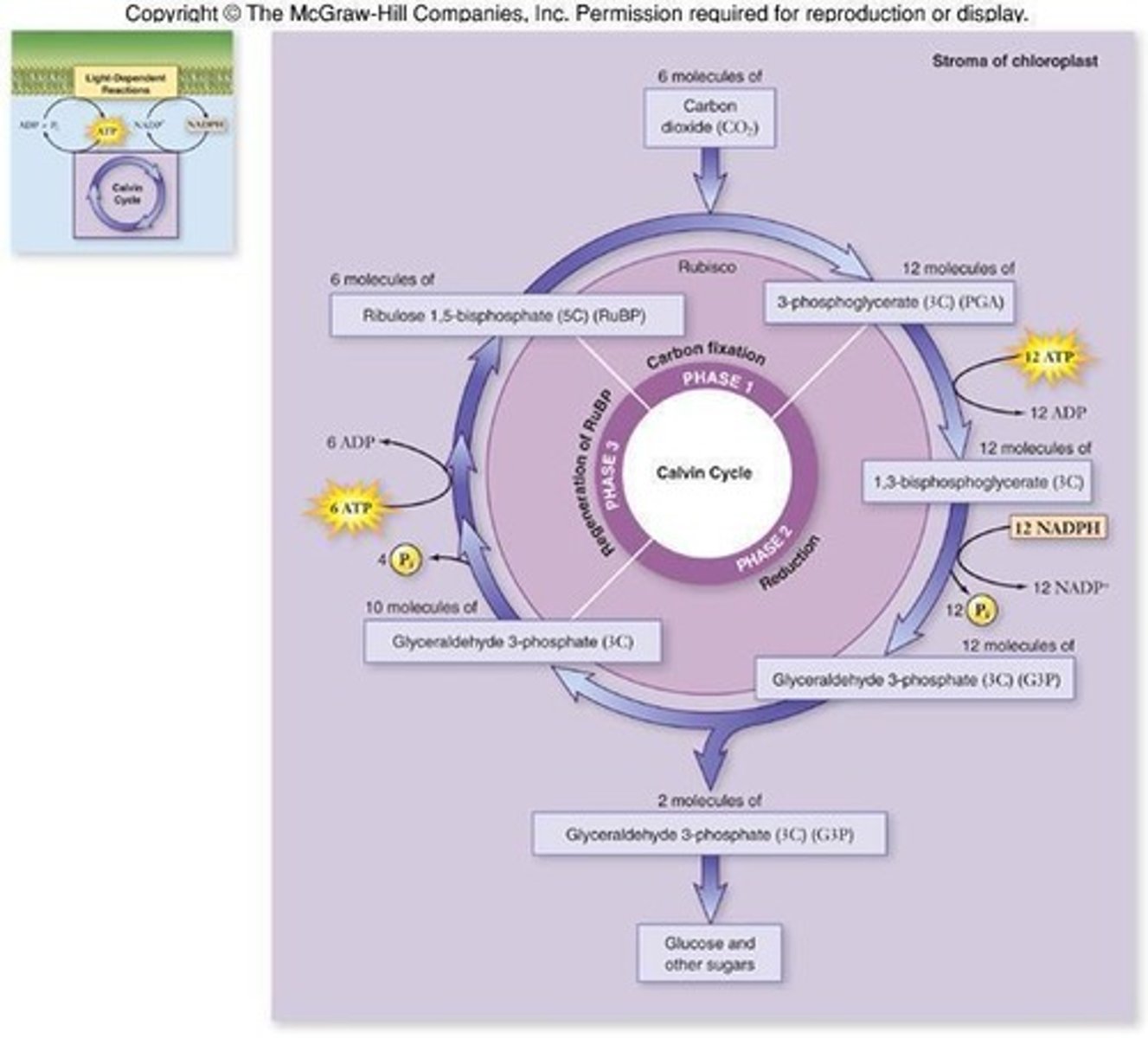
RuBP
5-carbon sugar, reacts with CO2 in Calvin cycle.
PGA
3-carbon compound formed from RuBP and CO2.
Glucose Production
Requires 2 G3P molecules from Calvin cycle.
ATP Requirement
Calvin cycle needs 18 ATP molecules for synthesis.
NADPH Requirement
Calvin cycle requires 12 NADPH molecules for reduction.
Cellulose
Polysaccharide made from glucose, forms cell walls.
Excess Glucose Storage
Stored in roots, tubers, seeds, and fruits.
Cellular Respiration
Uses carbohydrates from photosynthesis as fuel.
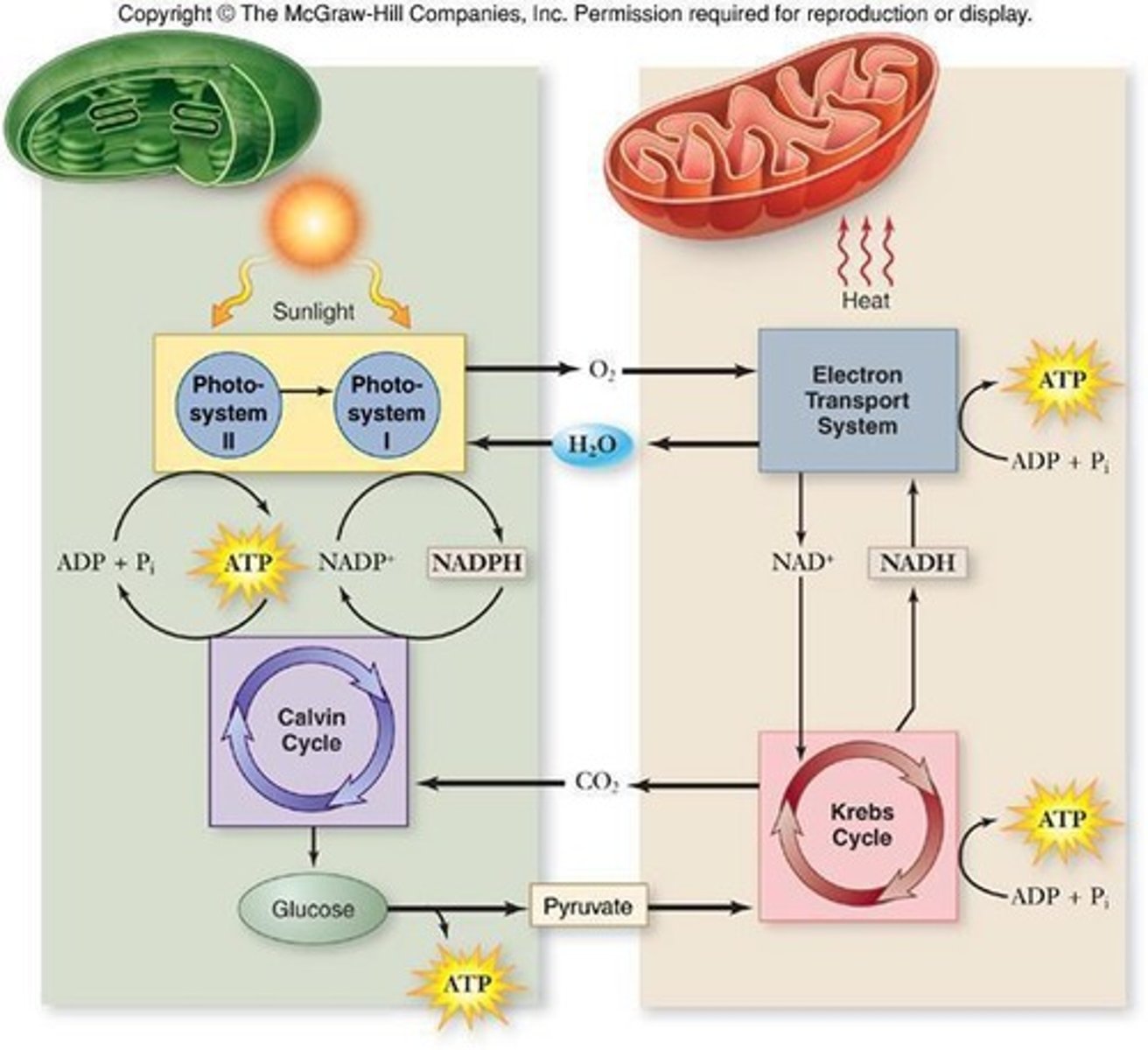
Organic Molecules
Sugars serve as precursors for proteins and lipids.
Greenhouse Effect
Solar radiation warms Earth's surface, affects plants.
Global Climate Change
Rising CO2 levels impact plant growth and health.
Photosynthesis Significance
Provides food and oxygen for nearly all life.
Greenhouse Effect
Natural heating from greenhouse gases retaining heat.
Greenhouse Gases
Gases like CO2 and methane trapping heat.
Global Warming
Increase in Earth's average temperature due to greenhouse gases.
Polar Ice Melting
Result of rising global temperatures affecting ice caps.
Rising Sea Levels
Increase in ocean levels due to melting ice.
Extreme Weather Patterns
Unusual weather events linked to climate change.
Droughts
Extended periods of deficient rainfall impacting ecosystems.
Increased Extinction Rates
Higher species loss due to changing habitats.
Tropical Diseases Spread
Expansion of diseases into new areas from climate change.
CO2 Levels
Higher concentrations can enhance plant productivity.
Growth Chambers
Controlled environments for studying plant responses to CO2.
Long-term Field Studies
Research involving large-scale CO2 manipulations over time.
Poison Ivy Growth Increase
149% growth in elevated CO2 compared to controls.
FACE Experiment
Study monitoring CO2 effects on forest ecosystems.
Ozone Layer
Protective layer absorbing harmful UV radiation.
CFCs
Industrial chemicals damaging the ozone layer.
Nobel Prize 1995
Awarded for research on CFCs and ozone depletion.
Ozone Recovery Timeline
Expected recovery of ozone layer by around 2060.
UV Radiation Effects
Increased UV linked to skin cancer and crop damage.
Autotrophs
Organisms producing their own food via photosynthesis.
Heterotrophs
Organisms obtaining food by consuming others.
Chloroplast Structure
Organelles in plants where photosynthesis occurs.
Photosynthetic Pigments
Molecules capturing light energy for photosynthesis.
Electron Transport Chain
Series of proteins generating ATP in light reactions.
Calvin Cycle
Process converting CO2 into glucose in plants.