unit 7.1: heavy metals
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/115
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:35 AM on 3/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
1
New cards
Lead
* Storage batteries, ammunition, metal alloys, solder, glass, plastics, pigments, and ceramics
* No useful purpose in the human body
* No useful purpose in the human body
2
New cards
respiratory and gastrointestinal tract
**Lead:** *Pharmacokinetics*
Absorbed slowly but consistently via ___
Absorbed slowly but consistently via ___
3
New cards
industrial exposure
**Lead:** *Pharmacokinetics*
Respiratory tract
Respiratory tract
4
New cards
non-industrial exposure
**Lead:** *Pharmacokinetics*
Intestinal tract
Intestinal tract
5
New cards
50%
**Lead:** *Pharmacokinetics*
in children
in children
6
New cards
10-15%
**Lead:** *Pharmacokinetics*
in adults
in adults
7
New cards
**Low dietary calcium, iron deficiency and ingestion** on an empty stomach
**Lead:** *Pharmacokinetics*
increases absorption
increases absorption
8
New cards
99% to 1%
**Lead:** *Pharmacokinetics*
RBCs to free plasma ratio
RBCs to free plasma ratio
9
New cards
* bone marrow, brain, kidney, liver, muscle and gonads; then bones
* placenta - may affect fetus
* placenta - may affect fetus
**Lead:** *Pharmacokinetics*
Distribution
Distribution
10
New cards
1-2 months
**Lead:** *Pharmacokinetics*
half life
half life
11
New cards
years to decades
**Lead:** *Pharmacokinetics*
half life in bones
half life in bones
12
New cards
in the urine
**Lead:** *Pharmacokinetics*
70%
70%
13
New cards
elevate blood lead concentrations
**Lead:** *Pharmacokinetics*
In patients with **high bone lead burdens**, slow release from the skeleton may ___ for years after exposure ceases
In patients with **high bone lead burdens**, slow release from the skeleton may ___ for years after exposure ceases
14
New cards
**pathologic high bone turnover states**
* hyperthyroidism
* prolonged immobilization
* hyperthyroidism
* prolonged immobilization
**Lead:** *Pharmacokinetics*
may result in **frank lead intoxication**
may result in **frank lead intoxication**
15
New cards
* Inhibition of enzymatic function
* Interference with action of essential cations (calcium, zinc, iron)
* Oxidative stress generation
* Gene expression changes
* Cell signaling alteration
* Disruption of membrane integrity
* Interference with action of essential cations (calcium, zinc, iron)
* Oxidative stress generation
* Gene expression changes
* Cell signaling alteration
* Disruption of membrane integrity
**Lead:** *Pharmacodynamics*
Mechanisms of Action
Mechanisms of Action
16
New cards
**developing central nervous system** of the fetus and young __child__
**Lead:** *Pharmacodynamics -* __*Nervous System*__
most sensitive target organ for lead’s toxic effect
most sensitive target organ for lead’s toxic effect
17
New cards
normocytic or microcytic and hypochromic
**Lead:** *Pharmacodynamics -* __*Blood*__
Lead can induce an **anemia** that may be ___
Lead can induce an **anemia** that may be ___
18
New cards
heme synthesis
**Lead:** *Pharmacodynamics -* __*Blood*__
Lead interferes with ___ by **blocking the incorporation of iron into protoporphyrin IX** and by **inhibiting the function of enzymes** in the heme synthesis pathway, including __aminolevulinic acid dehydratase and ferrochelatase__
Lead interferes with ___ by **blocking the incorporation of iron into protoporphyrin IX** and by **inhibiting the function of enzymes** in the heme synthesis pathway, including __aminolevulinic acid dehydratase and ferrochelatase__
19
New cards
increasing erythrocyte membrane fragility and decreasing red cell survival time
**Lead:** *Pharmacodynamics -* __*Blood*__
Lead also contributes to anemia by ___
Lead also contributes to anemia by ___
20
New cards
**Basophilic stippling** on the peripheral blood smear
**Lead:** *Pharmacodynamics -* __*Blood*__
suggestive—albeit insensitive and nonspecific—diagnostic clue to the presence of lead intoxication
* thought to be a consequence of lead inhibition of the enzyme **3′,5′-pyrimidine nucleotidase**
suggestive—albeit insensitive and nonspecific—diagnostic clue to the presence of lead intoxication
* thought to be a consequence of lead inhibition of the enzyme **3′,5′-pyrimidine nucleotidase**
21
New cards
renal interstitial fibrosis and nephrosclerosis
**Lead:** *Pharmacodynamics -* __*Kidneys*__
**Chronic** high-dose lead exposure
**Chronic** high-dose lead exposure
22
New cards
**“saturnine gout” -** recurrent bouts of gouty arthritis
**Lead:** *Pharmacodynamics -* __*Kidneys*__
Lead may alter **uric acid excretion** by the kidney, resulting in ___
Lead may alter **uric acid excretion** by the kidney, resulting in ___
23
New cards
transient azotemia, possibly as a consequence of intrarenal vasoconstriction
**Lead:** *Pharmacodynamics -* __*Kidneys*__
**Acute** high-dose lead exposure
**Acute** high-dose lead exposure
24
New cards
stillbirth or spontaneous abortion
**Lead:** *Pharmacodynamics -* __*Reproductive Organs*__
High-dose lead exposure
High-dose lead exposure
25
New cards
diminished or aberrant sperm production
**Lead:** *Pharmacodynamics -* __*Reproductive Organs*__
In **males**, blood lead concentrations __higher than 40 mcg/dL__
In **males**, blood lead concentrations __higher than 40 mcg/dL__
26
New cards
loss of appetite, constipation, diarrhea
**Lead:** *Pharmacodynamics -* __*Gastrointestinal Tract*__
Moderate lead poisoning
Moderate lead poisoning
27
New cards
**“lead colic” -** intermittent bouts of severe colicky abdominal pain
**Lead:** *Pharmacodynamics -* __*Gastrointestinal Tract*__
high dosage
high dosage
28
New cards
**spasmodic contraction** of the smooth muscles of the intestinal wall
* mediated by **alteration in synaptic transmission** at the smooth muscle-neuromuscular junction
* mediated by **alteration in synaptic transmission** at the smooth muscle-neuromuscular junction
**Lead:** *Pharmacodynamics -* __*Gastrointestinal Tract*__
lead colic mechanism
lead colic mechanism
29
New cards
**“gingival lead lines” -** sulfur ions released by microbial action may produce dark deposits of lead sulfide at the gingival margin
**Lead:** *Pharmacodynamics -* __*Gastrointestinal Tract*__
In heavily exposed individuals with **poor dental hygiene**
In heavily exposed individuals with **poor dental hygiene**
30
New cards
Inorganic
**Lead:** *Major Forms of Lead Intoxication*
lead oxides and salts
lead oxides and salts
31
New cards
Organic
**Lead:** *Major Forms of Lead Intoxication*
tetraethyl lead
tetraethyl lead
32
New cards
GI, Respiratory
**Lead:** *Major Forms of Lead Intoxication -* __*Major Routes*__
Inorganic
Inorganic
33
New cards
**Skin**, GI, Respiratory
**Lead:** *Major Forms of Lead Intoxication -* __*Major Routes*__
Organic
Organic
34
New cards
Soft tissues; **redistributed to skeleton**
**Lead:** *Major Forms of Lead Intoxication -* __*Distribution*__
Inorganic
Inorganic
35
New cards
Soft tissues **(esp liver and CNS)**
**Lead:** *Major Forms of Lead Intoxication -* __*Distribution*__
Organic
Organic
36
New cards
* CNS deficits
* peripheral neuropathy
* anemia
* nephropathy
* hypertension
* reproductive toxicity
* peripheral neuropathy
* anemia
* nephropathy
* hypertension
* reproductive toxicity
**Lead:** *Major Forms of Lead Intoxication -* __*Clinical Findings*__
Inorganic
Inorganic
37
New cards
Encephalopathy
**Lead:** *Major Forms of Lead Intoxication -* __*Clinical Findings*__
Organic
Organic
38
New cards
* Inhibits enzymes
* interferes with essential cations
* alters membrane structures
* interferes with essential cations
* alters membrane structures
**Lead:** *Major Forms of Lead Intoxication -* __*MOA*__
Inorganic
Inorganic
39
New cards
Hepatic dealkylation (fast) → Trialkyl metabolites (slow) → dissociation to lead
**Lead:** *Major Forms of Lead Intoxication -* __*MOA*__
Organic
Organic
40
New cards
* **Renal** (major)
* **feces and breast milk** (minor)
* **feces and breast milk** (minor)
**Lead:** *Major Forms of Lead Intoxication -* __*Metabolism & Elimination*__
Inorganic
Inorganic
41
New cards
* **Urine and feces** (major)
* **Sweat** (minor)
* **Sweat** (minor)
**Lead:** *Major Forms of Lead Intoxication -* __*Metabolism & Elimination*__
Organic
Organic
42
New cards
immediate termination of exposure, supportive care, and the judicious use of chelation therapy
**Lead:** *Treatment -* __*Inorganic*__
43
New cards
Lead encephalopathy
**Lead:** *Treatment -* __*Inorganic*__
medical emergency that requires intensive supportive care
medical emergency that requires intensive supportive care
44
New cards
corticosteroids and mannitol or hypertonic saline
**Lead:** *Treatment -* __*Inorganic*__
**Cerebral edema** may improve with ___
**Cerebral edema** may improve with ___
45
New cards
Radiopacities on **abdominal radiographs**
**Lead:** *Treatment -* __*Inorganic*__
suggest the presence of retained lead objects requiring gastrointestinal decontamination
suggest the presence of retained lead objects requiring gastrointestinal decontamination
46
New cards
5 days
**Lead:** *Treatment -* __*Inorganic*__
Intravenous **edetate calcium disodium (CaNa₂EDTA)** is administered at a dosage of **1000–1500 mg/m2/d** (approximately 30–50 mg/kg/d) by **continuous infusion** for up to ___
Intravenous **edetate calcium disodium (CaNa₂EDTA)** is administered at a dosage of **1000–1500 mg/m2/d** (approximately 30–50 mg/kg/d) by **continuous infusion** for up to ___
47
New cards
Oral Succimer (DMSA)
**Lead:** *Treatment -* __*Inorganic*__
after 5 days
after 5 days
48
New cards
gastrointestinal decontamination
**Lead:** *Treatment*
Retained lead objects
Retained lead objects
49
New cards
decontaminating the skin
**Lead:** *Treatment -* __*Organic*__
50
New cards
Empiric chelation
**Lead:** *Treatment -* __*Organic*__
if **high blood lead concentrations** are present
if **high blood lead concentrations** are present
51
New cards
anticonvulsants
**Lead:** *Treatment -* __*Organic*__
Treatment of seizures
Treatment of seizures
52
New cards
Arsenic
* Semiconductors, wood preservatives, nonferrous alloys, glass and turf herbicide monosodium methane arsonate (MSMA)
* Groundwater
* used as a pharmaceutical agent but now limited in use
* Groundwater
* used as a pharmaceutical agent but now limited in use
53
New cards
Arsine
**Arsenic:**
an arsenous hydride (AsH3) gas with potent hemolytic effects
an arsenous hydride (AsH3) gas with potent hemolytic effects
54
New cards
Fowler’s solution
**Arsenic:**
contains **1% potassium arsenite**, was widely used as a medicine for many conditions from the eighteenth century through the mid-twentieth century
contains **1% potassium arsenite**, was widely used as a medicine for many conditions from the eighteenth century through the mid-twentieth century
55
New cards
**lewisite** (dichloro-\[2-chlorovinyl\]arsine)
**Arsenic:**
developed in the early 20th century as **chemical warfare agents**
developed in the early 20th century as **chemical warfare agents**
56
New cards
Arsenic trioxide
**Arsenic:**
reintroduced into the United States Pharmacopeia in 2000 as an **orphan drug for the treatment of relapsed acute promyelocytic leukemia** and is finding expanded use in experimental cancer treatment protocol
reintroduced into the United States Pharmacopeia in 2000 as an **orphan drug for the treatment of relapsed acute promyelocytic leukemia** and is finding expanded use in experimental cancer treatment protocol
57
New cards
Melarsoprol
**Arsenic:**
used in the treatment of advanced **African trypanosomiasis**
used in the treatment of advanced **African trypanosomiasis**
58
New cards
respiratory and GI tract
**Arsenic:** *Pharmacokinetics*
Well-absorbed via ___
Well-absorbed via ___
59
New cards
Percutaneous absorption
**Arsenic:** *Pharmacokinetics*
**limited** but may be clinically significant after heavy exposure to concentrated arsenic reagents
**limited** but may be clinically significant after heavy exposure to concentrated arsenic reagents
60
New cards
methylation reactions
**Arsenic:** *Pharmacokinetics*
Metabolized by the liver via ___
Metabolized by the liver via ___
61
New cards
prolonged
**Arsenic:** *Pharmacokinetics*
After massive ingestions, the **elimination half-life** is ___
After massive ingestions, the **elimination half-life** is ___
62
New cards
**Arsenic binds to sulfhydryl groups** present in keratinized tissue, and following cessation of exposure, hair, nails, and skin
**Arsenic:** *Pharmacokinetics*
may contain elevated levels after urine values have returned to normal
may contain elevated levels after urine values have returned to normal
63
New cards
Urine (major), sweat and feces
**Arsenic:** *Pharmacokinetics*
Excreted in the ___
Excreted in the ___
64
New cards
Inhibition of enzymatic function
**Arsenic:** *Pharmacodynamics -* __*MOA*__
may result from **sulfhydryl group binding** by trivalent arsenic or by substitution for phosphate
may result from **sulfhydryl group binding** by trivalent arsenic or by substitution for phosphate
65
New cards
* Oxidative stress generation
* Gene expression changes
* Cell signaling alteration
* Gene expression changes
* Cell signaling alteration
**Arsenic:** *Pharmacodynamics -* __*MOA*__
Inorganic arsenic or its metabolites
Inorganic arsenic or its metabolites
66
New cards
two to ten times more acutely toxic
**Arsenic:** *Pharmacodynamics*
**inorganic trivalent arsenic** (As3+, arsenite) is generally ___ than **inorganic pentavalent arsenic** (As5+, arsenate)
**inorganic trivalent arsenic** (As3+, arsenite) is generally ___ than **inorganic pentavalent arsenic** (As5+, arsenate)
67
New cards
t**rivalent form of the methylated metabolites** (eg, monomethylarsonous acid \[MMAIII\])
**Arsenic:** *Pharmacodynamics*
more toxic than the inorganic parent compounds
more toxic than the inorganic parent compounds
68
New cards
Arsenic methylation requires *S*-adenosylmethionine
**Arsenic:** *Pharmacodynamics*
* a **universal methyl donor** in the body
* arsenic-associated perturbations in one-carbon metabolism
* may underlie some **arsenic-induced epigenetic effects** such as altered gene expression
* a **universal methyl donor** in the body
* arsenic-associated perturbations in one-carbon metabolism
* may underlie some **arsenic-induced epigenetic effects** such as altered gene expression
69
New cards
Arsine gas
**Arsenic:** *Pharmacodynamics*
* oxidized in vivo and exerts a **potent hemolytic effect** associated with **alteration of ion flux** across the erythrocyte membrane
* disrupts cellular respiration
* oxidized in vivo and exerts a **potent hemolytic effect** associated with **alteration of ion flux** across the erythrocyte membrane
* disrupts cellular respiration
70
New cards
arsenobetaine
**Arsenic:** *Pharmacodynamics*
Marine organisms
Marine organisms
71
New cards
arsenosugars
**Arsenic:** *Pharmacodynamics*
partially metabolized to dimethylarsinic acid
partially metabolized to dimethylarsinic acid
72
New cards
**Thioarsenite** compouns
**Arsenic:** *Pharmacodynamics*
occur as **minor metabolites** of inorganic arsenic
occur as **minor metabolites** of inorganic arsenic
73
New cards
GI, Respiratory
**Arsenic***: Arsenic Intoxication*
Major Routes
Major Routes
74
New cards
* Predominantly soft tissues (highest in liver and kidney)
* Tightly bound to skin, hair and nails
* Tightly bound to skin, hair and nails
**Arsenic***: Arsenic Intoxication*
Distribution
Distribution
75
New cards
* **Cardiovascular**: shock, arrythmias
* **CNS**: Encephalopathy, Peripheral Neuropathy
* **Others**: Gastroenteritis, Pancytopenias, Cancer
* **CNS**: Encephalopathy, Peripheral Neuropathy
* **Others**: Gastroenteritis, Pancytopenias, Cancer
**Arsenic***: Arsenic Intoxication*
Clinical Findings
Clinical Findings
76
New cards
* Methylation
* Excreted via **Urine** (major)
* **Sweat and Feces** (minor)
* Excreted via **Urine** (major)
* **Sweat and Feces** (minor)
**Arsenic***: Arsenic Intoxication*
Metabolism and Elimination
Metabolism and Elimination
77
New cards
Arsine gas poisoning
**Arsenic***: Arsenic Intoxication*
distinctive pattern of intoxication dominated by **profound hemolytic effects**
distinctive pattern of intoxication dominated by **profound hemolytic effects**
78
New cards
Oliguric renal failure
**Arsenic***: Arsenic Intoxication -* __*Gas poisoning*__
a consequence of **hemoglobin deposition in the renal tubules**, often appears within 1–3 days
a consequence of **hemoglobin deposition in the renal tubules**, often appears within 1–3 days
79
New cards
Paul Ehrlich’s “**magic bullet”**
**Arsenic***: Arsenic Intoxication -* __*Gas poisoning*__
for **syphilis** (arsphenamine, Salvarsan) was an arsenical
for **syphilis** (arsphenamine, Salvarsan) was an arsenical
80
New cards
**“Raindrop pattern”**
**Arsenic***:*
* Hyperpigmentation and hyperkeratosis involving hands and feet
* Usually due to chronic inorganic arsenic poisoning
* Dermatologic lesions associated with chronic ingestion of arsenic in **drinking water**
* Hyperpigmentation and hyperkeratosis involving hands and feet
* Usually due to chronic inorganic arsenic poisoning
* Dermatologic lesions associated with chronic ingestion of arsenic in **drinking water**
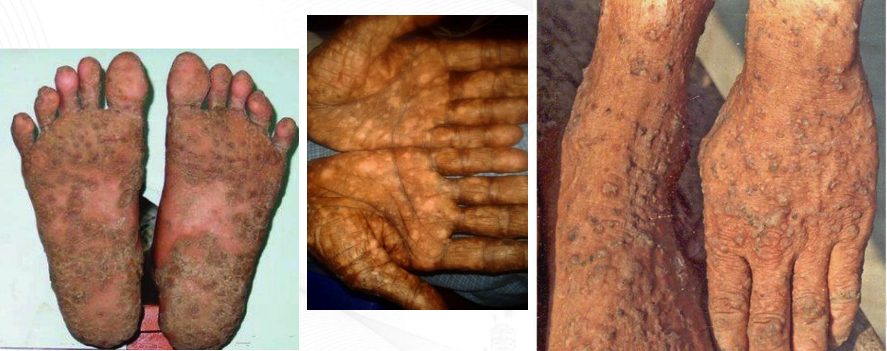
81
New cards
Chelation with **Unithiol** 3-5mg/kg every 4-6 hours or **Dimercaprol** every 4-6 hours
**Arsenic***: Treatment*
Acute Poisoning
Acute Poisoning
82
New cards
Mercury
* **Quicksilver** or liquid metal
* Mined predominantly as HgS in **cinnabar ores**
* Electrolytic production of chlorine and caustic soda; electrical equipment, thermometer, instruments, fluorescent lamps; dental amalgams; artisanal gold production
* Environmental release from burning of fossil fuels contributes to **bioaccumulation in fishes**
* Mined predominantly as HgS in **cinnabar ores**
* Electrolytic production of chlorine and caustic soda; electrical equipment, thermometer, instruments, fluorescent lamps; dental amalgams; artisanal gold production
* Environmental release from burning of fossil fuels contributes to **bioaccumulation in fishes**
83
New cards
Thimerosal
**Mercury:**
an **organomercurial preservative** that is metabolized in part to ethylmercury, has been removed from almost all the vaccines in which it was formerly present
an **organomercurial preservative** that is metabolized in part to ethylmercury, has been removed from almost all the vaccines in which it was formerly present
84
New cards
depending on chemical form
**Mercury:** *Pharmacokinetics*
absorption
absorption
85
New cards
Elemental mercury
**Mercury:** *Pharmacokinetics*
volatile and can be absorbed from the lungs
volatile and can be absorbed from the lungs
86
New cards
intact gastrointestinal tract
**Mercury:** *Pharmacokinetics*
poorly absorbed
poorly absorbed
87
New cards
Inhaled mercury
**Mercury:** *Pharmacokinetics*
**primary source** of occupational exposure
**primary source** of occupational exposure
88
New cards
kidneys
**Mercury:** *Pharmacokinetics*
Distributed well into **tissues** (most concentrated in ___)
Distributed well into **tissues** (most concentrated in ___)
89
New cards
**Alkylmercury** compounds
**Mercury:** *Pharmacokinetics*
appear to be well absorbed through the skin
appear to be well absorbed through the skin
90
New cards
acute contact with a few drops of **dimethylmercury**
**Mercury:** *Pharmacokinetics*
resulted in severe, delayed toxicity
resulted in severe, delayed toxicity
91
New cards
urine and feces
**Mercury:** *Pharmacokinetics*
Inorganic mercury is excreted through ___
Inorganic mercury is excreted through ___
92
New cards
1–3 months
**Mercury:** *Pharmacokinetics*
After **inhalation of elemental mercury vapor**, urinary mercury levels decline with a half-life of ___
After **inhalation of elemental mercury vapor**, urinary mercury levels decline with a half-life of ___
93
New cards
50 days
* undergoes biliary excretion and enterohepatic circulation
* undergoes biliary excretion and enterohepatic circulation
**Mercury:** *Pharmacokinetics*
Methylmercury blood and whole-body half-life
Methylmercury blood and whole-body half-life
94
New cards
sulfhydryl groups in keratinized tissue, and as with lead and arsenic
**Mercury:** *Pharmacokinetics*
appear in the hair and nails
appear in the hair and nails
95
New cards
**Acute** inhalation of __elemental__ mercury
**Mercury:** *Major Forms of Mercury Intoxication*
may cause chemical pneumonitis and noncardiogenic pulmonary edema
may cause chemical pneumonitis and noncardiogenic pulmonary edema
96
New cards
**Acute** ingestion of inorganic mercury salts
**Mercury:** *Major Forms of Mercury Intoxication*
an result in a corrosive, potentially life-threatening **hemorrhagic gastroenteritis** followed within hours to days by acute tubular necrosis and oliguric renal failure
an result in a corrosive, potentially life-threatening **hemorrhagic gastroenteritis** followed within hours to days by acute tubular necrosis and oliguric renal failure
97
New cards
**Chronic** poisoning from inhalation of mercury vapor
**Mercury:** *Major Forms of Mercury Intoxication*
classic triad of tremor, neuropsychiatric disturbance, and gingivostomatitis.
classic triad of tremor, neuropsychiatric disturbance, and gingivostomatitis.
98
New cards
Gingivostomatitis
**Mercury:** *Major Forms of Mercury Intoxication -* __*Chronic*__
accompanied by **loosening of the teeth**, may be reported after high-dose exposure
accompanied by **loosening of the teeth**, may be reported after high-dose exposure
99
New cards
Acrodynia
**Mercury:** *Major Forms of Mercury Intoxication -* __*Chronic*__
* uncommon **idiosyncratic reaction** to subacute or chronic mercury exposure and occurs mainly in children
* painful erythema of the extremities
* uncommon **idiosyncratic reaction** to subacute or chronic mercury exposure and occurs mainly in children
* painful erythema of the extremities
100
New cards
Respiratory tract
**Mercury:** *Major Forms of Mercury Intoxication -* __*Major Routes*__
Elemental Mercury
Elemental Mercury