Biochem Exam 4
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
The glycolytic enzymes are located in the:
ER
Mitochondrial Matrix
Inner Mitochondrial Membrane
Nucleus
Cytosol
Cytosol
What is the initial investment of ATP in the glycolytic pathway per molecule of glucose?
2 ATP
What is the net equation of glycolysis?
Glucose + 2 ADP + 2 Pi + 2 NAD+ --> 2 pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 4 H+
The enzyme phosphoglucomutase catalyzes the isomerization of glucose-6-phosphate to:
Glucose-1-Phosphate
Complete the analogy:
Glycogen synthase is to the branching enzyme as glycogen phosphorylase is to the ________ enzyme.
debranching
What is the net energetic cost of converting two pyruvate to one glucose by gluconeogenesis, in ATP equivalents?
6 (4 ATP and 2 GTP)
The anaerobic conversion of 1 mol of glucose to 2 mol of ethanol by fermentation is accompanied by the net gain of:
2 mol ATP
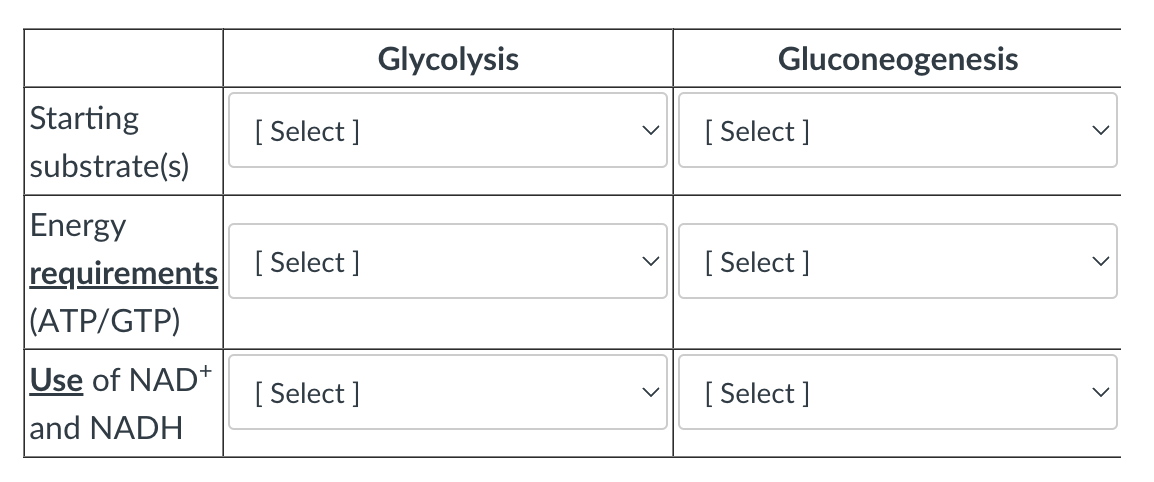
Compare and contrast Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis
Starting Substrates:
Glycolysis —> Glucose
Gluconeogenesis —> Pyruvate
Energy Requirements:
Glycolysis —> 2
Gluconeogenesis —> 6
Use of NAD+ and NADH:
Glycolysis —> 2 NAD+
Gluconeogenesis —> 2 NADH
Indicate which pathways each of the following enzymes are involved in:
Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) Carboxykinase
Aldolase
Hexokinase
Glucose-6-Phosphatase
Used only in gluconeogenesis
Used in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis
Used only in glycolysis
Used only in gluconeogenesis
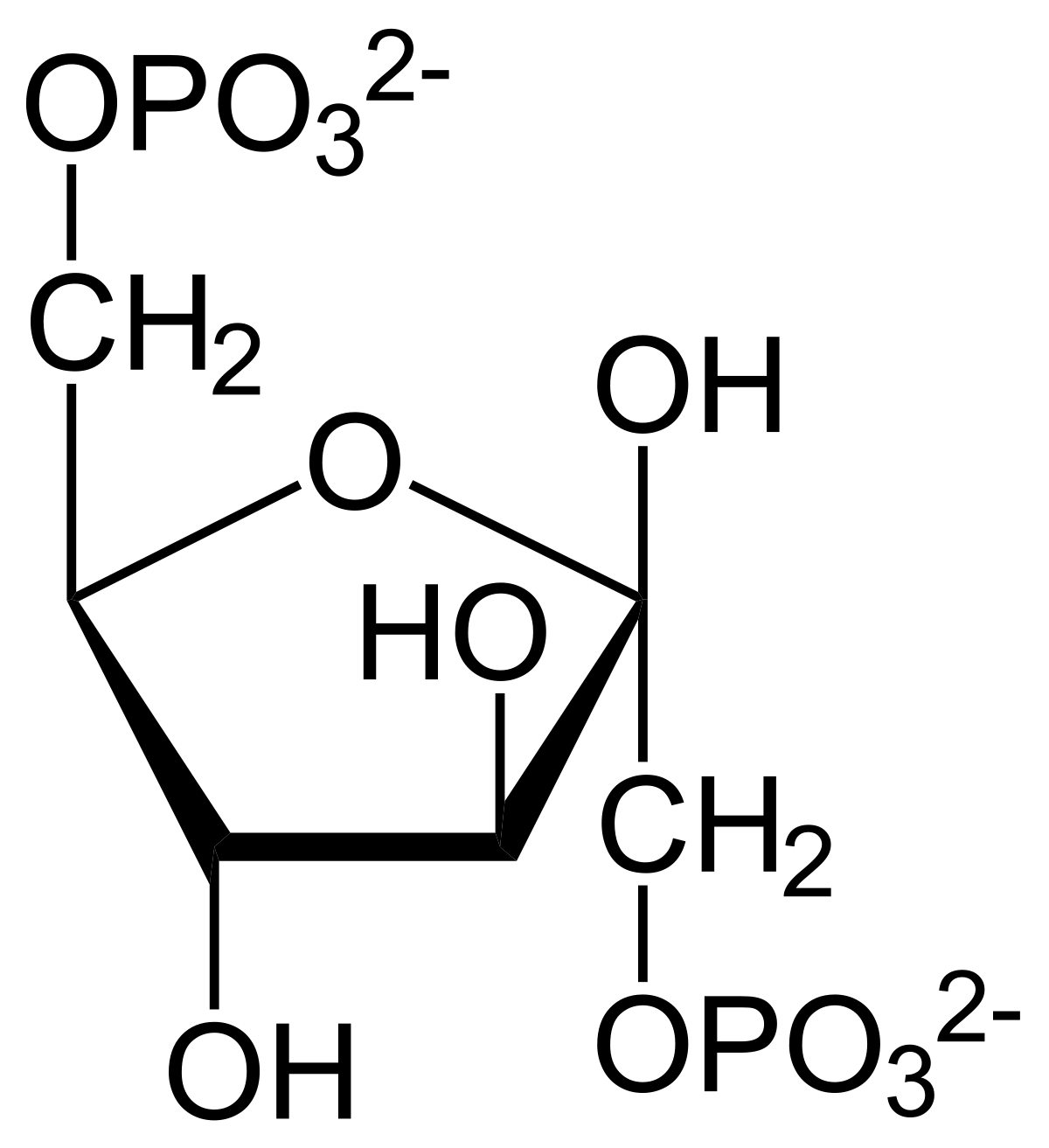
I. The molecule shown above is _______
II. In glycolysis, the substrates used to produce the molecule above are _______ and ______
III. The metabolic pathway/cycle that the molecule above participates in is _________
IV. The glycolytic enzyme that produces the molecule above is ________
Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate
Fructose-6-Phosphate and ATP
Glycolysis
PFK-1
One of the most important products of the pentose phosphate pathway is:
NADPH
A major allosteric regulator of both glycolysis and gluconeogenesis is:
Fructose-2,6-Bisphosphate
Both glycogen synthesis and glycogen breakdown share the metabolite:
Glucose-1-Phosphate
The steps in glycolysis that differ from those of gluconeogenesis are catalyzed by:
Pyruvate kinase, phosphofructokinase, hexokinase
The first reaction of gluconeogenesis is:
A carboxylation
Which of the following enzymes catalyzes the transfer of a phosphoryl group from ATP to glucose?
Hexokinase
What are the potential control points in glycolysis? What is the actual control point (commitment step)?
Possible
Steps 1, 3, and 10
Actual
Step 3
Glucose is converted to _____ in skeletal muscle under anaerobic conditions.
Lactate
From first to last, select the intermediates as they appear in glycogen synthesis.
Glucose
Glucose-6-Phosphate
Glucose-1-Phosphate
UDP-Glucose
Glycogen
The aldolase reaction is spontaneous in vivo because:
A) It is metabolically irreversible under standard biochemical conditions.
B) Aldolase uses ATP hydrolysis to make the reaction irreversible.
C) The rapid consumption of products pulls the reaction forward.
D) The reaction occurs very slowly.
C) The rapid consumption of products pulls the reaction forward
During the oxidation of acetyl-CoA through the TCA cycle, which steps involve oxidative decarboxylations?
Step 3
Step 4
Both
Both
Which reactions in the TCA cycle use a thioester substrate (a substrate with a CoA attached)?
Steps 1 and 5
Steps 1 and 3
Steps 2 and 3
Steps 1 and 5
Which reaction in the TCA cycle gives electrons to ubiquinone (Q)?
Step 6
Step 4
Step 2
Step 6
Flux through the TCA cycle is regulated at the _____ steps.
near-equilibrium
irreversible
Irreversible
Which of the following terms describes the TCA cycle as both catabolic and anabolic?
Amphipathic
Anaplerotic
Anaplerotic
The regulated enzymes of the TCA cycle include:
Fumarase
Malate dehydrogenase
Citrate lyase
⍺-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
⍺-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
Which reactions in the TCA cycle release CO2?
Steps 5 and 6
Steps 1 and 2
Steps 3 and 4
Steps 3 and 4
Which of the enzymes listed below require NAD+?
Hint: The enzymes may not just be those involved in the Citric Acid Cycle
Succinate dehydrogenase
Malate dehydrogenase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
Malate Dehydrogenase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
Which of the following answers complete the sentence correctly?
Succinate dehydrogenase...
A.) is an integral membrane protein, unlike the other enzymes of the citric acid cycle.
B.) contains FAD and NAD+ cofactors like pyruvate dehydrogenase.
B.) is a copper-sulfur protein.
D.) carries out an oxidative decarboxylation like isocitrate dehydrogenase.
A.) Is an integral membrane protein, unlike the other enzymes of the citric acid cycle.
What cellular location contains pyruvate dehydrogenase and most of the citric acid cycle enzymes?
Mitochondral Matrix
Which of the following pyruvate dehydrogenase enzymes is correctly paired with the coenzyme that is associated with it?
E3: lipoamide
E3: FAD
E2: thiamine pyrophosphate
E1: coenzyme A
E3: FAD
What makes the reaction catalyzed by citrate synthase highly exergonic?
Conversion from keto to enol tautomer
Hydrolysis of thioester
Decarboxylation reaction
Hydrolysis of ATP
Hydrolysis of Thioester
Which of the following condenses with oxaloacetate to form citrate?
Succinyl-phosphate
Carboxybiotin
Cis-aconitate
Acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA
The reaction catalyzed by fumarase is _____.
a hydroxylation of an alkene
a hydration of an alkene
a dehydration of an alcohol
an isomerization of an alcohol
A hydration of an alkene
Which of the following is activated by ADP?
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
Malate dehydrogenase
Aconitase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Put the TCA cycle enzymes in the correct order:
Citrate synthase
Aconitase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
α-Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
Succinyl-CoA synthetase
Succinate dehydrogenase
Fumarase
Malate dehydrogenase
How many NADH are produced when one acetyl group is oxidized in the TCA cycle?
3
Malonate is a competitive inhibitor of succinate dehydrogenase. Which of the following TCA intermediates accumulate if malonate is present in a preparation of isolated mitochondria?
Succinate
Malate
α-ketoglutarate
Succinyl-CoA
Fumarate
Succinate
α-ketoglutarate
Succinyl-CoA
Which component of ATP synthase functions as a transmembrane proton channel?
F0
How many electrons can be carried by the prosthetic group in cytochrome c?
1
When 2 electrons are passed through Complex I, ____ protons are transferred to the intermembrane space.
4
Identify if the following statement is true or false:
NADH accepts electrons during respiratory electron transport.
False

Select the answers below as they pertain to the indicated pathway.
Note: for the NET ATP yield include any and all ATP equivalents generated in a particular pathway (i.e. ATP, GTP). This should include the oxidation of reducing equivalents that may be generated in the pathway.
Assume that NADH=2.5 ATP and FADH2=1.5 ATP
Assume the carbon reactants are each going through the pathway once.
40, 140
Complex IV of the electron transport chain oxidizes_____, reduces ______ , and _______ protons in the process.
Cytochrome C
O2
Pumps
If the reduction potential for NAD+ is -0.315 V and the reduction potential for oxygen is 0.815 V, what is the potential for the oxidation of NADH by oxygen?
1.13 V
What is the ∆Gº' for the reduction of pyruvate to lactate by NADH given the following half reactions?
pyruvate + 2H+ + 2e- -> lactate ∆εº' = -0.185
NAD+ + H+ + 2e- -> NADH ∆εº' = -0.315
-25.1 kJ/mol
A man presents in the emergency room after ingesting an insecticide. The Poison Control Center indicates that the insecticide contains cyanide (CN-), which binds to and completely inhibits cytochrome c oxidase. Would ATP synthesis in this man’s mitochondria be stopped?
Yes
What is the terminal (final) electron acceptor in aerobic organisms?
O2 (Oxygen)
In the malate-aspartate shuttle, _____ is reduced to _____ in the cytosol.
malate; aspartate
oxaloacetate; malate
aspartate; malate
aspartate; oxaloacetate
Oxaloacetate; malate
What does the reduction potential of 0.815 V for the reduction of oxygen to water indicate?
Oxygen is a very strong oxidizing agent.
Water is a very strong reducing agent and oxygen is a very strong oxidizing agent.
Water is a very strong reducing agent.
Water will be spontaneously reduced to oxygen.
Oxygen is a very strong oxidizing agent
Which of the following is the location of the Q cycle?
Complex I
succinate dehydrogenase
Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase
Complex III
NADPH
Complex III
Complex II accepts electrons from _____ and transfers them to _____.
ubiquinol; fumarate
cytochrome c; cytochrome a
ubiquinone; cytochrome c
succinate; ubiquinone
Succinate; ubiquinone
Complex IV uses _____ and _____ ions to reduce oxygen to water.
manganese; iron
copper; iron
zinc; lead
manganese; copper
Copper; iron
How many cytochrome c molecules are oxidized by Complex IV for each molecule of oxygen (O2) that is reduced?
4
Which subunit of ATP synthase is responsible for the catalysis of ATP formation?
Gamma
Alpha
Beta
c
Beta
Which of the following occurs when the catalytic subunit of ATP synthase is in the loose state?
ATP is hydrolyzed
ADP and Pi bind
ATP is released
ADP and Pi are converted to ATP
ADP and Pi bind