Biology Honors Unit 2- Cell Structure and Function
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What are the three components of the cell theory?
all things are made of cells
cells are the basic unit of life and function
cells come from other cells
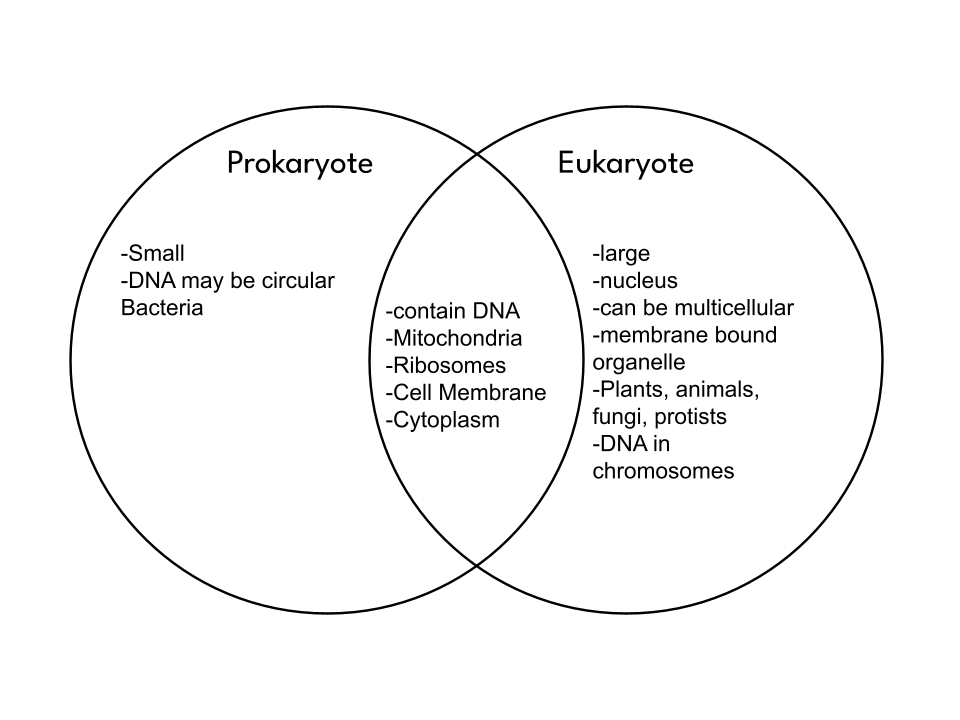
Differentiate between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. (3 differences)
Prokaryotes: No nucleus, unicellular, simple, bacteria only
Eukaryotes: complex, mainly multicellular, has a nucleus
Nucleus (Function and location)
Contains DNA; control center, found in animals and plants
Ribosomes (Function and location)
Synthesizes proteins; found in cytoplasm, found in both plants and animals
Plasma Membrane (Function and location)
Controls what enters and leaves the cell, found in both plants and animals
Cell Wall (Function and location)
Provides structural support; has cellulose in plants and chitin in fungi, not in animals only in plants
Mitochandria
Breaks down sugar to produce energy and is the site of cellular respiration, found in animals and plants
Chloroplast (Function and location)
Uses solar energy to create sugar, found in only plants
Vacuole (Function and location)
Stores water and nutrients, large in plants, small in animals
Cytoplasm (Function and location)
Holds organelles, found in plants and animals
Golgi Apparatu (Function and location)
Packages and distributes proteins outside of the cell, found in plants and animals
Lysosomes (Function and location)
Contains digestive enzymes that breaks down old cell parts, found in animals
Smooth ER (Function and location)
lipid synthesis, regulates calcium, removes toxins, found in plants and animals
Rough ER (Function and location)
Makes proteins, ships in cell, covered in ribosomes, found in plants and animals
What are the four things all cells have?
-ribosomes
-cell membrane
-DNA
-cytoplasm
Explain the role of the cristae in the mitochandria
Increases surface area for more cellular respiration leading to more ATP
Describe how the nucleus, ribosomes, and the golgi complex and cell membrane interact to produce and transport proteins
Nucleus has instructions for ribosomes to make proteins and then are shipped outside of the cell by golgi to cell membrane will allow it to exit
How are the stems and leaves of plants specialized to perform their functions?
Stems have xylem and phloem —> leaves have chloroplast
Eyespot

-a dark spot
-photo receptor/sensesl ight
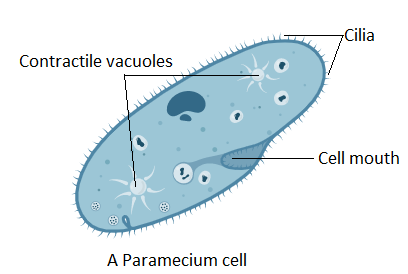
Contractile Vacuole
removes excess water

Pseudopod
-footlike projecting
-used for movement
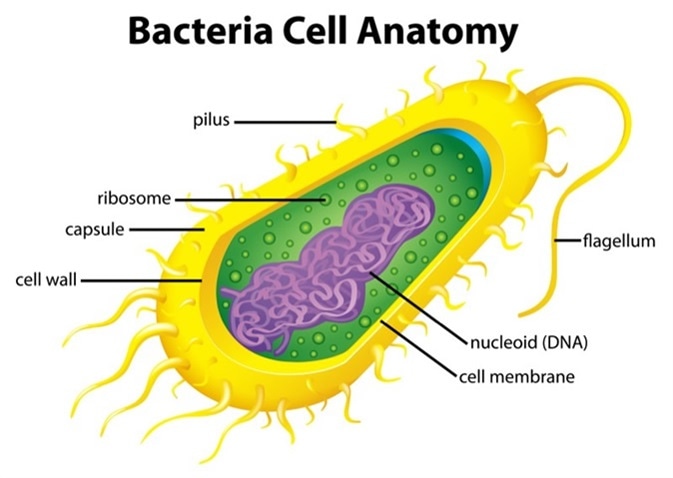
Flagellum
-hairlike projections found in organisms
-provides mobility/transportation
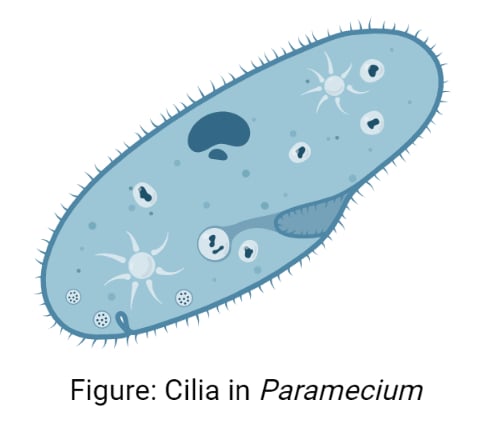
Cilia
-hairlike organelles
-sensory, signaling, mobility
What is a stem cell?
unspecialized cell
Why may stem cells be used for treating disease?
turn into almost any cell
Explain the role of gene activation in cell specialization
-all cells have almost the same DNA
-cells can turn functions on and off to specialize the cell

red blood cell
-carries oxygen

Muscle Cells
-movement and ATP
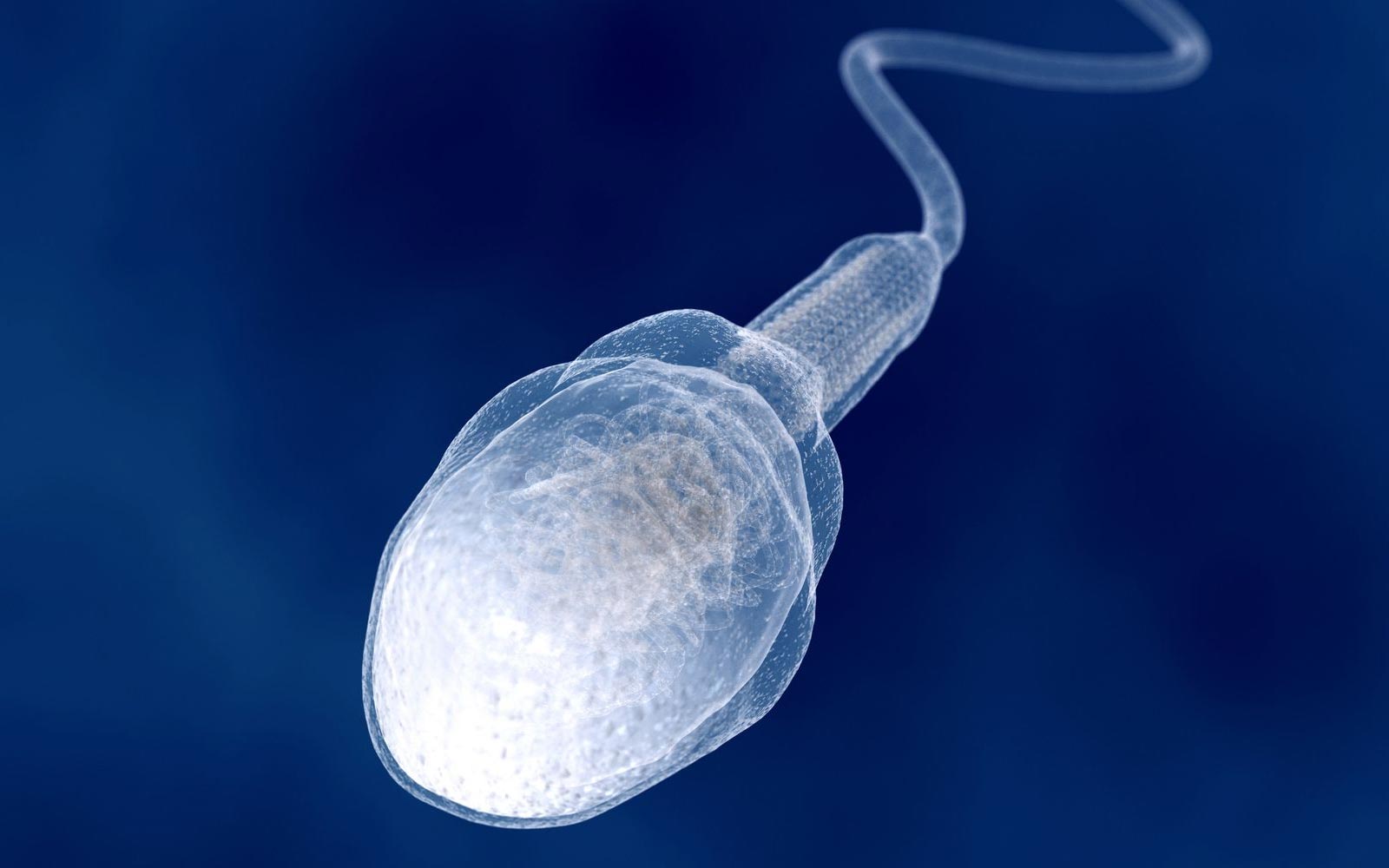
Sperm Cell
-reproduction
Nerve Cells
-transmits messages
What does the Endosymbiotic Theory propose about the origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts?
They were once photosynthetic prokaryote and aerobic prokaryote that invaded another cell

Endosymbiosis Theory
As a cell gets bigger, what happens to the surface area to volume ratio?
it gets smaller
Why is it best for cells to be small?
better surface area to volume ratio; helps nutrients move