Facial and nasal bones
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
2
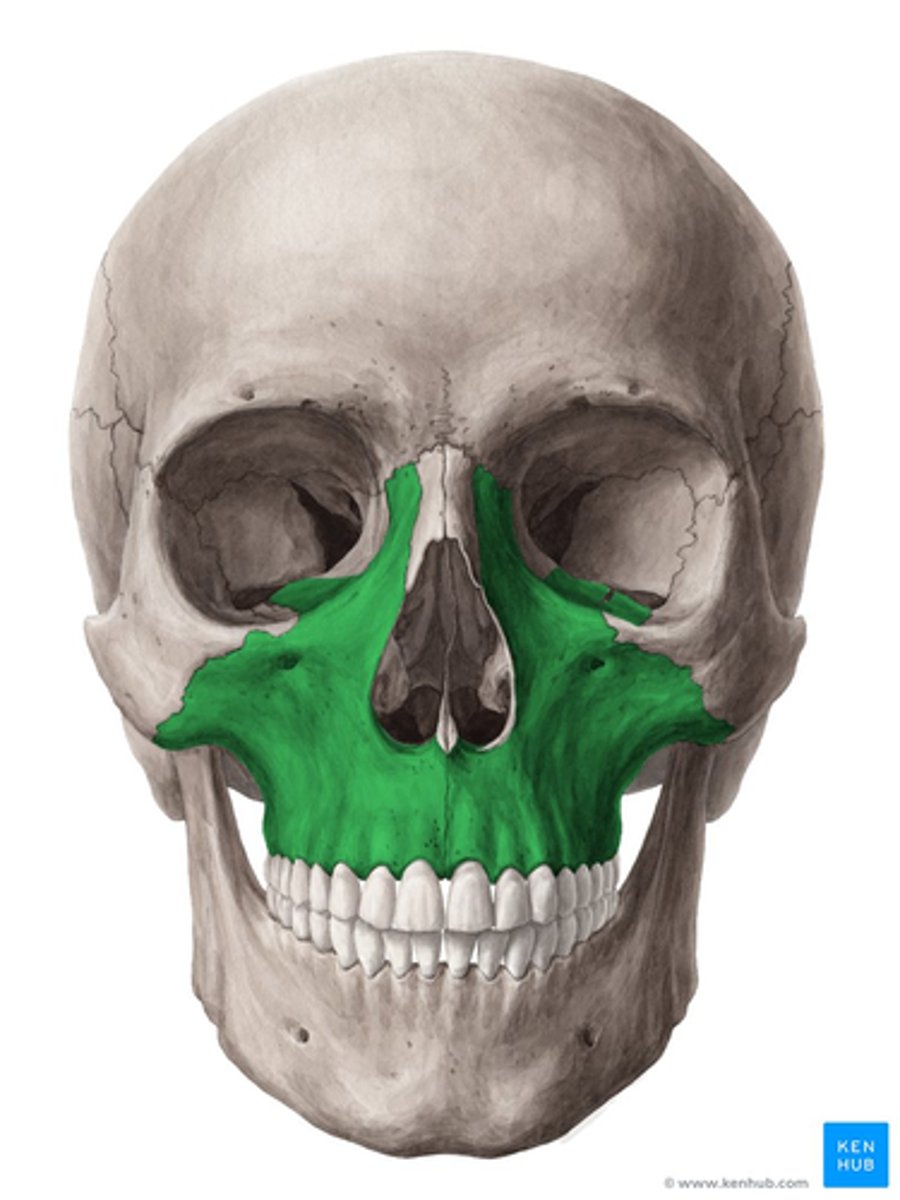
How many bones is the maxilla ?
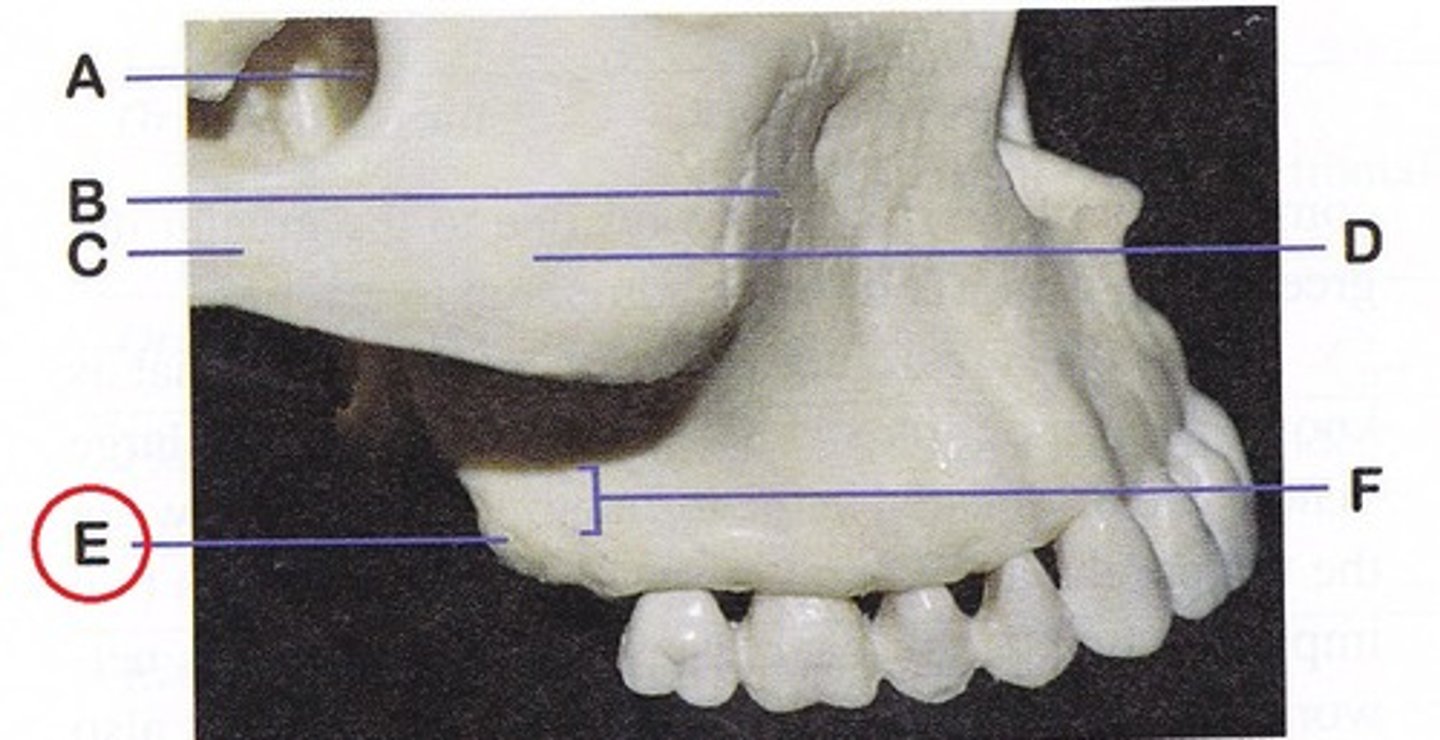
- Body
-forms the cheek and contains the maxillary sinuses.
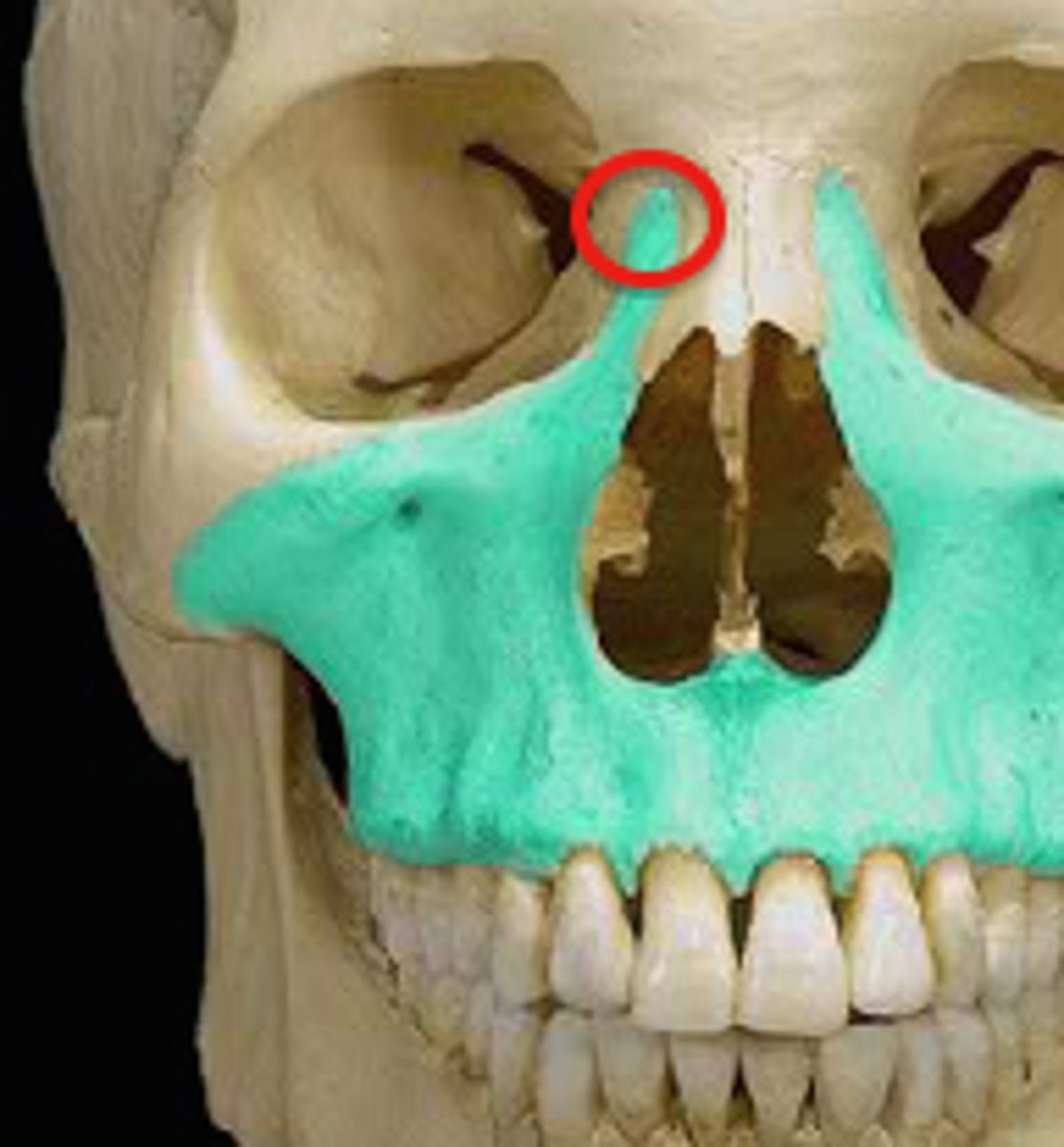
What is this and what does it do?
- Frontal process
- Extends up along the nose and the inner part of each infraorbital margin.
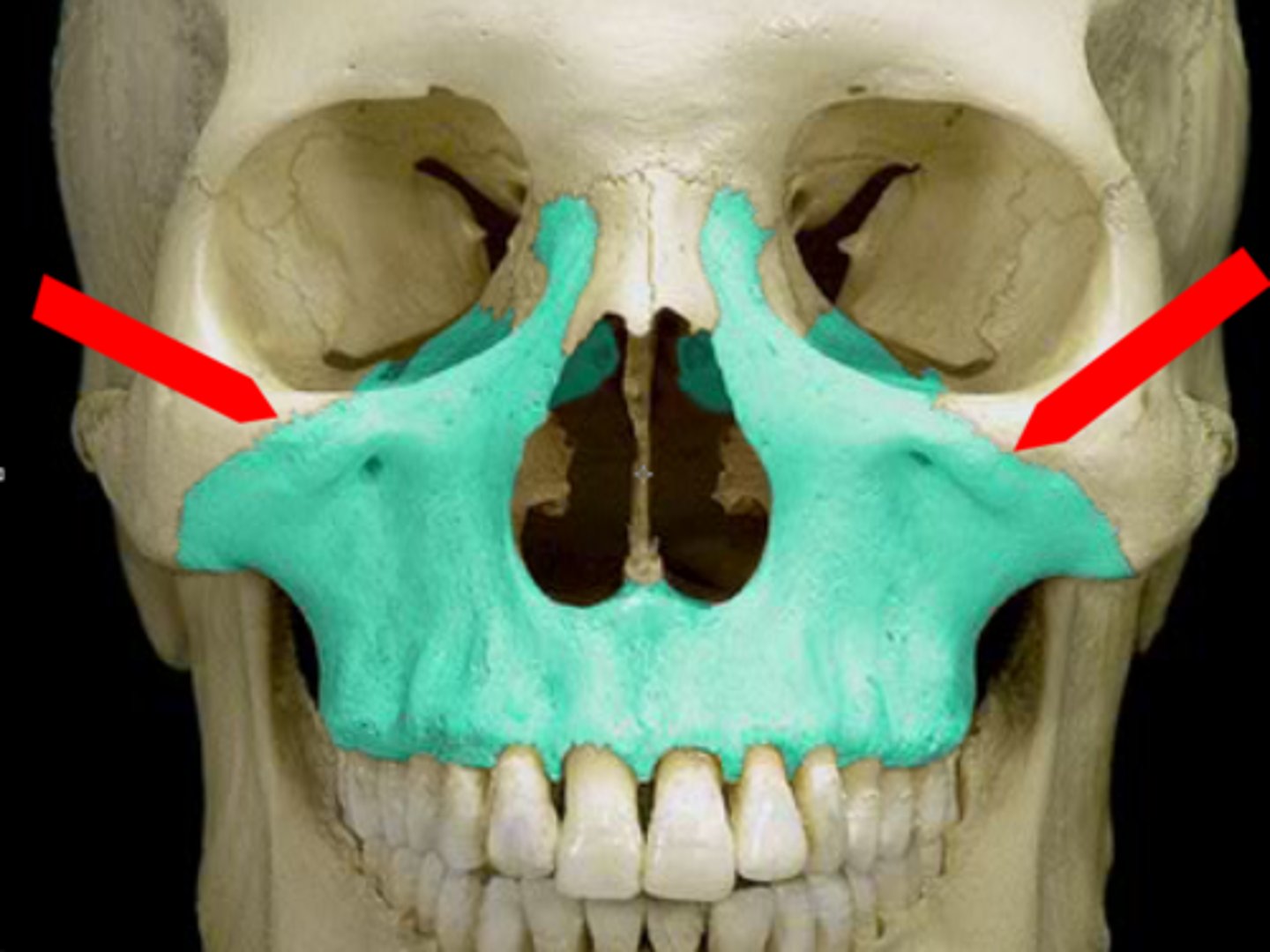
What is this and what does it do?
- Zygomatic process
- extends laterally from the body and touches the zygoma.
What is this and what does it do?
- Alveolar process
- Extends down to accommodate the teeth
What is this and what does it do?
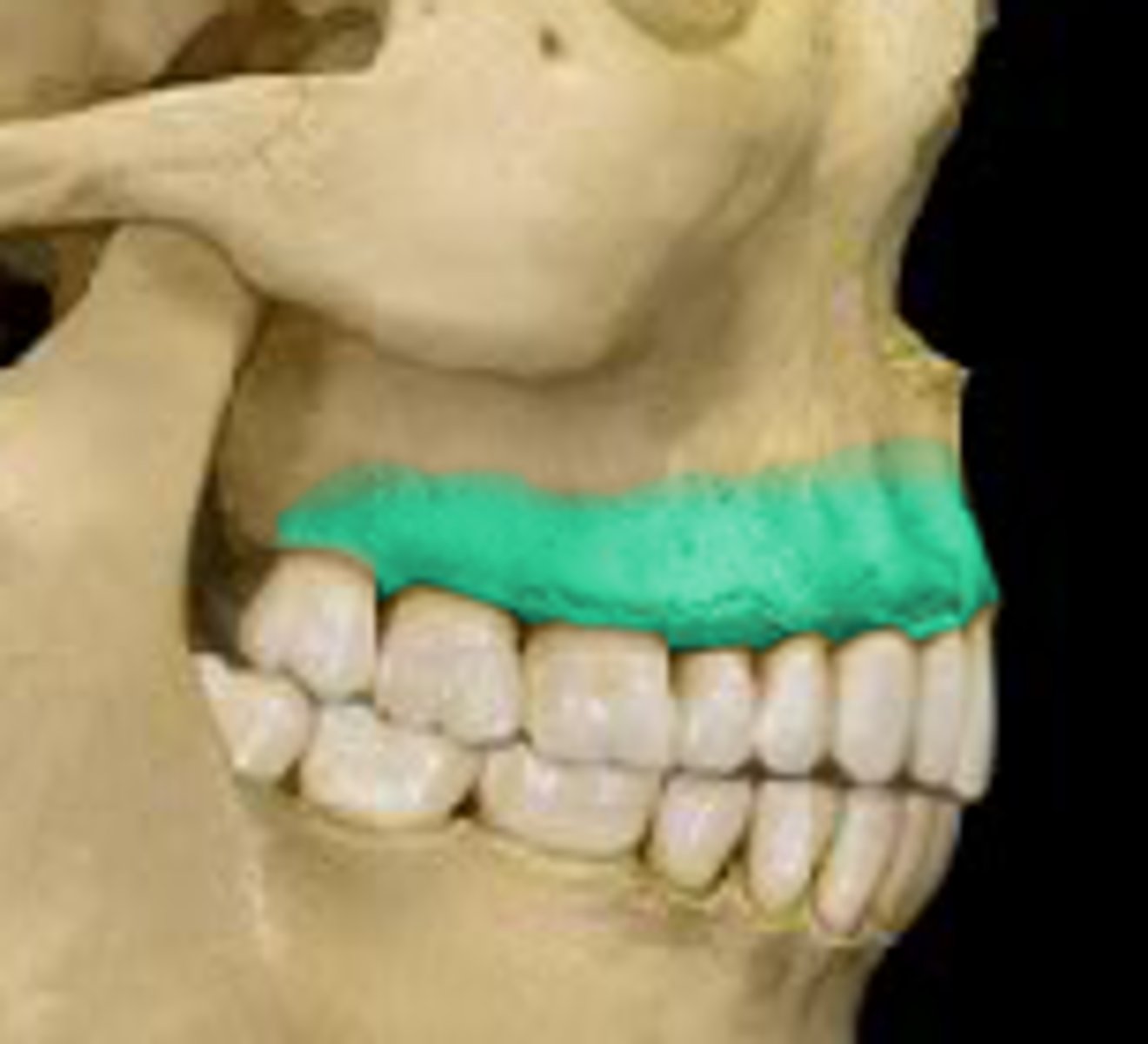
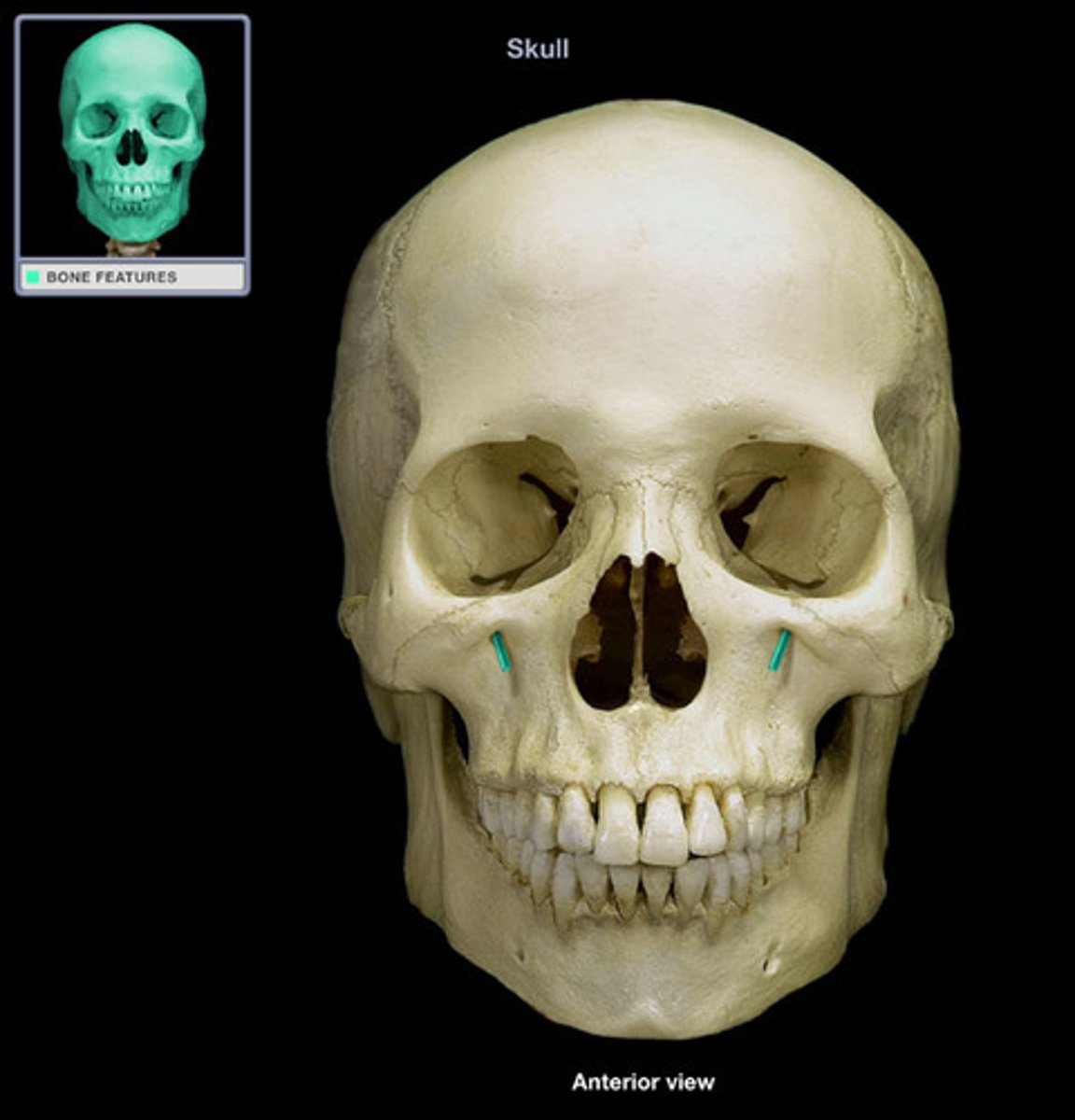
- infraorbital foramen
- opening in the body , allows nerves and vessels to pass through
What is this and where is it located ?
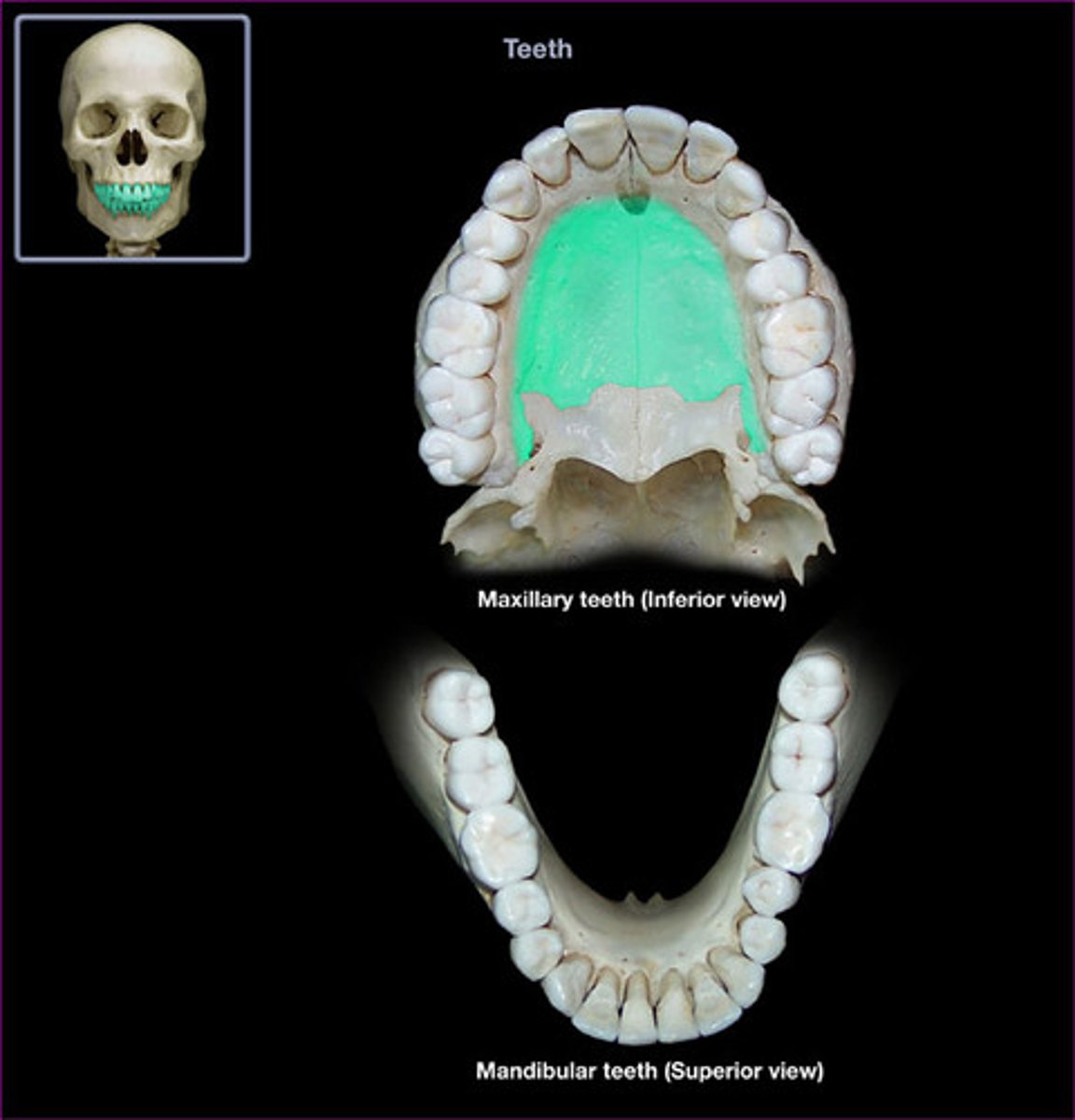
- Palatine process
- flat plate extends medially above the mouth
What is this and where is it located ?
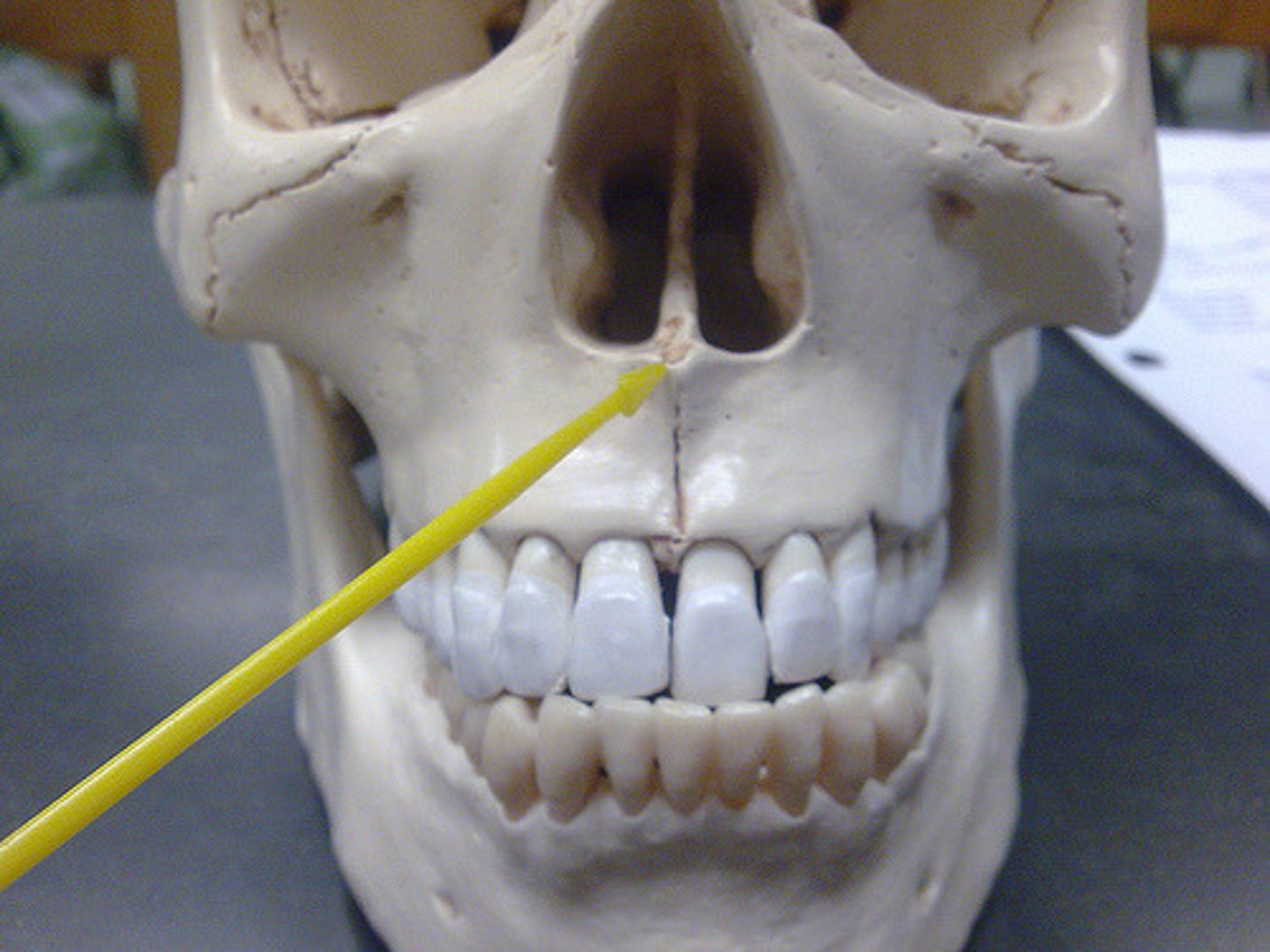
Anterior Nasal spine
- midpoint under the nose
What is this and where is it located?
Maxillary tuberosity
- small, bony prominence behind the last upper molar
What is this and where is it located?
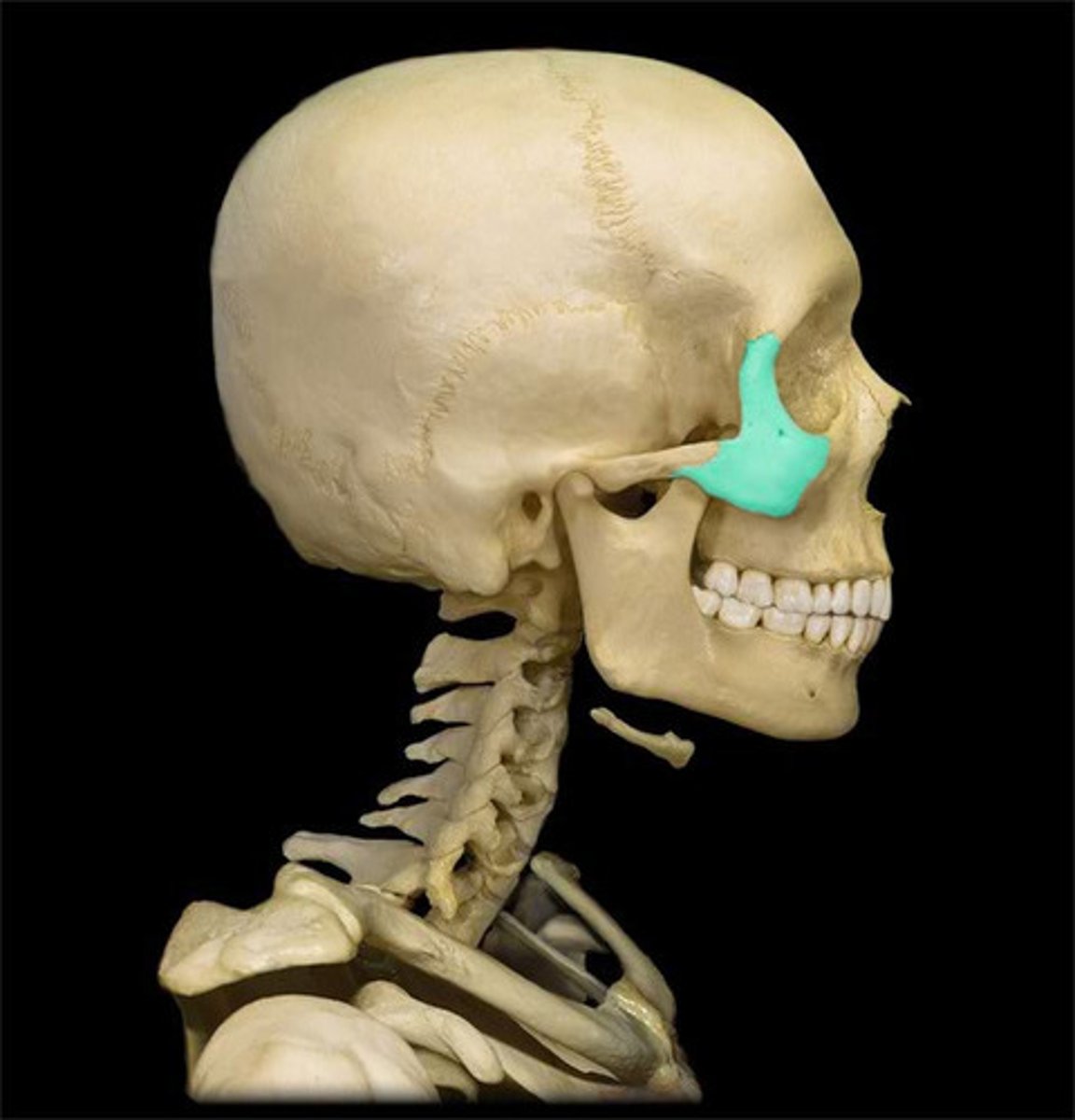
Zygomatic bone
- two zygomatic / malar bones
- temporal process extends posteriorly to join zygomatic process of temporal bone
- maxillary process extends anteriorly to join the maxilla bone
What is this, where is it found and what does it do?
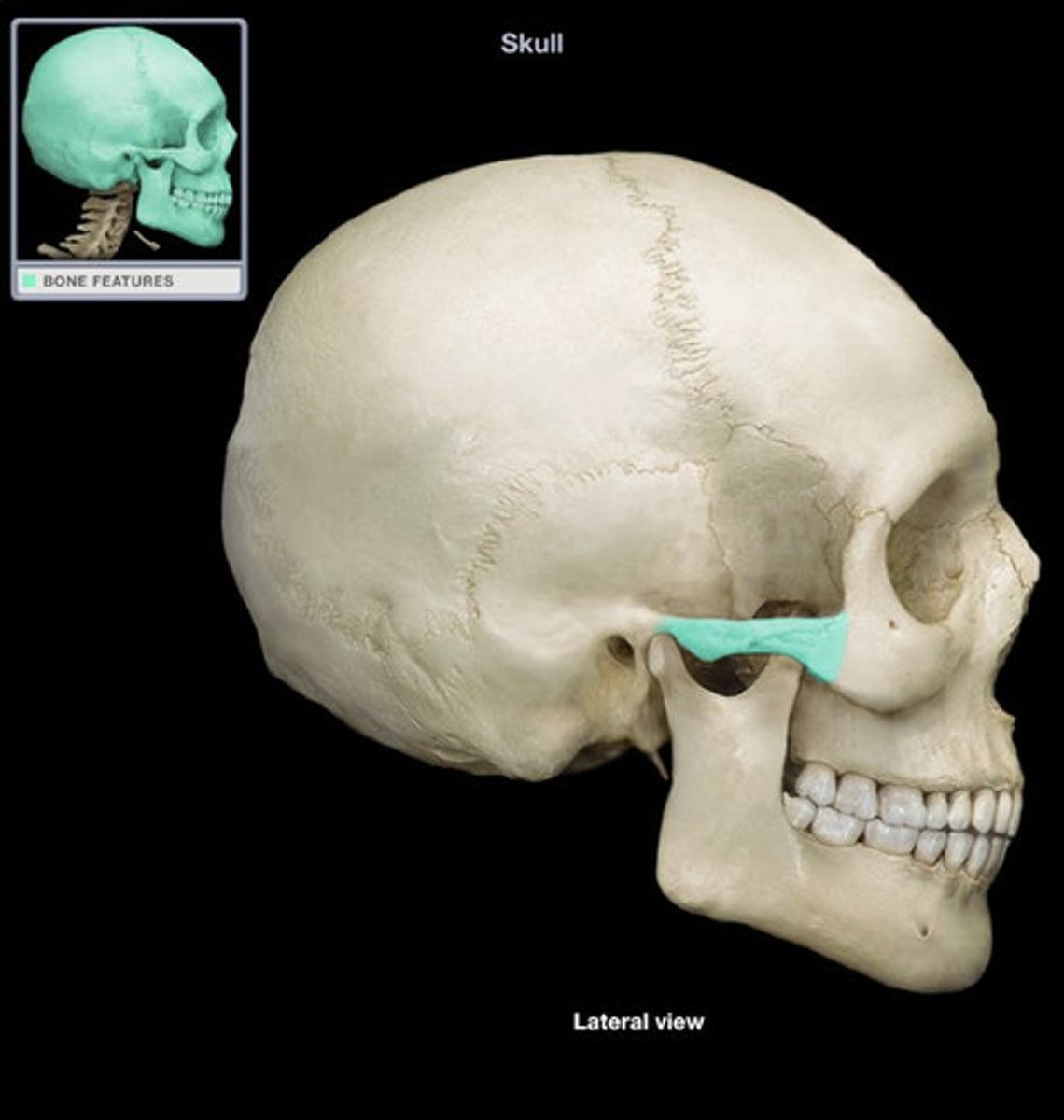
- zygomatic arch
- formed by the union of temporal process of zygoma and zygomatic process of the temporal bone
What is this and how is it formed?
Nasal bones
- form superior bony wall of nasal cavity
What is this and how is it formed?
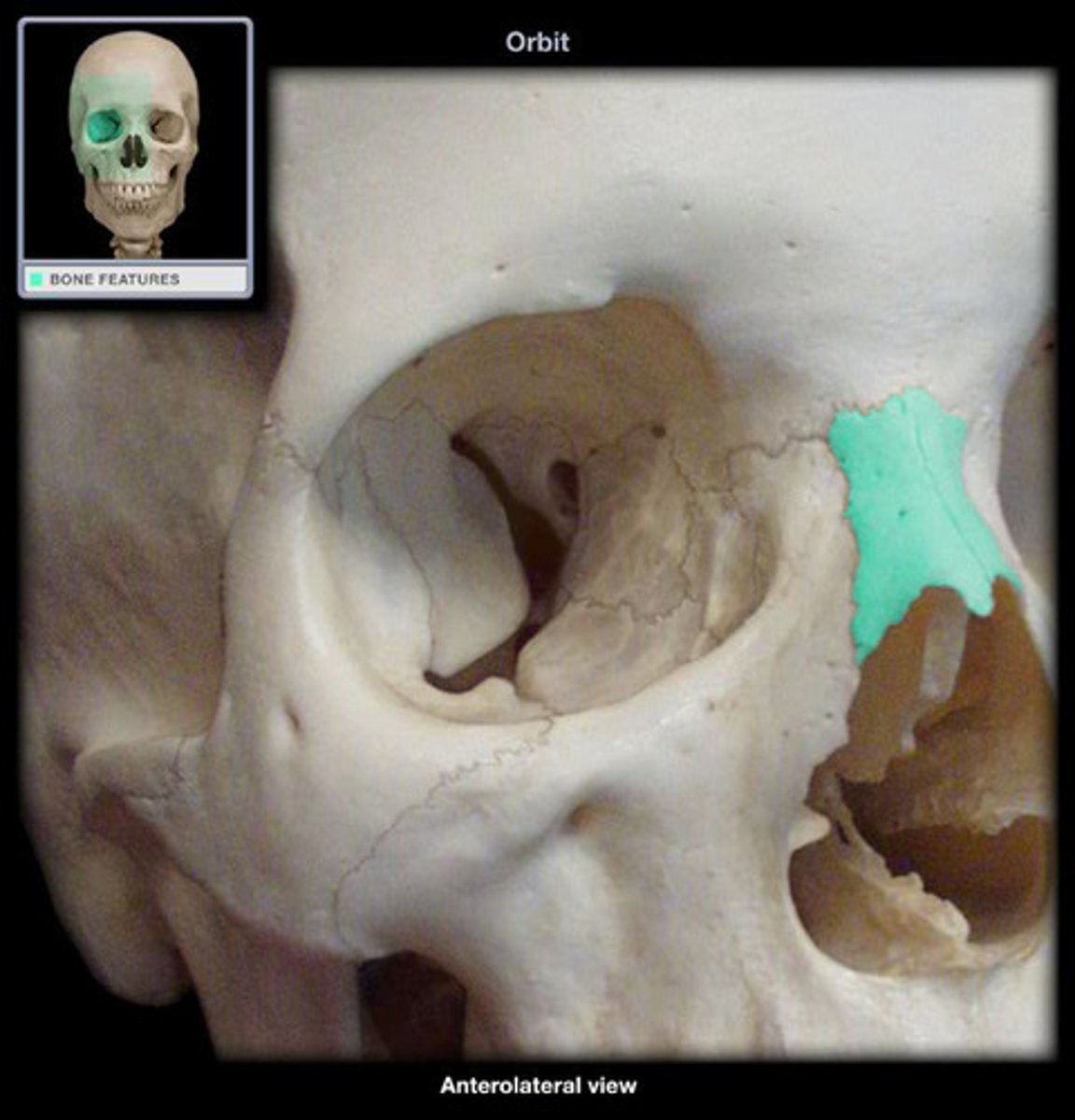
- Lacrimal bones
- each bone contains a lacrimal foramen though which the tear duct passes through
SMALLEST FACIAL BONE
what is this and what does it do ?
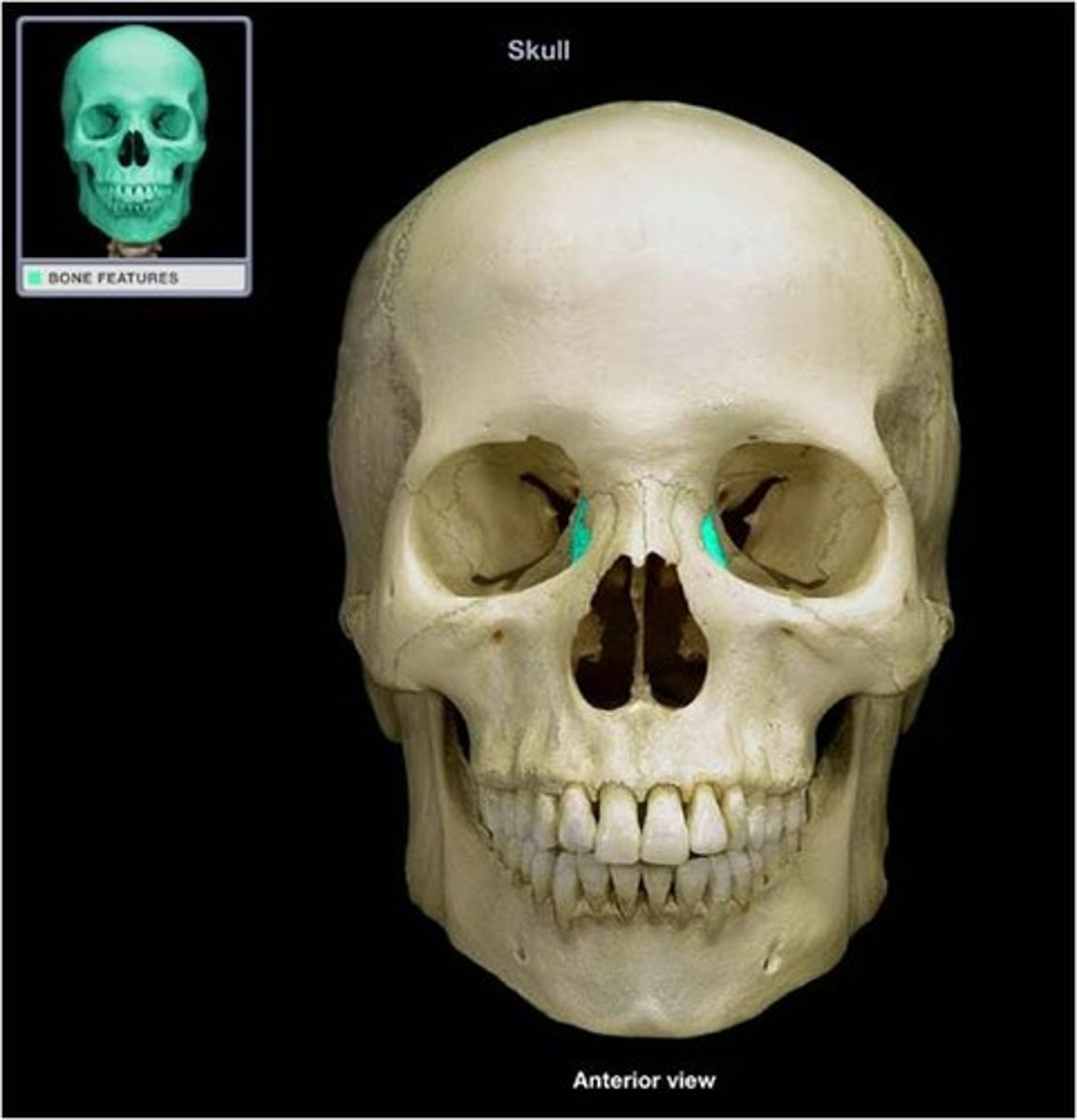
- Palatine bone
- two L-shaped bones composed of vertical and horizontal plates
- Horizontal articulates with maxillae
- Vertical portions extend upwards between maxillae and pterygoid processes of sphenoid in posterior nasal cavity
What is this and how is it formed ?
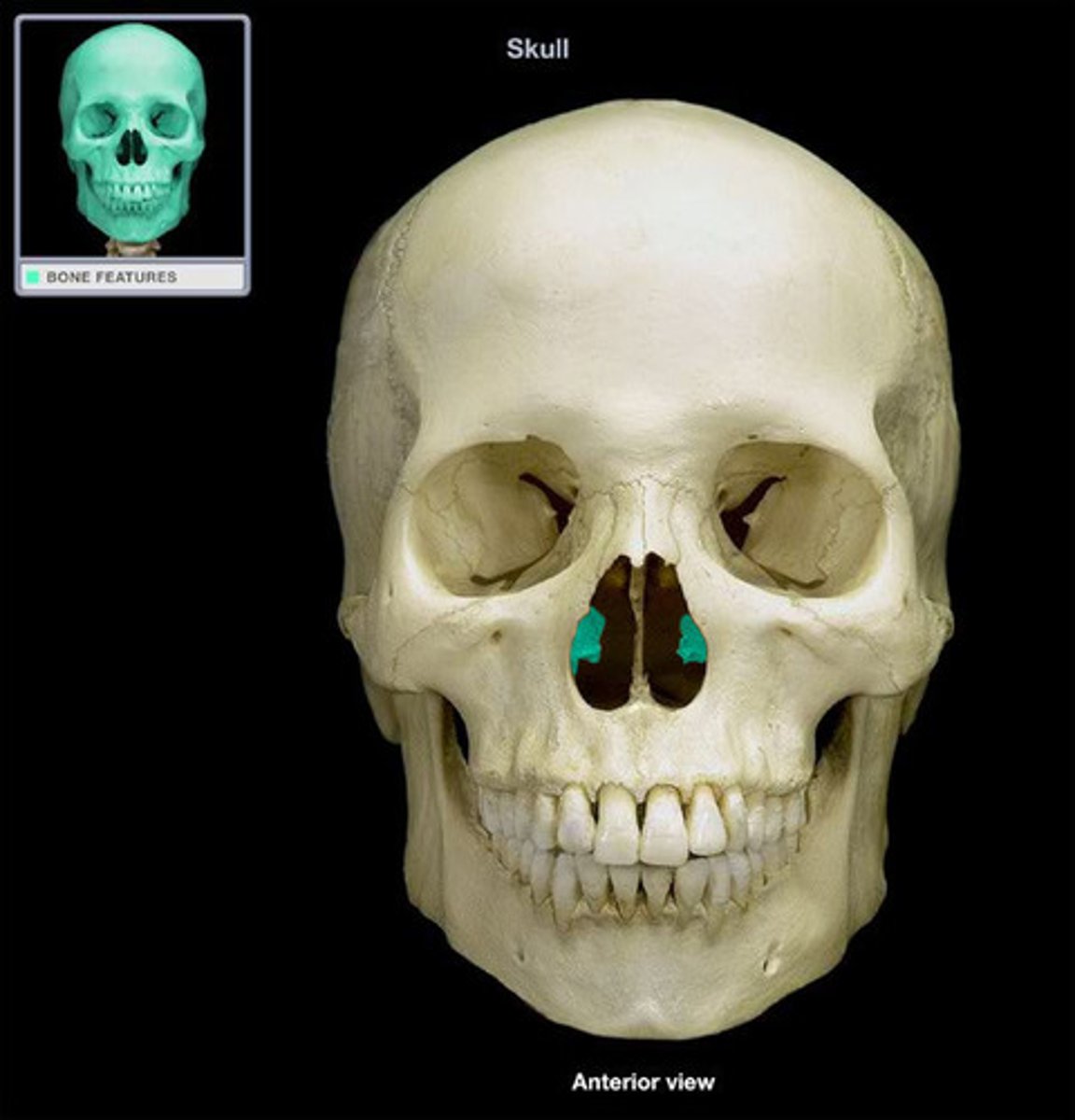
- Inferior Nasal conchae
- two ( one on each side ) , they humidify, warm air and increase the nasal cavity surface
- extend diagonally inferiorly from lateral wall of nasal cavity at the lower 3rd
What is this and how is it formed?
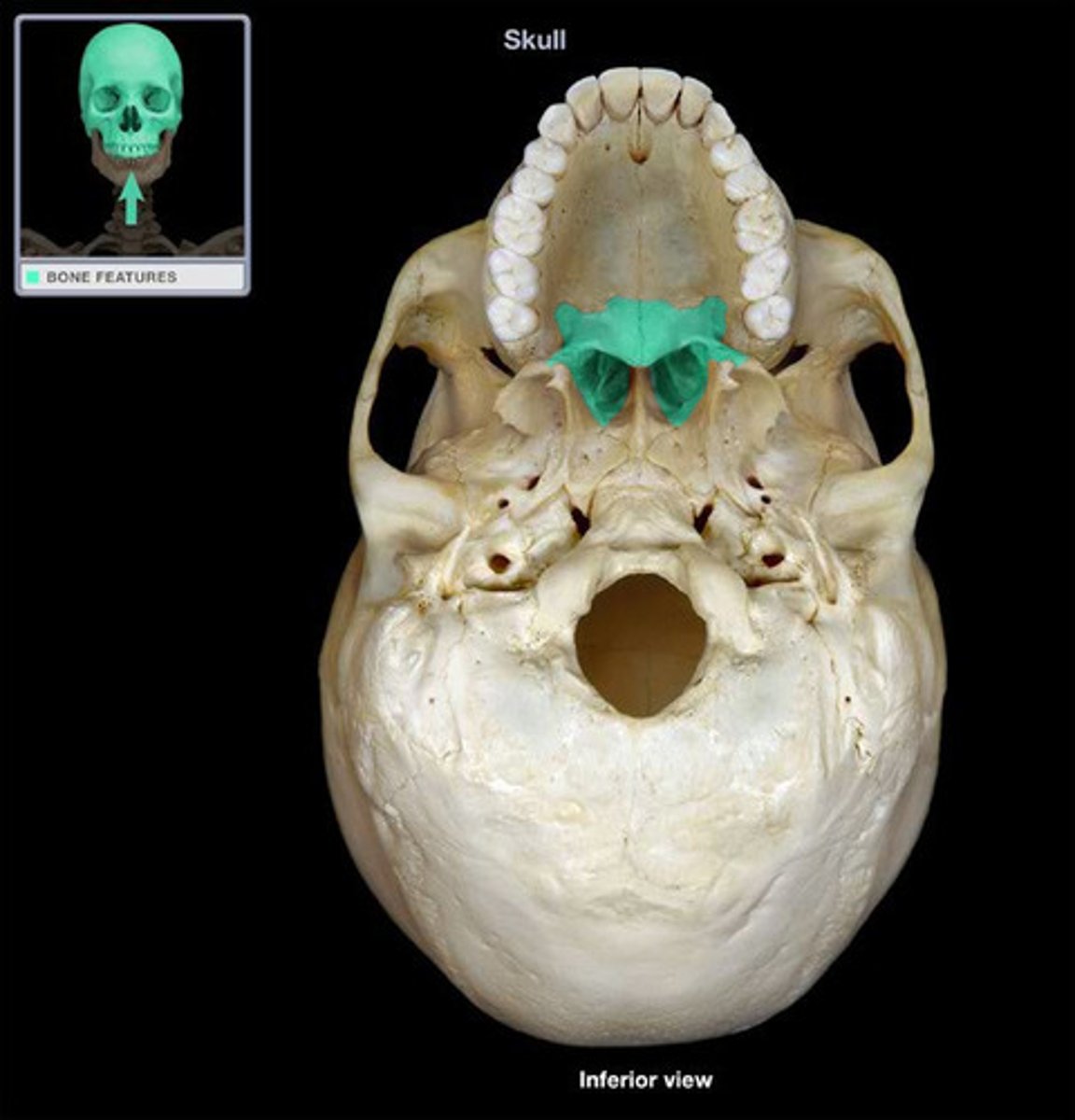
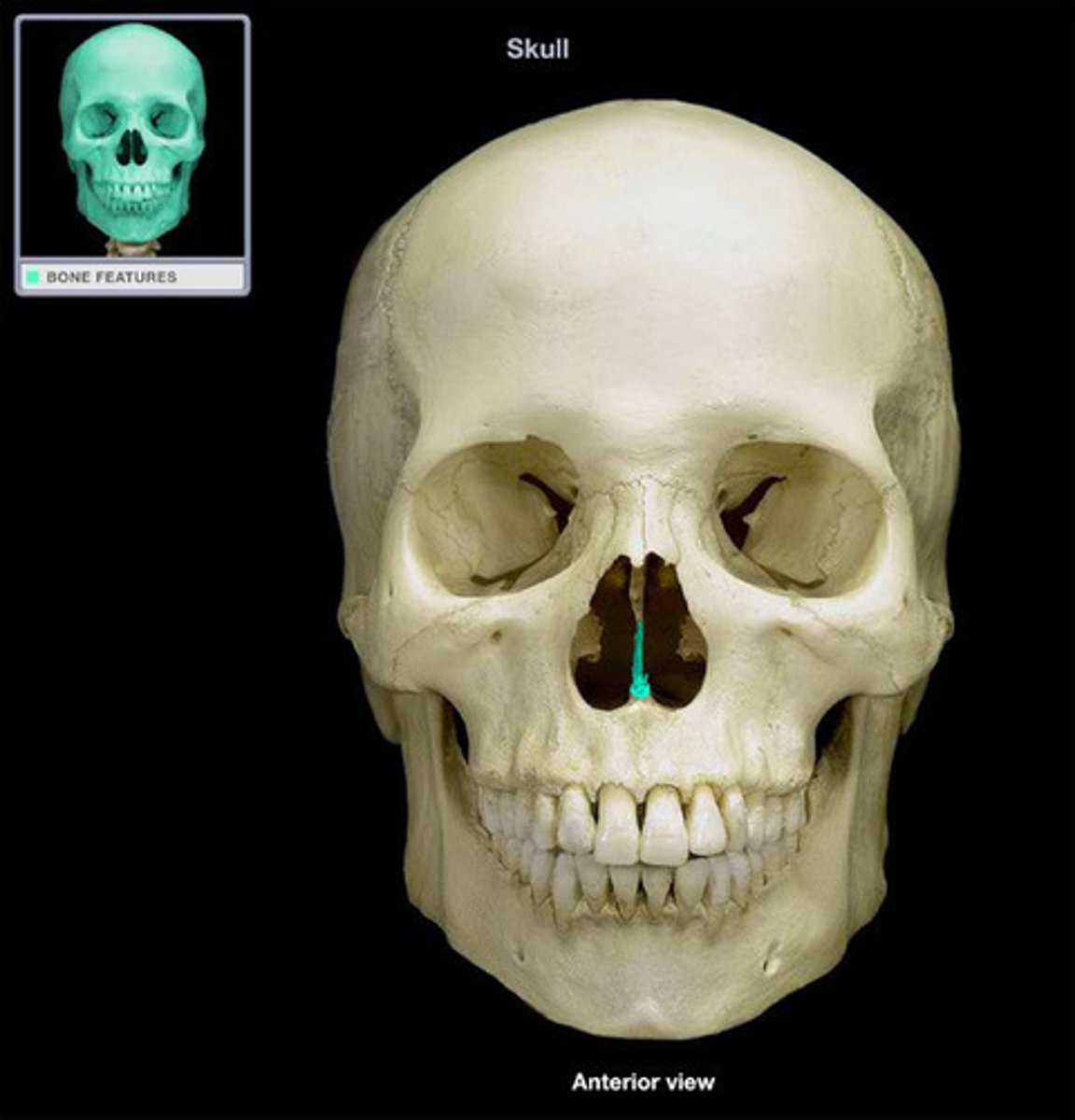
vomer
- lies vertically and helps form the nasal septum
- meets perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone
What is this ?
The horizontal section known as the body and two vertical sections known as the rami.
What are the two main sections of the mandible?
At the gonion, also known as the angle of the mandible.
Where do the body and rami of the mandible meet?
Symphysis
- faint ridge running vertically in the midline
What is this , and where is it found ?
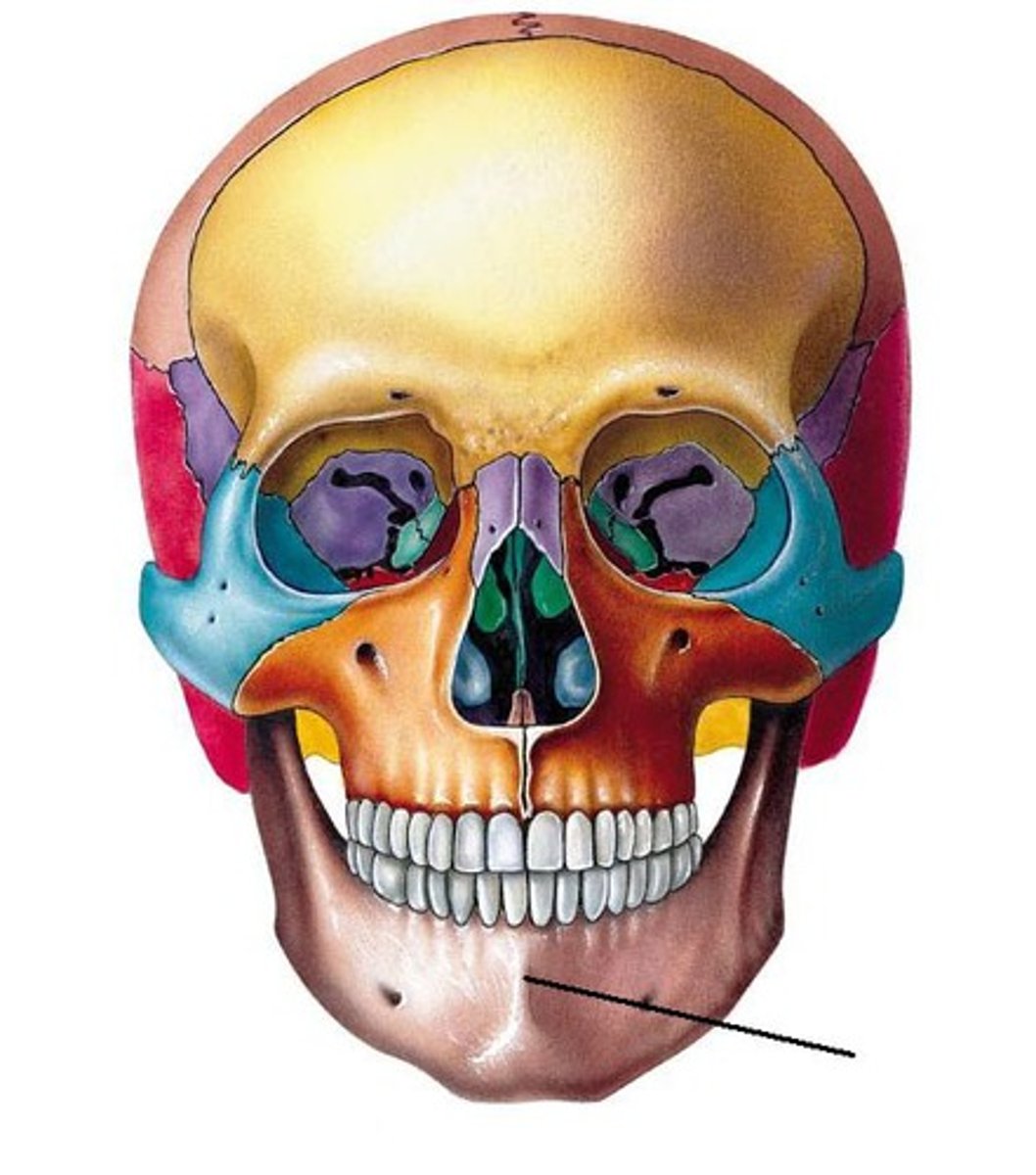
1st year of life
When do the 2 halves of the body fuse ?
Mental protuberance
- prominence at the lower border of the symphysis (mental point/ chin)
What is this and where is it found?
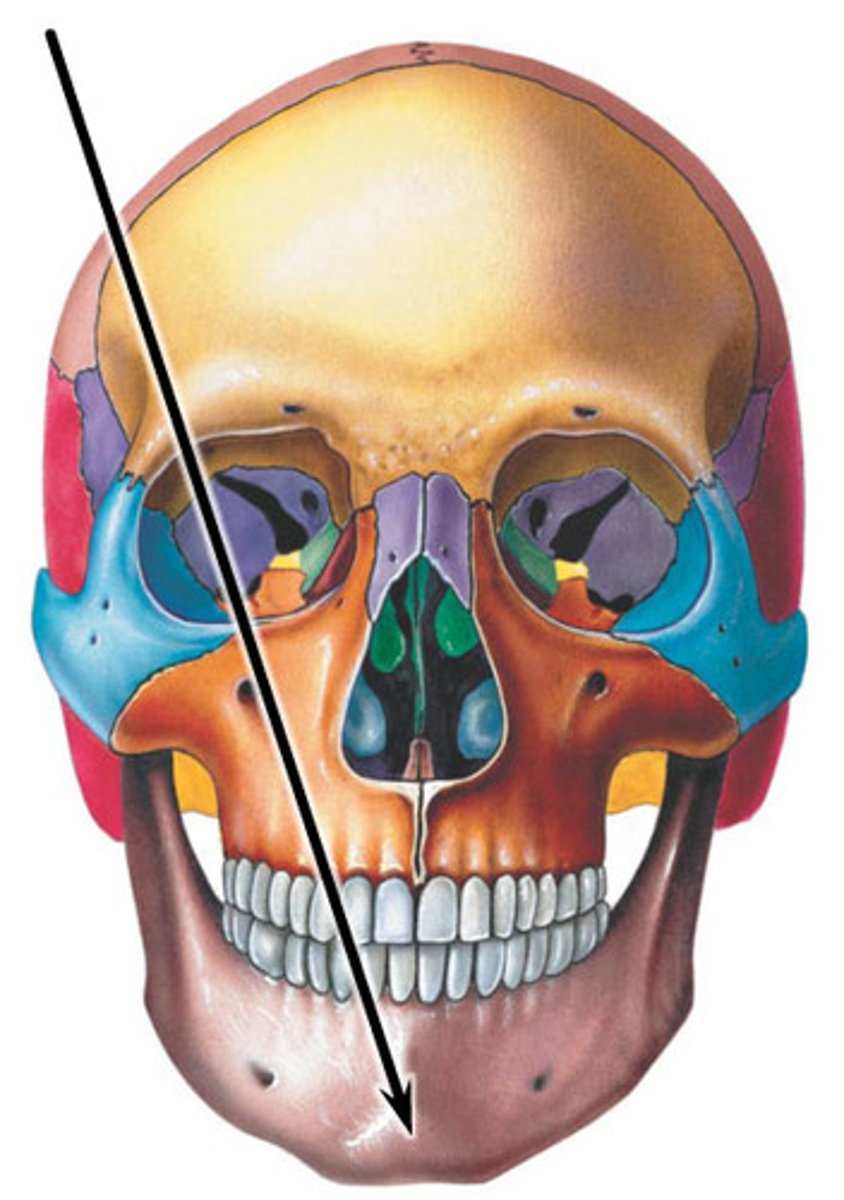
mental foramen
- small opening in the body where the mandibular passes through
what is this
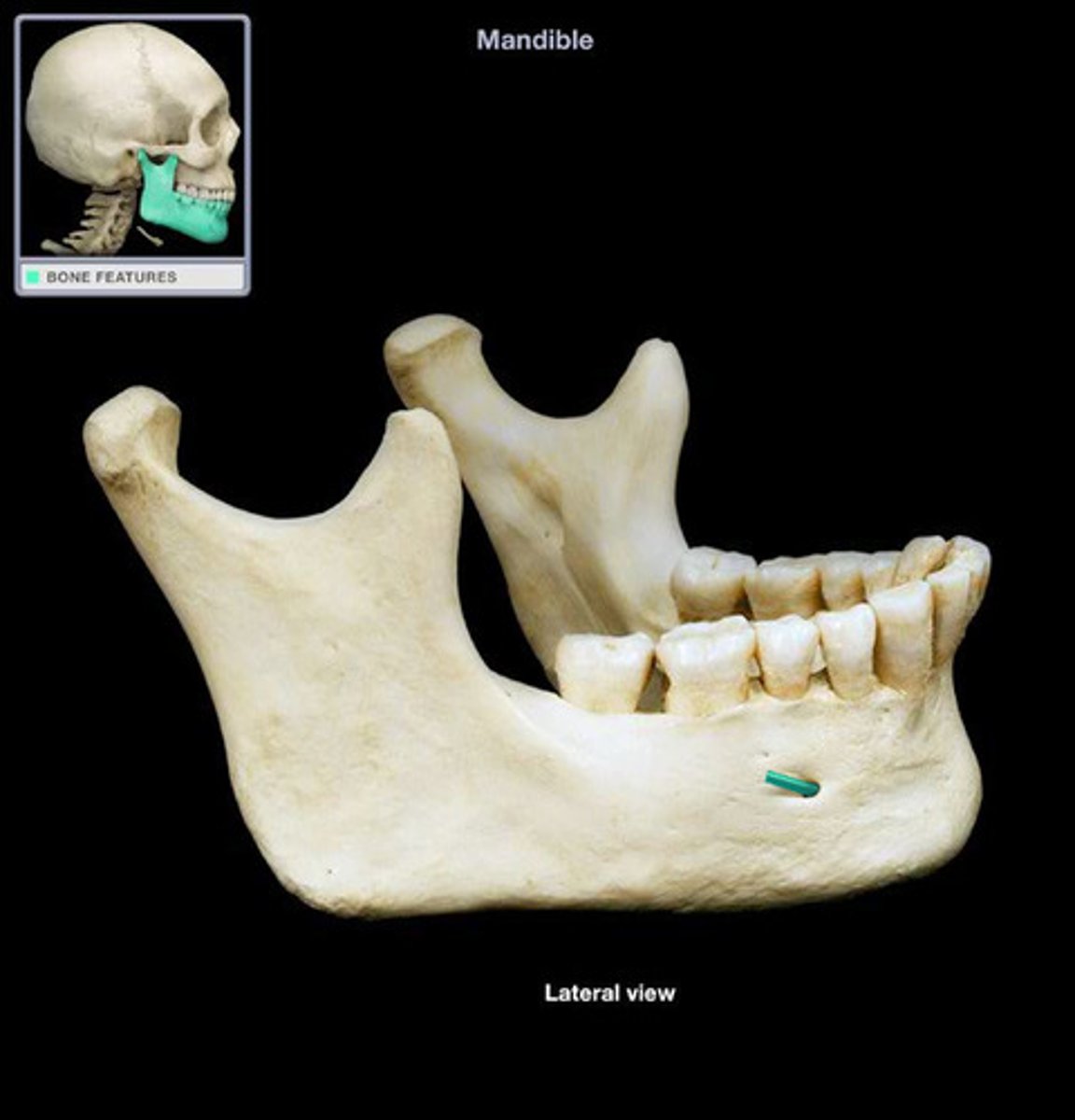
coronoid process ( anterior)
what is this
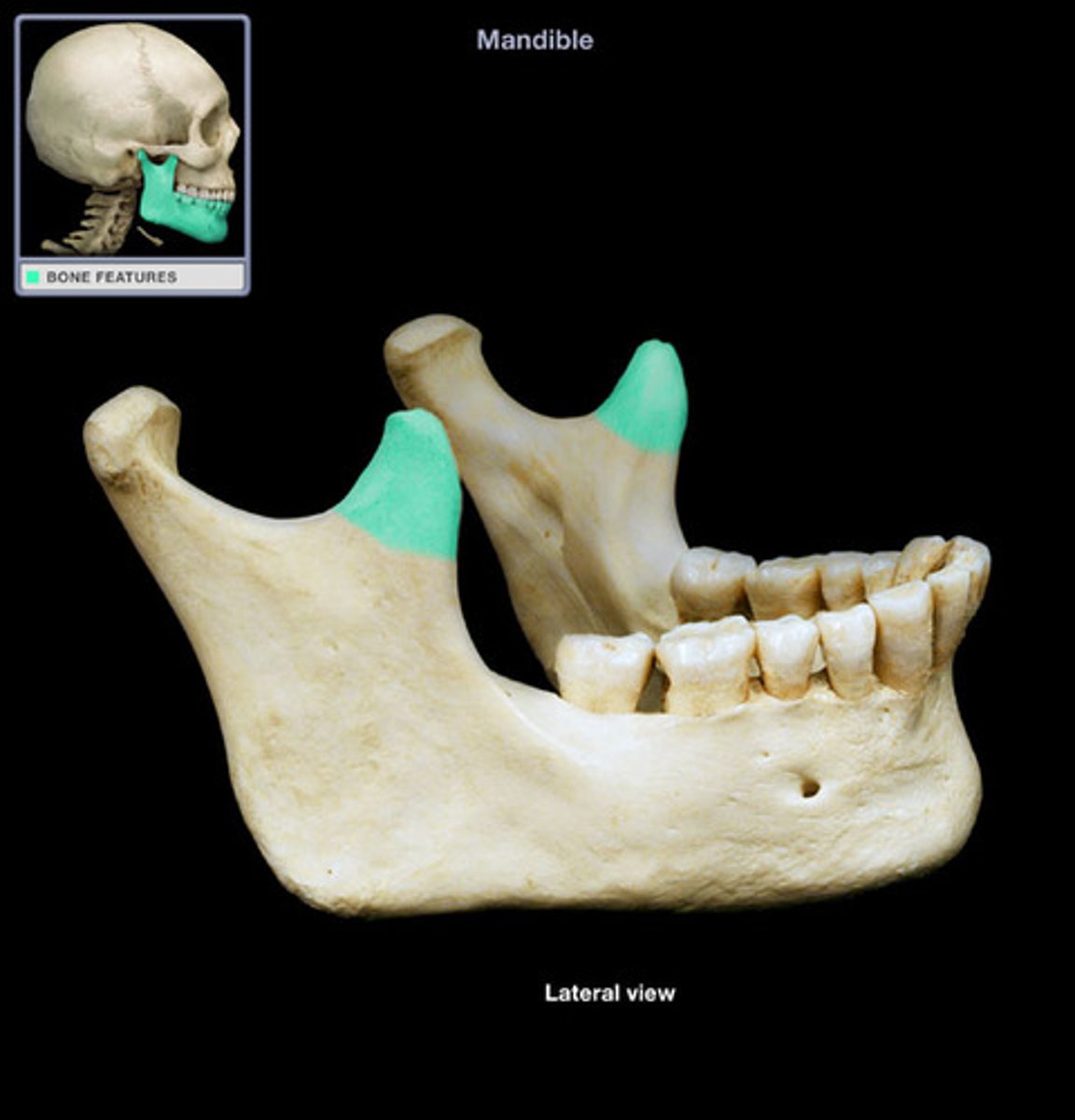
Mandibular notch
- between coronoid process and condyloid process
- forms lower part of Y
what is this
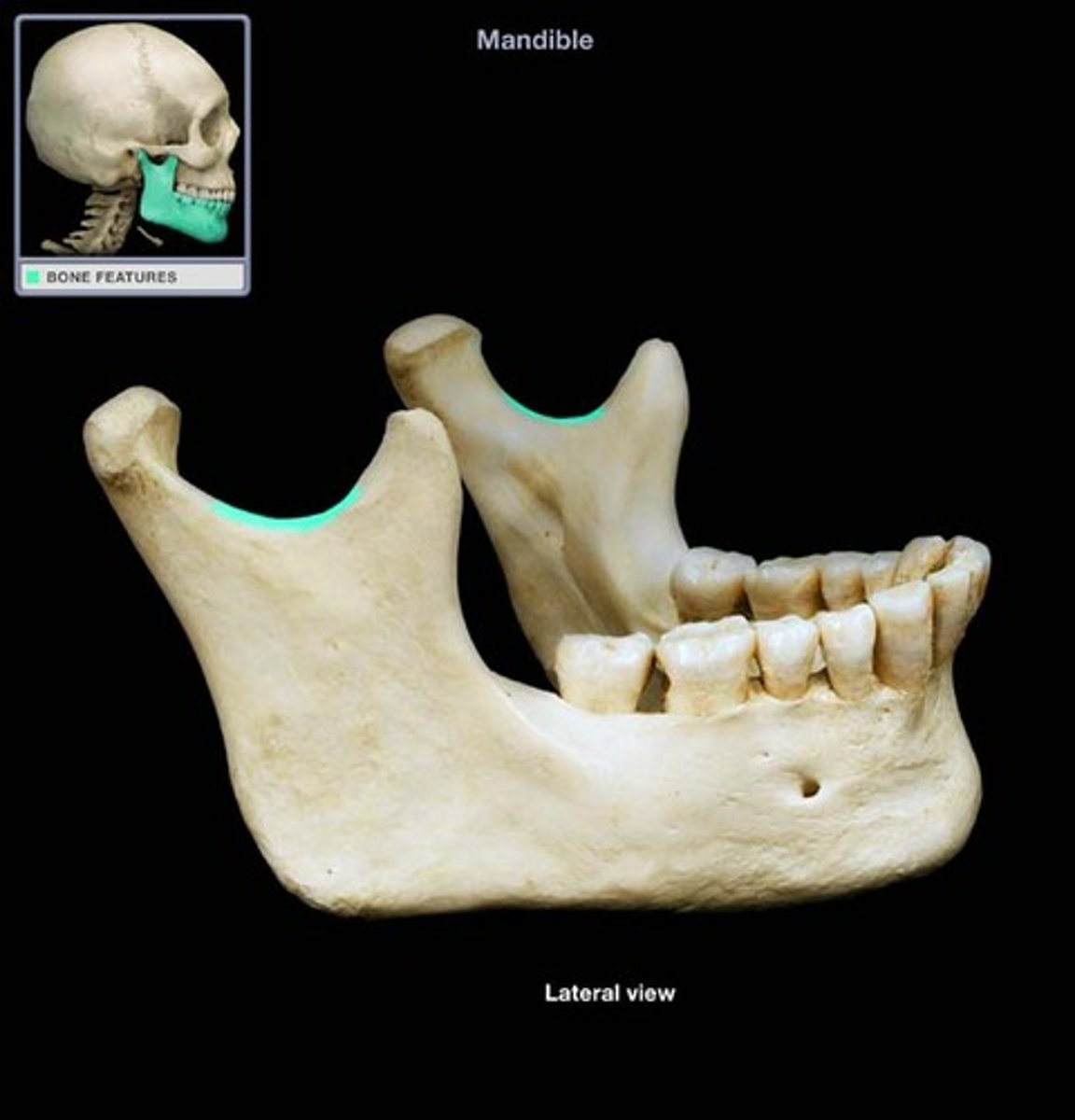
condyloid process ( posterior)
- makes up TMJ
what is this
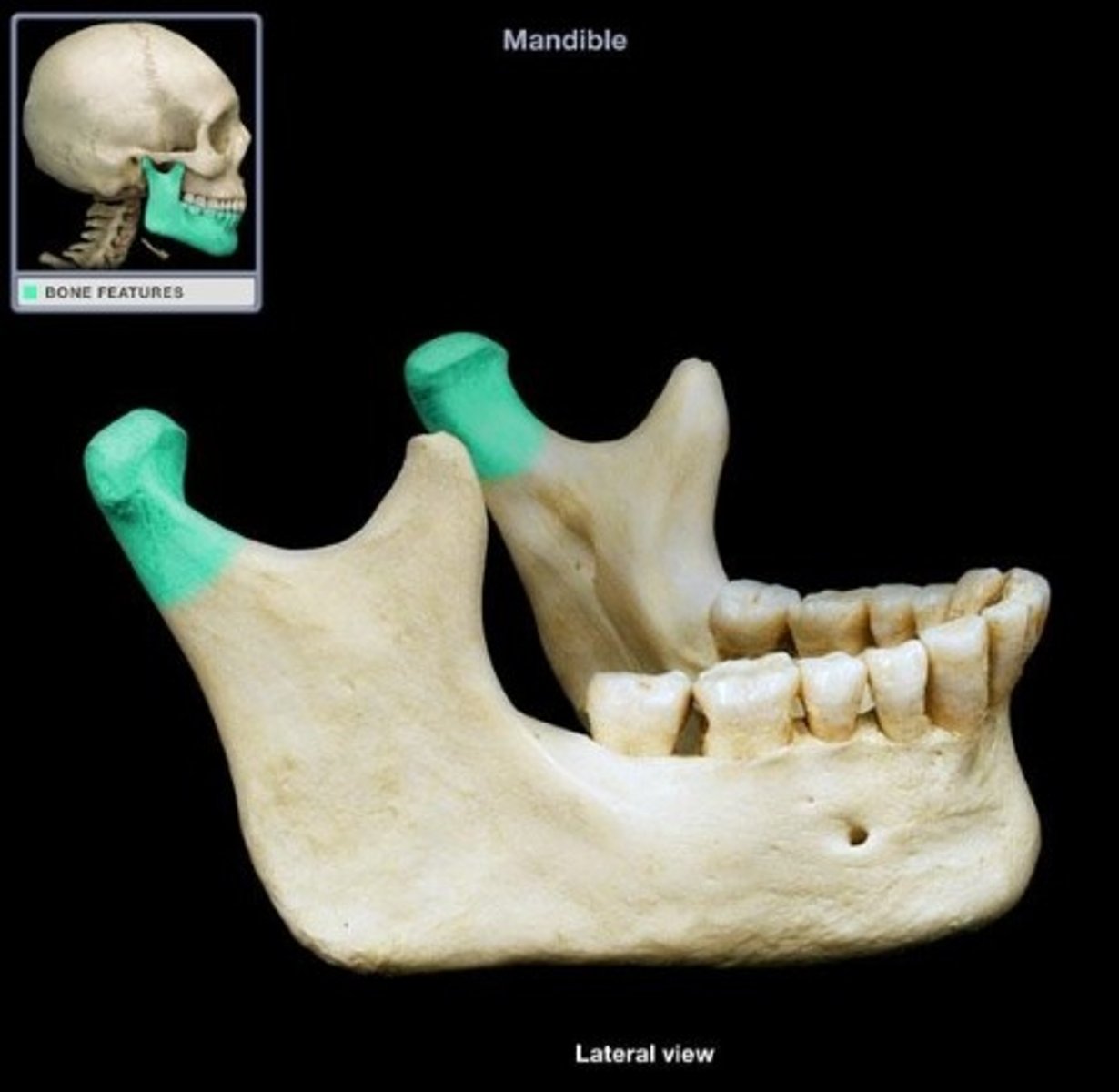
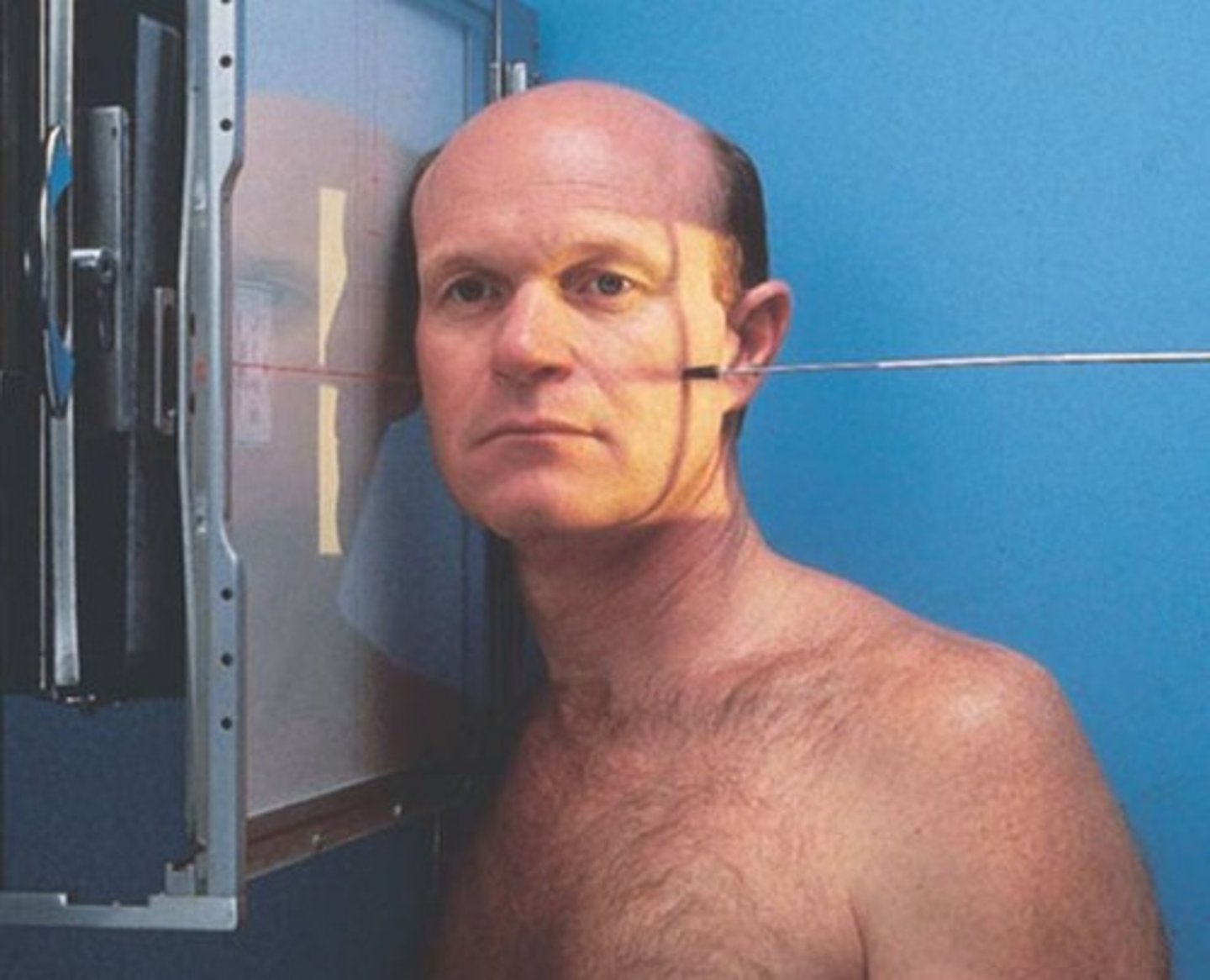
Lateral ( facial)
- Pt semi-prone/ head is in a true lateral / Mid-sag plane is parallel / interpupillary line is perpendicular to the IR
- Perp entering at the zygoma ( 1/2 way between the outer canthus and EAM)
- Lateral view of facial bones (orbits to mandible to ear) / no rotation of the head (mental point must be included)
What is this projection?
How is Patient positing?
What is the CR?
What are the structures shown?

Parietocanthial (water)
- Pt prone / nose 3/4 ( 2cm) away from the table OML forms a 37 degree with the board
- Perp , exiting at the acanthion
- Petrous ridges are projected below the maxillary sinuses/ Facial bones , orbits and maxillae/ zygomatic arches / Equidistant with lateral boarders of the skull and orbits
What is this projection?
How is Patient positing?
What is the CR?
What are the structures shown?
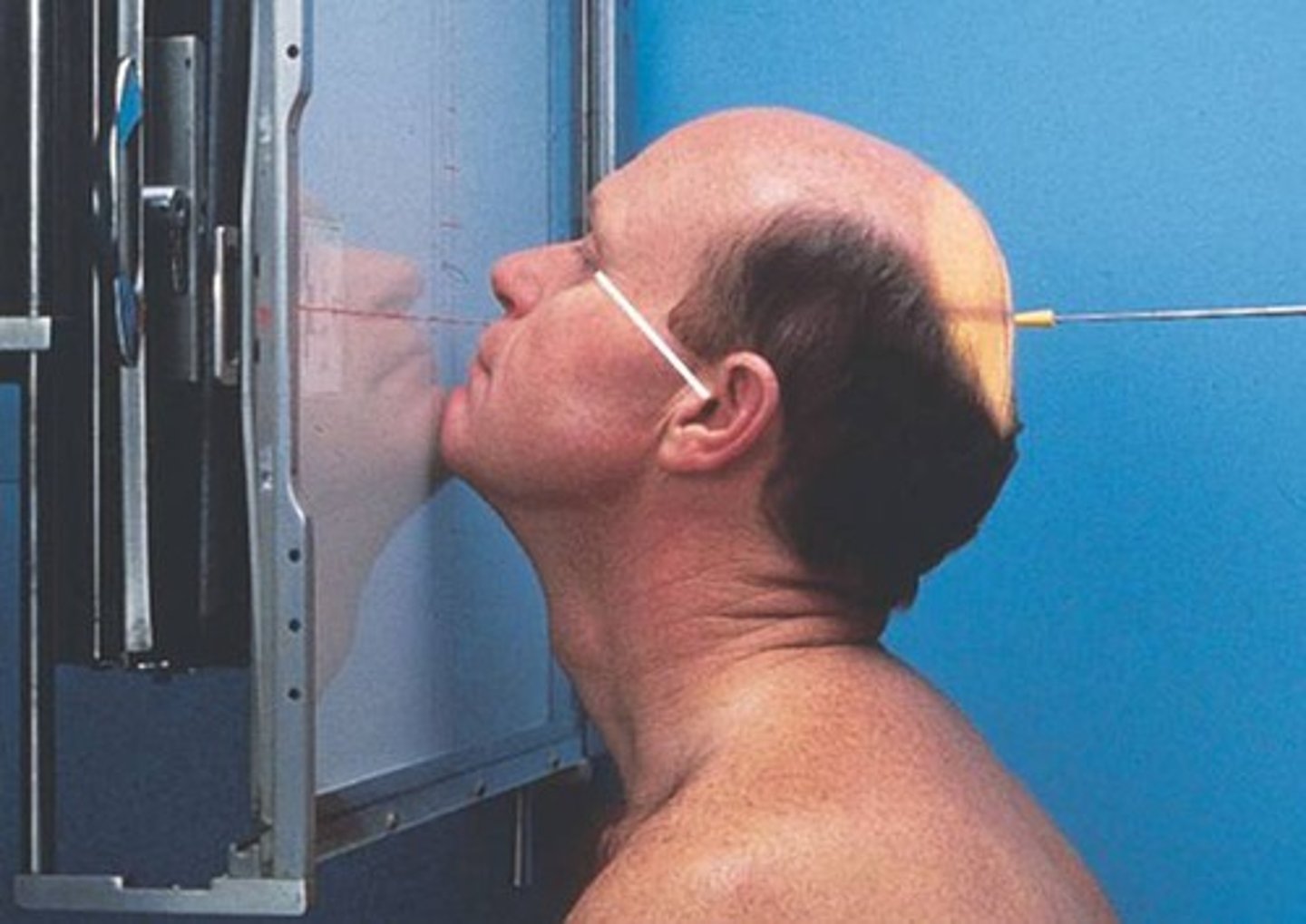
Acanthioparietal (Reverse Waters) Facial Bones (trauma)
- Pt supine/ Mentomeatal line(MML) is perpendicular to the IR( places the OML 37 to the IR
- Perp, entering at the acanthion
- Similar to those in a water, except structures are magnified / Petrous ridge will be BELOW the maxillary sinuses
What is this projection?
How is Patient positing?
What is the CR?
What are the structures shown?
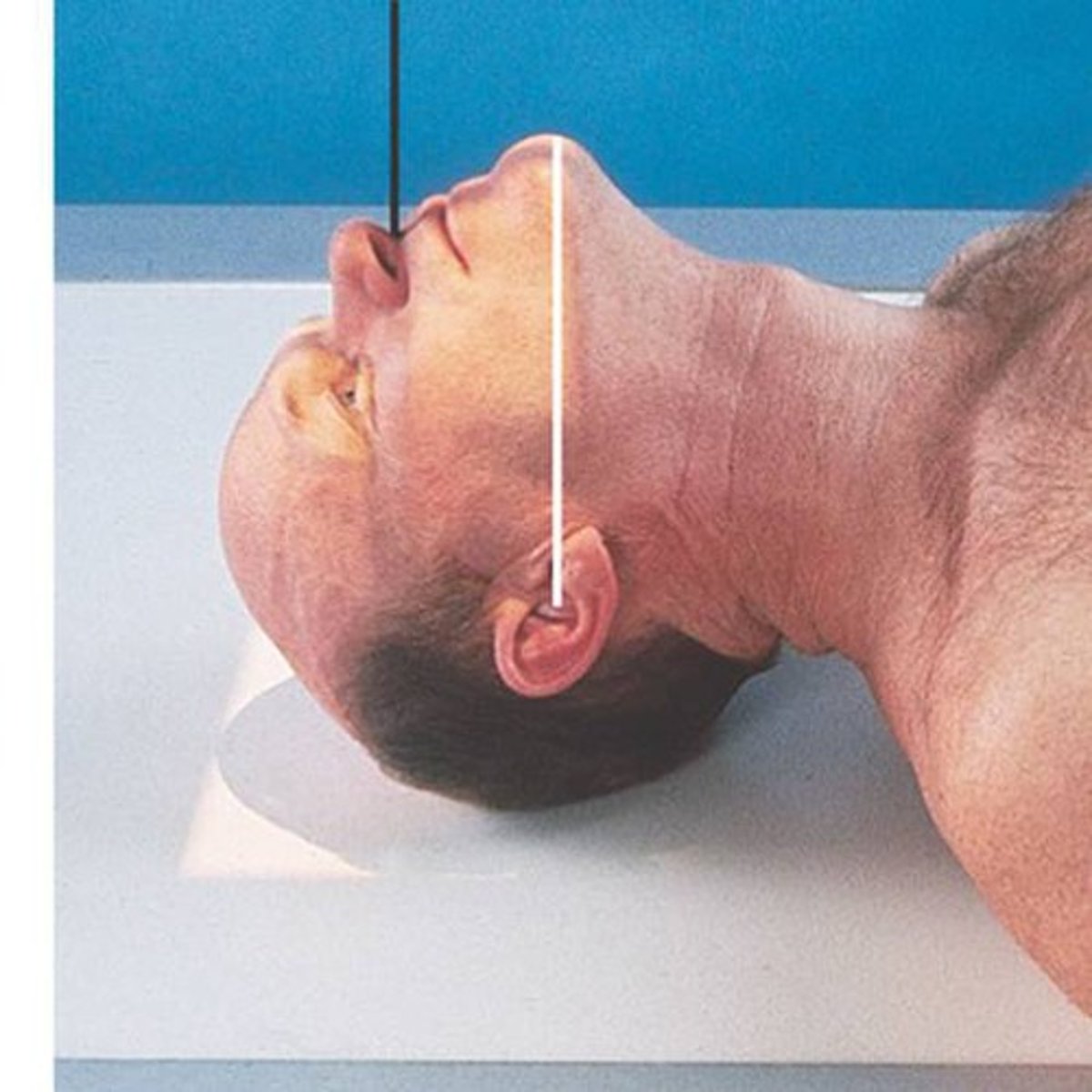
1. IOML
2. Perpendicular
3. 30 deg cephalic
4. Parallel
5. MML
If the patient CANNOT extend their neck for a Waters , you can use the _________ to be ___________ to the IR and angle the tube __________ ________?
Always adjust the CR so it remains______ to the _______?
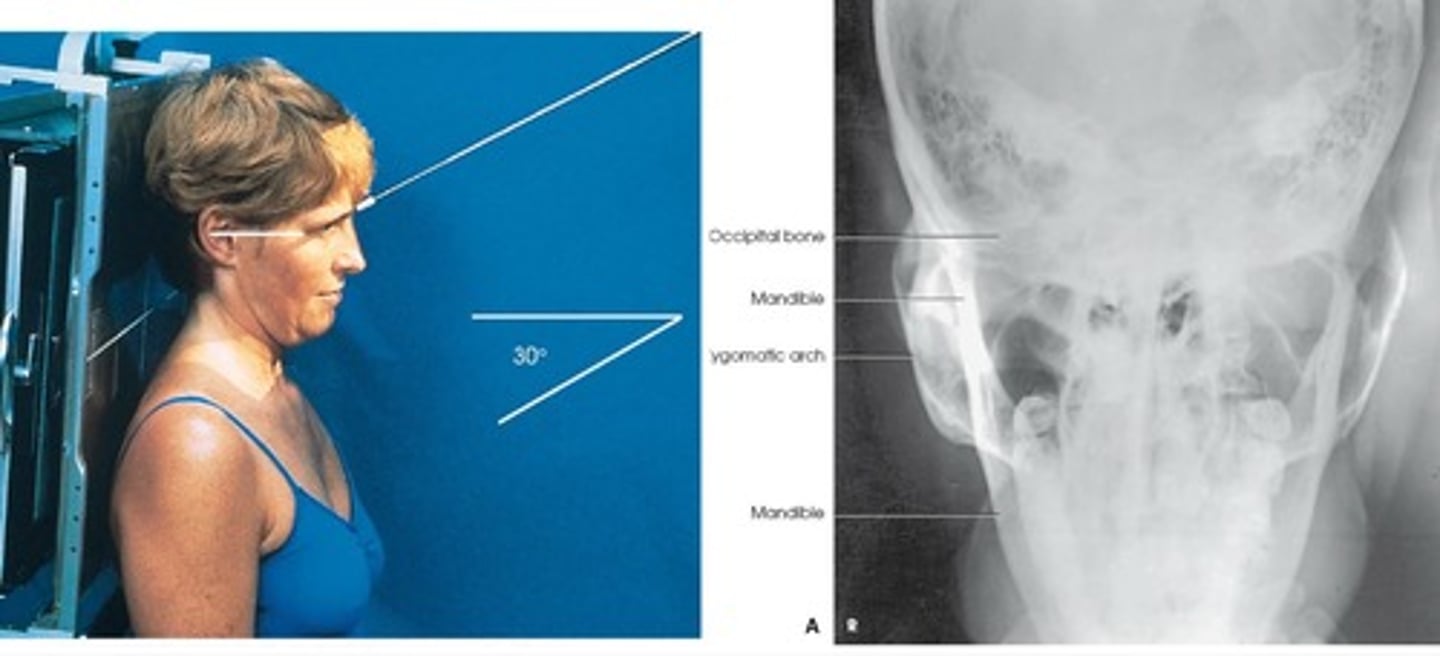
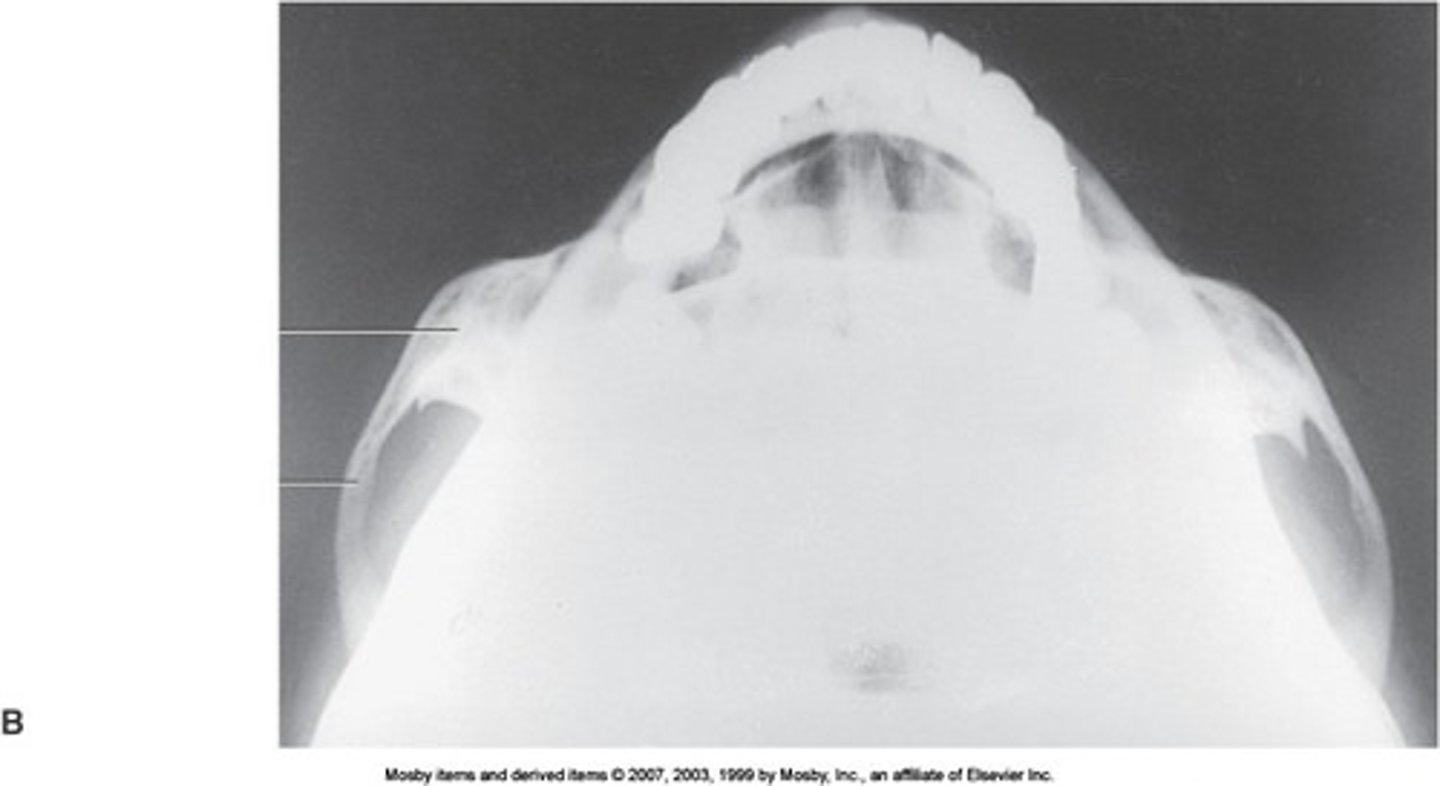
Submentovertical (SMV)
- Pt is seated/ recumbent supine / place vertex on grid/ IOML is parallel to IR
- Perp to the IOML ,( 1" posterior to the outer canthus)
- Zygomatic arches free of superimposition/ mandible/vomer/maxillae (palatine process)/ No rotation of the head
What is this projection?
How is Patient positing?
What is the CR?
What are the structures shown?
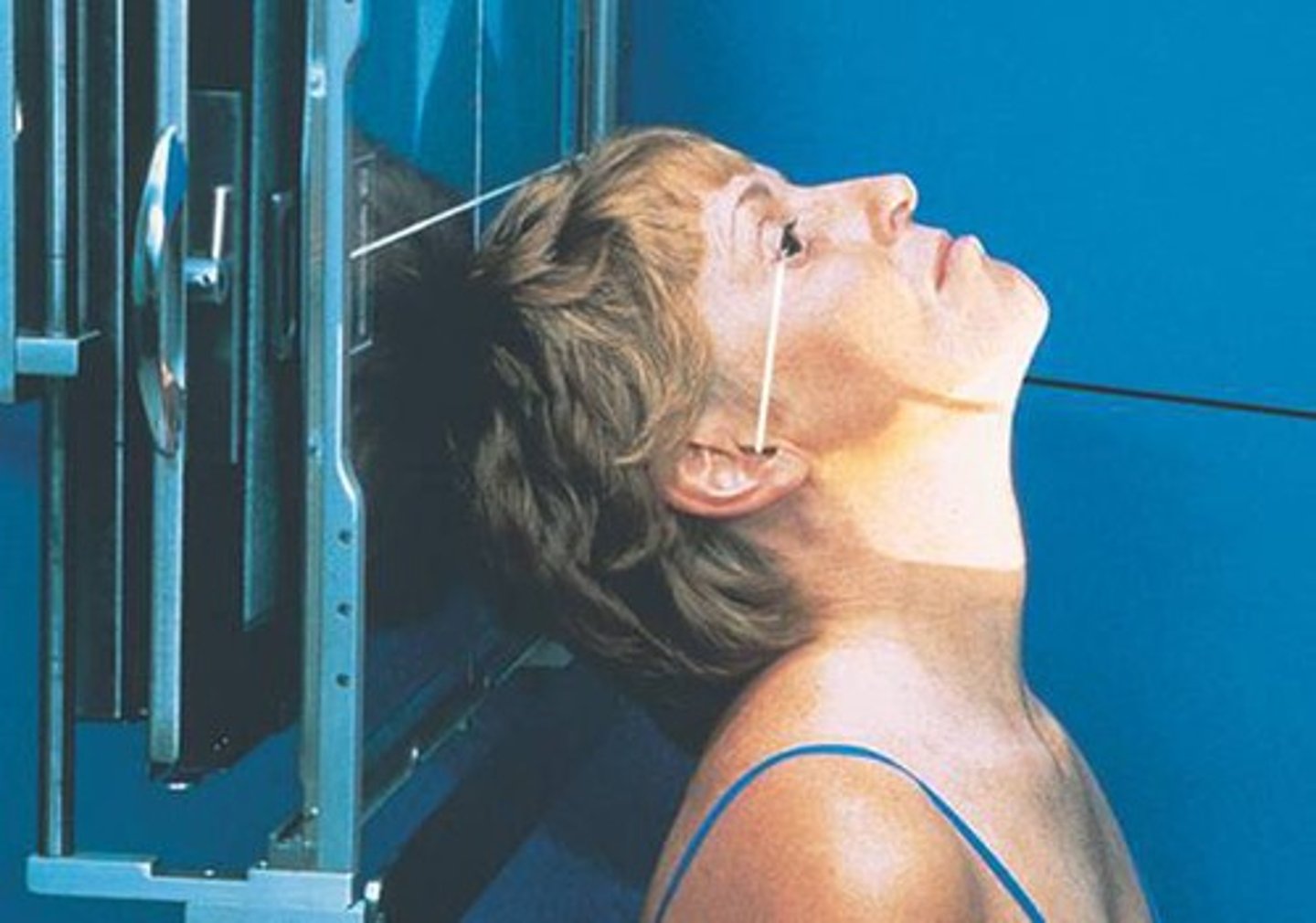
- Pt prone/ Center the bottom of IR 1" below the mandible / OML is perpendicular / Mid-Sag plane is perpendicular to the table
- CR is Perp, centered to the mid-point of the IR at level of the acanthion
- Mandibular rami & body/ PA facial bones
PA
How is Patient positing?
What is the CR?
What are the structures shown?
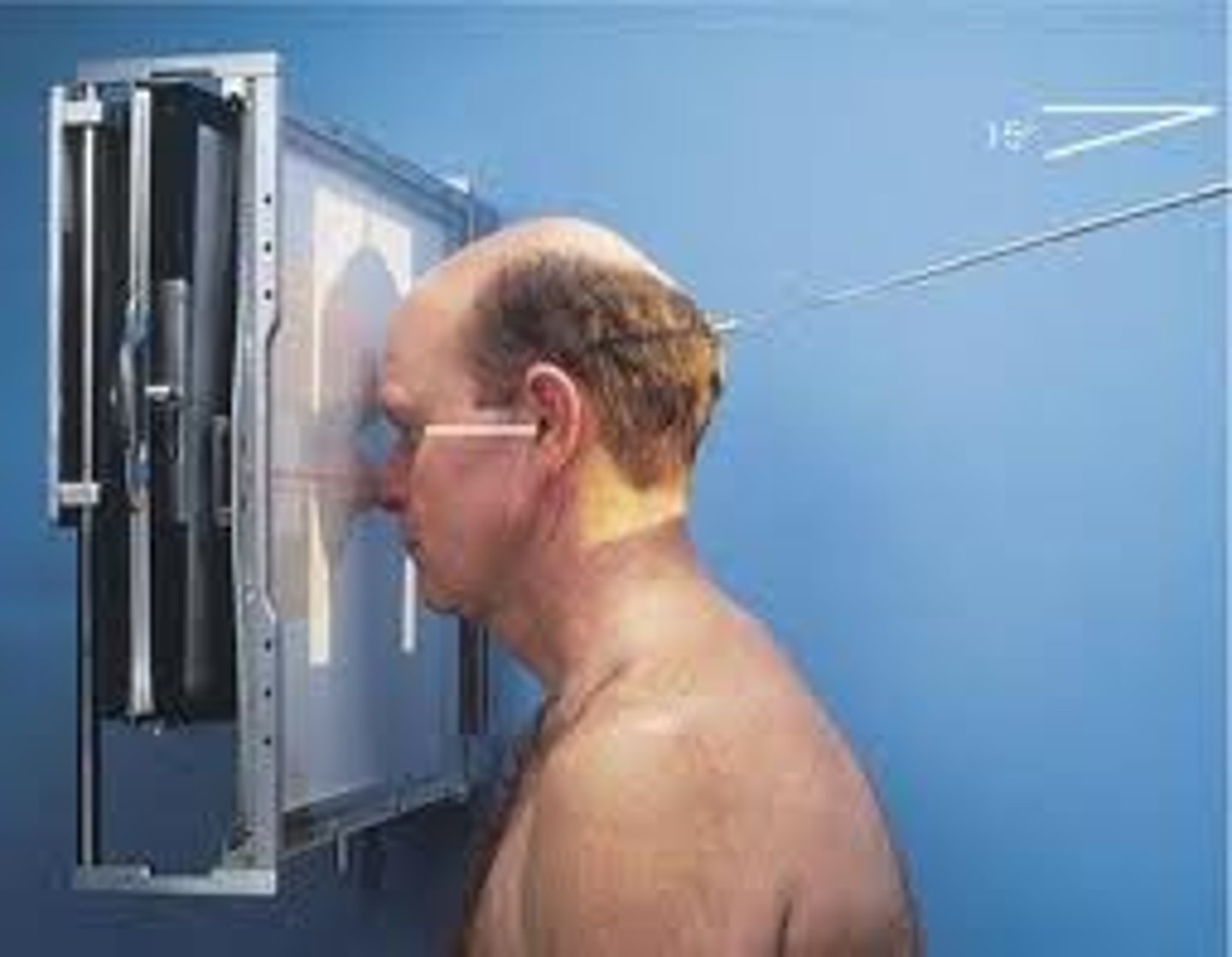
PA Axial ( Cadwell)
- Pt prone / OML and mid-sag are perpendicular to the IR
- 15 deg caudad exiting at the nasion
- Orbital rims/ maxillae/ nasal septum/ zygomatic bones/ anterior nasal spine
What is this projection?
How is Patient positing?
What is the CR?
What are the structures shown?
Orbital rims and orbital floors
If you add a 30 deg caudad angle to PA axial what is best demonstrated ?
In the lower 1/3 of the orbits
Where are the petrous ridges located for 15 deg caudad PA axial ?
Below the inferior margins of the orbits
Where are the petrous ridges located for 30 deg caudad PA axial ?
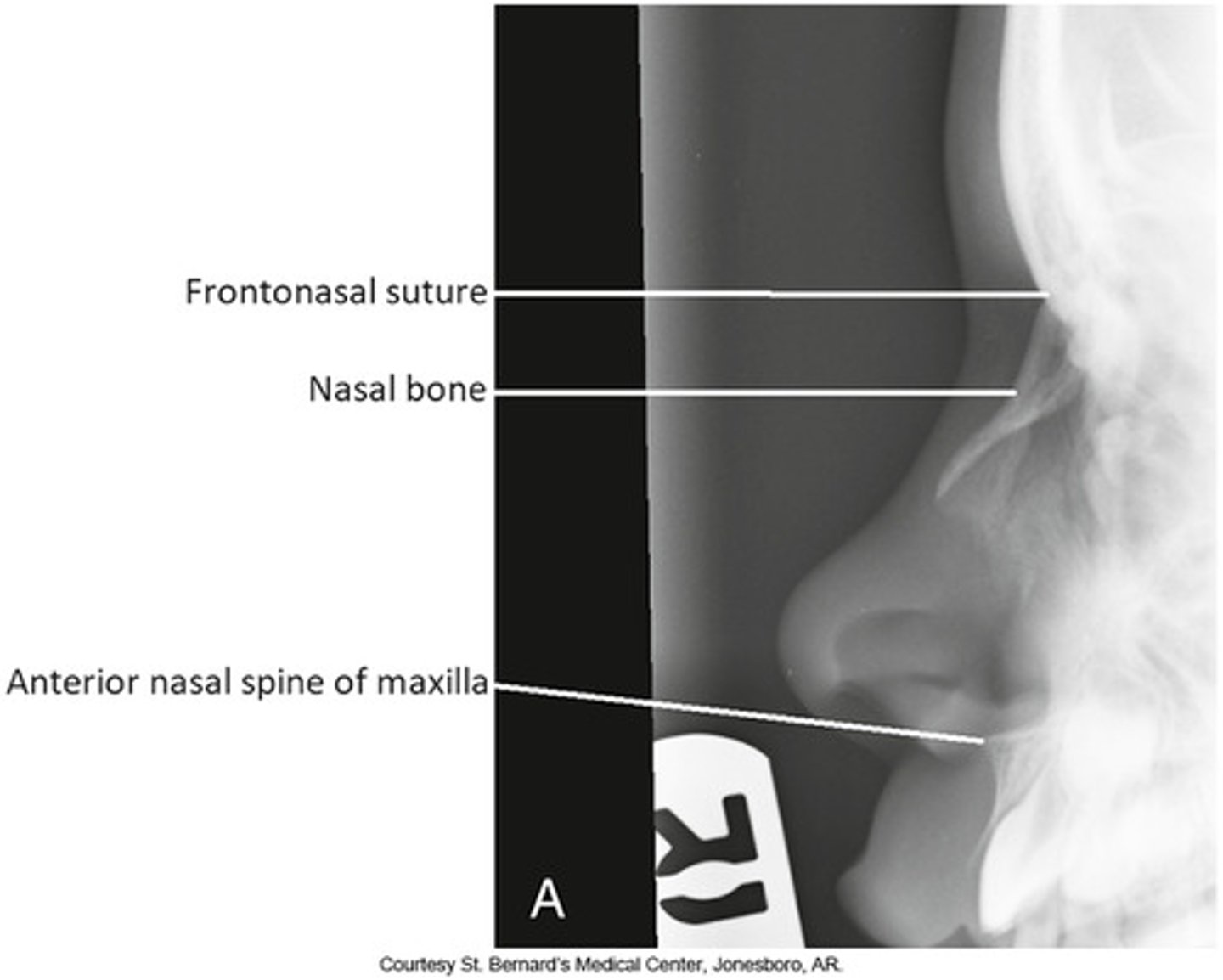
Lateral ( nasal bone)
- Pt semi-prone / head in a true lateral / Mid-sag is parallel to IR / Interpupillary is perpendicular to IR
- Perp to the bridge of the lower nose ( 1/2 distal to the nasion)
-Lateral views of nasal bones / soft tissue of the nose and anterior nasal spine )
*always do both sides *
What is this projection?
How is Patient positing?
What is the CR?
What are the structures shown?
Submentovertical (SMV) Zygomatic arches
- Pt upright seated/ IOML is parallel to the IR / vertex resting on upright bucky.
- Perp to the IOML / centered midway between the zygomatic arches.
- Symmetric images of the zygomatic arches projected free of superimposition
What is this projection?
How is Patient positing?
What is the CR?
What are the structures shown?
Tangential
- IOML is parallel to the IR / rotate mid-sag plane 15 deg towards the effected side/ center zygomatic arch to IR
- Perp to IOML, center to arch ( 1" posterior to outer canthus )
- 1 zygomatic arch free of superimposition/ find depressed fractures or flat cheek bones
* must do 2 images to show both sides*
What is this projection?
How is Patient positing?
What is the CR?
What are the structures shown?
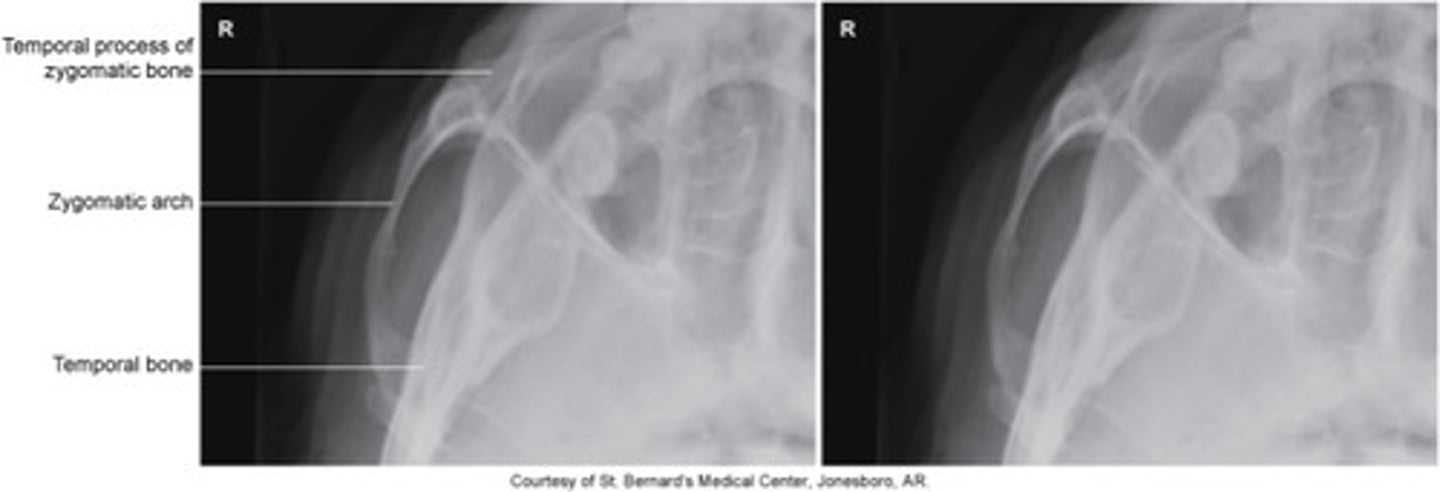
AP Axial (modified Townes Method)
- PT supine/ chin tucked so OML is per to the IR
- 30 deg caudad, entering at the glabella .
- Symmetric AP axial projection of both arches free of superimposition (lateral to mandibular rami)
What is this projection?
How is Patient positing?
What is the CR?
What are the structures shown?