AP Psychology: Unit 5: States of Consciousness Terms & Definitions
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
consciousness
the state of being aware of and able to perceive one's thoughts, feelings, sensations, and surroundings
levels of consciousness
consciousness
preconsciousness
- automatic behaviors
- subliminal perception
subconscious (unconscious)
altered states of consciousness
all the moments when we are not completely conscious
common characteristics:
- shallow cognitions
- altered perceptions
- lowered inhibitions
meditation
a set of techniques used for altering consciousness through contemplation (control the autonomic)
- concentrative
- yoga
- opening-up meditation
concentrative meditation
contemplation by focusing on an object
- cross-legged, "om," focused breathing
hypnic jerk
sudden jolt awake (usually bc of sleep deprivation)
suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)
(pair of cell clusters in hypothalamus)
controls circadian rhythm
- causes the pineal gland to adjust melatonin production when exposed to bright light, which modifies feelings of sleepiness
insomnia
Characteristics: inability to fall asleep or stay asleep
Suspected causes: stress, other sleep disorders, medical conditions, substance abuse
narcolepsy
Characteristics: excessive daytime sleepiness, uncontrollable sleep attacks
Suspected causes: genetics
sleep walking
Characteristics: walking and moving during sleep
Suspected causes: other sleep disorder, medical conditions, medication, mental health disorder, substance abuse
night terrors
Characteristics: wake up in intense fear with little to no memory of a nightmare
Suspected causes: sleep deprivation, head injury, sleep apnea, fever, other sleep disorder, medications, stroke, stress
Freud's Theory
dreams represent unconscious desires, thoughts, motivations
- dream rebound theory
dream rebound theory
suppression of thought sometimes results in dreaming about it (Freud's Theory)
Activation-Synthesis Theory (Hobson and McCarley)
circuits in brain are activated and trigger amygdala and hippocampus to create electrical impulses
- creates compilation of random thoughts, images, memories
Information-Processing Theory
dreaming is a byproduct/active part of experience of processing/consolidating information and memories from the day
Creativity Theory
purpose is to solve problems and create new ideas
- dreaming promotes creative thinking
Continuity Hypothesis
dreams reflect a person's life
- incorporate conscious experiences/memories in dreams
Primitive Instinct Rehearsal and Adaptive Strategy
dreaming prepares us to confront dangers in the real work
- practice important survival skills in a safe environment (simulation)
Emotional Regulation Theory
dreams help us process and cope with our emotions in a safe place
- amygdala and hippocampus consolidate information and move it from short-term to long-term memory during vivid/intense dreaming
hypnosis
social interaction in which a hypnotist makes suggestions about perceptions, feelings, thoughts, or behaviors will occur
- guided meditation
- divided consciousness
- post-hypnotic suggestion
sensory deprivation
any major reduction in amount or variety of sensory stimulation
benefits:
- sensory enhancement
- relaxation, stress reduction
- changing habits
REST (restricted environmental simulation therapy)
psychoactive drugs
drugs that produce a psychopharmacological effect
(affect behavior, mood, consciousness)
tolerance
it takes more than before to get the same feeling
withdrawal
physical illness or discomfort when not using the drug
addiction
physical or psychological dependence on a drug
(chronic brain disorder)
stimulants
a class of psychoactive drugs that arouse/excite CNS
- increase heart rate, stamina, respiration, blood pressure
- decrease appetite
caffeine
stimulant
- antagonist: suppresses adenosine (depressant of brain)
- increased feelings of alertness
withdrawal: lethargy, irritability, lack of concentration, headache
- link w/ birth defects
nicotine
stimulant
- agonist: activates/increases Ach & releases dopamine
★ one of the most addicting of all drugs ★
- makes user feel relaxed
acute intoxication: dizziness, nausea, muscle tremors
long-term risk: heart disease, gum disease, cancer, brittle bones, emphysema
- vaping
amphetamines
stimulant
- agonist: activates dopamine & norepinephrine
- initial rush then agitation
amphetamine psychosis: mental illness due to chronic amphetamine drug use
long-term risk: heart attacks, aggression, odd behavior
depressants
a class of psychoactive drugs that inhibit or slow the CNS
- reduce anxiety, help with insomnia, slows reflexes, impaired judgement
anti-anxiety
depressant
- agonist: activates/enhances GABA
benzodiazepines: lowers anxiety, reduce tension, relieve insomnia
- valium, xanax, halcion, rohypnol
★ dangerous ★
sedative-hypnotics
depressant
- agonist: activates/enhances GABA
barbiturates: depress brain activity, highly addictive, extreme risk of overdose
GHB (Gamma-hyproxybutyrate): relaxes & sedates body
- slows heartbeat and respiration, loss of muscle control, loss of gag reflex, loss of consciousness, death
★ dangerous ★
alcohol
depressant
- agonist: enhances GABA, initially increases dopamine but long-term leads to a decreased effectiveness of dopamine
- affects cerebral cortex, limbic system, cerebellum, hypothalamus, medulla
- euphoria to excitement to confusion to stupor and eventually to coma and death
binge drinking: 5 or more drinks, alcohol poisoning
- CNS damage, liver damage, Korsakoff's Syndrome
withdrawal: convulsions, hallucinations, tremors (hangover)
alcohol myopia
narcotics
a class of psychoactive drugs that reduce pain, reduce diarrhea, and suppress coughing
opiates/opioids
narcotic
- agonist: mimic endorphins, stimulates dopamine release
- euphoria, reduction of pain, depressed breathing, slowed heart rate, itching skin
- overdose danger due to tolerance
- highly addictive b/c withdrawal symptoms are so bad
heroin withdrawal: no appetite, severe diarrhea and cramps, chills, fever
- Naloxone/Narcan, Methadone
hallucinogens
a class of psychoactive drugs that alter consciousness of inner and outer worlds
lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD)
hallucinogens
- antagonist: blocks seratonin
- dizziness, creeping skin, nausea, tremors, loss of time, mood swings, hallucinations, extreme cognitions, paranoia
delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinal (THC)
hallucinogen
- agonist: mimics anandamide
- affect short-term memory, coordination, sensory/time perception, learning, hunger, pre-cancerous changes in lungs
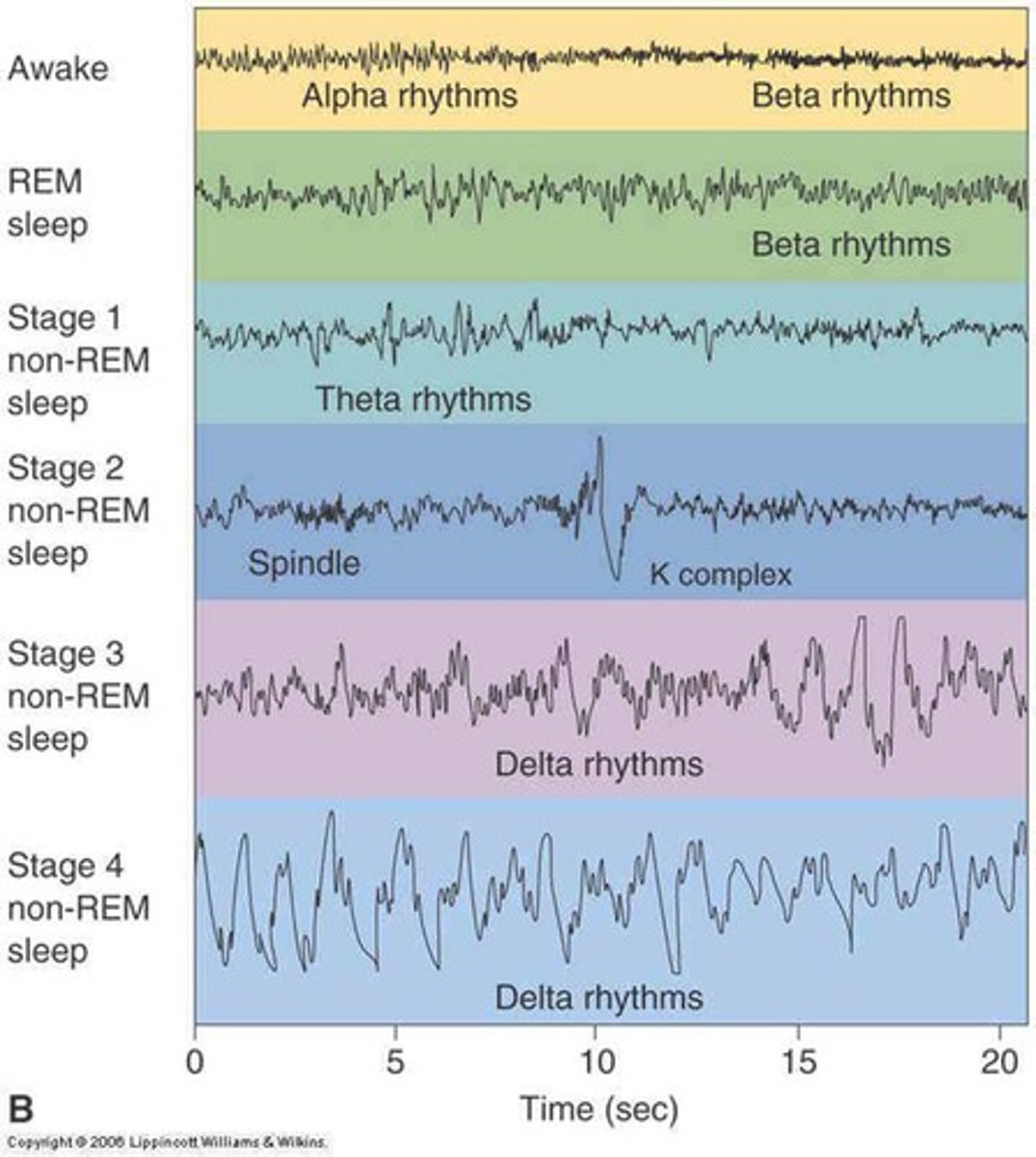
N-REM 1
light sleep
characteristics: brain, heart rate, eye movements, and breathing slow down. Body relaxes with occasional muscle twitches
- hypnic jerk
brain waves: high amplitude theta waves
N-REM 2
characteristics: body temp drops, eye movement stops, breathing and heart rate become more regular
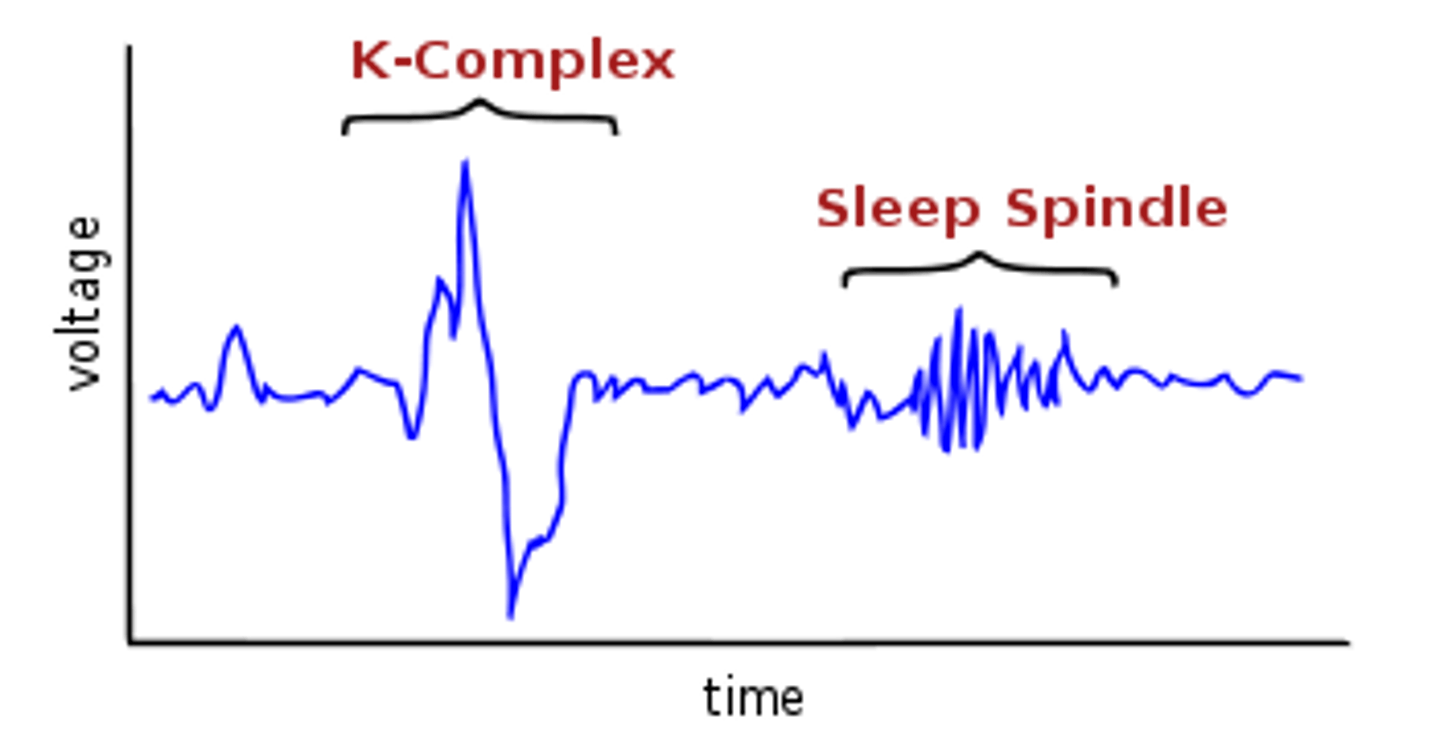
brain waves: sleep spindles & k complexes
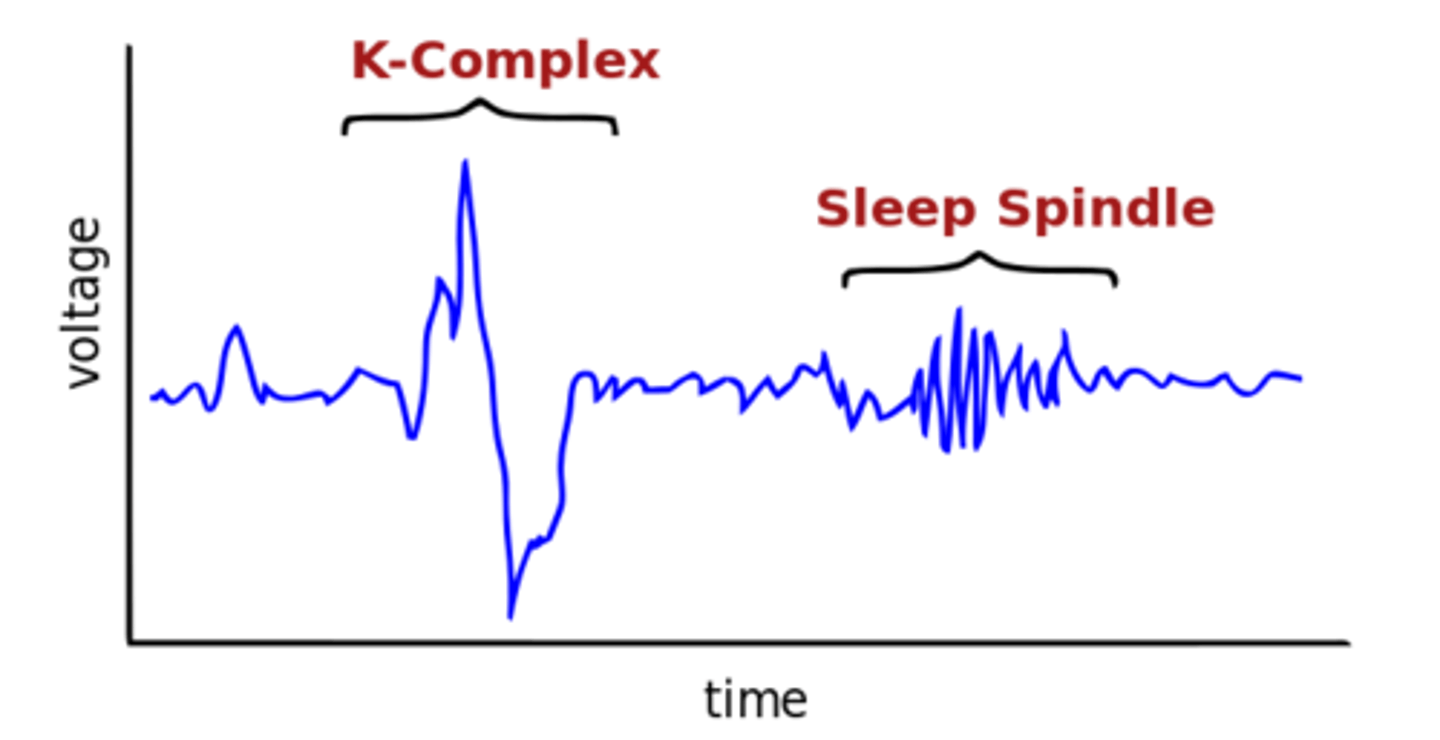
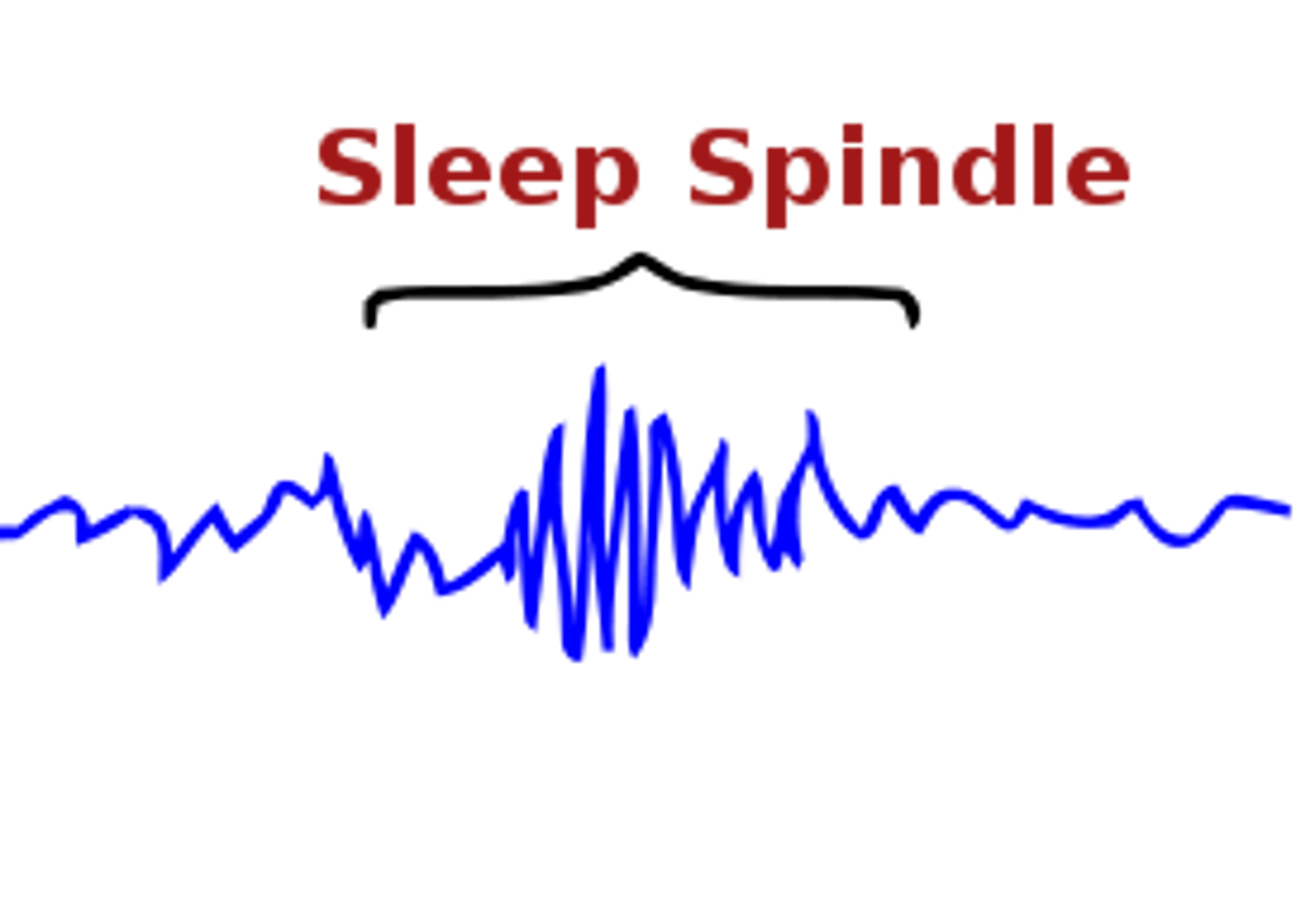
sleep spindles
bursts of rapid brain activity
(N-REM 2)
k complexes
sudden, short increase then decrease in brain activity
(N-REM 2)
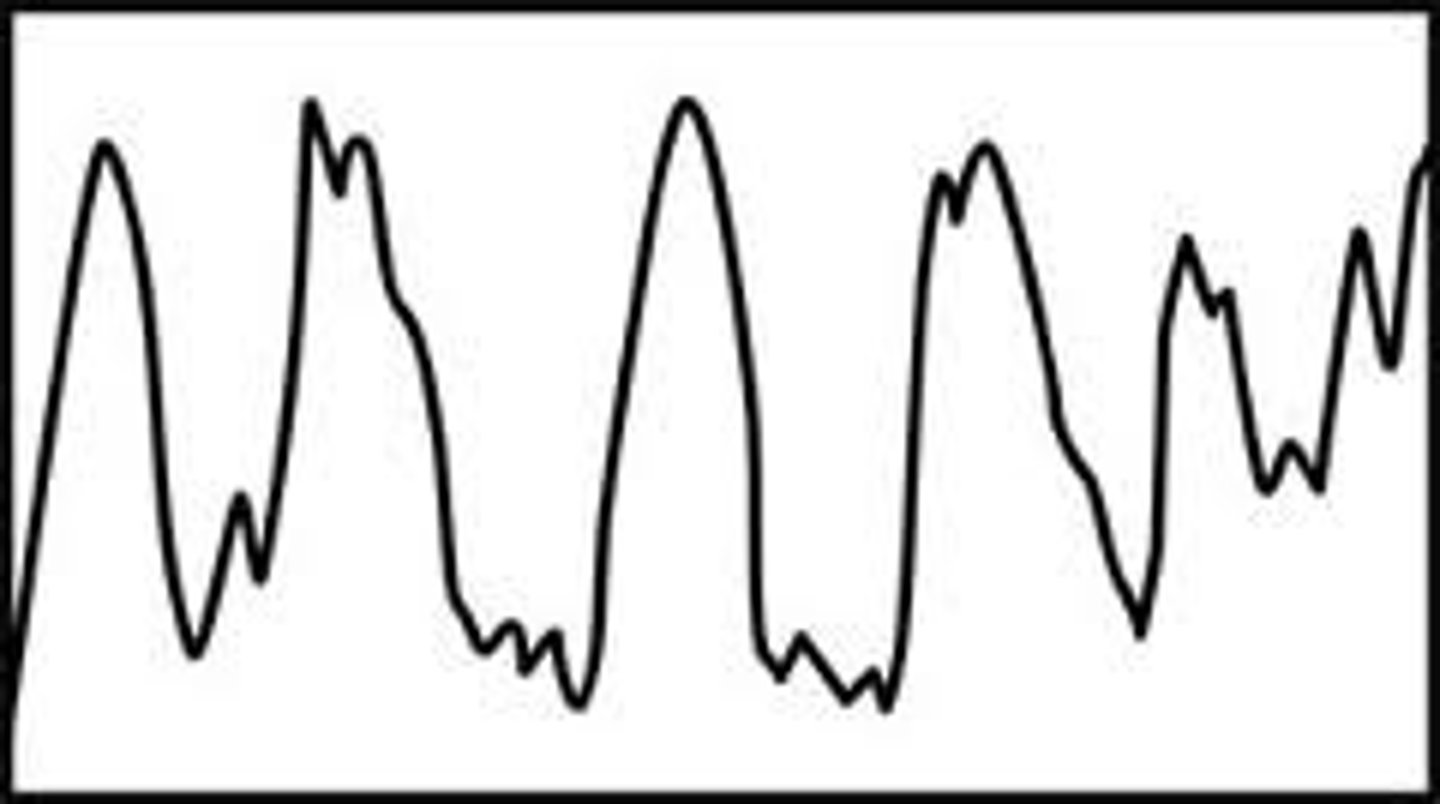
N-REM 3
deep sleep
characteristics: blood pressure drops, breathing slows, muscles completely relaxed
- sleepwalking
- bedwetting
brain waves: delta waves
delta waves
rolling/slow waves
(N-REM 3)
REM
dreams
characteristics: brain activity increases, body relaxed/immobilized, faster/irregular breathing, rapid eye movement
brain waves: highly active (almost identical to awake activity
order of sleep stages
1. N-REM 1
2. N-REM 2
3. N-REM 3
4. N-REM 2
5. REM
cocaine/crack
stimulant
- agonist: increases transmission of norepinephrine & dopamine
- euphoria and increased alertness
★ highly addictive ★
- increased body temp, heart attack, stroke, seizures
withdrawal: fatigue, anxiety, paranoia, boredom, depression, Anhedonia (inability to feel pleasure)
3, 4 methylenedioxy-methamphetamine (MDMA)
stimulant
- agonist: increases serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine
- euphoria, heightened sensory experiences, empathy, lowered inhibitions
- dry mouth, nausea, chills
overdose: increased body temp, kidney failure, heart failure, overdose of water
long-term effects: linked to damaged serotonin receptors
yoga
concentrated meditation as exercise
opening-up meditation
meditation during everyday life
- mindfulness, slow
circadian rhythm
every human's internal 24-hour biological clock full of sleep and wake cycles
sleep apnea
Characteristics: difficulty breathing during sleep
Suspected causes: narrowed airway, smoking, alcohol/drug abuse, diabetes, family history, hormone abnormalities, excess weight
sleep paralysis
Characteristics: paralysis of body when falling asleep or waking up or during REM
Suspected causes: other sleep disorder (narcolepsy), medical conditions, medication, mental health disorder, substance abuse
Still learning (38)
You've started learning these terms. Keep it up!