biology chapter 20 variation and inheritance
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
when leaves look pale or yellow
colour of leaves can be mostly due to genetics but also caused by environmental factors such as lack of light, mineral deficiencies and virus infections
what is chlorosis and some factors that affect it?
independent assortment, crossing over and random fusion of gametes
how is genetic variation created through meiosis?
a version of the gene that will always be expressed if present
what is a dominant allele?
only expressed if two copies of this allele are present
what is a recessive allele
two identical alleles for a characteristic
dominant - two alleles for the dominant phenotype
recessive - two alleles for the recessive phenotype
what is a homozygous characteristic?
what is homozygous dominant and recessive?
two different alleles for a characteristic
what is a heterozygous characteristic?
continuous - characteristic can take any value in a range
discontinuous - characteristic that can only appear in specific values
what are the two types of variation?
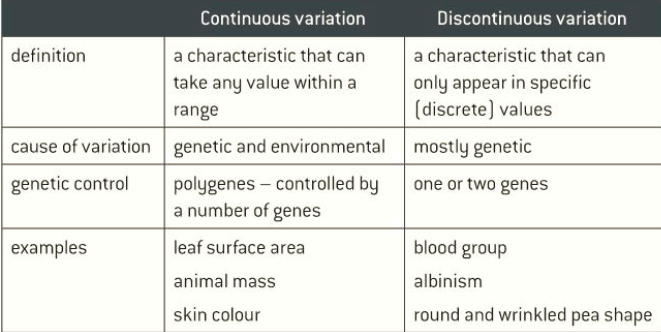
caused by genetics and environment
controlled by a number of genes
scatter or line graph
quantitative data
continuous variation characteristics
caused mostly by genetics
controlled by one or two genes
Bar chart or pie chart
qualitative data
discontinuous variation characteristics
state both phenotypes
state both genotypes in letters
state gametes with a circle around each letter
do punnett square
state proportion of each genotype per offspring
stae the corresponding phenotype
key steps in a genetic cross
the transmission of a characteristic determined by a single gene
what is monogenic inheritance?
organisms that have the homozygous alleles for a particular gene
RR or rr
what is pure or true breeding?
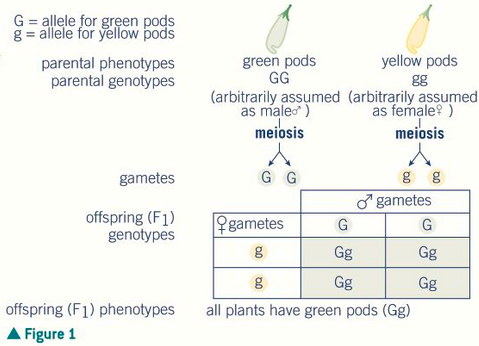
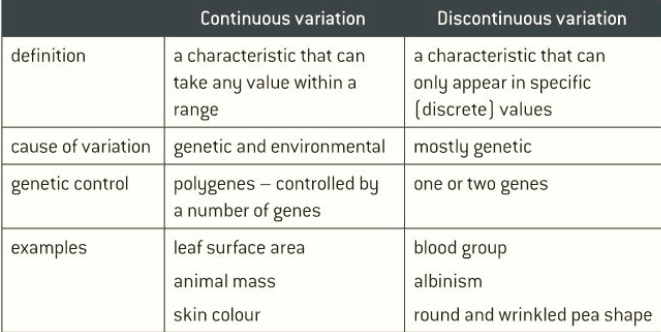
all are heterozygous
what are all the offspring of a homozygous cross?
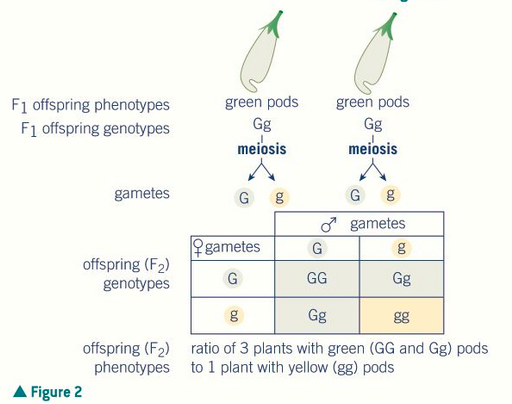
3:1 of green to yellow as green is the dominant allele
1:2:1 genotypic ratio
what is the ratio in a heterozygous monogenic cross?
to determine unknown genotype:
cross unknown with homozygous recessive (rr)
If all the babies are dominant phenotype then the original was homozygous dominant (RR)
If half show dominant and half show recessive then the original individual must have been heterozygous (Rr)
how to do a back/test cross?
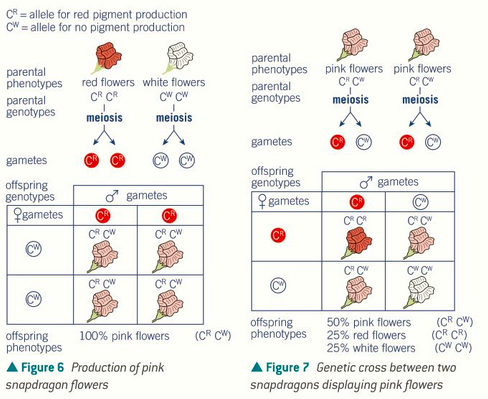
when two different alleles occur for a gene and both are equally dominant
can also produce a hybrid colour
what is codominance?
what does it produce as well as the two original phenotypes?
1:2:1
what is the codominance ratio of the heterozygous cross?
an upper and lower case letter would imply one is dominant or recessive
so a letter is chosen to represent the gene
CR or CW
why are superscript letters used for codominance?
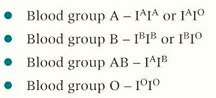
some genes have more than two versions but can only carry two (one on each homologous chromosome)
IA , IB, or IO
IA and IB are codominant while IO is recessive
how does codominance work in blood types?
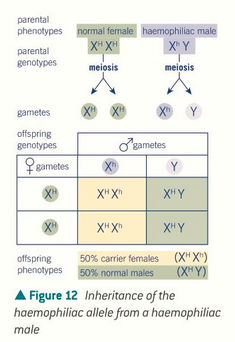
characteristics are determined by genes on the sex chromosomes
there are some genes on the X chromosome that are not on the Y because the Y is much smaller
any characteristic caused by a recessive allele on the X chromosome occurs more often in men because it is missing the Y
draw sex-linked conditions with the superscript of the chromosome they occur on (Y has no allele attached)
what is sex likage?
inheritance of two genes
four alleles are used at each stage rather than two
gametes are split into twoes
what is dihybrid inheritance?
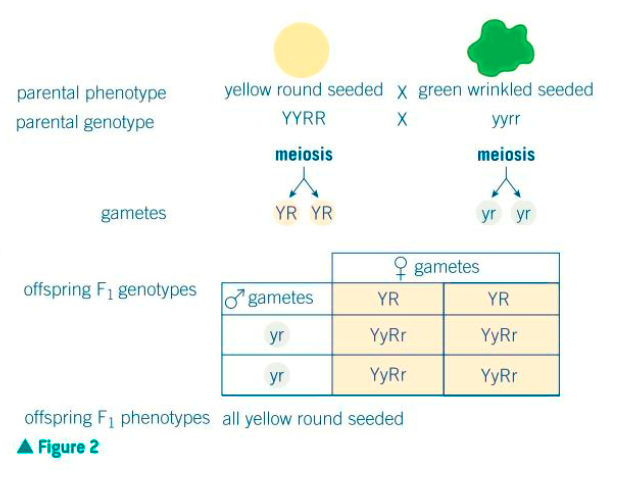
all heterozygous in the F1 generation
what would a homozygous (true breeding) cross of dihybrid inheritance produce?
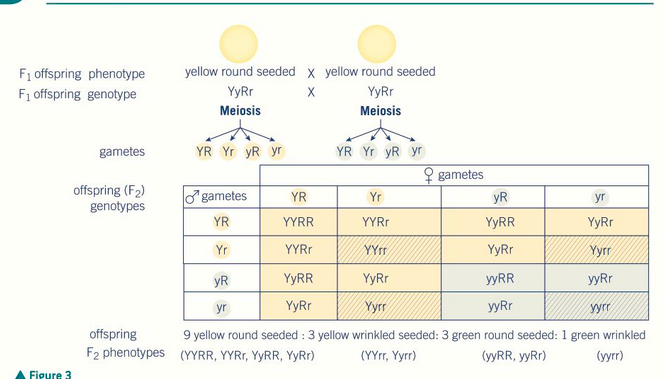
9:3:3:1
what is the genotypic ratio of an F2 generation or heterozygous cross in dihybrid?
fertilisation is random and can lead to ratio skews
if genes are on the same chromosome - linked genes cannot do crossing over
why can the actual ratios differ?
when genes are found on the same chromosome
linked genes are inherited as one unit
the closer the genes are chromosomes, the less likely to be separated during crossing over
what is autosomal linkage?
formed during crossing over, resulting in chromosomes that contain a mix of genetic material from both parental chromosomes
what are recombinant alleles?
number of recombinant offspring/total number of offspring
no linkage and genes on separate chromosomes
less than 50% shows linkage
recombinant frequency formula?
What does 50% recombinant frequency mean?
Less than 50%?
measures the size of the difference between the results you actually get (observe) and those expected to get
helps determine whether differences in results are significant or not
what is a chi-squared test used for?

null hypothesis - no significant difference between expected results
when the chi squared value is more than the critical value in the table
what is the null and equation for chi-squared?
when do you reject the null hypothesis?
find degrees of freedom by doing 1 minus the number of categories
p value is the significance level you are testing at
how to read critical value from table?
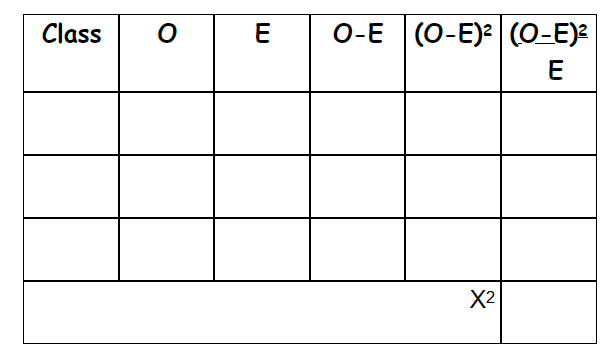
what does a table for chi squared have?
one gene affects the expression of another
You would be able to tell if the inheritance is epistatic if you get less than 4 phenotypes in the offspring.
what is epistasis?
hypostatic - gene affected by another gene
epistatic - genes that affects another gene
what does hypostatic and epistatic mean?
the presence of two recessive alleles affects expression of gene
(9:3:4)
what is recessive antagonistic epistasis?
ratio?
if a dominant allele has an affect on another gene
(12:3:1)
There can also be epistasis where white becomes a separate colour but blends into the no-colour animals. (13:3)
what is dominant antagonistic epistasis?
ratio?
only two phenotypes exist. Must have both big A and B to be purple. dihybrid
(9:7)
what is complementary epistasis and ratio in dihybrid heterozygous inheritance?
investigates how allele frequencies within populations change over time. The total genes in a population is called a gene pool.
what is population genetics?
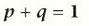
In diploid breeding with two potential alleles, the frequency of the dominant allele (RR) plus the frequency of the recessive allele (rr) will always be 1.
how to calculate allele frequency?
in a stable population with no distruption, the allele frequencies will remain constant from one generation to another
what is the Hardy-Weinberg principle?
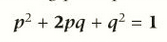
p2 = frequency of homozygous dominant genotype (RR)
2pq = frequency of heterozygous genotype (Rr)
q2 = frequency of homozygous recessive genotype (rr)
what is the hard weinberg equation and what do each of the letters mean?
mutations
sexual selection leads to increase in favourable characteristics
gene flow
genetic drift (change in allele frequency)
natural selection
factors that affect evolution?
density dependent: competittion predation disease
density independent: climate change, natural disasters
what are density dependent and independent factors?
when a population size drastically decreases for at least one generation, reducing genetic diversity. Recovery takes thousands of years.
what is a population bottleneck?
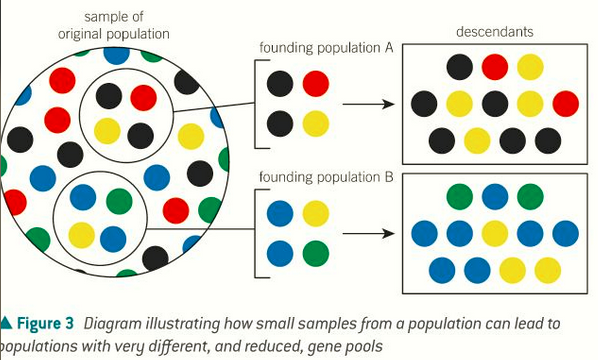
a small population sets up a habitat elsewhere. This would limit the gene pool to the initial founders and would have a lower allele frequency.
Less genetic diversity. It will take time for mutations to occur for the gene pool to expand.
what is the founder effect?
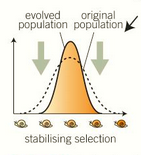
no extreme variations and narrow width of distribution in the centre
what is stabilising selection?
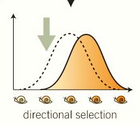
favours one extreme
one phenotype is more useful
what is directional selection?
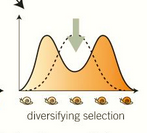
both extremes are favoured
what is disruptive selection?
the formation of a new species trough the process of evolution. The new species will no longer be able to breed with the original species.
what is speciation?
a geographical barrier divides pop. The environments will be different and have different selection pressures
what is allopatric speciation?
reproductive barrier even in the same geographical location.
Hybrid offspring cannot interbreed with the original offspring.
what is sympatric speciation?
Humans are selecting which organisms will breed and pass on their alleles. It’s also called selective breeding.
Populations are usually polymorphic.
example in plants is corn
what is artificial selection?
Possible loss of a whole population by a disease or environmental change
Increased chance of genetic disorders caused by harmful recessive alleles combining due to inbreeding
Seed banks are kept as a genetic resource to store biological samples of DNA, mostly plants, to increase genetic diversity.
problems from interbreeding?
Selective breeding often results in animals that are more susceptible to diseases and health problems.
ethical concerns of selective breeding?