free scored FL
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
What quantity of Compound 1 must be provided to prepare 100.00 mL of solution with a concentration equal to Ki?
Ki= 60.3 uM, Molar mass of compound 1 is 483.5
A.
48.4 mg
B.
24.2 mg
C.
5.64 mg
D.
2.92 mg
D
ki/100=6.03umol * molar mass= 292 redo decimal points bc of umol —→ 2.92 mg
bose einstein principal
collection of atoms cooled close to absolute zero will coalesce into a single quantum state
Heisenberg uncertainty principal
one cannot know both momentum and position of an object with absolute certainty
pauli exclusion principal
two or more identical fermions cannot occupy same quantum state
If only [I] is increased, then [ESI] or [EI] increases. This is an example of:
A.
the Bose–Einstein Principle.
B.
the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle.
C.
the Le Châtelier’s Principle.
D.
the Pauli Exclusion Principle
C,
Which structural change to Compound 1 would make it more water soluble?
A.
Replacing benzene CH with N in the ring
B.
Replacing C=O with C=CH2
C.
Replacing N-N=N with CH-CH=CH
D.
Replacing NH with NCH3
A, rest is adding more hydrogens to the compound making it less water soluble
What is Ki regardless of what number is given for it
a constant meaning it will never change for any variables apart of the equation like I
In μM•s–1 and μM, what should the approximate values of kcat/KM and Ki be, respectively, when [I] = 180 μM?
Compound 1 | KM | kcat | kcat/KM | Ki |
0 | 1.678 | 0.250 | 00.149 | — |
60.0 | 0.832 | 0.126 | 0.151 | 60.3 |
120 | 0.430 | 0.064 | 0.149 | 60.3 |
A.
33.5 and 15.7
B.
75 and 30.1
C.
150 and 60.3
D.
300 and 120.6
C
What functional group transformation occurs in the product of the reaction catalyzed by Na+-NQR?
“The NADH:quinone oxidoreductase (Na+-NQR) is a transmembrane protein that catalyzes the reaction between NADH and ubiquinone coupled to the pumping of Na+ across the plasma membrane, resulting in a Na+ concentration gradient”
A.
RC(=O)R → RCH(OH)R
B.
ROPO32- → ROH + Pi
C.
RC(=O)NHR'→ RCOOH + R'NH2
D.
RC(=O)OR'→ RCOOH + R'OH
A, its an oxireductase reaction meaning a oxygen will be reduced (addition of hydrogen)
What is the chemical structure of a component found in four of the five cofactors used by Na+-NQR? cofactor is flavin
A.
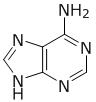
B.
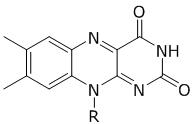
C.
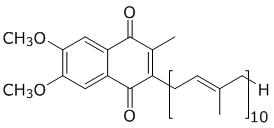
D.
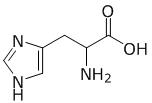
B
C is ubiquinone
D is histidine
A is adenine
What is the ratio of cation to enzyme in the Spectro electrochemical experiments described in the passage?
“Na+-NQR was diluted to a final concentration of 0.75 mM in 0.150 M LiCl, NaCl, KCl, RbCl, or NH4Cl (each solution also contained redox active mediators)”
A.
1:2
B.
2:1
C.
20:1
D.
200:1
D, first figure out whats enzyme and whats cation. Enzymes are smaller than cations in the passage we are given two values one in mM the smaller one and M. We can assume 0.75mM is the enzyme and 0.150M is the cation. We are asking to find ratio of cation to enzyme, first need to convert to same units
0.150M to mm —> 150mm, ratio being cation over enzyme we divide 150mm/0.75mm giving us ratio of 200:1
The reaction between NADH and ubiquinone is exergonic, but the reaction, when catalyzed by Na+-NQR, does not generate much heat in vivo. What factor accounts for this difference?
The reaction catalyzed by Na+-NQR in vivo:
A.
is more exothermic as a result of the lower activation energy.
B.
occurs sequentially in several small steps.
C.
maintains a large separation between the reacting centers.
D.
is coupled to the movement of a charged particle against a concentration gradient
D, we are talking about Na+ which is used primarily in concentration gradient, Na+ ions are pumped across the electron concentration membrane.
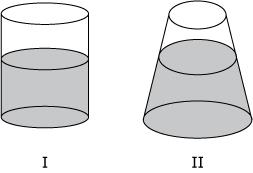
Two open flasks I and II contain different volumes of the same liquid. Suppose that the pressure is measured at a point 10 cm below the surface of the liquid in each container. How will the pressures compare?
A.
The pressures will be equal.
B.
Pressure in flask I will be less.
C.
Pressure in flask II will be less.
D.
The pressures cannot be compared from the information given.
A
What is the identity of an atom that contains six protons and eight neutrons?
A.
Nitrogen
B.
Carbon
C.
Oxygen
D.
Silicon
B
Which of the following substances is polar?
A.
NF3
B.
CCl4
C.
CO2
D.
Li2
A
If all else is held constant, which of the following changes would NOT double the volume of a gas?
A.
Doubling the pressure
B.
Doubling the absolute temperature
C.
Halving the pressure
D.
Doubling the number of gas molecules
A, boyle law states pressure in inverse to volume so increasing pressure will lower volume not increase it
What is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of the atom used to produce laser radiations?
fluorescence spectrometer depicted in Figure 2, which employs a 86Kr+ laser that simultaneously emits radiations of wavelengths 407 nm and 605 nm
A.
48
B.
49
C.
50
D.
51
C, 86- Kr proton (36) yields 50 neutrons
What is the molecular formula of the heterocyclic aromatic compound pyrrole?
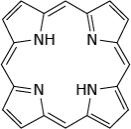
Figure 1 Structure of porphin
A.
C2H3N
B.
C4H5N
C.
C6H7N
D.
C8H9N
B
Approximately how many moles of Kr+ are contained in the laser tube at 0°C and 1 atm?
Inside the laser, the noble gas is contained in a 11-cm3 tube.
A.
3 x 10-7
B.
2 x 10-6
C.
4 x 10-5
D.
5 x 10-4
D, simplify everything we know its at 1 ATM meaning we can use 22.4 L in the equation. Now we got two values the tube being 11 and constant 22.4
11/22.4 shortcutting the math process so ignore .4 and just divide 11/22, gotta need to add zero to 11 converting 110/22 giving us a number of 5 which we see as one of the answer choice, we dont need to worry about significant decimal values as this is mcat not some math test so if we get the big number right we can assume its just whatever decimal value given as answer they won’t make us go that far.
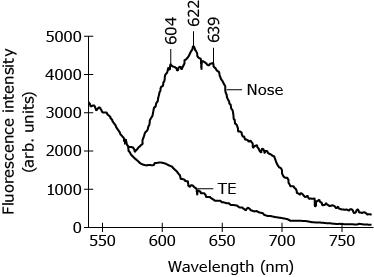
The radiation of wavelength 605 nm CANNOT be used to produce the fluorescence radiations depicted in Figure 3 because:
Two prisms were used to select the desired wavelength from the radiations emitted by the laser. A multi-fiber sensor assembly sent the 407-nm wavelength radiation to the skin sample and collected the fluorescence radiation emitted by the skin.
Spectral analysis showed that strong fluorescent radiation of wavelengths 604, 622, and 639 nm were emitted from the spots in the skin of the nasal area that contained large amounts of P. acnes
A.
the energy of the absorbed radiation must be larger than the energy of the fluorescence radiation.
B.
the energy of the absorbed radiation must be smaller than the energy of the fluorescence radiation.
C.
the 605-nm radiation has more energy than the 407-nm radiation.
D.
the 605-nm radiation is not visible.
A, the lowest intensity given by 405 was 604 which is smaller than 605, you cannot produce a smaller value its not possible and since it couldn’t produce the first peak we don’t worry about the rest. If the lowest peak was 622 or even 605 then yes it would be possible but the first peak was smaller by 1 not allowing 605 to work.
amide nitrogen
nitrogen in peptide bond that’s sp2 hybridized its planar doesn’t fulfill criteria of being chiral
carbonyl carbon
sp2, meaning its planar can’t be chiral
The CD spectroscopy signal that was used to generate the data in Figure 1 arises from the chirality of the:
A.
α carbon.
B.
amide nitrogen.
C.
carbonyl carbon.
D.
β carbon.
A, all a carbons are tetrahedral allowing them to be chiral carbons meaning carbon attached to four atoms
Which physical property does NOT change with the amino acid substitution made in TPMT*5?
“TPMT*5 (an L49S variant)”
A.
Molecular weight
B.
Hydrophobicity
C.
Hydrogen bonding capability
D.
Net charge
D, both amino acids are neutral not an acidic ( D and E) nor basic ( H R K)
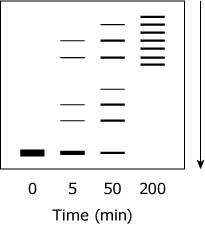
Samples from various time points of the proteolysis of TPMTwt were subjected to SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. Which figure best depicts the expected appearance of the gel?
(Note: The arrow indicates the movement of the protein through the gel.)
A.
B.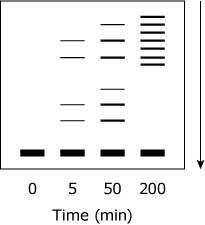
C.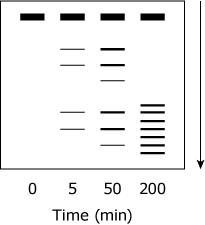
D.
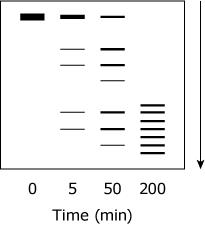
D, is the only way universally an SDS page should look if the arrow is that direction the Base will always be at the start of arrow and dissipating towards the arrow shown in only D
If the combined mass of the TPMT substrate and cofactor was determined before the enzymatically catalyzed reaction and then compared to the combined mass of the product and the cofactor after the reaction, the net change in molecular weight will be:
“Thiopurine S-methyltransferase (TPMT) is an enzyme that is responsible for the metabolism of the drugs azathioprine and 6‑mercaptopurine”
A.
+15 g/mol.
B.
0 g/mol.
C.
–15 g/mol.
D.
–16 g/mol.
B, TMPT is a transferase meaning not addition or subtracting just switching methyl group in this case from cofactor to substrate.
The ligand of hMPRα is derived from which compound?
“The steroid progesterone has an important role in the female reproductive system. Researchers interested in studying membrane progestin receptors (MPRs) developed a method to produce and purify the protein in active form.”
A.
Glucose
B.
Phenylalanine
C.
Glycerol
D.
Cholesterol
D, its derived from a steroid which is a cholesterol compound base
The second purification step is which type of chromatographic separation?
The second sequence consisted of six consecutive histidine residues (His)6. This sequence binds tightly to Ni2+ cations. In chromatography, (His)6 tag labeled proteins can be eluted from Ni2+-supported columns by adding a small molecule to the eluent that mimics the side chain of histidine.
A.
Affinity
B.
Size exclusion
C.
Cation exchange
D.
Anion exchange
A, His binds to an cation this is an affinity
cation exchange chromatography
separates proteins based on positive charges, a question would be like Suppose you separate two proteins at pH 7:
Protein A (pI = 9): at pH 7, it has a net positive charge → it binds to the cation-exchange resin.
anion exchange chromatgraphy
separates proteins based on negative charges an question would be like Protein B (pI = 5): at pH 7, it has a net negative charge → it does not bind and flows through.
The structure of Compound 2 is shown.
“hMPRα was then extracted from the membranes using n-decyl-β-D-maltopyranoside, Compound 2.”
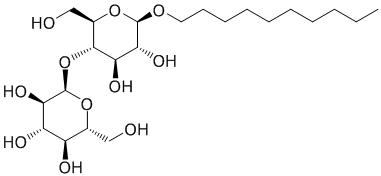
Compound 2
What structural feature(s) is(are) most important to the functioning of this compound as described in the passage?
A.
Specific configuration of numerous chirality centers
B.
Multiple hydrolysable linkages
C.
Combination of large hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
D.
Presence of a reducing sugar
C, used for its membrane shown in structure is hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
How many moles of NaCl were contained in 500 mL of the buffer solution used to elute hMPRα?
“The buffers used to elute the protein contained 300 mM NaCl, 50 mM NaH2PO4 (pKa = 7.2), and various amounts of NaOH (MM = 40 g/mol).”
A.
7.5 x 10-3
B.
3.0 x 10-3
C.
3.0 x 10-2
D.
1.5 x10-1
D, screw traditional math just use values we are given two values about NaCl first it was contained in 500ml of buffer and the protein contained 300mm, two ways to do this first just multiple them and see what you get or divide which ever shows on question probs it if both shows up then use best judgment in this case 3 × 5 =15 which was seen in 1.5 so we ball its D
Which experimental evidence suggests that the purified hMPRα obtained by the researchers was in its native state?
“During the first chromatography step, a specific chemical agent was immobilized on the stationary phase to bind to the Compound 1 tag. After the second chromatography step, which utilized the (His)6 tag, the researchers used the same binding assay and found that Kd was similar.”
The hMPRα that was obtained:
A.
retained both the Compound 1 and (His)6 tags.
B.
was purified by two separate chromatography steps.
C.
exhibited a binding affinity for progesterone that was similar to that exhibited by native hMPRα.
D.
had a nearly identical molecular weight to hMPRα obtained elsewhere.
saw it say kd was similar so just assumed it was talking about progesterone binding and picked C, the research concluded that so it gotta be important
A major obstacle to obtaining useful energy from a nuclear fusion reactor is containment of the fuel at the very high temperatures required for fusion. The reason such high temperatures are required is to:
A.
eliminate the strong nuclear force.
B.
remove electrical charge from reactants.
C.
decrease the density of the fuel.
D.
enable reactants to approach within range of the strong nuclear force.
D
Enantiomers can exhibit a difference in which chemical or physical property?
A.
Density
B.
Boiling point
C.
Smell
D.
IR spectrum
C
Blood flows with a speed of 30 cm/s along a horizontal tube with a cross-section diameter of 1.6 cm. What is the blood flow speed in the part of the same tube that has a diameter of 0.8 cm?
A.
7.5 cm/s
B.
15 cm/s
C.
60 cm/s
D.
120 cm/s
D, if we are decreasing cross section speed will increase so if we decrease by half speed will increase double but with area we need to account another 2x so if you halve the cross section speed will 4x
Which of the following species has an electron configuration equivalent to that of a noble gas?
A.
Ca2+
B.
Cu2+
C.
O
D.
H
A
Which Trp residue of carbonic anhydrase can be selectively modified with CHCl3 at 20°C?
Table 1 | Photochemically Modified in Carbonic Anhydrase |
Reactant | Buffer | W4 | W15 | W96 | W122 | W190 | W207 | W243 |
CHCl3 | A | 37% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 51% | 0% | 44% |
CHCl3 | B | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 55% |
CCl3CO2H | A | 72% | 66% | 0% | 100% | 100% | 0% | 75% |
A.
W4
B.
W96
C.
W190
D.
W243
D
Which classification of amino acids applies to the Trp residues after photochemical modification by CCl3CO2H?
(Figure 1).
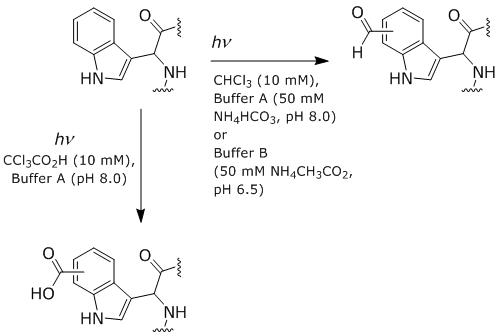
A.
Acidic
B.
Basic
C.
Hydrophobic
D.
Polar neutral
A, Two oxygen is added (carboxylic acid) in the name acid so its an increase in acidic
Which type of heterocycle is found on two amino acid residues blocking access to W15?
“Access to W15 in fully folded carbonic anhydrase is blocked by two His residues and one Lys residue”
A.
Imidazole
B.
Indole
C.
Pyrimidine
D.
Pyrrole
A, imidazole is linked to histidine
Based on the passage, what most likely causes W96 to be accessible to CHCl3 at 75°C?
“W15 and W96, which are in the interior of carbonic anhydrase, are 21% and 29% modified respectively by 10 mM CHCl3 in Buffer A at 75°C, a temperature which fully denatures carbonic anhydrase but leaves its primary structure intact.”
A.
Peptide bonds are broken, releasing W96.
B.
Reduction of disulfide bonds occurs.
C.
The protein unfolds and exposes W96 to the buffer.
D.
CHCl3 extracts W96 from the protein interior.
C
What is the name of the ionic compound used to make Buffer B?
Buffer B was NH4CH3CO2
A.
Ammonium formate
B.
Ammonium carbonate
C.
Ammonium bicarbonate
D.
Ammonium acetate
D
formula for ammonium formate
NH4HCO2
formula for ammonium carbonate
(NH4)2CO3
formula for ammonium bicarbonate
NH4HCO3
Which chromatographic technique would most likely separate a mixture of native carbonic anhydrase from carbonic anhydrase photochemically modified by CCl3CO2H?

A.
Anion-exchange chromatography
B.
Cation-exchange chromatography
C.
Gas-liquid chromatography
D.
Size-exclusion chromatography
A, what changed was the incoporation of carbonxyic acid which is positive charge meaning only works with anion exchange that deals with acidic/+ charge, not B bc thats negative charge so if a base was added instead like NaOH only
What is the name of the functional group containing the external oxygen on each ring of the MCS structures shown in Figure 1?
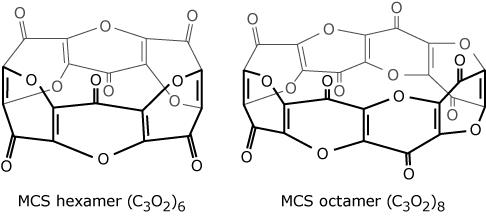
Figure 1 | Structures of MCS hexamer and octamer |
A.
Aldehyde
B.
Carboxylic acid
C.
Ester
D.
Ketone
D
Based on Reaction 1, when 1.0 atm of CO(g) completely reacts to form carbon suboxide at 550°C in a sealed container, what is the final pressure in the container?
4CO(g) → C3O2(g) + CO2(g)
Reaction 1
A.
0.00 atm
B.
0.10 atm
C.
0.25 atm
D.
0.50 atm
D, look at total moles of reaction and produce ratio goes from 4 total to 2 total meaning it divided by half
We are given that 1 atm is completely reacted how much is the final presssure in the container so if 4 moles became half we can assume pressure will also be cut in half leaving D
What does lipophilic mean
wouldnt dissolve readily in aqueous layer
In which phase(s) will the MCS precursor be predominantly found after the extraction step?
“MCS oligomers can be obtained from plants via a lipophilic MCS precursor. This MCS precursor was isolated from plant roots through an extraction that involved mixing an aqueous emulsion with tert-butyl methyl ether ((CH3)3COCH3).”
The MCS precursor will:
A.
be found in the aqueous layer.
B.
be found in the tert-butyl methyl ether layer.
C.
be distributed equally between the aqueous layer and the tert-butyl methyl ether layer.
D.
form a precipitate between the aqueous and tert-butyl methyl ether layers.
B
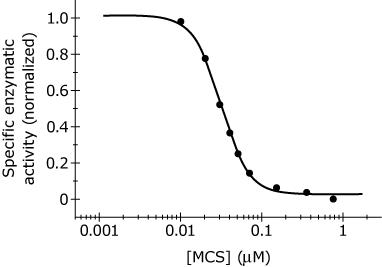
Figure 2 | Concentration-dependent inhibition of ATPase by the MCS oligomer mixture |
Adapted from F. Kerek, R. Stimac, H.-J. Apell, F. Freudenmann, and L. Moroder, Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. ©2002 Elsevier Science B. V.
Based on Figure 2, what is the approximate Ki of the MCS oligomers?
A.
12 nM
B.
30 nM
C.
170 nM
D.
800 nM
B, Ki is the concentration at half
Based on the reported Hill coefficient, in what way do the MCS oligomers affect inhibition?
“hill coefficent was 2.56”
A.
As one MCS oligomer binds to the ATPase, it makes it easier for the others to bind, leading to inhibition.
B.
As one MCS oligomer binds to the ATPase, it makes it more difficult for the others to bind, leading to inhibition.
C.
A single MCS oligomer binds to the ATPase, leading to inhibition.
D.
MCS oligomers randomly bind to the ATPase, leading to inhibition.
A
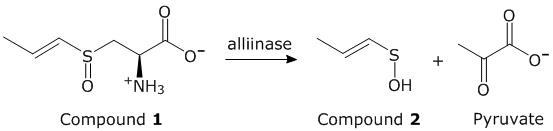
Based on the passage, which type of inhibitor will provide a flavorful onion that does not cause tearing?
“When an onion is cut, the cell components are allowed to mix and Compound 2 encounters an enzyme known as lachrymatory factor synthase (LFS). LFS catalyzes Reaction 3, which produces Compound 4. Compound 4 is a potent lachrymator (tearing agent)”
An inhibitor of:
A.
Compound 1 synthesis
B.
alliinase
C.
Reaction 2
D.
LFS
D
When the covalent attachment to alliinase is broken, PLP is still held rigidly in the active site by a salt bridge and a π-stacking interaction. These interactions are most likely provided by the side chains of which amino acids?
(Note: The salt bridging amino acid is listed first.)
A.
Asp and Tyr
B.
Glu and Ser
C.
Arg and Tyr
D.
Lys and Ser
C, arginine got that guanidine group which is composed of alot of hydrogens used for urine something linked that to salt bridge which uses alot of hydrogens
Which reactant and product (one equivalent each) are necessary to balance Reaction 1?
Reaction 1
A.
Reactant = H2O, product = NO3_
B.
Reactant = H2O, product = NH4+
C.
Reactant = O2, product = NO3_
D.
Reactant = O2, product = NH4+
B
Which energy features characterize the energy profile of Reaction 2?
“Compound 2 spontaneously and rapidly condenses to form Compound 3, which is one of the main flavor components of onions.”
A.
High Ea and ΔG > 0
B.
High Ea and ΔG < 0
C.
Low Ea and ΔG > 0
D.
Low Ea and ΔG < 0
D
Consider the fully protonated amino acid shown.
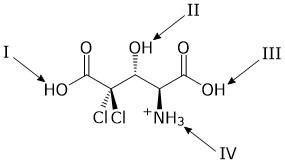
As the pH of a solution of this amino acid is raised, which group deprotonates first?
A.
I
B.
II
C.
III
D.
IV
A, least acidic of the bunch
The graph represents the energy change in an exothermic reaction:
A + B → C
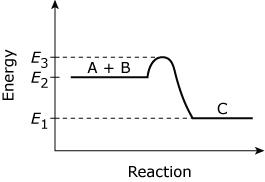
Which of the following expressions gives the activation energy for the reaction?
A.
E3 − E1
B.
E2 − E1
C.
E3 − E2
D.
None of the above
C
A 2 kg mass and a 5 kg mass are connected by a massless cord suspended over a massless and frictionless pulley. If the acceleration due to gravity is g, what will be the acceleration of the masses after they are released from rest?
A.
2g/7
B.
3g/7
C.
5g/7
D.
g
B
An ice cube at 0°C and 1 atm is heated to form steam at 100°C and 1 atm. Ignoring heat loss to the surroundings, what part of the process uses the most heat?
(Note: Specific heat of water = 1 cal/g°C. Heat of fusion = 80 cal/g. Heat of vaporization = 540 cal/g.)
A.
Melting the ice cube
B.
Heating all the water from 0°C to 50°C
C.
Heating all the water from 50°C to 100°C
D.
Vaporizing all the water
D
Based on the passage, which of the following is closest to the pressure exerted on the chest by a 10 × 5 cm rectangular paddle during defibrillation?
“discharging the capacitor through paddles pressed against the chest of the patient. Firm force (~100 N) and a conductive gel pad are used to improve the electrical contact between each paddle and the patient’s chest.”
(Note: 1 Pa = 1 N/m2.)
A.
5 kPa
B.
10 kPa
C.
15 kPa
D.
20 kPa
convert cm to m, divide Cm / 1000 to get M 10×5= 50 cm —→ 0.0005 m
given force of 100, 100/0.0005 = 20 kpa just ignore decimals and do 100/5 giving you 20 which is different than everything else so stop here
If the defibrillator described in the passage were fully charged and the entire charge were discharged through a patient in 10 ms, which of the following is closest to the average electrical current that would flow through the paddles?
voltage is 3000v capacitor is 25 microfold and resistance is 100
A.
7.5 A
B.
15 A
C.
22.5 A
D.
30 A
Current is composed of voltage and capacitor use the values given and just see what you can make of it, firstly multiple 3 and 25 you get 75 an answer choice has those two numbers next try dividing either way nothing from that is on the answer choice so yolo A
If both the capacitor and the power supply in Figure 1 are adjustable, which of the following changes would result in an increase in the charge on the capacitor?
A.
Decreasing the area of the parallel plates
B.
Decreasing the separation between the parallel plates
C.
Removing the dielectric from the capacitor
D.
Decreasing the voltage of the power supply
Capacitor is proportional with all the following except B so answer is B
If the 25 μF capacitor in the defibrillator in Figure 1 is replaced with a 30 μF capacitor, what new power supply setting would produce the same amount of charge?
current capacitor is 3000v
A.
3600 V
B.
3500 V
C.
3000 V
D.
2500 V
D
If the wavelength of a light beam were doubled, its frequency would be:
A.
quartered.
B.
halved.
C.
doubled.
D.
quadrupled.
B
If the energy of a photon is doubled, which of the following properties of the photon will also double?
A.
Amplitude
B.
Wavelength
C.
Frequency
D.
Intensity
C
formula to find wavelength or frequency when given one or the other
C= wavelength * F
C is speed constant 3e8
If the red line in the Balmer series has a wavelength of 656 nm, which of the following is closest to its frequency?
A.
4.6 × 1014 Hz
B.
4.6 × 10−14 Hz
C.
2.1 × 1015 Hz
D.
2.1 × 10−15 Hz
3e8=6e-6*f —→ F/frequency = c/wavelength —→ i can just figure out the e bc when you divide you substrate e so 8—6 gave me 14 giving me answer choice A
Which of the following is closest to the wavelength of a photon whose energy is 2 eV?
“λ = hc/E, where E is the energy of the photon, h = 4.1 × 10–15 eV•s is Planck’s constant, and c = 3 × 108 m/s is the speed of light”
A.
740 nm
B.
620 nm
C.
450 nm
D.
310 nm
B
What is the value of Kb for the conjugate base of a weak organic acid that has a pKa of 5?
A.
10−2.5
B.
10−5
C.
10−9
D.
10−10
C
An ester is prepared by the method of direct esterification using an esterase enzyme as a catalyst. Which of the following modifications will NOT appreciably increase the final yield of ester?

A.
Using 2 times as much enzyme
B.
Using 2 moles of RCOOH instead of 1 mole
C.
Using 2 moles of RCH2OH instead of 1 mole
D.
Removing RCOOCH2R from the reaction mixture as it is formed
A
A person pushes on a rolling cart with a force that diminishes with time because the person must walk faster to keep up with the accelerating cart. How much work does the person generate while pushing on the cart?
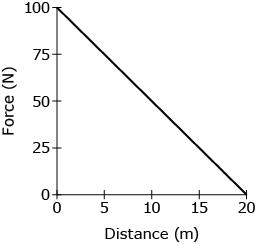
A.
500 J
B.
1000 J
C.
2000 J
D.
4000 J
B