med anatomy chapter 1
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
130 Terms
What are the regions of the lower limb? (front)
Inguinal. femoral, patellar, crural (leg).
What are the regions of the lower limb? (back)
Gluteal, femoral, popliteal, crural
What is the regions of the upper limb
Brachium, antecubital region, antebrachial region, carpus
What are the regions of the head?
Cranium (not eyes), Facial, cervical
What are the regions of the trunk? (front)
Thorax, abdomen, pelvis
What are the regions of the trunk? (back)
Back
osteo
bone
neuro
nerves
angi
blood vessels
cardio
heart
tympan
eardrum
crani
skull
oto
ear
hepato
liver
colo
large intestine
ileo
small intestine
pneumo/ pleuro
lung
macro
large
megalo
large / enlarged
hyper
high / elevated
tachy
fast / rapid
oma
tumour
chloro
green
eryth
red
genic
creating /causing
endo/intra
within
inter
between
extra
outside
echo
ultrasonic wave
ectomy
removal of
scopy
using a instrument for viewing
blast
immature cells
dys
not working
emia
blood condition
osis
condition disease
myo
muscle
derm
skin
veno / phleb
veins
rhino
nose
neph
kidney
opthalm/ oculo
eye
thromb
blood clot
mammo
breast
gastro
stomach
carcin
cancer
micro
small
histio
tissue
hypo
low / reduced
brady
slow / reduced
cyto
cell
leuk
white
cyan
blue
osteo
bone/ bony tissue
peri
around
trans
across
paed
child
electro
electricity
gram
picture
octomy
making a cut in
stomy
create an opening
sarco
tissue
mal
bad
it-is
inflammation
pathy
disease
oma
tumor
what does an osteocyte do?
mature osteoblasts
osteoblasts
builds bone
endochondral ossification
Process of transforming cartilage into bone.
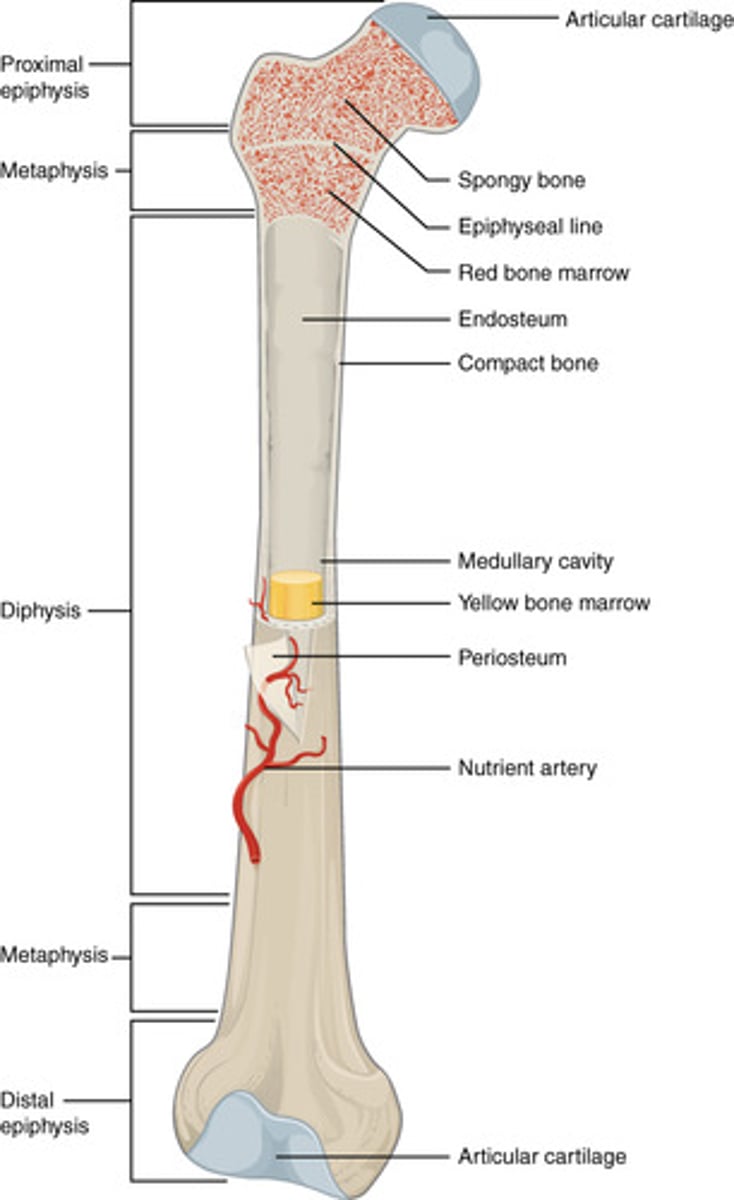
how is a cortical bone made up
periosteum, spongy bone, medullar cavity then bone marrow
what is bone made up of
gels (glycoproteins and glycosaminoglycans) and fibres (30%) and minerals (70%)
cortical bone
hard, dense, strong bone that forms the outer layer of bone; also called compact bone.
what does the cortical bone house
the medullary cavity
what does the medullary cavity contain
blood vessels, yellow bone marrow, red bone marrow and adipose tissue
yellow bone marrow
adipose tissue contains stem cells that can become cartilage fat or bone cells
red bone marrow
blood stem cells that can become red blood cells white or platelets
at what age do the red bone marrow change to yellow bone marrow
at age 7 we lose have of our red blood marrow
When does the epiphyseal plate close?
between 18-25
spongy bone
bones with holes and endosteum inside contains the cells
osteoclast
bone cell that absorbs and removes unwanted bony tissue
long bone features (top to bottom)
articular cartilage, proximal epiphysis, epiphyseal line proximal metaphysis, diaphysis (medullary cavity), distal metaphysis, distal epiphysis, articular cartilage
epiphysis
flared ends connected from metaphysis
metaphysis
tapered bone between epiphysis and diaphysis
Epiphyseal line
remnant of the epiphyseal plate, seen in adult bones radiolucent
diaphysis
thickest part
what are the long bones in humans
femur, tibia, fibular, humerus radius, ulna, metacarpals, metatarsals, phalanges, clavicles
bone matrix
part of bone tissue that forms most of the mass of the bone inorganic/ organic
organic
collagen and proteoglycan
inorganic
calcium and phosphate hydroxyapatite crystals
what is an osteon
structural unit of compact bone
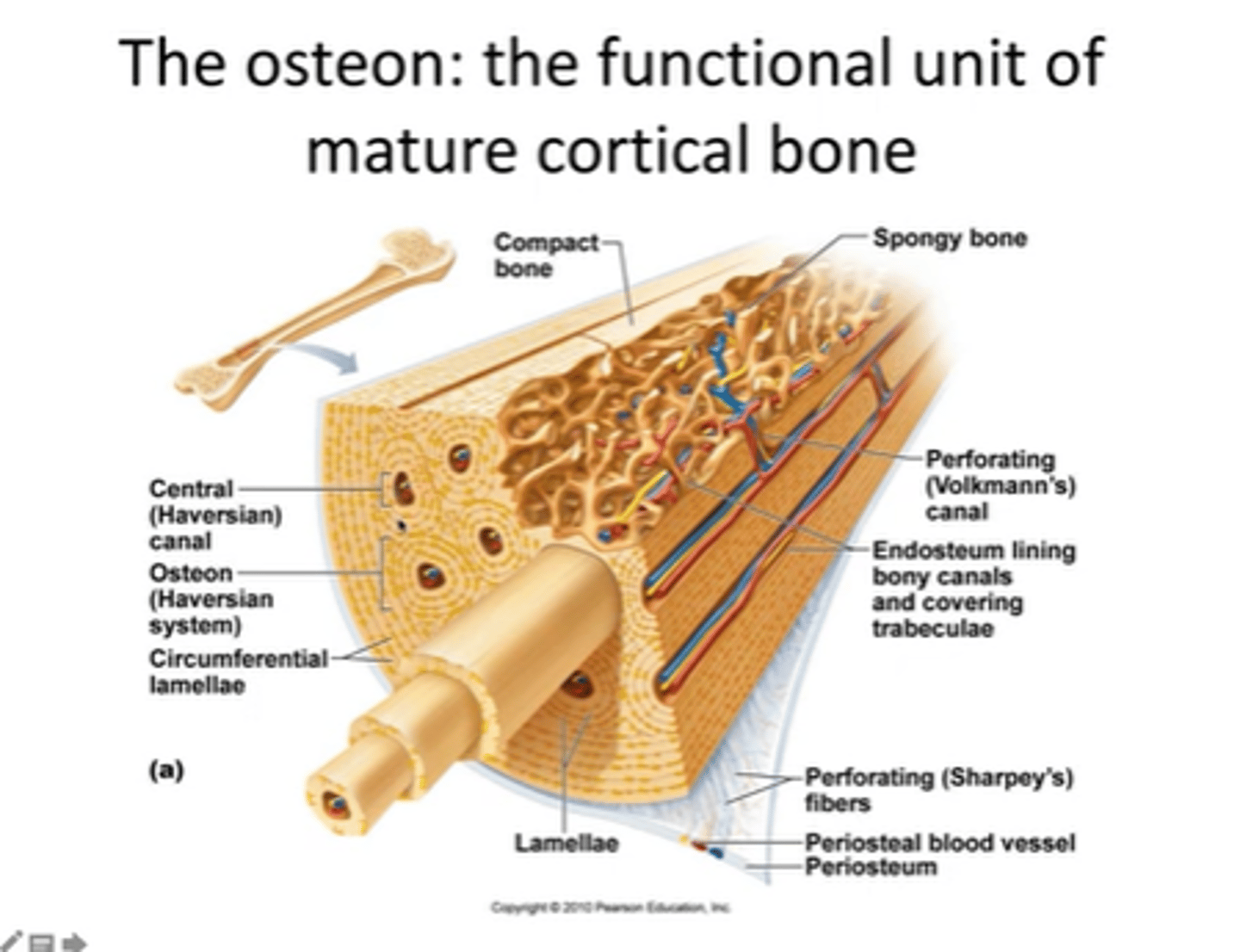
haverson canal
longitudinal canal contain blood vessels for osteocytes
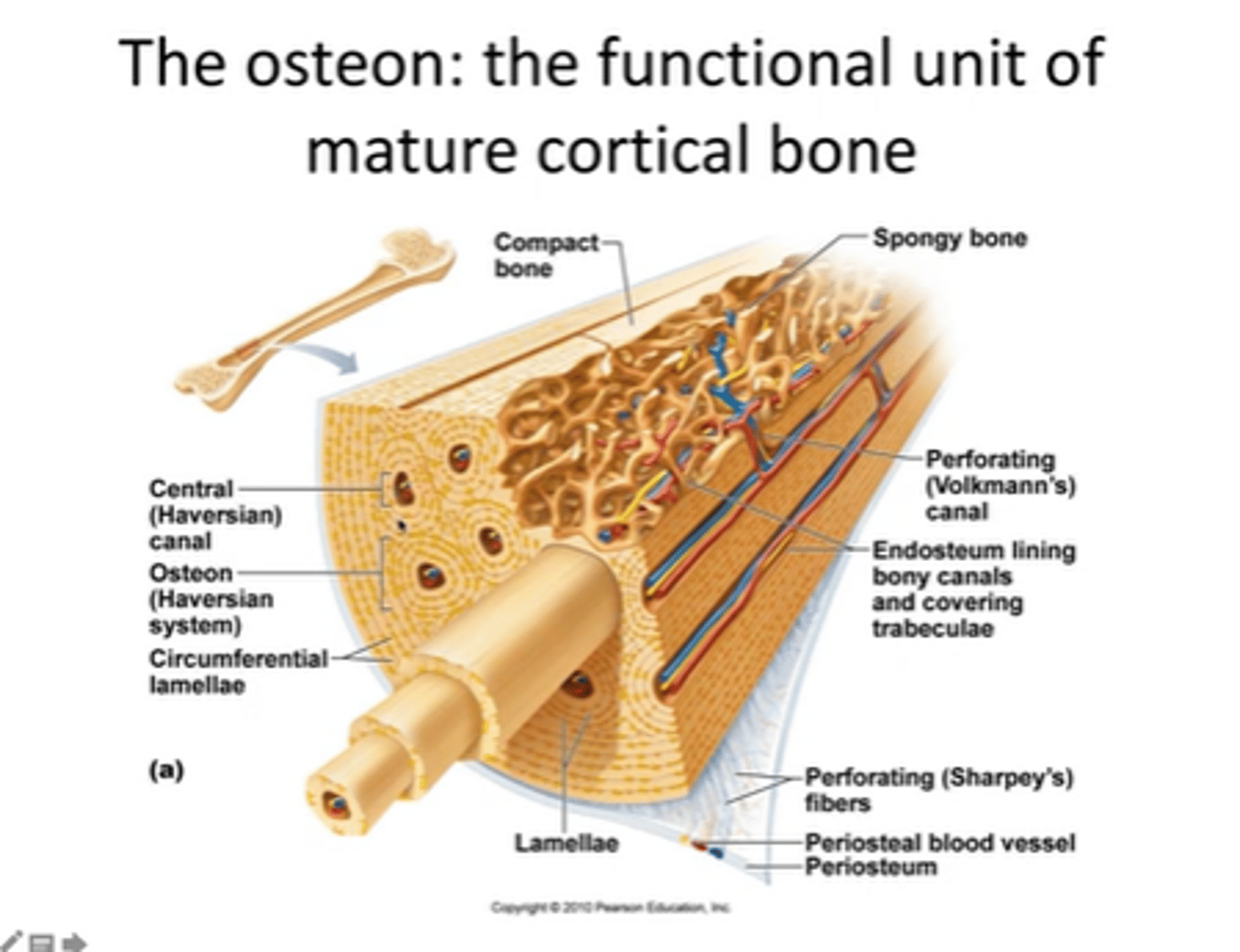
lamellae
Each osteon consists of concentric layers, or lamellae, of compact bone tissue that surround a central canal, the haversian canal.
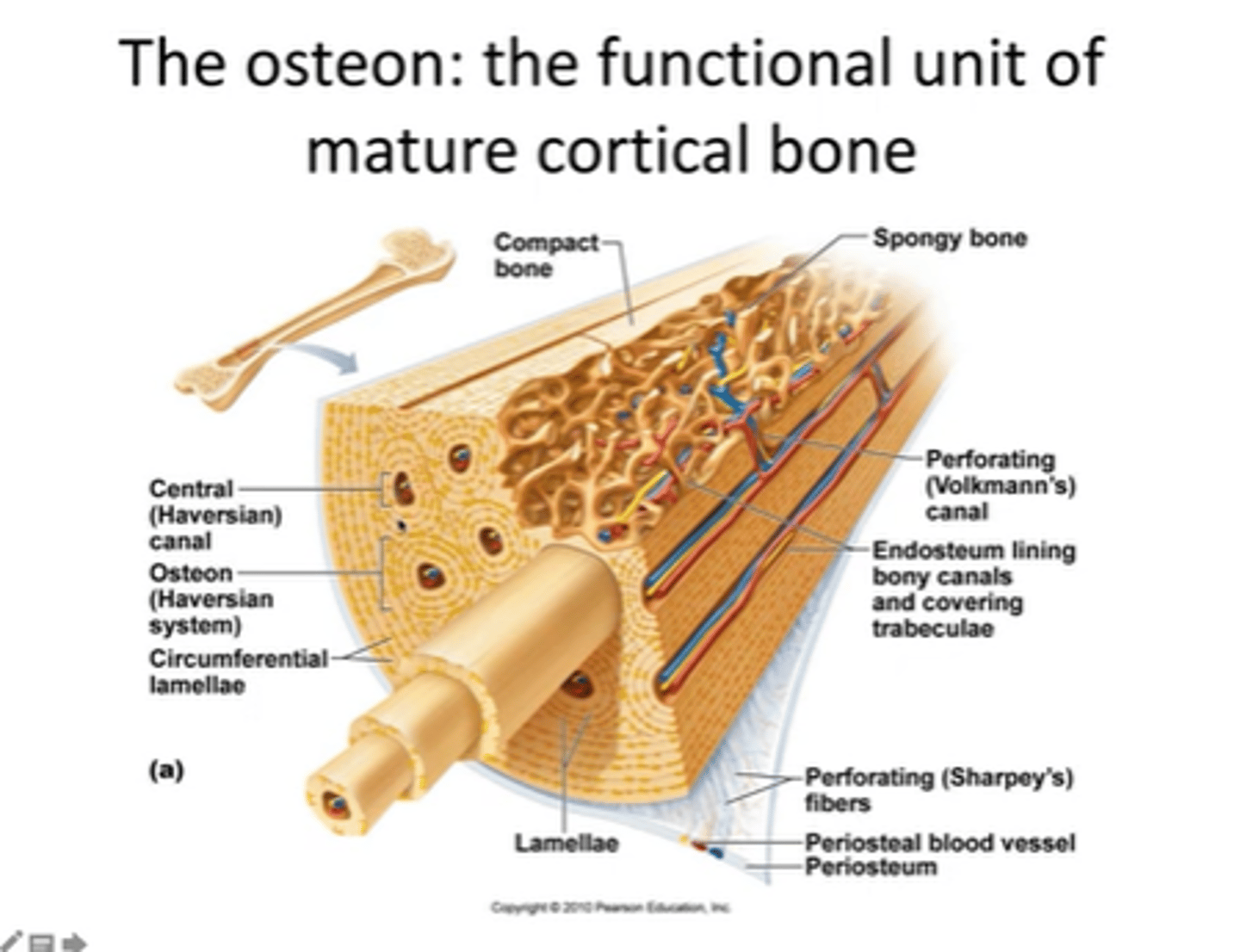
Canaliculi
Hairlike canals that connect lacunae to each other and the central canal
Volkmann's canals
channels lying at right angles to the central canal, connecting blood and nerve supply of the periosteum to that of the Haversian canal
Perisoteum
allows passage of nerve fibres and blood vessels pain sensitive osteoprogenitor cells. Thinnest most sensitive part as it houses a lot of blood vessels
central canal
contains blood vessels and nerve fibres that supply the Haversian system
endosteum
contains osteoprogenitor cells
Sharpay's fibers
very strong elastic fibres that attach the periosteum to the bone
lacunae
small cavities in bone that contain osteocytes
calcitonin
secreted by the parafollicular cells in the thyroid gland and is released in response to high calcium. Inhibits osteoclast activity and thus lengthens the life of osteoblasts decreasing the CA levels
calcitonin effect on calcium
reduce calcium in blood and increase renal excretion of calcium