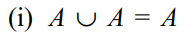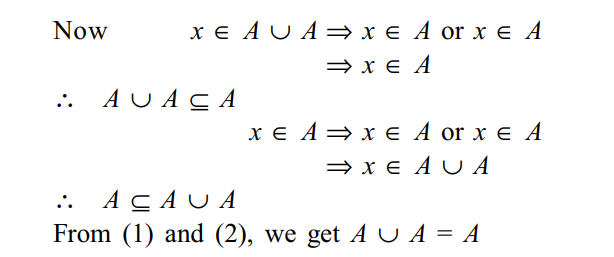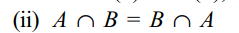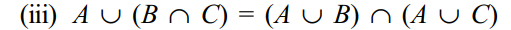Discrete Math
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Usually a set is represented in two ways, namely, (1) roster notation and (2) set builder notation.
In roster notation, all the elements of the set are listed, if possible, separated by commas and enclosed within braces. A few examples of sets in roster notation are given as follows:
Superset and proper set
For example, if A = {a, b}, B = {a, b, c} and C = {b, c, a}, then A and B are subsets of C, but A is a proper subset of C, while B is not, since B = C.

Power set
Given a set S, the set of all subsets of the set S is called the power set of S and is denoted by P(S). For example, if S = {a, b, c}, P(S) is the set of all subsets of {a, b, c}. i.e., P(S) = [ , {a}, {b}, {c}, {a, b}, {b, c}, {c, a}, {a, b, c}.]


ordered pairs

multiplication of multiple sets
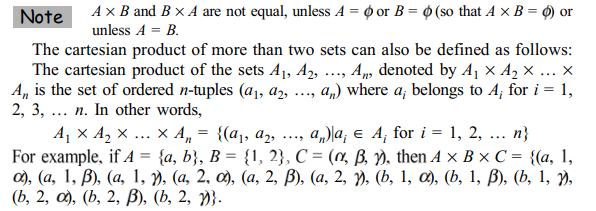
Difference of two sets

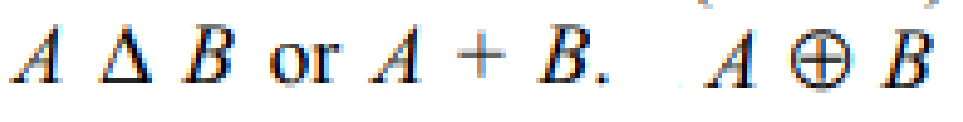
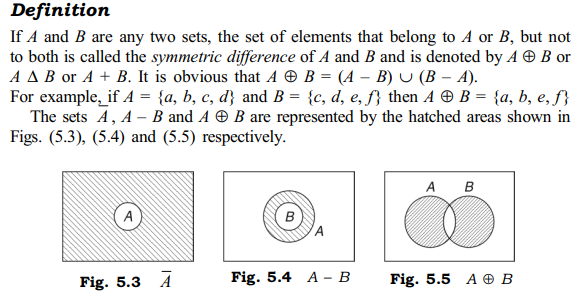
symmetric difference of two sets
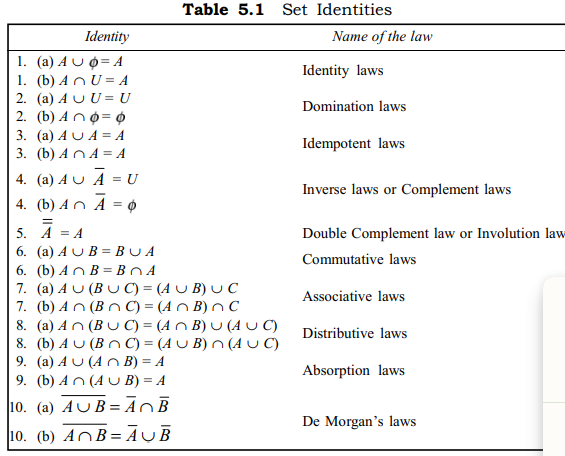
Identities and laws
Principle of duality