tissue 2
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
cell proliferation/division
increase in # of cells as a result of cell growth & cell division
cell differentition
process by which a less specialized cell develops or matures to possess a ore distinct form & function
cell migration
process by which cells move from one location to another by adopting different motility modes
cell death
terminal failure of a cell to maintain essential life functions
cell apoptosis
programmed sequence of events leads to the elimination of cells without releasing harmful substances into surrounding areas
what are challenges in cell growth?
do they look like they’re supposed to?
are cells exposed to proper environment?
are cells growing as needed?
do cells look like they’re supposed to?
cell bio, histology, microscopy
sre cells exposed to proper environment conditions?
nutrition, hormone, CO2/O2 gas levels
are cells growing as needed?
need models & assays for cell growth
cell proliferation is a _____________ regulated by important classes of proteins
highly ordered, evolutionarily conserved process
what is cell division characterized by?
cell cycle
cell cycle
M - mitosis
G1 - Gap 1
S - DNA synthesis
G2 - Gap 2
duration of cell cycle
M - constant
G1 - variable length
S - constant
G2 - constant
how is the success of DNA replication assessed?
during G2 phase
what is the result of DNA replication?
exact duplication & segregation of DNA into 2 daughter cells
what is G0?
quiescent state; cell that is not “in cycle”
(6) characteristics of cell cycle:
turns each event on at a specific time
initiating events in correct order
each event is triggered once
binary switches
backup mechanisms
adaptable to environment
what are the 3 cell cycle checkpoints?
G1
G2
M1
usually operated by negative signals
G1 checkpoint (3)
is environment favorable?
is DNA damaged?
is cell big enough?
go ahead → complete CC & divide
G2 checkpoint (2)
is all DNA replicated?
is cell big enough?
prepare for cell division
M1 checkpoint (1)
are all chromosomes attached to spindle?
cell cycle control
cyclin-dependent kinases complex w/ cyclins
CdK activity
oscillates & phosphorylates lots of intracellular proteins
types of CdK complexes w/ cyclins (3)
G1/S-cyclins
S-cyclins
M-cyclins
activating/inactivating CdKs controlled by: (3)
phosphorylation state of kinase sub-unit
cyclin availability, controlled by degradation & synthesis
specific proteins that bind that affect activity by inhibiting phosphor/protecting from degrad
cancer has: (2)
too much cyclin D
defective P53
cyclin D
required to pass the restriction point
but once passes, do not require anymore to enter S phase
cell growth in vitro (2)
isolation of cells
culturing of cells & cell lines
how do cells grow (2)?
in suspension
anchorage dependent
cell growth in suspension
cancer, hematopoietic, & transformed cells
anchorage dependent cell growth
most mammalian cells
assays for cell proliferation (6)
cell counting
metabolic activity
DNA based assay
protein content
fluorescence based assay
relative/absolute
DNA based assay (2)
3H thymidine
bromodeoxyuridine incorp
modeling cell proliferation
cells divide at a rate that is proportional to # of cells that are in cycle at a given point in time
dX/dt = uX
contact inhibition
arresting cell growth when 2 of more cells come into contact with each other
used to distinguish b/n normal & cancer cells (cancer cells don’t arrest aka stop growing)
monod model of cell growth
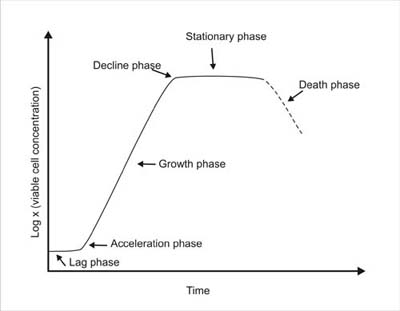
phases of cell growth (4):
lag phase
phase II
phase III
phase IV
lag phase (4)
adjusting to new environment
synthesizing machinery for division
transporting molecules
utilizing substances
phase II
growth rate is proportional to concentration of cells - max growth rates
phase III
stationary due to depletion of essential nutrients & accumulation of wastes
phase IV
cell death occurs due to nutrient depletion or toxic substances
cell senescence (ageing) (3)
terminally differentiated state
absences of growth promoting signals - CdK inhibition of G1
disassemble control mech from cell cycle & exit from cell cycle entering G0
cell apoptosis failure
part of tumor formation
greek word meaning “dropping off” of petals/leaves from a plant/tree
3 phases of apoptosis:
induction
effector
degradation
induction phase
depends on specific death-inducing signals
effector phase
“central executioner” is activated & the cell commits suicide
degradation phase
biochem & morphological changes occur
induction of apoptosis (4)
murder - extrinsic pathway
survival signals
stress-induced - intrinsic pathway
caspase is activated, leading to activation of endogenous endonucleases & fragmentation of genomic DNA
murder - extrinsic pathway
signaling through Fas receptor
survival signals
regulation by Bcl-2 family of proteins
block translocation of Cyt-C from mitochondria to cytosol
stress-induced - intrinsic pathway
damaged mitochondria
release of cytochrome C
what does differentiation begin with?
lineage commitment followed by coordinated gene expression
what changes occur in differentiated cells? (3)
cell structure
cell function
cell metabolism
how can u tell the differentiation state of a cell?
cell surface markers
cell morphology
cell functions
what factors affect growth vs. differentiation? (5)
intrinsic & extrinsic:
transcription factors
ECM
cell shape/cell-cell contact
EC growth factors
EC metabolites
why is differentiation important in tissue engineering?
cell growth of one or more cell types followed y differentiation of those cells
and/or
cell growth of a differentiated cell population
modeling cell dkifferentiation
compartmental model
clonal succession
0 stem cell daughters
deterministic
1 stem cell daughter
stochastic
0,1, or 2 stem cell daughters
telomerase
reverse transcriptase enzyme that carries its own RNA molecule
autophagy
degrading & recycling cell components
significance of autophagy research (8)
can rapidly provide fuel for energy & building blocks for renewal of cell
after infection, can eliminate invading intracell bacteria & viruses
contributes to embryo development & differentiation
to eliminate damaged proteins & organelles, quality control mechanism
disrupted has been linked to parkinsons, type 2, etc.
mutations can cause genetic disease
disturbances in machinery have been linked to cancer
develop drugs that can target it
basic properties of cells (9)
highly complex & organized
possess a genetic program & the means to use it
capable of producing more of themselves
acquire & utilize energy
carry out a variety of chemical reactions
engage in mechanical activities
are able to respond to stimuli
are capable of self-regulation
evolve
cells are highly complex & organized (4)
can grow & reproduce in culture for extended periods
HeLa cells are cultured tumor cells isolated from cancer patient
highly regulated
different species share similar structures, comp, metabolic
cells possess a genetic program & the means to use it (2)
info for building is encoded in genes
can be haploid or diploid
cells are capable of producing more of themselves
divide, mother cell → 2 daughter cells
cells acquire & utilize energy (2)
animals get energy from products of photosynthesis (sugar)
store sugar bond energy in ATP
cells carry out a variety of chem rxns (4)
like miniaturized chem plants
bacterial cell is capable of 100s of diff. chem rxns
all chem changes that take place in cells require enzymes to increase rate
sum total of the chem rxns in a cell represents that cell’s metabolism
cells engage in mechanical activities
cells are very active which is based on dynamic, mechanical changes within cells initiated by changes in the shape of motor proteins
cells are able to respond to stimuli (4)
single-celled protest can move away from an object in path or toward nutrients
cells in plants/animals are covered with receptors that interact with substances in environment
hormones, growth factors, ECM, etc. on surface interact
respond by altering metabolism, moving, committing suicide
cells are capable of self-regulation (5)
cells are protected from dangerous fluctuations in comp & behavior
feedback circuits
constant regulation
info in nucleic acids
each step must occur spontaneously so that the next step is automatically triggered
cells evolve (2)
common genetic code, plasma membrane, & ribosomes
LUCA - last universal common ancestor
what are the 4 basic cell processes
proliferation
differentiation
migration
senescence (aging) & apoptosis
the adept tissue engineer needs an in depth & mechanistic understanding of: (6)
how many diff. types of cells & tissues
what cells compose each tissue
how those cells can be isolated cultured
how diff. properties of cell can be controlled/manipulated to elicit cell function
understand quantitative aspects of cell growth
think creatively to solve problems
cells commonly measured in
micrometers, nanometers
cell size is limited by: (3)
volume of cytoplasm supported by genes in nucleus
volume of cytoplasm supported by exchange of nutrients
distance over which substances can travel via diffusion
cell organelles (9)
nucleus
mitochondria
endoplasmic reticulum
golgi apparatus
lysosomes
peroxisomes
cytosol
cytoskeleton
vesicles
nucleus (3)
nuclear envelope
chromatin & DNA
nucleolus
mitochondria (3)
double membrane
mitochondrial DNA
power house of the cell - ATP
endoplasmic reticulum (2)
where membrane & exported materials are made
ribosomes (rough) - make proteins
golgi apparatus (2)
receives & modifies
directs new material
lysosomes (3)
intracell digestion
releases nutrients
breakdown of waste
peroxisomes
hydrogen peroxide generated & degraded
cytosol (2)
water based gel
chem rxns
cytoskeleton (3)
filaments (actin, intermed, microtub)
movement of organelles
structure/strengthen cell
vesicles (2)
material transport
membrane, ER, golgi
org molecules of cells (4)
proteins
carbs
lipids
nucleic acids
proteins (2)
structure, function, & info
linearly arranged AA residues - folded up w/ active regions
types of proteins (9)
enzymes
structural
motility
regulatory
storage
hormonal
receptors
transport
special purpose
enzymes
catalyzes covalent bond breakage or formation, trypsin, DNA polymerase
structural
collagen, elastin, keratin
motility
actin, myosin, tubulin
regulatory
bind to DNA to switch genes on or off
storage
ovalbumin, casein
hormonal
insulin, nerve growth factor
receptors
hormone & neurotransmitter receptors
transport
carries small molecules or irons
special purpose
green fluorescent protein
4 types of tissues
epithelial
connective
muscular
nervous