Forces Y11
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Newton’s 1st law extra
constant velocity = balanced forces
changing velocity = unbalanced forces
What is an action reaction pair?
happens when things collide like a footballer’s head with a ball → (footballer’s head exerts a force on ball and ball exerts force on footballer’s head)
action reaction forces are the same size but they don’t have the same effort on two objects because the objects are diff masses
stopping distance
the distance a vehicle travels between the driver seeing a hazard and the vehicle coming to a complete stop
equation for stopping distance
thinking distance + braking distance (distance travelled (distance travelled during reaction time) between driver beginning to break and coming to a stop)
factors that increase thinking distance
going fast (going faster increases the distance you travel per sec)
tiredness
alcohol
depressant drugs
distractions
(those factors increase the reaction time)
factors that increase braking distance
going faster
mass of vehicle
faster/heavier cars have more kinetic energy so the brakes will have to do more work to stop the car
poor road conditions
worn tyres
worn brakes
reduce the friction so less work is done each second & the car takes longer to stop
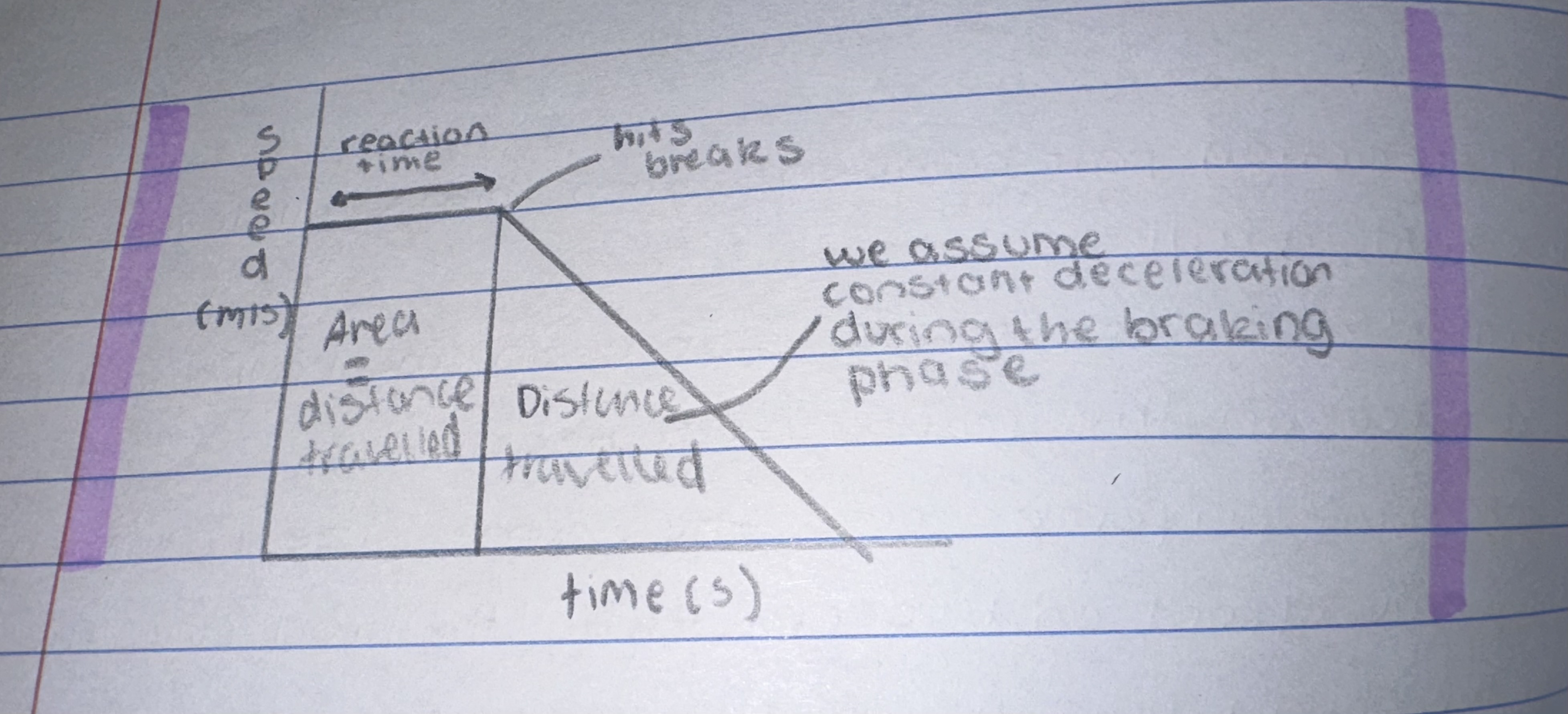
speed time graph
reaction time = time before brakes are hit (straight line )
area= distance travelled
diagonal line is braking time
equation for acceleration
a =
equation for acceleration and distance
2 a s = v2- u2
force and elasticity graph
shows how extension changes when force is applied to a spring
Hooke’s Law
extension of spring is directly proportional to force applied (provided limit is not exceeded)
when a force stretches/compresses spring → work is done on spring and e.p.e is stored in spring
elastic deformation
temporarily (changes shape)
plastic deformation
permanently (changes shape)
equation for force using spring constant and extension
F = k x e
equation for elastic potential energy
E = ½ k e2
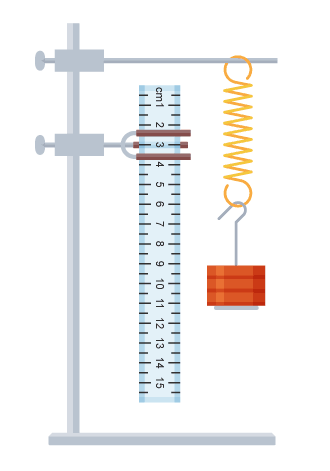
Practical that shows how forces affect the extension of a spring
Secure a clamp stand to the bench using a G-clamp or a large mass on the base.
Use bosses to attach two clamps to the clamp stand.
Attach the spring to the top clamp, and a ruler to the bottom clamp.
Adjust the ruler so that it is vertical, and with its zero level with the top of the spring.
Measure and record the unloaded length of the spring.
Hang a 100 g slotted mass carrier - weight 0.98 newtons (N) - from the spring. Measure and record the new length of the spring.
Add a 100 g slotted mass to the carrier. Measure and record the new length of the spring.
Repeat step 7 until you have added a total of 1,000 g.
resultant force
single force acting on an object
summarises all the forces acting on an object → can cause objects to change speed, direction or shape
when vectors are at a right angle
draw vectors tip-to-tail
draw in the resultant (complete triangle)
use pythagoras to find magnitude of the resultant vector
use trig to find a relative direction (angle from horizontal/vertical)
momentum
all moving objects have it
the greater the momentum the harder the object is to stop or change direction
momentum equation
p = m x v
conservation of momentum
in a closed system the total momentum before an event and a total momentum after an event are equal
Impact forces
force = change in momentum / time
impact forces
the greater the rate of change of momentum then the greater the impact
Ft = m (change in) x v
inertia
is the property of an object that describes the resistance to change motion
car safety features
front crumple zone → front of car designed crumple dissipating energy of impact slowing down the car
anti-lock braking system
side impact bars
air bag → automatically inflated with compressed air within 1/100th of a second on impact to cushion passengers
safety belts → inertia reel safety belts lock to keep wears tightly pressed to their seats when a car decelerates rapidly
rear crumple zone → trunk of saloon car crumples protects passengers from rear impact
Moment
turning effect of a force
moment of force about any point is → force x distance from turning point to line of action of force
equation for moments
moment = F x d
unit Nm
what is a turning point called?
pivot
centre of mass
weight of object may be considered to act at a single point → object’s ‘centre of mass’
centre of mass of symmetrical body is along axis of symmetry
if suspended a body will come to rest with its centre of a mass directly below the point of suspension
principle of moments
when an object isn’t turning(e.g) balanced the total clockwise moment equals total anticlockwise moment i.e equilibrium
lever (principle of moments)
applies a smaller effort force further from the pivot to create a larger output force closer to the pivot e.g hammer, car jack, arm
A student is struggling to loosen a bolt using a 10 cm spanner. Explain how they could increase the moment acting on the bolt and why this would help. (3)
To increase the moment, the student should increase the distance from the pivot by using a longer spanner.
A longer spanner means a larger perpendicular distance, so the same force produces a bigger moment.
This larger moment makes it easier to turn the bolt and loosen it.
What are gears?
Gears are wheels with toothed edges that rotate on an axle or shaft. Their teeth interlock so one gear turns another.
How do gears affect direction of rotation?
When two gears mesh, they always rotate in opposite directions.
What happens when the driven gear is larger?
It rotates more slowly but produces a greater moment (low gear ratio).
What happens when the driven gear is smaller?
It rotates faster but with a smaller moment (high gear ratio).
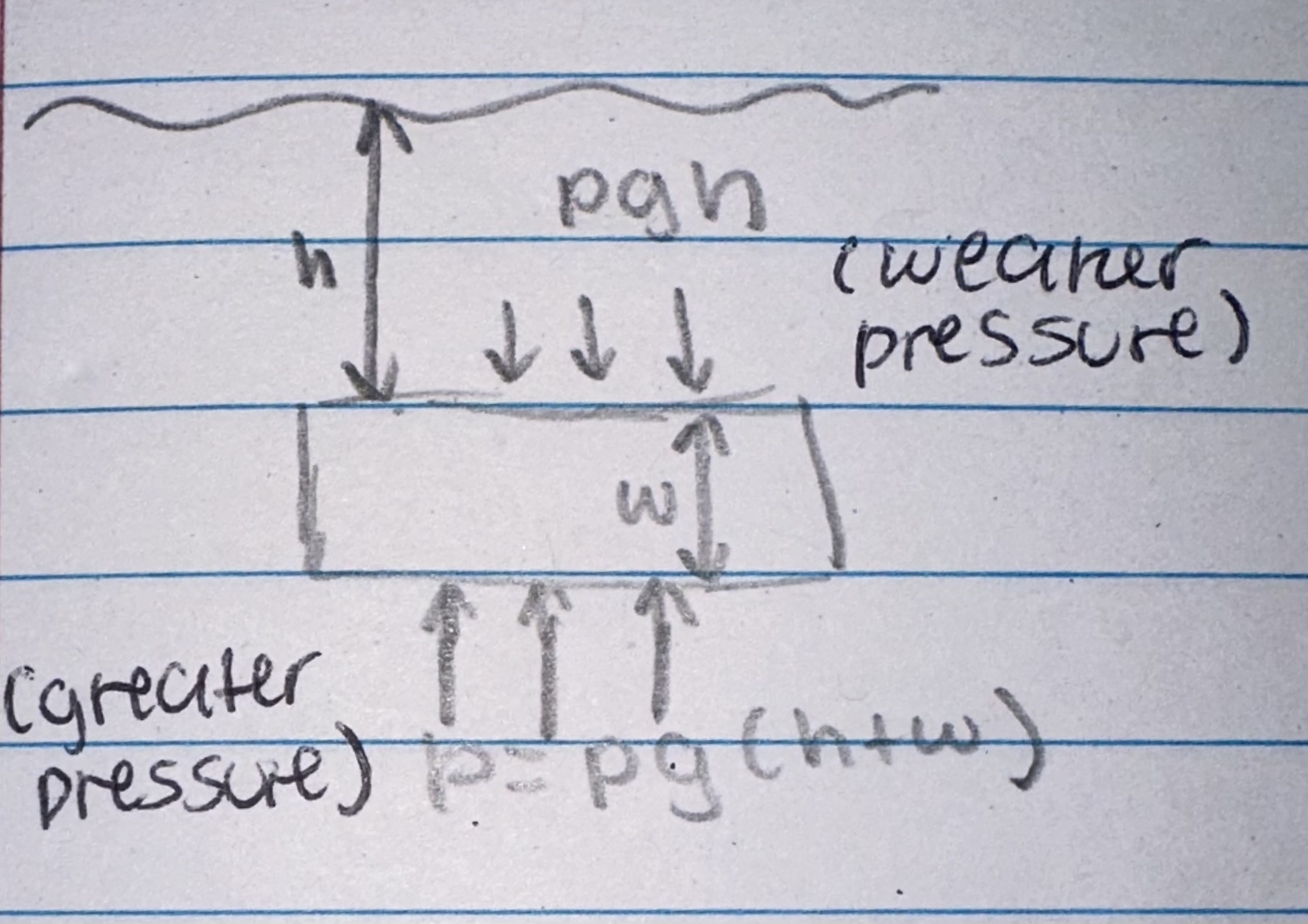
pressure in fluids ( liquids & gases)
causes a force normal to ( at right angles) any surface
the pressure at the surface of a fluid can be calculated using a diff equation
pressure = force normal to a surface / area of that surface
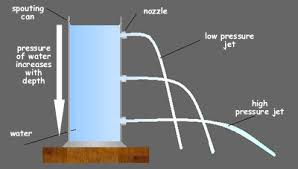
pressure increases as depth increases
this because the weight of the column of liquid above increases with depth
therefore water at the bottom hole comes out with more force and shoots further
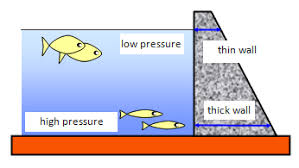
Why does the thickness of dam increase with depth? (3)
pressure of water increases with depth → high amount of pressure at bottom of water
the force acting at a right angle to the container to increase with depth
wall at bottom of dam needs to be thicker to provide a larger reaction force inwards to balance outwards force → withstand higher amount of pressure
pressure due to a column of liquid can be calculated using the equation:
pressure = height of column x density of liquid x gravitational field strength
p=hpg or change in pressure = p x g x change in height
How does atmospheric pressure change with altitude?
Atmospheric pressure decreases as altitude increases.

Why is air pressure higher at ground level than at the top of a mountain?
Because there is more air above you at lower altitudes, creating a larger weight of air and therefore higher pressure.

How is pressure in gases similar to pressure in liquids?
In both, pressure increases with depth because particles exert force from above.
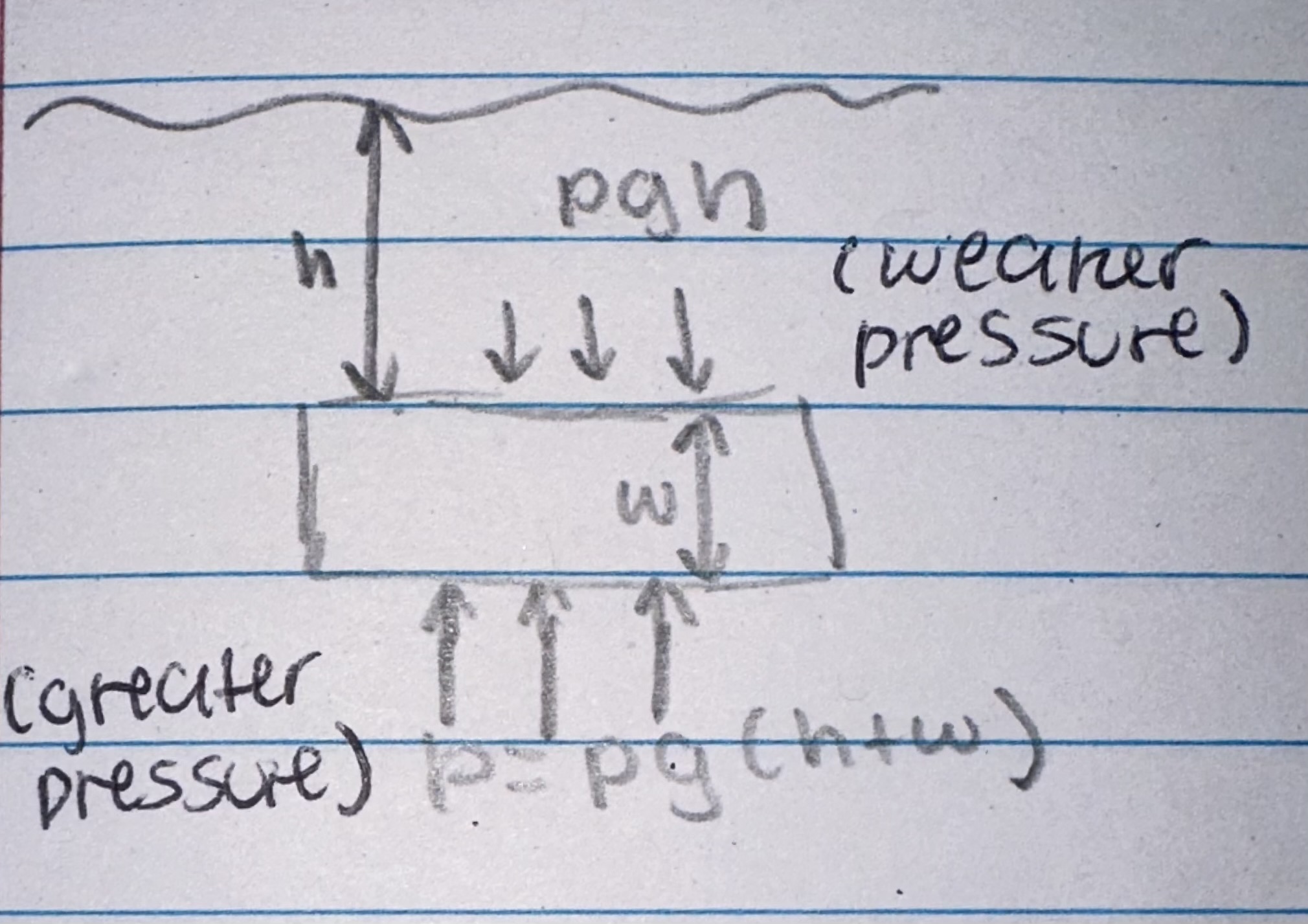
What causes upthrust on a submerged object?
The pressure at the bottom of the object is greater than the pressure at the top, creating a resultant upward force called upthrust.