Lecture 3- Integumentary System
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
epidermis
avascular, keratinized, stratified squamous, protection
dermis
flexible connective tissue, fibroblasts, mast, macrophage
hypodermis
(subcutaneous tissue), and note that it is not truly part of the skin. under dermis. adipose (fat)
stratum basale
Simple keratinocytes, regenerative, Melanocytes
& Merkels present
stratum
stratum spinosum
Desmosomes create web, Melanin granules, Langerhans cells
stratum granulosum
3-5 layers, keratinocyte appearance changes
granules accumulate
stratum lucidum
(in thick skin only) thin & clear, keratinocytes
stratum corneum
keratinized cells, ¾ of epidermis, waterproofs, protects (physical, biological, chemical)
melanocyte
make melanin. In the basale layer and hair
keratinocyte
make keratin. in stratum basale, granulosum, and lucidem
papillary layer
Areolar CT,
Dermal Papillae
Loops
Meissner’s Corpuscles
nerve ending
skin
functions include protection, regulation of body temperature, sensation, metabolism, serving as a blood reservoir, and excretion
vitamin D
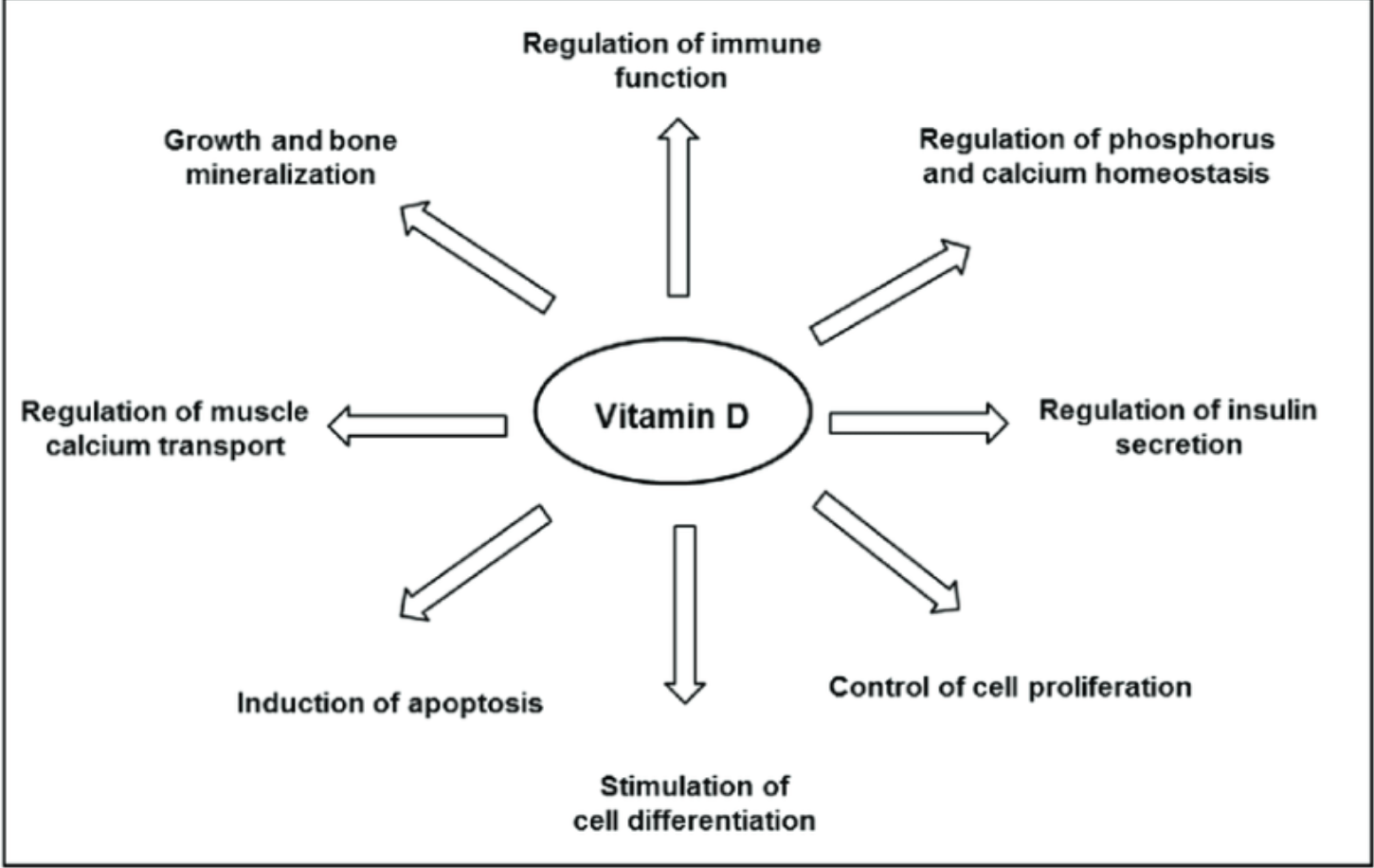
protection from UV radiation
Prevents skin damage, risk of skin cancer, protects eyes, percents dna damage, protects overall health
sudoriferous glands
Sweat Glands.
-Eccrine ~ palms/soles, forehead
•Apocrine ~ Axillary, Anogenital
sebaceous glands
everywhere. Sebum softens skin
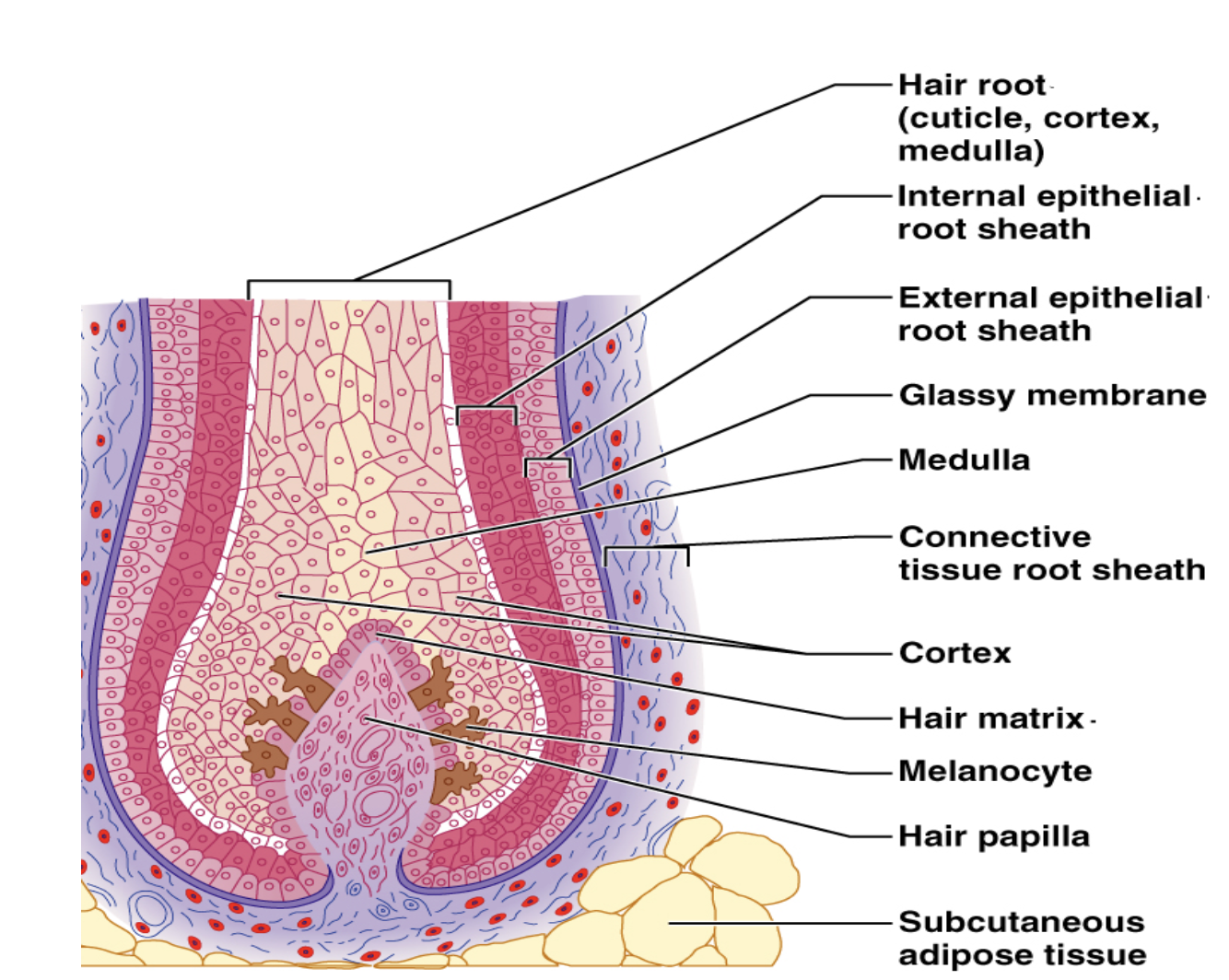
hairs
warmth, protection, sensation.
Hard Keratin ~ Shaft + Root
Medulla / Cortex / Cuticle
Melanocytes
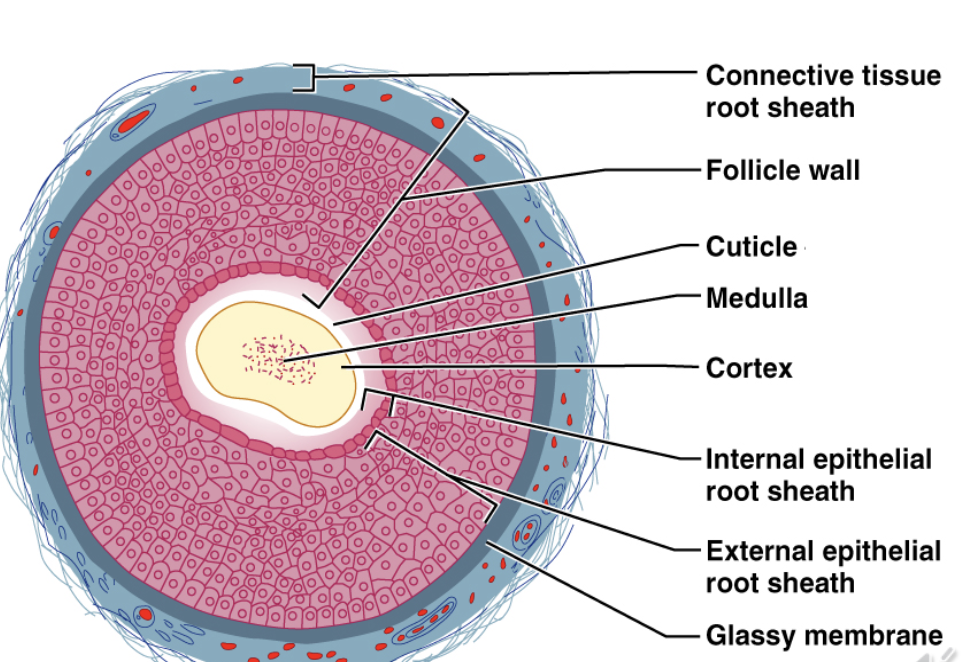
hair follicles
epithelial tissue, Dermis
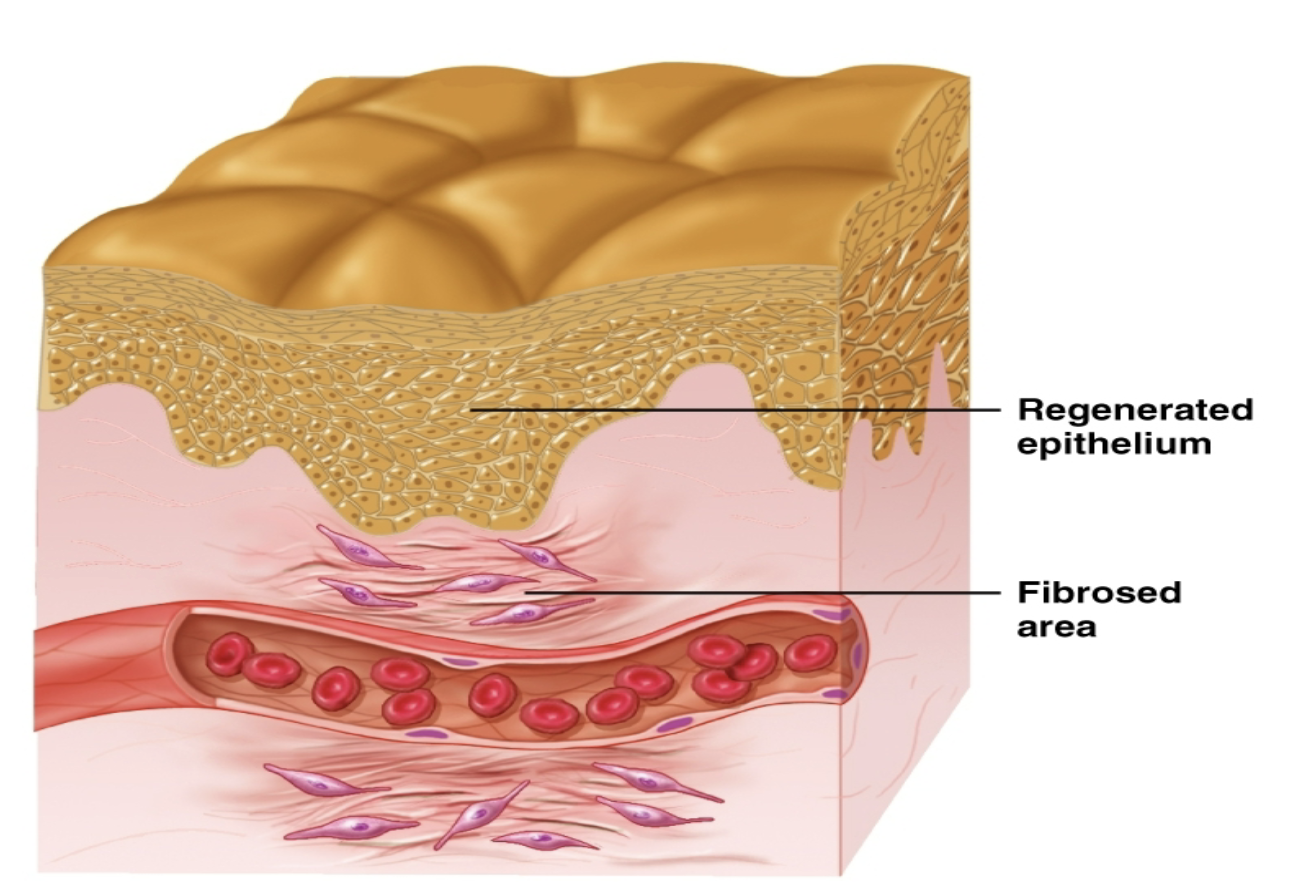
tissue repair
inflammation, organization, regeneration
fibrosis
a condition characterized by the excessive production and accumulation of fibrous connective tissue, typically in response to injury, inflammation, or disease
Inflammation
injured Macrophage & Mast →chemicals
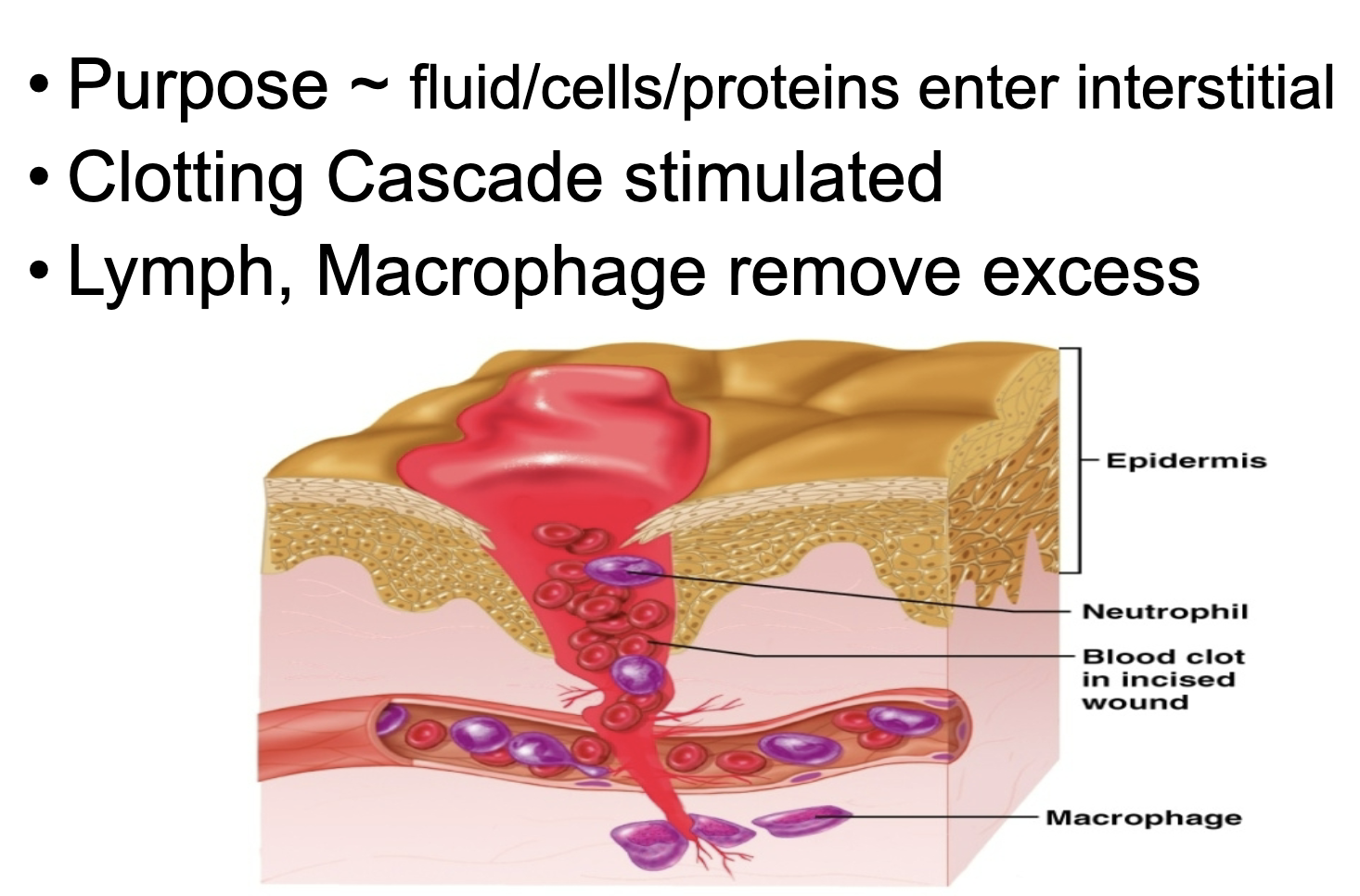
Organization
stages, multiple cells, new tissue forms
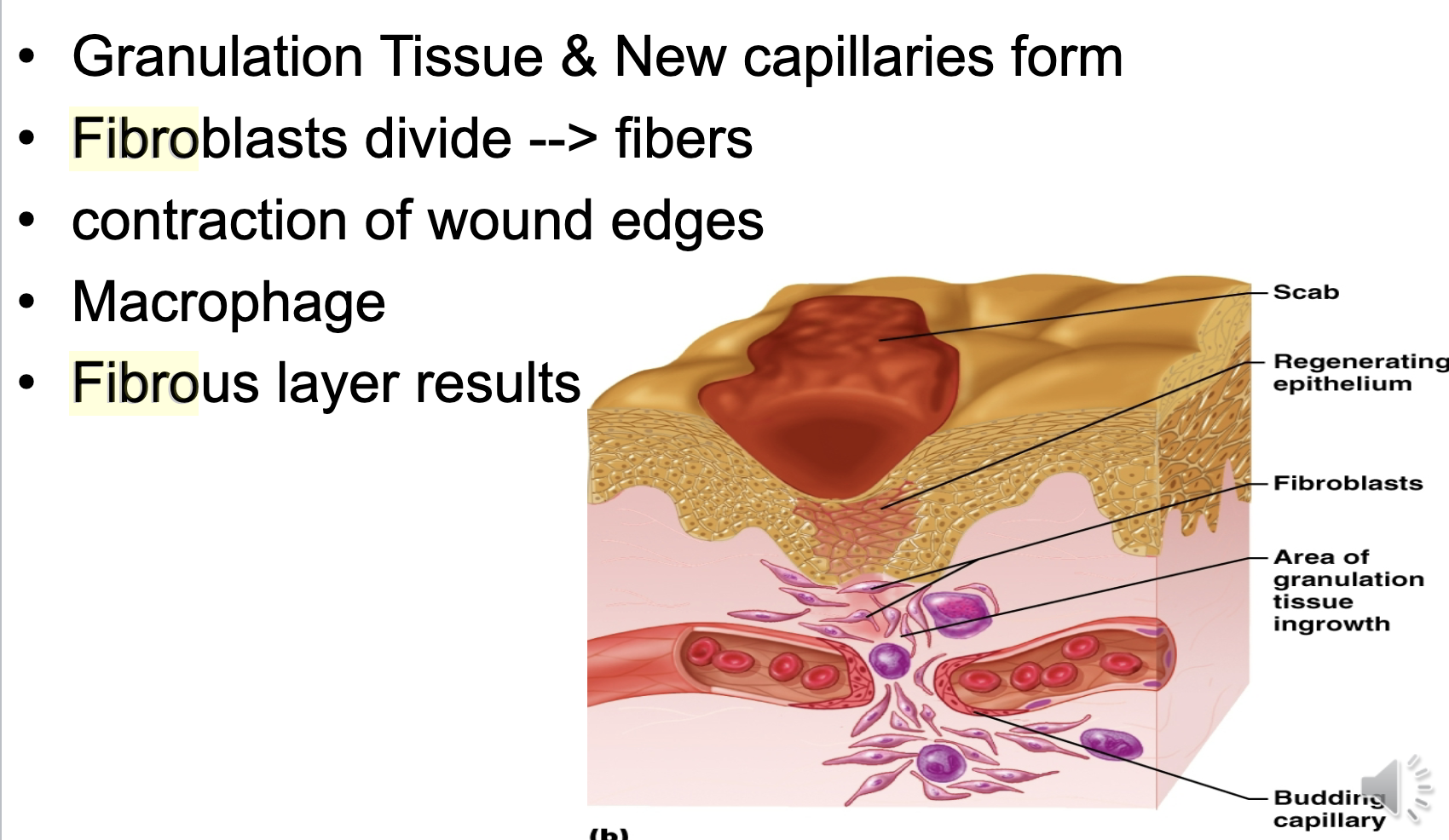
Regeneration
fibrosis, surface epithelia replaced, fibrous layer contracts