8.1 Patient synchrony and Unique Considerations
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Common patient/asynchromies
missied inspiratory effort
patient trigger delay
auto-triggering
end of breath delay
patient/ventilator async con’t
impedes gas exchange
increase O2 comsumption and metabolic demands
increases intrathoracic pressures
agitates patients
asunchrony solutions
paralysis
sedation
paralysis
no commonly done
consider
drug toxicity
increase O2 requirements (especially small infants)
failure of skeltal muscle growth
delay in weaning
sedation
disadvantanges: Hypotension, may modify EEG activity
both paralysis and sedation would suppress ___
ventilatory drive
best way to reduce asynchrony
ensure ventolator can reconginze your patient
proximal flow sensing
Edi signal and NAVA
proximal flow sensing
most common way to synchronize ventilation in our NICU today
ventilator like ____ and ____ very good internal flow sensors- still currently used for larger infants/peds
servo-u and PB980
pneumotachometer
device that measures gas flow then integrates the signal to give a volume measurement
“proximal” measuremnts is considered more accurate than a distal measurement
Mostly common pneumotachometer
heated aneumometer
variable orfice
flow sensor measurement principle - no gas flow
two tiny platinum wires are heated to 40o
flow sensor measurement principle - no gas flow - with gas flow
gas flow cools the wire down
from the amount of cooling the amount of gas flowing can be calculated
Drager flow sensor
flow sensor housing two different types
difference deadspace volumes
flow sensor cables

ISO deadspace drager flow sensor
0.9 mL
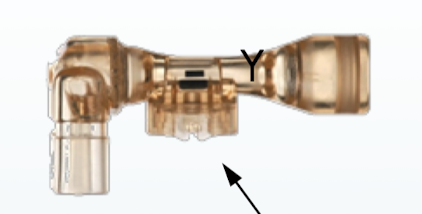
deadspace in this drager flowsensor
1.7 mL
variabke orifice pneuomotach
uses resustance to create a pressure drop that is proportional to the flow
bidirectional and disposable
design relies on variable orficed to generation the flow-pressure signal
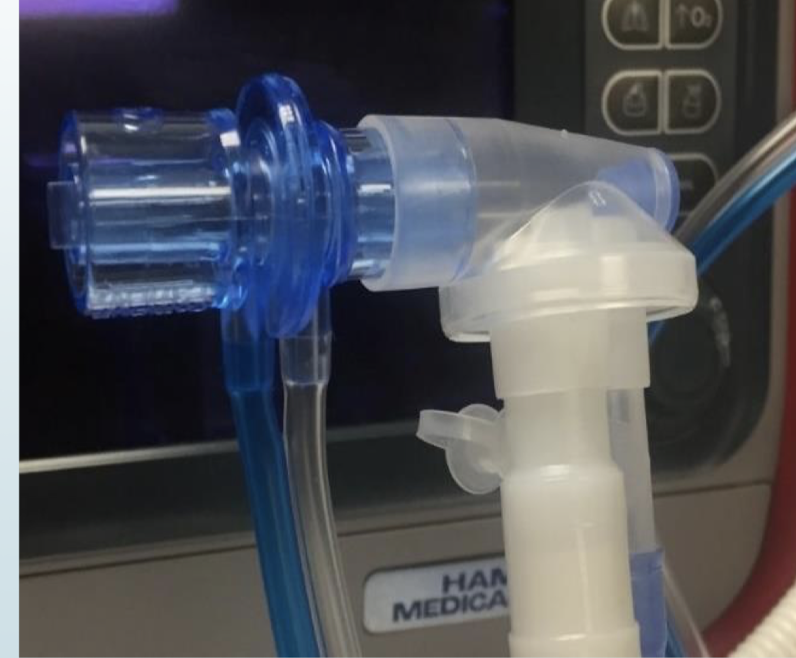
hamilton G5,C1, T1
<1.3 ml
problem with penumotachs
moisture
secretion
ambient temperature
humidity
altitude
placement of the sensor
compressible volume loss
accuracy ± 10-15%
most neonatal ETT are
uncuffed
do we want small amount of leak around the ETT
yes
adapting to leaks (Trigger and cycle) - Hamilton G5
intelliTrig automatically adjusts inspiratory and expiratory trigger sensitivity to airway leaks
PB980 ventilator
leak sync tech
Servo-I, Servo-U and Servo-n
leak compensation tech and of course NAVA which was developed to improve patient/vent synchrony
Flow trigger are highly recommened, what is the rule of thumb for sensitivity
start as sensitive as possibel and decrease sensitivity if autotrigging occurs
Drager VN500 V500 sensitive setting
0.3 lpm
Fabian HFO
0.12 lpm
G5, Servo u
flow trigger, (pressure trigger)
leak compensation during breath delivery
many ventilator have ability to compensated for volume loss due to leak.
In the VN500, how is leak compesnation, how does vent determine the leak during insipration
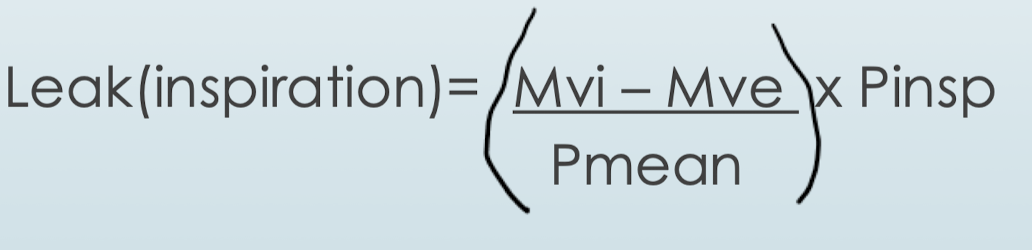
In the VN500, how is leak compensation, how does vent determine the leak during expiration
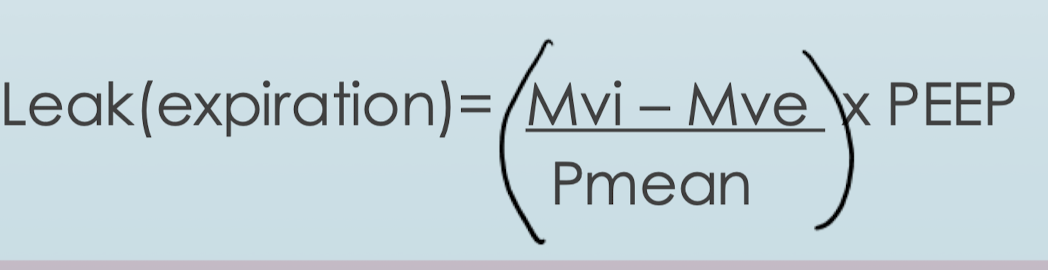
leak compensation turned OFF
Vtmand = 200ml (target)
Vtimand =200ml
Vtemand = 119
(40% leak)
Leak Compesation turn ON
Vtmand = 200ml (target)
Vtimand =279ml
Vtemand = 169ml
(40% leak)