Circuits KS3
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is a current?
The rate of the flow of electricity between two objects (amount per second). Current flows from the positive to the negative end of a power supply.
What is a current measured in?
Amperes/Amps/A
Define potential difference
The energy transfer between two points (strength). This can also be explained as the ‘push’ electricity gets to move around.
What is potential difference measured in?
Volts (V)
What is used to measure amperes?
An ammeter
What is used to measure volts?
A voltmeter
What is the difference between potential difference and current?
Potential difference is the strength of one power source in comparison to a conductor or from conductor to conductor. Current is the effect of potential difference; it is the outflow of charge with its strength dependent on the strength of the potential difference. PD is the cause, A is the effect.
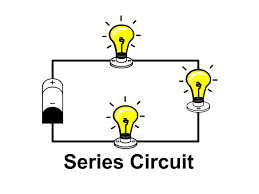
What type of circuit is this?
Series
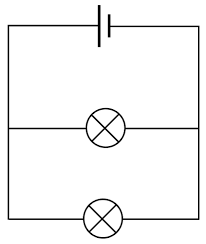
What type of circuit is this?
Parallel
Why are series circuits unreliable?
Because charge is distributed along one path, meaning that there is no extra pathway for the current to take and it must pass through multiple components. Without extra access to a power source, the voltage drops when each new component is added. This is why two bulbs in a series circuit shine dimmer than just one.
Why do components of a parallel circuit all share the same amount of charge without malfunctioning?
Because they are all directly connected to one source of voltage, not to one another like in a series circuit. This means that the current can pass from the power source directly to the components instead of through them, which then would cause the voltage to divide.

What is this circuit symbol?
Bulb
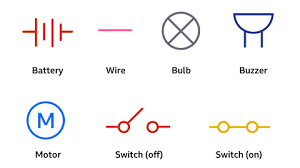
(FLASHCARD) What do you know about these symbols? (And more)
A battery is comprised of multiple cells, with positive and negative ends for output.
Wires are straight lines connecting all components from both sides.
Bulbs’ filaments light up when connected to charge.
Buzzers make noise when connected to charge.
Motors move cyclically around in circles when connected to charge.
Switches allow you to manually open and close a circuit.
What are the advantages of parallel circuits?
Independent component operation
Easier to troubleshoot when something goes wrong
Reduced risk of overload due to current having more paths.
What is Ohm’s law?
The current through a conductor at two points is directly proportional to the voltage. Increasing the voltage will increase the current and decreasing will do the same. When resistance is applied, the current will decrease.
What is the formula for Ohm’s law?
V = I*R (Voltage = Current x Resistance)
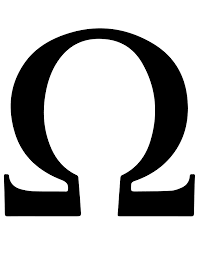
What is resistance measured in?
Ohms
How does resistance work?
Electrons colliding with the atoms of the material they are attempting to pass through, impeding the current’s speed and ability to flow. Every component and even wires have resistance (though wires’ are small enough to ignore).
Define ‘resistance’ (electricity)
The opposition to a current’s flow.
What does it mean to be ‘in series’ or ‘parallel to’ in a circuit?
In series - Within the same loop of wire
Parallel - Attached to a specific component that you wish to measure
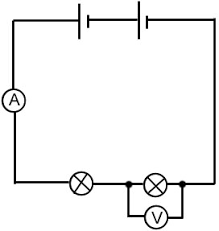
Where do voltmeters have to be to measure the potential difference of a component?
Parallel to the selected component.
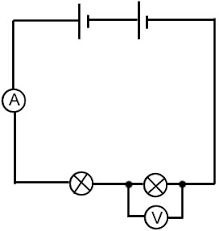
Where do ammeters have to be in a circuit to measure current?
In series with the path of current flow you want to measure (just within the loop).
What are the charges of protons, neutrons, and electrons?
Protons - Positive (+1)
Neutrons - Neutral (0)
Electrons - Negative (-1)
How is positive, negative or neutral charge determined?
If the number of protons outweighs the number of electrons, the atom is positive and vice versa for if the electrons outweigh the protons. If they cancel each other out, the atom is neutrally charged.
How does electricity (electrons) flow?
The electrons become detached from an atoms power source and move freely through a conductor. Potential difference creates a form of pressure that ‘pushes’ them from areas of high potential to areas of low potential (similarly to water).
How do neutral objects become positively or negatively charged?
Friction between insulators. Negative charges (electrons) move through friction between insulators.
BONUS: The object gaining electrons becomes negatively charged and vice versa.
What is static electricity?
A build-up of positive or negative charge within an object.
Why do electrons escape so easily compared to protons?
Electrons have a much lower mass and make up the outer shell of an atom, meaning they can transfer easily. Protons and positive ions have a far larger mass, significantly hindering movement.
What are electrostatic forces?
Force between charged objects that causes them to attract or repel.
What happens when objects have like or unlike charges?
They repel/attract
Why do charged balloons stick to neutral walls? (THIS IS KNOWN AS POLARISATION)
Because the negative charge of the balloon repels the negative ions and attracts the positive, which are much harder to move.
Why are ions attracted to each other?
They attempt to form ionic bonds.
What is the relationship between power sources and electrons?
Power sources input energy into electrons, increasing their potential energy.
The positive and negative terminals create a deficiency and an efficiency of energy, causing the electrons to move.
Energy is lost throughout a circuit due to components.
Electrons carry and release energy.
The amount of electrons in a circuit never changes.